Abstract
This study presents an analytical and multiscale investigation of the degradation of elastic properties in ordinary Portland cement (OPC) paste subjected to calcium leaching. Eight representative microstructures and three homogenization schemes (Mori–Tanaka, Hashin–Shtrikman, and Voigt) were evaluated to determine the most suitable configuration for predicting stiffness evolution. Model validation against benchmark experimental data at 14 and 56 days demonstrated good agreement, with prediction errors within 10%. Simulation results reveal that progressive decalcification leads to significant reductions in both bulk and shear moduli, with the calcium hydroxide (CH) phase being the most sensitive, followed by low-density (LD) and high-density (HD) calcium silicate hydrate (CSH). The overall stiffness loss increases with the water-to-cement ratio (), exceeding 90% at under complete decalcification. A sensitivity analysis further shows that the rate of modulus degradation decreases with increasing , reflecting a mechanical normalization effect rather than improved chemical stability. These findings highlight the dominant role of calcium preservation in maintaining mechanical integrity and provide a robust theoretical framework for predicting the chemo-mechanical degradation and long-term durability of cement-based materials in aggressive environments.
1. Introduction
Cement-based materials, due to their excellent structural strength and cost-effectiveness, are widely used in modern construction and infrastructure development [1,2]. However, these materials often face environmental challenges such as chemical corrosion during long-term use. For instance, in scenarios involving nuclear waste storage or deep infrastructure, cement structures may be exposed to aqueous environments [3,4,5]. In such environments, the concentration of calcium ions in cement paste is significantly higher than in pure water, creating a pronounced calcium ion concentration gradient. This gradient facilitates the diffusion of calcium ions from the micro-pores of the concrete, disrupting the chemical balance of calcium hydroxide (CH) and calcium silicate hydrate (CSH), and ultimately leads to the gradual decalcification of these solid hydration products [6]. This chemical process not only reduces the quality of the hardened cement paste and increases its porosity but also significantly weakens the material’s mechanical properties, particularly the elastic properties, which are critical parameters affecting the stress distribution and deformation of concrete structures [7,8,9,10]. Therefore, a deep understanding of how calcium leaching affects the elastic properties of cement-based materials is crucial as it will help enhance the performance of materials in harsh environments and extend their service life.
To accurately determine the elastic modulus of cement paste affected by calcium leaching, researchers have employed three main methods. First, experimental methods including compression testing, bending testing, and nanoindentation testing are used to directly measure the elastic modulus of cement paste samples in a laboratory setting [11,12,13]. Although these methods provide tangible physical test data, they are typically time-consuming and costly, especially when simulating long-term environmental impacts. Consequently, some researchers have turned to numerical simulation methods, such as finite element methods (FEM), which can simulate complex loading conditions and design variables, making them suitable for predicting long-term performance changes in materials [8,14,15]. However, the accuracy of numerical simulations greatly depends on the precision of model assumptions and input parameters. Inaccurate assumptions can lead to significant deviations between the results and actual material behavior, and the complexity and iterative demands of the models limit their widespread application in engineering practice. In light of this, methods based on analytical models, particularly multi-scale models based on micromechanics [7,10,16], are widely used because they allow for a thorough theoretical description of material behavior by establishing mathematical models and analytical solutions, directly linking microstructural characteristics with macroscopic mechanical properties.
Using multi-scale analytical models is a profound mechanism for examining the complex relationship between the microstructure and mechanical properties of cement-based materials [17,18]. By systematically analyzing structural features at various scales, these models help to deepen our understanding of their mechanical behavior. Many researchers utilize analytical models to explore the determination of the elastic modulus of cement paste affected by calcium leaching. For instance, Constantinides and Ulm [16] employed nanoindentation tests on non-degraded and calcium-leached cement paste, analyzing changes in the microstructure of the cement paste using a micromechanical model to predict changes in the macroscopic elastic modulus before and after leaching. Stora et al. [10] developed a multi-scale homogenization model that succinctly links the dissolution of hydrates like CH with reductions in Young’s modulus and increases in material diffusion coefficients. Recently, Zhou et al. [7] proposed a new multi-scale analytical model that considers the dissolution of CH and the decalcification of CSH in cement paste, impacting the elastic modulus, thereby further connecting microstructural characteristics with macroscopic mechanical properties. These studies highlight the significant value of analytical models in understanding and predicting changes in the mechanical properties of cement-based materials. However, these models still rely to some extent on calibration with experimental data and face limitations in prediction accuracy when dealing with more complex environmental impacts.
On the other hand, multi-scale models designed to predict the mechanical properties of cement-based materials exhibit significant diversity [19,20]. For example, the micromechanical model introduced by Constantinides and Ulm [16] employs the Mori-Tanaka (MT) scheme to combine low-density CSH (LD-CSH) and high-density CSH (HD-CSH), with LD-CSH serving as the matrix. This approach describes the matrix of the cement paste, integrating capillary porosity, unhydrated particles (clinker), and CH, using the MT scheme to assess the behavior of the cement paste. Moving up to the mortar scale, the MT scheme clarifies the dynamic relationship between aggregate and cement paste—viewed respectively as inclusions and the matrix—providing an estimation of overall elastic properties. Moreover, to address the complexity of autogenous shrinkage, Pichler et al. [21] introduced a new scale centered on porous CSH, wherein CSH and capillary pores are unified under the MT scheme to define the matrix of the structural body. Similarly, Sanahuja et al. [22] conceptualized HD-CSH as a coating over unhydrated particles at the cement paste scale, with the nature of porous LD-CSH characterized by the self-consistent (SC) scheme. Despite these advancements, a universal multi-scale model for cement-based materials remains elusive.
In this paper, we propose an innovative multiscale mechanical model that spans from the microscale structure of CSH to the macroscopic mechanical behavior of cement-based materials. The study focuses on OPC paste, whose primary hydration products—CH and CSH—govern the mechanical and chemical behavior of the material under calcium leaching. This model will enable more precise predictions of the performance changes in cement-based materials during the calcium leaching process. Initially, to select a representative microstructure and homogenization scheme for cement paste, eight typical multiscale models—considering various phase combinations of LD-CSH, HD-CSH, CH, pores, and unhydrated particles—were systematically analyzed using three classical homogenization schemes (MT, Hashin–Shtrikman (HS), and Voigt) to identify the most suitable configuration for predicting stiffness evolution. Subsequently, based on the optimal multi-scale model, we established a multi-scale mechanical model using hydration reactions and micromechanics to describe the elastic model of the cement paste, with particular consideration given to the percentage of calcium leaching in the cement paste and their impact on the elastic properties. Finally, the model was validated and analyzed using experimental data.
2. Evaluating Microstructures and Homogenization Schemes
To establish the methodological foundation for the proposed multiscale analytical model, this section outlines the evaluation procedure adopted to determine the effective elastic properties of cement paste. The investigation focuses on OPC paste, whose constitutive phases and material parameters are defined based on experimental data reported in the literature. Eight representative microstructures and three homogenization schemes—MT, HS, and Voigt—were systematically analyzed to identify the most appropriate configuration for subsequent model development and validation. These classical micromechanical homogenization schemes differ in their fundamental assumptions: the Voigt model assumes uniform strain throughout the composite and provides an upper bound for the effective stiffness, while the HS bounds represent theoretical limits derived from variational principles. In contrast, the MT approach accounts for inclusion–matrix interactions, offering a more physically representative estimate of composite stiffness. Because hardened cement paste consists of multiple solid phases dispersed within a porous matrix, the MT scheme has been widely recognized as particularly suitable for modeling its heterogeneous microstructure.
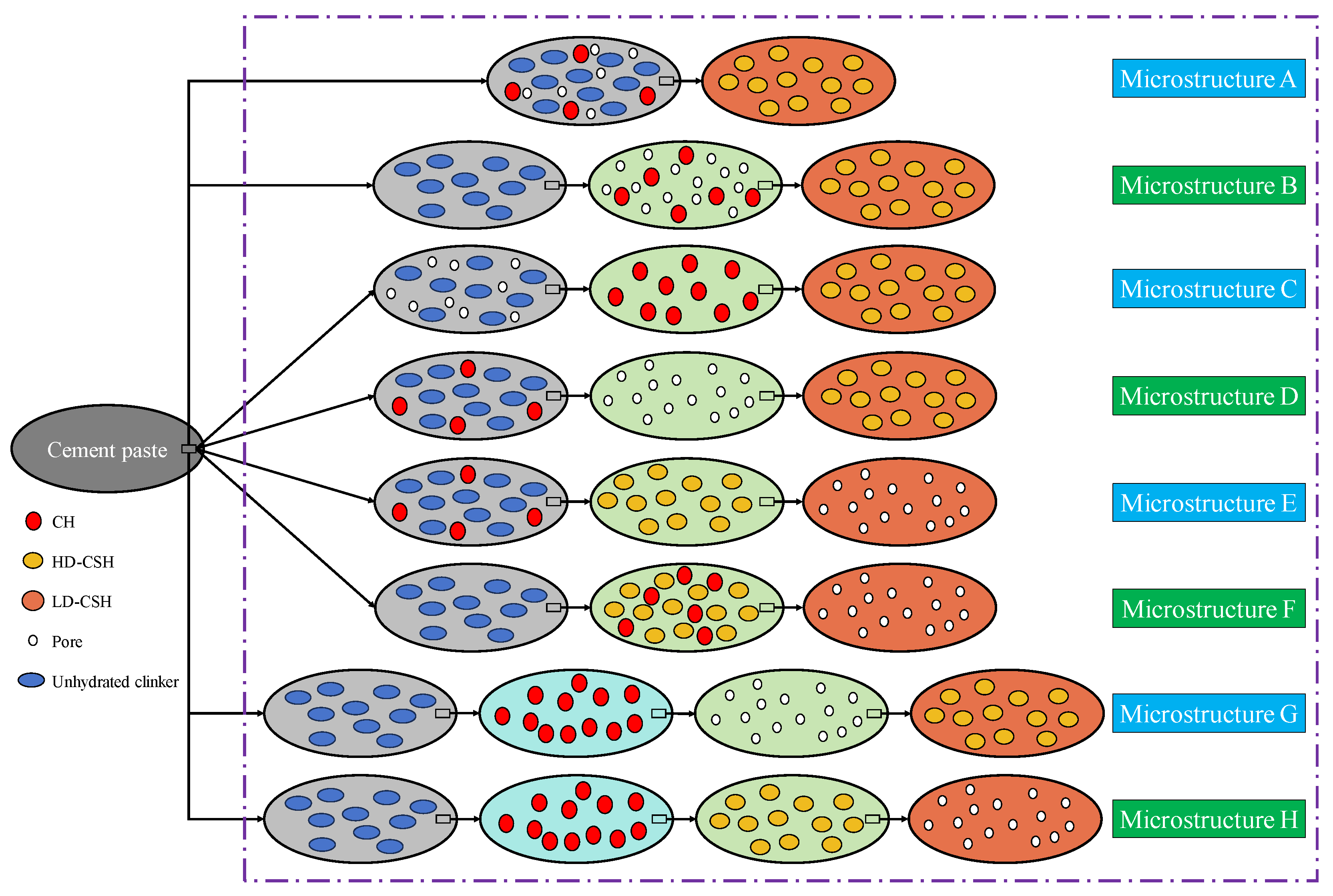
Upon mixing cement with water, a cascade of chemical reactions unfolds, yielding various hydration products and transforming the cement paste into a heterogeneous material at the microscopic scale [23]. To simulate the elastic stiffness of cement paste, the following assumptions are made. The investigated material corresponds to OPC paste, primarily composed of CH, LD-CSH, HD-CSH, and unhydrated clinker phases resulting from the hydration of C3S and C2S. Although supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), such as fly ash, slag, and silica fume, are often used to enhance the durability of concrete, this study does not consider these materials due to their complex chemical reactions. As mentioned in the introduction section, multi-scale models exhibit significant diversity when predicting the mechanical properties of cement-based materials. In this context, we introduce eight common microstructures for cement paste [7,24,25,26], as illustrated in Figure 1. These structures, which include LD-CSH, HD-CSH, CH, pores, and unhydrated particles, highlight the material’s compositional variety. Each model’s uniqueness arises from the spatial distribution of the cement paste’s phases across different scales, offering detailed insights into the material’s composition and behavior. For instance, Microstructure-A primarily considers LD-CSH and HD-CSH, expanding to encompass inclusions, pores, and unhydrated particles, eventually leading to a homogenized representation of the cement paste. This layered approach facilitates meticulous validation of each microstructure using empirical data from existing literature, with the mechanical parameters of each phase detailed in Table 1 and their respective unit volumes listed in Table 2. By employing homogenization schemes such as the Mori-Tanaka (MT) scheme, the Hashin-Shtrikman (HS) upper bound, and the Voigt upper bound (see Appendix A), we undertake a step-by-step calculation of the cement paste’s effective elastic modulus. This process reveals variations in stiffness values across different microstructures and homogenization schemes, as presented in Table 3.
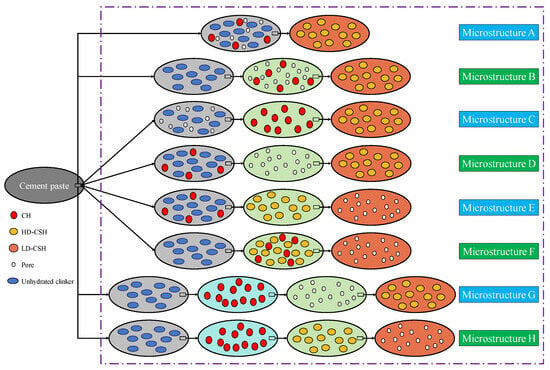
Figure 1.
Selected multiscale representative volume element of cement paste with pores and solid particles.

Table 1.
Elastic properties of different phases of cement paste.

Table 2.
Unit volume of different phases in cement pastes [30].

Table 3.
Comparative stiffness values of cement paste using different microstructure and homogenization schemes.
According to the results presented in Table 3, we observed that the stiffness values obtained using the MT scheme are notably the lowest, followed by those from the HS upper bound, with the Voigt upper bound producing the highest stiffness values. Interestingly, the stiffness values determined by the Voigt upper bound show consistency across all microstructures. Further analysis of the MT scheme results indicates that the stiffness associated with Microstructure-C is the highest, whereas Microstructure-F records the lowest. This observation highlights the significant impact of material components at the smallest scales on the macroscopic stiffness of the material. Considering the experimental data provided a reference Young’s modulus of 21.7 GPa [30], we used percentage error as a metric to evaluate the accuracy of the Young’s modulus calculated by different models. Table 4 presents the percentage errors corresponding to the effective Young’s modulus obtained by different models. As seen in Table 4, the MT scheme yielded the most accurate results among all schemes. Additionally, the MT calculations for Microstructure-C and Microstructure-H displayed the maximum and minimum errors, respectively, yet all errors remained below 10%. Based on this error analysis, although Microstructure-H seems most suitable for our multiscale mechanical modeling study, given the relative simplicity and smaller error range of Microstructure-A, we have chosen it as the basis for exploring the degradation process of cement paste.

Table 4.
Comparison of percentage prediction errors in Young’s modulus (relative to experimental data [30]) for different microstructures and homogenization schemes.
Furthermore, among the three homogenization schemes compared (MT, HS, and Voigt), the MT scheme was selected for the subsequent analysis because it consistently yielded the lowest prediction errors relative to experimental data and provided a good balance between computational efficiency and physical accuracy. The Voigt model offers an upper bound assuming uniform strain, whereas the HS bound represents an idealized limit that is difficult to achieve in practice. In contrast, the MT approach explicitly accounts for inclusion-matrix interactions, which aligns well with the heterogeneous microstructure of hardened cement paste where CH and CSH act as inclusions within a continuous matrix. Nonetheless, we acknowledge that this selection is not unique; future studies will compare alternative micromechanical frameworks to further evaluate the robustness of the chosen scheme under different degradation scenarios.
In addition to the choice of homogenization scheme, the overall representation of the leached cement paste structure was also simplified for analytical tractability. It should be noted that this two-phase representation serves as a first-order approximation. In reality, the pore system of hardened cement paste exhibits a complex multi-scale morphology comprising gel pores, capillary pores, and microcracks, which influence local stress transfer and stiffness degradation. The present assumption simplifies this heterogeneity to focus on the dominant effect of overall porosity on elastic properties while maintaining analytical tractability. Future work will extend this framework to multi-phase and morphology-resolved models (e.g., treating CSH, CH, and pores as separate constituents) to further investigate the influence of pore geometry and connectivity on mechanical deterioration.
3. Multi-Scale Model for Predicting Elastic Modulus
3.1. Multi-Scale Model of Hardened Cement Paste
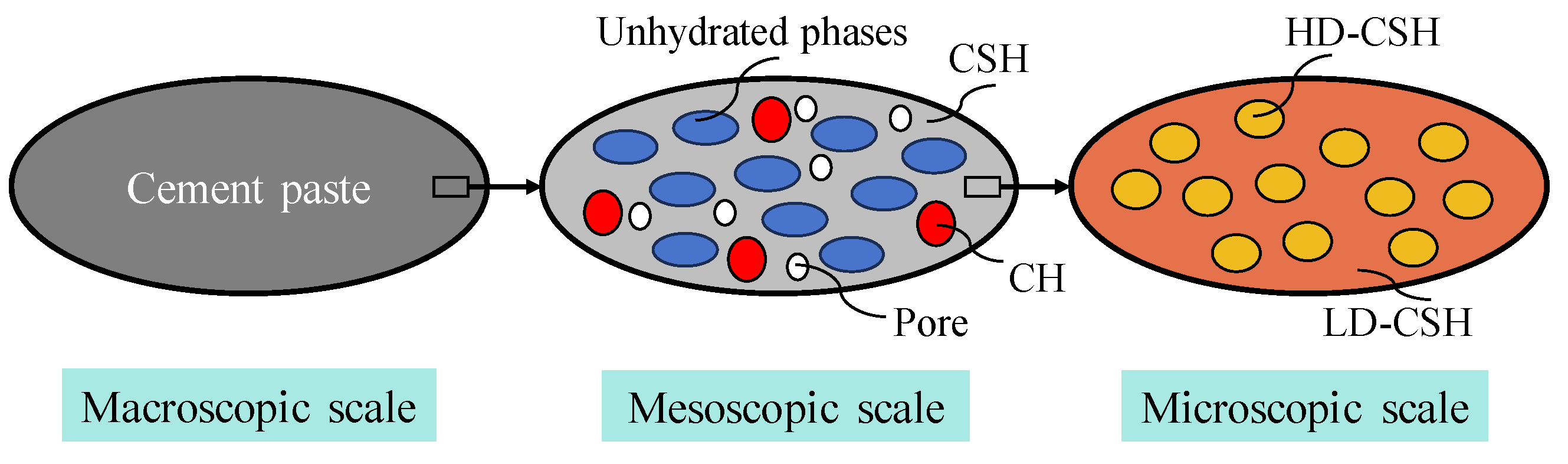
Based on the above analysis, cement paste materials are divided into three scales in this paper. The representative volume elements (RVE) of the materials are shown in Figure 2.
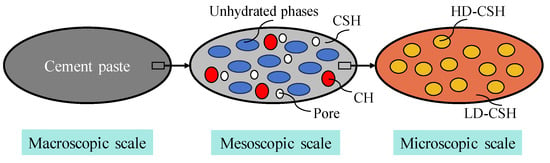
Figure 2.
Selected representative volume element of heterogeneous materials with pores and mineral inclusions.
At the microscopic scale, the CSH consists of HD-CSH and LD-CSH, where LD-CSH acts as the matrix material and HD-CSH as an inclusion confined within it. Consequently, the MT scheme is applied to estimate the elastic stiffness of the CSH. Mechanical stiffness values are reported in Table 1. The Jennings-Tennis model [31] is employed to quantitatively compute the volume fractions of LD-CSH and HD-CSH. The ratio of the mass of LD-CSH to the total mass of the two types of CSH is expressed as [31]
where denotes the degree of hydration; to achieve more precise modeling, it is essential to experimentally ascertain the true hydration degree. Utilizing the mass density of LD-CSH and HD-CSH, the fractions of LD-CSH and HD-CSH can be calculated as follows:
where and represent the volume fractions of LD-CSH and HD-CSH, respectively, while = 1.70 and = 2.00 [28] denote the mass density of LD-CSH and HD-CSH, respectively.
At the mesoscopic scale, CSH is incorporated alongside CH, unhydrated phases, and pores, where CSH is regarded as the matrix and the other phases as inclusions. Again, the elastic stiffness is estimated according to the MT scheme. The mechanical stiffness values for each phase are shown in Table 1. The volume fraction of unhydrated phase can be determined by a combination of backscattered electron (BSE) image analysis [32]. However, further separation of the CSH matrix and CH in the hydration products proves challenging. Additionally, the total volume fraction of pores cannot be determined based solely on BSE image analysis due to resolution limitations. Therefore, the classical Powers hydration model is employed to estimate the degree of hydration and the volume fraction of pores. Despite being derived in the 1940s, the Powers hydration model remains widely used due to its reliability and ease of implementation [33,34]. Based on the Powers model, the degree of hydration and the volume fraction of pores can be determined according to Equation (3):
where , and represent the volume fractions of pores, hydrates, and unhydrated phases, respectively. To determine the volume fractions of CH and the CSH matrix, two chemical equations defining the quantities of CH and the CSH matrix are employed [31]:
The numbers of moles for tricalcium silicate () and dicalcium silicate () per unit volume of cement can be calculated as follows:
and denote the mass densities of and , where = 3.15 and = 3.28 [28,33]. Similarly, and represent the molar masses of and , with = 228.30 and = 172.20 , respectively [28,33]. Additionally, and stand for the volume fractions of and , respectively. In this study, for simplicity, it is assumed that and share the same degree of hydration, which is denoted as [33]. By combining Equations (4) and (5), the numbers of moles of CH and the CSH matrix ( and ) formed from one unit volume of cement can be expressed as follows:
The corresponding volumes of CH and CSH matrix can be expressed as follows:
In the given context, and represent the mass densities of CH and the CSH matrix, respectively. Here, = 2.24 [28,33]. The density of the CSH matrix () is determined by the weighted sum of the mass densities of its constituent phases, denoted as and , with their corresponding volume fractions and . Mathematically, . Additionally, and stand for the molar masses of CH and the CSH matrix and have assigned values of = 74.00 and = 227.20 , respectively [28,33]. Referring to Equation (8), the volume fractions of CH and the CSH matrix ( and ) can be determined.
At the macroscopic scale, the cement paste material is depicted through a concept of homogenized equivalent medium (HEM). This model enables the prediction of its effective elastic properties utilizing the aforementioned research methodologies.
3.2. Multi-Scale Model of Leached Cement Paste
In this study, we explore the dynamics of cement paste interactions with water, focusing on the significant role of heterogeneity in these interactions. When exposed to water, a concentration gradient of calcium ions emerges, leading to the gradual decalcification of key components such as CH and CSH [35]. This decalcification increases porosity and consequently decreases the elastic stiffness of the material. It should be noted that the diffusion rate of calcium ions and the evolution of the pore network are strongly affected by the water-to-cement ratio (). At lower , the dense microstructure restricts ion migration, producing a slower and more localized leaching front. In contrast, higher mixtures exhibit more connected capillary pores, which facilitate ion diffusion and promote deeper decalcification. This coupling between transport kinetics and pore morphology provides the physical basis for the dissolution path of CH and CSH considered in the present analytical model.
While our analysis assumes that concrete structures primarily contact pure deionized water, it is noteworthy that underground structures are often exposed to groundwater or solutions containing dissolved carbon dioxide (). This exposure can lead to carbonation, a chemical interaction between dissolved and leached calcium that compacts the cementitious matrix and alters the progression of the leaching front. Although the lattice Boltzmann method can simulate the complex interactions between calcium leaching and carbonation [36], analyzing such interactions analytically remains challenging. Therefore, in this work, the leaching process in pure water is deliberately chosen as a baseline condition to isolate the mechanical consequences of decalcification. Future model extensions will incorporate coupled effects such as carbonation, sulfate attack, or chloride ingress to better reflect real underground and marine environments. The initial structure of the cement paste is referenced in Figure 2.
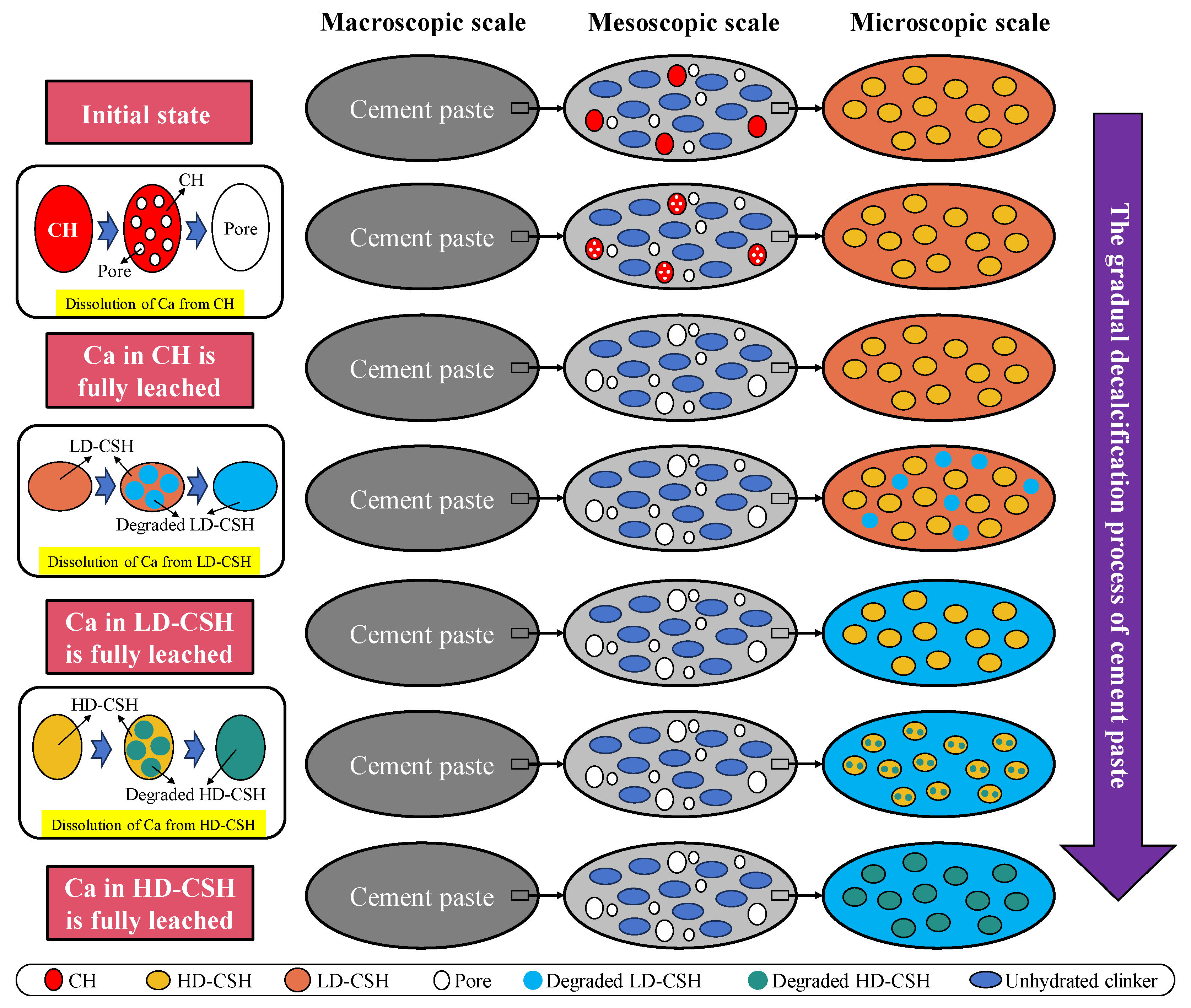
We analyze the calcium leaching process in cement-based materials exposed to pure water environments, adopting a simplified analytical approach to explore the impact of this process on material performance. Initially, leaching primarily affects CH, where the reaction of CH with water leads to the formation of pores in a 1:1 volume ratio, directly increasing the material’s porosity [7,37]. As the leaching of CH is fully completed, the focus shifts to CSH, specifically starting with LD-CSH followed by HD-CSH [7,37]. Unlike the direct pore formation resulting from CH leaching, the CSH leaching process does not accompany the formation of new pores but rather induces a transition of CSH from its original state to a degraded state, forming degraded LD-CSH and degraded HD-CSH, without directly altering the porosity. The entire process of the calcium leaching model in cement paste is shown in Figure 3. For each stage, the elastic properties of the cement paste at each scale are calculated using the MT scheme.
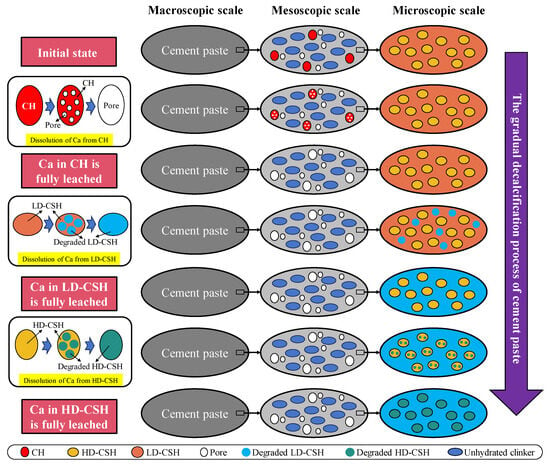
Figure 3.
Schematic representative volume element of hardened cement paste during the leaching process.
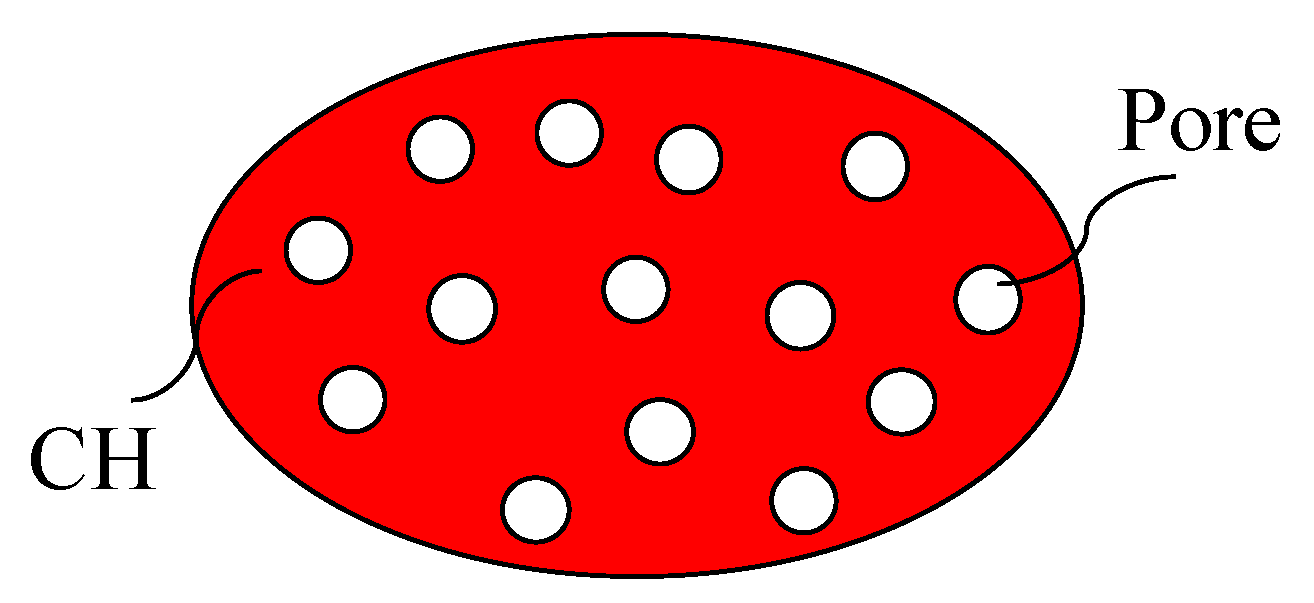
To accurately assess the changes in elastic stiffness, we introduce a microstructural model for partially dissolved CH. The initial decrease in the elastic stiffness of cement paste is predominantly attributed to the dissolution of CH. Consequently, accurately assessing the elastic modulus of CH during partial dissolution becomes essential. To address this, we introduce a microstructural model for partially dissolved CH. Before leaching, the elastic modulus of CH can be ascertained through nanoindentation techniques. Upon full dissolution, CH transforms into a pore structure. During the dissolution phase, partially dissolved CH comprises a combination of CH and pore structures, as illustrated in Figure 4. Within this framework, CH is regarded as the matrix phase with the pore serving as the inclusion, allowing for the calculation of its elastic modulus using the MT scheme.
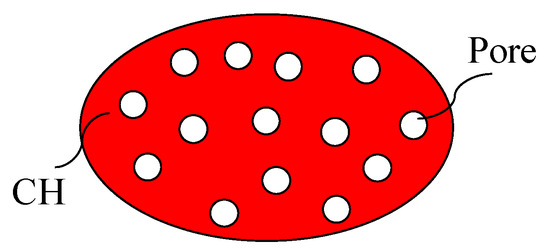
Figure 4.
Unit cell for partially dissolved CH.
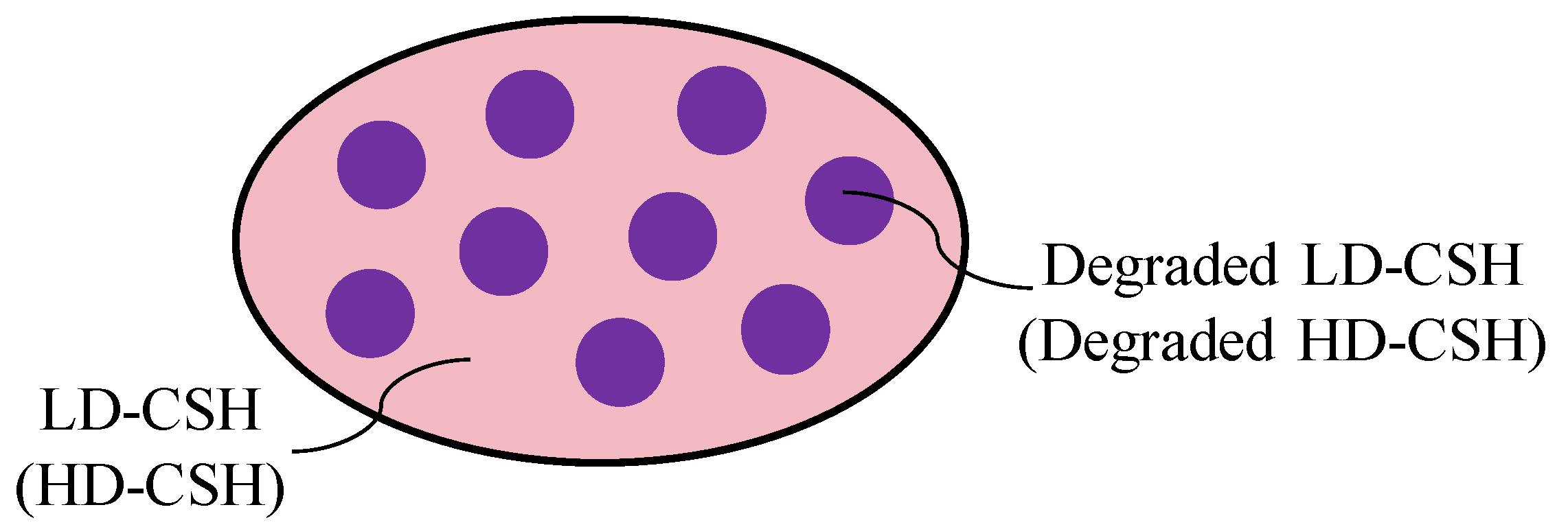
As the leaching progresses, a gradual decalcification of CSH is observed, leading to a corresponding reduction in the cement paste’s elastic stiffness. To capture the effects of decalcification on the microstructure, a model for partially decalcified CSH is also introduced. Decalcification of CSH unfolds in two distinct phases: it initially affects the LD-CSH, followed by the HD-CSH. Before decalcification, elastic parameters for both LD-CSH and HD-CSH can be determined through nanoindentation. Following complete decalcification, the resultant degraded phases, namely degraded LD-CSH and degraded HD-CSH, maintain measurable mechanical stiffness, as documented in Table 1. Throughout decalcification, the intermediate state comprises a blend of intact and degraded CSH, detailed in Figure 5. Here, the intact CSH is considered the matrix phase, with the degraded CSH acting as the inclusion, and their combined elastic modulus is derived employing the MT scheme.
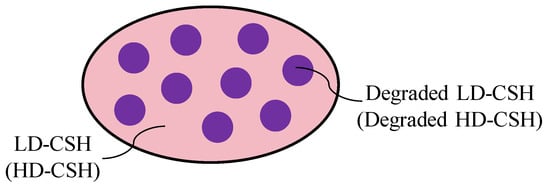
Figure 5.
Unit cell for partially dissolved LD-CSH or HD-CSH.
To further explore the relationship between the leachable calcium content and the effective elastic performance in cement paste, it is crucial to first determine the initial amount of leachable calcium. Based on the chemical equations of hydration reactions (see Equation (4)), we can calculate the amounts of hydration products, namely CH and CSH, according to the composition and degree of hydration of the original cement. Therefore, the initial leachable calcium content in these substances can be determined by the following formula:
At the microscopic level, the initial leachable calcium in LD-CSH and HD-CSH is distributed based on their respective volume proportions, as shown below:
This comprehensive multi-scale model helps elucidate the impact of leaching on the structural performance of cement-based materials, providing a robust theoretical framework for understanding the leaching process in pure water environments and its influence on material properties.
4. Model Analysis and Application
4.1. Validation and Analysis of Hardened Cement Paste Model
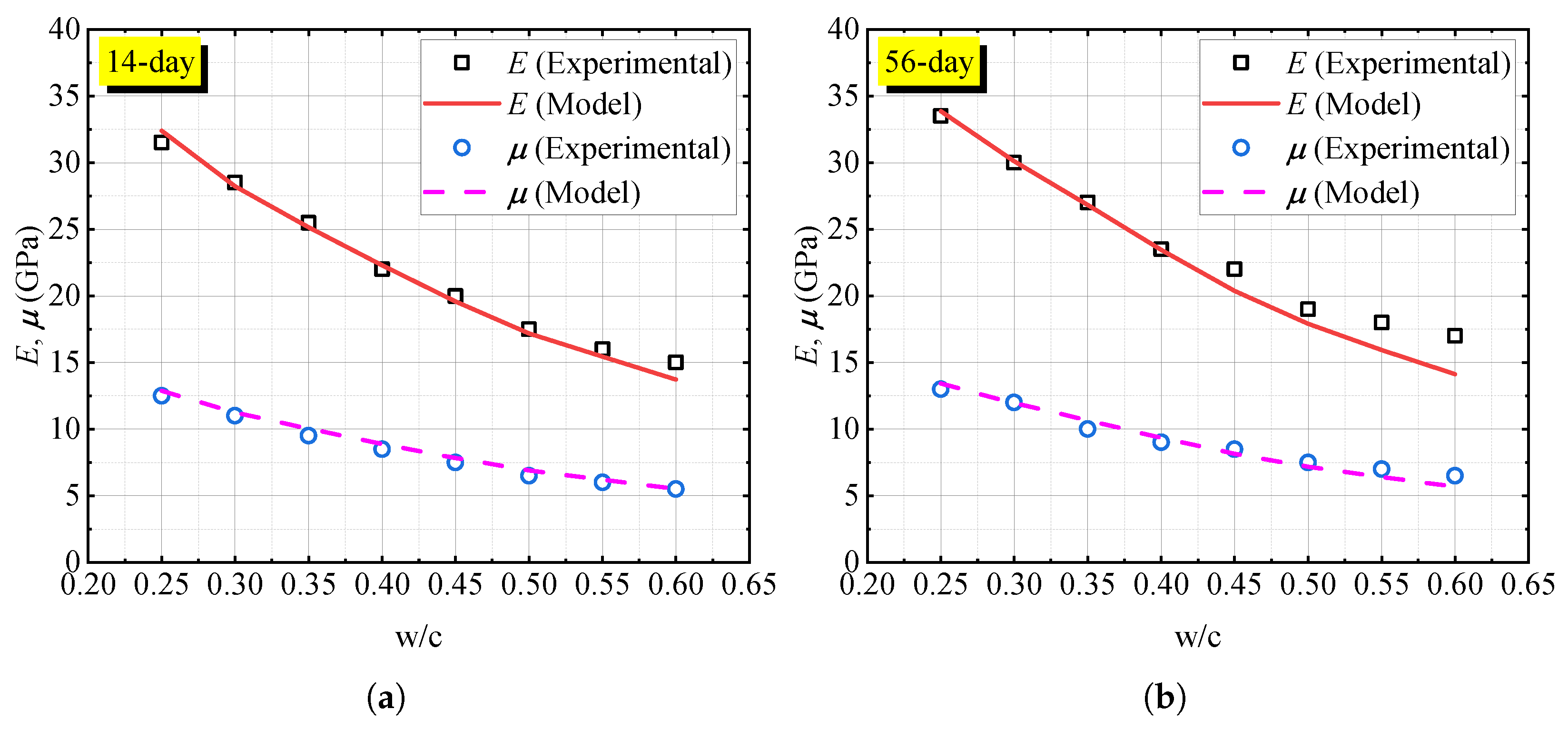
This section presents an empirical validation analysis of the hardened cement paste model. The validation process aims to assess the accuracy and reliability of the model in predicting the elastic properties of hardened cement paste. The empirical data used for validation are obtained from [38], comprising measured values of Young’s modulus and shear modulus at curing ages of 14 and 56 days, across various water-to-cement (w/c) ratios. It should be clarified that these experimental datasets were adopted from published literature rather than obtained through new laboratory tests. Therefore, a separate experimental section is not included, as this study focuses on analytical modeling and validation using existing benchmark data.
Figure 6 illustrates the comparison between the model’s predictions and the empirical data for Young’s modulus E and shear modulus . At 14 days, the model demonstrates a strong correlation with the experimental results, indicating its capability to capture the early-stage hydration dynamics. However, slight discrepancies are observed, particularly at lower w/c, where the model tends to slightly overestimate E and . As the curing age progresses to 56 days, the model’s predictions align more closely with the empirical data, especially for a w/c of 0.25. This suggests an improvement in the model’s accuracy as hydration advances. Nonetheless, minor deviations persist, emphasizing the need for further refinement, particularly at higher w/c.
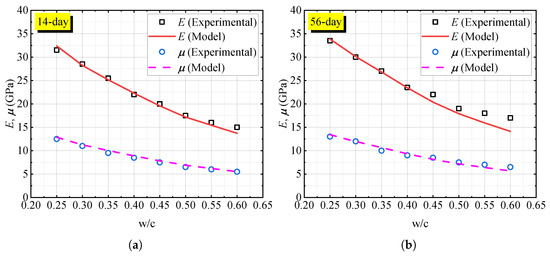
Figure 6.
Correlation between water-to-cement ratio and elastic properties of hardened cement paste at different curing ages, with experimental data from [38] and model predictions from this study: (a) 14-day. (b) 56-day.
Overall, the empirical validation confirms the model’s effectiveness in simulating the evolution of elastic properties in hardened cement paste. The discrepancies observed provide valuable insights for enhancing the model’s predictive precision, particularly in capturing the intricate effects of hydration on material properties. Quantitatively, the relative deviation between predicted and experimental elastic moduli remained within approximately 10%, confirming the good predictive accuracy of the proposed model.
It should be noted that the experimental data used for model validation cover only two curing periods (14 and 56 days), which primarily represent the early and middle stages of hydration. This limited temporal coverage does not fully capture the long-term evolution of the elastic properties of cement-based materials throughout the service life of concrete structures. Nevertheless, the selected time points were chosen because they correspond to well-documented benchmark datasets that are widely used in the literature for validating micromechanical and multi-scale models [28,38]. They provide a reliable basis for assessing the model’s capability to reproduce the principal hydration-related stiffening behavior. Future work will incorporate extended experimental datasets covering later-age hydration (e.g., 90, 180, and 365 days) and coupling effects, such as temperature, humidity, and chemical exposure, to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the long-term evolution of elastic properties.
4.2. Investigation of Leached Cement Paste
In this study, we investigated the effects of gradual calcium leaching from CH, LD-CSH, and HD-CSH on the bulk and shear moduli of hardened cement paste immersed in pure water. This analysis utilized a multiscale model described in Section 3.2, focusing on cement paste samples that had been cured for 56 days as discussed in Section 4.1, while excluding the impact of additional hydration. Given the absence of actual laboratory data for comparison, the reliability of our model will be confirmed by correlating the phenomena observed in the model with the trends described in published literature. We particularly emphasized the impact of varying water-to-cement ratios (w/c = 0.3, 0.4, 0.5).
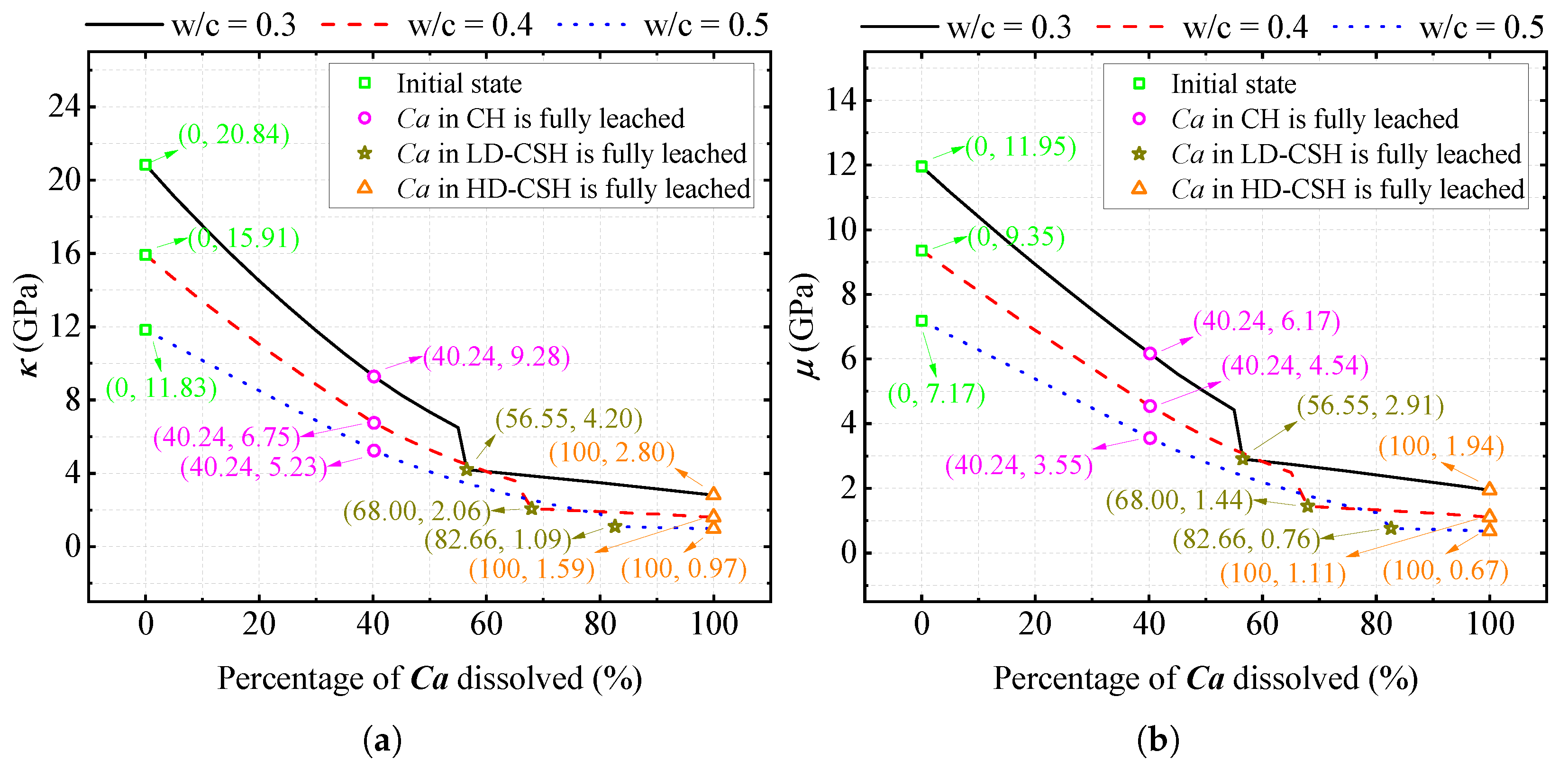
Figure 7 demonstrates the adverse impact of progressive calcium leaching from various phases (CH, LD-CSH, and HD-CSH) on the mechanical properties of hardened cement paste, notably affecting both bulk and shear moduli. This degradation is evident across all examined water-to-cement ratios (w/c = 0.3, 0.4, 0.5), where a marked decline in both moduli occurs as calcium dissolution progresses. The initial leaching of calcium from the CH phase results in the most significant reduction in these moduli, followed by more gradual decreases as leaching continues from LD-CSH and HD-CSH. Under complete decalcification, the simulation results indicate that the percentage reduction of elastic stiffness increases with the water-to-cement ratio. In particular, when , both the bulk and shear moduli decrease by approximately 90% relative to their initial values, indicating a more pronounced ultimate stiffness loss in mixtures with higher water content. Although mixtures with higher initially exhibit lower absolute stiffness due to increased porosity, they also experience a larger relative modulus loss at full decalcification, highlighting the coupled influence of initial pore structure and chemical degradation. These observations underscore the pivotal role of calcium in preserving the structural integrity of cement paste, aligning with findings from previous studies [39,40], which emphasize the detrimental effects of calcium depletion on cementitious materials’ mechanical properties.
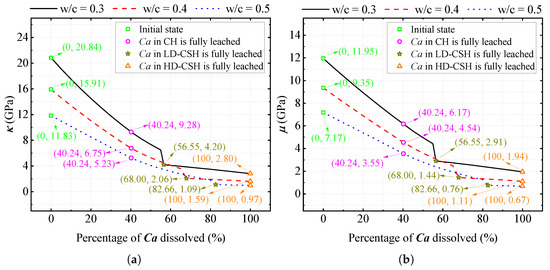
Figure 7.
Simulated variation of elastic properties with calcium leaching percentage at different water-to-cement ratios, as predicted by the proposed multiscale model: (a) Bulk modulus . (b) Shear modulus .
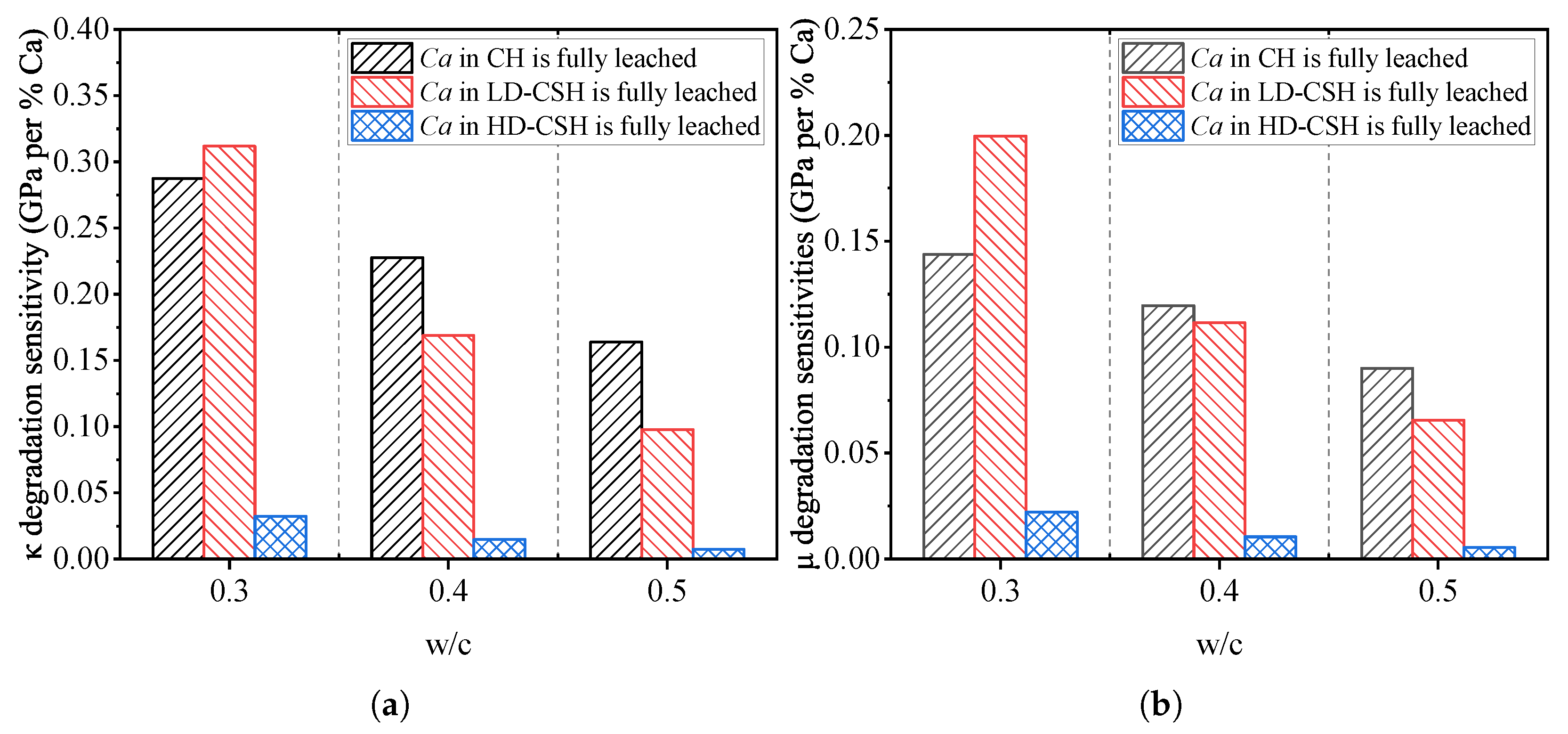
To further quantify the sensitivity of elastic properties to calcium leaching, the variation rate of the elastic modulus with respect to calcium loss was evaluated under different water-to-cement ratios (, , and ), as illustrated in Figure 8. The rate is defined as the incremental change in elastic modulus per unit percentage of calcium leached, expressed as:
where represents the modulus degradation sensitivity (GPa/%Ca), and are the elastic moduli at two consecutive leaching stages, and and denote the corresponding percentages of calcium leached. The modulus M can refer to either the bulk modulus or the shear modulus .
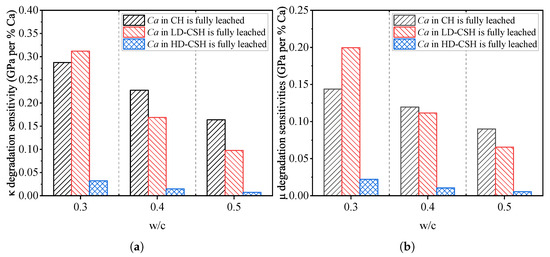
Figure 8.
Simulated evolution of modulus degradation sensitivity under different water-to-cement ratios, as predicted by the proposed multiscale model: (a) Bulk modulus degradation sensitivity. (b) Shear modulus degradation sensitivity.
It should be emphasized that does not represent the overall chemical stability of the cement paste but rather the local mechanical sensitivity of stiffness to incremental calcium loss-that is, the slope of the M- degradation curve. A smaller at higher values therefore indicates a more gradual stiffness decline per unit Ca loss, which mainly results from (i) the lower initial modulus of high- pastes and (ii) the transition from rapid CH dissolution to slower CSH decalcification. Hence, this apparent reduction in should be interpreted as a normalization effect within the modulus–leaching relationship rather than as evidence of improved chemical durability at higher .
From Figure 8, it can be observed that the decreases with increasing water-to-cement ratio. This apparent trend, however, should not be interpreted as an indication of higher chemical stability at larger . Instead, it primarily reflects a normalization effect arising from the lower initial stiffness and the progressive transition of the leaching mechanism. In low- pastes, the dense microstructure leads to higher initial modulus and thus a steeper modulus decline when calcium is removed from CH and LD-CSH. Conversely, in high- systems, the initial modulus is smaller and the subsequent CSH decalcification proceeds more gradually, resulting in a smaller numerical value. Among the individual phases, the leaching of calcium from the CH phase causes the sharpest modulus degradation under all conditions, demonstrating its dominant contribution to stiffness loss during the early stage of leaching. The LD-CSH phase also exhibits noticeable sensitivity at low , whereas the HD-CSH phase shows the lowest degradation sensitivity, implying its relatively minor role in the overall elastic response of the hardened paste.
These results highlight that the observed difference in among mixtures arises primarily from mechanical normalization and microstructural characteristics rather than intrinsic chemical resistance. It should also be noted that the simulated water-to-cement ratios in this study range from 0.3 to 0.5. The apparent reduction in modulus degradation sensitivity () at higher therefore applies only within this interval. This trend represents a relative moderation of stiffness loss per unit calcium leached, rather than an absolute improvement in chemical durability. At very high values (e.g., >0.6), the increased porosity and ion diffusivity would be expected to accelerate calcium leaching and mechanical deterioration, which lies beyond the scope of the present model. This clarification ensures that the interpretation of “enhanced chemical stability” remains confined to the modeled range and reflects the internal normalization behavior of the model rather than a universal material property. Recognizing this distinction provides a more accurate understanding of the leaching-induced degradation process and supports the optimization of mixture design for long-term durability in chemically aggressive environments.
To further understand the impact of calcium leaching on the modulus of cement paste, we normalized the vertical axis of Figure 7 to represent the percentage of the initial modulus, as illustrated in Figure 9. This adjustment allows us to observe that as the percentage of dissolved calcium increases, both the bulk modulus and shear modulus of the cement paste, relative to their initial values, show a marked decreasing trend. Statistical analysis has enabled us to model this change accurately using an exponential decay function, commonly expressed as:
where denotes the percentage of the initial modulus, denotes the percentage of dissolved calcium, and , , and are model parameters determined through regression analysis of the actual data. The high value of this model confirms its strong fit and validates its effectiveness.
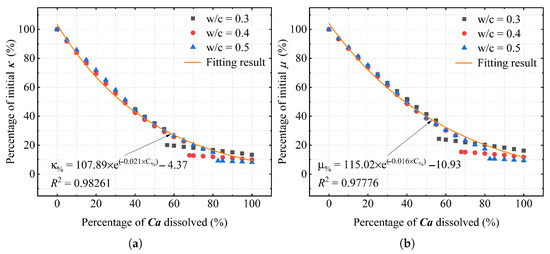
Figure 9.
Normalized elastic modulus degradation with calcium leaching percentage and corresponding exponential fitting, as predicted by the proposed multiscale model: (a) Percentage of the initial bulk modulus . (b) Percentage of the initial shear modulus .
To further evaluate the reliability of the exponential fitting (Equation (12)), additional statistical indicators—including the root-mean-square error (RMSE) and Akaike information criterion (AIC)—were calculated for each fitted curve, complementing the analysis. The results indicate consistently low RMSE and stable AIC values across all water-to-cement ratios, verifying the robustness of the exponential fitting. Residuals exhibited random scatter without systematic bias, further supporting the adequacy of the model. In addition, a one-way ANOVA performed on the fitted parameters (, , and ) revealed no statistically significant difference () among the three ratios, demonstrating that the normalized modulus–Ca loss relationship is statistically independent of .
The results confirm that the normalized modulus degradation is governed primarily by the degree of calcium leaching and is largely independent of the water-to-cement ratio. This finding emphasizes that decalcification acts as the dominant mechanism controlling the reduction in elastic stiffness. The progressive depletion of calcium leads directly to a proportional decline in the normalized modulus, thereby weakening the mechanical performance of the material.
Through this comprehensive analysis, we emphasize the importance of focusing on calcium stability in the design of cement-based materials to bolster their resistance against chemical erosion. Preserving calcium integrity is essential for maintaining and enhancing the structural integrity of the cement paste, particularly in applications susceptible to chemically aggressive environments. These insights offer crucial scientific guidance for the formulation and enhancement of the durability of cement materials, aiding in the proactive mitigation of the detrimental effects of chemical erosion during the design phase.
5. Concluding Remarks
This study developed a multiscale analytical model to investigate the degradation of elastic properties in OPC paste subjected to calcium leaching. By integrating hydration chemistry, microstructural hierarchy, and micromechanical homogenization, the model quantitatively captures how decalcification alters the stiffness of cement-based materials. Among eight evaluated microstructures and three homogenization schemes, the Mori–Tanaka approach combined with Microstructure-A was identified as the most representative configuration, offering a good balance between physical fidelity and computational efficiency.
Model validation against benchmark experimental data demonstrated that the proposed framework accurately reproduces the elastic behavior of hardened cement paste at different curing ages, with prediction errors within 10%. Simulation results reveal that calcium leaching induces substantial reductions in both bulk and shear moduli, with the CH phase being the most sensitive, followed by LD- and HD-CSH. The overall stiffness loss increases with the water-to-cement ratio, exceeding 90% at under complete decalcification. A sensitivity analysis further shows that the modulus degradation rate decreases with increasing , reflecting a mechanical normalization effect rather than improved chemical stability. Normalized analysis indicates that stiffness degradation is primarily governed by the degree of calcium loss rather than the initial water-to-cement ratio, underscoring the dominant role of decalcification in elastic deterioration.
The present model simplifies chemical interactions by focusing exclusively on calcium leaching in pure water, while other coupled processes—such as carbonation (Ca(OH)2 + CO2), C2SH → CSH conversion, and ettringite transformation—may further affect long-term durability. Future extensions will incorporate these coupled reactions, together with transport–reaction kinetics, temperature–humidity variations, and supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs), to improve predictive reliability. The developed multiscale analytical framework provides a solid theoretical foundation for modeling chemo-mechanical degradation and offers potential applications in the prediction of strength loss and service-life performance of cementitious materials under aggressive environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.S.; methodology, J.S.; software, J.X.; validation, J.S.; formal analysis, J.X. and J.S.; investigation, J.X.; data curation, J.X.; writing—original draft, J.X.; writing—review & editing, J.X. and J.S.; visualization, J.X.; supervision, J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work has been partially supported by the European Commission project EURAD through the work package MAGIC. This work was supported by the China Atomic Energy Authority (CAEA) through the Geological Disposal Program and by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grant Number 2025M774385.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Homogenization Scheme
Micromechanics, a pivotal discipline in materials science, bridges the microscopic and macroscopic properties of composite materials through quantitative analysis of the phase interactions and their collective influence on the overall mechanical behavior. This paper delves into the foundational role of micromechanics in predicting the elastic properties of cement paste, a composite material critical in construction and engineering. The study is structured around three principal micromechanical models—Voigt, Hashin-Shtrikman, and Mori-Tanaka—each providing unique insights into the effective bulk and shear moduli of cement paste. These models serve as theoretical frameworks to understand the synergy between the constituent phases of the cement paste, each contributing differently based on its mechanical properties and volume fraction:
- Voigt upper bound [41]:where , , and are the bulk modulus, shear modulus, and volume fraction of the r-th phase, respectively. In this paper, is effective bulk moduli, and is effective shear moduli. is the total number of phases contained in the material.
- Hashin-Shtrikman (HS) bounds [42]:The upper bound is obtained when the highest values of constituent moduli are used for and .
- Mori-Tanaka scheme [43,44]:where and are the bulk modulus and shear modulus of matrix respectively, is the volume fraction of matrix, and ; .
By integrating these microscale mechanical models, we aim to comprehensively evaluate the effective elastic properties of cement slurries. This approach not only deepens our understanding of material behavior under various environmental conditions but also assists in optimizing the composition of cement slurries to attain desired mechanical properties, thereby guiding engineering applications and material selection for constructing durable concrete infrastructure. To facilitate comparison with the experimental data, we determined the effective Poisson’s ratio and Young’s modulus at each level according to the following form:
References
- Makul, N. Modern sustainable cement and concrete composites: Review of current status, challenges and guidelines. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhou, J.; Hou, J.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, Z.; Sun, M.; Hu, J.; Huang, J. Building the future: Smart concrete as a key element in next-generation construction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 429, 136364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phung, Q.T.; Maes, N.; Jacques, D. Current concerns on durability of concrete used in nuclear power plants and radioactive waste repositories. In Proceedings of the 4th Congrès International de Géotechnique-Ouvrages-Structures: CIGOS 2017, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 26–27 October 2018; pp. 1107–1121. [Google Scholar]
- Kanagaraj, B.; Anand, N.; Andrushia, A.D.; Naser, M. Recent developments of radiation shielding concrete in nuclear and radioactive waste storage facilities—A state of the art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Neshawy, F.; Abo Ba Ragaa, B.; Punkki, J. Comprehensive State-Of-The-Art Report for Long-Term Behaviour of Concrete Structures in Repository Environment; Aalto University: Espoo, Finland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Gawin, D.; Pesavento, F.; Schrefler, B.A. Modeling deterioration of cementitious materials exposed to calcium leaching in non-isothermal conditions. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2009, 198, 3051–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Z.; Han, Z.Y.; Zheng, J.J.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, X.H. A multi-step scheme for evaluating the elastic moduli of partially leached cement paste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 344, 128095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, F.; Kamali-Bernard, S.; Prince, W. 3D multi-scale modelling of mechanical behaviour of sound and leached mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Liu, D.; Qiao, P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, L. Micro-CT-based micromechanics and numerical homogenization for effective elastic property of ultra-high performance concrete. Int. J. Damage Mech. 2020, 29, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stora, E.; Bary, B.; He, Q.C.; Deville, E.; Montarnal, P. Modelling and simulations of the chemo–mechanical behaviour of leached cement-based materials: Leaching process and induced loss of stiffness. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, G. The elastic properties of calcium leached cement pastes and mortars: A multi-scale investigation. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Shao, J.F.; Burlion, N. Experimental study of mechanical behaviour of cement paste under compressive stress and chemical degradation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2008, 38, 1416–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gîrboveanu, A.; Jebli, M.; Jamin, F.; Huon, V.; Bonnet, L.; Georgescu, D.; El Youssoufi, M.S. Mechanical tensile behaviour of cement paste/aggregate bond exposed to leaching. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Shao, J.F.; Burlion, N.; Liu, Z. A microstructure-based constitutive model for cement paste with chemical leaching effect. Mech. Mater. 2020, 150, 103571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Bian, H.; Xie, S.; Burlion, N.; Shao, J. A numerical study of mechanical behavior of a cement paste under mechanical loading and chemical leaching. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2017, 41, 1848–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, G.; Ulm, F.J. The effect of two types of CSH on the elasticity of cement-based materials: Results from nanoindentation and micromechanical modeling. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Qiu, J.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wan, X.; Sun, X. Microscale and macroscale strength behaviors of blast furnace slag-cement based materials: Modeling and analysis. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 376, 131016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.y.; Xiong, Q.X.; Zhang, M.; Meng, Z.; Meftah, F.; Liu, Q.F. Multi-scale modelling and statistical analysis of heterogeneous characteristics effect on chloride transport properties in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 367, 130096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Hong, Y.; Qiao, G.; Han, P. Quantifying the evolution of mechanical behaviours of concrete materials resting on realistic microstructural characteristics: A micro-to-macro validated combination analysis method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 409, 133843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, F.; Fraj, A.B.; Bayane, I.; Barthélémy, J. Estimating the mechanical properties of hydrating blended cementitious materials: An investigation based on micromechanics. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 104, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichler, B.; Hellmich, C. Upscaling quasi-brittle strength of cement paste and mortar: A multi-scale engineering mechanics model. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanahuja, J.; Dormieux, L.; Chanvillard, G. Modelling elasticity of a hydrating cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Dong, Q.; Yuan, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, J. Micro-scale characterization of the heterogeneous properties of in-service cement-treated base material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 264, 120696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, B.; Ramaswamy, A. A multi-physics-based approach to predict mechanical behavior of concrete element in a multi-scale framework. Mech. Mater. 2023, 176, 104509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Bian, C. Numerical modeling of elastic modulus for cement paste using homogenization method. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2013, 28, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, B.F.; Jin, D.; Yang, B.; Park, S.; Lee, H.K. Multi-level homogenization for the prediction of the mechanical properties of ultra-high-performance concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honorio, T.; Bary, B.; Benboudjema, F. Estimation of elastic properties of cement based materials at early age based on a combined numerical and analytical multiscale micromechanics approach. In Proceedings of the CONMOD 2014-RILEM International Symposium on Concrete Modelling, Beijing, China, 12–14 October 2014; Volume 91, pp. 236–243. [Google Scholar]
- Bernard, O.; Ulm, F.J.; Lemarchand, E. A multiscale micromechanics-hydration model for the early-age elastic properties of cement-based materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 1293–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R. Evaluation of the elastic modulus of concrete based on indentation test and multi-scale homogenization method. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 43, 102758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Wei, Y.; Wu, Z. Multiscale modeling elastic properties of cement-based materials considering imperfect interface effect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennis, P.D.; Jennings, H.M. A model for two types of calcium silicate hydrate in the microstructure of Portland cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, S.I.; Watanabe, A.; Kawamura, M. Evaluation of capillary pore size characteristics in high-strength concrete at early ages. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Krabbenhoft, K.; Lyamin, A. Statistical homogenization of elastic properties of cement paste based on X-ray microtomography images. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2013, 50, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, S.I.; Kawamura, M.; Watanabe, A. Analysis of cement pastes and mortars by a combination of backscatter-based SEM image analysis and calculations based on the Powers model. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2004, 26, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Li, Y.; Sun, W. Experimental and modelling research of the accelerated calcium leaching of cement paste in ammonium nitrate solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.A.; Churakov, S.V.; Prasianakis, N.I. A multi-level pore scale reactive transport model for the investigation of combined leaching and carbonation of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.; Miao, C.; Bullard, J.W. A model of phase stability, microstructure and properties during leaching of portland cement binders. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2014, 49, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haecker, C.J.; Garboczi, E.J.; Bullard, J.W.; Bohn, R.; Sun, Z.; Shah, S.P.; Voigt, T. Modeling the linear elastic properties of Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, P. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, and Materials; McGraw-Hill Publishing: Columbus, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, H.F.W. Cement Chemistry; Thomas Telford: London, UK, 1997; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Watt, J.P.; Davies, G.F.; O’Connell, R.J. The elastic properties of composite materials. Rev. Geophys. 1976, 14, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashin, Z.; Shtrikman, S. A variational approach to the theory of the elastic behaviour of multiphase materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1963, 11, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Tanaka, K. Average stress in matrix and average elastic energy of materials with misfitting inclusions. Acta Metall. 1973, 21, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benveniste, Y. A new approach to the application of Mori-Tanaka’s theory in composite materials. Mech. Mater. 1987, 6, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).