Lithium-Ion Battery Lifetime Prediction Model Based on a Fusion Expert Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis and Methodology
2.1. Degradation of Battery SOH and EOL Determination
2.2. Model Design Principles and Motivation
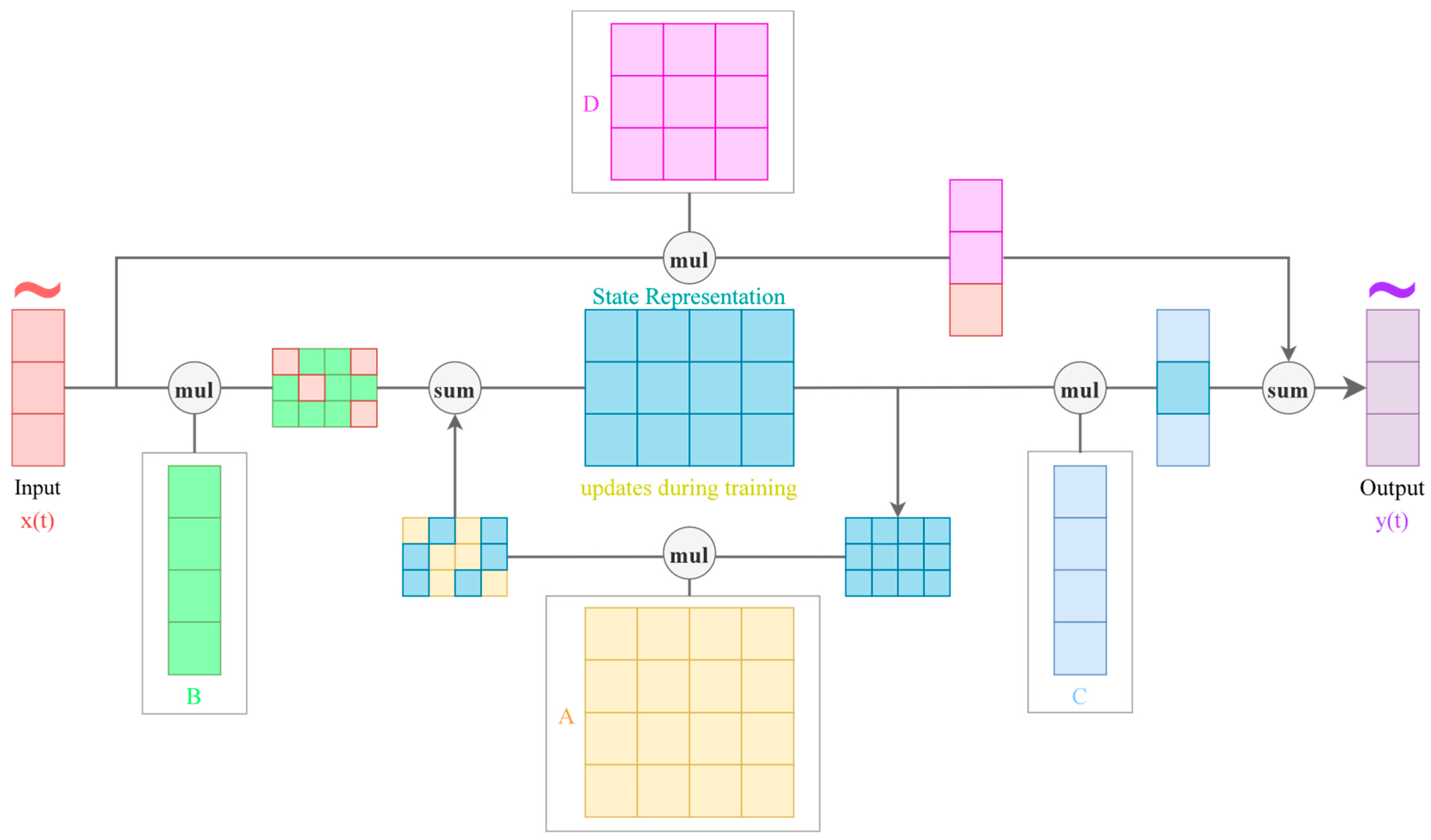
2.3. Structured State Space Models
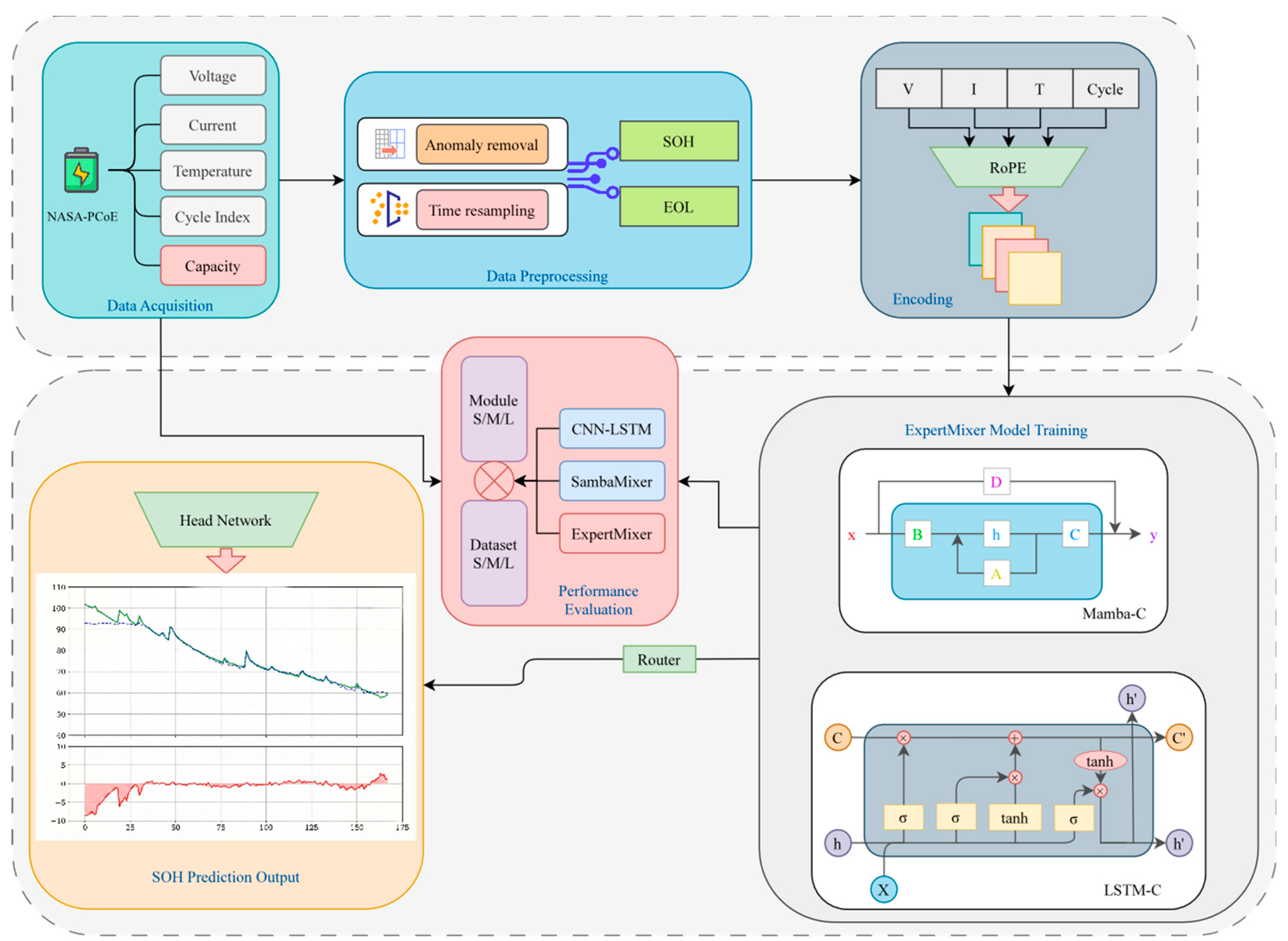
3. ExpertMixer Prediction Model
3.1. Model Architecture
3.2. Feature Extraction Network
3.3. Expert Fusion Network
3.4. Rotary Position Embeddings
4. Experimental Setup and Data Analysis
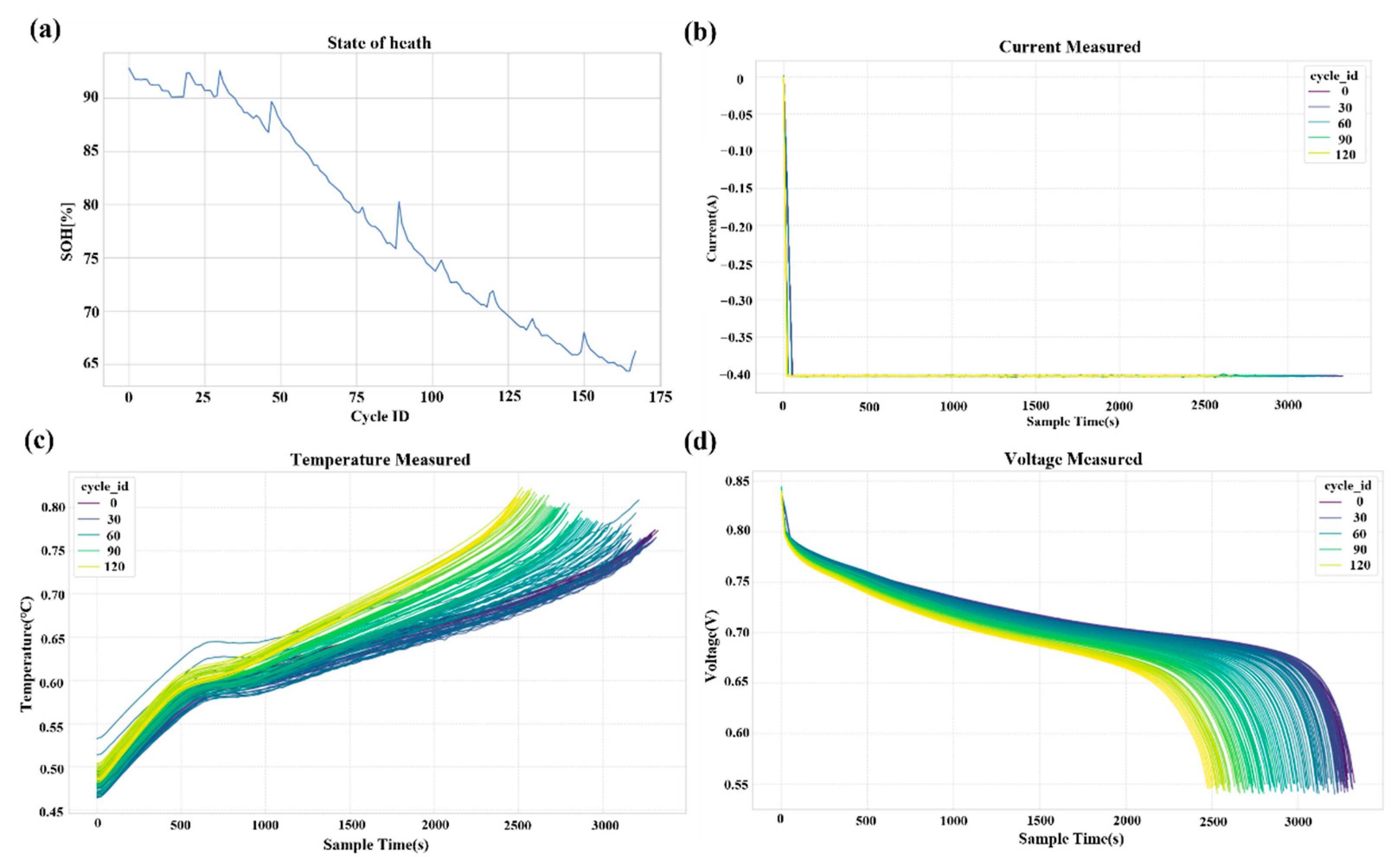
4.1. Experimental Setup
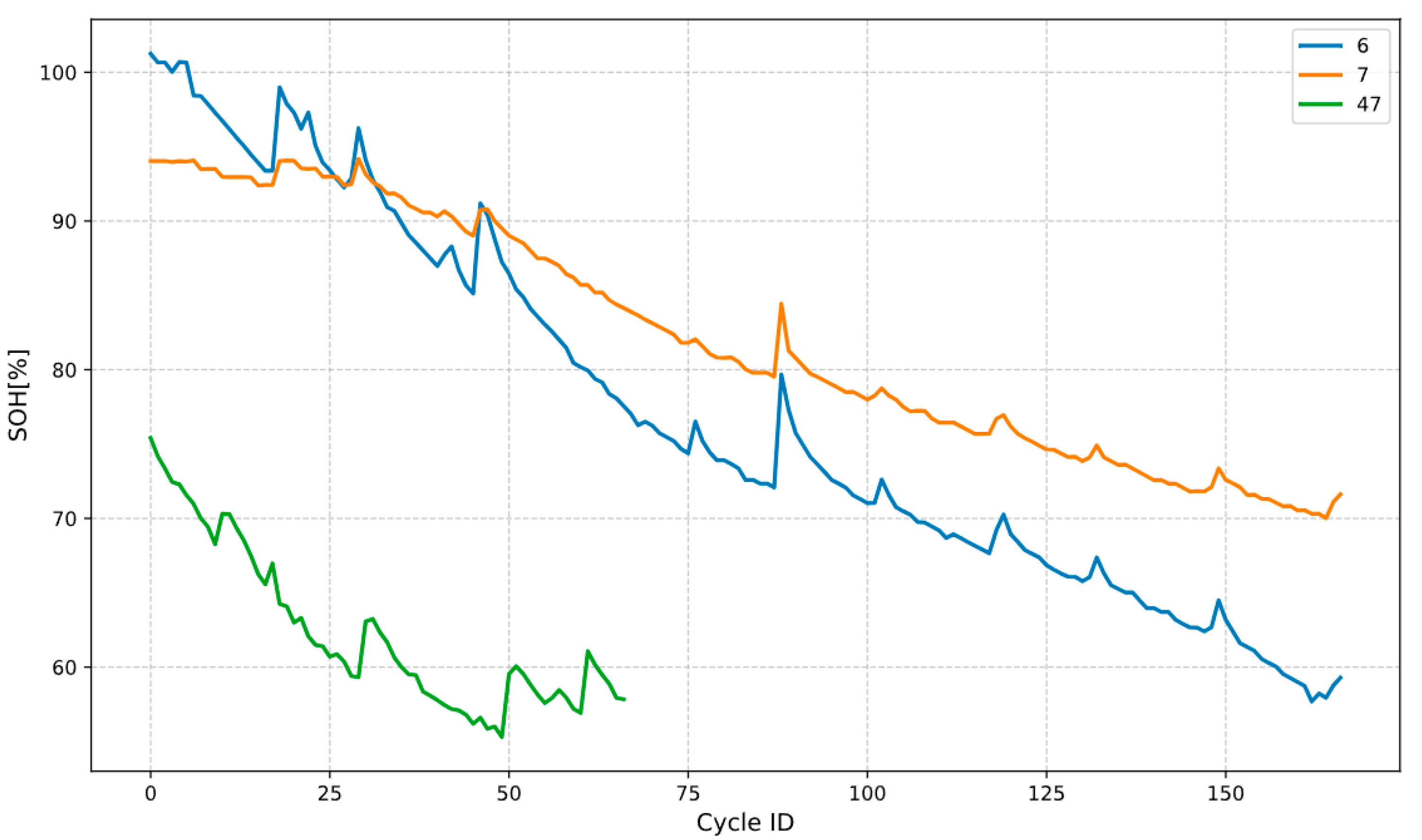
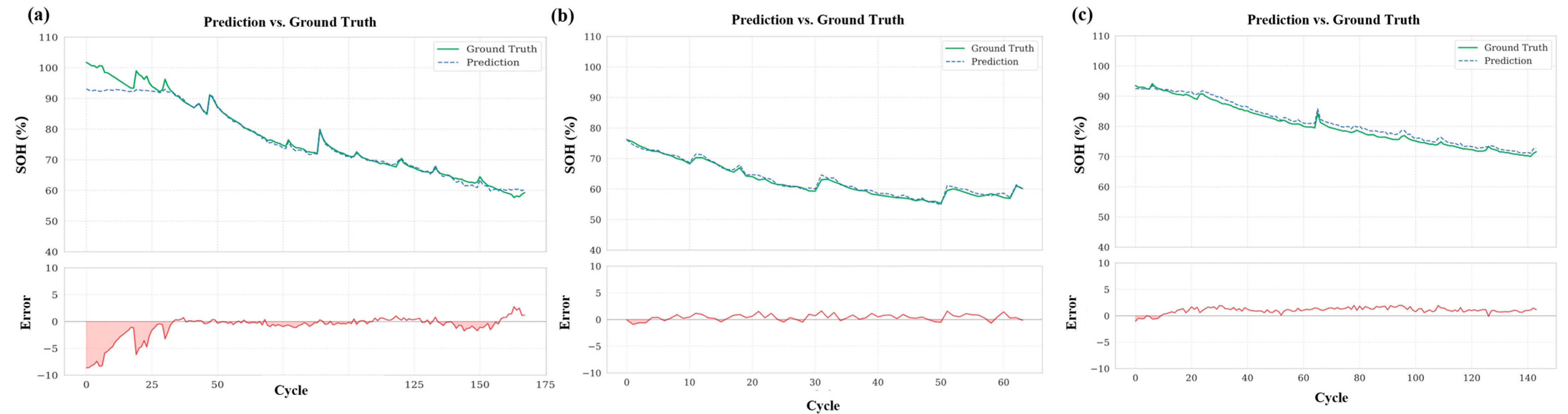
4.2. Estimation of SOH over the Battery Lifecycle
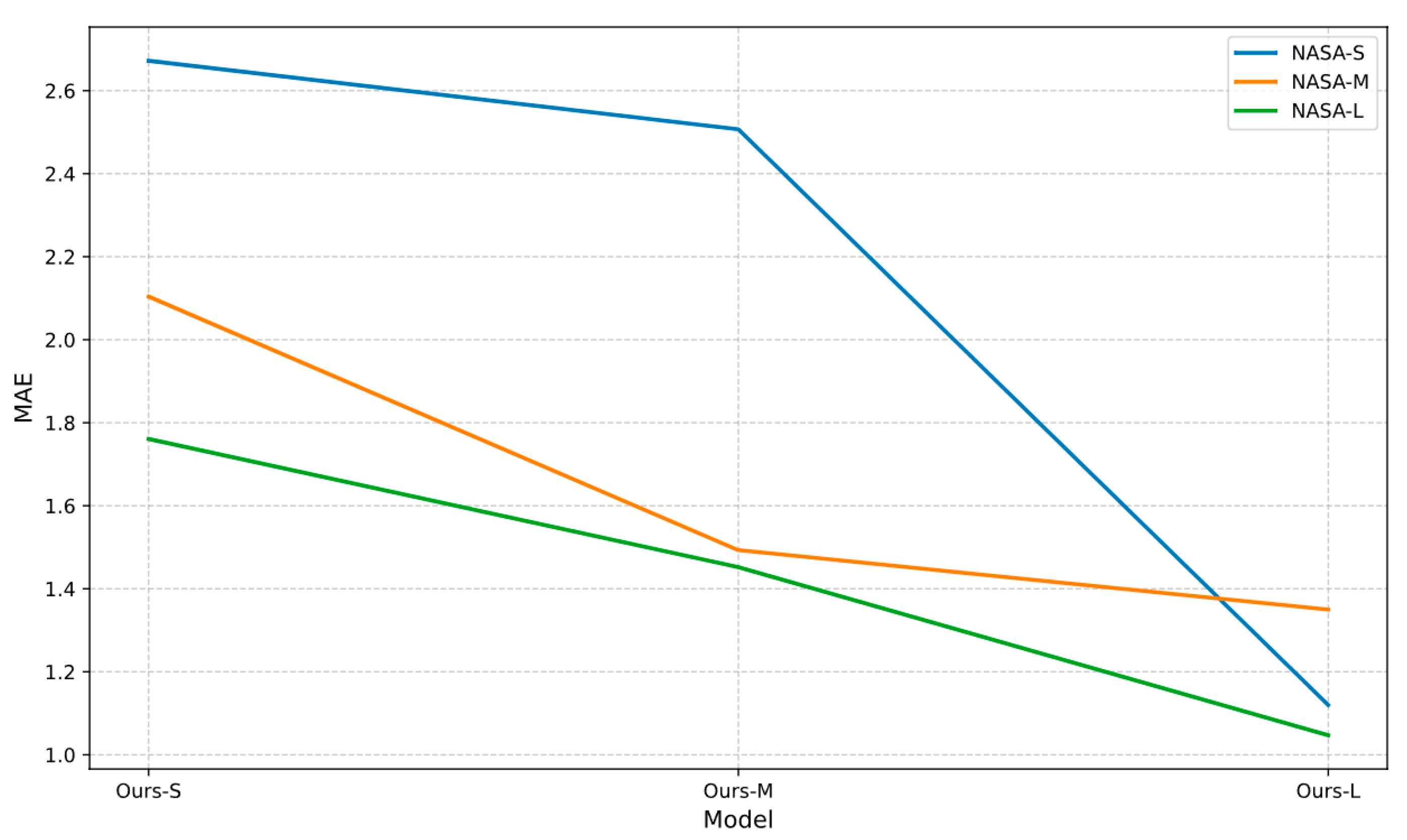
4.3. Analysis of Dataset Size and Model Parameters
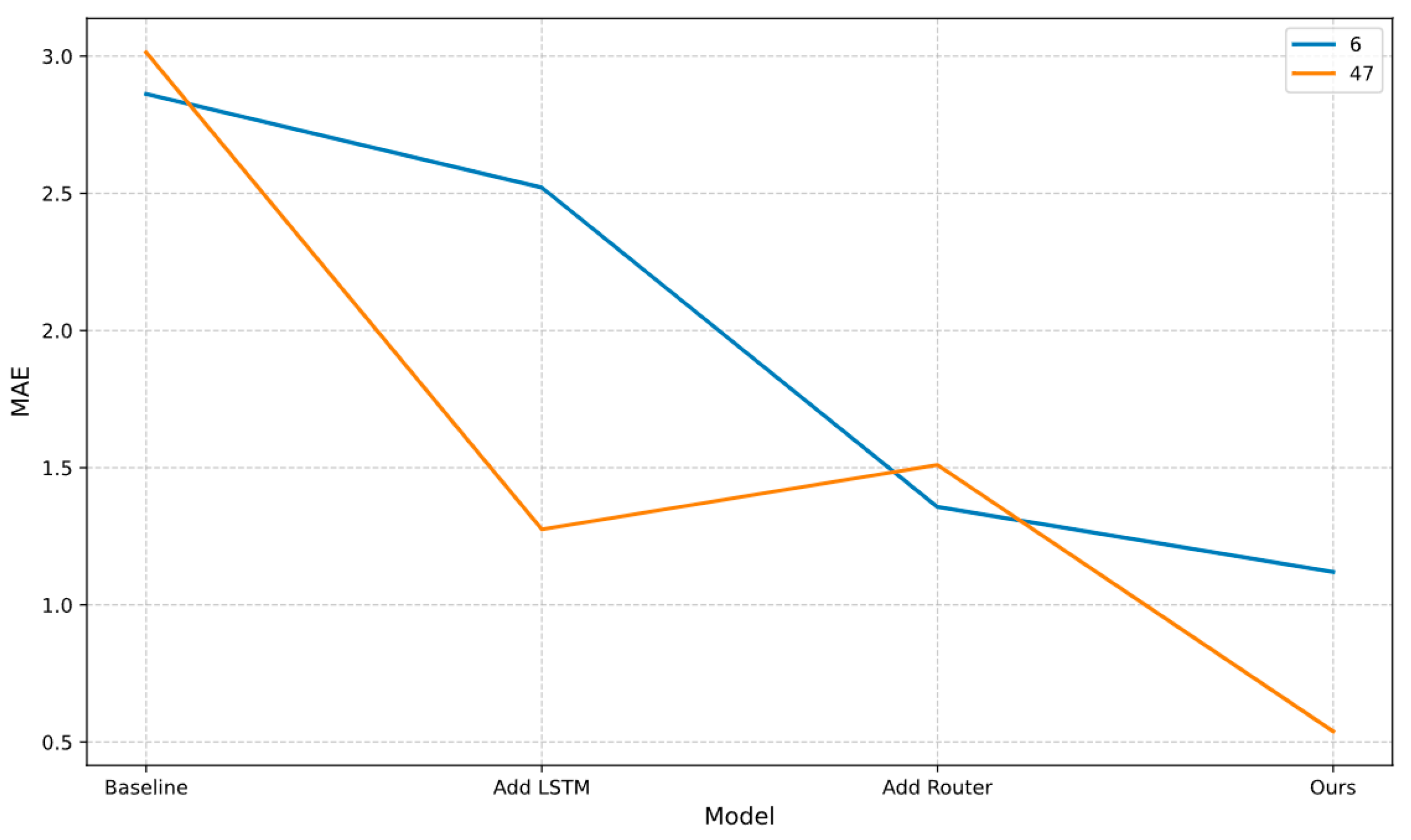
4.4. Ablation Experiment
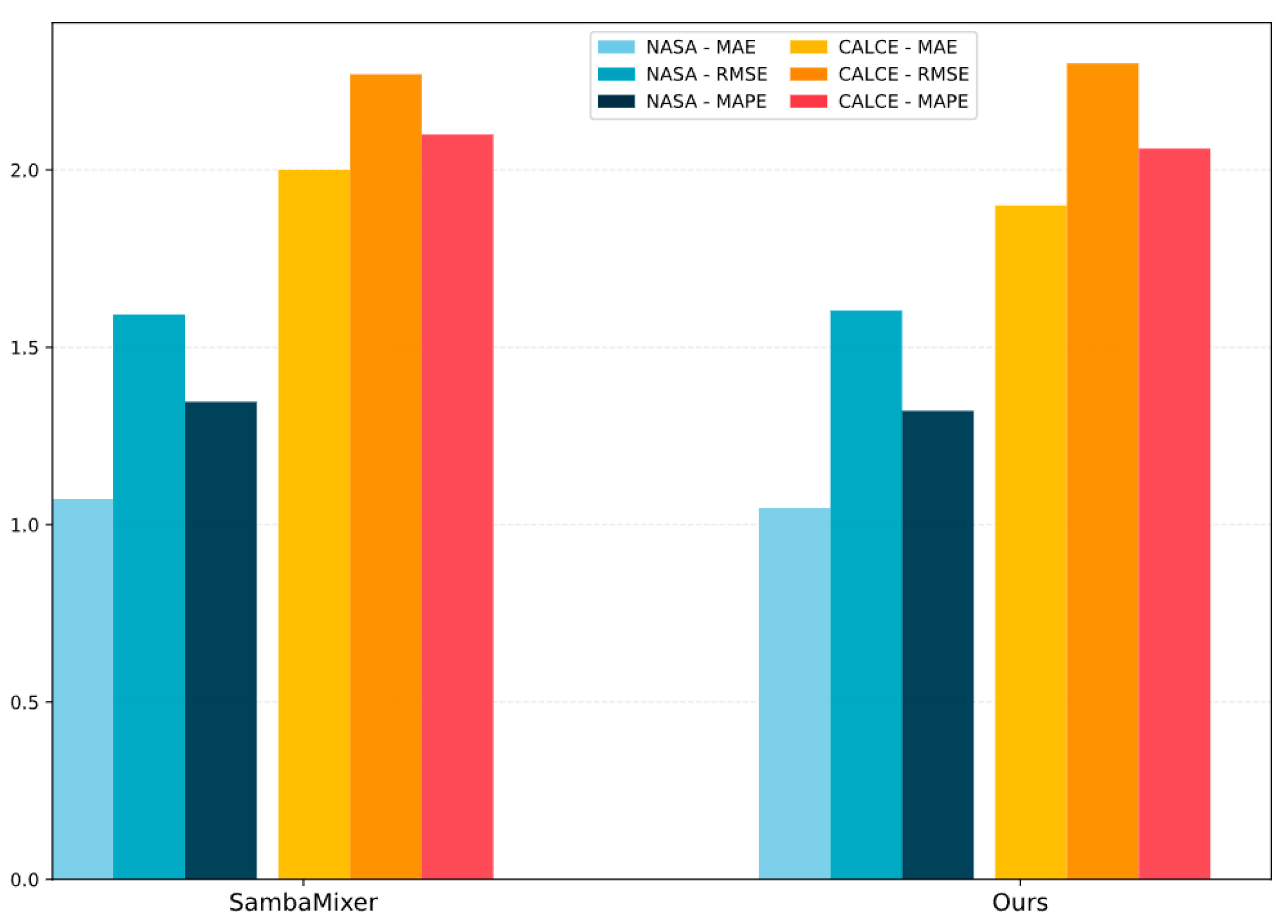
4.5. Cross-Dataset Generalization Validation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Liao, C.; Wang, L. Unified physics-informed subspace identification and transformer learning for lithium-ion battery state-of-health estimation. J. Energy Chem. 2026, 112, 350–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Tuo, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, G.; Lyu, Z.; Zeng, X. Physics-informed machine learning for accurate SOH estimation of lithium-ion batteries considering various temperatures and operating conditions. Energy 2025, 318, 134937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Sun, Z.; Han, Y.; Cai, N.; Zhou, Y. A multi-strategy attention regression network for joint prediction of state of health and remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries using only charging data. J. Power Sources 2025, 636, 236507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarari, S.; Byun, Y. XGBoost-Based Remaining Useful Life Estimation Model with Extended Kalman Particle Filter for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sensors 2022, 22, 9522. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Aitio, A.; Howey, D. Learning Li-ion battery health and degradation modes from data with aging-aware circuit models. Appl. Energy 2025, 397, 126375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzi, Y.; Sassi, H.B.; Errahimi, F. Lithium-ion battery state of health estimation using a hybrid model based on a convolutional neural network and bidirectional gated recurrent unit. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 127, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Song, X.; Xie, W. State of health estimation of lithium-ion battery based on cnn-wnn-wlstm. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Chen, J.X.; Feng, X.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, Q. State of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using autoencoders and ensemble learning. J. Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Gao, D.X. Attention-based cnn-bilstm for soh and rul estimation of lithium-ion batteries. J. Algorithms Comput. Technol. 2022, 16, 17483026221130598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Dong, J.B.; Wang, X.K.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, L.; Deen, M.J. A data-driven auto-cnn-lstm prediction model for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 3478–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Miao, J.; Tong, S.; Lu, Y. Early prediction of remaining useful life for lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid machine learning method. J. Clean Prod. 2021, 317, 128265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocioni, G.; Pau, D.; Delorme, J.M.; Gruosso, G. Li-ion batteries parameter estimation with tiny neural networks embedded on intelligent IOT microcontrollers. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 122135–122146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yuan, C.; Wang, Z. State of health estimation for li-ion battery via partial incremental capacity analysis based on support vector regression. Energy 2020, 203, 117852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Song, Z.; Hofmann, H.; Sun, J. Robust state of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using convolutional neural network and random forest. J. Energy Storage 2020, 8, 103857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, V.; Vaniar, A.M.; Bazmohammadi, N.; Vasquez, J.C.; Keysan, O.; Guerrero, J.M. Early prediction of battery remaining useful life using CNN-XBGoost model and Coati optimization algorithm. J. Energy Storage 2024, 98, 113176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Q.; Cai, N.; Wu, K. A self-attention knowledge domain adaptation network for commercial lithium-ion batteries state-of-health estimation under shallow cycles. J. Energy Storage 2024, 86, 111197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Z. GPT4Battery: An LLM-driven framework for adaptive state of health estimation of raw li-ion batteries. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.00068. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, W.; Wang, F.K.; Chou, J.H. Li-ion battery capacity prediction using improved temporal fusion transformer model. Energy 2024, 296, 131114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, C.; Song, T.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Sparse self-attentive transformer with multiscale feature fusion on long-term soh forecasting. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2024, 39, 10399–10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keles, F.D.; Wijewardena, P.M.; Hegde, C. On the computational complexity of self-attention. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.04881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Tanaka, K. State of health estimation of electric vehicle batteries using transformer-based neural network. J. Energy Resour. Technol.-Trans. ASME 2024, 146, 101703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J.; Pei, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, K.; Lu, T.; Wang, L. Video Mamba Suite: State space model as a versatile alternative for video understanding. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.09626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Ma, W.; Shu, X.; Shen, S.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Accurate state of health estimation for lithium-ion batteries under random charging scenarios. Energy 2023, 279, 128092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Johnson, I.; Goel, K.; Saab, K.; Dao, T.; Rudra, A.; Ré, C. Combining recurrent, convolutional, and continuous-time models with linear state-space layers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.13985. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Goel, K.; Re, C. Efficiently modeling long sequences with structured state spaces. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2111.00396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2312.00752v2. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Zimerman, I.; Wolf, L. The hidden attention of Mamba models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.01590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrouz, A.; Santacatterina, M.; Zabih, R. MambaMixer: Efficient selective state space models with dual token and channel selection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.19888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingzeng, S.; Yue, G.; Guo, D.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, B. Prediction of the remaining useful life of lithium-ion batteries based on mode decomposition and ED-LSTM. Batteries 2025, 11, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Liqun, C.; Shen, W.; Kangkang, X. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery via a sequence decomposition and deep learning integrated approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2022, 71, 1466–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, F.; Qiao, J.; Xu, T. Review on degradation mechanism and health state estimation methods of lithium-ion batteries. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2023, 10, 578–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekenes-Huskey, P.M.; Scott, C.E.; Atalay, S. Quantifying the influence of the crowded cytoplasm on small molecule diffusion. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 8696–8706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Jia, Y.; Xu, J. Mechanistic understanding of the electrochemo-dependent mechanical behaviors of battery anodes. J. Power Sources 2021, 510, 230428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Fahmy, H.M.; Hasanien, H.M.; Alhsrbi, M.; Ji, H. Hybrid extended Kalman filter with Newton Raphson method for lifetime prediction of lithium-ion batteries. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 14592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio, O.J.; Sascha, K.; Clara, P.; Sergio, M. SambaMixer: State of health prediction of Li-ion batteries using Mamba state space models. IEEE Access 2024, 13, 2313–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xin, F.; Whittingham, M.S.; Liaw, B. Lithium inventory tracking as a non-destructive battery evaluation and monitoring method. Nat. Energy 2024, 9, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahe, C.; Kelly, S.T.; Rad, M.N.; Sauer, D.U.; Mayer, J.; Figgemeier, E. Nanoscale X-ray imaging of ageing in automotive lithium ion battery cells. J. Power Sources 2019, 433, 126631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Su, X.; Liang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhong, L.; Ye, Y. Graph gating-mixer for sequential recommendation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Dong, P. Remaining useful life prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on a hybrid model combining the long short-term memory and Elman neural networks. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, S. SOH estimation method for lithium-ion batteries under low temperature conditions with nonlinear correction. J. Energy Storage 2024, 75, 109690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Battery Serial Number | Electricity | Voltage | Temperature | Initial Battery Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #5 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.7 V | 24 °C | 1.8565 Ah |
| #6 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.5 V | 24 °C | 2.0353 Ah |
| #7 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.2 V | 24 °C | 1.8911 Ah |
| #18 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.5 V | 24 °C | 1.8550 Ah |
| #25 | (PWM 0.05 Hz) 4.0 A | 2.0 V | 24 °C | 1.8470 Ah |
| #26 | (PWM 0.05 Hz) 4.0 A | 2.2 V | 24 °C | 1.8133 Ah |
| #27 | (PWM 0.05 Hz) 4.0 A | 2.5 V | 24 °C | 1.8233 Ah |
| #28 | (PWM 0.05 Hz) 4.0 A | 2.7 V | 24 °C | 1.8047 Ah |
| #29 | (const.) 4.0 A | 2.0 V | 43 °C | 1.8447 Ah |
| #31 | (const.) 1.5 A | 2.5 V | 43 °C | 1.8329 Ah |
| #34 | (const.) 4.0 A | 2.2 V | 24 °C | 1.6623 Ah |
| #36 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.7 V | 24 °C | 1.8011 Ah |
| #45 | (const.) 1.0 A | 2.0 V | 4 °C | 0.9280 Ah |
| #46 | (const.) 1.0 A | 2.2 V | 4 °C | 1.5161 Ah |
| #47 | (const.) 1.0 A | 2.5 V | 4 °C | 1.5244 Ah |
| #48 | (const.) 1.0 A | 2.7 V | 4 °C | 1.5077 Ah |
| #54 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.2 V | 4 °C | 1.1665 Ah |
| #55 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.5 V | 4 °C | 1.3199 Ah |
| #56 | (const.) 2.0 A | 2.7 V | 4 °C | 1.3444 Ah |
| Battery Serial Number | NASA-S | NASA-M | NASA-L |
|---|---|---|---|
| #5 | train | train | train |
| #18 | - | train | train |
| #25 | train | - | - |
| #26 | - | - | - |
| #27 | - | - | - |
| #28 | - | - | - |
| #29 | train | - | - |
| #31 | - | - | train |
| #34 | - | - | train |
| #36 | - | - | train |
| #45 | - | train | train |
| #46 | - | train | train |
| #48 | train | train | train |
| #54 | - | - | train |
| #55 | - | - | train |
| #56 | - | - | train |
| Model Name | Layer | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ExpertMixer-S | 256 | 16 | 8 |
| ExpertMixer-M | 512 | 16 | 8 |
| ExpertMixer-L | 1024 | 24 | 12 |
| Battery Serial Number | Model | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| #06 | Mazzi | 2.448 | 3.177 | 1.579 |
| SambaMixer | 1.173 s | 2.068 | 1.406 | |
| ExpertMixer | 1.120 | 2.108 | 1.331 | |
| #07 | Mazzi | 1.861 | 2.252 | 1.114 |
| SambaMixer | 1.197 | 1.285 | 1.498 | |
| ExpertMixer | 1.136 | 1.229 | 1.423 | |
| #47 | Mazzi | 2.549 | 3.094 | 1.969 |
| SambaMixer | 0.612 | 0.645 | 0.832 | |
| ExpertMixer | 0.539 | 0.717 | 0.814 |
| Model | Dataset | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ExpertMixer-S | NASA-S | 2.672 | 3.602 | 3.552 |
| NASA-M | 2.507 | 3.049 | 3.158 | |
| NASA-L | 1.120 | 2.108 | 1.331 | |
| ExpertMixer-M | NASA-S | 2.104 | 2.861 | 2.676 |
| NASA-M | 1.493 | 2.162 | 1.823 | |
| NASA-L | 1.350 | 1.912 | 1.695 | |
| ExpertMixer-L | NASA-S | 1.761 | 2.460 | 2.296 |
| NASA-M | 1.452 | 2.050 | 1.788 | |
| NASA-L | 1.047 | 1.603 | 1.321 |
| Model | Dataset | MAE | RMSE | MAPE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mazzi et al. [6] | NASA-S | 2.220 | 2.778 | 1.451 |
| SambaMixer | NASA-S | 1.764 | 2.404 | 2.320 |
| NASA-M | 1.334 | 1.902 | 1.641 | |
| NASA-L | 1.072 | 1.592 | 1.346 | |
| This work | NASA-S | 1.761 | 2.360 | 2.296 |
| NASA-M | 1.452 | 2.050 | 1.788 | |
| NASA-L | 1.047 | 1.603 | 1.321 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Song, Y.; Xie, R.; Liu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ren, F. Lithium-Ion Battery Lifetime Prediction Model Based on a Fusion Expert Network. Batteries 2025, 11, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11120440
Meng Y, Sun Q, Wang Z, Yang Q, Song Y, Xie R, Liu Q, Lin Y, Ren F. Lithium-Ion Battery Lifetime Prediction Model Based on a Fusion Expert Network. Batteries. 2025; 11(12):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11120440
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Yawei, Qiang Sun, Zhi Wang, Qizheng Yang, Yuchen Song, Rui Xie, Quanyi Liu, Yang Lin, and Fei Ren. 2025. "Lithium-Ion Battery Lifetime Prediction Model Based on a Fusion Expert Network" Batteries 11, no. 12: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11120440
APA StyleMeng, Y., Sun, Q., Wang, Z., Yang, Q., Song, Y., Xie, R., Liu, Q., Lin, Y., & Ren, F. (2025). Lithium-Ion Battery Lifetime Prediction Model Based on a Fusion Expert Network. Batteries, 11(12), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/batteries11120440







