Synergistic Toxicity Reduction of Cadmium in Rice Grains by Foliar Co-Application of Nano-Silica and Surfactants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Design
2.2. Preparation of Surfactant
2.3. Study Area Description
2.4. Sample Collection and Analysis
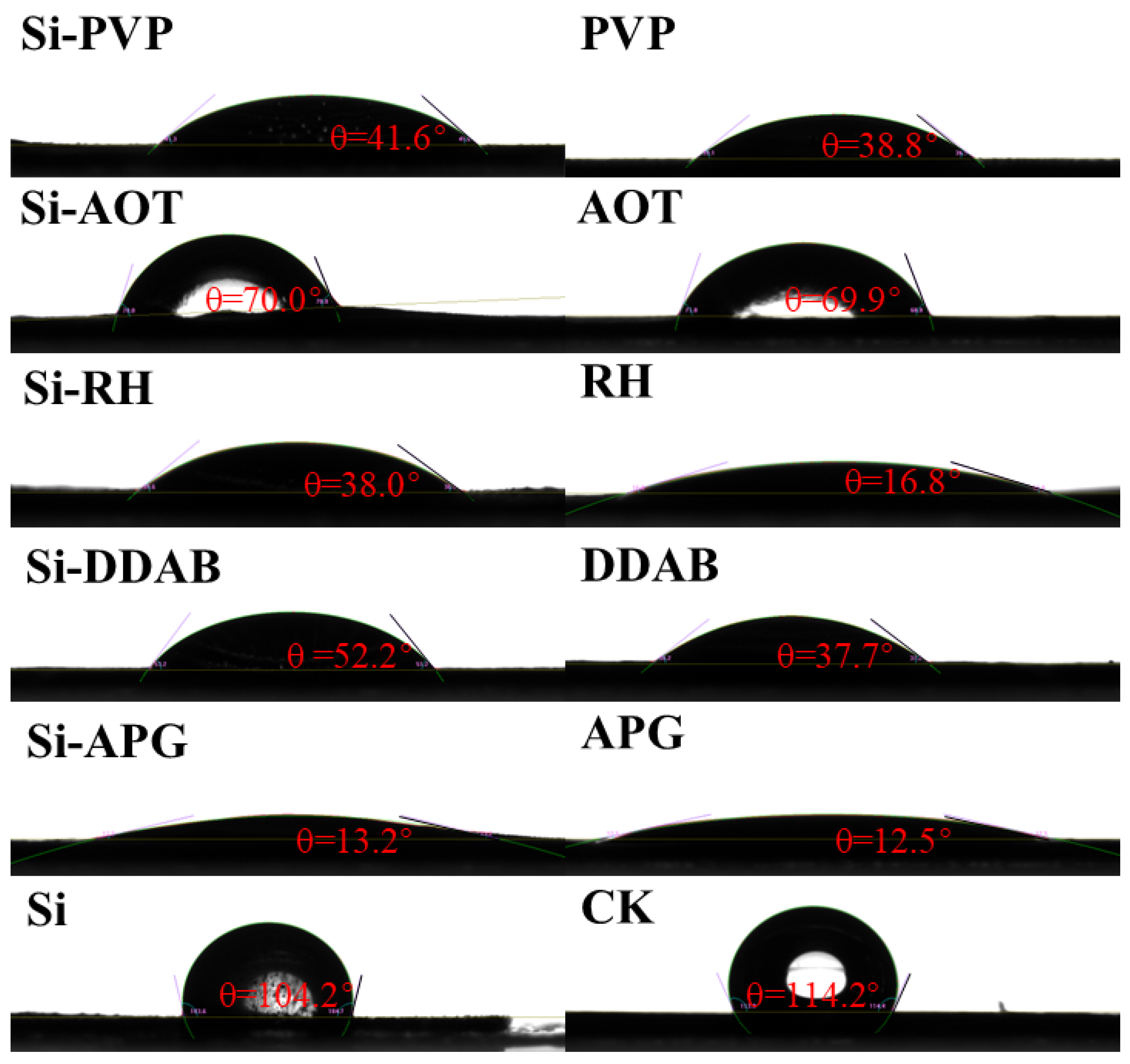
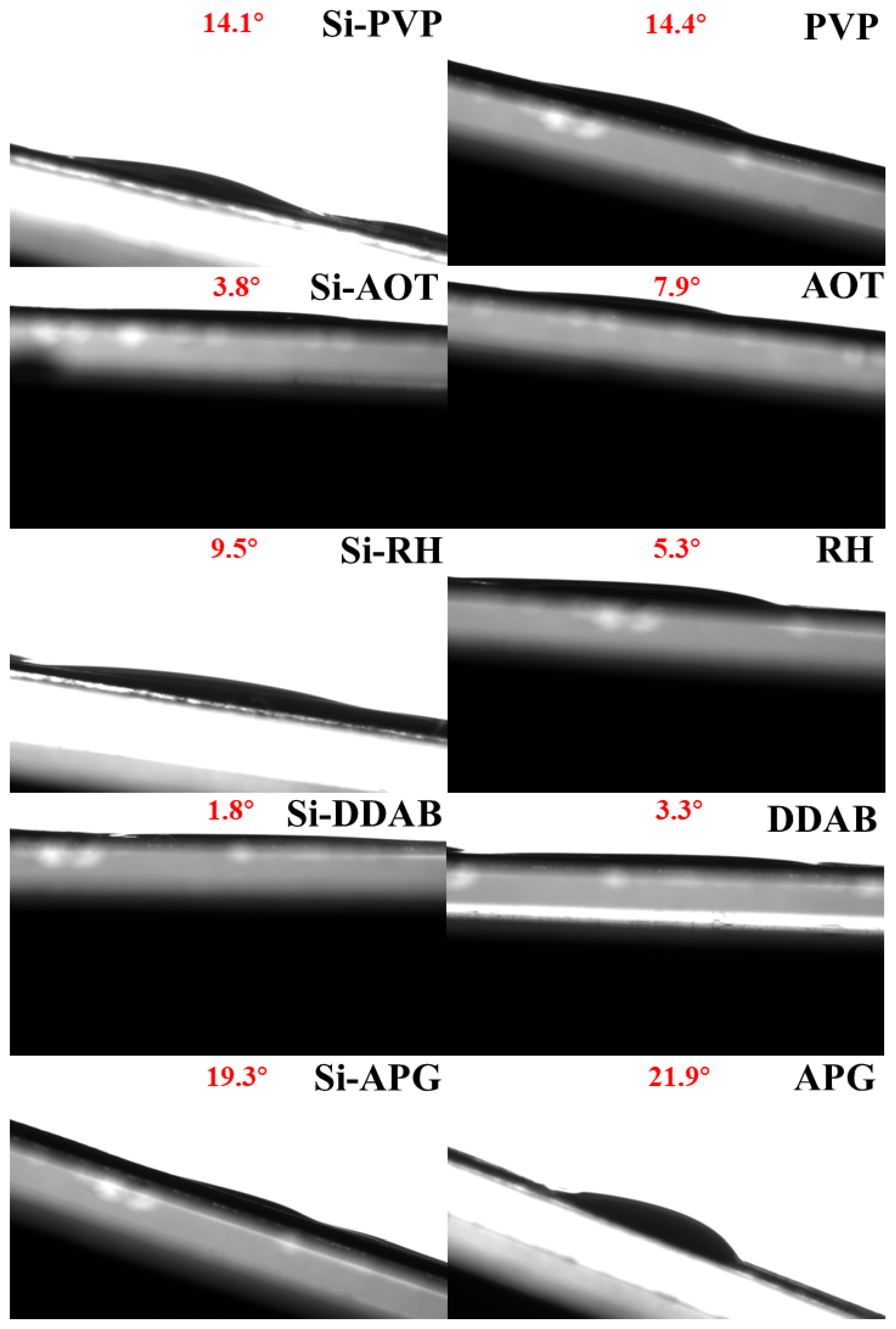
2.5. Analysis of Contact Angles and Rolling Angles
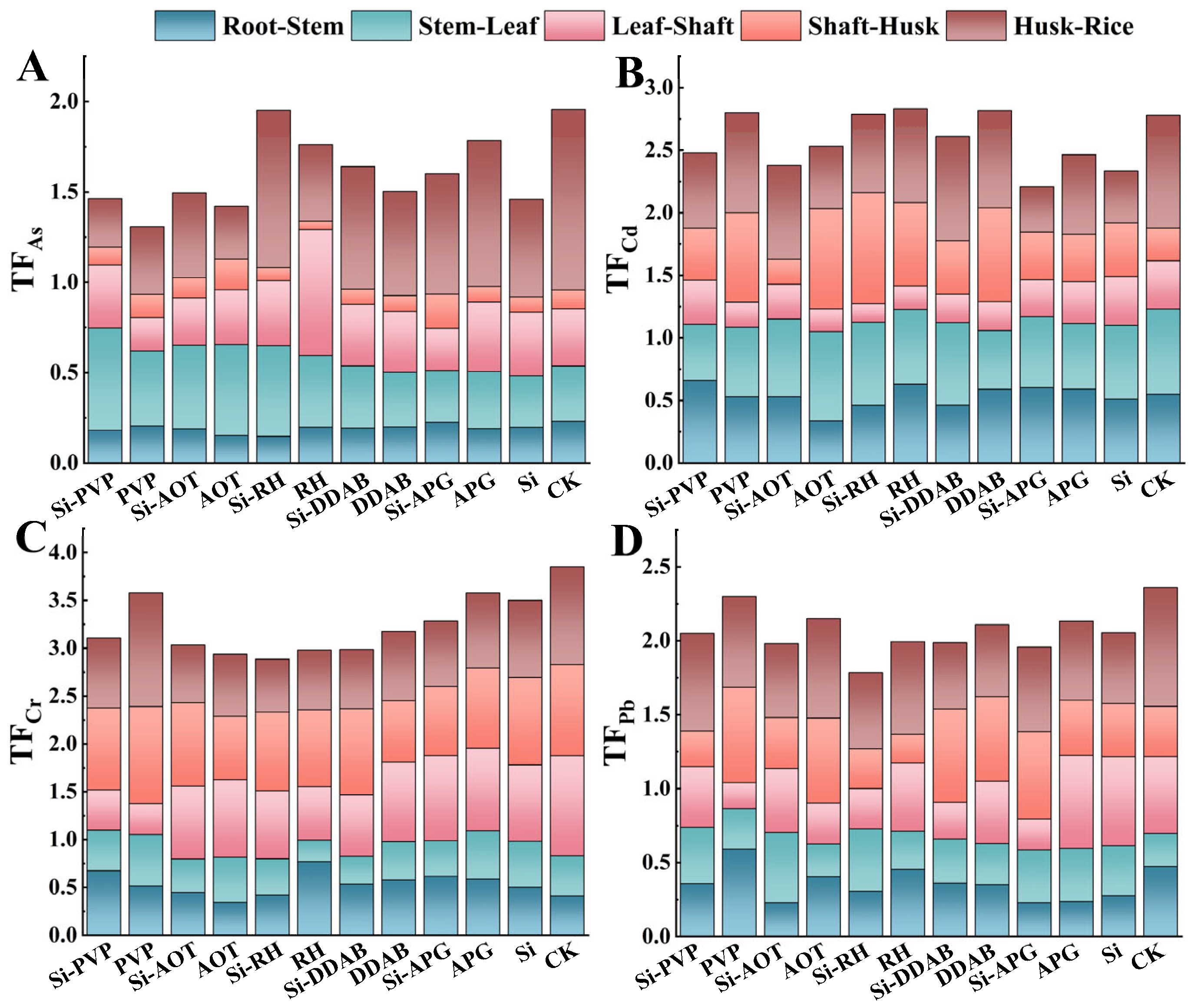
2.6. Calculation of Translocation Factor
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Surfactants on Wettability of Nano-Silica
3.2. Surfactants Exhibit a Synergistic Effect in Increasing the Rolling Angle
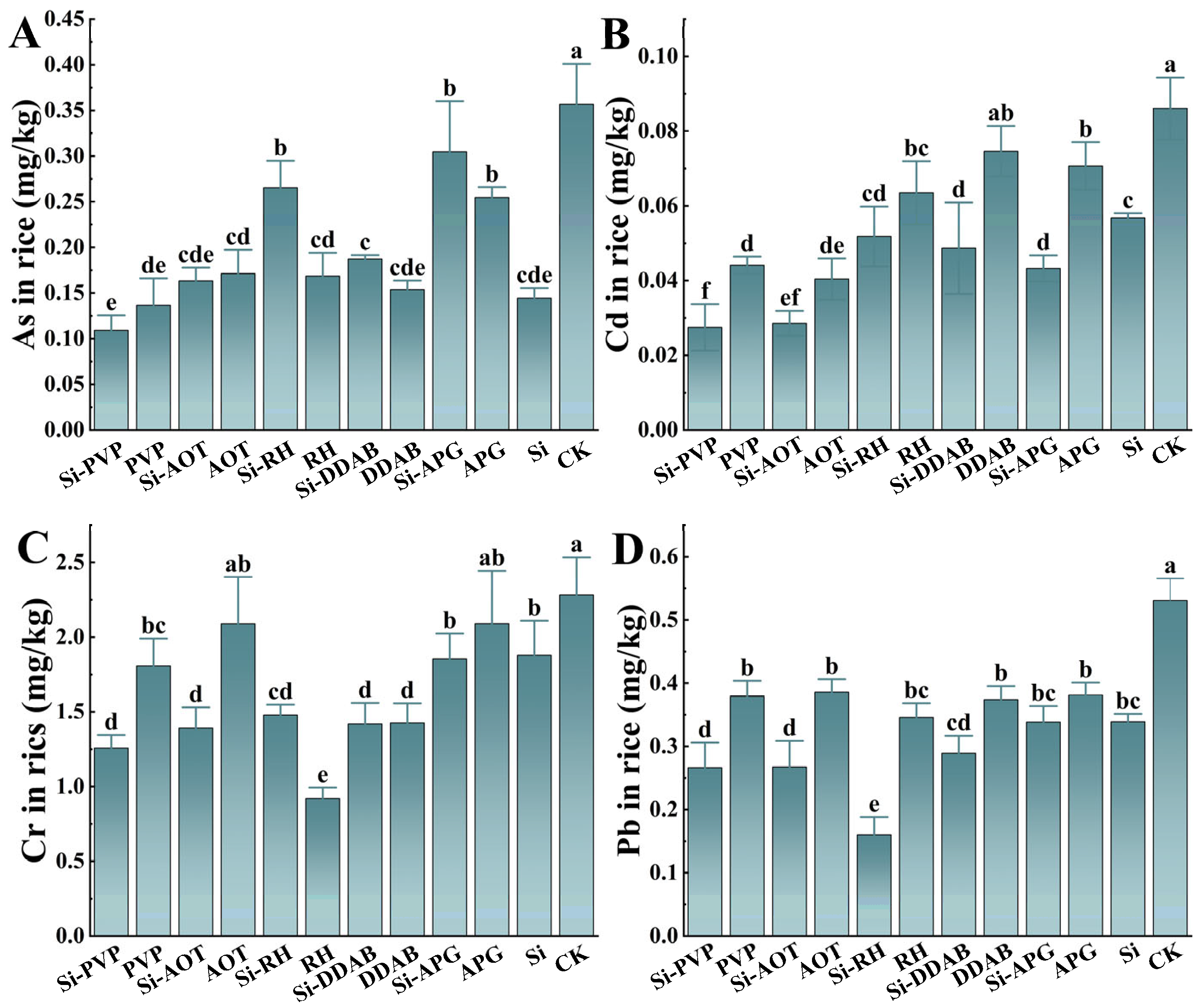
3.3. Effect of Different Treatments in Blocking Heavy Metals in Rice
3.4. Regulation of Heavy Metal Translocations Between Rice Organs by Different Treatments
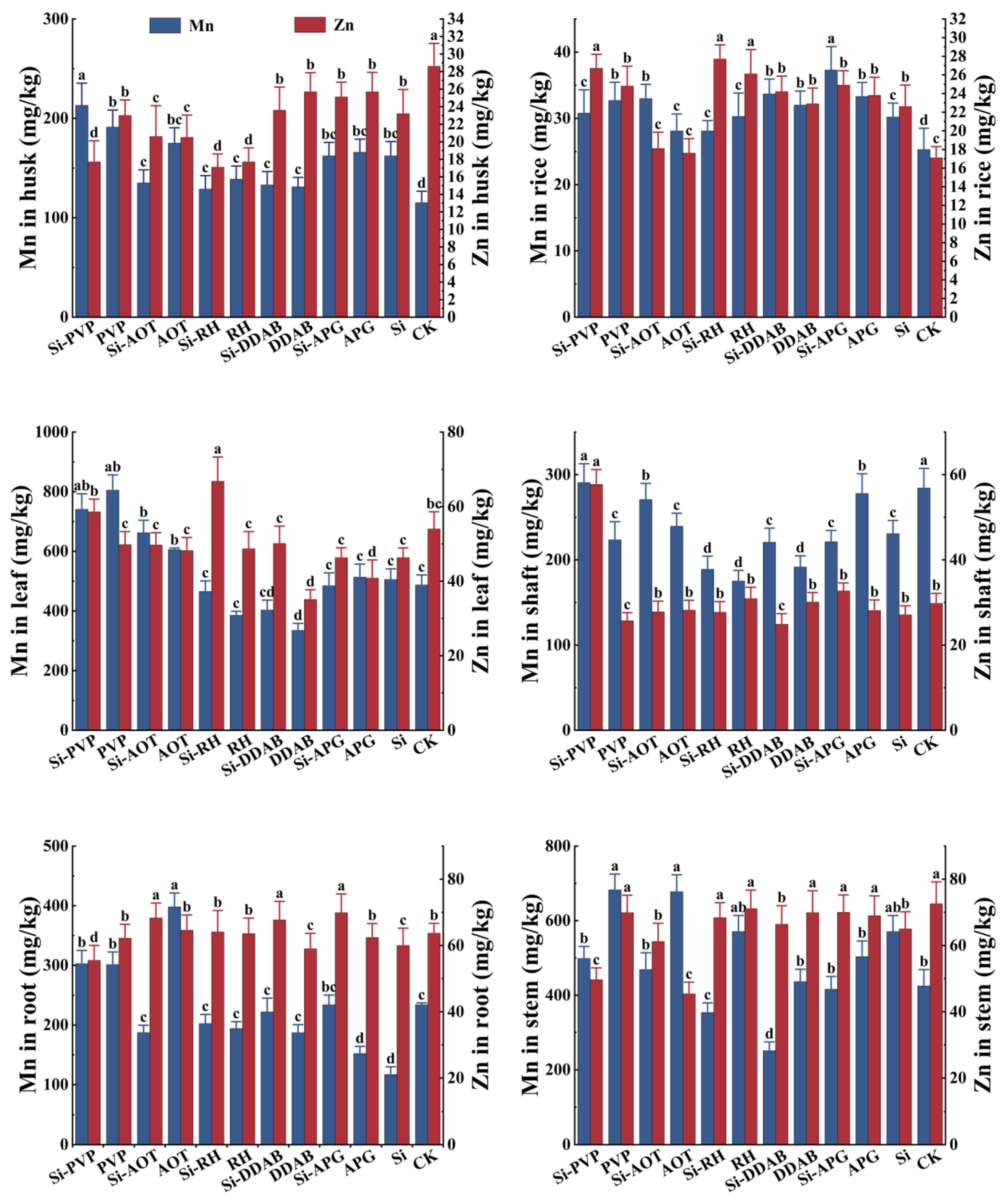
3.5. Promotional Effects of Different Treatments on the Accumulation of (Mn, Zn)
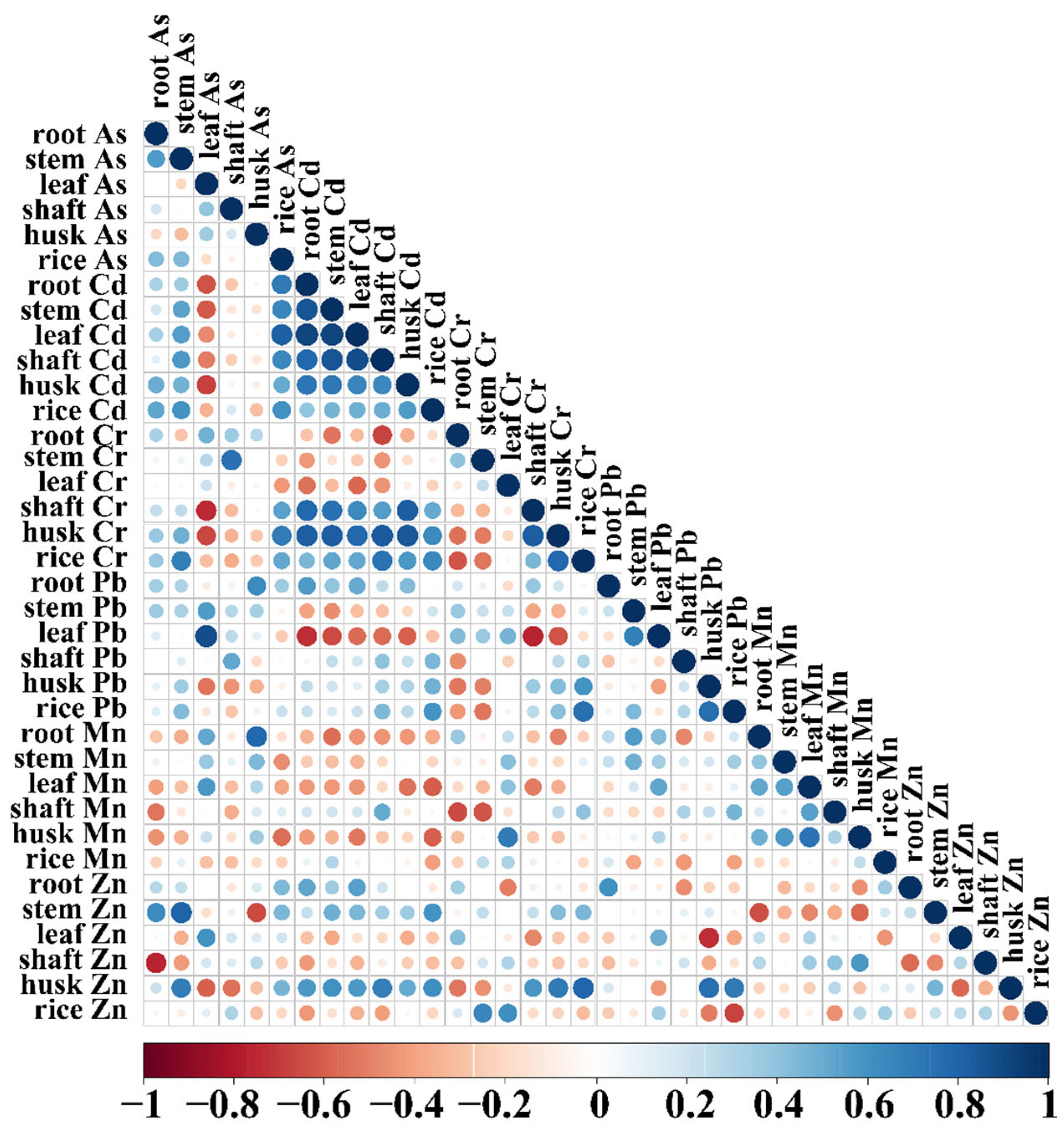
3.6. Correlation Analysis Between Elements in Various Parts of Rice
4. Discussion
4.1. Surfactants Enhanced the Duration and Efficacy of Nano-Silica
4.2. Facilitation Mechanism of Surfactants for Heavy Metal Reduction in Rice by Nano-Silica
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Si-PVP | Nano-silicon–Polyvinyl pyrrolidone |
| PVP | Polyvinyl pyrrolidone |
| Si-AOT | Nano-silicon–Aerosol OT |
| AOT | Aerosol OT |
| Si-RH | Nano-silicon–Rhamnolipid |
| RH | Rhamnolipid |
| Si-DDAB | Nano-silicon–Didodecyldimethylammonium Bromide |
| DDAB | Didodecyldimethylammonium Bromide |
| Si-APG | Nano-silicon–Alkyl Polyglycoside |
| APG | Alkyl Polyglycoside |
| Si | Nano-silicon |
References
- Liu, Z.P.; Zhang, Q.F.; Han, T.Q.; Ding, Y.F.; Sun, J.W.; Wang, F.J.; Zhu, C. Heavy metal pollution in a soil–rice system in the Yangtze River region of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appah, S.; Jia, W.; Ou, M.; Wang, P.; Asante, E.A. Analysis of potential impaction and phytotoxicity of surfactant-plant surface interaction in pesticide application. Crop Prot. 2020, 127, 104981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chen, H.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J. Cadmium contamination in agricultural soils of China and the impact on food safety. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Emran, T.B.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrova, L.; Nedyalkov, M.; Platikanov, D.; Razzetti, R.; Bianco, F. Wetting behavior of pulmonary surfactant aqueous solutions. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 2725–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Ruiter, J.; Lagraauw, R.; van den Ende, D.; Mugele, F. Wettability-independent bouncing on flat surfaces mediated by thin air films. Nat. Phys. 2015, 11, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Wang, C.; Tai, X.; Wang, G.; Liu, X. Optimization and characterization of biocompatible oil-in-water nanoemulsion for pesticide delivery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.R.; Cheng, T.T.; Liu, H.T.; Zhou, F.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.Y.; Shi, W.J.; Cao, T. Nano-selenium controlled cadmium accumulation and improved photosynthesis in indica rice cultivated in lead- and cadmium-contaminated paddy soils. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, H.J.; Xue, W.J.; Wang, C.R.; Zhang, C.B.; Huang, Y.C.; Liu, Z.Q. Effects of malate-aspartic acid metabolism on cadmium uptake and transport in rice. J. Agro.-Environ. Sci. 2023, 42, 2147–2154. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Yi, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, H. Silica nanoparticles alleviate cadmium toxicity in rice cells: Mechanisms and size effects. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Ali, B.; Adrees, M.; Arshad, M.; Hussain, A.; Zia Ur Rehman, M.; Waris, A.A. Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 2019, 214, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Malik, S.; Adrees, M.; Qayyum, M.F.; Alamri, S.A.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Effect of foliar applications of silicon and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on growth, oxidative stress, and cadmium accumulation by rice (Oryza sativa). Acta Physiol. Plant. 2019, 41, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.C.; Liu, M.S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Q.P.; Gu, Y.Q.; Song, X.P.; Li, Y.; Ye, Y.X.; Wang, F.B.; et al. Foliar spraying of Zn/Si affects Cd accumulation in paddy grains by regulating the remobilization and transport of Cd in vegetative organs. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Gao, S.; Wang, X. Heavy Metal Accumulation in Different Rice Cultivars as Influenced by Foliar Application of Nano-silicon. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, Q.; Lu, D.; Wang, C.; Cheng, T.; Fu, S. Reducing Cd Uptake and Translocation in Wheat Seedlings through Integrated Approaches Using Nanosilicon and Extracellular Polymeric Substances. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 18617–18631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; He, S.J.; Liu, T.L.; Zhang, Q.M.; Yu, J.; Gao, Y.F.; Wang, X.Y. Alleviation of Cadmium Toxicity by Nano-silicon Dioxide in Momordica charantia L. Seedlings. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 23, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Iqbal, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Iqbal, M.A.; Artyszak, A.; Sabagh, A.E.L.; Alharby, H.F.; Hossain, A. Foliar application of silicon-based nanoparticles improve the adaptability of maize (Zea mays L.) in cadmium contaminated soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 41002–41013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Hussain, A.; Zia Ur Rehman, M.; Ali, B.; Yousaf, B.; Wijaya, L.; Alyemeni, M.N.; Ahmad, P. Silicon nanoparticles enhanced the growth and reduced the cadmium accumulation in grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saadony, M.T.; Desoky, E.M.; Saad, A.M.; Eid, R.S.M.; Selem, E.; Elrys, A.S. Biological silicon nanoparticles improve Phaseolus vulgaris L. yield and minimize its contaminant contents on a heavy metals-contaminated saline soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 106, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z. Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, T.; Barman, S.; Mukherjee, A.; Kundu, R. Nano-scale zero valent iron modulates Fe/Cd transporters and immobilizes soil Cd for production of Cd free rice. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, P.; He, M.; Cao, Y.; Adeel, M.; Shakoor, N.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Iron-based nanomaterials reduce cadmium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by modulating phytohormones, phytochelatin, cadmium transport genes and iron plaque formation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wei, M.; Wang, Z.; Hou, S.; Li, X.; Xu, H. Bioremediation of cadmium polluted soil using a novel cadmium immobilizing plant growth promotion strain Bacillus sp. TZ5 loaded on biochar. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 122065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Song, H.; Zhao, Z.; Kuang, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chai, Y.; Bai, M.; Peng, L. Foliar spraying with a mixture of transpiration inhibitor-rhamnolipid reduces the Cd content in rice grains. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 885, 163844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, G.; Lan, Y.; Wen, S. The dynamic wetting and spreading behavior of pesticide droplet on rice leaf surface. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleva, M.; Garmash, E.; Chukina, N.; Malec, P.; Waloszek, A.; Strzałka, K. Effect of the exogenous anthocyanin extract on key metabolic pathways and antioxidant status of Brazilian elodea (Egeria densa (Planch.) Casp.) exposed to cadmium and manganese. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, L.Y.; Pashirova, T.N.; Doktorovova, S.; Fernandes, A.R.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Silva, A.M.; Souto, S.B.; Souto, E.B. Cationic Surfactants: Self-Assembly, Structure-Activity Correlation and Their Biological Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehlake, P.B. Experimental Assessment of Heavy Crude Oil Production Using Emulsion Flooding. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2017, 159, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, A.; Kalam, S.; Kamal, M.S.; Hussain, S.M.S.; Solling, T. EOR Perspective of microemulsions: A review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 208, 109681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.Y.; Yu, P.Y.; Zuo, M.; Tong, Z.L.; Huang, Z.; Xie, Z.Y.; Chang, R.M.; Peng, J.W.; Deng, Y.C.; Huang, Y. Screening of rice varieties with low accumulation of heavy metals based on leaf morphology. J. Plant Physiol. 2025, 293, 15454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Levels of Pollutants in Foods. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Lv, G.; Luo, Z.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, D.; Li, B. Foliar application of Zn-EDTA at early filling stage to increase grain Zn and Fe, and reduce grain Cd, Pb and grain yield in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 105, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, W.; Sui, H.; Yong, L.; Yang, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y. Dietary cadmium exposure assessment among the Chinese population. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C. Effects and Mechanisms of Seed Treatment and Foliar Application of Mn, Fe and Mo Fertilizers on Wheat Growth and Nutrient Uptake. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Shaanxi, China, 2019; p. 158. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Gu, Z.; Pi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Luo, J. Remediation efficiency of different immobilization treatments combined with foliar inhibitors in Cd-contaminated paddy fields. Hubei Agric. Sci. 2023, 62, 130–134+140. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, M. Hazards and remediation technologies of heavy-metal contamination in farmland soils. South. Agric. 2022, 16, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Shao, G.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wu, K. Research and application progress of agronomic practices for mitigating cadmium pollution in rice. China Rice 2021, 27, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Song, N.; Ning, L.; Zhang, J.; Liang, Y. Variation of Cd Concentration in Various Rice 446 Cultivars and Derivation of Cadmium Toxicity Thresholds for Paddy Soil by Species-Sensitivity Distribution. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1845–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, L.; Song, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, H. Effects of combined application of different straw-decomposing inoculants on wheat straw decomposition and rice yield in paddy fields. Soils 2022, 54, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, T.; Sun, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Q. Remediation efficiency of immobilizing agents and their physiological effects on pakchoi grown in cadmium-contaminated soil. Environ. Chem. 2020, 39, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Zhou, W.; Peng, D. Research progress on the effects of foliar inhibitors on cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. Crop Res. 2020, 34, 290–296. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, R.; Zhang, J.; Cao, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z. Influence of combined application of zinc and organic amendments on cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. China Rice 2022, 28, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Effects of different foliar conditioners on slightly heavy-metal-contaminated farmland. J. Hunan Ecol. Sci. 2023, 10, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, Q.; Ali, S. Seed priming with silicon nanoparticles improved the biomass and yield while reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat grains. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 7579–7588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Treatments | Ingredients and Concentration |
|---|---|
| Si-PVP | PVP (1 mmol/L) + nano-silicon (0.5 mmol/L) |
| PVP | PVP (0.4 mmol/L) |
| Si-AOT | AOT (1 mmol/L) + nano-silicon (0.5 mmol/L) |
| AOT | AOT (1 mol/L) |
| Si-RH | rhamnolipid (1 mmol/L) + nano-silicon (0.5 mmol/L) |
| RH | rhamnolipid (1 mol/L) |
| Si-DDAB | DDAB (1 mmol/L) + nano-silicon( 0.5 mmol/L) |
| DDAB | DDAB (1 mol/L) |
| Si-APG | APG lauryl ether nano-emulsion (1 mmol/L) + nano-silicon (0.5 mmol/L) |
| APG | APG lauryl ether nano-emulsion (1 mmol/L) |
| Si | Nano-silicon (0.5 mmol/L) |
| CK | Deionized water |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, J.; Yu, P.; Huang, Z.; Tong, Z.; Chang, R.; Xie, Z.; Gui, S.; Huang, Y. Synergistic Toxicity Reduction of Cadmium in Rice Grains by Foliar Co-Application of Nano-Silica and Surfactants. Toxics 2025, 13, 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121047
Kang J, Yu P, Huang Z, Tong Z, Chang R, Xie Z, Gui S, Huang Y. Synergistic Toxicity Reduction of Cadmium in Rice Grains by Foliar Co-Application of Nano-Silica and Surfactants. Toxics. 2025; 13(12):1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121047
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Jihao, Pengyue Yu, Zhi Huang, Zhenglong Tong, Ruimin Chang, Zhiyan Xie, Shiyu Gui, and Ying Huang. 2025. "Synergistic Toxicity Reduction of Cadmium in Rice Grains by Foliar Co-Application of Nano-Silica and Surfactants" Toxics 13, no. 12: 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121047
APA StyleKang, J., Yu, P., Huang, Z., Tong, Z., Chang, R., Xie, Z., Gui, S., & Huang, Y. (2025). Synergistic Toxicity Reduction of Cadmium in Rice Grains by Foliar Co-Application of Nano-Silica and Surfactants. Toxics, 13(12), 1047. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13121047






