Polychlorinated Biphenyl 138 Induces Toxicant-Associated Steatohepatitis via Hepatic Iron Overload and Adipose Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animal Studies
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.4. Transwell Co-Culture
2.5. Histology
2.6. Staining and Imaging
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.9. Protein Extraction and Western Blot
2.10. Cytokine Array
2.11. Glucose and Insulin Tolerance Tests
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
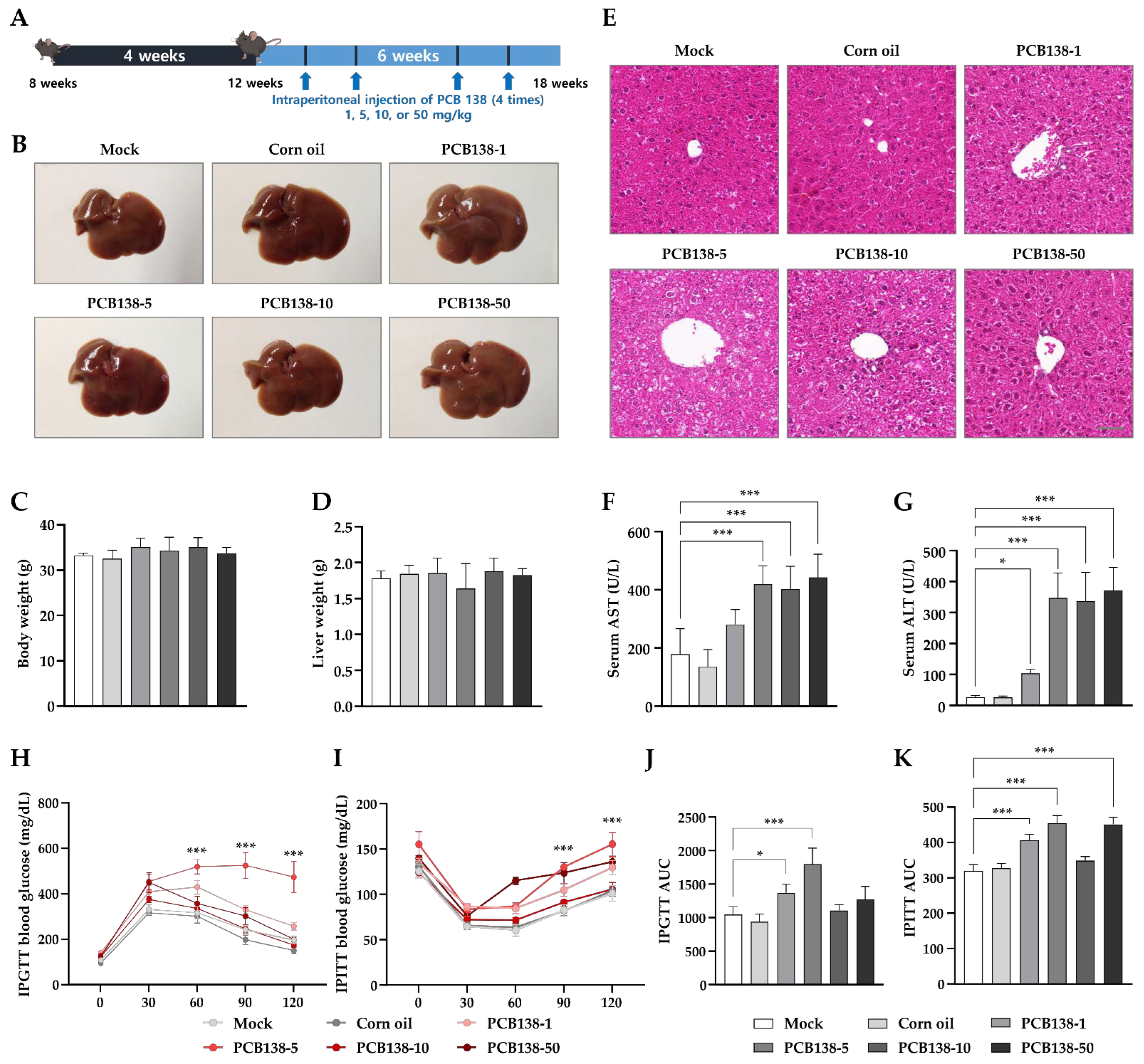
3.1. PCB138 Induces Liver Injury and Metabolic Alterations In Vivo
3.2. PCB138 Induces Hepatic Inflammation and Fibrosis In Vivo
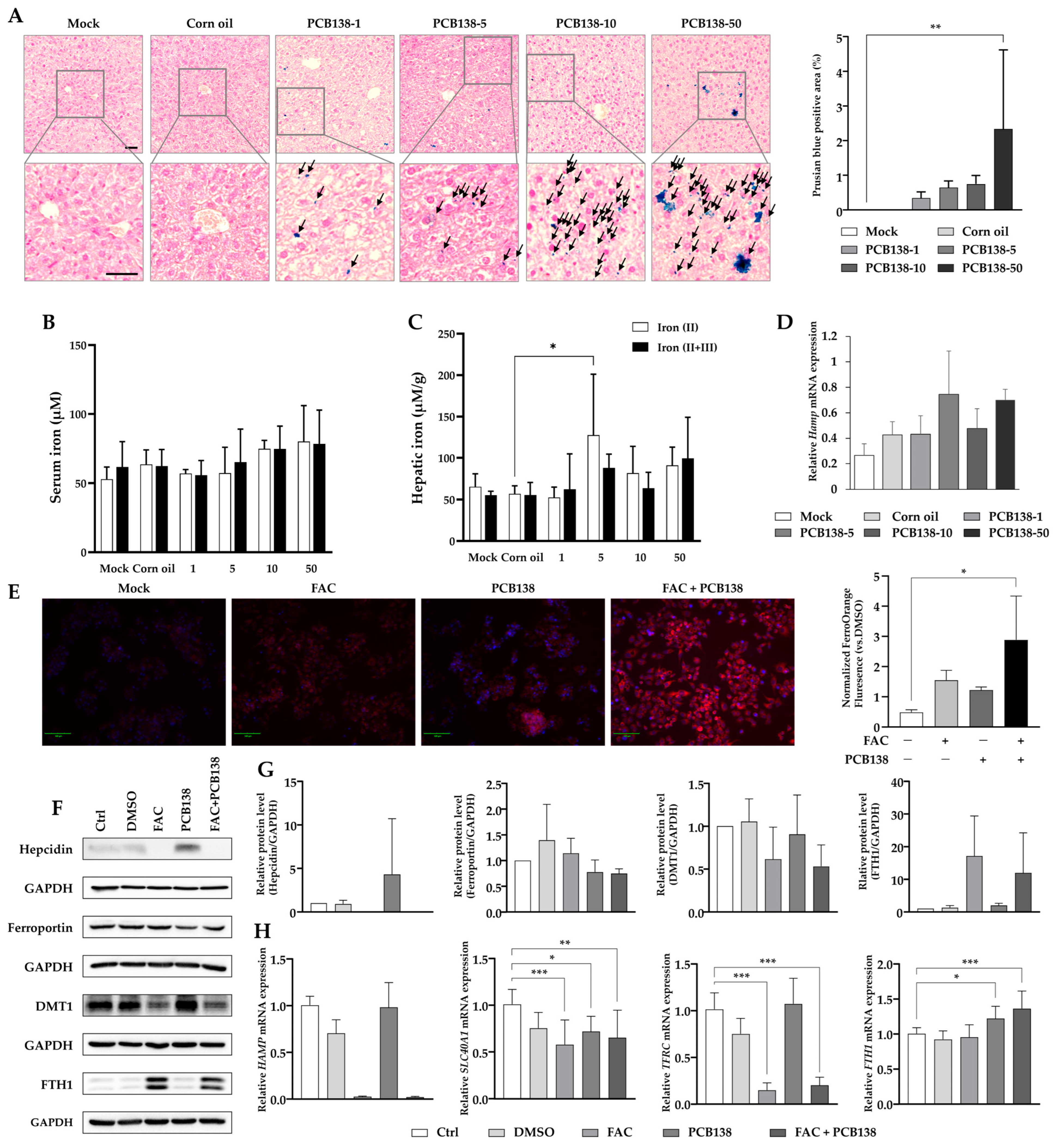
3.3. PCB138 Induces Hepatic Iron Overload and Dysregulates Iron Metabolism
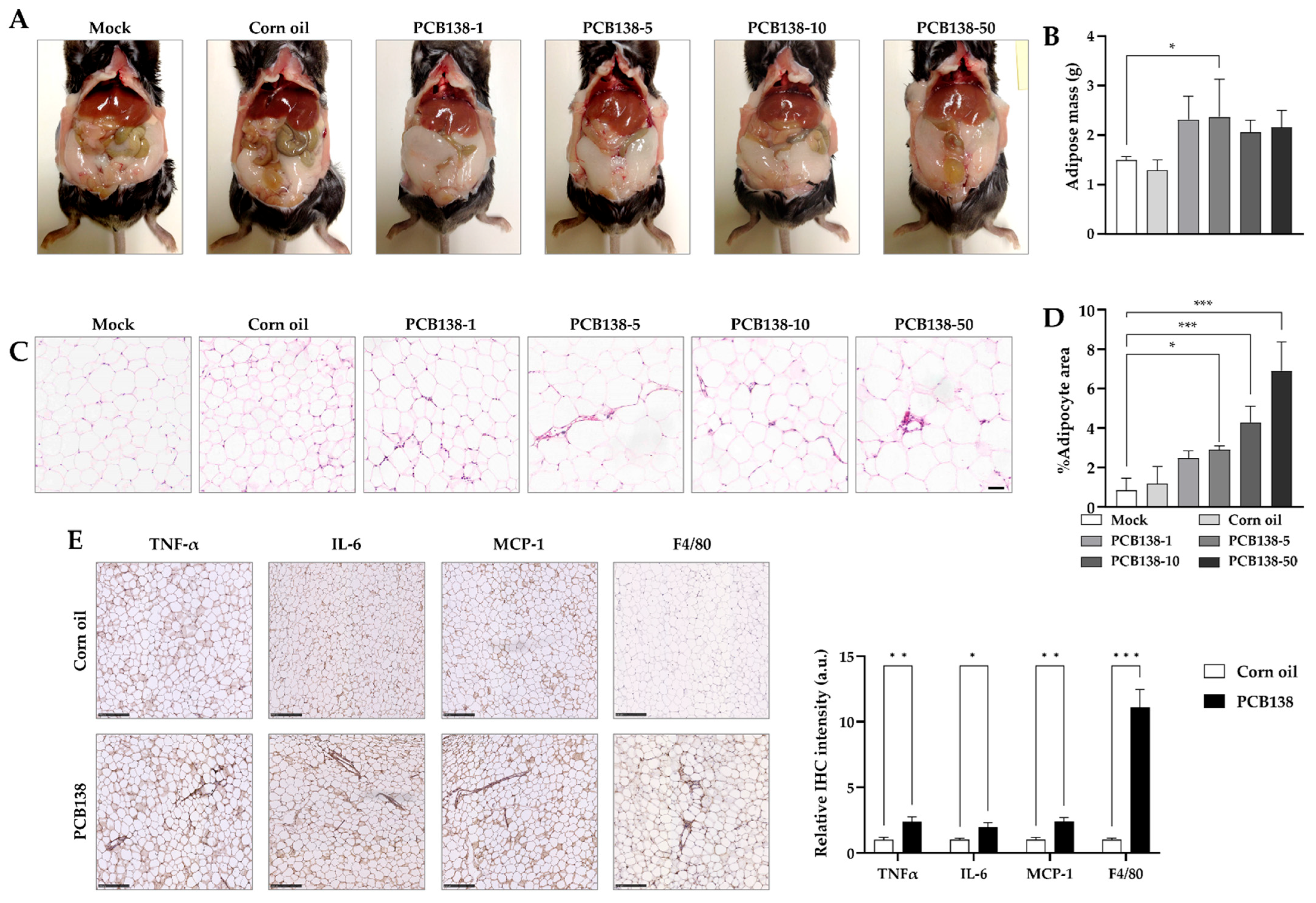
3.4. PCB138 Promotes Adiposity and Adipose Inflammation In Vivo
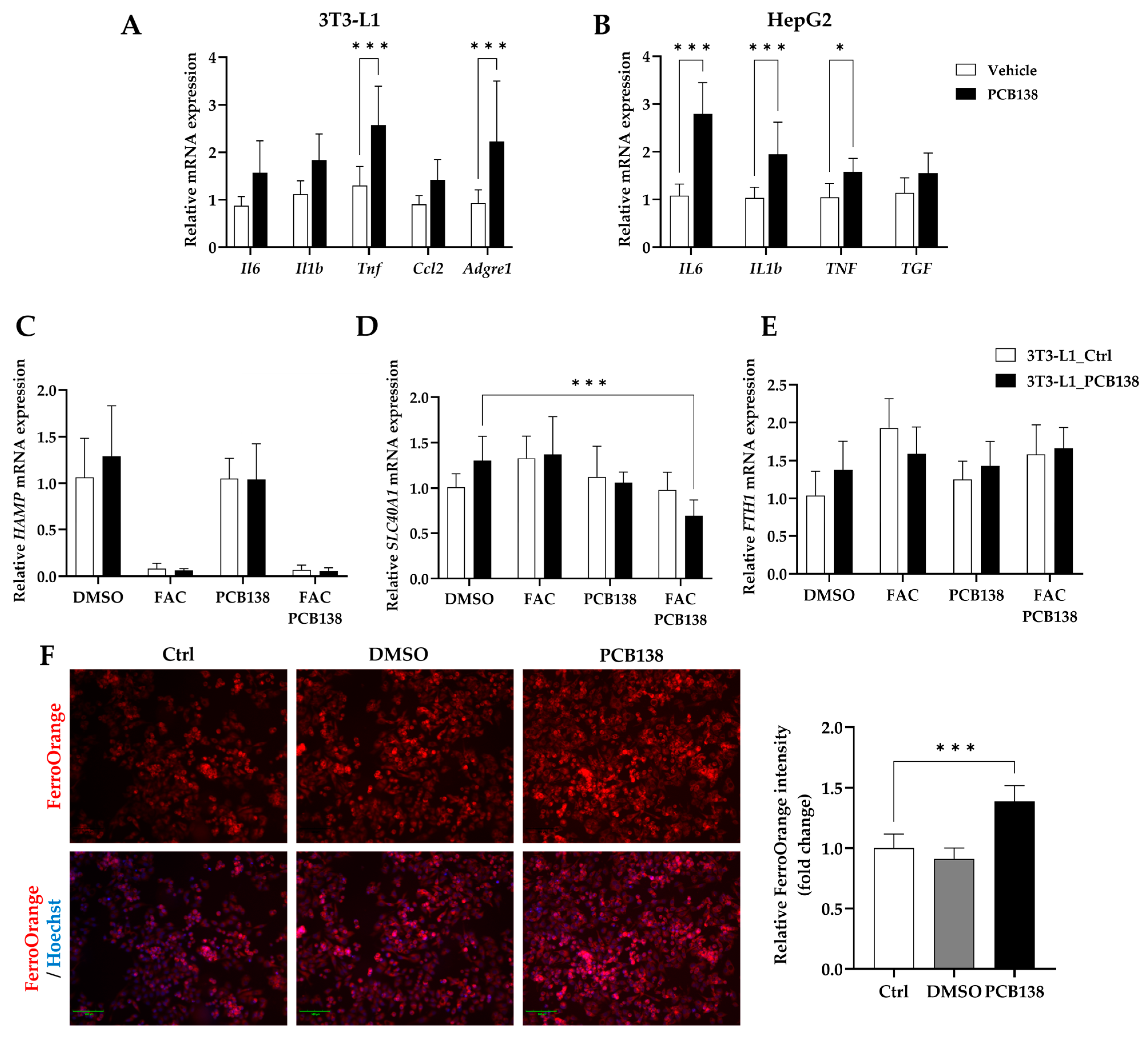
3.5. PCB138-Primed Adipocytes Drive Hepatocyte Iron Overload and Inflammatory Signaling
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Accacha, S.; Barillas-Cerritos, J.; Srivastava, A.; Ross, F.; Drewes, W.; Gulkarov, S.; De Leon, J.; Reiss, A.B. From Childhood Obesity to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Hyperlipidemia Through Oxidative Stress During Childhood. Metabolites 2025, 15, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandireddy, R.; Sakthivel, S.; Gupta, P.; Behari, J.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, B.K. Systemic impacts of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) on heart, muscle, and kidney related diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1433857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Xing, J. Mechanism of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease: Important role of lipid metabolism. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2024, 12, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlang, B.; Beier, J.I.; Clair, H.B.; Bellis-Jones, H.J.; Falkner, K.C.; McClain, C.J.; Cave, M.C. Toxicant-associated steatohepatitis. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 41, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cave, M.; Falkner, K.C.; Ray, M.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Brock, G.; Khan, R.; Bon Homme, M.; McClain, C.J. Toxicant-associated steatohepatitis in vinyl chloride workers. Hepatology 2010, 51, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi-Barve, S.; Kirpich, I.; Cave, M.C.; Marsano, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Alcoholic, Nonalcoholic, and Toxicant-Associated Steatohepatitis: Mechanistic Similarities and Differences. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, J.I.; Luo, J.; Vanderpuye, C.M.; Brizendine, P.; Muddasani, P.; Bolatimi, O.; Heinig, S.A.; Ekuban, F.A.; Siddiqui, H.; Ekuban, A.; et al. Environmental Pollutants, Occupational Exposures, and Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2025, 45, 148–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ruan, J.; Ruan, F.; Ding, X.; Han, C.; Huang, C.; Zhong, H.; He, C.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, J. Estradiol protects female mice from hyperuricemia induced by PCB138 exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 261, 115093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cave, M.; Appana, S.; Patel, M.; Falkner, K.C.; McClain, C.J.; Brock, G. Polychlorinated Biphenyls, Lead, and Mercury Are Associated with Liver Disease in American Adults: NHANES 2003–2004. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, A.; Pavuk, M.; Foushee, H.R.; Carpenter, D.O.; for the Anniston Environmental Health Research Consortium. Blood Pressure in Relation to Concentrations of PCB Congeners and Chlorinated Pesticides. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovoli, F.; Stefanini, B.; Mandrioli, D.; Mattioli, S.; Vornoli, A.; Sgargi, D.; Manservisi, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Curti, S.; Bolondi, L. Exploring occupational toxicant exposures in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A prospective pilot study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2024, 56, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Ruan, F.; Xue, F.; Ye, L.; Yu, Y.; Zuo, Z.; He, C. Mechanisms of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease induced by 48-week PCB138 exposure and theabrownin intervention. Environ. Int. 2025, 203, 109780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kublbeck, J.; Niskanen, J.; Honkakoski, P. Metabolism-Disrupting Chemicals and the Constitutive Androstane Receptor CAR. Cells 2020, 9, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.J.; Farnaud, S.J.; Sharp, P.A. Iron and liver fibrosis: Mechanistic and clinical aspects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaschella, C.; Nai, A.; Silvestri, L. Iron metabolism and iron disorders revisited in the hepcidin era. Haematologica 2020, 105, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginzburg, Y.Z. Hepcidin-ferroportin axis in health and disease. Vitam. Horm. 2019, 110, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kwon, W.Y.; Park, J.B.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Suh, S.; Baek, Y.H.; Jeong, J.S.; Yoo, Y.H. Hepatic STAMP2 mediates recombinant FGF21-induced improvement of hepatic iron overload in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 12354–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, C.H.; Park, J.B.; Ko, K.; Lee, M.H.; Chung, J.; Yoo, Y.H. Hepatic STAMP2 alleviates polychlorinated biphenyl-induced steatosis and hepatic iron overload in NAFLD models. Environ. Toxicol. 2022, 37, 2223–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlang, B.; Jin, J.; Beier, J.I.; Hardesty, J.E.; Daly, E.F.; Schnegelberger, R.D.; Falkner, K.C.; Prough, R.A.; Kirpich, I.A.; Cave, M.C. Mechanisms of Environmental Contributions to Fatty Liver Disease. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2019, 6, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. Hepcidin-Ferroportin Interaction Controls Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Suh, S.H.; Choi, Y.; Nam, T.G.; Kwon, W.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoo, Y.H. Cilostazol Improves HFD-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Upregulating Hepatic STAMP2 Expression through AMPK. Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 94, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.E.; Jeong, Y.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoo, Y.H.; Lee, K.S.; Yang, W.T.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, J.M. Hepatic Steatosis Alleviated in Diabetic Mice upon Dietary Exposure to Fibroin via Transgenic Rice: Potential STAMP2 Involvement in Hepatocytes. Dev. Reprod. 2020, 24, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barouki, R.; Samson, M.; Blanc, E.B.; Colombo, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Lazaridis, K.N.; Miller, G.W.; Coumoul, X. The exposome and liver disease—How environmental factors affect liver health. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Rho, J.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Jung, H.U.; Yoo, S.H.; Jeong, N.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Suh, S.; et al. Hepatic STAMP2 alleviates high-fat diet–induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, E.J.; Stayton, A.S.; Sethuraman, A.; Rao, P.K.; Meyer, A.; Gomes, C.K.; Mulcahy, M.C.; McAllan, L.; Puchowicz, M.A.; Pierre, J.F.; et al. Chronic intake of high dietary sucrose induces sexually dimorphic metabolic adaptations in mouse liver and adipose tissue. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Tang, Y.; Tan, X.; Li, Q.; Zhong, W.; Sun, X.; Jia, W.; McClain, C.J.; Zhou, Z. Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma by rosiglitazone improves lipid homeostasis at the adipose tissue-liver axis in ethanol-fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2012, 302, G548–G557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clair, H.B.; Pinkston, C.M.; Rai, S.N.; Pavuk, M.; Dutton, N.D.; Brock, G.N.; Prough, R.A.; Falkner, K.C.; McClain, C.J.; Cave, M.C. Liver Disease in a Residential Cohort With Elevated Polychlorinated Biphenyl Exposures. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammella, E.; Correnti, M.; Cairo, G.; Recalcati, S. Iron Availability in Tissue Microenvironment: The Key Role of Ferroportin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawula, Z.J.; Wallace, D.F.; Subramaniam, V.N.; Rishi, G. Therapeutic Advances in Regulating the Hepcidin/Ferroportin Axis. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billesbolle, C.B.; Azumaya, C.M.; Kretsch, R.C.; Powers, A.S.; Gonen, S.; Schneider, S.; Arvedson, T.; Dror, R.O.; Cheng, Y.; Manglik, A. Structure of hepcidin-bound ferroportin reveals iron homeostatic mechanisms. Nature 2020, 586, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feaver, R.E.; Cole, B.K.; Lawson, M.J.; Hoang, S.A.; Marukian, S.; Blackman, B.R.; Figler, R.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; Wamhoff, B.R.; Dash, A. Development of an in vitro human liver system for interrogating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e90954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Yoo, Y.H. Recombinant FGF21 Attenuates Polychlorinated Biphenyl-Induced NAFLD/NASH by Modulating Hepatic Lipocalin-2 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Porta, M.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Vandenberg, L.N. Chlorinated persistent organic pollutants, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 557–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardesty, J.E.; Wahlang, B.; Falkner, K.C.; Shi, H.; Jin, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wilkey, D.W.; Merchant, M.L.; Watson, C.T.; Feng, W.; et al. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Novel Mechanisms by Which Polychlorinated Biphenyls Compromise the Liver Promoting Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1582–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlang, B.; Barney, J.; Thompson, B.; Wang, C.; Hamad, O.M.; Hoffman, J.B.; Petriello, M.C.; Morris, A.J.; Hennig, B. Editor’s Highlight: PCB126 Exposure Increases Risk for Peripheral Vascular Diseases in a Liver Injury Mouse Model. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 160, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midya, V.; Colicino, E.; Conti, D.V.; Berhane, K.; Garcia, E.; Stratakis, N.; Andrusaityte, S.; Basagana, X.; Casas, M.; Fossati, S.; et al. Association of Prenatal Exposure to Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals With Liver Injury in Children. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2220176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kwon, W.Y.; Kim, Y.A.; Oh, Y.J.; Yoo, S.H.; Lee, M.H.; Bae, J.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Yoo, Y.H. Polychlorinated biphenyls exposure-induced insulin resistance is mediated by lipid droplet enlargement through Fsp27. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2353–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.A.; Kim, H.Y.; Oh, Y.J.; Kwon, W.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Bae, J.Y.; Woo, M.S.; Kim, J.M.; Yoo, Y.H. Polychlorinated biphenyl 138 exposure-mediated lipid droplet enlargement endows adipocytes with resistance to TNF-alpha-induced cell death. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 292, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haber, L.T.; Dourson, M.L.; Allen, B.C.; Hertzberg, R.C.; Parker, A.; Vincent, M.J.; Maier, A.; Boobis, A.R. Benchmark dose (BMD) modeling: Current practice, issues, and challenges. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2018, 48, 387–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappenberg, F.; Duda, J.C.; Schurmeyer, L.; Gul, O.; Brecklinghaus, T.; Hengstler, J.G.; Schorning, K.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. Guidance for statistical design and analysis of toxicological dose-response experiments, based on a comprehensive litera-ture review. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2741–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Gurley, E.C.; Chen, W.; Hylemon, P.B.; et al. Cholangiocyte-Derived Exosomal lncRNA H19 Promotes Macrophage Activation and Hepatic Inflammation under Cholestatic Conditions. Cells 2020, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Jiao, J.; Cai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lin, J.; Shang, Z.; Qian, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, H.; et al. C-C motif chemokine ligand 5 confines liver regeneration by down-regulating reparative macrophage-derived hepatocyte growth factor in a forkhead box O 3a-dependent manner. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1706–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanovsky, D.A.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Shrivastava, I.; Bahar, I.; Tyurin, V.A.; Protchenko, O.; Jadhav, S.; Bolevich, S.B.; Kozlov, A.V.; Vladimirov, Y.A.; et al. Iron catalysis of lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis: Regulated enzymatic or random free radical reaction? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Yu, Y.; Xie, E.; Wu, Q.; Yin, X.; Zhao, B.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Hepatic HDAC3 Regulates Systemic Iron Homeostasis and Ferroptosis via the Hippo Signaling Pathway. Research 2023, 6, 0281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Yong, C.; Zhang, R.; Qi, D.; Wang, D. Hepcidin Alleviates LPS-Induced ARDS by Regulating the Ferritin-Mediated Suppression of Ferroptosis. Shock 2022, 57, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlebois, E.; Pantopoulos, K. Iron overload inhibits BMP/SMAD and IL-6/STAT3 signaling to hepcidin in cultured hepatocytes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Xu, Y.; Joachim, K.; Xiao, X.; Phillips, S.; Moschetta, G.A.; Alfaro-Magallanes, V.M.; Babitt, J.L. Functional role of endothelial transferrin receptor 1 in iron sensing and homeostasis. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jiao, H.; Yue, Y.; He, K.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Luo, H.; Hao, Z.; et al. Ubiquitin ligase E3 HUWE1/MULE targets transferrin receptor for degradation and suppresses ferroptosis in acute liver injury. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, X.; Li, J.; Chu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, L.; Lun, P.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; Jiao, Q.; Jiang, H. Dysregulation of Iron Homeostasis Mediated by FTH Increases Ferroptosis Sensitivity in TP53-Mutant Glioblastoma. Neurosci. Bull. 2025, 41, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimin, P.; Andrade, M.L.; Belchior, T.; Paschoal, V.A.; Magdalon, J.; Yamashita, A.S.; Castro, E.; Castoldi, A.; Chaves-Filho, A.B.; Yoshinaga, M.Y.; et al. Adipocyte mTORC1 deficiency promotes adipose tissue inflammation and NLRP3 inflammasome activation via oxidative stress and de novo ceramide synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1797–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Watanabe, H.; Nakano, T.; Imafuku, T.; Kato, H.; Tokumaru, K.; Arimura, N.; Enoki, Y.; Maeda, H.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Indoxyl Sulfate Contributes to Adipose Tissue Inflammation through the Activation of NADPH Oxidase. Toxins 2020, 12, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathne, S.; Stull, A.J.; Miranda, A.; Scoggin, S.; Claycombe-Larson, K.; Kim, J.H.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Tart Cherry Reduces Inflammation in Adipose Tissue of Zucker Fatty Rats and Cultured 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Xu, J.; Tan, J.; Song, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Chi, Y.; Liu, Y. Mesenteric adipose tissue B lymphocytes promote local and hepatic inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease mice. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3375–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugam, N.K.; Chen, K.; Cherayil, B.J. Commensal Bacteria-induced Interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta) Secreted by Macrophages Up-regulates Hepcidin Expression in Hepatocytes by Activating the Bone Morphogenetic Protein Signaling Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 30637–30647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Guo, S.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, B. Adipose knockout of H-ferritin improves energy metabolism in mice. Mol. Metab. 2024, 80, 101871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, M.P.; Lefebvre, C.; Chapados, N.A. The effects of PCB126 on intra-hepatic mechanisms associated with non alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2015, 14, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Fang, R.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.X.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Cozzolino, D.; Fang, M.; Huang, Y. A review of environmental metabolism disrupting chemicals and effect biomarkers associating disease risks: Where exposomics meets metabolomics. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Ko, K.; Baek, Y.H.; Kwon, W.Y.; Suh, S.; Han, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Yoo, Y.H. Pharmacological Prevention of Ectopic Erythrophagocytosis by Cilostazol Mitigates Ferroptosis in NASH. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Guo, F.F.; Liu, H.; Zeng, T. Iron overload in alcoholic liver disease: Underlying mechanisms, detrimental effects, and potential therapeutic targets. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyffenegger, N.; Flace, A.; Doucerain, C.; Durrenberger, F.; Manolova, V. The Oral Ferroportin Inhibitor VIT-2763 Improves Erythropoiesis without Interfering with Iron Chelation Therapy in a Mouse Model of beta-Thalassemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, J.; Alay, A.; Vaquero, J.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Bertran, E.; Sánchez, A.; Herrera, B.; Meyer, K.; Maus, M.; Serrano, M.; et al. Iron chelation as a new therapeutic approach to prevent senescence and liver fibrosis progression. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Izawa, T.; Inai, Y.; Fujiwara, S.; Aikawa, R.; Kuwamura, M.; Yamate, J. Dietary iron overload differentially modulates chemically-induced liver injury in rats. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Shi, D.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liang, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, F. Integrating Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling-Based Forward Dosimetry and in Vitro Bioassays to Improve the Risk Assessment of Organophosphate Esters on Human Health. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 1764–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, E.; Shoemaker, R.; Larian, N.; Cassis, L. Adipose Tissue as a Site of Toxin Accumulation. Compr. Physiol. 2017, 7, 1085–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, S.; Hegstad-Pettersen, M.M.; Siriyappagouder, P.; Olsvik, P.A. Enhanced neurotoxic effect of PCB-153 when co-exposed with polystyrene nanoplastics in zebrafish larvae. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iszatt, N.; Janssen, S.; Lenters, V.; Dahl, C.; Stigum, H.; Knight, R.; Mandal, S.; Peddada, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Midtvedt, T.; et al. Environmental toxicants in breast milk of Norwegian mothers and gut bacteria composition and metabolites in their infants at 1 month. Microbiome 2019, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Abulitipu, A.; Pang, P.; Bai, L.; Liu, L.; Tuerxunmaimaiti, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, S.; Lv, H.; Fu, Y.; et al. ECM1 protects against liver steatosis through PCBP1-mediated iron homeostasis. Hepatology 2025. Advance online publication. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenovic, D.; Veskovic, M.; Sutulovic, N.; Hrncic, D.; Stanojlovic, O.; Radic, L.; Macut, J.B.; Macut, D. Adipose-derived extracellular vesicles—A novel cross-talk mechanism in insulin resistance, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and polycystic ovary syndrome. Endocrine 2024, 85, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benede-Ubieto, R.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. Breaking the barriers: The role of gut homeostasis in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2331460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, H.J.; Lee, M.H.; Lee, S.H.; Sung, B.-J.; Kim, J.-G.; Seo, D.Y.; Hur, D.Y.; Yoo, Y.H.; Cheong, J.; Kim, H.Y. Polychlorinated Biphenyl 138 Induces Toxicant-Associated Steatohepatitis via Hepatic Iron Overload and Adipose Inflammation. Toxics 2025, 13, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110932
Hwang HJ, Lee MH, Lee SH, Sung B-J, Kim J-G, Seo DY, Hur DY, Yoo YH, Cheong J, Kim HY. Polychlorinated Biphenyl 138 Induces Toxicant-Associated Steatohepatitis via Hepatic Iron Overload and Adipose Inflammation. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110932
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Hyeon Jeong, Mi Hwa Lee, Seung Hui Lee, Byung-Jun Sung, Joong-Gook Kim, Dae Yun Seo, Dae Young Hur, Young Hyun Yoo, JaeHun Cheong, and Hye Young Kim. 2025. "Polychlorinated Biphenyl 138 Induces Toxicant-Associated Steatohepatitis via Hepatic Iron Overload and Adipose Inflammation" Toxics 13, no. 11: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110932
APA StyleHwang, H. J., Lee, M. H., Lee, S. H., Sung, B.-J., Kim, J.-G., Seo, D. Y., Hur, D. Y., Yoo, Y. H., Cheong, J., & Kim, H. Y. (2025). Polychlorinated Biphenyl 138 Induces Toxicant-Associated Steatohepatitis via Hepatic Iron Overload and Adipose Inflammation. Toxics, 13(11), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110932








