Sustainable Cyanobacterial Bloom Control: Inhibitory Effects of Nano Zero-Valent Iron on Microcystis aeruginosa and Metabolic Disruption
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Strain Cultivation and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of nZVI
2.3. Cell Membrane Integrity Assay and Characterization of Algal Cells
2.4. Non-Targeted LC-MS Metabolomics
2.4.1. LC-MS Sample Preparation
2.4.2. LC-MS Analysis
2.4.3. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
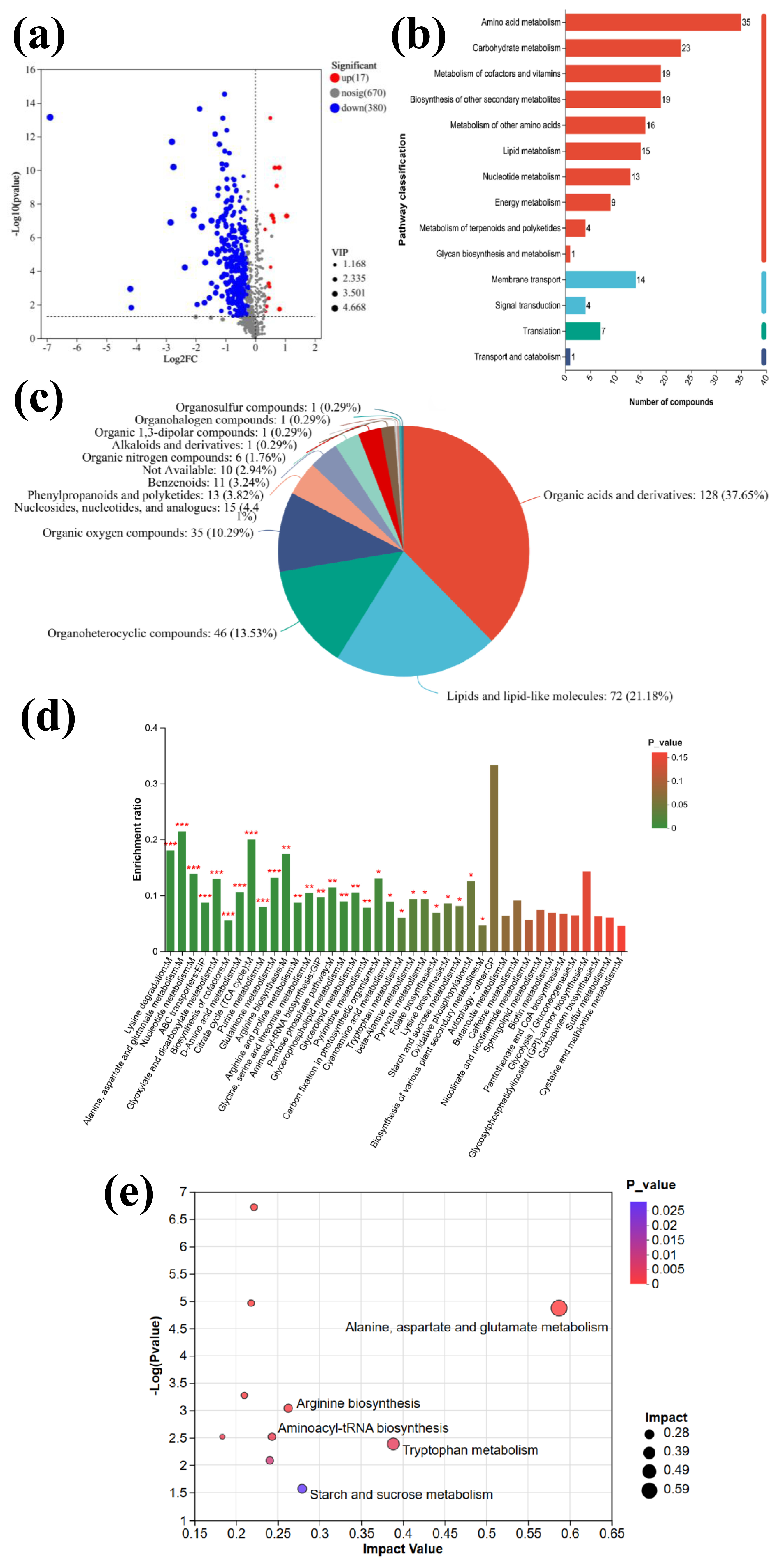
3.1. Metabolomics Analysis
3.1.1. Data Quality Control and Metabolomic Analysis
3.1.2. Identification of Differential Metabolites
3.1.3. Functional Pathway Analysis of Differential Metabolites
3.1.4. Analysis of Differential Metabolite Enrichment
3.1.5. Analysis of Key Metabolites
3.1.6. Metabolite Cluster Analysis
3.2. Inhibitory Performance of nZVI on M. aeruginosa
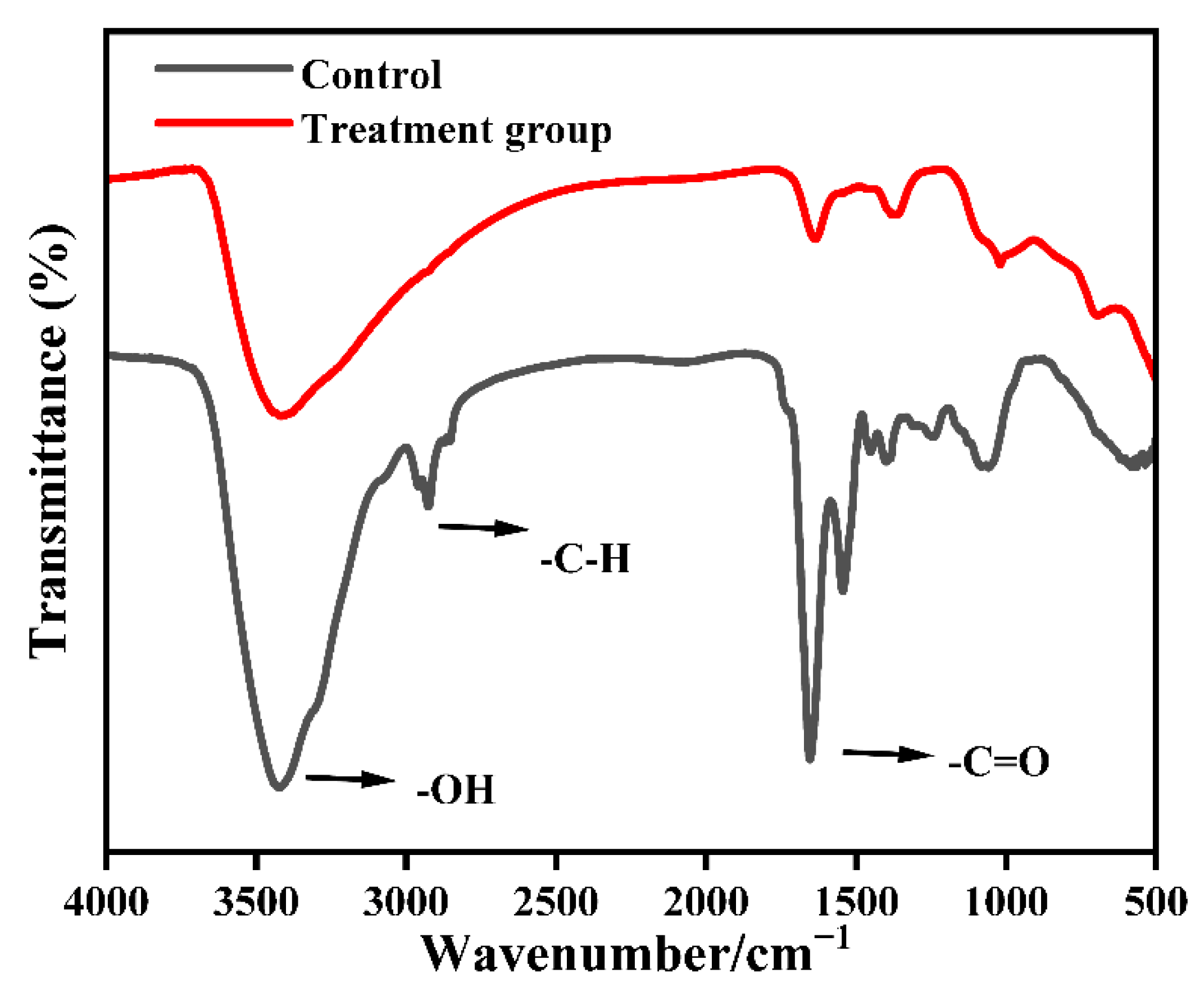
3.2.1. Changes in the Functional Groups of M. aeruginosa
3.2.2. Changes in Cell Morphology of Microalgae Cells
4. Conclusions
5. Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kordahi, M.A.; Ayoub, G.M.; Zayyat, R.M. A Critical Review of Current Research on Cyanobacterial Cells and Associated Toxins in Aquatic Environments: Occurrence, Impact, and Treatment Methods. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Molnárová, M.; Motola, M. Metallic Nanoparticles and Photosynthesis Organisms: Comprehensive Review from the Ecological Perspective. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 358, 120858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamed, S.M.; El Tablawy, N.H.; Mohamed, M.Y.A.; Alammari, B.S.; AbdElgawad, H. Accumulation and Nano-Ecotoxicological Impact of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles on Cyanobacteria: Understanding Photosynthesis, Detoxification, and Antioxidant Responses. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Z.L.; Low, S.S.; Ezeigwe, E.R.; Chew, K.W.; Chai, W.S.; Bhatnagar, A.; Yap, Y.J.; Show, P.L. A Review on the Diverse Interactions between Microalgae and Nanomaterials: Growth Variation, Photosynthetic Performance and Toxicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 127048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Zhang, R.; Liang, D.; Wang, F.; Han, Y.; Luo, Y.; Gao, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Yu, C. Comparison of the Advantages and Disadvantages of Algae Removal Technology and Its Development Status. Water 2023, 15, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsalek, B.; Jancula, D.; Marsalkova, E.; Mashlan, M.; Safarova, K.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Multimodal Action and Selective Toxicity of Zerovalent Iron Nanoparticles against Cyanobacteria. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 2316–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Qian, D.; Adeleye, A.S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Jassby, D.; Zhang, Y. Impact of Ageing on the Fate of Molybdate-Zerovalent Iron Nanohybrid and Its Subsequent Effect on Cyanobacteria (Microcystis aeruginosa) Growth in Aqueous Media. Water Res. 2018, 140, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Du, L.; Cheng, Q.; Jin, Z.; Hui, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xu, L. Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron Alters Physiological, Biochemical, and Transcriptomic Response of Nonylphenol-Exposed Algae (Dictyosphaerium sp.). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 20711–20720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeap, C.S.; Nguyen, N.H.; Spanek, R.; Too, C.C.; Benes, V.; Provaznik, J.; Cernik, M.; Sevcu, A. Dissolved Iron Released from Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron (Nzvi) Activates the Defense System in Bacterium Pseudomonas Putida, Leading to High Tolerance to Oxidative Stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 439, 129627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-M.; Naseer, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, S.-G.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.-Z.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Tao, H.-Y. Dual Effects of Nzvi on Maize Growth and Water Use Are Positively Mediated by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi via Rhizosphere Interactions. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhou, S.; Jin, F.; Huang, J.; Bao, N. Characterization and Mechanism Analysis of Activated Carbon Fiber Felt-Stabilized Nanoscale Zero-Valent Iron for the Removal of Cr (Vi) from Aqueous Solution. Colloid. Surface A 2014, 447, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J. Metabolic and Oxidative Stress Response of Sea Cucumber Apostichopus japonicus Exposed to Acute High Concentration of Bisphenol Af. Aquat. Toxicol. 2023, 262, 106654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.K.; Moon, J.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C. Microalgal Ecotoxicity of Nanoparticles: An Updated Review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2020, 201, 110781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Beisson, Y.; Thelen, J.J.; Fedosejevs, E.; Harwood, J.L. The Lipid Biochemistry of Eukaryotic Algae. Prog. Lipid Res. 2019, 74, 31–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capote, T.; Barbosa, P.; Usié, A.; Ramos, A.M.; Inácio, V.; Ordás, R.; Gonçalves, S.; Morais-Cecílio, L. Chip-Seq Reveals That Qsmyb1 Directly Targets Genes Involved in Lignin and Suberin Biosynthesis Pathways in Cork Oak (Quercus suber). BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armagan, G.; Kanıt, L.; Yalcin, A. D-Serine Treatment Induces Oxidative Stress in Rat Brain. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 34, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tian, Q.; Zhou, H.; Kang, J.; Yu, X.; Shen, L. Key Metabolites and Regulatory Network Mechanisms in Co-Culture of Fungi and Microalgae Based on Metabolomics Analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 388, 129718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Wang, W.-X. A Surge of Copper Accumulation in Cell Division Revealed Its Cyclical Kinetics in Synchronized Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Jin, X.; Li, M.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Tang, S.; Zhou, H.; Wang, K.; Dou, R.; Sun, J. Degradation Mechanism of Tetracycline Using Sulfidated Nanoscale Zerovalent Iron Driven Peroxymonosulfate and Metabolomic Insights into Environmental Risk of Intermediates Products. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Inabe, K.; Hidese, R.; Kondo, A.; Hasunuma, T. Metabolomics-Based Engineering for Biofuel and Bio-Based Chemical Production in Microalgae and Cyanobacteria: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 344, 126196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, N.; Srinivasan, B.; Yang, J.; Tang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. Photosynthetic Response Mechanism to Polybrominated Diphenyl Ether Exposure in Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2023, 263, 115245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Yao, B.-T.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Y.-X.; Xiang, L. Biochemical Insights into Proline Metabolism and Its Contribution to the Endurant Cell Wall Structure under Metal Stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safe 2024, 282, 116725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, P.; Gitau, M.M.; Maróti, G. Salinity Stress Responses and Adaptation Mechanisms in Eukaryotic Green Microalgae. Cells 2019, 8, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Huang, S.; Yang, S.; Zhu, H.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Mechanism of Cyanobacterial Bloom Control by Magnetic Lanthanum-Based Material. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yan, L.; Lu, J.; Zhou, X. Glycyl-L-Histidyl-L-Lysine-Cu2+ Attenuates Cigarette Smoke-Induced Pulmonary Emphysema and Inflammation by Reducing Oxidative Stress Pathway. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 925700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, F.; Jichao, Z.; Yanzheng, W.; Yanzhen, Y. Resource Preparation of Poly-Al–Zn–Fe (Pazf) Coagulant from Galvanized Aluminum Slag: Characteristics, Simultaneous Removal Efficiency and Mechanism of Nitrogen and Organic Matters. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, X.; Shi, X. Effects of Ultrasound on Microcystis aeruginosa Cell Destruction and Release of Intracellular Organic Matter. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2020, 63, 104909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, G.; Ma, Z.; Lei, X.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, Y. Sustainable Cyanobacterial Bloom Control: Inhibitory Effects of Nano Zero-Valent Iron on Microcystis aeruginosa and Metabolic Disruption. Toxics 2025, 13, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110915
Zeng G, Ma Z, Lei X, Xiao Y, Sun D, Huang Y. Sustainable Cyanobacterial Bloom Control: Inhibitory Effects of Nano Zero-Valent Iron on Microcystis aeruginosa and Metabolic Disruption. Toxics. 2025; 13(11):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110915
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Guoming, Zilong Ma, Xiaoling Lei, Yong Xiao, Da Sun, and Yuanyuan Huang. 2025. "Sustainable Cyanobacterial Bloom Control: Inhibitory Effects of Nano Zero-Valent Iron on Microcystis aeruginosa and Metabolic Disruption" Toxics 13, no. 11: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110915
APA StyleZeng, G., Ma, Z., Lei, X., Xiao, Y., Sun, D., & Huang, Y. (2025). Sustainable Cyanobacterial Bloom Control: Inhibitory Effects of Nano Zero-Valent Iron on Microcystis aeruginosa and Metabolic Disruption. Toxics, 13(11), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13110915







