Extended Environmental Multimedia Modeling System (EEMMS) with Analytic Hierarchy Process for Dual Evaluation of Energy Consumption and Pollutants in Solid Waste
Abstract
1. Introduction
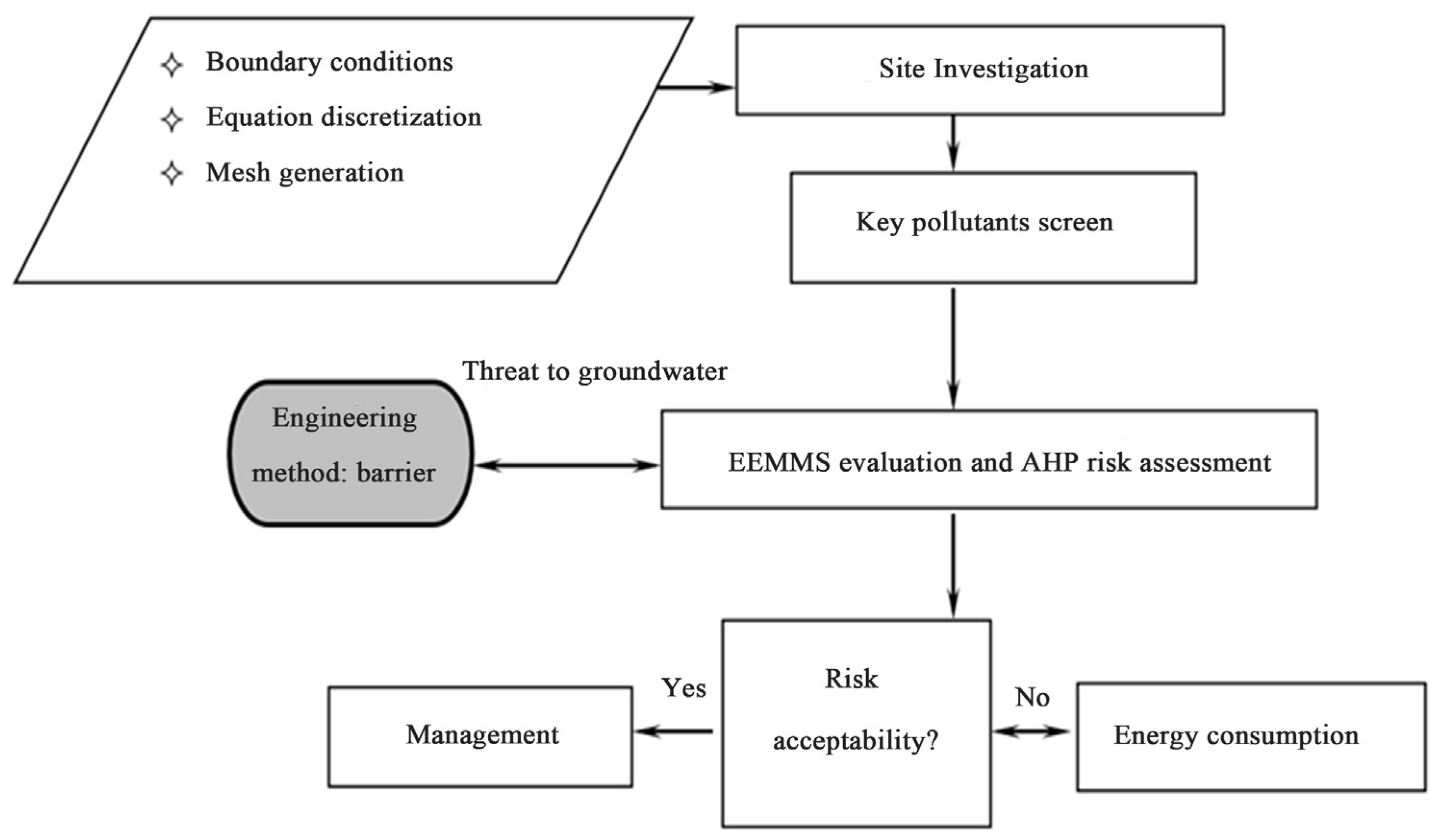
2. Methodology
2.1. EEMMS Model
2.2. Case Study—CFSWMA Landfill
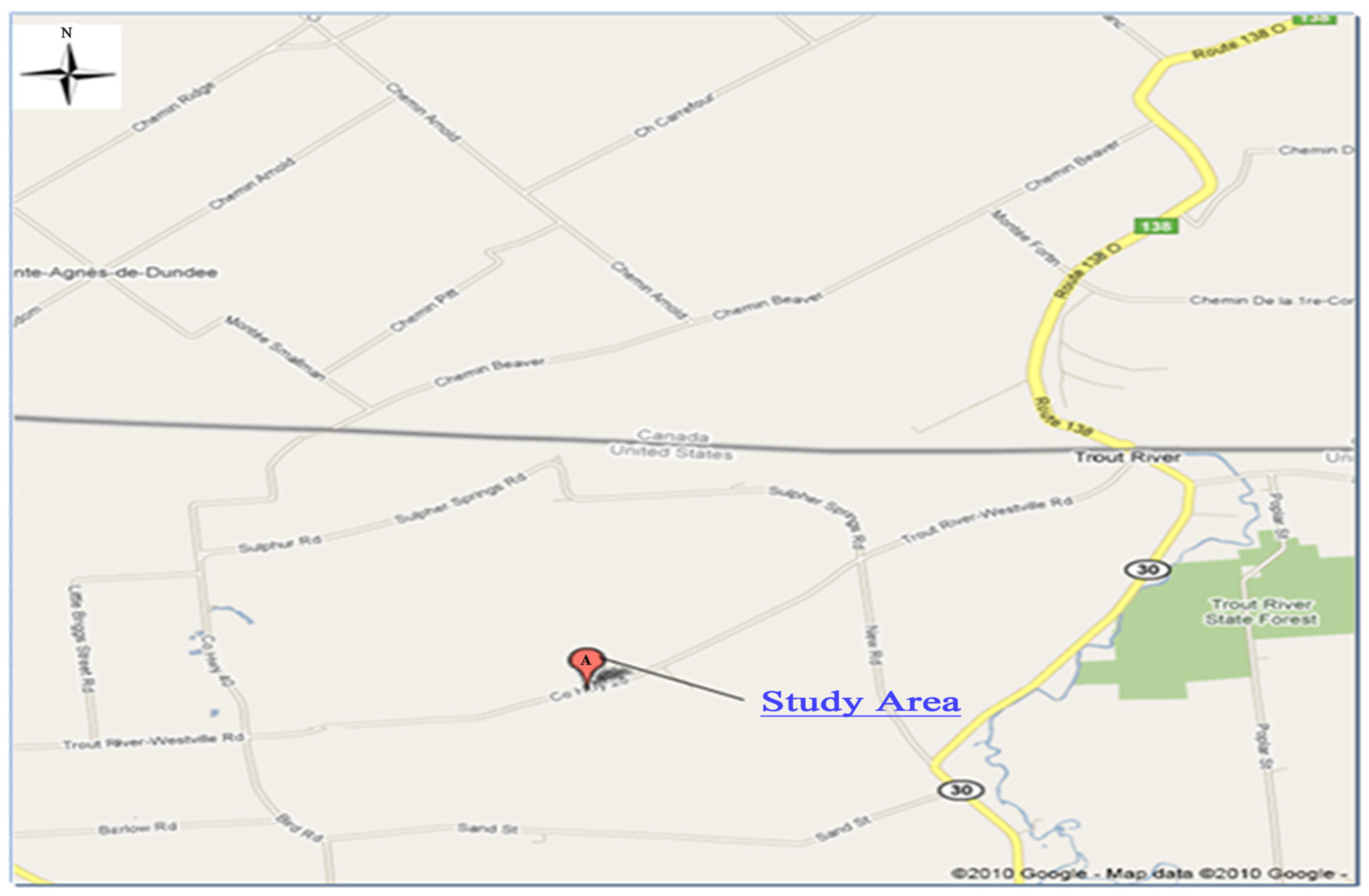
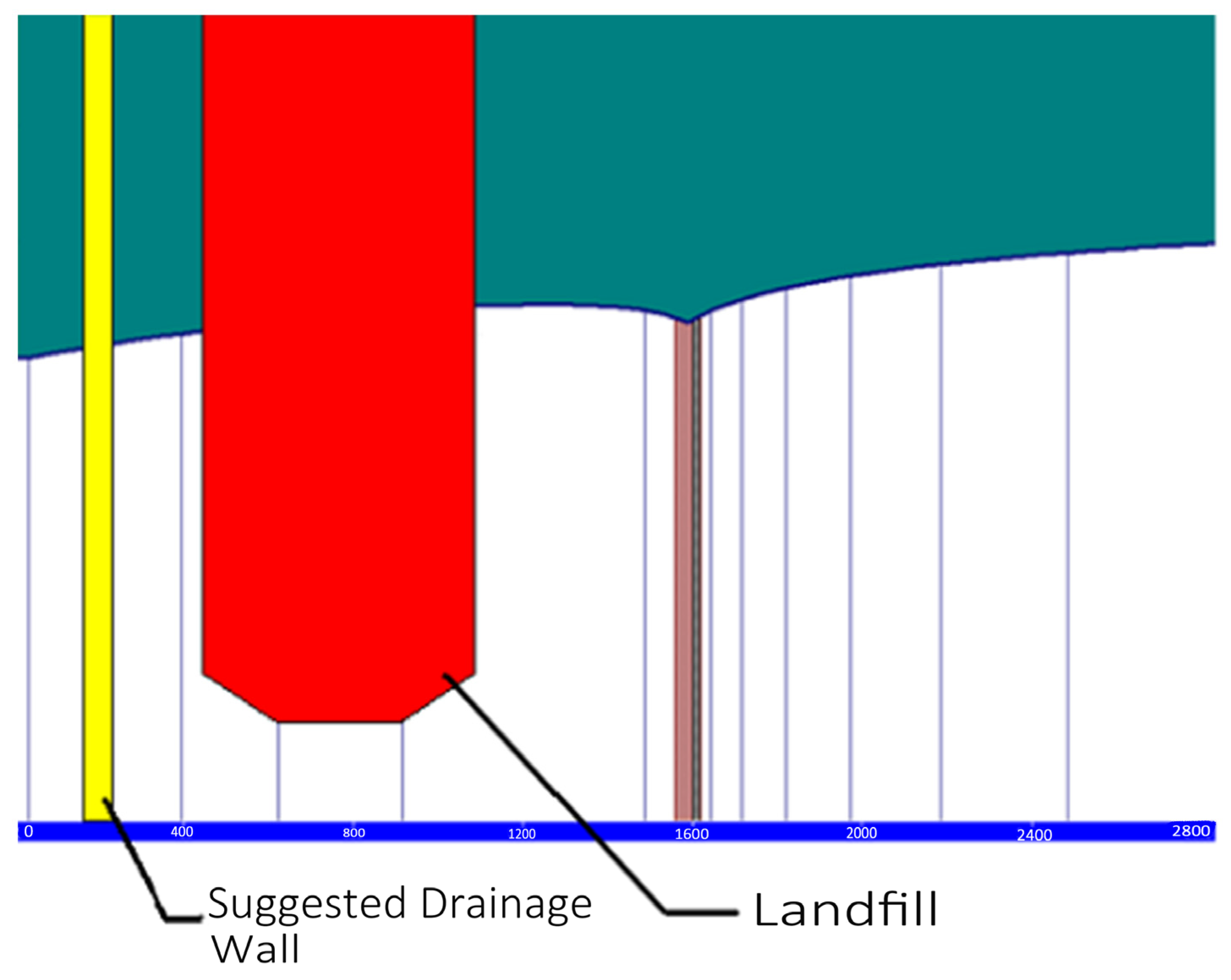
2.2.1. Site Information
2.2.2. Site Hydrological Characteristics and Contaminant Sources
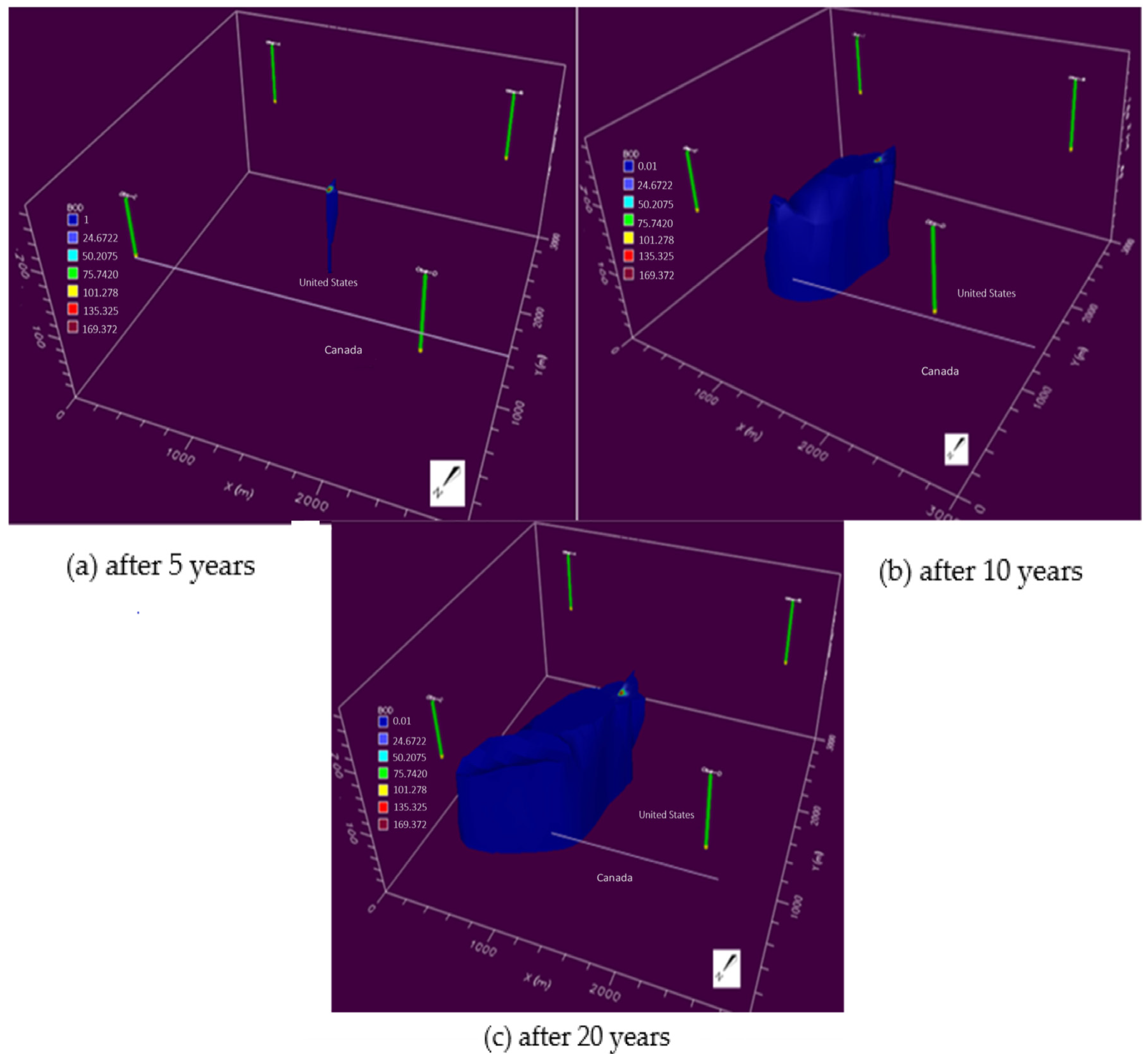
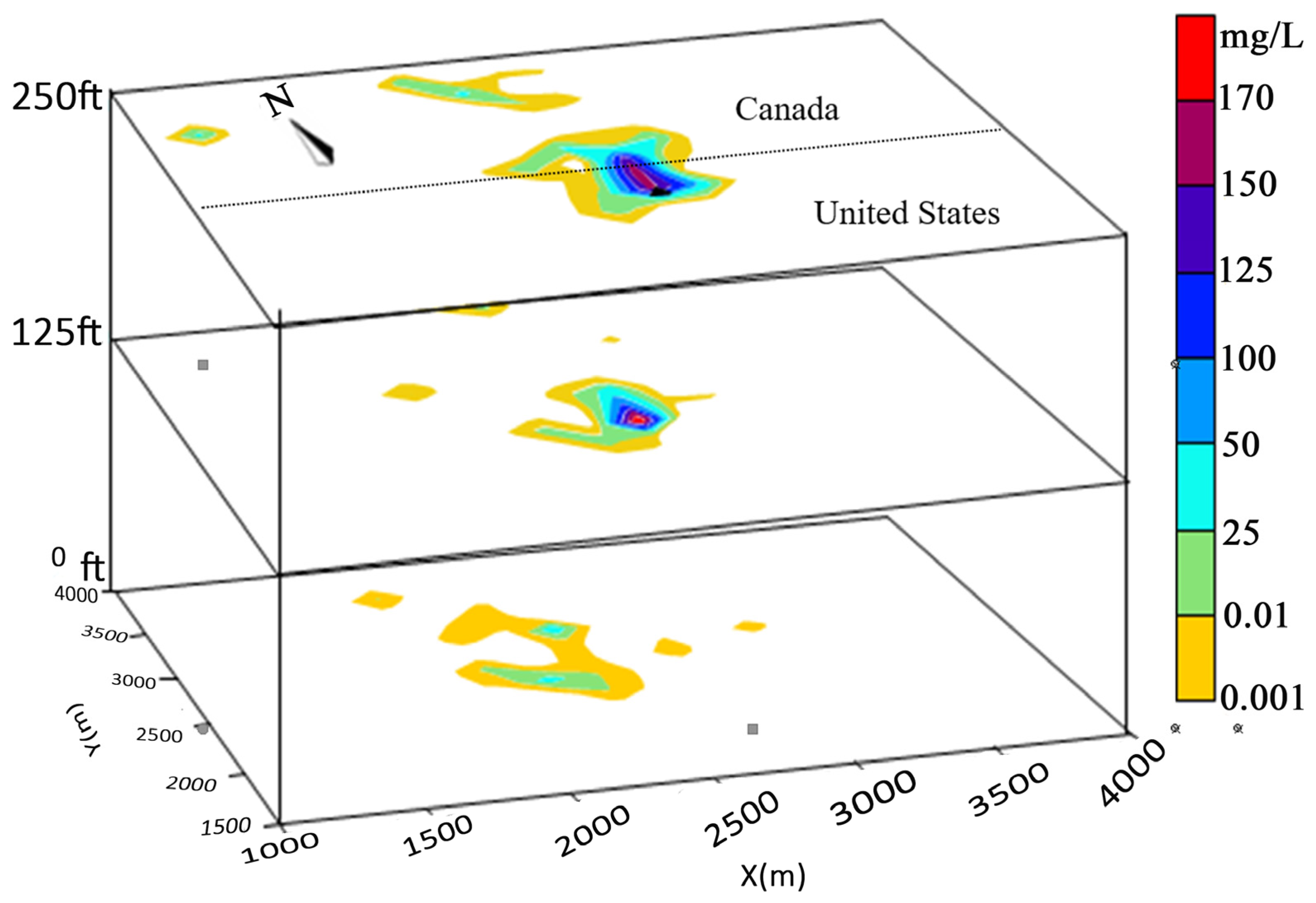
2.2.3. Model Result
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogers, E.R.; Zalesny, R.S.; Lin, C.-H. A systematic approach for prioritizing landfill pollutants based on toxicity: Applications and opportunities. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 2894, 112031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Elektorowicz, M. Extended environmental multimedia modeling system assessing the risk carried by pollutants in interacted air-unsaturated-groundwater zones. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 381, 120852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, C.; Dietmar, R.; Eugster, M. The recycling and disposal of electrical and electronic waste in China—Legislative and market responses. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2005, 25, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Elektorowicz, M.; Dabros, T. 3D Field-Scale Environmental Multimedia System Validation of the Dispersion of Benzene for Trail Road Landfill Site and Its Risk Assessment. J. Environ. Prot. 2012, 3, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, R.; Schnabel, U. Decision making under uncertainty in case of soil remediation. J. Environ. Manag. 2005, 80, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhong, M. Risk Assessment of Groundwater Contamination: A Multilevel Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation Approach Based on DRASTIC Model. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldrup, P.; Olesen, T.; Gamst, J.; Schjønning, P.; Yamaguchi, T.; Rolston, D.E. Predicting the Gas Diffusion Coefficient in Repacked Soil Water-Induced Linear Reduction Model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Escudero, A.; Vera-García, F.; Molina-García, A.; de Nicolás, A.P. A spatial decision framework for sustainable desalination: Mapping optimal sites for zero liquid discharge in Europe. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 344, 120226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, J. An extended environmental multimedia modeling system (EEMMS) for landfill case studies. Environ. Forensics 2009, 10, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houba, C. Distribution of heavy metals in sediments of the River Vesdre (Belgium). Environ. Technol. Lett. 1982, 3, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivik, K.; Eckhardt, S.; McLachlan, M.S.; Wania, F. Introducing a nested multimedia fate and transport model for organic contaminants (NEM). Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2021, 23, 1146–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.X.; Song, S.; Huang, Y.C.; Xia, H.M.; Yu, M.Z. Advancing fugacity modeling of POPs: Critical evaluation of multimedia frameworks and future pathways. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 202, 107722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLeod, M.; Von Waldow, H.; Tay, P.; Armitage, J.M.; Wöhrnschimmel, H.; Riley, W.J.; McKone, T.E.; Hungerbuhler, K. BETR global—A geographically-explicit global-scale multimedia contaminant fate model. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrey, I.; Odiyo, J.O.; Makungo, R.; Kataka, M. Vadose zone infiltration and its implication for groundwater contamination risk assessment in Siloam village, Limpopo province, South Africa. Jamba J. Disaster Risk Stud. 2019, 11, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Abadi, A.; Al-Shamma, A. Groundwater Potential Mapping of the Major Aquifer in Northeastern Missan Governorate, South of Iraq by Using Analytical Hierarchy Process and GIS. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 4, 125–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Tao, S.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Zhu, L.; Shen, G.; Huang, H.; Cai, C.; et al. Multimedia modelling of the PAH concentration and distribution in the Yangtze River Delta and human health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 647, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galarneau, E.; Hollebone, B.P.; Yang, Z.; Schuster, J. Preliminary measurement-based estimates of PAH emissions from oil sands tailings ponds. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 97, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini, L.; Garciaramos, J.V.; Domingo, C. Sensing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons with dithiocarbamate—Functionalized ag nanoparticles by surface—Enhanced Raman scattering. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yang, M.; Lai, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhan, J. A colorimetric and surface-enhanced Raman scattering dual-signal sensor for H92+based on Bismuthiol II-capped gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 723, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, A.; Giot, R.; Homand, F. Poromechanical modelling and inverse approach of drying tests on weakly permeable porous rocks. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 76, 45–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dong, J.X.; Asif, Z. A regional numerical environmental multimedia modeling approach to assess spatial Eco-Environmental exposure risk of perfluorooctane sulfonate (PFOS) in the Pearl river basin. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahiablame, L.M.; Engel, B.A.; Chaubey, I. Effectiveness of low impact development practices: Literature review and suggestions for future research. Water. Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4253–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaratne, N.; Zulfic, H.; Ashman, G.; Vial, H.; Swaffer, B.; Frizenschaf, J. Groundwater risk assessment model (GRAM): Groundwater risk assessment model for wellfield protection. Water 2013, 5, 1419–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Pu, S.; Zheng, C.; Yi, S. An improved method for the calculation of unsaturated-saturated water flow by coupling the FEM and FDM. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monarkh, V.V.; Pantsyreva, H.V. Stages of the Environmental Risk Assessment. Ukr. J. Ecol. 2019, 9, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Security, N.; Series, S.; Security, E.; Dima, C.; Draghici, C.; Transilvania, U. Case Study on Gas Station Enviromental Qualitative Risks Assessment. In Exposure and Risk Assessment of Chemical Pollution—Contemporary Methodology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 110–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yuan, J. A two-step modelling approach for the recovery of free phase LNAPL in petroleum contaminated groundwater systems. In New Developments in Sustainable Petroleum Engineering; Nova Science Pub Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; Chapter b. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Y.; Hikari, S.; Tomohito, M.; Akira, K. Environmental assessment of lead with spatial gradient in the Lake Biwa-Yodo River basin of Japan: The development of distributional multimedia model. Environ. Adv. 2023, 13, 100392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Cheng, Y.B.; Yuan, Y.L.; Sun, R.L. Quantitative analysis and risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in an intensive industrialand agricultural region. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mighanetara, K.; Braungardt, C.B.; Rieuwerts, J.S.; Azizi, F. Contaminant fluxes from point and diffuse sources from abandoned mines in the River Tamar catchment, UK. J. Geochem. Explor. 2009, 100, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.H.; Huang, D.N.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R.X.; Yu, P.F.; Gao, Y.N.; Wu, D.B.; Gao, Y. An analytic hierarchy process combined with artificial neural network model to evaluate sustainable sludge treatment scenarios. Waste Manag. 2025, 201, 114821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndatuwong, L.G.; Yadav, G.S. Integration of Hydrogeological Factors for Identification of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Remote Sensing and GIS Techniques. J. Geosci. Geomat. 2014, 2, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Kouli, M.; Lydakis-Simantiris, N.; Soupios, P. GIS-Based Aquifer Modeling and Planning Using Integrated Geoenvironmental and Chemical Approaches. Groundw. Model. Manag. Contanimation 2008, 125, 86–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, A.; Ahmad, Z. Regional groundwater flow modelling of Upper Chaj Doab of Indus Basin, Pakistan using finite element model (Feflow) and geoinformatics. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 173, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.M.; Feng, Z.Y.; Chang, K.T. Landslide hazard zoning based on numerical simulation and hazard assessment. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2018, 9, 368–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Q.; Jia, Y. Application of an environmental multimedia modeling system for health risk assessment: Key influencing factors and uncertainties research. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2021, 17, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helser, J.; Vassilieva, E.; Cappuyns, V. Environmental and human health risk assessment of sulfidic mine waste: Bioaccessibility, leaching and mineralogy. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, I.; Martínez Bueno, M.J.; Agüera, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Environmental and human health risk assessment of organic micro-pollutants occurring in a Spanish marine fish farm. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, T.E.; Paustenbach, D.J. Risk Assessment in Environmental Remediation. In Toxicology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 1051–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Sophocleous, M. Interactions Between Groundwater and Surface Water: The State of the Science. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, S.A.; Leij, F.J.; Schijven, J.; Torkzaban, S. Critical Role of Preferential Flow in Field-Scale Pathogen Transport and Retention. Vadose Zone J. 2017, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babendreier, J.E.; Castleton, K.J. Investigating uncertainty and sensitivity in integrated, multimedia environmental models: Tools for FRAMES-3MRA. Environ. Model. Softw. 2005, 20, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, H.S.; Zhao, B.; Juanes, R.; Shokri, N. Pore geometry control of apparent wetting in porous media. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Elektorowicz, M. 2-D numerical multimedia environmental analysis system (NMEAS) for pollution and risk assessment. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2013, 55, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.D.; Hu, X.Y.; Zhang, L.X.; Chen, Y.R.; Hao, R.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Deng, X.; Li, Y.; et al. A new framework integrating crop growth–level IV fugacity model and eco-indicator sensitivity to assess neonicotinoid fate and ecological risk in tropical rice–vegetable rotations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 499, 140098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.F.; Huang, W.K.; Tan, C.H. Failure impact assessment for large-scale landslides located near human settlement: Case study in southern Taiwan. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Fu, L.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Deng, Z.; Xie, Y. Spatiotemporal change detection of ecological quality and the associated affecting factors in Dongting Lake Basin, based on RSEI. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 302, 126995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, G.; Abdulwahab, A.; Salameh, A.A.; Ali, H.E.; Le, B.N. Evaluation of waste management and energy saving for sustainable green building through analytic hierarchy process and artificial neural network model. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, J.D.; Dey, P.K.; Ghosh, S.K.; Davies, P.A. Evaluation of options for energy recovery from municipal solid waste in India using the hierarchical analytical network process. Energy 2013, 59, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basirian, S.; Najafzadeh, M.; Demir, I. Water quality monitoring for coastal hypoxia: Integration of satellite imagery and machine learning models. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2026, 222, 118735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solaimanian, S. Environmental risk assessment of concrete construction projects in developing countries based on Analytical Hierarchy Process method. Green Technol. Sustain. 2025, 3, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramod, K.; Deval, J.S.; Siby, J. Multi-criteria decision support system for sustainable municipal solid waste management: A case study of Chandigarh, India. Environ. Dev. 2025, 55, 101228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M.; Harbaugh, A. USGS directions in MODFLOW development. Ground Water 2006, 44, 771–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency). Ecological Risk Assessments. 2014. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/risk/ecological-risk-assessment (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Ma, J.M.; Rene, E.R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Ma, W.F. Fate of PAHs in treated wastewater reused as irrigation water: Environmental risks in water-soil-ryegrass multimedia system. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton; Loguidice, P. County of Franklin Solid Waste Management Authority (CFSWMA) Final Environmental Impact Statement (FEIS); 2008; pp. 110–140. Available online: https://cdn.prod.website-files.com/610bd1c314553e291d310b00/6114183068533a2112706ebc_CFSWMA%20FEIS%20Main%20File%202-26-09.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Bordeleau, G.; Rivard, C.; Lavoie, D.; Lefebvre, R.; Malet, X.; Ladevèze, P. Geochemistry of groundwater in the Saint-Édouard area, Quebec, Canada, and its influence on the distribution of methane in shallow aquifers. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 89, 92–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türker, U.; Okaygün, M.; Almaqadma, S.J. Impact of anaerobic lagoons on the performance of BOD and TSS removals at the Haspolat (Mia Milia) Wastewater Treatment Plant. Desalination 2009, 249, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. EPA. Onsite Wastewater Treatment Systems Manual; EPA 625/R-00/008; U.S. EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2002.
- Pinpatthanapong, K.; Khetkorn, W.; Honda, R.; Phattarapattamawong, S.; Treesubsuntorn, C.; Panasan, N.; Boonmawat, P.; Tianthong, Y.; Lipiloet, S.; Sorn, S.; et al. Effects of high-strength landfill leachate effluent on stress-induced microalgae lipid production and post-treatment micropollutant degradation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 324, 116367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.; Aleix Comas-Vives, A.; Copéret, D. Ga and Zn increase the oxygen affinity of Cu-based catalysts for the COx hydrogenation according to ab initio atomistic thermodynamics. Chem. Sci. 2022, 13, 13442–13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, L.K.; Pandey, M.; Raj, P.A. Impact of airfoil collar on scour reduction around the bridge pier. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 290, 116271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.S.; Ju, L.W.; Yang, S.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Tan, Z.F. A multi-objective robust optimal dispatch and cost allocation model for microgrids-shared hybrid energy storage system considering flexible ramping capacity. Appl. Energy 2024, 369, 123565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.; Achari, G. A Comprehensive Numerical Model Simulating Gas, Heat, and Moisture Transport in Sanitary Landfills and Methane Oxidation in Final Covers. Environ. Model. Assess. 2010, 15, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowski, H.; Janicka-Klos, A.; Brasun, J.; Gaggelli, E.; Valensin, D.; Valensin, G. Copper, iron, and zinc ions homeostasis and their role in neurodegenerative disorders (metal uptake, transport, distribution and regulation). Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 2665–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model Name | Simple Introduction | Developer |
|---|---|---|
| A Multimedia Total Exposure Model for Hazardous Waste Sites (CalTOX) | Mainly models the risk value of soil pollution to the recipient | Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory |
| Multimedia Environmental Pollutant Assessment System (MEPAS) | Mainly estimates environmental chronic diseases due to exposure | Pacific Northwest National Laboratory |
| The Multimedia Contaminant Fate, Transport, and Exposure Model (MMSOILS) | Mainly estimates the release of chemical contaminants from hazardous waste sites | USEPA Office of Research and Development |
| Multimedia, Multipathway, Multireceptor Risk Assessment (3MRA) | Mainly estimates the different exposures caused by pollutants | USEPA Office of Research and Development Office of Solid Waste |
| Extended Environmental Multimedia Modeling Analysis System (EEMMS) | The developed EEMMS can model air, landfill, unsaturated zones, and groundwater zones in 2D or 3D using the finite element method. | [36,44] |
| Layer | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Porosity (n) % | Specific Storage (Ss) 1/ft | Specific Yield (Sy) 1/ft | Hydraulic Conductivity (K) ft/day | Dispersion (ft) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper glacial till | 2200 | 20 | 3 × 10−5 | 0.055 | 1.86 × 10−3 | 40 |
| Lower glacial till | 2200 | 20 | 3 × 10−5 | 0.055 | 1.24 × 10−4 | 40 |
| Total overburden | 1700 | 20 | 3 × 10−5 | 0.082 | 1.53 × 10−3 | 46 |
| Surface Head (ft) | Depth (ft) | Top Elevation (ft) | Bottom Elevation (ft) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250.23 | 19 | 242.73 | 232.73 |
| 245.37 | 26.4 | 229.17 | 219.17 |
| 247.69 | 58 | 202.69 | 192.69 |
| 248.78 | 51 | 207.78 | 197.78 |
| Z | Heavy Metal | Organic | Inorganic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy metal | 1 | 5 | 7 |
| Organic | 1/5 | 1 | 3 |
| Inorganic | 1/7 | 1/3 | 1 |
| Heavy Metal | Organic | Inorganic | W | AW | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heavy metal | 0.7447 | 0.7895 | 0.6364 | 0.7235 | 2.2726 |
| Organic | 0.1489 | 0.1579 | 0.2727 | 0.1932 | 0.5879 |
| Inorganic | 0.1064 | 0.0526 | 0.0909 | 0.0833 | 0.2511 |
| Contaminant | Concentration (mg/L) | Kd (L/mg) |
|---|---|---|
| BOD | 1000 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, M. Extended Environmental Multimedia Modeling System (EEMMS) with Analytic Hierarchy Process for Dual Evaluation of Energy Consumption and Pollutants in Solid Waste. Toxics 2025, 13, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100878
Yuan J, Wang H, Chen M. Extended Environmental Multimedia Modeling System (EEMMS) with Analytic Hierarchy Process for Dual Evaluation of Energy Consumption and Pollutants in Solid Waste. Toxics. 2025; 13(10):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100878
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jing, Heng Wang, and Meifeng Chen. 2025. "Extended Environmental Multimedia Modeling System (EEMMS) with Analytic Hierarchy Process for Dual Evaluation of Energy Consumption and Pollutants in Solid Waste" Toxics 13, no. 10: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100878
APA StyleYuan, J., Wang, H., & Chen, M. (2025). Extended Environmental Multimedia Modeling System (EEMMS) with Analytic Hierarchy Process for Dual Evaluation of Energy Consumption and Pollutants in Solid Waste. Toxics, 13(10), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13100878







