The Effect of an Alternating Magnetic Field-Assisted Freezing Process on the Quality of Frozen Penaeus Japonicus
Abstract
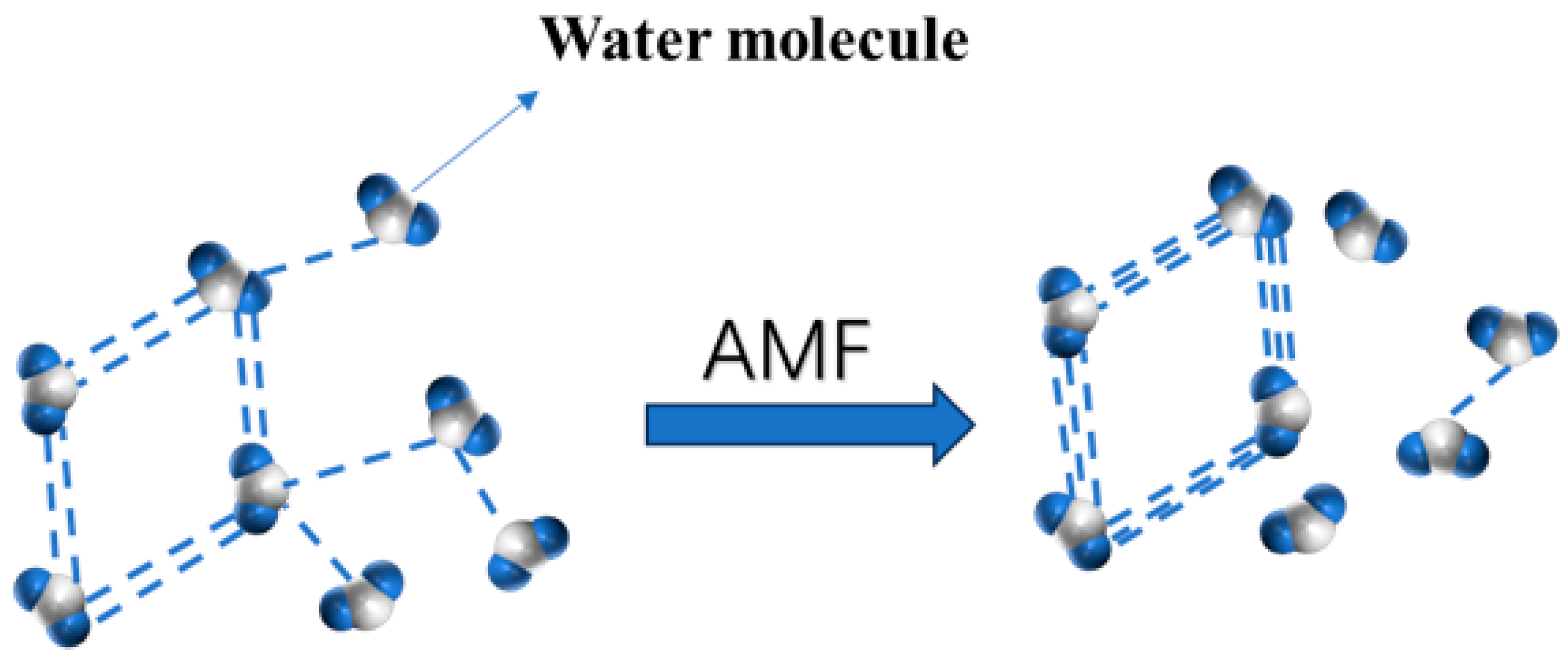
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
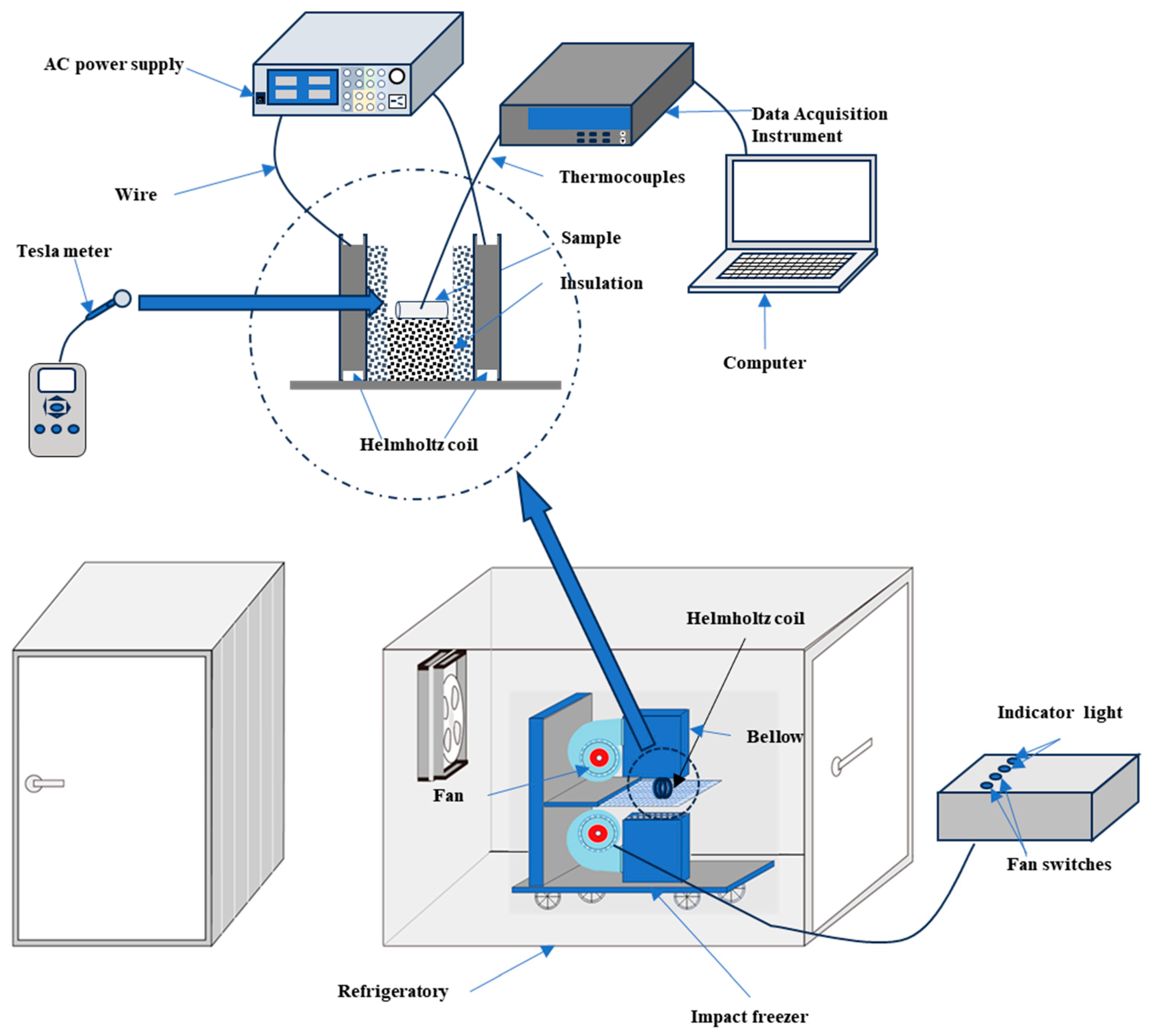
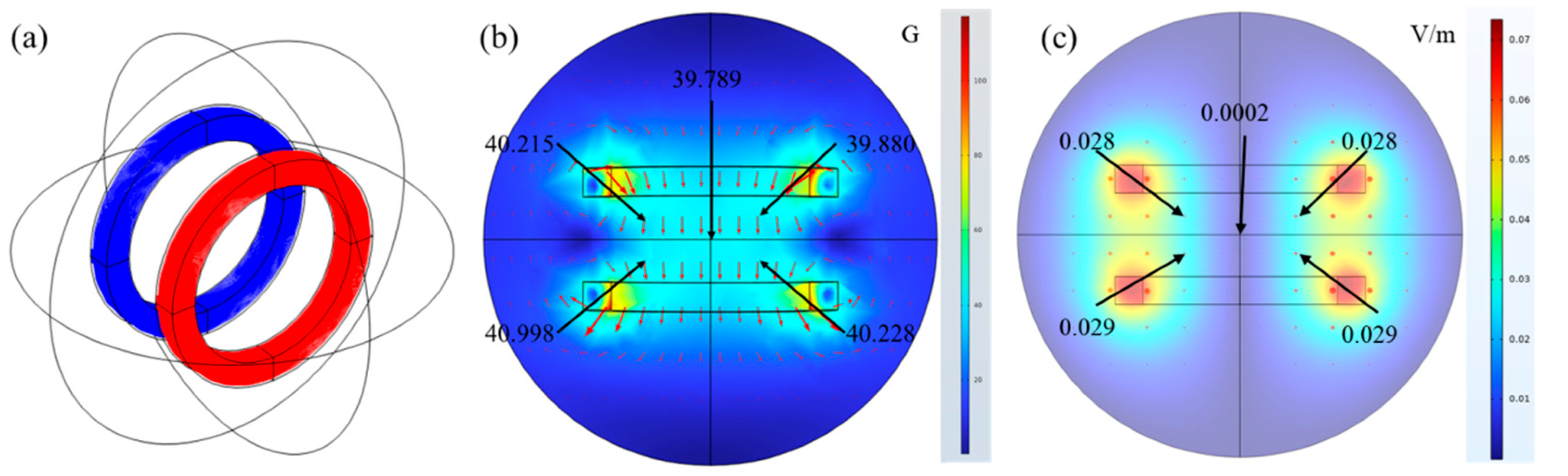
2.1. Magnetic Field-Assisted Freezing System
2.2. Pre-Treatment of Shrimp
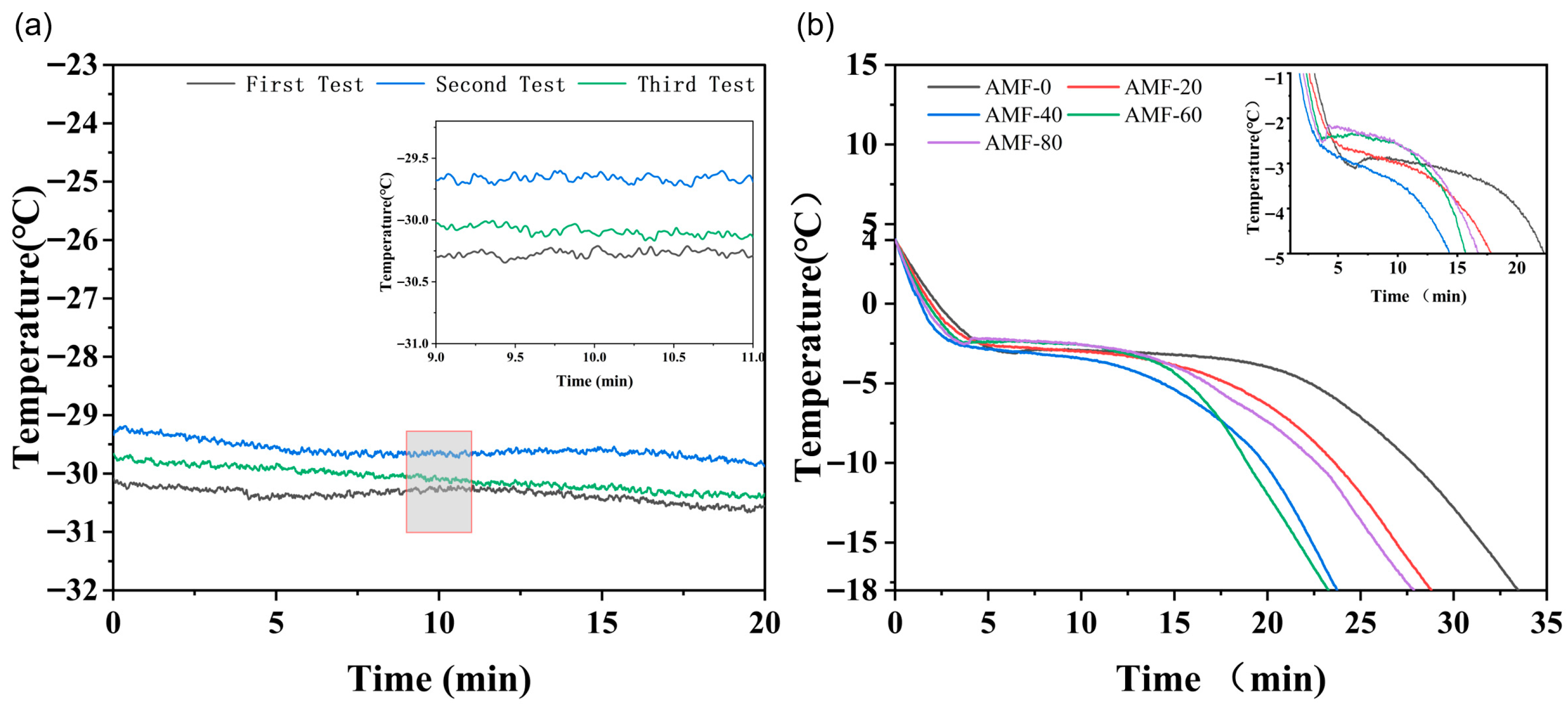
2.3. Determination of Freezing Curves
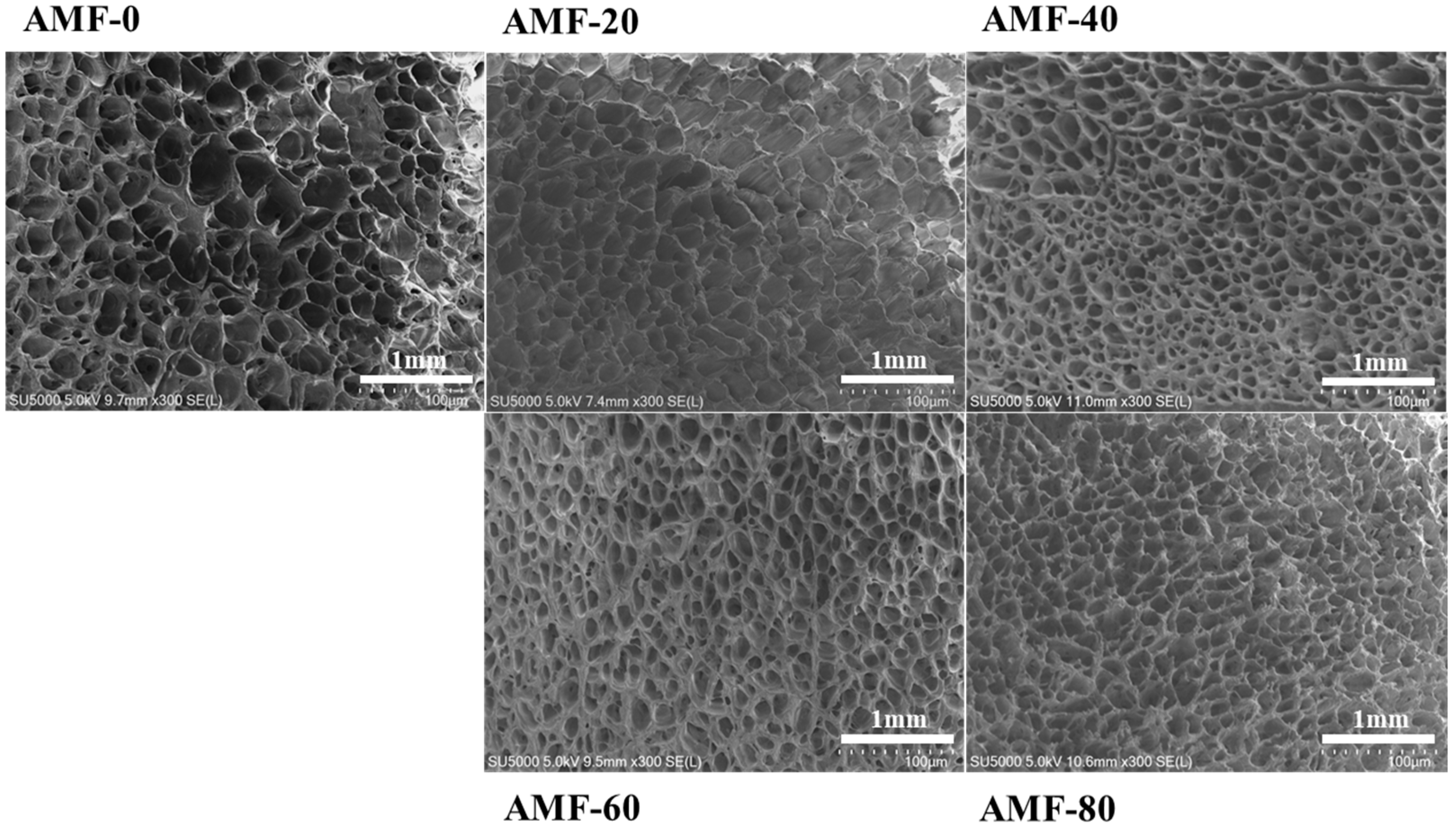
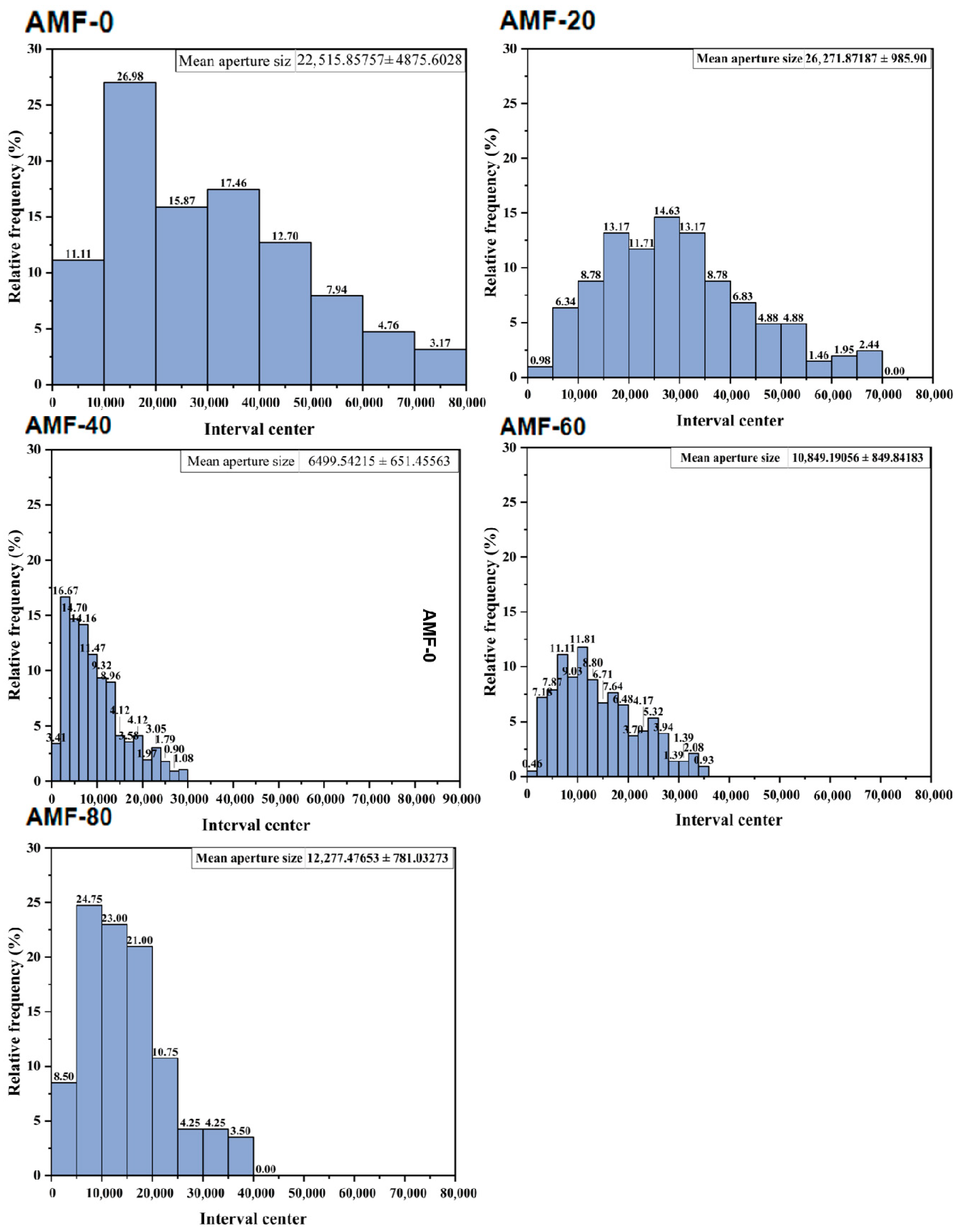
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
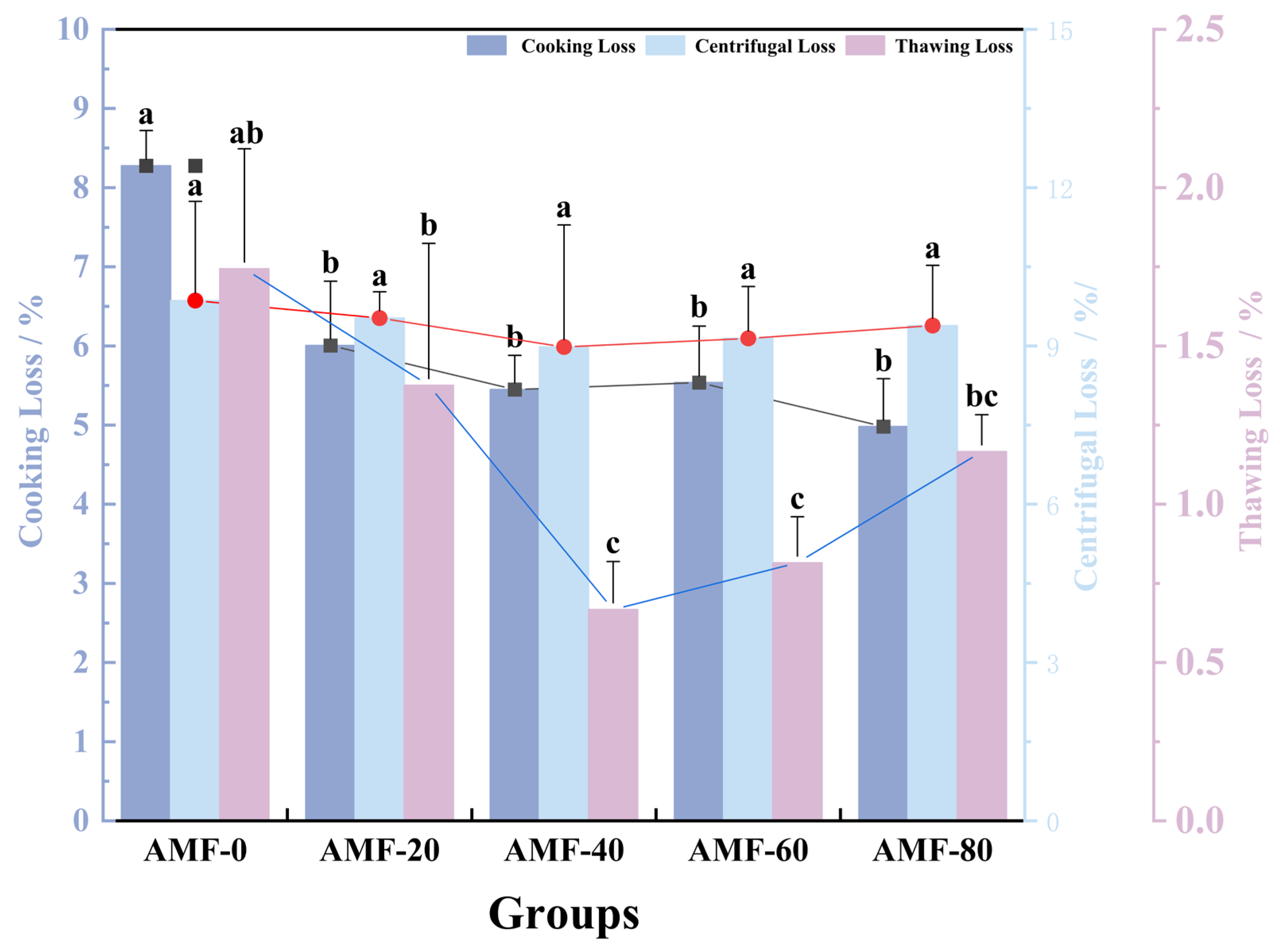
2.5. Determination of Thawing Loss, Cooking Loss, and Centrifugal Loss
2.6. Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Analysis
2.7. Determination of Color
2.8. Measurement of pH
2.9. Determination of Texture Properties
2.10. Determination of Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Effect of Magnetic Field Strength
3.1.1. Changes in Freezing Time at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
3.1.2. Changes in the Microstructure of Shrimp
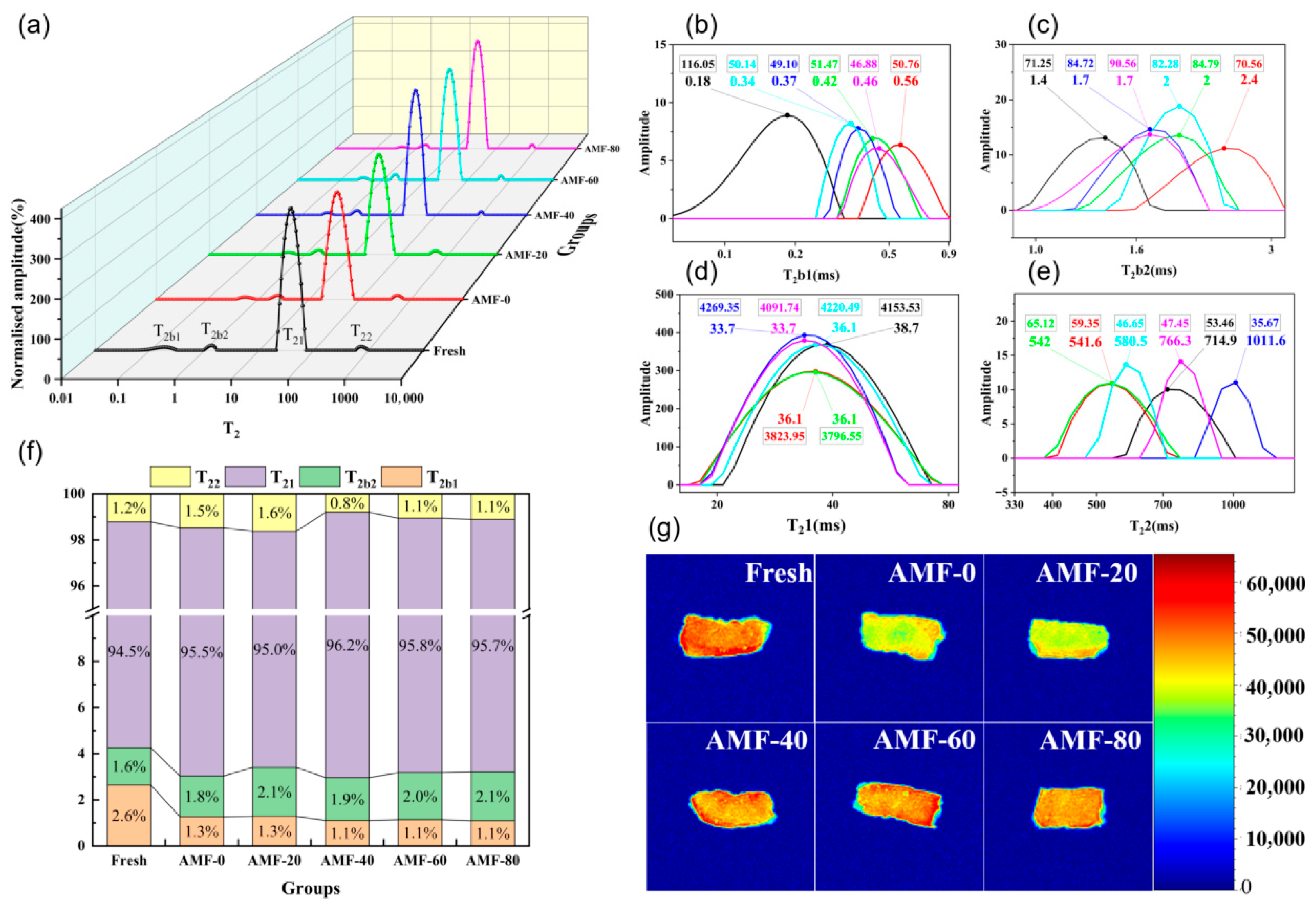
3.1.3. Moisture Characteristics at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
Water-Holding Capacity Analysis at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
Changes in Water Distribution of Shrimp at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
3.1.4. Physicochemical Property at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
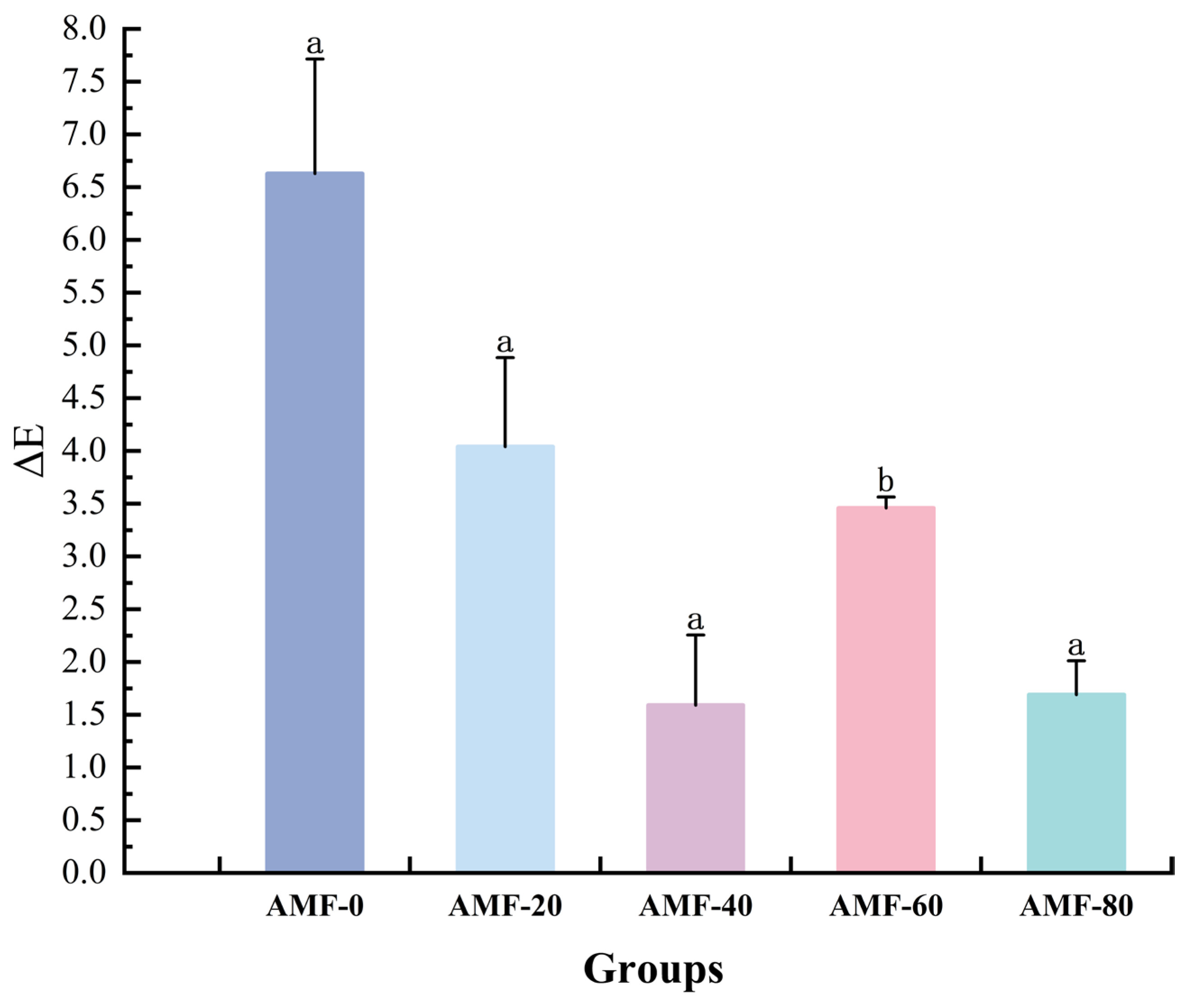
Color Changes Analysis at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
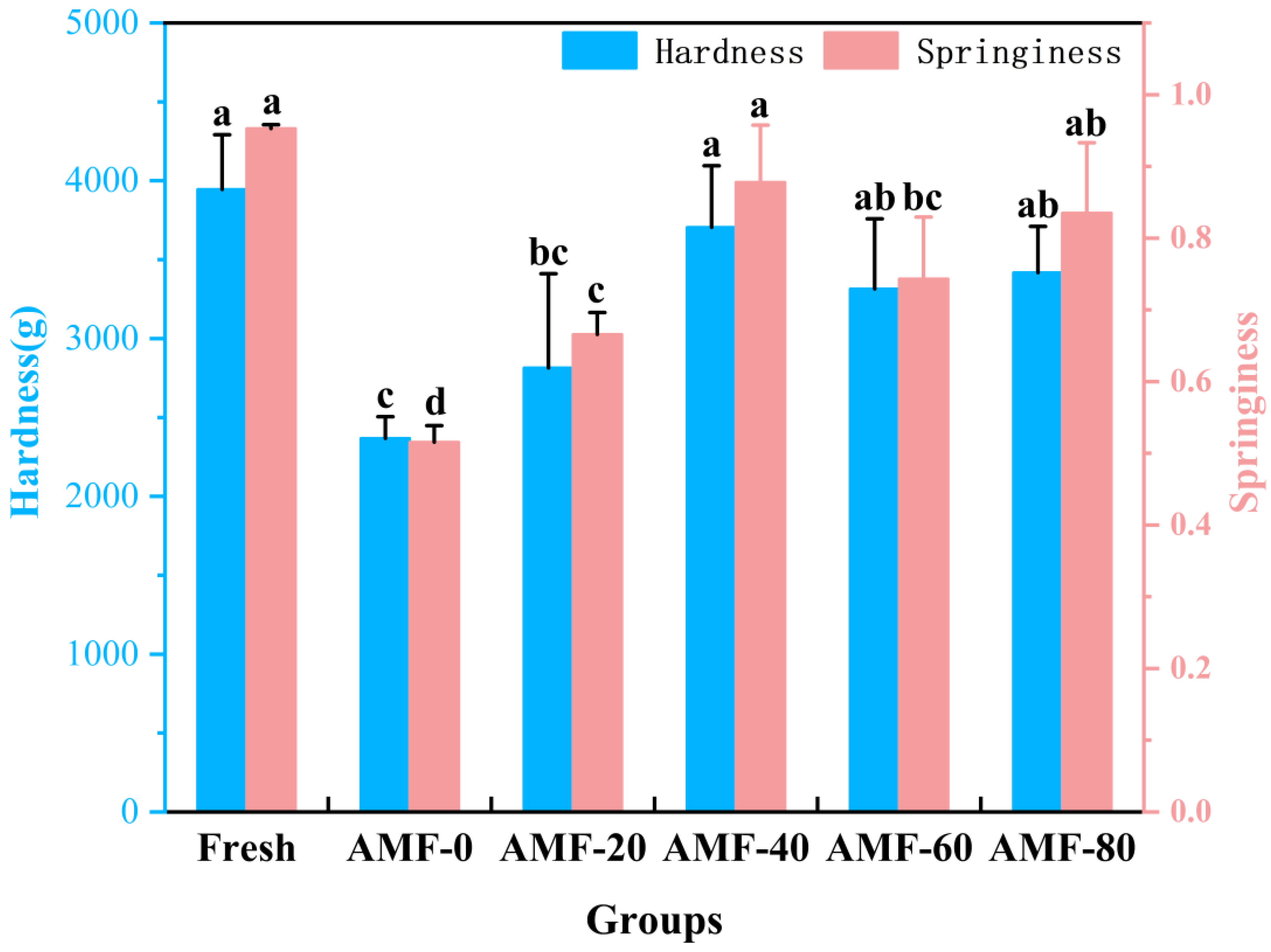
Texture Analysis at Different Magnetic Field Strengths
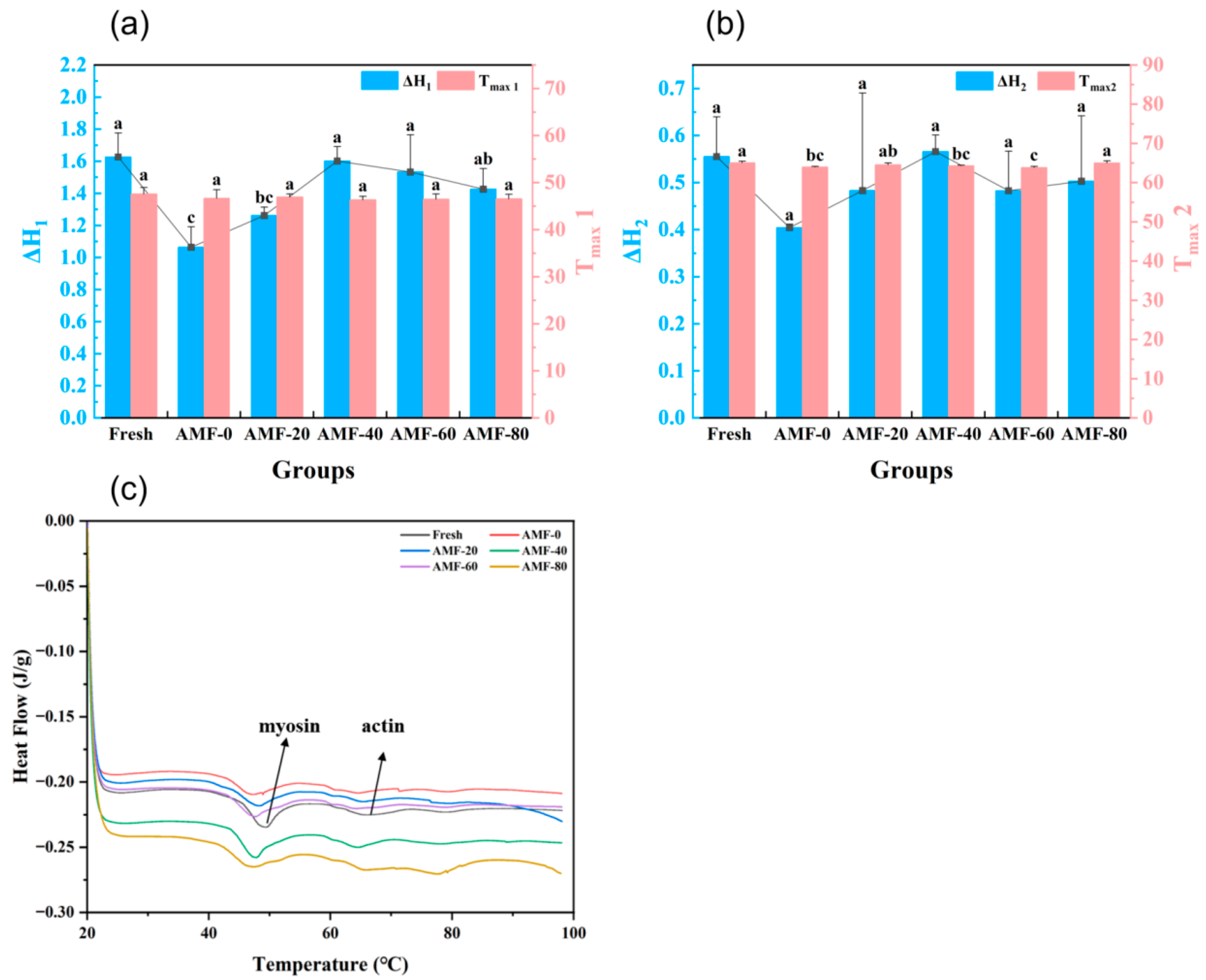
DSC Analysis
3.2. The Effect of Magnetic Field Frequency
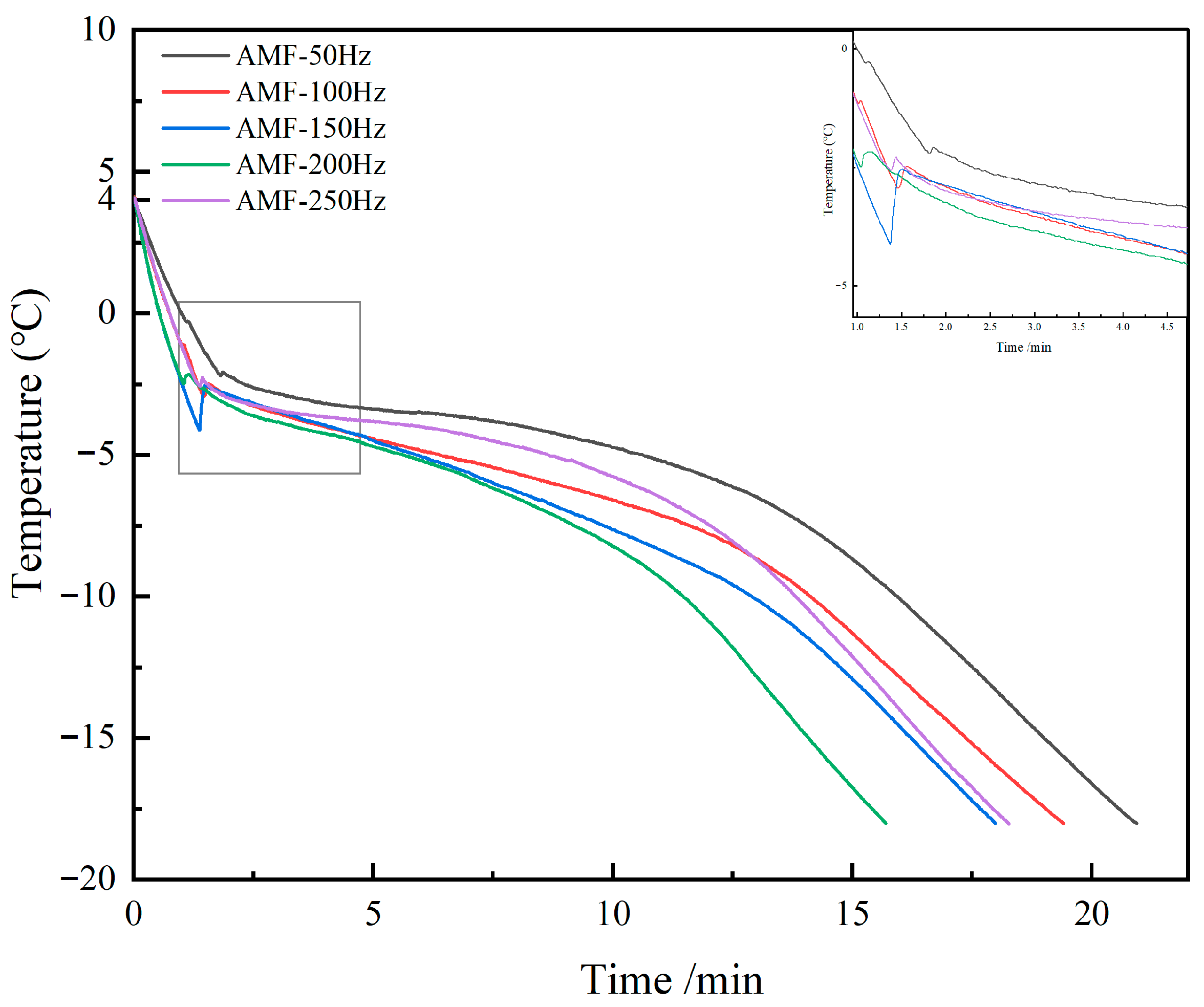
3.2.1. Changes in Freezing Time at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
3.2.2. Physicochemical Property at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
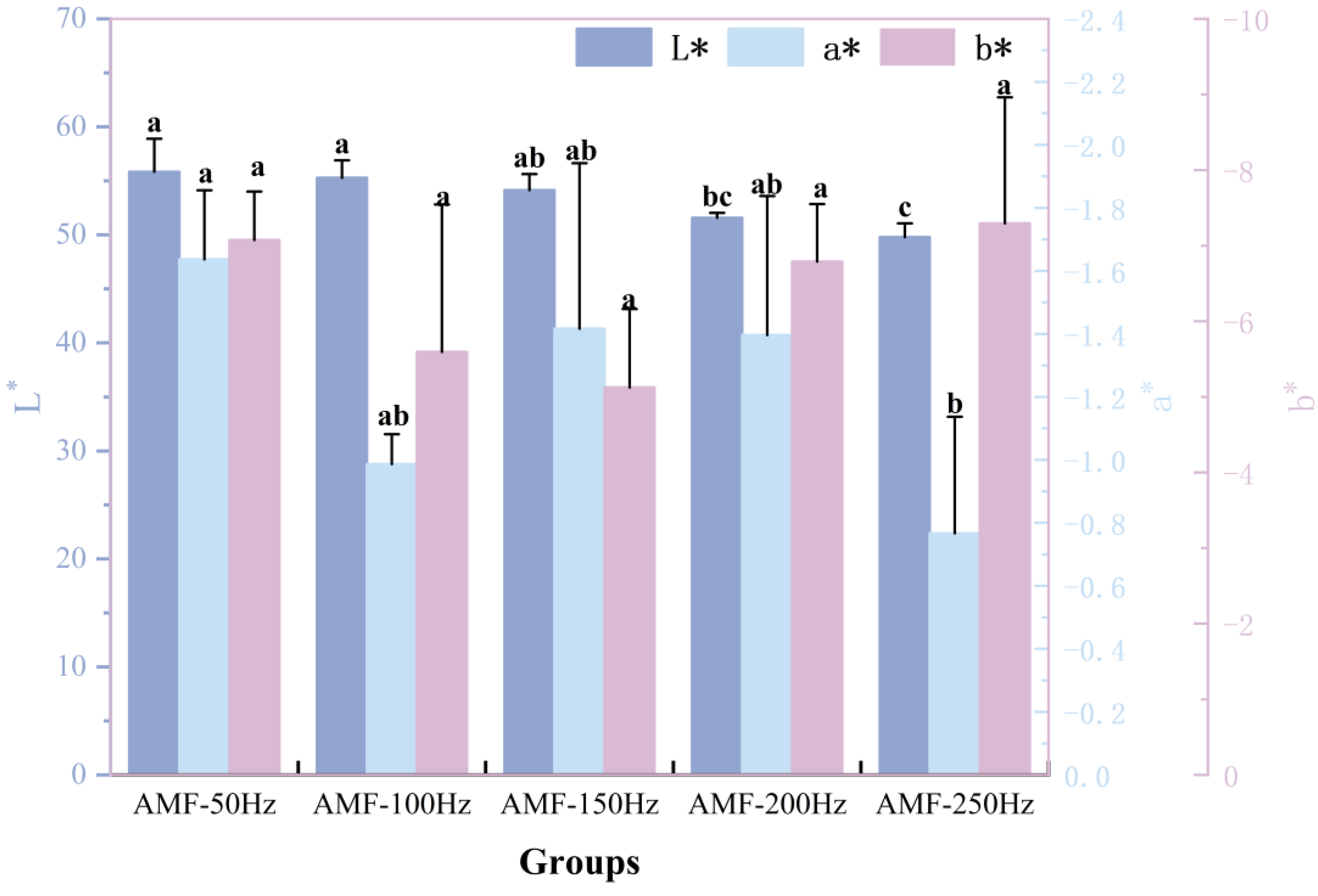
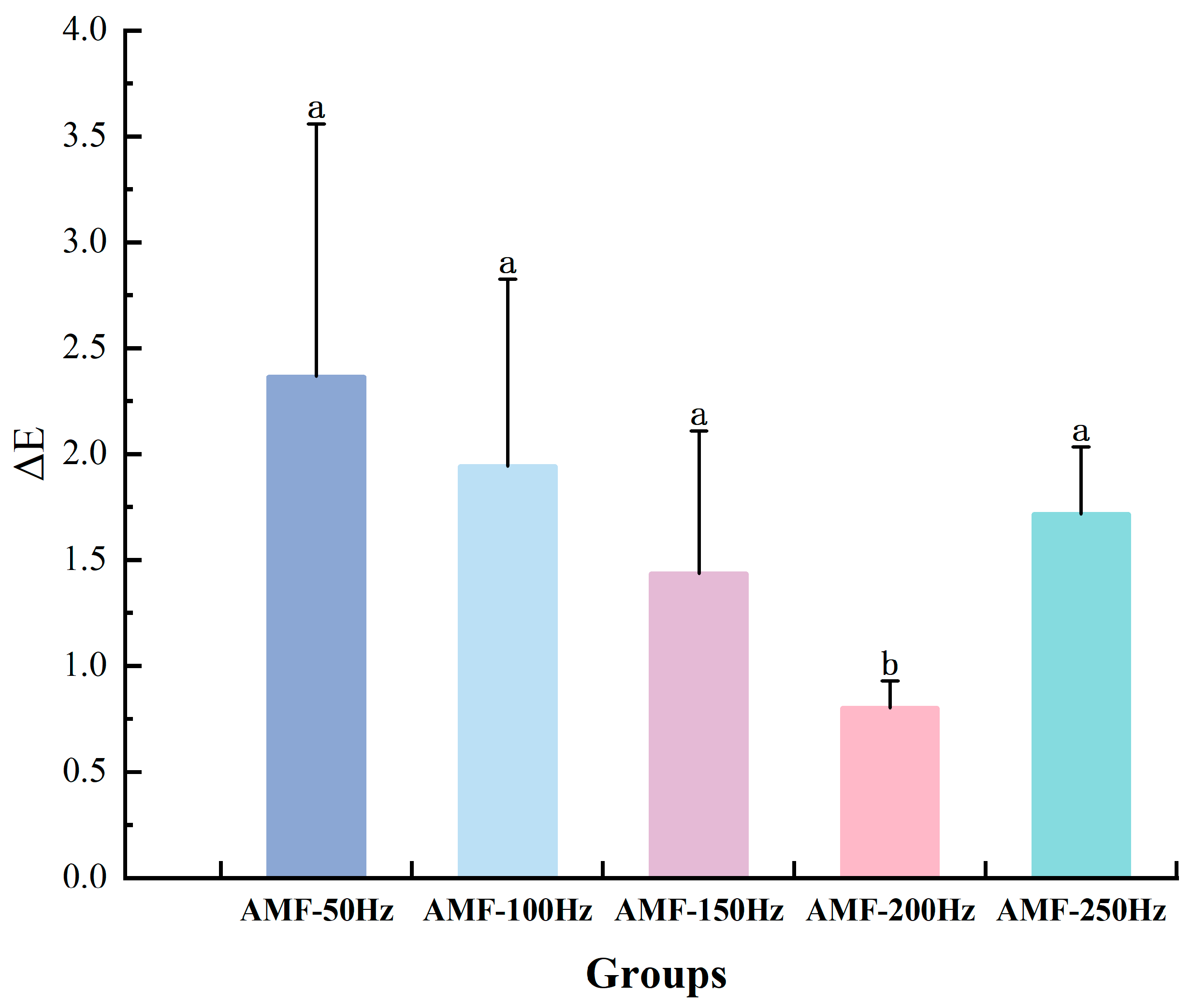
Color Changes Analysis at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
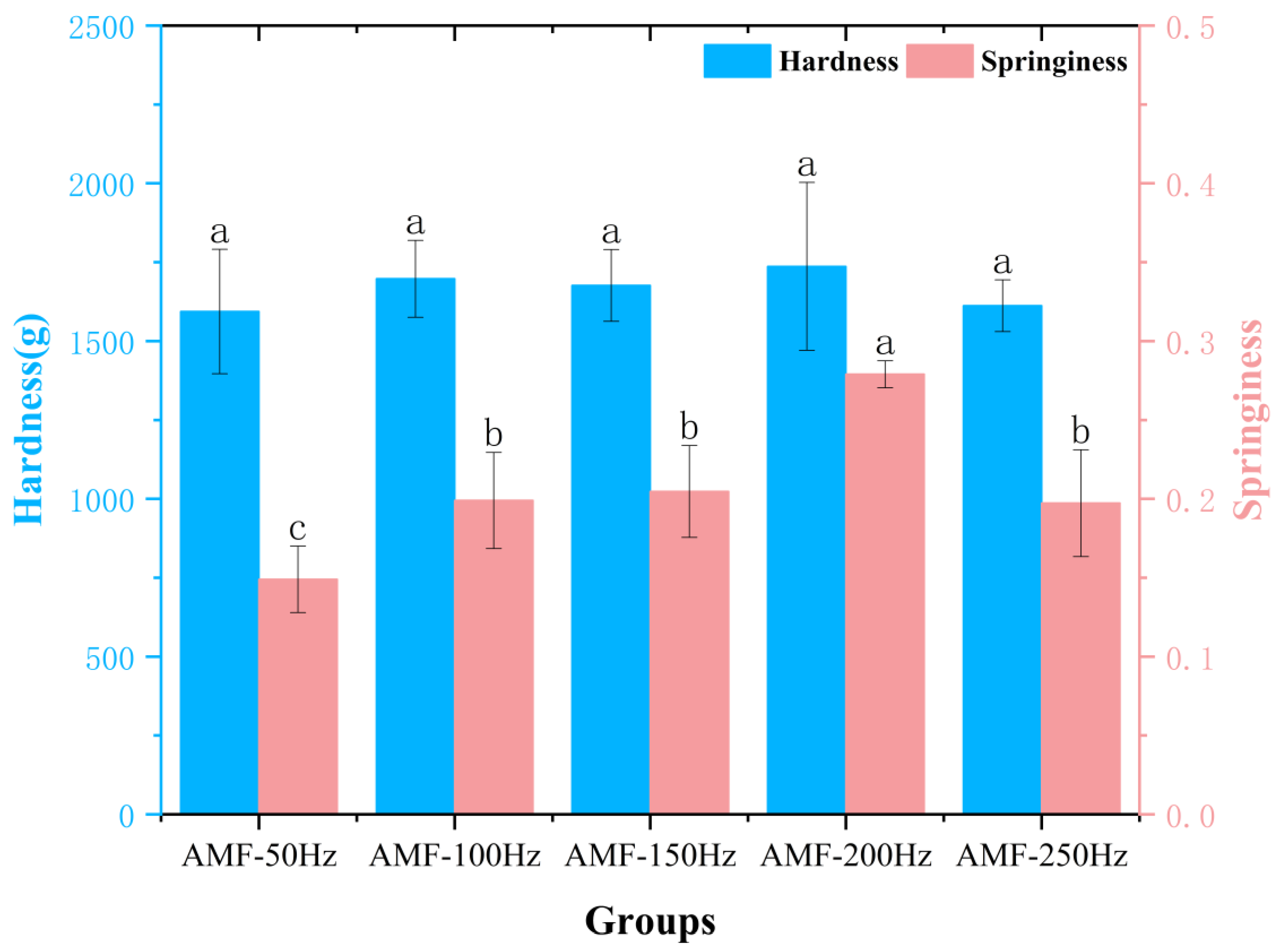
Texture Analysis at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
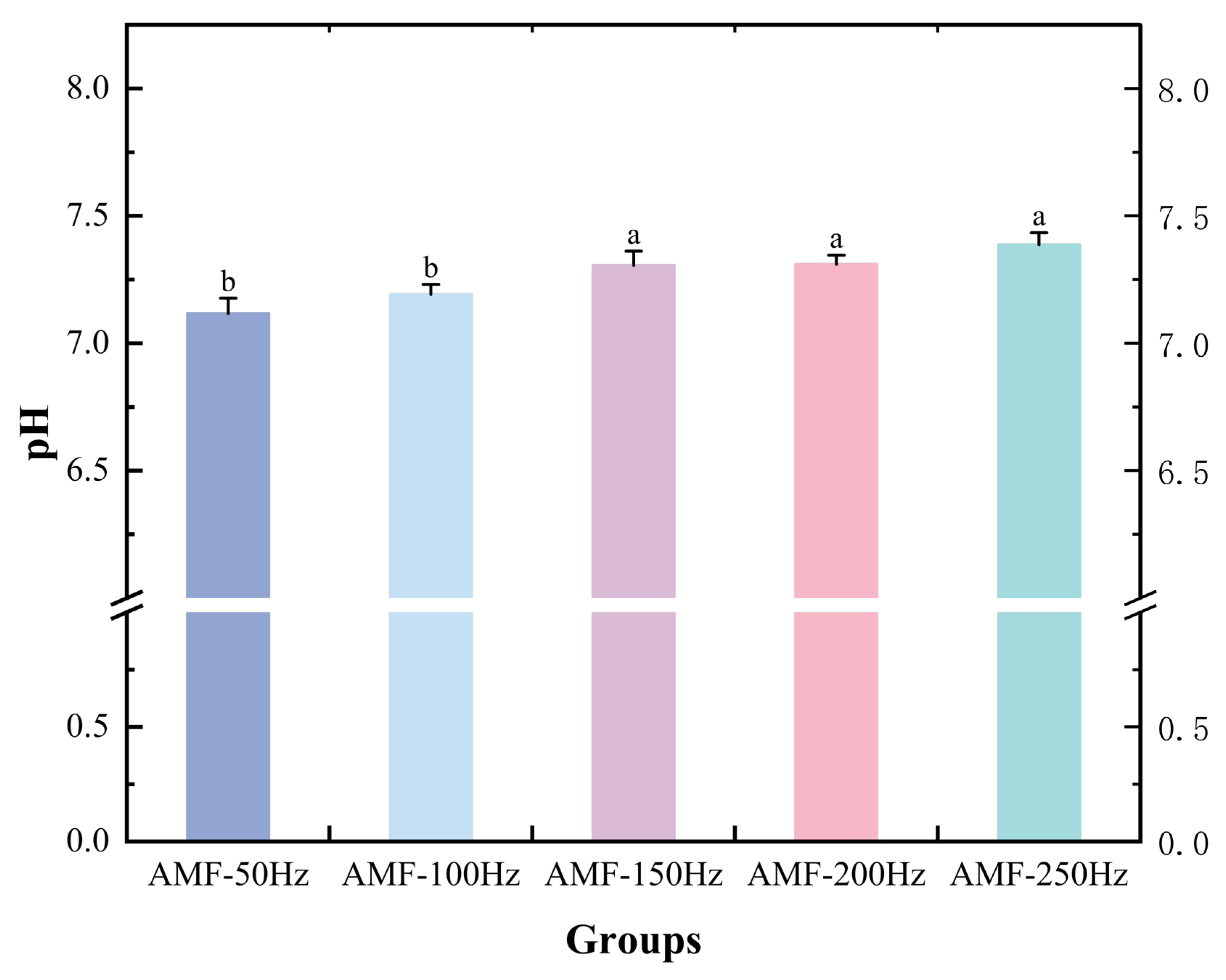
pH Analysis
3.2.3. Moisture Characteristics at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
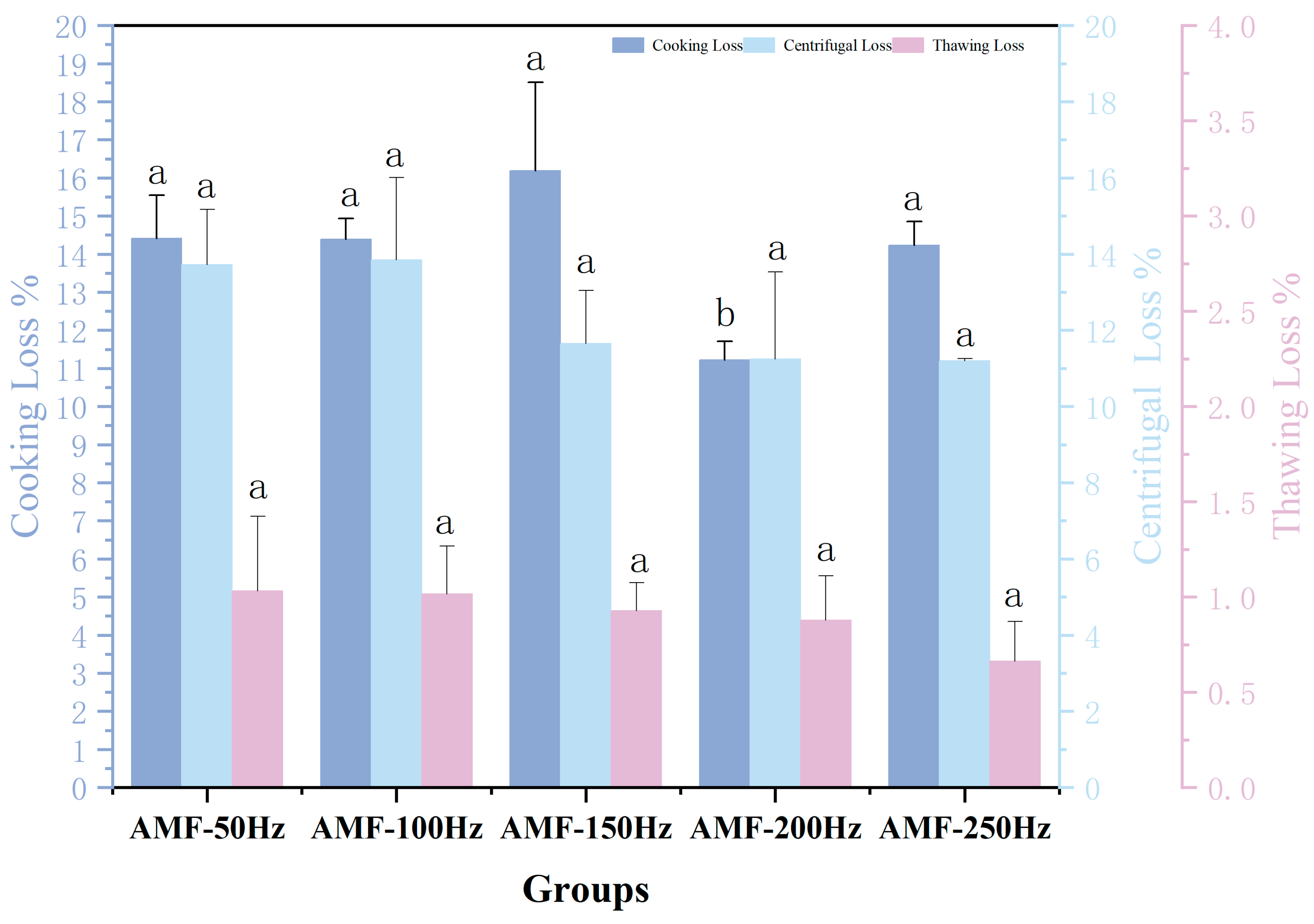
Water-Holding Capacity Analysis at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
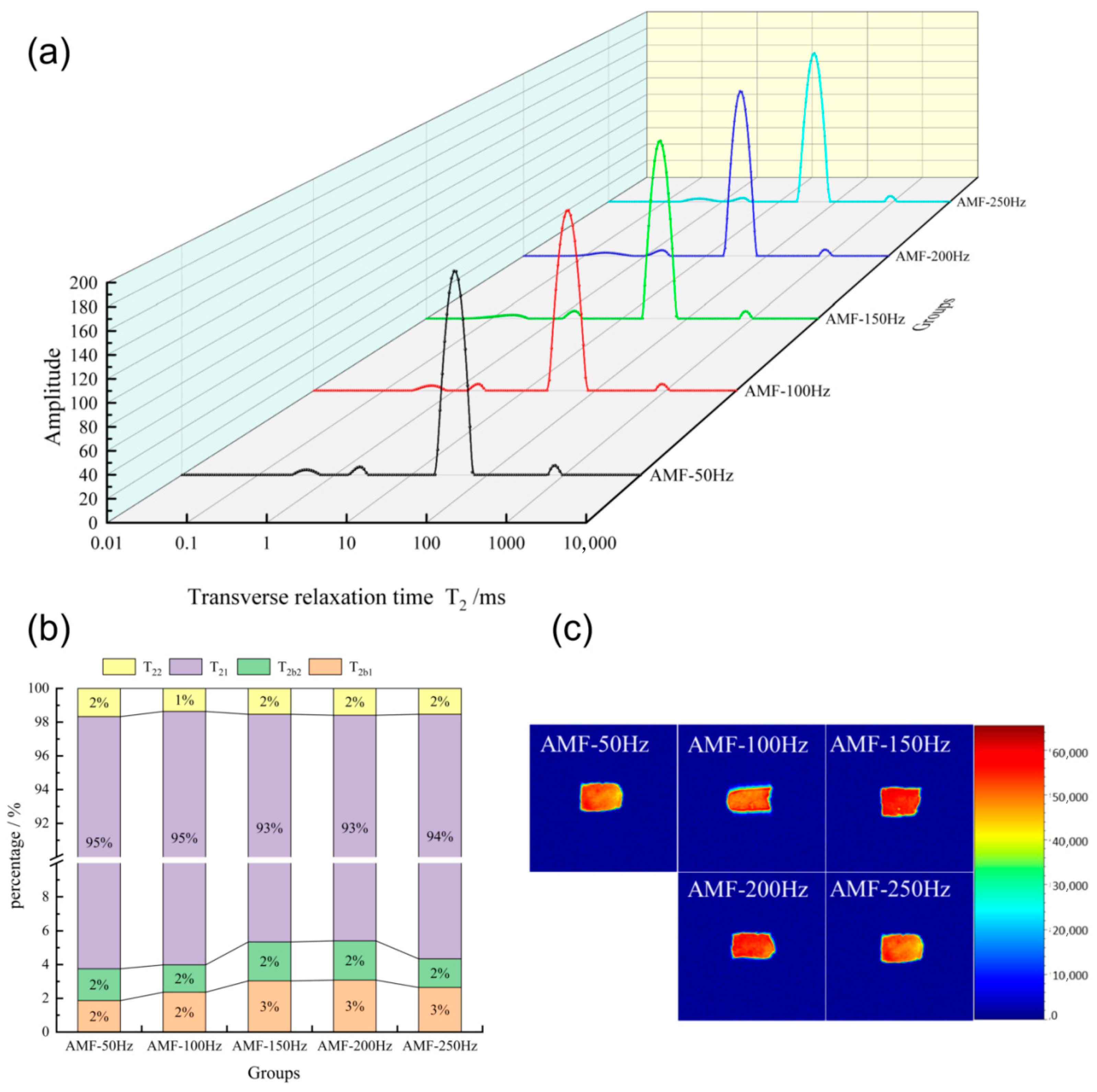
Changes in Water Distribution of Shrimp at Different Magnetic Field Frequencies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bian, C.; Yu, H.; Yang, K.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Effects of Single-, Dual-, and Multi-Frequency Ultrasound-Assisted Freezing on the Muscle Quality and Myofibrillar Protein Structure in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea). Food Chem. X 2022, 15, 100362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Tan, G.; Chen, H.; Li, T.; Du, D. Effects of Low-Intensity DC Magnetic Field on the Freezing Process of Aqueous Solution and Beef. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e72221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kumar, M.; Sethi, V. Maintaining the Freeze Thawing Characteristics of Tomato through Development and Evaluation of Magnetic Field-assisted Freezing System. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, 16900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, D.; Zhang, H.; Tian, C.; Li, P.; Kong, F.; Zhan, B. Static Magnetic Field Assisted Freezing of Four Kinds of Fruits and Vegetables: Micro and Macro Effects. Int. J. Refrig. 2023, 146, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yang, L.; Xu, R.; Jiang, S.; Lin, L.; Lu, J. Effects of Static Magnetic Field (SMF) and Alternating Magnetic Field (AMF) Assisted Freezing on the Microstructure and Protein Properties of Channel Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fillet. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El May, A.; Snoussi, S.; Ben Miloud, N.; Maatouk, I.; Abdelmelek, H.; Ben Aïssa, R.; Landoulsi, A. Effects of Static Magnetic Field on Cell Growth, Viability, and Differential Gene Expression in Salmonella. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-T.; Weng, C.-I. The Effect of an External Magnetic Field on the Structure of Liquid Water Using Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 100, 043917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnell, G.; James, C.; James, S.J. The Effects of Applying Oscillating Magnetic Fields During the Freezing of Apple and Potato. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 2113–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.; Fu, J. Effect of Static Magnetic Field Assisted Freezing on the Product Quality of Korla Fragrant Pear. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tian, C.; Shao, S. Effects of Different Magnetic Fields on the Freezing Parameters of Cherry. J. Food Eng. 2020, 278, 109949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Yu, D.; Luo, Z. Freezing of Green Peppers Assisted by Combined Electromagnetic Fields: Effects on Juice Loss, Moisture Distribution, and Microstructure after Thawing. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Feng, R.; Tao, H.; Zhang, B. A Comparative Study of Magnetic Field on the Maximum Ice Crystal Formation Zone and Whole Freezing Process for Improving the Frozen Dough Quality. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, S.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Q. Pork Freezing and Quality Improvement: The Effect of Immersion Freezing Assisted by Magnetic Field. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z. A Novel Synergistic Freezing Assisted by Infrared Pre-Dehydration Combined with Magnetic Field: Effect on Freezing Efficiency and Thawed Product Qualities of Beef. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2022, 15, 1392–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yang, N.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Y.; Jin, Z.; Xu, X. Effect of Weak Magnetic Field on the Water-Holding Properties, Texture, and Volatile Compounds of Pork and Beef during Frozen Storage. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, A.C.; James, C.; James, S.J. Effects of Weak Oscillating Magnetic Fields on the Freezing of Pork Loin. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 1615–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Effect of a Magnetic Field on Droplet Freezing and Frost Formation on Cold Surfaces. Cryobiology 2024, 114, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, D.; Zhang, H.; Tian, C.; Xu, H.; Li, P. The Effect of Magnetic Field on the Quality of Channel Catfish under Two Different Freezing Temperatures. Int. J. Refrig. 2022, 140, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jin, Y.; Hong, T.; Yang, N.; Cui, B.; Xu, X.; Jin, Z. Effect of Static Magnetic Field on the Quality of Frozen Bread Dough. LWT 2022, 154, 112670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhu, Z.; Sun, D.-W. Effects of Freezing on Cell Structure of Fresh Cellular Food Materials: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Bu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, X. Effects of Nanowarming on Water Holding Capacity, Oxidation and Protein Conformation Changes in Jumbo Squid (Dosidicus gigas) Mantles. LWT 2020, 129, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, C.; Xia, X.; Sun, F.; Kong, B. Ultrasound-Assisted Immersion Freezing Accelerates the Freezing Process and Improves the Quality of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) at Different Power Levels. LWT 2019, 108, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, X.-N.; Zhu, K.-X. Effects of Frozen Storage on the Quality Characteristics of Frozen Cooked Noodles. Food Chem. 2019, 283, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stormo, S.K.; Skåra, T. Liquid Loss in Thawed Cod—Deconvoluting the Effects of Freezing-rate, Freezing Cycles, Frozen Storage Time, and Thawing-rate through a Full Factorial Design. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leygonie, C.; Britz, T.J.; Hoffman, L.C. Impact of Freezing and Thawing on the Quality of Meat: Review. Meat Sci. 2012, 91, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Bhandari, B.; Chen, J. Effect of Magnetic Field on Quality Improvement of Medium-term Delivery Frozen Pepper. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solo-de-Zaldívar, B.; Herranz, B.; Borderías, A.J.; Tovar, C.A. Effect of Freezing and Frozen Storage on Restructured FISH Prototypes Made with Glucomannan and FISH Mince. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Sun, F.; Xia, X.; Xu, H.; Kong, B. The Comparison of Ultrasound-Assisted Immersion Freezing, Air Freezing and Immersion Freezing on the Muscle Quality and Physicochemical Properties of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) during Freezing Storage. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 51, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Alonso, I.; Moreno, P.; Careche, M. Low Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR) Relaxometry in Hake (Merluccius merluccius, L.) Muscle after Different Freezing and Storage Conditions. Food Chem. 2014, 153, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Luo, K.; Fu, R.; Lin, X.; Feng, A. Impact of the Magnetic Field-assisted Freezing on the Moisture Content, Water Migration Degree, Microstructure, Fractal Dimension, and the Quality of the Frozen Tilapia. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S. Novel Assistive Technologies for Efficient Freezing of Pork Based on High Voltage Electric Field and Static Magnetic Field: A Comparative Study. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 80, 103087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Dong, X.; Kong, B.; Sun, Q.; Ji, H.; Liu, S. Effects of Magnetic Field-Assisted Immersion Freezing at Different Magnetic Field Intensities on the Muscle Quality of Golden Pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Food Chem. 2023, 407, 135092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, G. Effect of Static Magnetic Field Assisted Thawing on Physicochemical Quality and Microstructure of Frozen Beef Tenderloin. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 914373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lei, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hong, H.; Luo, Y. Efficacy of Freeze-Chilled Storage Combined with Tea Polyphenol for Controlling Melanosis, Quality Deterioration, and Spoilage Bacterial Growth of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Food Chem. 2022, 370, 130924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Chen, Q.; Xia, X.; Kong, B.; Diao, X. Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Freezing at Different Power Levels on the Structure and Thermal Stability of Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio) Proteins. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 54, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Ye, J.; Xie, J. Freezing-induced myofibrillar protein denaturation: Role of pH change and freezing rate. LWT 2021, 152, 112381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panayampadan, A.S.; Shafiq Alam, M.; Aslam, R.; Kumar Gupta, S.; Kaur Sidhu, G. Effects of Alternating Magnetic Field on Freezing of Minimally Processed Guava. LWT 2022, 163, 113544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Luo, K.; Feng, A.; Zhao, D.; Wang, D.; Lin, X.; Liu, Z. Magnetic Field Improves the Quality of Frozen Tilapia Fillets by Decreasing the Ice Crystals during Freezing Process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 8961–8971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, K.; Yin, X.; Ma, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Han, M. Effect of Low-Frequency Magnetic Field on the Gel Properties of Pork Myofibrillar Proteins. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, L.; Rodríguez, A.C.; Sanz, P.D. Effect of the Frequency of Weak Oscillating Magnetic Fields on Supercooling and Freezing Kinetics of Pure Water and 0.9% NaCl Solutions. J. Food Eng. 2020, 273, 109822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Pre-Cooling Time/s | Phase Transition Time/s | Subcooling Time/s | Total Freezing Time/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF-0 | 179 ± 4.72 a | 1054 ± 88.26 a | 549 ± 108.89 a | 1782 ± 197.18 a |
| AMF-20 | 141 ± 14.19 b | 891 ± 51.16 b | 539 ± 105.69 a | 1571 ± 152.21 a |
| AMF-40 | 112 ± 18.23 c | 723 ± 32.59 c | 646 ± 69.97 a | 1482 ± 59.66 a |
| AMF-60 | 135 ± 10.69 b | 832 ± 53.41 b | 500 ± 42.93 a | 1469 ± 92.08 a |
| AMF-80 | 130 ± 24.34 b | 844 ± 51.97 b | 553 ± 131.19 a | 1528 ± 198.16 a |
| Groups | Pre-Cooling Time/s | Phase Transition Time/s | Subcooling Time/s | Total Freezing Time/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMF-50 Hz | 82 | 556 | 618 | 1256 |
| AMF-100 Hz | 59 | 335 | 780 | 1164 |
| AMF-150 Hz | 43 | 311 | 725 | 1079 |
| AMF-200 Hz | 43 | 294 | 605 | 942 |
| AMF-250 Hz | 58 | 298 | 740 | 1096 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, J.; Ding, G. The Effect of an Alternating Magnetic Field-Assisted Freezing Process on the Quality of Frozen Penaeus Japonicus. Foods 2025, 14, 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234112
Yang D, Zhang Q, Xie J, Ding G. The Effect of an Alternating Magnetic Field-Assisted Freezing Process on the Quality of Frozen Penaeus Japonicus. Foods. 2025; 14(23):4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234112
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Dazhang, Qifei Zhang, Jing Xie, and Guoqing Ding. 2025. "The Effect of an Alternating Magnetic Field-Assisted Freezing Process on the Quality of Frozen Penaeus Japonicus" Foods 14, no. 23: 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234112
APA StyleYang, D., Zhang, Q., Xie, J., & Ding, G. (2025). The Effect of an Alternating Magnetic Field-Assisted Freezing Process on the Quality of Frozen Penaeus Japonicus. Foods, 14(23), 4112. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14234112







