Nested U-Net-Based GAN Model for Super-Resolution of Stained Light Microscopy Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Construction
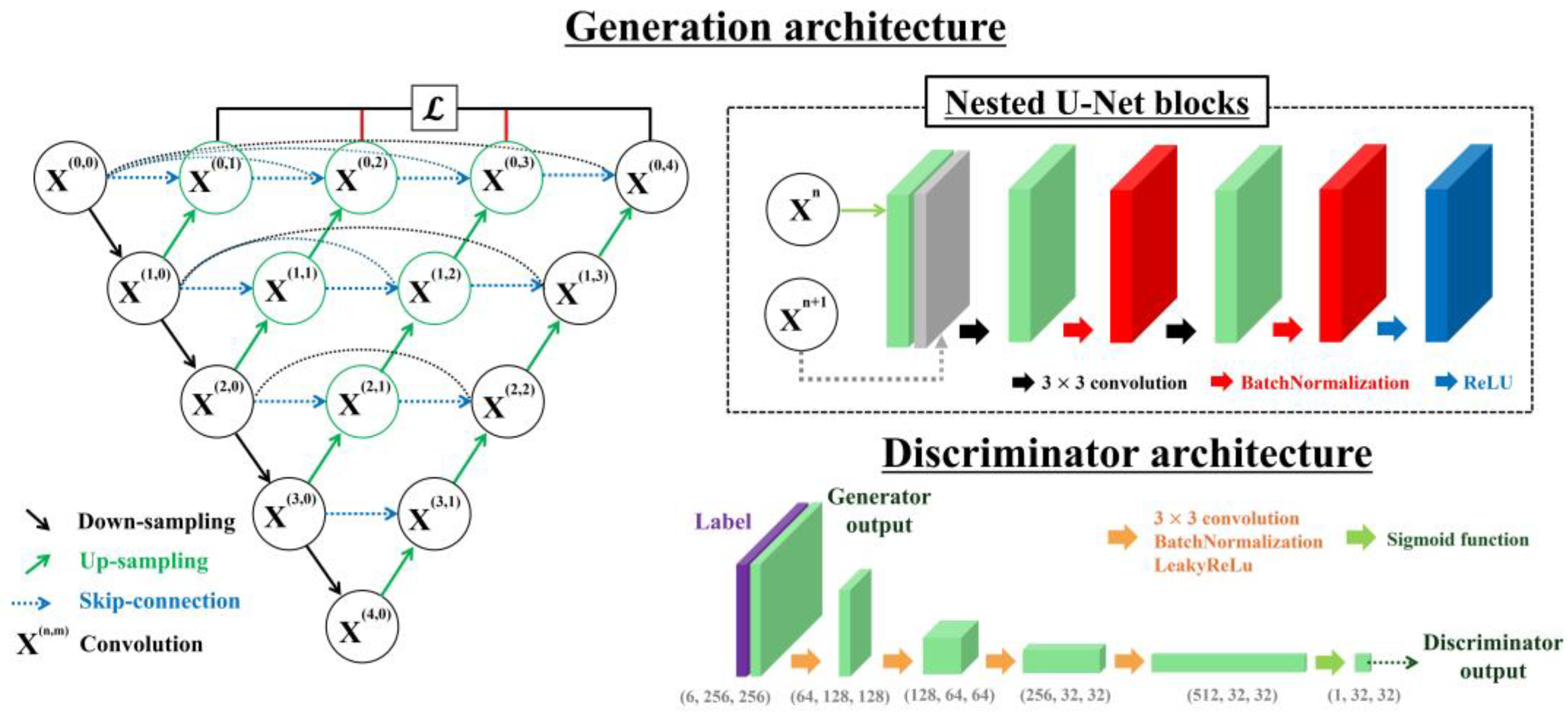
2.2. Nested U-Net-Based GAN Model
2.2.1. Comparison with Previous Super-Resolution Models in Microscopy
2.2.2. Generation Architecture
2.2.3. Discriminator Architecture
2.3. Quantitative Evaluation
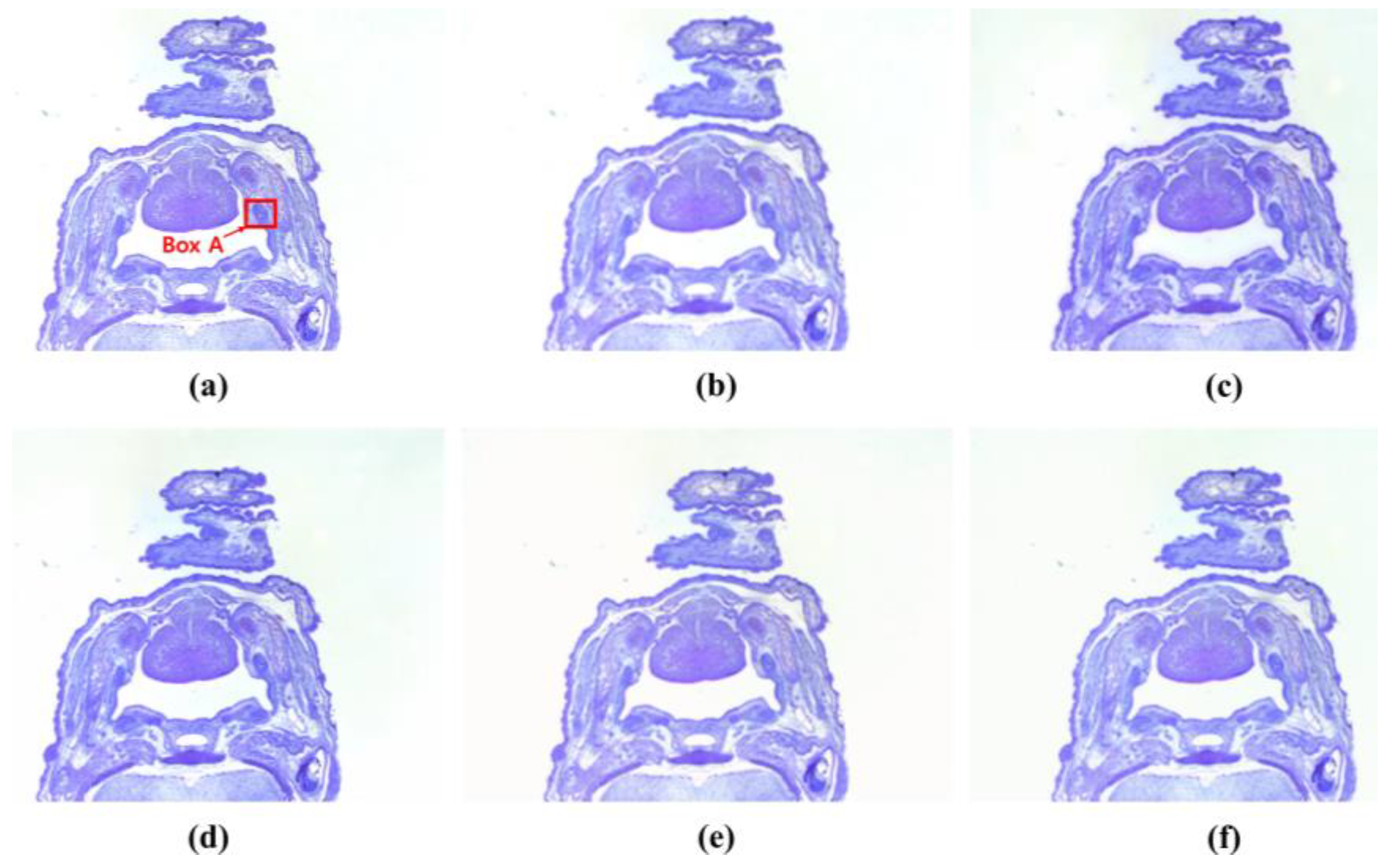
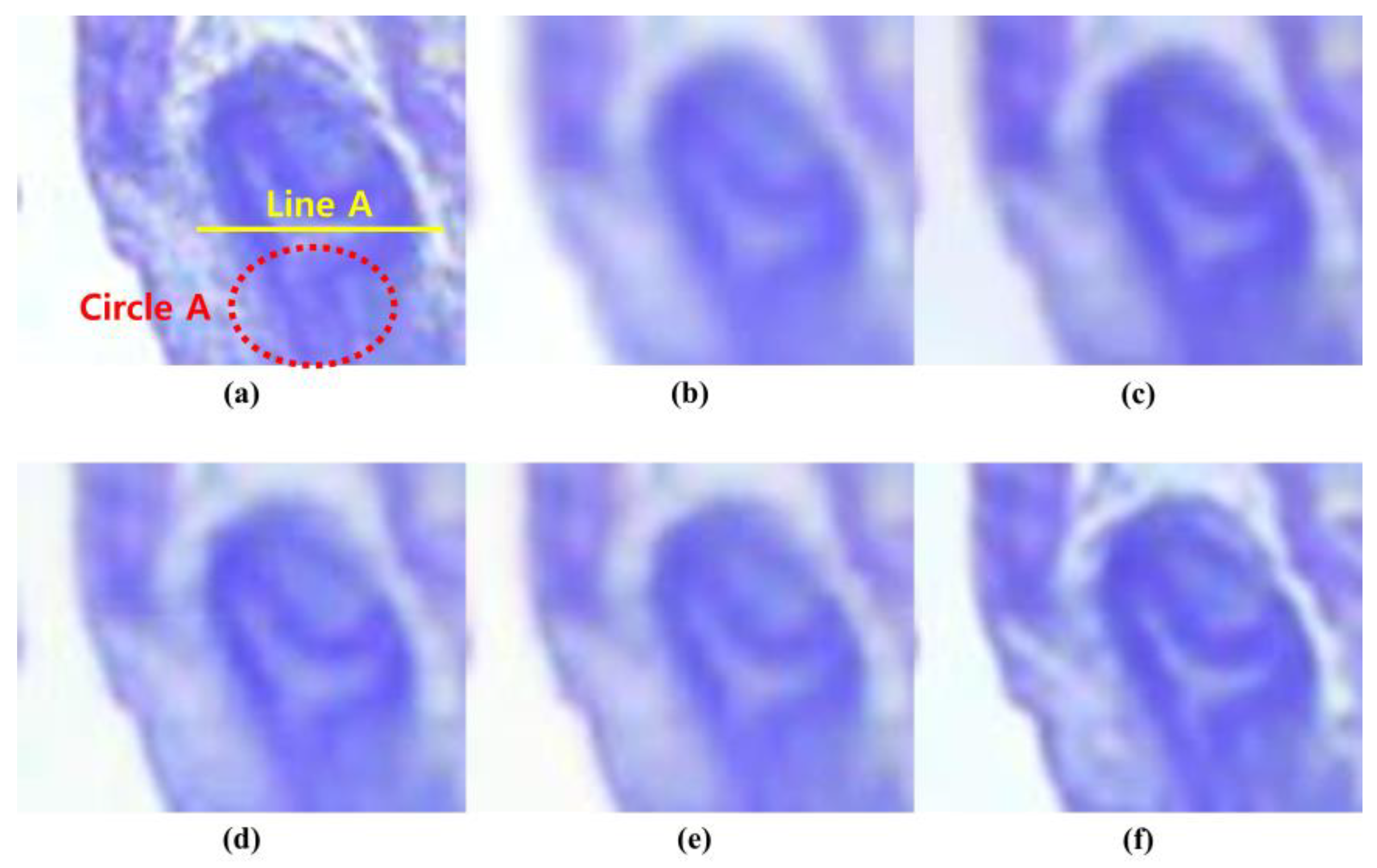
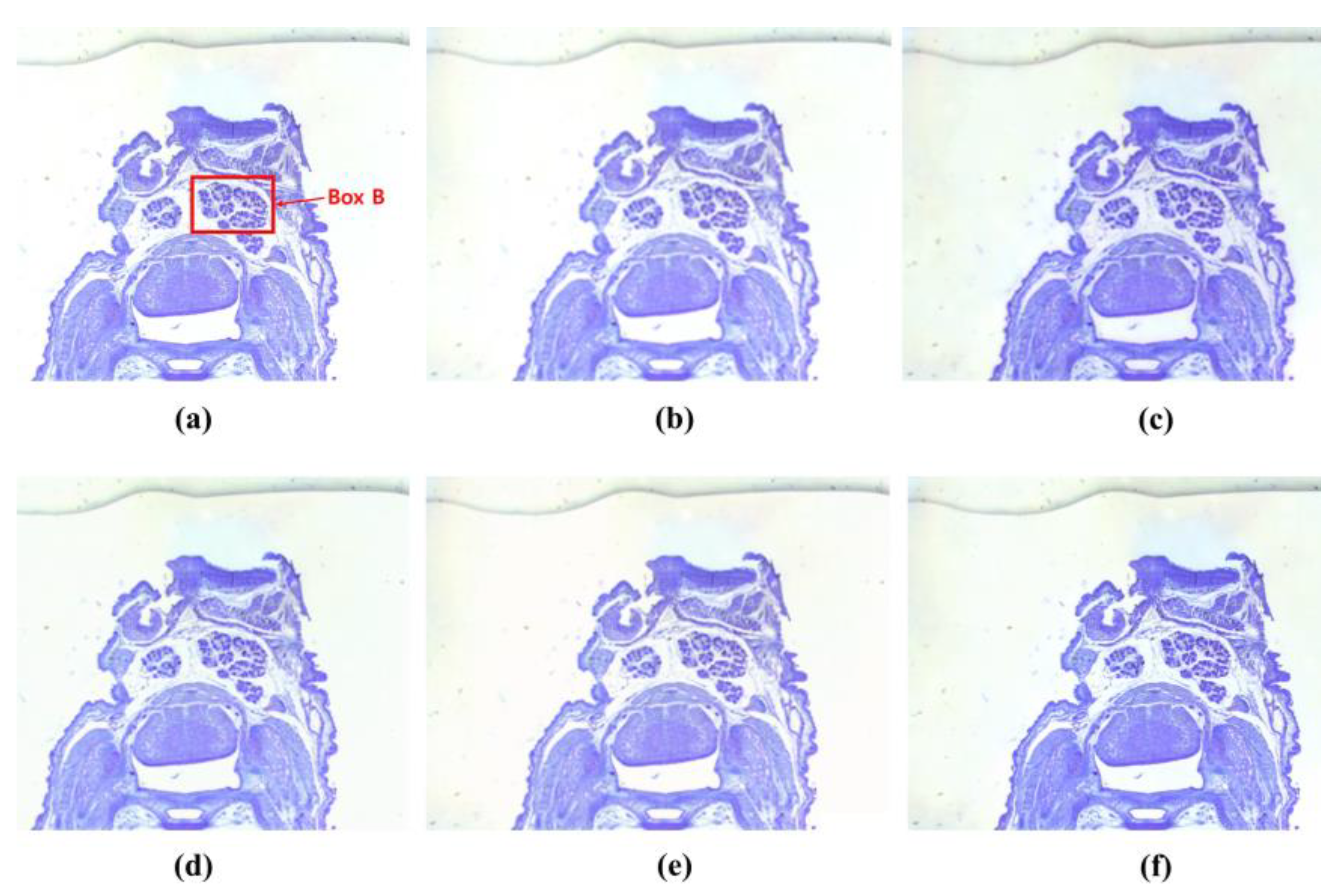
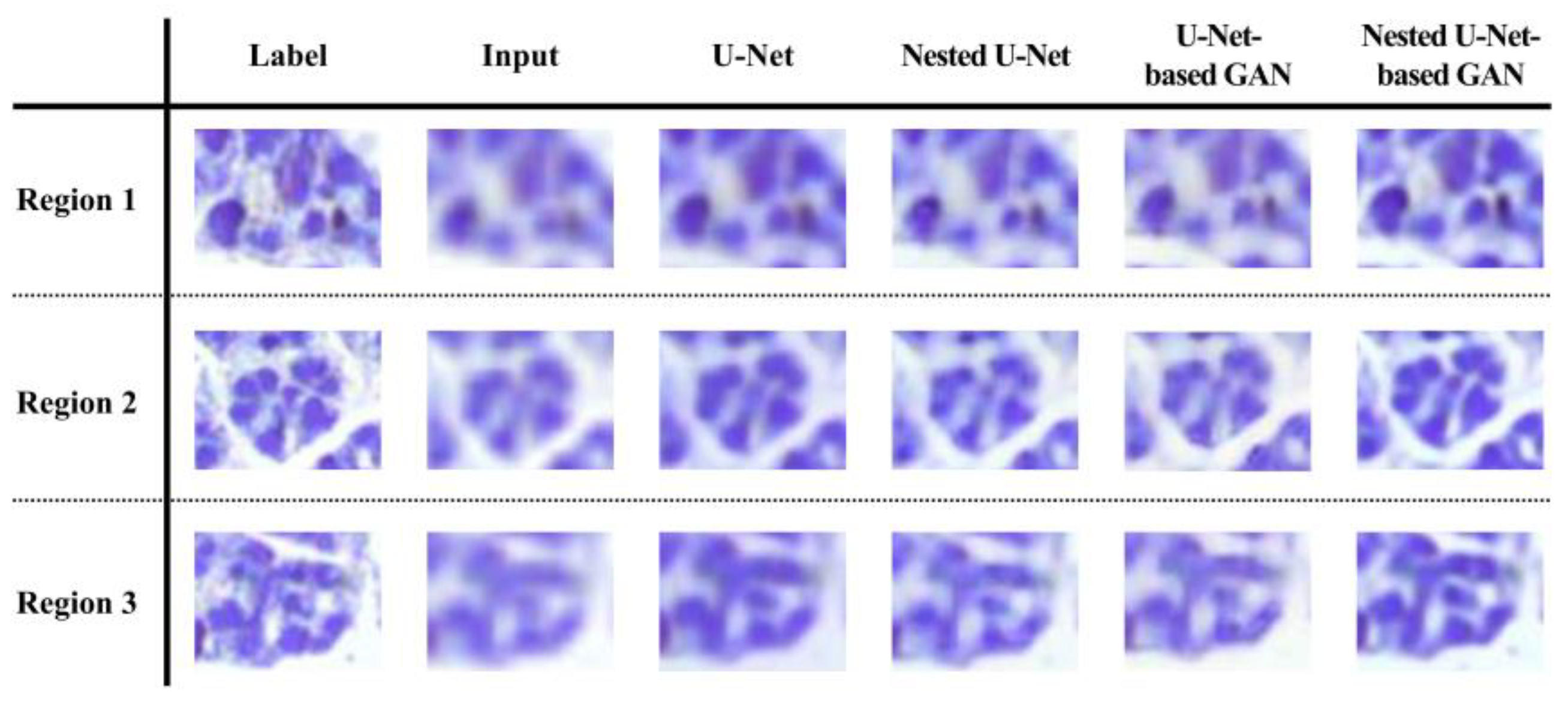
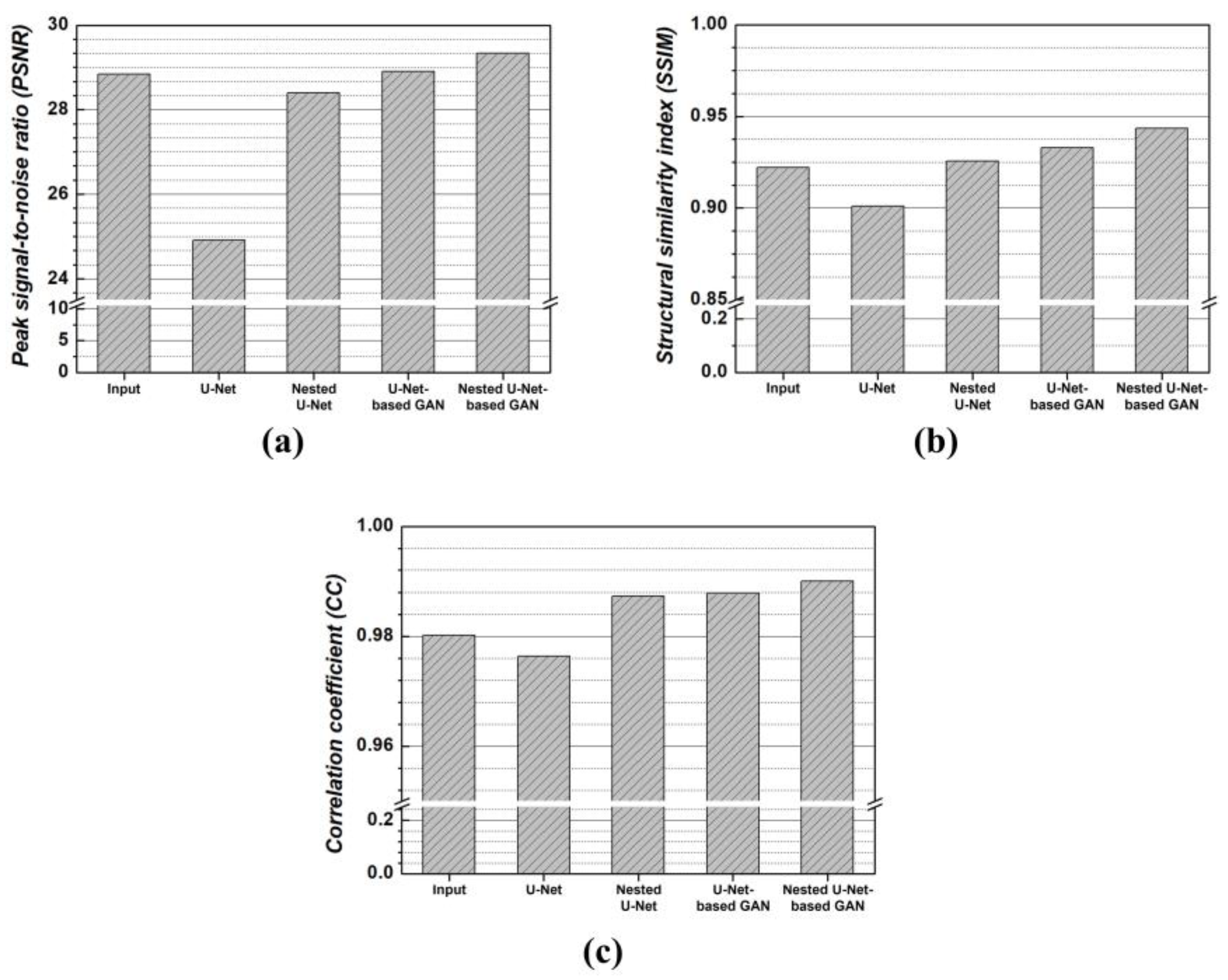
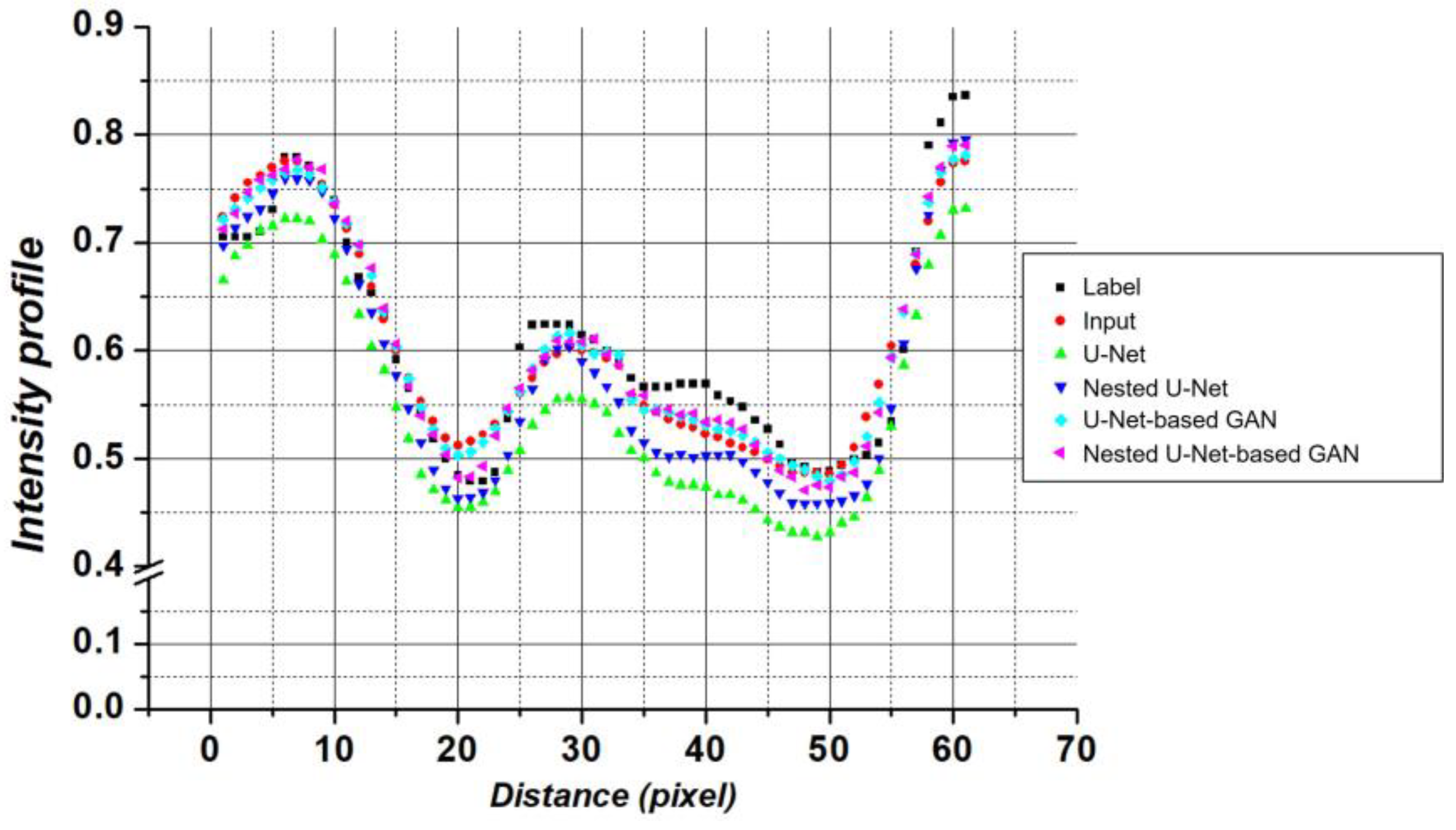
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friedrich, R.P.; Kappes, M.; Cicha, I.; Tietze, R.; Braun, C.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Nagy, R.; Alexiou, C.; Janko, C. Optical microscopy systems for the detection of unlabeled nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2022, 17, 2139–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitaev, V.G.; Tupitsyn, N.N.; Pronichev, A.N.; Dmitrieva, V.V.; Polyakov, E.V.; Liberis, K.A.; Grigorieva, M.S.; Paladina, A.D. Analysis of biological objects by digital optical microscopy using neural networks. Bull. Lebedev Phys. Inst. 2021, 48, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.H. Continuous optical zoom microscopy imaging system based on liquid lenses. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 20322–20335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimas, A.; Gallagher, B.R.; Wijesekara, P.; Fekir, S.; DiBernardo, E.F.; Cheng, Z.; Stolz, D.B.; Cambi, F.; Watkins, S.C.; Brody, S.L.; et al. Magnify is a universal molecular anchoring strategy for expansion microscopy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melanthota, S.K.; Gopal, D.; Chakrabarti, S.; Kashyap, A.A.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Mazumder, N. Deep learning-based image processing in optical microscopy. Biophys. Rev. 2022, 14, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liu, Y.T.; Khan, F.S.; Fox, M.C.; Reichenberg, J.S.; Lopes, F.C.P.S.; Sebastian, K.R.; Markey, M.K.; Tunnell, J.W. Single color digital H&E staining with In-and-Out Net. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2024, 118, 102468. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.Z.; Keskinarkaus, A.; Nyberg, P.; Seppänen, T. Stain normalization methods for histopathology image analysis: A comprehensive review and experimental comparison. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Hu, P.; Huang, Y.; He, L.; Hu, R.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, H.; Liu, C. Molecular mechanism of ethylparaben on zebrafish embryo cardiotoxicity based on transcriptome analyses. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fives, C.; Toulouse, A.; Kenny, L.; Brosnan, T.; McCarthy, J.; Fitzgerald, B. Cytology techniques can provide insight into human placental structure including syncytiotrophoblast nuclear spatial organisation. J. Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekoka Mbassi, F.-A.; Mombo-Ngoma, G.; Ndzebe Ndoumba, W.; Yovo, E.K.; Eberhardt, K.A.; Ekoka Mbassi, D.; Adegnika, A.A.; Agnandji, S.T.; Bouyou-Akotet, M.K.; Ramharter, M.; et al. Comparison of special stains (Giemsa stain and modified toluidine blue stain) with immunohistochemistry as gold standard for the detection of H. pylori in gastric biopsies. Arab J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 23, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Park, C.-H.; Kwon, H. Quality assessment of Wright-Giemsa staining in digital cell imaging. J. Lab. Med. Qual. Assur. 2023, 45, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.; Park, E.; Misra, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Baik, J.W.; Kim, K.G.; Jung, C.K.; Kim, C. Deep learning-based virtual staining, segmentation, and classification in label-free photoacoustic histology of human specimens. Light Sci. Appl. 2024, 13, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, M.G.L. Nonlinear structured-illumination microscopy: Wide-field fluorescence imaging with theoretically unlimited resolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13081–13086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, M.J.; Bates, M.; Zhuang, X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 793–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, D. Total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 2008, 89, 169–221. [Google Scholar]
- Balzarotti, F.; Eilers, Y.; Gwosch, K.C.; Gynnå, A.H.; Westphal, V.; Stefani, F.D.; Elf, J.; Hell, S.W. Nanometer resolution imaging and tracking of fluorescent molecules with minimal photon fluxes. Science 2017, 355, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dertinger, T.; Colyer, R.; Iyer, G.; Weiss, S.; Enderlein, J. Fast, background-free, 3D super-resolution optical fluctuation imaging (SOFI). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22287–22292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalapathy, M.; Belapurkar, V.; Jose, M.; Gautier, A.; Nair, D. Live cell super resolution imaging by radial fluctuations using fluorogen binding tags. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 3626–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtengel, G.; Galbraith, J.A.; Galbraith, C.G.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Gillette, J.M.; Manley, S.; Sougrat, R.; Waterman, C.M.; Kanchanawong, P.; Davidson, M.W.; et al. Interferometric fluorescent super-resolution microscopy resolves 3D cellular ultrastructure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3125–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, A.G.; Chandris, P.; Nogare, D.D.; Head, J.; Wawrzusin, P.; Fischer, R.S.; Chitnis, A.; Shroff, H. Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1122–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-C.; Legant, W.R.; Wang, K.; Shao, L.; Milkie, D.E.; Davidson, M.W.; Janetopoulos, C.; Wu, X.S.; Hammer, J.A., III; Liu, Z.; et al. Lattice light-sheet microscopy: Imaging molecules to embryos at high spatiotemporal resolution. Science 2014, 346, 1257998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hüpfel, M.; Kobitski, Y.; Zhang, W.; Nienhaus, G.U. Wavelet-based background and noise subtraction for fluorescence microscopy images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Huang, T.; Tang, P.; Di, J.; Zhong, L.; Zhang, W. Enhancing scanning electron microscopy imaging quality of weakly conductive samples through unsupervised learning. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhen, J.; Wu, Y.; Wu, R.; Luo, Z.; Liu, M.; Luo, J.; Xie, R.; Yan, L. Fast color Fourier ptychographic microscopic imaging technology with fusion color correction. Opt. Laser Eng. 2024, 181, 108385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, E.; Ferdman, B.; Weiss, L.E.; Naor, T.; Freedman, D.; Michaeli, T.; Shechtman, Y. Learning optimal wavefront shaping for multi-channel imaging. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 2179–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kong, L.; Peng, X.; Luo, Z.; Shi, J.; Tian, L. Multi-color channel gamma correction in fringe projection profilometry. Photonics 2025, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borah, B.J.; Sun, C.K. A radial distortion compensation method for artifact-free multi-adjacent-tile stitching/mosaicking in mesoscopic optical microscopy. Proc. SPIE 2022, 11965, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Archit, A.; Freckmann, L.; Nair, S.; Khalid, N.; Hilt, P.; Rajashekar, V.; Freitag, M.; Teuber, C.; Buckley, G.; von Haaren, S.; et al. Segment anything for microscopy. Nat. Methods 2025, 22, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Kuang, W.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Z.L. ResNet-based image inpainting method for enhancing the imaging speed of single molecule localization microscopy. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 31766–31784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Ma, T.; Evans, J.; He, S. Deep neural networks for image super-resolution in optical microscopy by using modified hybrid task cascade U-Net. Prog. Electromagn. Res. 2021, 171, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.H.; Müller, M.; Wang, T.-C.; Scheidig, P.M.; Schneider, A.; Schüttpelz, M.; Huser, T.; Schenck, W. Deep-learning based denoising and reconstruction of super-resolution structured illumination microscopy images. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, B168–B181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Siddiquee, M.M.R.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. UNet++: A nested U-Net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support: 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; Volume 11045, pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Creswell, A.; White, T.; Dumoulin, V.; Arulkumaran, K.; Sengupta, B.; Bharath, A.A. Generative adversarial networks: An overview. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2018, 35, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgadevi, M. Generative adversarial network (GAN): A general review on different variants of GAN and applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 6th International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 8–10 July 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Luo, T.; Li, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, H.; Chang, C.C. ARWGAN: Attention-guided robust image watermarking model based on GAN. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajitha, D.; Shanmugavalli, T.; Pillai, H.N. A deep learning approach for enhanced clarity: Transforming underwater imagery with U-Net GAN. Int. J. Adv. Res. Interdiscip. Sci. Endeav. 2025, 2, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivenson, Y.; Göröcs, Z.; Günaydin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Ozcan, A. Deep learning microscopy. Optica 2017, 4, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, E.; Weiss, L.E.; Michaeli, T.; Shechtman, Y. Deep-STORM: Super-resolution single-molecule microscopy by deep learning. Optica 2018, 5, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Rivenson, Y.; Jin, Y.; Wei, Z.; Gao, R.; Günaydın, H.; Bentolila, L.A.; Kural, C.; Ozcan, A. Deep learning enables cross-modality super-resolution in fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Jiang, T.; Dai, Q.; Li, D. Evaluation and development of deep neural networks for image super-resolution in optical microscopy. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y. CIEGAN: A deep learning tool for cell image enhancement. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 913372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Shen, Y.; Li, T.; Chung, C.H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; et al. Single-frame deep-learning super-resolution microscopy for intracellular dynamics imaging. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Zeng, Y.; Meng, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Jiang, T.; Wei, R.; Guo, J.; Fu, W.; Lu, H.; et al. Zero-shot learning enables instant denoising and super-resolution in optical fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Wu, Y.; Hobson, C.M.; Su, Y.; Qian, S.; Krueger, E.; Christensen, R.; Kroeschell, G.; Bui, J.; Chaw, M.; et al. Deep learning-based aberration compensation improves contrast and resolution in fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zou, Y.; Yang, Z. U-GAN: Generative adversarial networks with U-Net for retinal vessel segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th International Conference on Computer Science & Education (ICCSE), Coimbatore, India, 17–19 July 2019; pp. 642–646. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Li, J.; Shen, S.; Liu, K.; Wong, K.K.; He, T.; Wong, S.T. Image-to-image translation of label-free molecular vibrational images for a histopathological review using the UNet+/seg-cGAN model. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, Y.; Zhu, X.; Jin, X.; Dou, Q.; Zhou, W.; Duan, Q. Color-UNet++: A resolution for colorization of grayscale images using improved UNet++. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80, 35629–35648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Kong, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, G. CT synthesis from MR images using frequency attention conditional generative adversarial network. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 170, 107983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajjadi, M.S.M.; Schölkopf, B.; Hirsch, M. EnhanceNet: Single image super-resolution through automated texture synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4491–4500. [Google Scholar]
- Aadarsh, Y.G.; Singh, G. Comparing UNet, UNet++, FPN, PAN and Deeplabv3+ for gastrointestinal tract disease detection. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Evolutionary Algorithms and Soft Computing Techniques (EASCT), Bengaluru, India, 20–21 October 2023; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.-I.; Chang, Y.-J.; Liao, S.-C.; Nguyen, T.D.; Yang, J.; Kuo, Y.-A.; Hong, S.; Liu, Y.-L.; Rylander, H.G.; Santacruz, S.R.; et al. Generative adversarial network enables rapid and robust fluorescence lifetime image analysis in live cells. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivenson, Y.; Liu, T.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; De Haan, K.; Ozcan, A. PhaseStain: The digital staining of label-free quantitative phase microscopy images using deep learning. Light Sci. Appl. 2019, 8, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaban, M.T.; Baur, C.; Navab, N.; Albarqouni, S. StainGAN: Stain style transfer for digital histological images. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019), Venice, Italy, 8–11 April 2019; pp. 953–956. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, H.; Devalla, S.K.; Chuangsuwanich, T.; Tun, T.A.; Wang, X.; Aung, T.; Schmetterer, L.; Buist, M.L.; Boote, C.; Thiéry, A.H.; et al. OCT-GAN: Single step shadow and noise removal from optical coherence tomography images of the human optic nerve head. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 1482–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ying, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Jiang, X.; Shuai, J.; Li, X.; Zhong, J. UNet-Att: A self-supervised denoising and recovery model for two-photon microscopic image. Complex Intell. Syst. 2025, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Liu, C.; Forsyth, B.; Singer, Z.S.; Laine, A.F.; Danino, T.; Guo, J. Segmentation with residual attention U-Net and an edge-enhancement approach preserves cell shape features. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 2115–2118. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Wang, G.; Lou, J.; Jian, M.; Dong, J.; Chen, R.C.; Stevens, B.; Yu, H. Perceptual loss guided generative adversarial network for saliency detection. Inf. Sci. 2024, 654, 119625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, P.; Gaertner, M.; Jansche, A.; Bernthaler, T.; Schneider, G. Reducing artifact generation when using perceptual loss for image deblurring of microscopy data for microstructure analysis. Methods Microsc. 2025, 1, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.W.; Baek, N.R.; Koo, J.H.; Park, K.R. Modified perceptual cycle generative adversarial network-based image enhancement for improving accuracy of low light image segmentation. IEEE Access 2020, 9, 6296–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Li, J.; Lu, L.; Sun, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Shen, Q.; Wang, B.; Zhang, R.; et al. Smart computational light microscopes (SCLMs) of smart computational imaging laboratory (SCILab). PhotoniX 2021, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaznavi, A.; Rychtáriková, R.; Saberioon, M.; Štys, D. Cell segmentation from telecentric bright-field transmitted light microscopy images using a residual attention U-Net: A case study on HeLa line. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 147, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daksh, D.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Landfester, K.; Lieberwirth, I. Multi-resolution cross-modality image registration using unsupervised deep learning approach. Microsc. Microanal. 2023, 29, 1964–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Year | Input Type | Architecture | Generator Loss | Discriminator Loss | Notable Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rivvenson et al. [38] | 2017 | Multichannel | DCNN | L2 | Registration-based dataset, direct image-to-image mapping, self-feeding | |
| Nehme et al. [39] | 2018 | Single channel | FCN | L1 + L2 | Localization-free reconstruction, sparse regression optimization | |
| Wang et al. [40] | 2019 | Multichannel | U-Net + patchGAN | MSE, SSIM | BCE | Hybrid loss design, platform-adaptive, patch-based discriminator |
| Qiao et al. [41] | 2021 | Multichannel | cGAN + Fourier Channel Attention | MSE, SSIM, BCE | BCE | Spatial-frequency domain integration |
| Sun et al. [42] | 2022 | Multichannel | DCGAN | MSE, VGG19, Gram, TV | BCE | Multi-component loss for texture restoration |
| Chen et al. [43] | 2023 | Multichannel | U-Net + Residual-dense based patchGAN | L1, SSIM, VGG19 | BCE | Dual-stage (signal enhancement + SR), U-Net discriminator, frequency domain L1 |
| Qiao et al. [44] | 2024 | Multichannel | U-Net + 3D RCAN | MSE, Hessian Reg., Gap Amend. Reg. | Self-supervised with image re-corruption, dual-stage denoise + deconvolution | |
| Guo et al. [45] | 2025 | Multichannel | 3D RCAN | MSE | Multi-stage synthetic degradation for self-supervision, scalable multi-step restoration |
| Model | MSE | MAE | PCC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | 0.949 | ||
| U-Net | 0.963 | ||
| Nested U-Net | 0.979 | ||
| U-Net-based GAN | 0.966 | ||
| Nested U-Net-based GAN | 0.972 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, S.-H.; Kim, J.-Y. Nested U-Net-Based GAN Model for Super-Resolution of Stained Light Microscopy Images. Photonics 2025, 12, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070665
Kang S-H, Kim J-Y. Nested U-Net-Based GAN Model for Super-Resolution of Stained Light Microscopy Images. Photonics. 2025; 12(7):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070665
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Seong-Hyeon, and Ji-Youn Kim. 2025. "Nested U-Net-Based GAN Model for Super-Resolution of Stained Light Microscopy Images" Photonics 12, no. 7: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070665
APA StyleKang, S.-H., & Kim, J.-Y. (2025). Nested U-Net-Based GAN Model for Super-Resolution of Stained Light Microscopy Images. Photonics, 12(7), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070665





