Preparation and Performance Testing of EC-PEG/EC-MA for Asphalt Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. PCM Preparation Process
2.3. Asphalt and Aggregate Parameters
2.4. Testing and Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
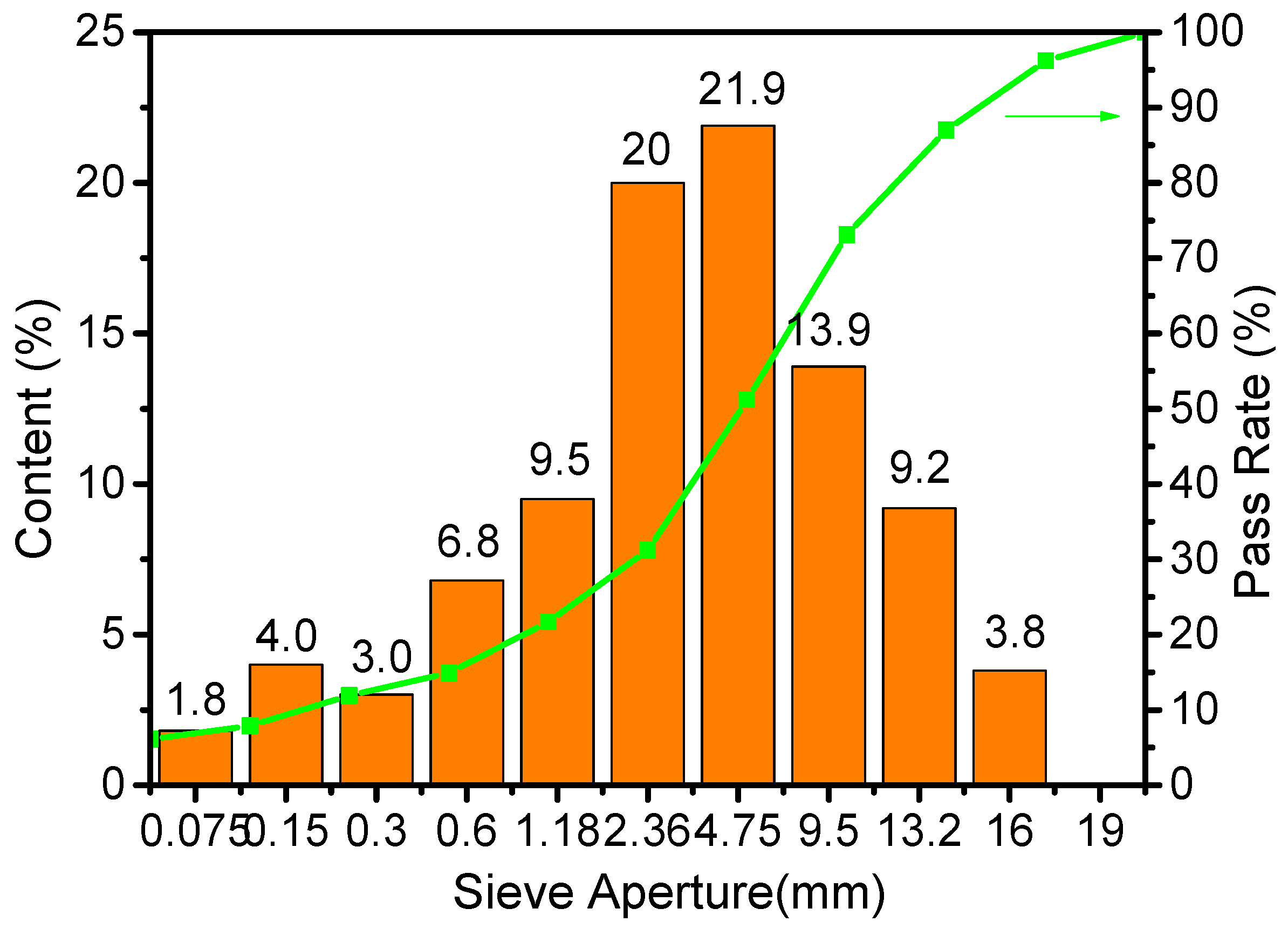
3.1. Particle Size Analysis
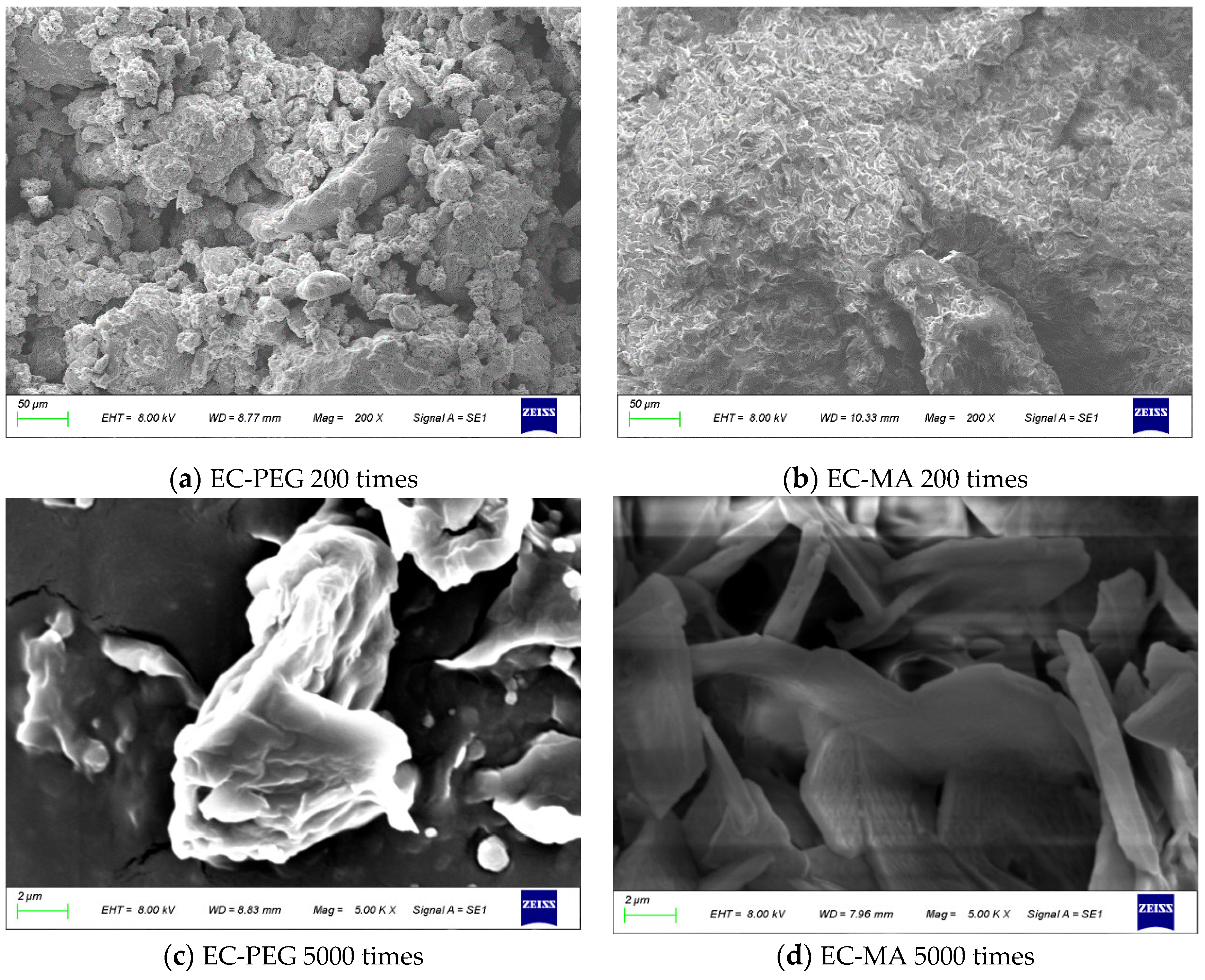
3.2. SEM Analysis
3.3. FTIR Analysis
3.4. Thermogravimetric–Differential Thermal Analysis
- (1)
- DSC analysis
- (2)
- TGA analysis
3.5. Mechanical Testing of Asphalt Mixtures
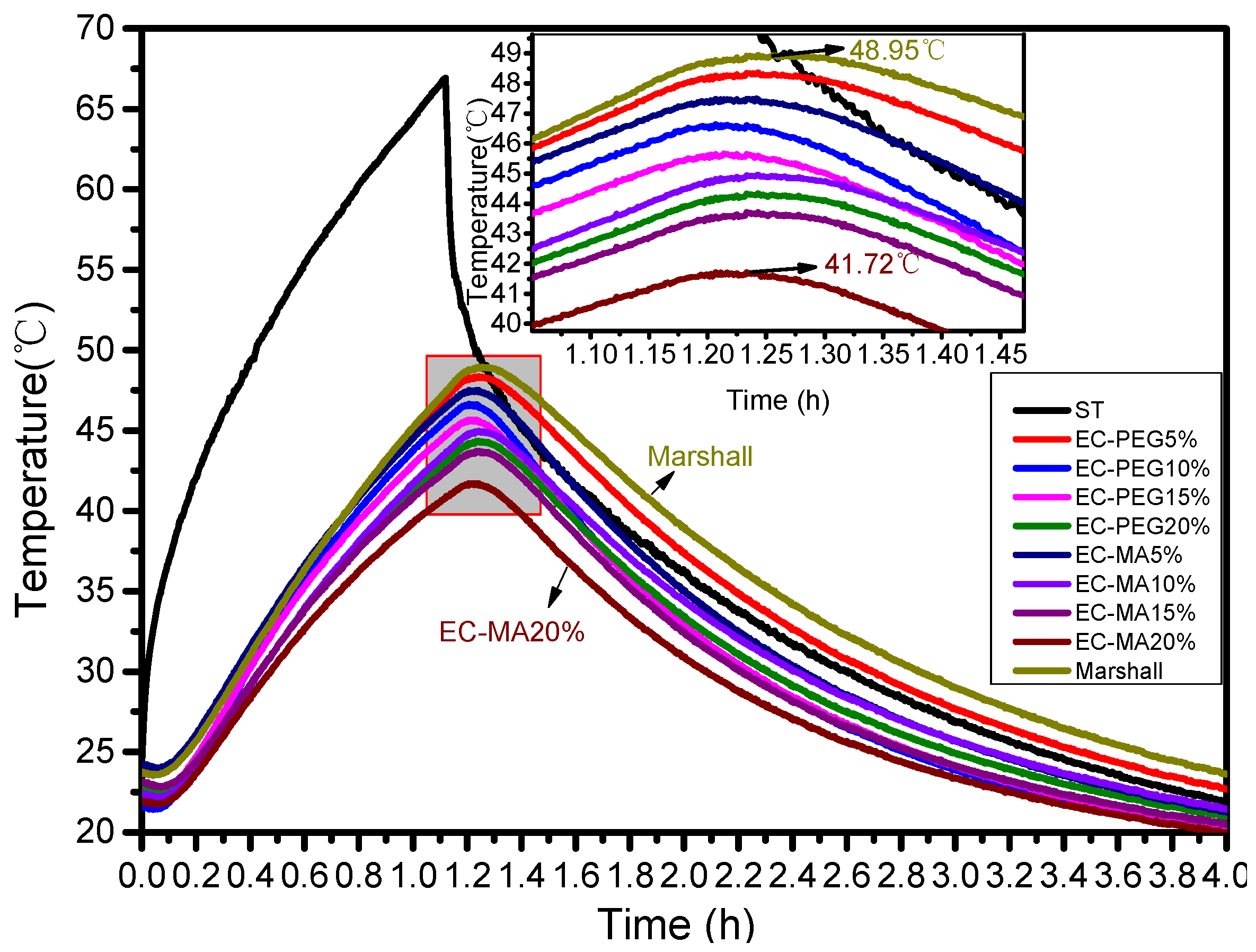
3.6. Temperature Adjustment Analysis of Asphalt Mixture
4. Conclusions
Limitations of Present Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | Ethyl cellulose |
| MA | Myristic acid |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol 2000 |
| EC-MA | Ethyl cellulose-myristic acid |
| EC-PEG | Ethyl cellulose-polyethylene glycol |
References
- Su, A.; Yin, H. Grey correlation analysis of asphalt-aggregate adhesion with high and low-temperature performance of asphalt mixtures. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Xiao, J.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, W. Damage characterization of high- and low-temperature performance of porous asphalt mixtures under multi-field coupling. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, T.; Sun, J.; Shan, Z.; He, D. Meso-structural characteristics of porous asphalt mixture based on temperature-stress coupling and its influence on aggregate damage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 128064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, L.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Effect of key design parameters on high temperature performance of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuhong, W.; Zhichao, W. Prediction model for rutting of asphalt concrete pavement considering temperature influence. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ruan, P.; Lu, Z.; Liang, L.; Han, B.; Hong, B. Effects of the high temperature and heavy load on the rutting resistance of cold-mix emulsified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Fu, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Dong, W.H.; Dai, J.S. Evaluation of High-Temperature Performance of Asphalt Mixtures Based on Climatic Conditions. Coatings 2020, 10, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Flintsch, G.W.; Dawson, A.R.; Parry, T. Examining effects of climatic factors on flexible pavement performance and service life. Transp. Res. Rec. 2013, 2349, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Zhou, X. Resilience assessment of asphalt pavement rutting under climate change. Transp. Res. Part D-Transp. Environ. 2022, 109, 103395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, B.; Cao, J.; Huang, W.; Ma, T.; Shi, Z. Rutting prediction model of asphalt pavement based on RIOHTrack full-scale ring road. Measurement 2025, 242, 115915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzarowski, L. The Development of Asphalt Mix Creep Parameters and Finite Element Modeling of Asphalt Rutting. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Waterloo, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, T. Developments and thermal properties of thermochromic microcapsule and thermochromic asphalt-based composite coatings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Gao, A.; Niu, Q.; Xie, S.; Xu, B.; Pan, B. Study on the Performance of Phase-Change Self-Regulating Permeable Asphalt Pavement. Buildings 2023, 13, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Ma, F.; Fu, Z.; Sangiorgi, C.; Tataranni, P.; Tarsi, G.; Li, C.; Hou, Y.; Guo, Y. Binary eutectic phase change materials application in cooling asphalt: An assessment for thermal stability and durability. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 700, 134790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, C.; Han, S.; Fan, L.; Huan, X.; Chen, H.; Kuang, D. Thermal storage kinetics of phase-change modified asphalt: The role of shell design and asphalt influence. Energy 2025, 322, 135660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, H.; Song, W.; Yin, J.; Zhan, Y.; Yu, J.; Abubakar Wada, S. Thermal fatigue and cracking behaviors of asphalt mixtures under different temperature variations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 369, 130623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Song, W.; Chen, X.; Wada, S.A.; Liao, H. Meso-mechanical characterization on thermal damage and low-temperature cracking of asphalt mixtures. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 316, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qu, H.; Huang, W.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, B. Evaluation of phase change thermoregulated asphalt on low temperature cracking performance of asphalt pavements. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, G.H.; Asadi, A.H.; Zarrinfam, J. Investigating the effect of fundamental properties of materials on the mechanisms of thermal cracking of asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wei, J.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, M.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, X. Preparation and Experimental Study of Phase Change Materials for Asphalt Pavement. Materials 2023, 16, 6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J. Numerical modelling of rutting performance of asphalt concrete pavement containing phase change material. Eng. Comput. 2023, 39, 1167–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Jimenez, D.; Montoya, M.; Haddock, J.; Youngblood, J.P.; Martinez, C.J. Regulating asphalt pavement temperature using microencapsulated phase change materials (PCMs). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupam, B.R.; Sahoo, U.C.; Rath, P.; Pattnaik, S. Thermal Behavior of Phase Change Materials in Concrete Pavements: A Long-term Thermal Impact Analysis of Two Organic Mixtures. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2024, 17, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, W.; Ying, H. Phase Change Heat-induced Structure of Asphalt Pavement for Reducing the Pavement Temperature. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 1655–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, M.A.; Betancourt, D.; Rahbar-Rastegar, R.; Youngblood, J.; Martinez, C.; Haddock, J.E. Environmentally Tuning Asphalt Pavements Using Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials. Transp. Res. Rec. 2022, 2676, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athukorallage, B.; Dissanayaka, T.; Senadheera, S.; James, D. Performance analysis of incorporating phase change materials in asphalt concrete pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Ma, B.; Ren, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y. Temperature responses of asphalt pavement structure constructed with phase change material by applying finite element method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 244, 118088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wang, S.; Deng, J.; Gao, Z.; Liu, Z. Study on the Cooling Effect of Asphalt Pavement Blended with Composite Phase Change Materials. Materials 2022, 15, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Sani, B.M.; Xu, P.; Liu, K.; Gu, F. Preparation and characterization of binary eutectic phase change material laden with thermal conductivity enhancer for cooling steel slag asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Sha, A.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.; Yuan, D. Adhesion, rheology and temperature-adjusting performance of polyurethane-based solid–solid phase change asphalt mastics subjected to laboratory aging. Mater. Struct. 2023, 56, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, N.; Hayati, P.; Latifi, H. Evaluation of Rutting and Fatigue Behavior of Modified Asphalt Binders with Nanocomposite Phase Change Materials. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2023, 16, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.; Kakar, M.R.; Refaa, Z.; Worlitschek, J.; Stamatiou, A.; Partl, M.N. Modification of asphalt mixtures for cold regions using microencapsulated phase change materials. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakar, M.R.; Refaa, Z.; Worlitschek, J.; Stamatiou, A.; Partl, M.N.; Bueno, M. Impregnation of Lightweight Aggregate Particles with Phase Change Material for Its Use in Asphalt Mixtures. In Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Asphalt Pavements & Environment (APE); Pasetto, M., Partl, M.N., Tebaldi, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 337–345. [Google Scholar]
- Kataware, A.V.; Shantharam, A. Review on Influence of Organic and Inorganic Phase Change Materials on Performance of Asphalt Binder and Asphalt Mix. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizwar, I.K.; Napiah, M.; Sutanto, M.H. Effect of Phase Change Material on Rheological Properties of Asphalt Mastic. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Civil, Offshore and Environmental Engineering (ICCOEE2020); Mohammed, B.S., Shafiq, N., Kutty, S.R.M., Mohamad, H., Balogun, A.-L., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 836–843. [Google Scholar]
- Engleng, B.; Kalita, E. Cellulose-Based Nanocomposites for Tissue Engineering. In Novel Bio-Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications; Sharma, K., Tiwari, S.K., Kumar, V., Kalia, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, X.-q.; Zhou, X.-y.; Wei, K.; Huang, W. Measurement and analysis of thermophysical parameters of the epoxy resin composites shape-stabilized phase change material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 223, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Ma, J.; Wang, D.L.; Peng, S.G. Preparation and Properties of Composite Shape-Stabilized Phase Change Material for Asphalt Mixture. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 71, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feczkó, T.; Kardos, A.F.; Németh, B.; Trif, L.; Gyenis, J. Microencapsulation of n-hexadecane phase change material by ethyl cellulose polymer. Polym. Bull. 2014, 71, 3289–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildy, M.; Hao, Q.; Wei, W.; Nguyen, D.H.; Xu, K.; Schossig, J.; Hu, X.; Salas-de la Cruz, D.; Hyun, D.C.; Wang, Z.; et al. Tunable chemotherapy release using biocompatible fatty acid-modified ethyl cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 9, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildy, M.; Wei, W.; Xu, K.; Schossig, J.; Hu, X.; Salas-de la Cruz, D.; Hyun, D.C.; Lu, P. Exploring temperature-responsive drug delivery with biocompatible fatty acids as phase change materials in ethyl cellulose nanofibers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266, 131187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, Z.; Iqbal, K. Encapsulation of Coconut Oil Using Ethyl Cellulose as Coating Shell for Thermoregulating Response of Cotton. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 14422–14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaib, S.S.A.; Niu, Z.; Qian, Z.; Qi, S.; Yuan, W. Self-luminous, shape-stabilized porous ethyl cellulose phase-change materials for thermal and light energy storage. Cellulose 2023, 30, 1841–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, A. Preparation, characterization, and thermal properties of microencapsulated palmitic acid with ethyl cellulose shell as phase change material impregnated wood. J. Energy Storage 2023, 66, 107382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhu, C.; Alva, G.; Fang, G. Microencapsulation and thermal properties of myristic acid with ethyl cellulose shell for thermal energy storage. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, A.V.; Alekseeva, O.V.; Guseinov, S.S. A Differential Scanning Calorimetry Study of Phase Transitions in Ethyl cellulose/Bentonite Polymer Composites. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2023, 59, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Ding, Y. Preparation and properties of composite phase change material based on solar heat storage system. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberkar, T.; Mahanwar, P. Microencapsulation study of bioderived phase change material beeswax with ethyl cellulose shell for thermal energy storage applications. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2023, 45, 11803–11818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phadungphatthanakoon, S.; Poompradub, S.; Wanichwecharungruang, S.P. Increasing the thermal storage capacity of a phase change material by encapsulation: Preparation and application in natural rubber. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 3691–3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, J.; Németh, B.; Gyenis, J. Formation of Microcapsulated Aluminium Potassium Sulfate Dodecahydrate by Phase Separation Method. Period. Polytech.-Chem. Eng. 2015, 59, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K. Silk Fibroin Nanofiber Design via Electrospinning for Temperature-Responsive and Ethanol-Sensitive Drug Delivery Systems. Master’s Thesis, Rowan University, Glassboro, NJ, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.L.; Xie, D.H.; Zhao, Z.M.; Wang, S.J.; Meng, F.B. Novel method for microencapsulation of eutectic hydrated salt as a phase change material for thermal energy storage. Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol. 2022, 17, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway ENGINEERING (JTG 3410-2025); China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2025.





| Name | Main Technical Indicators | Source Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| EC | Model: M70, viscosity 40.0–100.0 cPa·s (50 g/L 1:4 ethanol-benzene solution), loss on drying ≤ 2% | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| MA | Melting point 52–54 °C, boiling point 100 mmHg (250 °C), density 0.862 g/cm3 | Nanjing Dongde Chemical Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) |
| PEG | Molecular weight 1900–2200, crystallization point 43–48 °C | Wuxi Yatai United Chemical Co., Ltd. (Wuxi, China) |
| OP-10 | Active ingredient ≥ 98.0%, pH 6.0–8.0 | Tianjin Kemiou Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Tianjin, China) |
| Anhydrous ethanol | Content ≥ 99.5%, density 1.112–1.115 g/cm3 | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| Ethyl phthalate | Purity 99%, melting point 235 °C, density 0.965 g/mL | Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China) |
| No. | Samples | PCM Enthalpy (J/g) | Enthalpy of the Core Material (J/g) | Theoretical Core Content (%) | Theoretical Encapsulation Rate (%) | Actual Packaging Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EC-PEG | 57.05 | 188.10 | 30.33 | 45.29 | 36.33 |
| 2 | EC-MA | 89.15 | 199.63 | 44.66 | 66.39 | 58.93 |
| No. | Samples | 180 °C Loss on Ignition (%) | Mass0 (°C) | Mass5% (°C) | Mass10% (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EC | 0.07 | 165.35 | 304.59 | 324.43 |
| 2 | PEG | 0 | 331.61 | 384.04 | 391.58 |
| 3 | MA | 0 | 192.55 | 223.24 | 235.45 |
| 4 | EC-PEG | 0.26 | 169.05 | 252.45 | 329.30 |
| 5 | EC-MA | 0.07 | 178.67 | 221.54 | 236.33 |
| No. | Name | Stability (kN) | Flow Value (mm) | Marshall Modulus (kN/mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ordinary Asphalt Mixture | 13.55 | 3.51 | 3.86 |
| 2 | EC-PEG Content 5% | 17.48 | 4.20 | 4.16 |
| 3 | EC-PEG Content 10% | 15.04 | 3.76 | 4.00 |
| 4 | EC-PEG Content 15% | 15.15 | 2.05 | 7.39 |
| 5 | EC-PEG Content 20% | 13.23 | 4.41 | 3.00 |
| 6 | EC-PEG Content 25% | 13.08 | 3.23 | 4.05 |
| 7 | EC-PEG Content 30% | 11.79 | 4.02 | 2.93 |
| 8 | EC-MA Content 5% | 9.46 | 2.37 | 3.99 |
| 9 | EC-MA Content 10% | 12.25 | 3.14 | 3.90 |
| 10 | EC-MA Content 15% | 11.03 | 2.46 | 4.48 |
| 11 | EC-MA Content 20% | 14.55 | 2.73 | 5.33 |
| 12 | EC-MA Content 25% | 13.10 | 5.40 | 2.43 |
| 13 | EC-MA Content 30% | 10.08 | 4.37 | 2.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Wei, J.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, X. Preparation and Performance Testing of EC-PEG/EC-MA for Asphalt Mixtures. Processes 2025, 13, 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123916
Huang Z, Wei J, Fu Q, Zhou Y, Feng Z, Zhang X. Preparation and Performance Testing of EC-PEG/EC-MA for Asphalt Mixtures. Processes. 2025; 13(12):3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123916
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhuqiang, Jianguo Wei, Qilin Fu, Yuming Zhou, Zhitao Feng, and Xiangchao Zhang. 2025. "Preparation and Performance Testing of EC-PEG/EC-MA for Asphalt Mixtures" Processes 13, no. 12: 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123916
APA StyleHuang, Z., Wei, J., Fu, Q., Zhou, Y., Feng, Z., & Zhang, X. (2025). Preparation and Performance Testing of EC-PEG/EC-MA for Asphalt Mixtures. Processes, 13(12), 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr13123916







