Effects of Nicorandil on Inflammation, Apoptosis and Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Mouse Treatment
2.2. Atherosclerotic Plaque Staining
2.3. Endothelial Cell Culture
2.4. Static Adhesion Assay
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.6. mRNA Purification and Quantitative PCR
2.7. Protein Determination
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
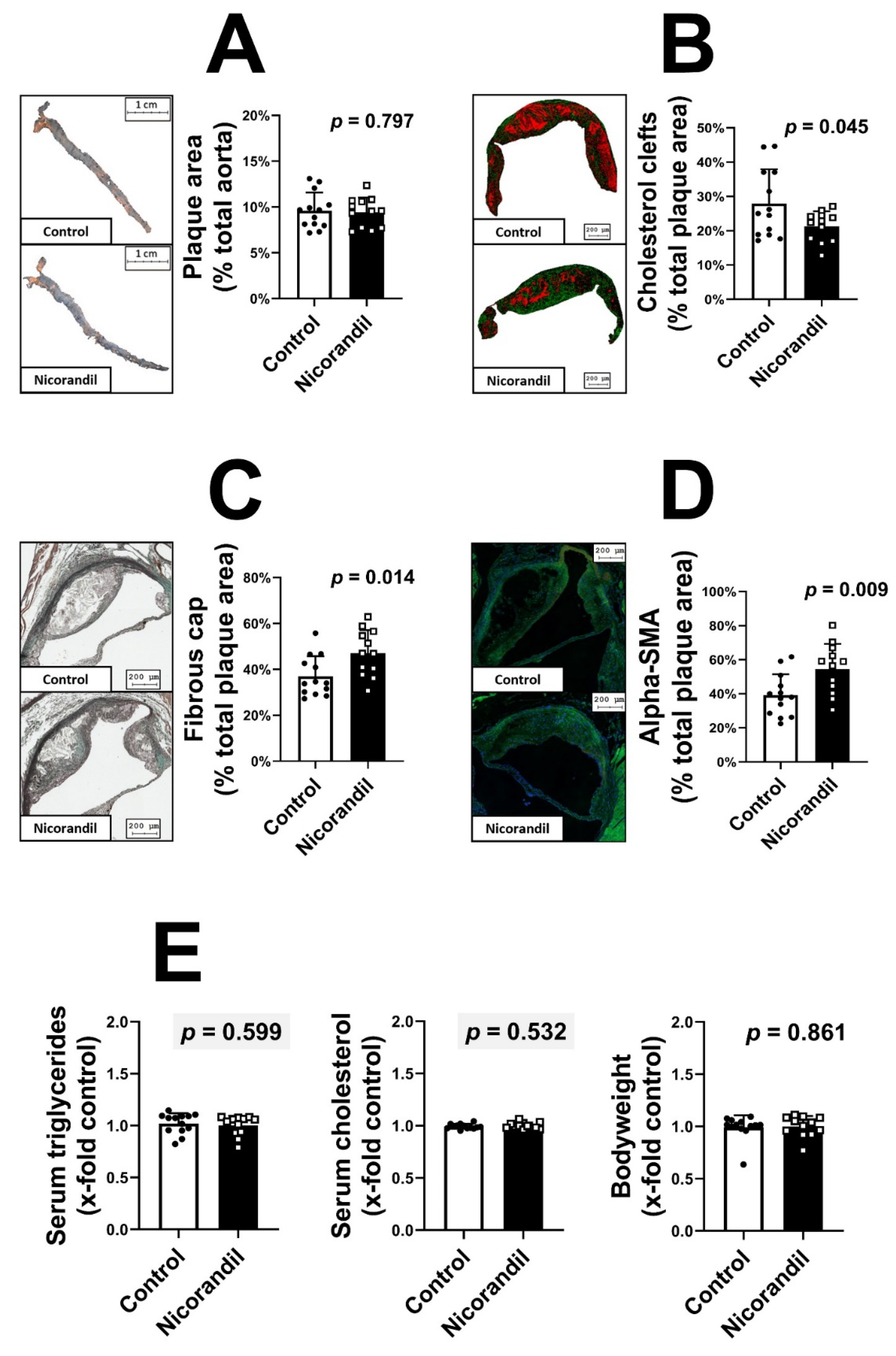
3.1. Effects of Nicorandil on Plaque Size and Stability in LDL-R -/- Knockout Mice
3.2. Effects of Nicorandil on Endothelial Adhesion Molecules
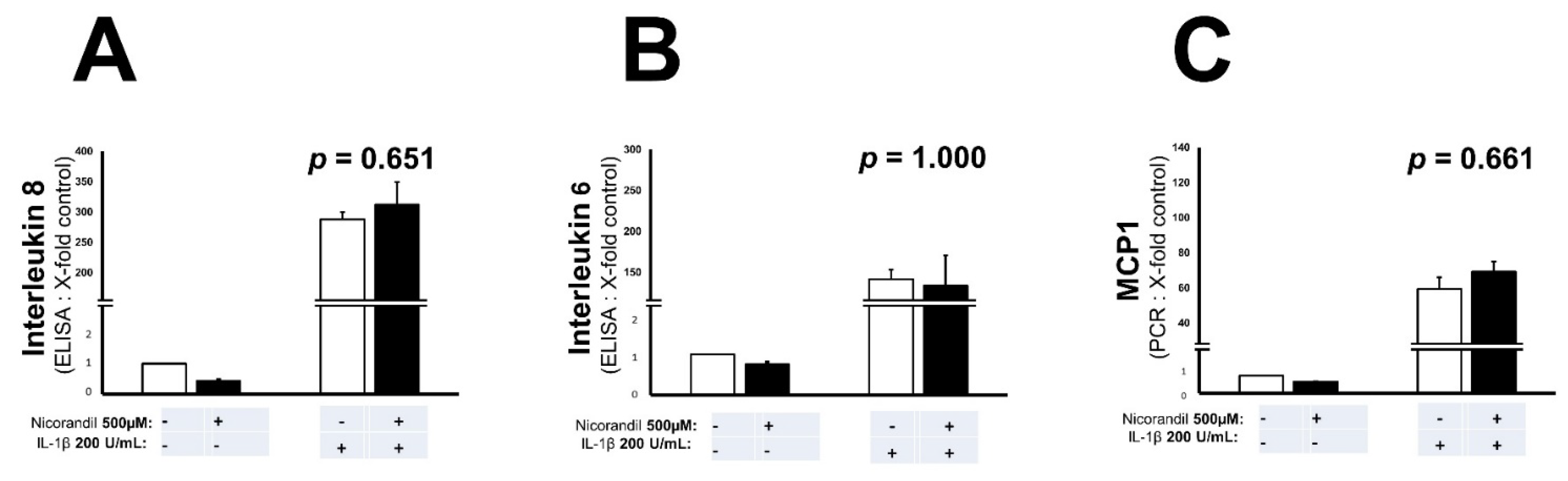
3.3. Effects of Nicorandil on Inflammation Associated Interleukins and MCP-1
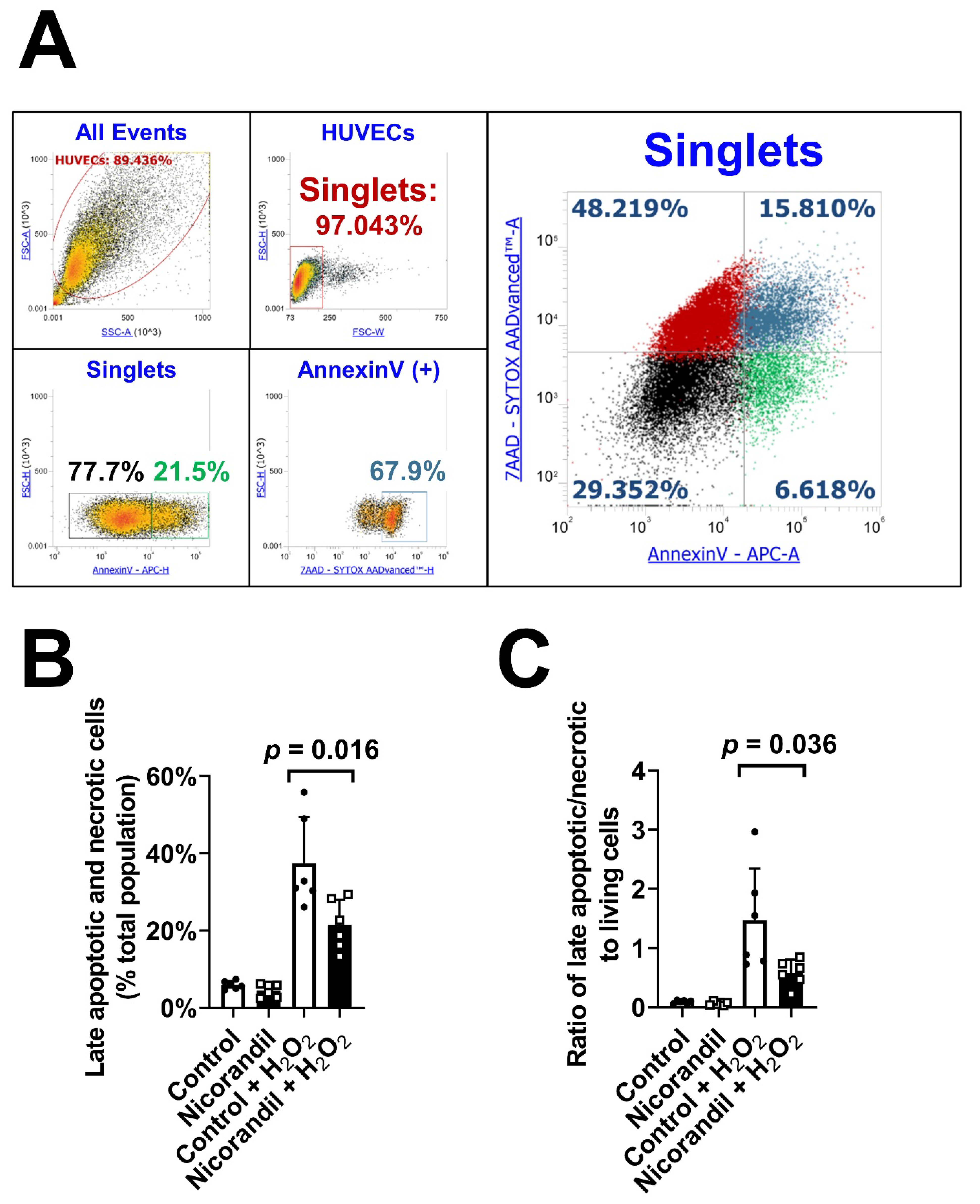
3.4. Effects of Nicorandil on Apoptosis In Vitro
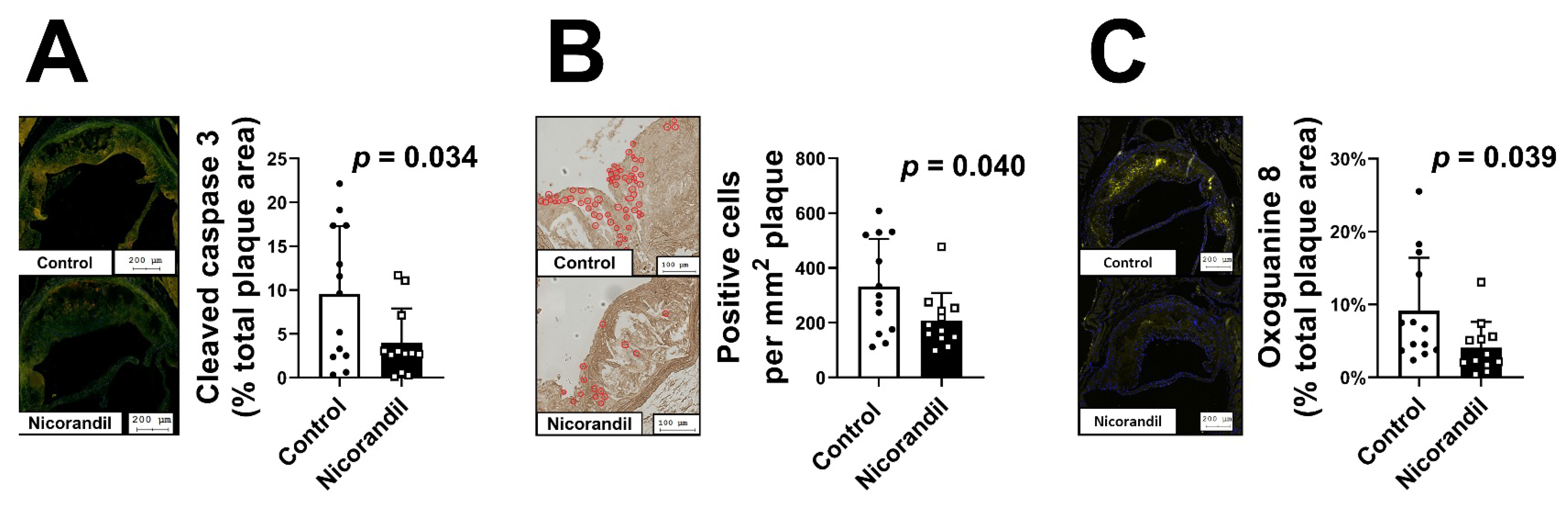
3.5. Effects of Nicorandil on Apoptosis In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Timmis, A.; Townsend, N.; Gale, C.P.; Torbica, A.; Lettino, M.; Petersen, S.E.; Mossialos, E.A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Kazakiewicz, D.; May, H.T.; et al. European Society of, European Society of Cardiology: Cardiovascular Disease Statistics 2019. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 12–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opie, L.H. Angina pectoris: The evolution of concepts. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 9 (Suppl. 1), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.K.; Mintz, G.S.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, S.W.; Song, J.M.; Han, K.H.; Kang, D.H.; Song, J.K.; Kim, J.J.; et al. Comparison of coronary plaque rupture between stable angina and acute myocardial infarction: A three-vessel intravascular ultrasound study in 235 patients. Circulation 2004, 110, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuuti, J.; Wijns, W.; Saraste, A.; Capodanno, D.; Barbato, E.; Funck-Brentano, C.; Prescott, E.; Storey, R.F.; Deaton, C.; Cuisset, T.; et al. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of chronic coronary syndromes. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 407–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukovetz, W.R.; Holzmann, S.; Poch, G. Molecular mechanism of action of nicorandil. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1992, 20 (Suppl. 3), S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IONA Study Group. Effect of nicorandil on coronary events in patients with stable angina: The Impact Of Nicorandil in Angina (IONA) randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumiya, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kojima, S.; Araki, S.; Usuku, H.; Matsubara, J.; Sakamoto, K.; Tsujita, K.; Nagayoshi, Y.; Kaikita, K.; et al. Long-term use of oral nicorandil stabilizes coronary plaque in patients with stable angina pectoris. Atherosclerosis 2011, 214, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Lv, X.; Sun, Y.; Ye, Z.; Kong, B.; Qin, Z. Role of TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in coronary microembolization-induced myocardial injury prevented and treated with nicorandil. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.S.; Jo, J.H.; Kim, B.S.; Jun, G.J.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, M.B.; Oh, C.K.; Kwon, K.S. A case of severe tongue ulceration and laryngeal inflammation induced by low-dose nicorandil therapy. Br. J. Dermatol. 2004, 151, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Allen, P.B.; Caddy, G.R.; Mainie, I. Nicorandil associated colonic ulceration: Case series of an increasingly recognized complication. Digest. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 2404–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, D.; Aboumarzouk, O.; Bates, C. Nicorandil-induced penile ulceration: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Hong, H.J.; Hao, W.R.; Cheng, T.H.; Liu, J.C.; Sung, L.C. Nicorandil prevents doxorubicin-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Inada, K.; Matsuo, S.; Miyanaga, S.; Yamane, T.; Abe, Y.; Sugimoto, K.; Mochizuki, S. Nicorandil inhibits serum starvation-induced apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2005, 46, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Su, Q.; Liang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, L. The protective effect of nicorandil on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after coronary microembolization by activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zuo, X.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Xie, L.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Xie, W. Nicorandil inhibits hypoxia-induced apoptosis in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells through activation of mitoKATP and regulation of eNOS and the NF-kappaB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teshima, Y.; Akao, M.; Baumgartner, W.A.; Marban, E. Nicorandil prevents oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in neurons by activating mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Brain Res. 2003, 990, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease. Am. Heart J. 1999, 138, S419–S420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, Z.; Tedgui, A. Apoptosis in the vasculature: Mechanisms and functional importance. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 130, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.C.; Figg, N.; Maguire, J.J.; Davenport, A.P.; Goddard, M.; Littlewood, T.D.; Bennett, M.R. Apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells induces features of plaque vulnerability in atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I. Consequences and therapeutic implications of macrophage apoptosis in atherosclerosis: The importance of lesion stage and phagocytic efficiency. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venegas-Pino, D.E.; Banko, N.; Khan, M.I.; Shi, Y.; Werstuck, G.H. Quantitative analysis and characterization of atherosclerotic lesions in the murine aortic sinus. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohensinner, P.J.; Takacs, N.; Kaun, C.; Thaler, B.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Pfaffenberger, S.; Aliabadi, A.; Zuckermann, A.; Huber, K.; Wojta, J. Urokinase plasminogen activator protects cardiac myocytes from oxidative damage and apoptosis via hOGG1 induction. Apop. Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2017, 22, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krychtiuk, K.A.; Watzke, L.; Kaun, C.; Buchberger, E.; Hofer-Warbinek, R.; Demyanets, S.; Pisoni, J.; Kastl, S.P.; Rauscher, S.; Groger, M.; et al. Levosimendan exerts anti-inflammatory effects on cardiac myocytes and endothelial cells in vitro. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 113, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.V. Nicorandil-induced colonic ulceration. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samra, K.; Manikam, L.; Pathmakanthan, S. When treatment can be worse than the disease: Nicorandil-induced colitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titi, M.A.; Seow, C.; Molloy, R.G. Nicorandil-induced colonic ulceration: A new cause of colonic ulceration. Rep. Four Cases Dis. Colon Rectum 2008, 51, 1570–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kashef, D.H. Nicorandil ameliorates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of silicosis. Int. Immun. 2018, 64, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Wang, X.; Hu, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; An, G.; Su, G. Intracoronary application of nicorandil regulates the inflammatory response induced by percutaneous coronary intervention. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 4863–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.P.; Dong, Y.F.; Liu, W.; Gu, J.; Sun, X.L. Nicorandil inhibits inflammasome activation and Toll-like receptor-4 signal transduction to protect against oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced inflammation in BV-2 cells. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Obata, K.; Odashima, M.; Yamada, A.; Somura, F.; Nishizawa, T.; Ichihara, S.; Izawa, H.; Iwase, M.; Hayakawa, A.; et al. Nicorandil inhibits oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cardiac myocytes through activation of mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channels and a nitrate-like effect. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2003, 35, 1505–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Tatsumi, T.; Shiraishi, J.; Matsunaga, S.; Takeda, M.; Mano, A.; Kobara, M.; Keira, N.; Okigaki, M.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Nicorandil regulates Bcl-2 family proteins and protects cardiac myocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 40, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Ke, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, D.; Ji, F. Protective effect of nicorandil on collapseinduced lung injury in rabbits by inhibiting apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Fan, C.; Zhang, W.; Wen, Z.; Hu, L.; Yang, L.; Feng, Y.; Yin, K.J.; Mo, X. Neuroprotective effect of nicorandil through inhibition of apoptosis by the PI3K/Akt1 pathway in a mouse model of deep hypothermic low flow. J. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 357, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahara, M.; Sata, M.; Morita, T.; Hirata, Y.; Nagai, R. Nicorandil attenuates monocrotaline-induced vascular endothelial damage and pulmonary arterial hypertension. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, J.; Lv, B.; Yu, B. Nicorandil protects mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizawa, K.; Takahari, Y.; Higashijima, N.; Serizawa, K.; Yogo, K.; Ishizuka, N.; Endo, K.; Fukuyama, N.; Hirano, K.; Ishida, H. Nicorandil prevents sirolimus-induced production of reactive oxygen species, endothelial dysfunction, and thrombus formation. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 127, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lenz, M.; Kaun, C.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Haider, P.; Brekalo, M.; Maier, N.; Goederle, L.; Binder, C.J.; Huber, K.; Hengstenberg, C.; et al. Effects of Nicorandil on Inflammation, Apoptosis and Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020120
Lenz M, Kaun C, Krychtiuk KA, Haider P, Brekalo M, Maier N, Goederle L, Binder CJ, Huber K, Hengstenberg C, et al. Effects of Nicorandil on Inflammation, Apoptosis and Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(2):120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020120
Chicago/Turabian StyleLenz, Max, Christoph Kaun, Konstantin A. Krychtiuk, Patrick Haider, Mira Brekalo, Nadine Maier, Laura Goederle, Christoph J. Binder, Kurt Huber, Christian Hengstenberg, and et al. 2021. "Effects of Nicorandil on Inflammation, Apoptosis and Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression" Biomedicines 9, no. 2: 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020120
APA StyleLenz, M., Kaun, C., Krychtiuk, K. A., Haider, P., Brekalo, M., Maier, N., Goederle, L., Binder, C. J., Huber, K., Hengstenberg, C., Wojta, J., Hohensinner, P. J., & Speidl, W. S. (2021). Effects of Nicorandil on Inflammation, Apoptosis and Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression. Biomedicines, 9(2), 120. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020120





