Quantum Private Array Content Comparison Based on Multi-Qubit Swap Test
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We introduce a QPACC scheme capable of securely determining the equality of two arrays, moving beyond the limitation of single-integer comparisons that characterizes existing schemes.
- (2)
- The scheme is constructed using near-term feasible quantum technologies, including single-qubit states as quantum resources, rotation operations for encoding, quantum homomorphic encryption (QHE) for encrypting the encoded quantum states, and the multi-qubit swap test for comparison, avoiding the need for complex operations like entanglement swapping or high-dimensional quantum state preparation.
- (3)
- The protocol incorporates decoy photons for eavesdropping detection and rotation operations to obscure the encoded data, thereby providing robustness against external attacks and the curiosity of internal participants.
- (4)
- We construct a quantum circuit for a concrete case of the proposed scheme and perform simulations on the IBM Qiskit, providing empirical validation of its feasibility and correctness.
2. Preliminaries
2.1. Rotation Operation
2.2. Quantum Homomorphic Encryption (QHE)
- Key Generation (KeyGen): Randomly select two classical bits to form the secret key.
- Encryption (Enc): Compute the quantum ciphertext by applying single-qubit operators to the quantum plaintext based on the secret key: . This encryption method is proven theoretically secure in Ref. [46].
- Decryption (Dec): Recover the quantum plaintext by applying again single-qubit operators to the quantum ciphertext based on the secret key: .
- Evaluation (Eval): To apply a permitted operation homomorphically to the quantum ciphertext , the evaluator performs a transformed rotation , where the angle is adjusted based on the secret key: . This transformation satisfies the homomorphic property: . Consequently, the evaluation on the ciphertext is equivalent to performing the desired operation on the plaintext, followed by encryption. The output state is given by: . Crucially, this evaluation is performed directly on the ciphertext without any decryption.
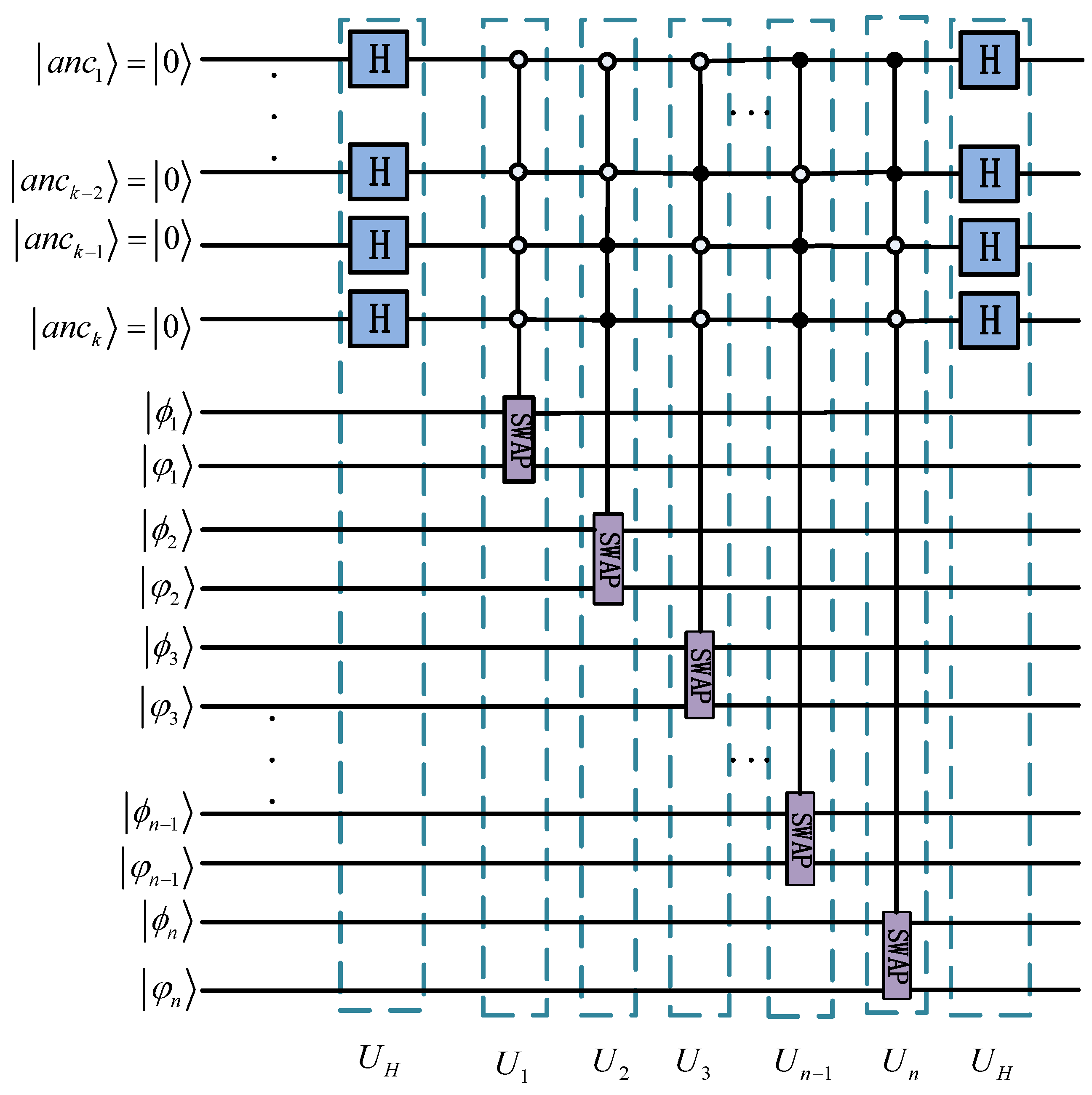
2.3. Multi-Qubit Swap Test
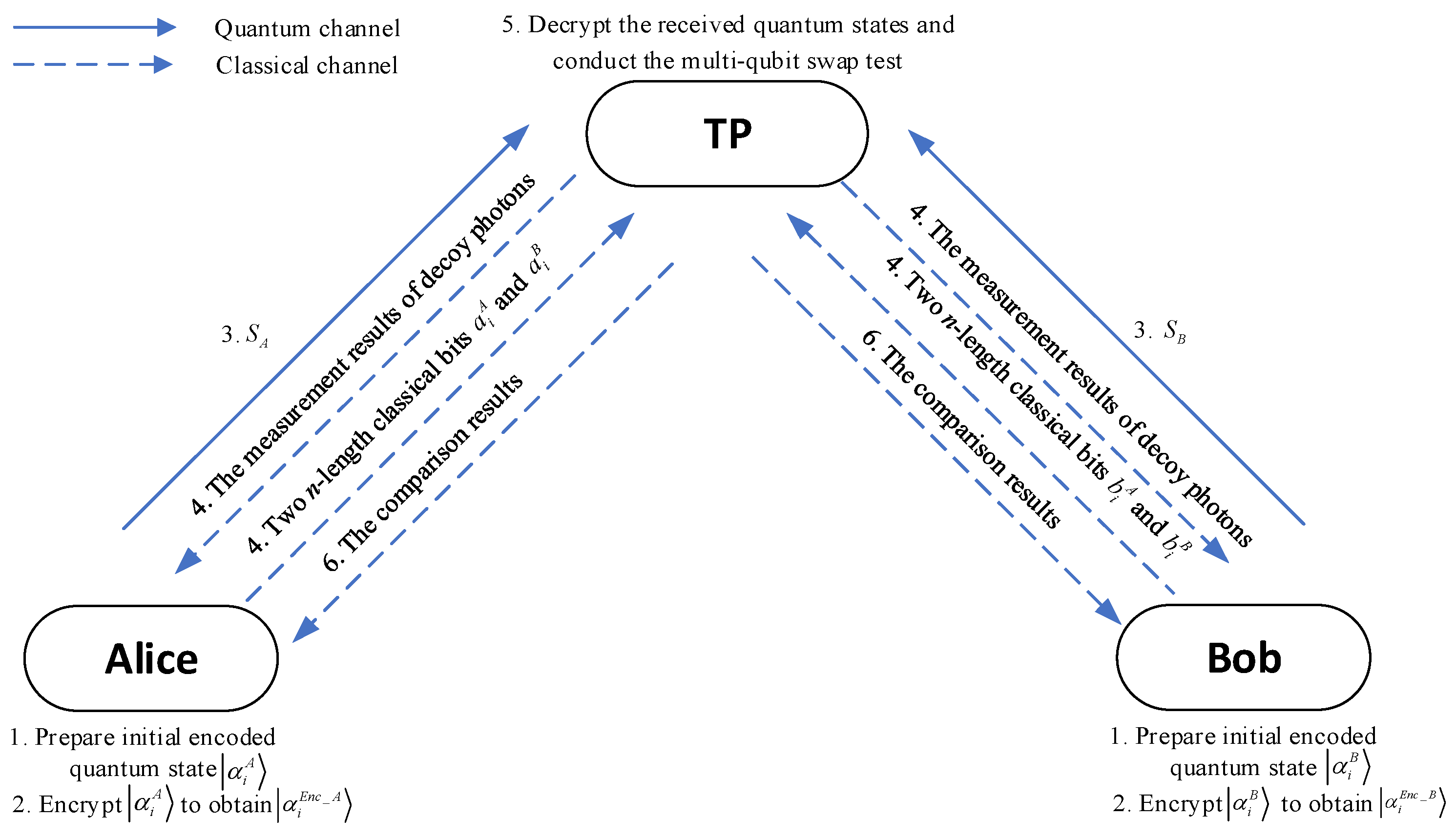
3. The Proposed QPACC Scheme
- Correctness: If all participants adhere to the protocol, TP will always output the correct comparison result.
- Security: The proposed scheme protects the secrecy of the input arrays X and Y from two primary threat models: external attacks on the quantum channel and internal curiosity from all other parties, even the TP.
- Fairness: Both Alice and Bob receive the final result simultaneously, preventing either from gaining an advantage.
- All quantum channels are assumed to be lossless and noiseless. In a practical implementation, the effects of noise and loss can be mitigated through quantum error-correcting codes [48].
- All classical channels are authenticated to ensure integrity and prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Prior to the protocol’s execution, Alice and Bob have securely established a shared secret key, , using an unconditionally secure QKD protocol (e.g., the BB84 protocol [2]).
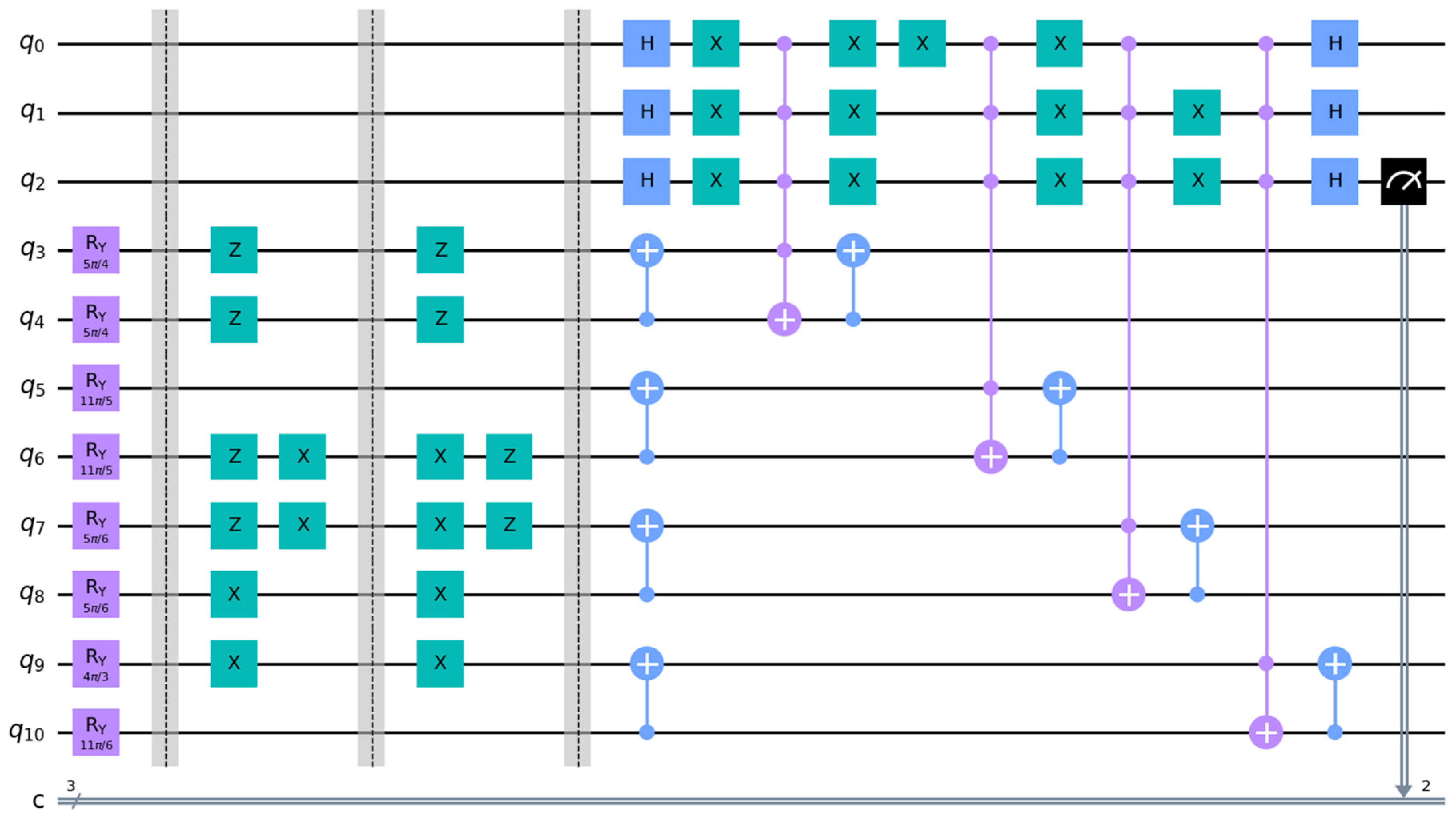
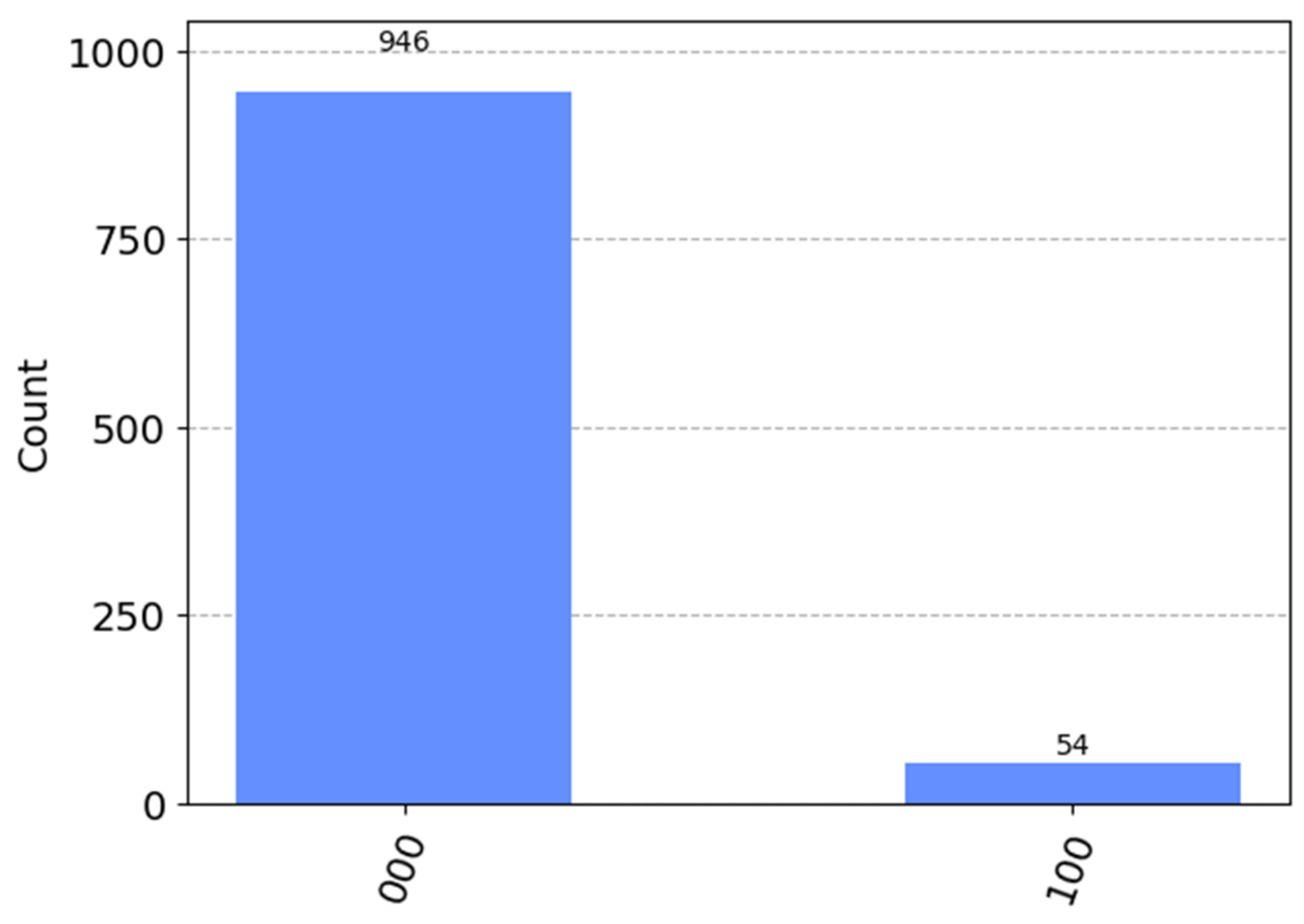
4. Simulation Experiment
5. Analysis
5.1. Correctness
5.2. Security Analysis
5.2.1. External Attacks
5.2.2. Participant Attacks
5.3. Fairness
6. Discussion
- (1)
- It extends comparison capability from single integer to full array, improving functional scalability for practical applications.
- (2)
- In contrast to protocols that rely on complex multi-qubit or high-dimensional states, our scheme utilizes only single-photon states, single-qubit rotations, and the multi-qubit swap test. All of these components are compatible with current quantum technology, which significantly enhances its experimental feasibility.
- (3)
- The substitution of Bell-basis measurements with single-particle measurements streamlines the measurement process, thereby lowering the experimental overhead.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, S.; Guo, H. Continuous-variable quantum key distribution system: Past, present, and future. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2024, 11, 011318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; van Leent, T.; Redeker, K.; Garthoff, R.; Schwonnek, R.; Fertig, F.; Eppelt, S.; Rosenfeld, W.; Scarani, V.; Lim, C.C.; et al. A device-independent quantum key distribution system for distant users. Nature 2022, 607, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Tan, H.; Lu, Y.; Liao, S.K.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Mao, H.K.; Yan, B.; et al. High-rate quantum key distribution exceeding 110 Mb s–1. Nat. Photonics 2023, 17, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadlinger, D.P.; Drmota, P.; Nichol, B.C.; Araneda, G.; Main, D.; Srinivas, R.; Lucas, D.M.; Ballance, C.J.; Ivanov, K.; Tan, E.Z.; et al. Experimental quantum key distribution certified by Bell’s theorem. Nature 2022, 607, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Cao, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, W.B.; Weng, C.X.; Yin, H.L.; Chen, Z.B. Experimental quantum secret sharing based on phase encoding of coherent states. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2023, 66, 260311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhong, W.; Du, M.M.; Shen, S.T.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, A.L.; Zhou, L.; Sheng, Y.B. Device-independent quantum secret sharing with noise preprocessing and postselection. Phys. Rev. A 2024, 110, 042403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Cheng, J.; Ma, J.; Zhao, D.; Yan, Z.; Jia, X.; Xie, C.; Peng, K. Efficient and secure quantum secret sharing for eight users. Phys. Rev. Res. 2024, 6, 033036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Long, Y.; Li, Q. Quantum summation using d-level entanglement swapping. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, M. Measurement-device-independent quantum secure multiparty summation. Quantum Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. Quantum Private Set Intersection Scheme Based on Bell States. Axioms 2025, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S. Quantum multi-party private set intersection using single photons. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2024, 649, 129974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.D.; Zheng, L.Q.; Yu, K.; Lin, S. Authenticated Multi-Party Quantum Private Set Intersection with Single Particles. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, Y. Secure multiparty computation. Commun. ACM 2020, 64, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.C. Protocols for secure computations. In Proceedings of 23rd IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS’ 82), Chicago, IL, USA, 3–5 November 1982; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Boudot, F.; Schoenmakers, B.; Traore, J. A fair and efficient solution to the socialist millionaires’ problem. Discret. Appl. Math. 2001, 111, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, P.W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, L.K. Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Wen, Q.Y. An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2009, 42, 055305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wu, Y. Single-photon-based quantum secure protocol for the socialist millionaires’ problem. Front. Phys. 2024, 12, 1364140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, T.Y.; Che, B.C.; Dou, Z.; Chen, X.B.; Lai, Y.P.; Li, J. Efficient quantum private comparison protocol utilizing single photons and rotational encryption. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 060307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xiao, D.; Huang, W.; Jia, H.Y.; Song, T.T. Quantum private comparison employing single-photon interference. Quantum Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q. Quantum private comparison with six-particle maximally entangled states. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 37, 2250149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.X.; Zhang, H.G.; Fan, P.R. Two-party quantum private comparison protocol with maximally entangled seven-qubit state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2019, 34, 1950229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Rahman, A.U.; Ji, Z.; Ji, X.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, H. Two-party quantum private comparison based on eight-qubit entangled state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 37, 2250026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Quantum private comparison protocols with a number of multi-particle entangled states. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44613–44621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.Y.; Ji, Z.X. Two-party quantum private comparison with five-qubit entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2017, 56, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.B.; Chang, Y.; Hou, M.; Cheng, W. Efficient quantum private comparison based on entanglement swapping of bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2021, 60, 3783–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianni, J.; Qu, Z. New quantum private comparison using hyperentangled ghz state. J. Quantum Comput. 2021, 3, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Efficient quantum private comparison protocol based on the entanglement swapping between four-qubit cluster state and extended Bell state. Quantum Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wu, Y. Quantum Private Comparison Protocol with Cluster States. Axioms 2025, 14, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.F.; Yao, Z.Q. Quantum private comparison protocol with d-dimensional Bell states. Quantum Inf Process 2013, 12, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.Z.; Gao, F.; Qin, S.J.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Q.Y. Quantum private comparison protocol based on entanglement swapping of d-level Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2013, 12, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.Y.; Hu, J.L. Multi-party quantum private comparison based on entanglement swapping of Bell entangled states within d-level quantum system. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2021, 60, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.Q.; Zhao, Y.X. Quantum private comparison of size using d-level Bell states with a semi-honest third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.F. Quantum private magnitude comparison. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2022, 61, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Hou, M.; Zhang, S.B. Quantum private comparison of arbitrary single qubit states based on swap test. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 040303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.B.; Ye, C.Q.; Li, C.Y.; Hou, Y.Y. An efficient semi-quantum private comparison without pre-shared keys. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.Z. Semi-quantum private comparison based on Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.H.; Li, M.L.; Cao, H.; Wang, B. Novel semi-quantum private comparison protocol with Bell states. Laser Phys. Lett. 2024, 21, 055209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.R.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Gong, L.H. Multi-party semi-quantum private comparison protocol of size relation with d-level GHZ states. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2025, 8, 2400530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.H.; Ye, Z.J.; Liu, C.; Zhou, S. One-way semi-quantum private comparison protocol without pre-shared keys based on unitary operations. Laser Phys. Lett. 2024, 21, 035207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Khan, M.K. QF2PM: Quantum-Secure Fine-Grained Privacy-Preserving Profile Matching for Mobile Social Networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chang, Y.; Yang, F.; Hou, M.; Cheng, W. Quantum secure direct communication based on quantum homomorphic encryption. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2021, 36, 2150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M. Symmetric quantum fully homomorphic encryption with perfect security. Quantum Inf. Process. 2013, 12, 3675–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, B. Quantum neural networks model based on swap test and phase estimation. Neural Netw. 2020, 130, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiyed, A.I. Quantum Error Correction in Cryptographic Applications: Ensuring Robustness against Quantum Noise and Attacks. Acad. Nexus J. 2025, 4. Available online: http://academianexusjournal.com/index.php/anj/article/view/16 (accessed on 25 November 2025).
- Tsai, C.W.; Hwang, T. Deterministic quantum communication using the symmetric W state. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2013, 56, 1903–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozubov, A.; Gaidash, A.; Miroshnichenko, G. Quantum control attack: Towards joint estimation of protocol and hardware loopholes. Phys. Rev. A 2021, 104, 022603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.B.; Chang, Y.; Qiu, C.; Liu, D.M.; Hou, M. Quantum key agreement protocol based on quantum search algorithm. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2021, 60, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Xin, X.; Li, C.; Li, F. Security analysis of the semi-quantum secret-sharing protocol of specific bits and its improvement. Quantum Inf. Process. 2024, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, H.B.; Wei, K. Improved security bounds against the Trojan-horse attack in decoy-state quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Process. 2024, 23, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, X.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Improved finite-key security analysis of measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution against a trojan-horse attack. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 044022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protocol | Quantum Resource | Quantum Operations | Quantum Communication Method | Quantum Measurement for Users | Quantum Measurement for TP | Comparison Scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [30] | Bell state | Entanglement swapping | One-way | GHZ-basis | No | Integer |
| Ref. [31] | Hyper-entangled GHZ state | Entanglement swapping | One-way | Bell-basis | Bell-basis | Integer |
| Ref. [32] | Bell state | Rotation operation | Two-way | No | Bell-basis | Integer |
| Ref. [33] | Four-particle cluster and extend Bell state | Entanglement swapping | One-way | Bell basis and extended Bell basis | No | Integer |
| Ref. [34] | Four-particle cluster state | Bit-flip and phase-shift | One-way | No | Bell-basis | Integer |
| Ref. [35] | d-dimensional Bell state | Unitary operation | One-way | d-dimensional single-particle | No | Integer |
| Ref. [36] | d-dimensional Bell state | Entanglement swapping and qudit shifting | One-way | d-dimensional Bell state | d-dimensional Bell state | Integer |
| Ours | Singe photons | Rotation operation | One-way | No | single-particle | Array |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. Quantum Private Array Content Comparison Based on Multi-Qubit Swap Test. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233827
Hou M, Wu Y, Zhang S. Quantum Private Array Content Comparison Based on Multi-Qubit Swap Test. Mathematics. 2025; 13(23):3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233827
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Min, Yue Wu, and Shibin Zhang. 2025. "Quantum Private Array Content Comparison Based on Multi-Qubit Swap Test" Mathematics 13, no. 23: 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233827
APA StyleHou, M., Wu, Y., & Zhang, S. (2025). Quantum Private Array Content Comparison Based on Multi-Qubit Swap Test. Mathematics, 13(23), 3827. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233827





