Transcriptome Mining to Identify Molecular Markers for the Diagnosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Bloodstream Infections
Abstract
:1. Introduction
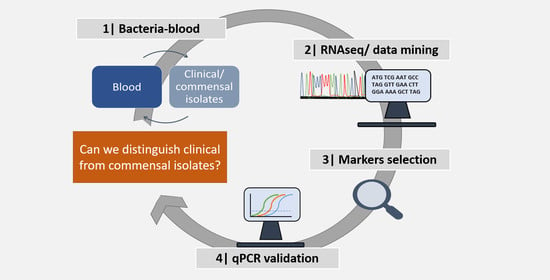
2. Results
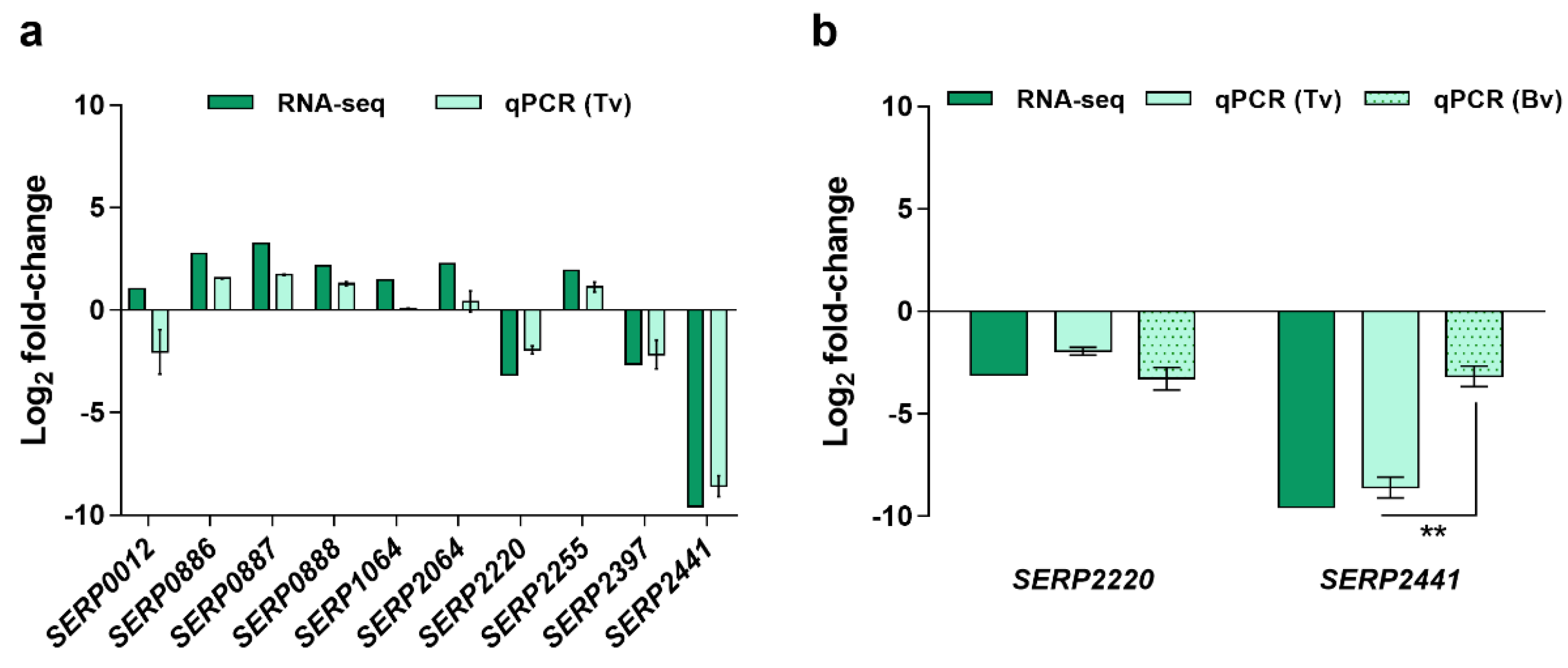
2.1. Identification and Selection of Candidate Diagnostic Markers
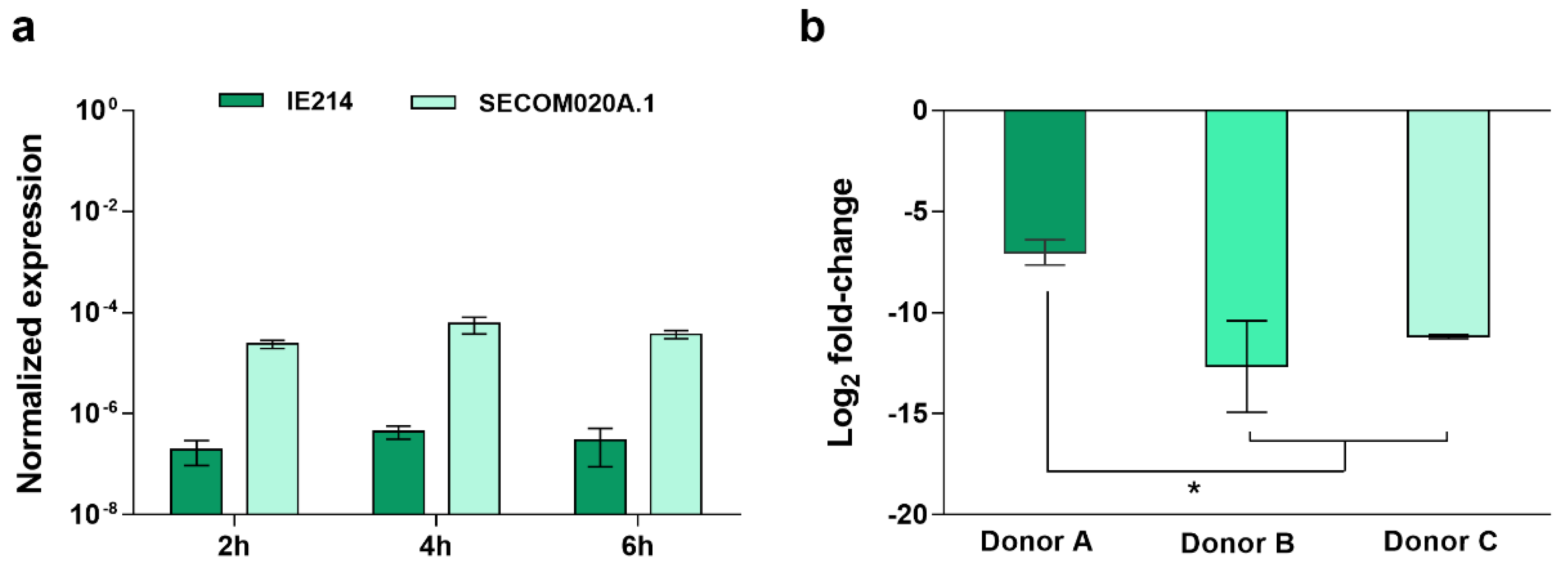
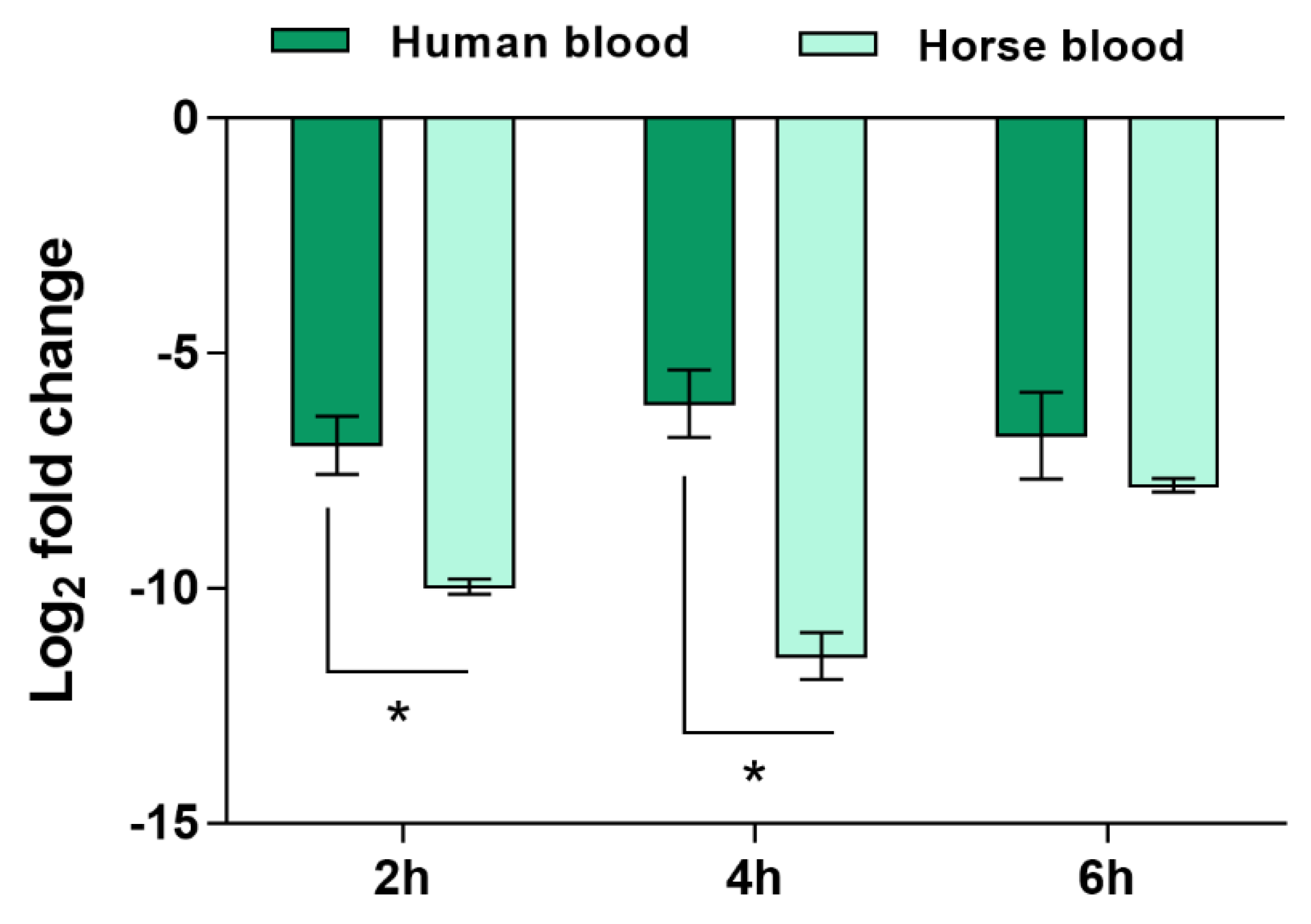
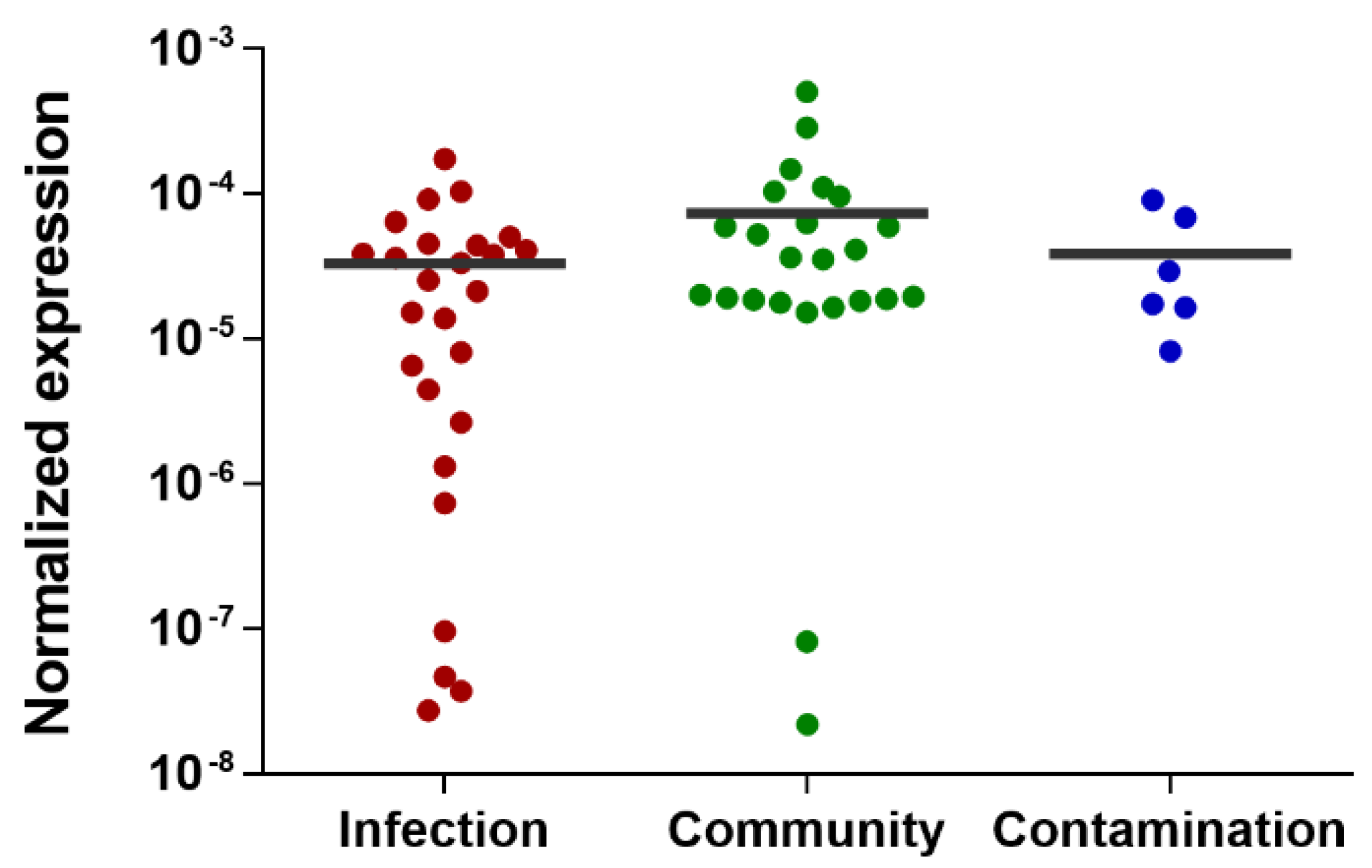
2.2. Validation of the Candidate Diagnostic Marker
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Bacterial Strains
4.3. Identification of Potential Molecular Markers
4.3.1. RNA Sequencing Analysis
4.3.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.4. Validation of Candidate Diagnostic Markers
4.4.1. PCR Detection of Genes with Potential Discriminatory Power
4.4.2. Co-Incubation of Bacteria and Blood
4.4.3. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The “accidental” pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hogan, S.; Stevens, N.T.; Humphreys, H.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. Current and future approaches to the prevention and treatment of staphylococcal medical device-related infections. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 21, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.K.; Lyman, J.A. Updated review of blood culture contamination. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conlan, S.; Mijares, L.A.; Becker, J.; Blakesley, R.W.; Bouffard, G.G.; Brooks, S.; Coleman, H.; Gupta, J.; Gurson, N.; Park, M.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis pan-genome sequence analysis reveals diversity of skin commensal and hospital infection-associated isolates. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espadinha, D.; Sobral, R.G.; Mendes, C.I.; Méric, G.; Sheppard, S.K.; Carriço, J.A.; de Lencastre, H.; Miragaia, M. Distinct phenotypic and genomic signatures underlie contrasting pathogenic potential of staphylococcus epidermidis clonal lineages. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Vuong, C.; Otto, M.; Wen, Y.; Gao, Q. Bacterial insertion sequence IS256 as a potential molecular marker to discriminate invasive strains from commensal strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Hosp. Infect. 2005, 61, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherifi, S.; Byl, B.; Deplano, A.; Nonhoff, C.; Denis, O.; Hallin, M. Comparative epidemiology of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from patients with catheter-related bacteremia and from healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgueiro, V.C.; Iorio, N.L.P.; Ferreira, M.C.; Chamon, R.C.; Santos, K.R.N. Methicillin resistance and virulence genes in invasive and nasal Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates from neonates. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, T.; Luo, T.; Sun, G.; Yang, C.; Cao, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, M. Molecular analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis strains isolated from community and hospital environments in China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Larsen, J.; Li, M.; Walter, A.; Slavetinsky, C.; Both, A.; Sanchez Carballo, P.M.; Stegger, M.; Lehmann, E.; Liu, Y.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis clones express Staphylococcus aureus-type wall teichoic acid to shift from a commensal to pathogen lifestyle. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanAken, S.M.; Newton, D.; VanEpps, J.S. Improved diagnostic prediction of the pathogenicity of bloodstream isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0241457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coenye, T. Do results obtained with RNA-sequencing require independent verification? Biofilm 2021, 3, 100043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitney, A.R.; Diehn, M.; Popper, S.J.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Relman, D.A.; Brown, P.O. Individuality and variation in gene expression patterns in human blood. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1896–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cobb, J.P.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Miller-Graziano, C.; Calvano, S.E.; Baker, H.V.; Xiao, W.; Laudanski, K.; Brownstein, B.H.; Elson, C.M.; Hayden, D.L.; et al. Application of genome-wide expression analysis to human health and disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4801–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eady, J.J.; Wortley, G.M.; Wormstone, Y.M.; Hughes, J.C.; Astley, S.B.; Foxall, R.J.; Doleman, J.F.; Elliott, R.M. Variation in gene expression profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells from healthy volunteers. Physiol. Genomics 2005, 22, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miragaia, M.; Thomas, J.C.; Couto, I.; Enright, M.C.; Lencastre, H. Inferring a population structure for Staphylococcus epidermidis from multilocus sequence typing data. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 2540–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- França, A.; Cerca, N. Plasma is the main regulator of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms virulence genes transcription in human blood. Pathog. Dis. 2016, 74, ftv125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cau, L.; Williams, M.R.; Butcher, A.M.; Nakatsuji, T.; Kavanaugh, J.S.; Cheng, J.Y.; Shafiq, F.; Higbee, K.; Hata, T.R.; Horswill, A.R.; et al. Staphylococcus epidermidis protease EcpA can be a deleterious component of the skin microbiome in atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 955–966.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Both, A.; Huang, J.; Qi, M.; Lausmann, C.; Weißelberg, S.; Büttner, H.; Lezius, S.; Failla, A.V.; Christner, M.; Stegger, M.; et al. Distinct clonal lineages and within-host diversification shape invasive Staphylococcus epidermidis populations. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichmann, P.; Both, A.; Wolz, C.; Hornef, M.W.; Rohde, H.; Yazdi, A.S.; Burian, M. The Staphylococcus epidermidis transcriptional profile during carriage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 896311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Spoto, M.; Hardy, R.; Guan, C.; Fleming, E.; Larson, P.J.; Brown, J.S.; Oh, J. Host-specific evolutionary and transmission dynamics shape the functional diversification of Staphylococcus epidermidis in human skin. Cell 2020, 180, 454–470.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerca, N.; Martins, S.; Sillankorva, S.; Jefferson, K.K.; Pier, G.B.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. Effects of growth in the presence of subinhibitory concentrations of dicloxacillin on Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus haemolyticus biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8677–8682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerca, N.; Pier, G.B.; Vilanova, M.; Oliveira, R.; Azeredo, J. Influence of batch or fed-batch growth on Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 39, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christensen, G.D.; Simpson, W.A.; Bisno, A.L.; Beachey, E.H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect. Immun. 1982, 37, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freitas, A.I.; Lopes, N.; Oliveira, F.; Brás, S.; França, Â.; Vasconcelos, C.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N. Comparative analysis between biofilm formation and gene expression in Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, D.; Siemssen, N.; Laufs, R. Parallel induction by glucose of adherence and a polysaccharide antigen specific for plastic-adherent Staphylococcus epidermidis: Evidence for functional relation to intercellular adhesion. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, F.; Cerca, N. Antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation ability among coagulase-negative staphylococci in healthy individuals from portugal. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.R.; Fouts, D.E.; Archer, G.L.; Mongodin, E.F.; DeBoy, R.T.; Ravel, J.; Paulsen, I.T.; Kolonay, J.F.; Brinkac, L.; Beanan, M.; et al. Insights on evolution of virulence and resistance from the complete genome analysis of an early methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain and a biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerca, N.; Gomes, F.; Bento, J.C.; França, A.; Rolo, J.; Miragaia, M.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R. Farnesol induces cell detachment from established S. epidermidis biofilms. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- França, A.; Carvalhais, V.; Vilanova, M.; Pier, G.B.; Cerca, N. Characterization of an in vitro fed-batch model to obtain cells released from S. epidermidis biofilms. AMB Express 2016, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A.I.; Vasconcelos, C.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N. Optimization of an automatic counting system for the quantification of Staphylococcus epidermidis cells in biofilms. J. Basic Microbiol. 2014, 54, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- França, A.; Pier, G.B.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N. Transcriptomic analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm-released cells upon interaction with human blood circulating immune cells and soluble factors. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- França, A.; Carvalhais, V.; Maira-Litrán, T.; Vilanova, M.; Cerca, N.; Pier, G. Alterations in the Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm transcriptome following interaction with whole human blood. Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- França, A.; Freitas, A.I.; Henriques, A.F.; Cerca, N. Optimizing a qPCR gene expression quantification assay for S. epidermidis biofilms: A comparison between commercial kits and a customized protocol. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mortazavi, A.; Williams, B.; McCue, K.; Schaeffer, L.; Wold, B. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3-new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brás, S.; França, A.; Cerca, N. Optimizing a reliable ex vivo human blood model to analyze expression of Staphylococcus epidermidis genes. PeerJ 2020, 2020, e9295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brás, S.; França, A. Transcriptome Mining to Identify Molecular Markers for the Diagnosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Bloodstream Infections. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111596
Brás S, França A. Transcriptome Mining to Identify Molecular Markers for the Diagnosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Bloodstream Infections. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111596
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrás, Susana, and Angela França. 2022. "Transcriptome Mining to Identify Molecular Markers for the Diagnosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Bloodstream Infections" Antibiotics 11, no. 11: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111596
APA StyleBrás, S., & França, A. (2022). Transcriptome Mining to Identify Molecular Markers for the Diagnosis of Staphylococcus epidermidis Bloodstream Infections. Antibiotics, 11(11), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics11111596