Can the Thermodynamic Hodgkin-Huxley Model of Voltage-Dependent Conductance Extrapolate for Temperature?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. K+ Current Data
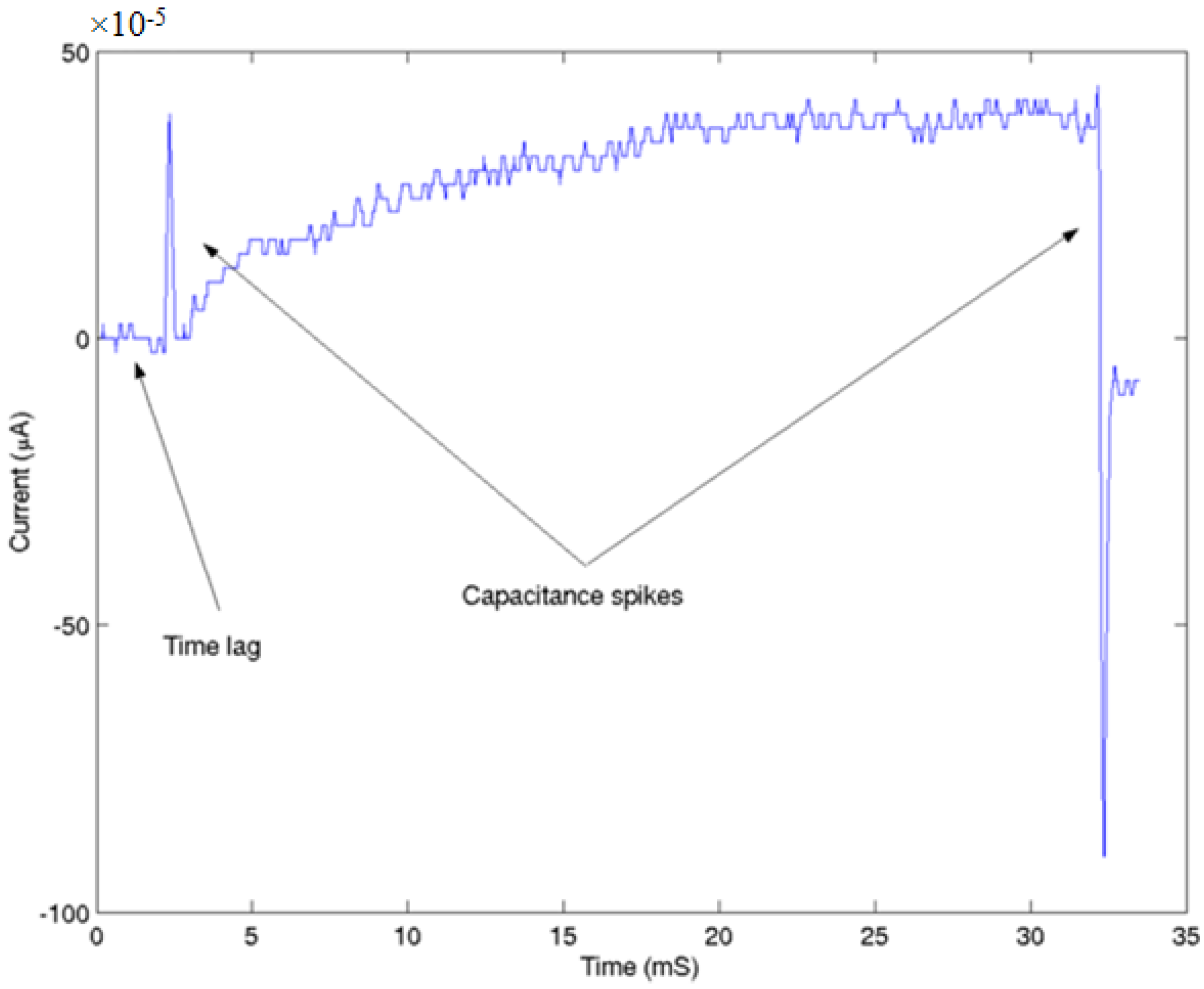
2.2. Thermodynamic H-H Models

2.2.1. Linear Variant


2.2.2. Non-Linear Variant (Quadratic)


2.3. Thermodynamic H-H Model of a Non-Inactivating K+ Current (IK), Recorded in a Gonadotroph Cell Line



2.4. Fitting the Thermodynamic H-H Model to the K+ Current (IK) Data
2.5. Temperature Extrapolation
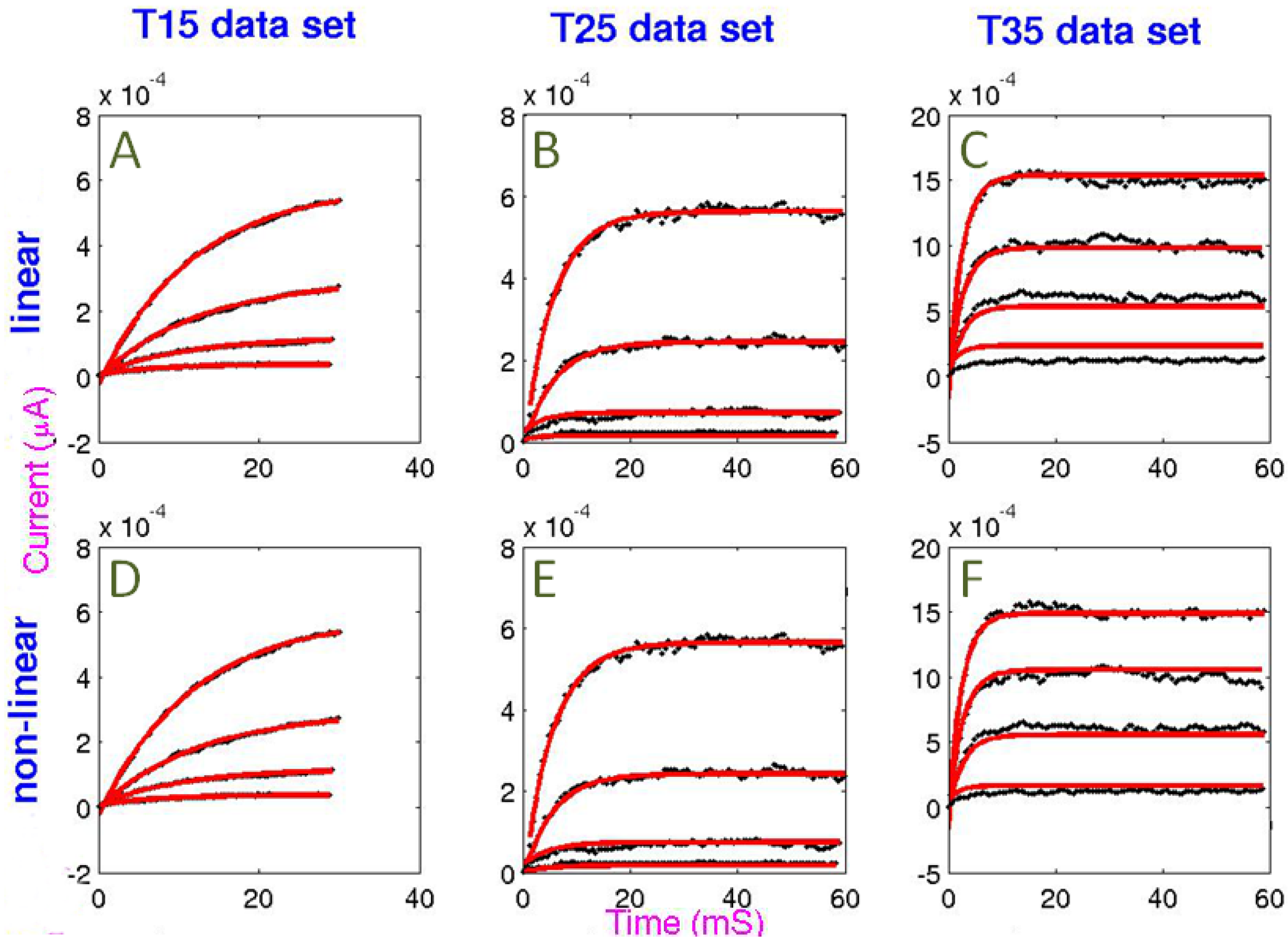
3. Results and Discussion
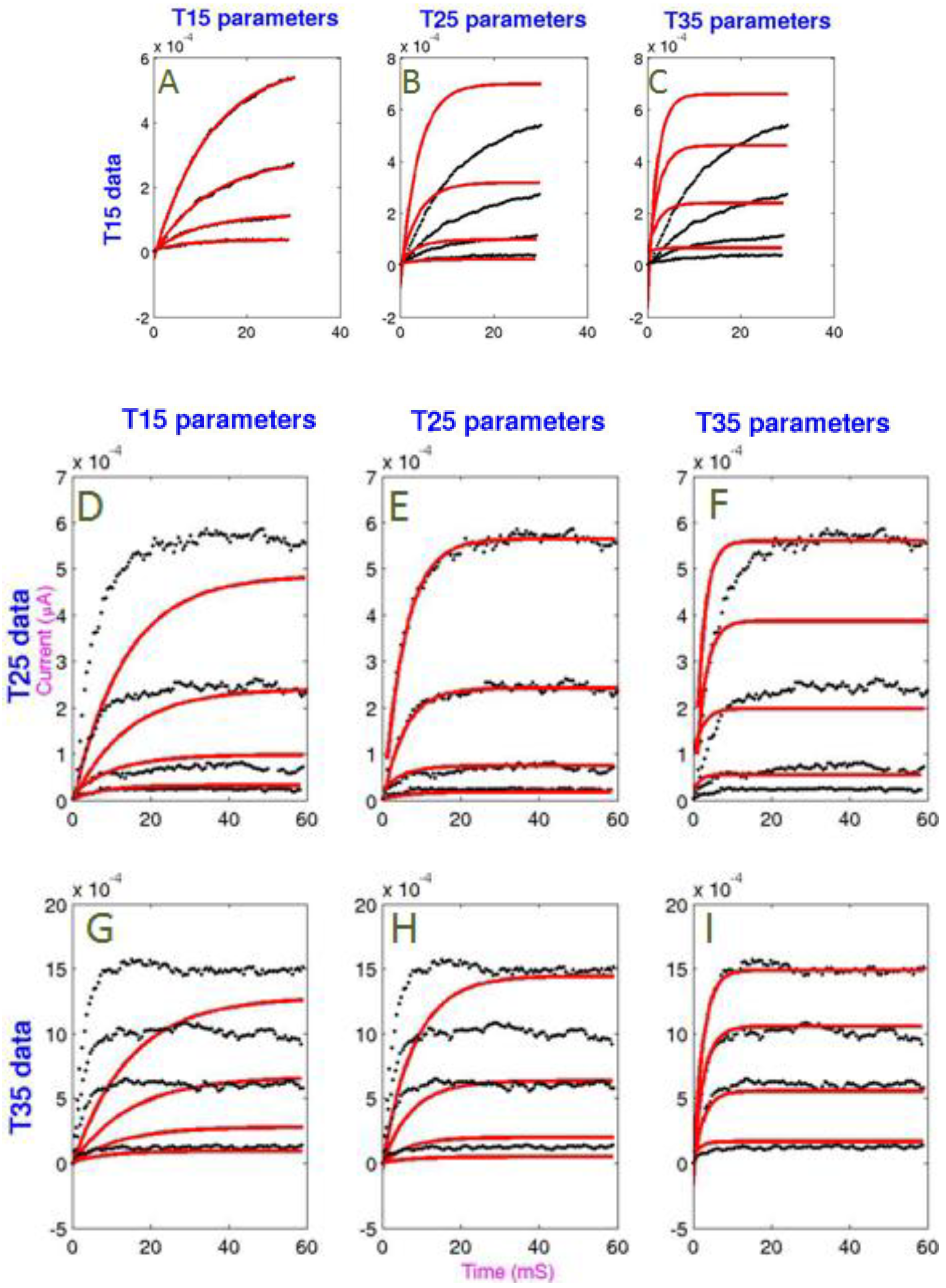
3.1. Curve Fitting
 = −0.05. The worst fit was still good in absolute terms: the linear model fit to the T35 data set has a logged reduced chi-square metric: log10
= −0.05. The worst fit was still good in absolute terms: the linear model fit to the T35 data set has a logged reduced chi-square metric: log10  = 1.69. Temperature and goodness of fit were inversely related, possibly due to data variance being a function of temperature. The non-linear model provided a slightly better fit than the linear model.
= 1.69. Temperature and goodness of fit were inversely related, possibly due to data variance being a function of temperature. The non-linear model provided a slightly better fit than the linear model.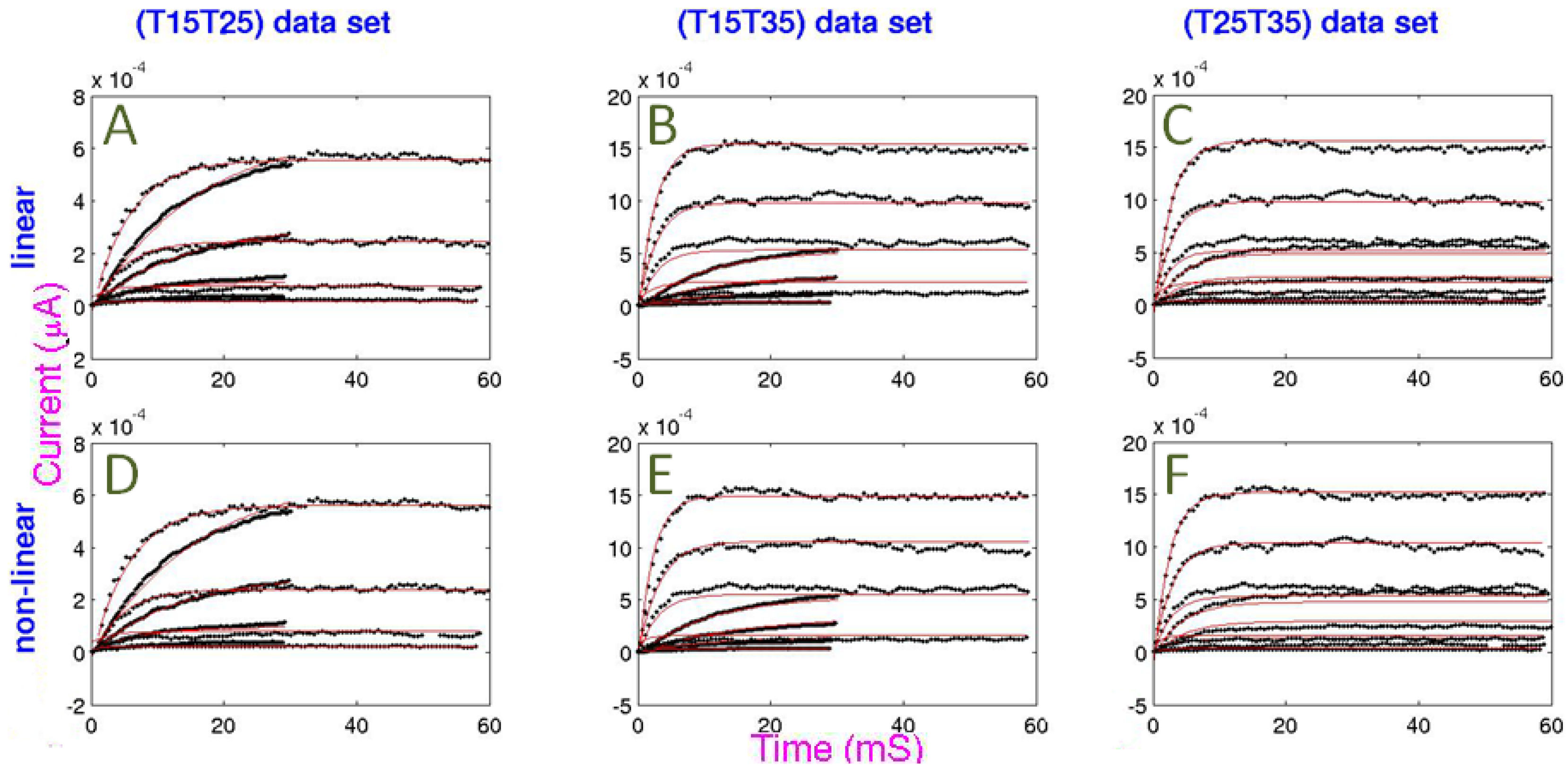
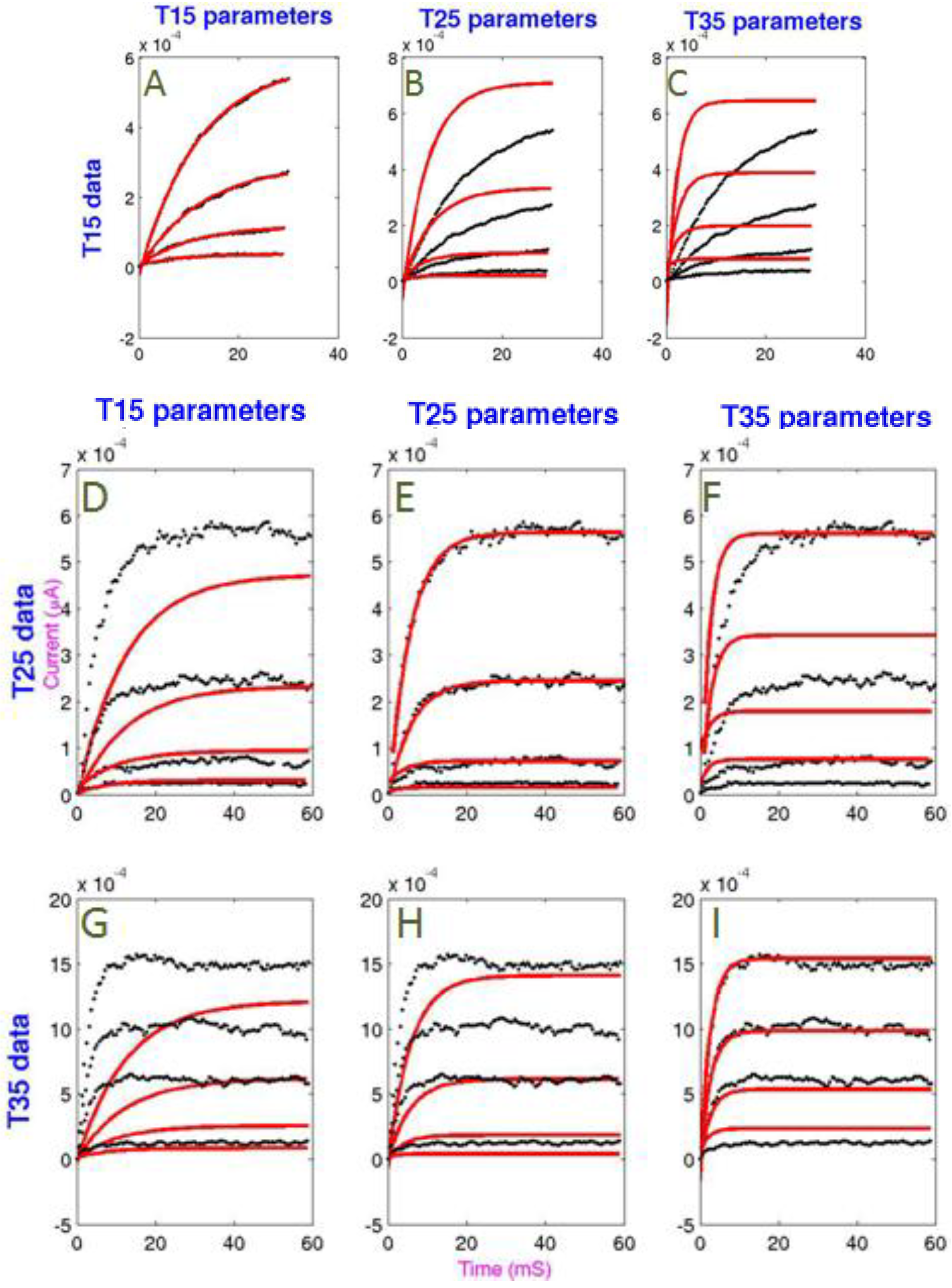
3.2. Temperature Extrapolation of the Model
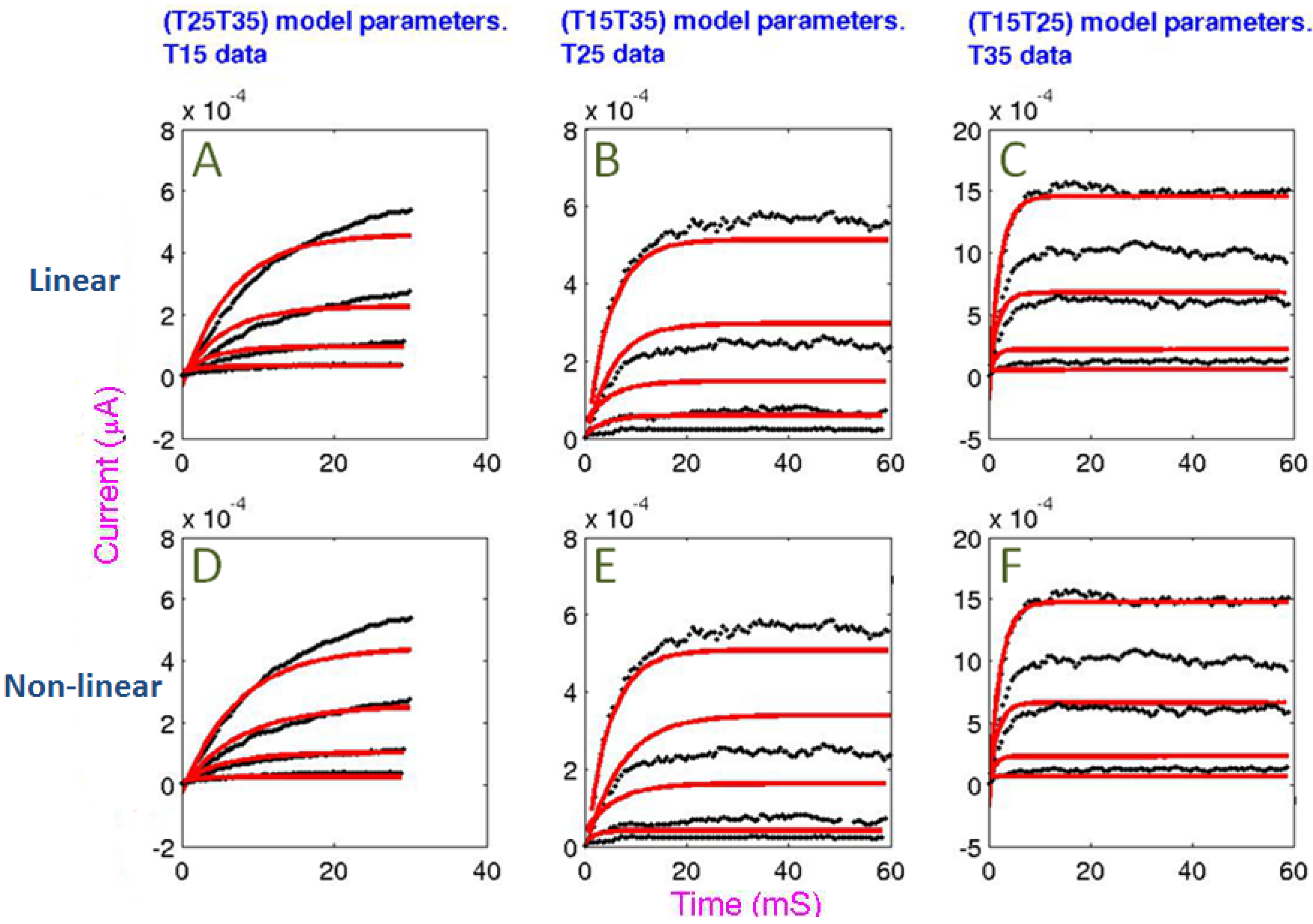

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 1952, 117, 500–544. [Google Scholar]
- Hille, B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eyring, H. The activated complex in chemical reactions. J. Chem. Phys. 1935, 3, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, R.W.; Noble, D. A transition state theory approach to kinetics of conductance changes in excitable membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 1969, 1, 248–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, T.L.; Chen, Y.-D. On the theory of ion transport across the nerve membrane. VI. Free energy and activation free energies of conformational change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 1723–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Destexhe, A.; Huguenard, J.R. Which formalism to use for modelling voltage-dependent conductances? In Computational Neuroscience: Realistic modelling for experimentalists; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Destexhe, A.; Huguenard, J.R. Nonlinear thermodynamic models of voltage dependent currents. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2000, 9, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, J.K.; Sikdar, S.K. Temperature dependent conformational changes in a voltage-gated potassium channel. Eur. Biophys. J. 1999, 28, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical Recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Creighton, T.E. Proteins; WH Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B.; Bray, D.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Watson, J.D. Molecular Biology of the Cell; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Stryer, L. Biochemistry; WH Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, D. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1975, 8, 185–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, A.D. Nonlinear temperature modulation of sodium channel kinetics in GH3 cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1511, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ruta, V.; Chen, J.; Lee, A.; MacKinnon, R. The principle of gating charge movement in a voltage-dependent K+ channel. Nature 2003, 423, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, C.A.; Bezanilla, F. A model of sodium channel gating based on single channel, macroscopic ionic, and gating currents in the squid giant axon. Biophys. J. 1991, 60, 1511–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perozo, E.; Bezanilla, F. Phosphorylation affects voltage gating of the delayed rectifier K+ channel by electrostatic interactions. Neuron 1990, 5, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M.D.; Wall, M.J.; Press, D.A.; Feng, J. The Sodium-Potassium Pump Controls the Intrinsic Firing of the Cerebellar Purkinje Neuron. PLoS One 2012, 7, e51169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M.D. Mathematical Model of Bursting in Dissociated Purkinje Neurons. PLoS One 2013, 8, e68765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, J.I.; Waxman, S.G. Hodgkin and Huxley and the basis for electrical signalling: A remarkable legacy still going strong. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 2569–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M.D. Can Thermodynamic Models of Voltage-Dependent Conductances Extrapolate for Temperature? Master’s Thesis, September 2003. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Forrest, M.D. Can the Thermodynamic Hodgkin-Huxley Model of Voltage-Dependent Conductance Extrapolate for Temperature? Computation 2014, 2, 47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation2020047
Forrest MD. Can the Thermodynamic Hodgkin-Huxley Model of Voltage-Dependent Conductance Extrapolate for Temperature? Computation. 2014; 2(2):47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation2020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleForrest, Michael D. 2014. "Can the Thermodynamic Hodgkin-Huxley Model of Voltage-Dependent Conductance Extrapolate for Temperature?" Computation 2, no. 2: 47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation2020047
APA StyleForrest, M. D. (2014). Can the Thermodynamic Hodgkin-Huxley Model of Voltage-Dependent Conductance Extrapolate for Temperature? Computation, 2(2), 47-60. https://doi.org/10.3390/computation2020047





