Evaluating the Immune Response in Rabbits to an Escalating Dose of mRNA-Based HIV-1 Env Immunogens
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rabbit Immunizations and Blood Collections
2.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.3. In Vitro Transcription, mRNA Purification and mRNA-LNP Preparation
2.4. Protein Expression and Purification
2.5. SOSIP Display on Synthetic Viral-like Particles
2.6. Rabbit Anesthesia and Euminthanasia
2.7. Generation of Single-Round Pseudoviruses
2.8. Viral Neutralization Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
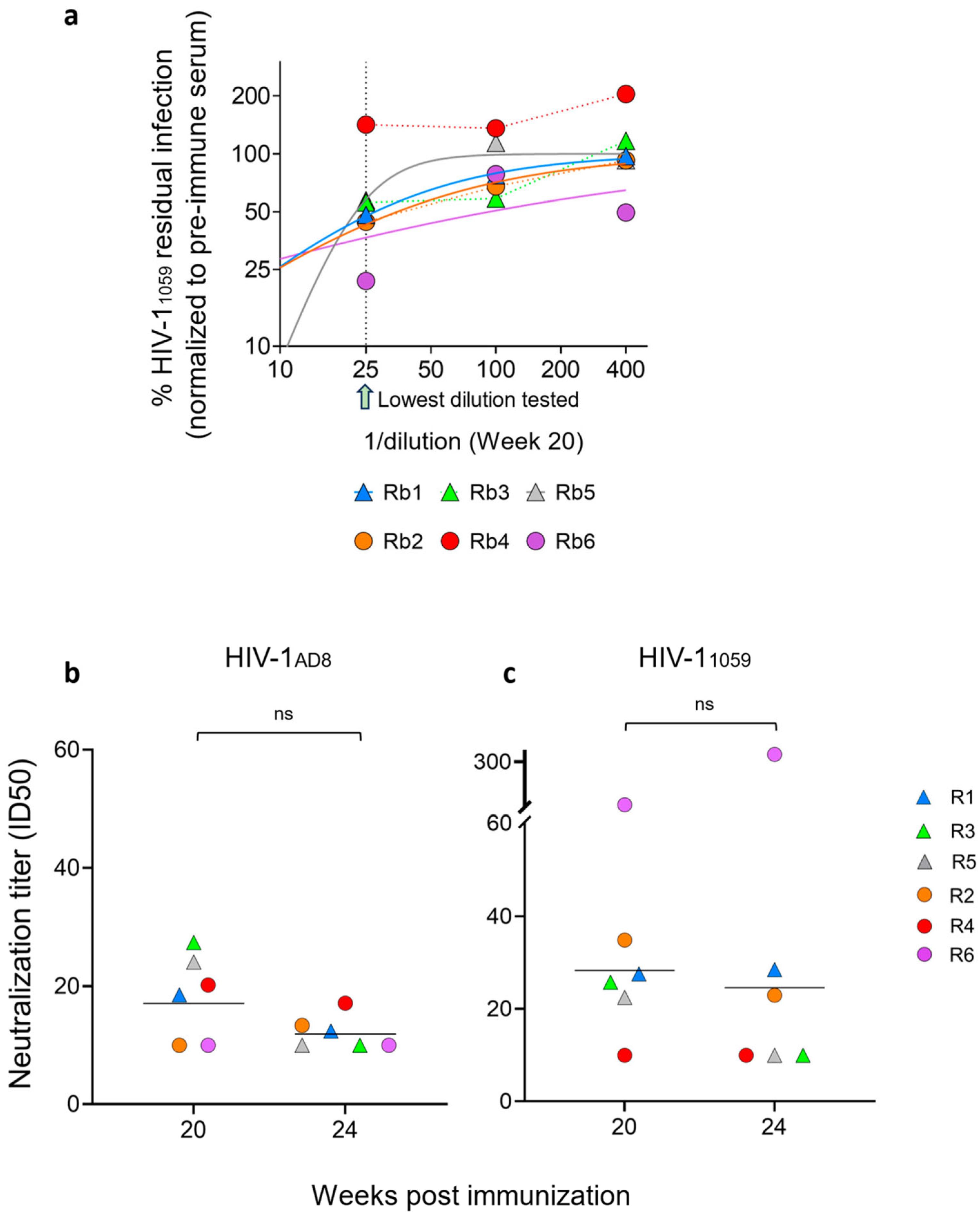
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- HIV Data and Statistics. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/global-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-programmes/hiv/strategic-information/hiv-data-and-statistics (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Nitayaphan, S.; Kaewkungwal, J.; Chiu, J.; Paris, R.; Premsri, N.; Namwat, C.; DeSouza, M.; Adams, E.; et al. Vaccination with ALVAC and AIDSVAX to Prevent HIV-1 Infection in Thailand. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2209–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, M.L.; Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Nitayaphan, S.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Kaewkungwal, J.; Kunasol, P.; Khamboonruang, C.; Thongcharoen, P.; Morgan, P.; Benenson, M.; et al. Risk behaviour and time as covariates for efficacy of the HIV vaccine regimen ALVAC-HIV (vCP1521) and AIDSVAX B/E: A post-hoc analysis of the Thai phase 3 efficacy trial RV 144. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akapirat, S.; Karnasuta, C.; Vasan, S.; Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Pitisuttithum, P.; Madnote, S.; Savadsuk, H.; Rittiroongrad, S.; Puangkaew, J.; Phogat, S.; et al. Characterization of HIV-1 gp120 antibody specificities induced in anogenital secretions of RV144 vaccine recipients after late boost immunizations. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottardo, R.; Bailer, R.T.; Korber, B.T.; Gnanakaran, S.; Phillips, J.; Shen, X.; Tomaras, G.D.; Turk, E.; Imholte, G.; Eckler, L.; et al. Plasma IgG to linear epitopes in the V2 and V3 regions of HIV-1 gp120 correlate with a reduced risk of infection in the RV144 vaccine efficacy trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.E.; Huang, Y.; Grunenberg, N.; Laher, F.; Roux, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; De Rosa, S.C.; Flach, B.; Randhawa, A.K.; Jensen, R.; et al. Immune correlates of the Thai RV144 HIV vaccine regimen in South Africa. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dommaraju, K.; Kijak, G.; Carlson, J.M.; Larsen, B.B.; Tovanabutra, S.; Geraghty, D.E.; Deng, W.; Maust, B.S.; Edlefsen, P.T.; Sanders-Buell, E.; et al. CD8 and CD4 Epitope Predictions in RV144: No Strong Evidence of a T-Cell Driven Sieve Effect in HIV-1 Breakthrough Sequences from Trial Participants. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartland, A.J.; Li, S.; McNevin, J.; Tomaras, G.D.; Gottardo, R.; Janes, H.; Fong, Y.; Morris, D.; Geraghty, D.E.; Kijak, G.H.; et al. Analysis of HLA A*02 Association with Vaccine Efficacy in the RV144 HIV-1 Vaccine Trial. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 8242–8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Janes, H.; Frahm, N.; Isaacs, A.; Kim, J.H.; Montefiori, D.; McElrath, M.J.; Tomaras, G.D.; Gilbert, P.B. Predictors of durable immune responses six months after the last vaccination in preventive HIV vaccine trials. Vaccine 2017, 35, 1184–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitisuttithum, P.; Rerks-Ngarm, S.; Bussaratid, V.; Dhitavat, J.; Maekanantawat, W.; Pungpak, S.; Suntharasamai, P.; Vanijanonta, S.; Nitayapan, S.; Kaewkungwal, J.; et al. Safety and Reactogenicity of Canarypox ALVAC-HIV (vCP1521) and HIV-1 gp120 AIDSVAX B/E Vaccination in an Efficacy Trial in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.P.; Fiore-Gartland, A.; Carpp, L.N.; Cohen, K.W.; Rouphael, N.; Fleurs, L.; Dintwe, O.; Zhao, M.; Moodie, Z.; Fong, Y.; et al. Landscapes of binding antibody and T-cell responses to pox-protein HIV vaccines in Thais and South Africans. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0226803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolla-Pazner, S.; deCamp, A.; Gilbert, P.B.; Williams, C.; Yates, N.L.; Williams, W.T.; Howington, R.; Fong, Y.; Morris, D.E.; Soderberg, K.A.; et al. Vaccine-Induced IgG Antibodies to V1V2 Regions of Multiple HIV-1 Subtypes Correlate with Decreased Risk of HIV-1 Infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, B.F.; Gilbert, P.B.; McElrath, M.J.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Tomaras, G.D.; Alam, S.M.; Evans, D.T.; Montefiori, D.C.; Karnasuta, C.; Sutthent, R.; et al. Immune-correlates analysis of an HIV-1 vaccine efficacy trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Herschhorn, A. Insights from HIV-1 vaccine and passive immunization efficacy trials. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 908–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, E.S.; Madiga, M.C.; Hermanus, T.; Moore, P.L.; Wibmer, C.K.; Tumba, N.L.; Werner, L.; Mlisana, K.; Sibeko, S.; Williamson, C.; et al. The Neutralization Breadth of HIV-1 Develops Incrementally over Four Years and Is Associated with CD4+ T Cell Decline and High Viral Load during Acute Infection. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4828–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hraber, P.; Seaman, M.S.; Bailer, R.T.; Mascola, J.R.; Montefiori, D.C.; Korber, B.T. Prevalence of broadly neutralizing antibody responses during chronic HIV-1 infection. AIDS 2014, 28, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikell, I.; Sather, D.N.; Kalams, S.A.; Altfeld, M.; Alter, G.; Stamatatos, L. Characteristics of the Earliest Cross-Neutralizing Antibody Response to HIV-1. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simek, M.D.; Rida, W.; Priddy, F.H.; Pung, P.; Carrow, E.; Laufer, D.S.; Lehrman, J.K.; Boaz, M.; Tarragona-Fiol, T.; Miiro, G.; et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Elite Neutralizers: Individuals with Broad and Potent Neutralizing Activity Identified by Using a High-Throughput Neutralization Assay together with an Analytical Selection Algorithm. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 7337–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaras, G.D.; Binley, J.M.; Gray, E.S.; Crooks, E.T.; Osawa, K.; Moore, P.L.; Tumba, N.; Tong, T.; Shen, X.; Yates, N.L.; et al. Polyclonal B Cell Responses to Conserved Neutralization Epitopes in a Subset of HIV-1-Infected Individuals. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 11502–11519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschhorn, A.; Gu, C.; Espy, N.; Richard, J.; Finzi, A.; Sodroski, J.G. A broad HIV-1 inhibitor blocks envelope glycoprotein transitions critical for entry. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschhorn, A.; Ma, X.; Gu, C.; Ventura, J.D.; Castillo-Menendez, L.; Melillo, B.; Terry, D.S.; Smith, A.B., III; Blanchard, S.C.; Munro, J.B.; et al. Release of gp120 Restraints Leads to an Entry-Competent Intermediate State of the HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins. mBio 2016, 7, e01598-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, D.; Pickthorn, S.; Ahmed, S.; Mazurov, D.; Jeffy, J.; Shukla, R.K.; Sharma, A.; Herschhorn, A. Incompletely closed HIV-1CH040 envelope glycoproteins resist broadly neutralizing antibodies while mediating efficient HIV-1 entry. Npj Viruses 2025, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.R.; Hangartner, L. Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies to HIV and Their Role in Vaccine Design. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 635–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, B.F.; Burton, D.R.; Mascola, J.R. Multiple roles for HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaz2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschhorn, A. Indirect Mechanisms of HIV-1 Evasion from Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies In Vivo. ACS Infect. Dis. 2023, 9, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, P.-J.; Herschhorn, A.; Haim, H.; Salas, I.; Gu, C.; Sodroski, J.; Gabuzda, D. Loss of a Conserved N-Linked Glycosylation Site in the Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope Glycoprotein V2 Region Enhances Macrophage Tropism by Increasing CD4-Independent Cell-to-Cell Transmission. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 5014–5028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Sutton, H.J.; Cottrell, C.A.; Phung, I.; Ozorowski, G.; Sewall, L.M.; Nedellec, R.; Nakao, C.; Silva, M.; Richey, S.T.; et al. Long-primed germinal centres with enduring affinity maturation and clonal migration. Nature 2022, 609, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal Centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 429–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victora, G.D.; Nussenzweig, M.C. Germinal Centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 40, 413–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauthner, M.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Sok, D.; Nkolola, J.P.; Bastidas, R.; Boopathy, A.V.; Carnathan, D.G.; Chandrashekar, A.; Cirelli, K.M.; Cottrell, C.A.; et al. Elicitation of Robust Tier 2 Neutralizing Antibody Responses in Nonhuman Primates by HIV Envelope Trimer Immunization Using Optimized Approaches. Immunity 2017, 46, 1073–1088.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.K.; Lee, J.H.; Menis, S.; Skog, P.; Rossi, M.; Ota, T.; Kulp, D.W.; Bhullar, D.; Kalyuzhniy, O.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; et al. Precursor Frequency and Affinity Determine B Cell Competitive Fitness in Germinal Centers, Tested with Germline-Targeting HIV Vaccine Immunogens. Immunity 2018, 48, 133–146.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havenar-Daughton, C.; Lee, J.H.; Crotty, S. Tfh cells and HIV bnAbs, an immunodominance model of the HIV neutralizing antibody generation problem. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 275, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, H.H.; Melo, M.B.; Kang, M.; Pelet, J.M.; Ruda, V.M.; Foley, M.H.; Hu, J.K.; Kumari, S.; Crampton, J.; Baldeon, A.D.; et al. Sustained antigen availability during germinal center initiation enhances antibody responses to vaccination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, E6639–E6648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirelli, K.M.; Carnathan, D.G.; Nogal, B.; Martin, J.T.; Rodriguez, O.L.; Upadhyay, A.A.; Enemuo, C.A.; Gebru, E.H.; Choe, Y.; Viviano, F.; et al. Slow Delivery Immunization Enhances HIV Neutralizing Antibody and Germinal Center Responses via Modulation of Immunodominance. Cell 2019, 177, 1153–1171.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauthner, M.G.; Nkolola, J.P.; Havenar-Daughton, C.; Murrell, B.; Reiss, S.M.; Bastidas, R.; Prévost, J.; Nedellec, R.; von Bredow, B.; Abbink, P.; et al. Vaccine-Induced Protection from Homologous Tier 2 SHIV Challenge in Nonhuman Primates Depends on Serum-Neutralizing Antibody Titers. Immunity 2019, 50, 241–252.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel, M.; Amara, R.R.; Bar, K.J.; Crotty, S.; Deeks, S.G.; Duplessis, C.; Gaiha, G.; McElrath, M.J.; McMichael, A.; Palin, A.; et al. Exploring synergies between B- and T-cell vaccine approaches to optimize immune responses against HIV—Workshop report. npj Vaccines 2024, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruel, T.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Amraoui, S.; Malbec, M.; Richard, L.; Bourdic, K.; Donahue, D.A.; Lorin, V.; Casartelli, N.; Noël, N.; et al. Elimination of HIV-1-infected cells by broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Su, Y.; Jiao, A.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B. T cells in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parks, K.R.; Moodie, Z.; Allen, M.A.; Yen, C.; Furch, B.D.; MacPhee, K.J.; Ozorowski, G.; Heptinstall, J.; Hahn, W.O.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Vaccination with mRNA-encoded membrane-anchored HIV envelope trimers elicited tier 2 neutralizing antibodies in a phase 1 clinical trial. Sci. Transl. Med. 2025, 17, eady6831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Parthasarathy, D.; Newhall, R.; Picard, T.; Aback, M.; Ratnapriya, S.; Arndt, W.; Vega-Rodriguez, W.; Kirk, N.M.; Liang, Y.; et al. Enhancing anti-viral neutralization response to immunization with HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein immunogens. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Narayanan, E.; Liu, Q.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Boswell, K.; Ding, S.; Hu, Z.; Follmann, D.; Lin, Y.; Miao, H.; et al. A multiclade env-gag VLP mRNA vaccine elicits tier-2 HIV-1-neutralizing antibodies and reduces the risk of heterologous SHIV infection in macaques. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2234–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Herschhorn, A. mRNA-based HIV-1 vaccines. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e00041-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alving, C.R.; Peachman, K.K.; Matyas, G.R.; Rao, M.; Beck, Z. Army Liposome Formulation (ALF) Family of Vaccine Adjuvants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2020, 19, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Adjuvant MF59: A 10-Year Perspective Gary Ott, Ramachandran Radhakrishnan|Springer Nature Experiments. Available online: https://experiments.springernature.com/articles/10.1385/1-59259-083-7:211 (accessed on 20 September 2025).
- Calabro, S.; Tritto, E.; Pezzotti, A.; Taccone, M.; Muzzi, A.; Bertholet, S.; De Gregorio, E.; O’Hagan, D.T.; Baudner, B.; Seubert, A. The adjuvant effect of MF59 is due to the oil-in-water emulsion formulation, none of the individual components induce a comparable adjuvant effect. Vaccine 2013, 31, 3363–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, G.; Barchfeld, G.L.; Chernoff, D.; Radhakrishnan, R.; van Hoogevest, P.; Van Nest, G. MF59: Design and evaluation of a safe and potent adjuvant for human vaccines. Pharm. Biotechnol. 1995, 6, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R.W.; Derking, R.; Cupo, A.; Julien, J.-P.; Yasmeen, A.; de Val, N.; Kim, H.J.; Blattner, C.; de la Peña, A.T.; Korzun, J.; et al. A Next-Generation Cleaved, Soluble HIV-1 Env Trimer, BG505 SOSIP.664 gp140, Expresses Multiple Epitopes for Broadly Neutralizing but Not Non-Neutralizing Antibodies. PLOS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahikainen, R.; Rijal, P.; Tan, T.K.; Wu, H.-J.; Andersson, A.-M.C.; Barrett, J.R.; Bowden, T.A.; Draper, S.J.; Townsend, A.R.; Howarth, M. Overcoming Symmetry Mismatch in Vaccine Nanoassembly through Spontaneous Amidation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, D.; Pothula, K.R.; Ratnapriya, S.; Cervera Benet, H.; Parsons, R.; Huang, X.; Sammour, S.; Janowska, K.; Harris, M.; Sodroski, J.; et al. Conformational flexibility of HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins modulates transmitted/founder sensitivity to broadly neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herschhorn, A.; Gu, C.; Moraca, F.; Ma, X.; Farrell, M.; Smith, A.B.; Pancera, M.; Kwong, P.D.; Schön, A.; Freire, E.; et al. The β20–β21 of gp120 is a regulatory switch for HIV-1 Env conformational transitions. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffy, J.; Parthasarathy, D.; Ahmed, S.; Cervera-Benet, H.; Xiong, U.; Harris, M.; Mazurov, D.; Pickthorn, S.; Herschhorn, A. Alternative substitutions of N332 in HIV-1AD8 gp120 differentially affect envelope glycoprotein function and viral sensitivity to broadly neutralizing antibodies targeting the V3-glycan. bioRxiv 2023, 2023.11.20.567910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnapriya, S.; Chov, A.; Herschhorn, A. A Protocol for Studying HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Function. STAR Protoc. 2020, 1, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawi, R.; Rutten, L.; Lai, Y.-T.; Olia, A.S.; Blokland, S.; Juraszek, J.; Shen, C.-H.; Tsybovsky, Y.; Verardi, R.; Yang, Y.; et al. Automated Design by Structure-Based Stabilization and Consensus Repair to Achieve Prefusion-Closed Envelope Trimers in a Wide Variety of HIV Strains. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnapriya, S.; Perez-Greene, E.; Schifanella, L.; Herschhorn, A. Adjuvant-mediated enhancement of the immune response to HIV vaccines. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 3317–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, S.; Parthasarathy, D.; Picard, T.C.; Matyas, G.R.; Rao, M.; Herschhorn, A. Evaluating the Immune Response in Rabbits to an Escalating Dose of mRNA-Based HIV-1 Env Immunogens. Vaccines 2025, 13, 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111161
Ahmed S, Parthasarathy D, Picard TC, Matyas GR, Rao M, Herschhorn A. Evaluating the Immune Response in Rabbits to an Escalating Dose of mRNA-Based HIV-1 Env Immunogens. Vaccines. 2025; 13(11):1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111161
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Shamim, Durgadevi Parthasarathy, Tashina C. Picard, Gary R. Matyas, Mangala Rao, and Alon Herschhorn. 2025. "Evaluating the Immune Response in Rabbits to an Escalating Dose of mRNA-Based HIV-1 Env Immunogens" Vaccines 13, no. 11: 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111161
APA StyleAhmed, S., Parthasarathy, D., Picard, T. C., Matyas, G. R., Rao, M., & Herschhorn, A. (2025). Evaluating the Immune Response in Rabbits to an Escalating Dose of mRNA-Based HIV-1 Env Immunogens. Vaccines, 13(11), 1161. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines13111161





