Enhanced Immune Response Against Echinococcus Granulosus Through a CTLA-4/B7 Affinity-Based Vaccine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Obtaining the Acid Sequence, Signal Peptide, and Transmembrane Domains of Proteins
2.2. The Prediction of T-Cell Epitopes of Proteins
2.3. Prediction of Protein B-Cell Epitopes
2.4. Construction of the Multi-Epitope Vaccine CVE31-162
2.5. Prediction of Physicochemical Properties of Vaccine CVE31-162
2.6. Analysis Antigenicity and Allergenicity of Vaccine CVE31-162
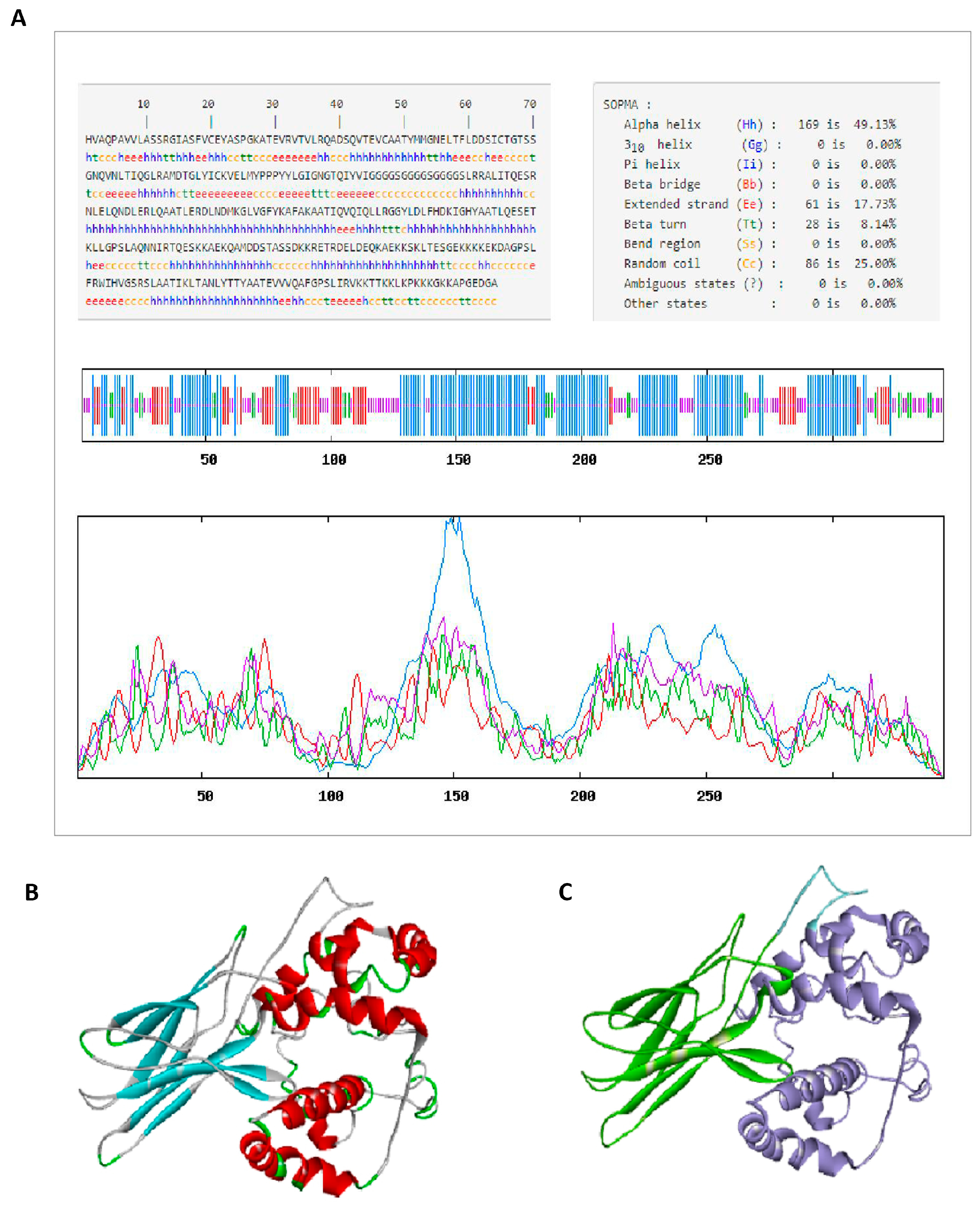
2.7. Secondary Structure Prediction of CVE31-162
2.8. The Prediction and Quality Validation of the Tertiary Structure of the Vaccine CVE31-162
2.9. Molecular Docking for CVE31-162 and B7
2.9.1. Acquirement of B7 Molecules
2.9.2. The Docking of Vaccine CVE31-162 with B7
2.10. Molecular Dynamics and Principal Component Analysis
2.11. Immune Simulation
2.12. In Vitro Experiment
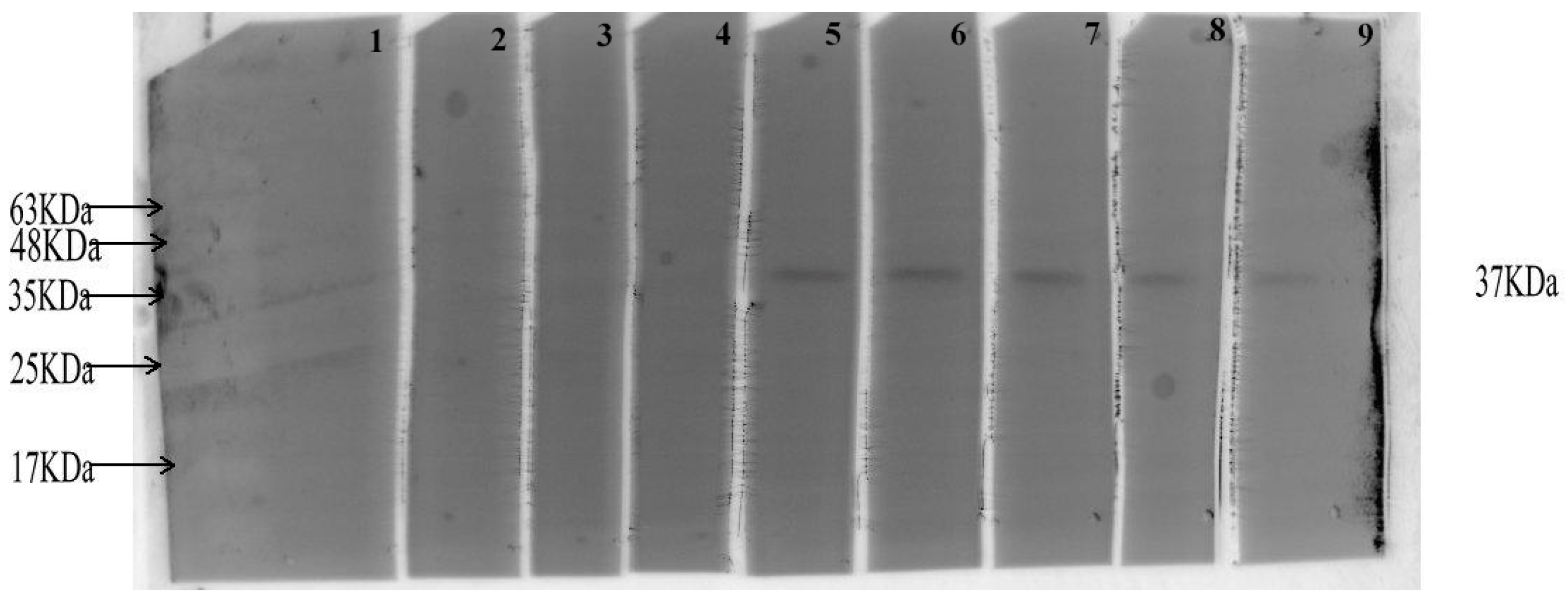
2.12.1. Detecting the Antigenicity of CVE31-162 by WB
2.12.2. Detecting the Immunogenicity of CVE31-162 by ELISA
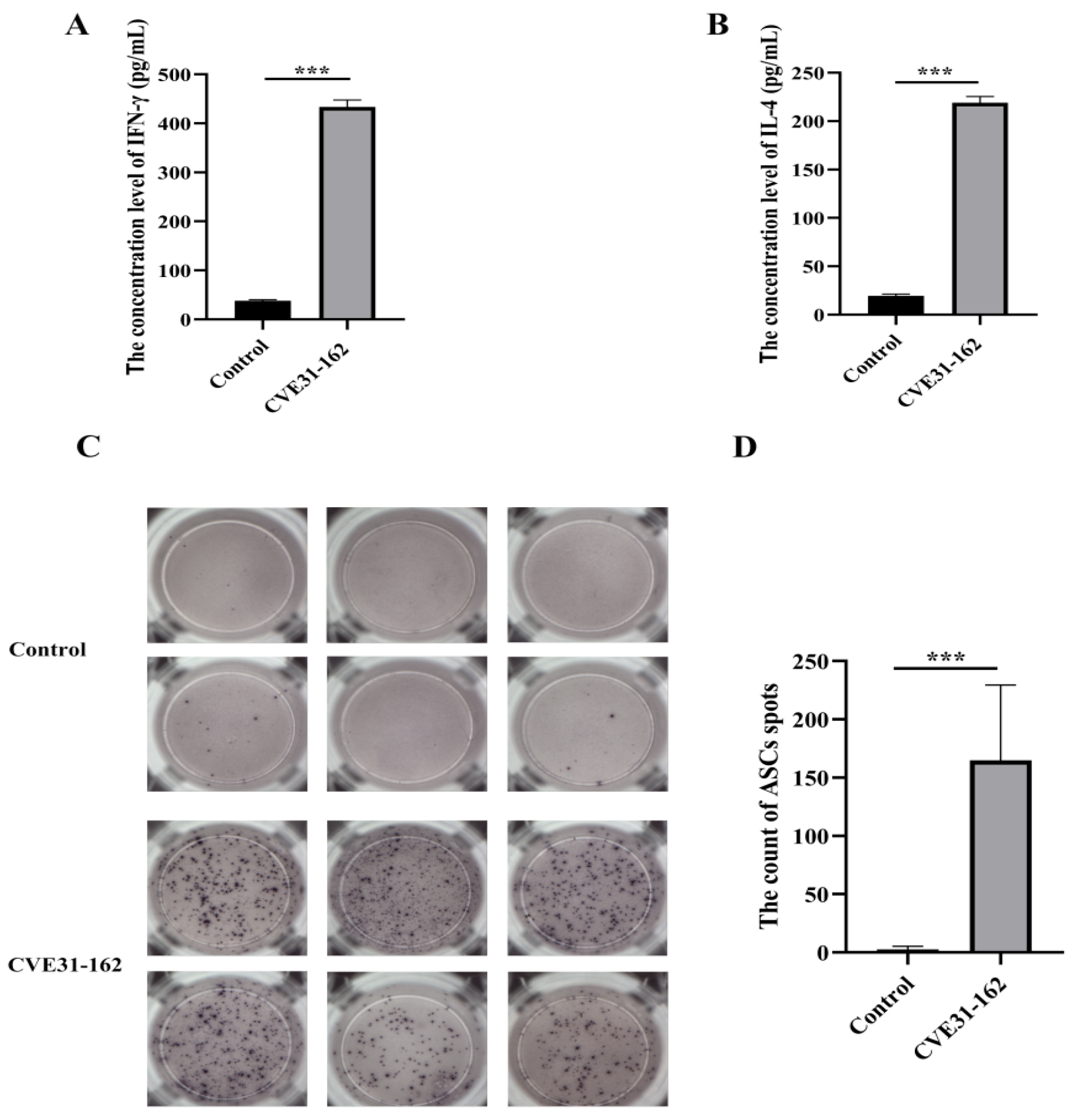
2.12.3. Detecting the Immunogenicity of CVE31-162 by ELISPOT
2.13. In Vivo Experiment
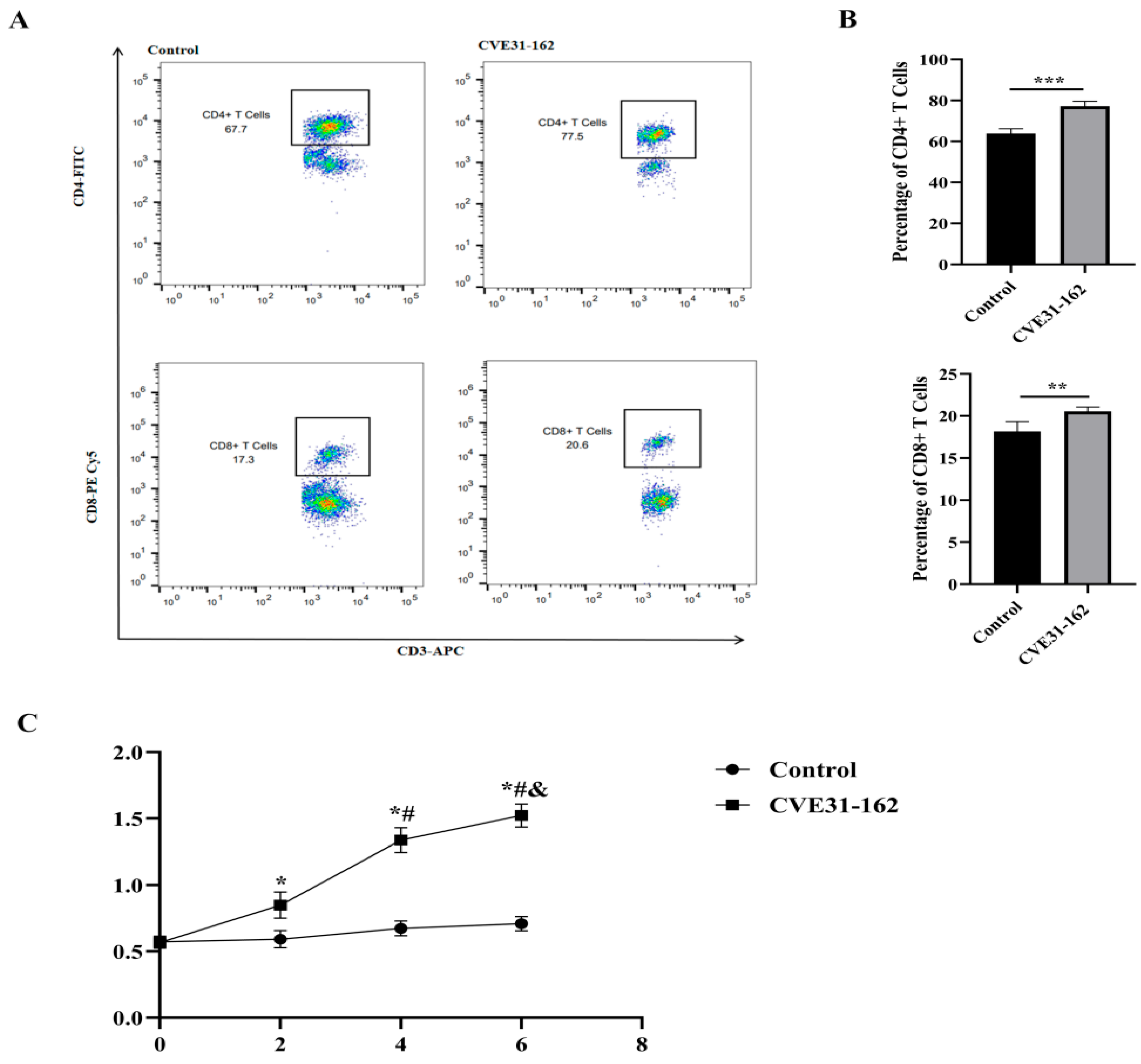
2.13.1. Analysis of Specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Levels by FCM
2.13.2. Analysis of the Specific Antibody Level by ELISA
2.13.3. Detection of the Macrophages Level in Spleen and Liver with FCM
2.13.4. Assessing the Uptake of CVE31-162 by Macrophages
2.13.5. Assessment of CVE31-162’s Potential Protective Effects
3. Results
3.1. Detection of EgA31 and EgG1Y162 by Bioinformatics Method
3.2. Prediction of Protein T-Cell and B-Cell Epitopes
3.3. Construction of CVE31-162
3.4. The Prediction of the Physicochemical Parameters and Structure of Vaccine CVE31-162
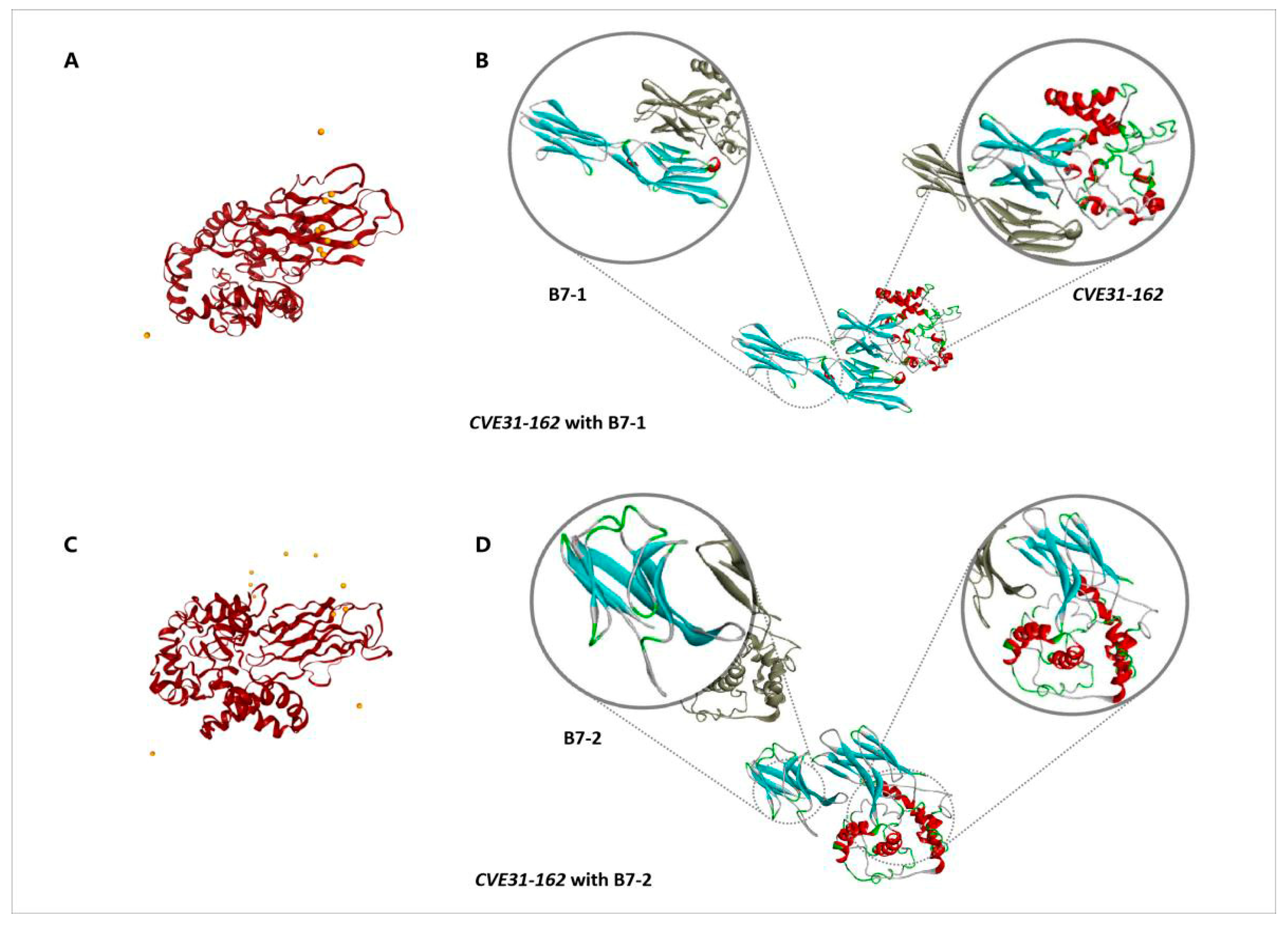
3.5. Molecular Docking for CVE31-162 and B7
3.5.1. Acquisition of B7-1 and B7-2 Molecules
3.5.2. The Docking of CVE31-162 with B7
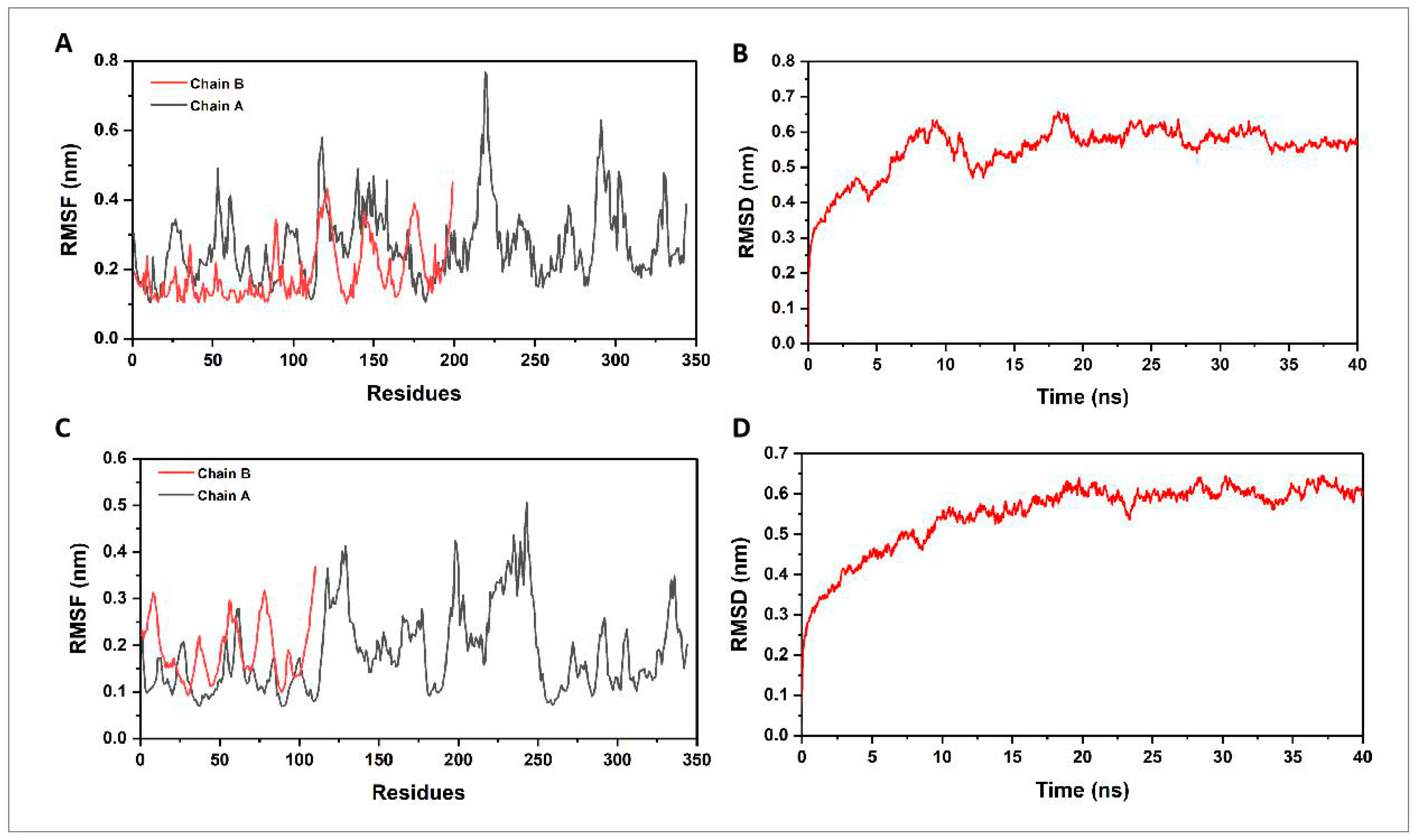
3.6. Molecular Dynamics Simulation and Principal Component Analysis
3.6.1. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.6.2. Principal Component Analysis
3.7. Immune Simulation
3.8. In Vitro Experiment
3.8.1. Detecting the Antigenicity of CVE31-162 by WB
3.8.2. Assessment of T-Cell Immune Response Induced by the Vaccine
3.8.3. Assessment of B-Cell Immune Response Induced by the Vaccine
3.9. In Vivo Experiment
3.9.1. Analysis of Specific CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Levels by FCM
3.9.2. Detection of the Specific Antibody
3.9.3. Detection of the Macrophages Level in Spleen and Liver with FCM
3.9.4. Assessing the Uptake of CVE31-162 by Macrophages
3.9.5. Evaluation of Potential Protective Effects of CVE31-162
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckert, J.; Deplazes, P. Biological, epidemiological, and clinical aspects of echinococcosis, a zoonosis of increasing concern. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 107–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez Rojas, C.A.; Romig, T.; Lightowlers, M.W. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes infecting humans--review of current knowledge. Int. J. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, R.C. Biology and Systematics of Echinococcus. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 65–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolsey, I.D.; Miller, A.L. Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato and Echinococcus multilocularis: A review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 135, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romig, T.; Deplazes, P.; Jenkins, D.; Giraudoux, P.; Massolo, A.; Craig, P.S.; Wassermann, M.; Takahashi, K.; de la Rue, M. Ecology and Life Cycle Patterns of Echinococcus Species. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 213–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, D.P.; Gray, D.J.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y. Diagnosis, treatment, and management of echinococcosis. BMJ 2012, 344, e3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilnathan, P.; Inamdar, S.; Nalankilli, V.P.; Vijay, A.; Rajapandian, S.; Parthsarathi, R.; Raj, P.; Palanivelu, C. Long-term results of hepatic hydatid disease managed using palanivelu hydatid system: Indian experience in tertiary center. Surg. Endosc. 2014, 28, 2832–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, E.; Kern, P.; Vuitton, D.A.; Writing Panel for the WHO-IWGE. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.; Menezes da Silva, A.; Akhan, O.; Mullhaupt, B.; Vizcaychipi, K.A.; Budke, C.; Vuitton, D.A. The Echinococcoses: Diagnosis, Clinical Management and Burden of Disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 259–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne-Odom, J.; Cozzi, G.D.; Franco, R.A.; Njei, B.; Tita, A.T.N. Treatment and prevention of viral hepatitis in pregnancy. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 226, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.Q.; Yan, H.B.; Li, L.; Jia, W.Z. Advances in research on vaccines against echinococcosis. Chin. J. Zoonoses 2019, 35, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- De Groot, A.S.; Moise, L.; Terry, F.; Gutierrez, A.H.; Hindocha, P.; Richard, G.; Hoft, D.F.; Ross, T.M.; Noe, A.R.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Better Epitope Discovery, Precision Immune Engineering, and Accelerated Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics Tools. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzon-Charry, A.; McPhun, V.; Kienzle, V.; Hirunpetcharat, C.; Engwerda, C.; McCarthy, J.; Good, M.F. Low doses of killed parasite in CpG elicit vigorous CD4+ T cell responses against blood-stage malaria in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2967–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Longhi, R.; Peri, C.; Colombo, G. Peptides for immunological purposes: Design, strategies and applications. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourseif, M.M.; Moghaddam, G.; Daghighkia, H.; Nematollahi, A.; Omidi, Y. A novel B-and helper T-cell epitopes-based prophylactic vaccine against Echinococcus granulosus. Bioimpacts 2018, 8, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, H.; Jia, H.Y.; Zhang, L.N.; Liu, X.X.; Ma, X.-M.; Wen, H.; Ding, J.-B. Bioinformatics prediction of egA31 recombinant antigen epitopes of Echinococcus granulosus. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 2012, 30, 78–80. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, C.B.; Ma, X.M.; Ding, J.B.; Jia, H.Y.; Mamuty, W.; Ma, H.M.; Wen, H. Cloning and sequence analysis of the egG1Y162 gene of Echinococcus granulosus. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 2009, 27, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Martinez, C.; Chalar, C.; Craig, P.S.; Ehrlich, R.; Petavy, A.F.; Bosquet, G. A new potent antigen from Echinococcus granulosus associated with muscles and tegument. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1999, 102, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Saint-Andre Marchal, I.; Marchal, T.; Bosquet, G.; Petavy, A.F. Cellular immune response of lymph nodes from dogs following the intradermal injection of a recombinant antigen corresponding to a 66 kDa protein of Echinococcus granulosus. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2000, 74, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Pang, N.; An, M.; Wang, H.; Ding, J.; et al. Immunization of mice with egG1Y162-1/2 provides protection against Echinococcus granulosus infection in BALB/c mice. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 94, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; An, M.; Li, Y.; Pang, N.; Ding, J. Bioinformatics analysis of EgA31 and EgG1Y162 proteins for designing a multi-epitope vaccine against Echinococcus granulosus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, J. Immmunoinformatics-based design of a multi-epitope vaccine with CTLA-4 extracellular domain to combat Helicobacter pylori. FASEB J. 2022, 36, e22252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linsley, P.S.; Clark, E.A.; Ledbetter, J.A. T-cell antigen CD28 mediates adhesion with B cells by interacting with activation antigen B7/BB-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5031–5035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, D.; Foley, S.F.; Hronowski, X.L.; Gu, S.; Meier, W. Discovery and investigation of O-xylosylation in engineered proteins containing a (GGGGS)n linker. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4805–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Guo, J.H.; Fan, M.W. The effect of antigen size on the immunogenicity of antigen presenting cell targeted DNA vaccine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2012, 12, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Shi, J.; Shang, K.; Tian, T.; Shi, H.; Ding, J.; Zhang, F. Design a novel of Brucellosis preventive vaccine based on IgV_CTLA-4 and multiple epitopes via immunoinformatics approach. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 195, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Evavold, B.D.; Zhu, C. Accumulation of dynamic catch bonds between TCR and agonist peptide-MHC triggers T cell signaling. Cell 2014, 157, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sha, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J. Design of a Novel Multi-Epitope Vaccine Against Echinococcus granulosus in Immunoinformatics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 668492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Olsson, N.; Wagar, L.E.; Fast, E.; Liu, C.L.; Muftuoglu, Y.; Sworder, B.J.; Diehn, M.; Levy, R.; et al. Predicting HLA class II antigen presentation through integrated deep learning. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, B.; Alvarez, B.; Paul, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.1 and NetMHCIIpan-4.0: Improved predictions of MHC antigen presentation by concurrent motif deconvolution and integration of MS MHC eluted ligand data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, A.M.; Palmer, N.; Aleman, F.; Chen, G.; Pla, A.; Jiang, N.; Chew, W.L.; Law, M.; Mali, P. Immune-orthogonal orthologues of AAV capsids and of Cas9 circumvent the immune response to the administration of gene therapy. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins 2006, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.H.; Sidney, J.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Sette, A. Development of an epitope conservancy analysis tool to facilitate the design of epitope-based diagnostics and vaccines. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Chu, Z.; Yu, F.; Zha, Y. Contriving Multi-Epitope Subunit of Vaccine for COVID-19: Immunoinformatics Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, T.J.; Jiang, C.; Yuan, J.Y.; Othman, Y.; Xie, X.Q.; Feng, Z.W. Differential performance of RoseTTAFold in antibody modeling. Brief. Bioinform. 2022, 23, bbac152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoffer, C.; Chen, S.; Bharadwaj, V.; Aderinwale, T.; Kumar, V.; Hormati, M.; Kihara, D. LZerD webserver for pairwise and multiple protein-protein docking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W359–W365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Jung, Y. Delfos: Deep learning model for prediction of solvation free energies in generic organic solvents. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 8306–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaston, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Polizzi, N.; Liu, L.; Wang, J.; DeGrado, W.F. X-ray Crystal Structure of the Influenza A M2 Proton Channel S31N Mutant in Two Conformational States: An Open and Shut Case. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11481–11488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, P.M.; Pallassana, N.; Bowden, R.; Cunningham, B.; Joy, A.; Kohn, J.; Babensee, J.E. Predicting biomaterial property-dendritic cell phenotype relationships from the multivariate analysis of responses to polymethacrylates. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1699–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, K.N.; Pfeffer, J. Using THz Spectroscopy, Evolutionary Network Analysis Methods, and MD Simulation to Map the Evolution of Allosteric Communication Pathways in c-Type Lysozymes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapin, N.; Lund, O.; Bernaschi, M.; Castiglione, F. Computational immunology meets bioinformatics: The use of prediction tools for molecular binding in the simulation of the immune system. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathollahi, M.; Fathollahi, A.; Motamedi, H.; Moradi, J.; Alvandi, A.; Abiri, R. In silico vaccine design and epitope mapping of New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM): An immunoinformatics approach. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.L.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, H.J.; Qian, T.T.; Qi, L.W.; Wang, X.R.; Zeng, Q.-Y. Subcellular Relocalization and Positive Selection Play Key Roles in the Retention of Duplicate Genes of Populus Class III Peroxidase Family. Plant Cell. 2014, 26, 2404–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-El, M.L.; Vankova, P.; Yeheskel, A.; Simhaev, L.; Engel, H.; Man, P.; Haitin, Y.; Giladi, M. Structural basis of heterotetrameric assembly and disease mutations in the human cis-prenyltransferase complex. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zhu, X.F.; Pu, Z.J.; Duan, Y.X.; Hao, L.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.-Q.; Jeon, C.O.; Xuan, Y.H. Integrative View of the Diversity and Evolution of SWEET and SemiSWEET Sugar Transporters. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, R.; Sahoo, P.; Mahapatra, S.R.; Dey, J.; Ghosh, M.; Kushwaha, G.S.; Misra, N.; Suar, M.; Raina, V.; Son, Y.-O. Development of a Conserved Chimeric Vaccine for Induction of Strong Immune Response against Staphylococcus aureus Using Immunoinformatics Approaches. Vaccines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neek, M.; Tucker, J.A.; Kim, T.I.; Molino, N.M.; Nelson, E.L.; Wang, S.W. Co-delivery of human cancer-testis antigens with adjuvant in protein nanoparticles induces higher cell-mediated immune responses. Biomaterials 2018, 156, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.R.; Dey, J.; Kushwaha, G.S.; Puhan, P.; Mohakud, N.K.; Panda, S.K.; Lata, S.; Misra, N.; Suar, M. Immunoinformatic approach employing modeling and simulation to design a novel vaccine construct targeting MDR efflux pumps to confer wide protection against typhoidal Salmonella serovars. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 11809–11821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadzadeh, R.; Soleimanpour, S.; Pishdadian, A.; Farsiani, H. Designing and development of epitope-based vaccines against Helicobacter pylori. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 48, 489–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, S.P.; De Moura Mattaraia, V.G.; Almeida, R.R.; Valentine, E.J.G.; Sales, N.S.; Ferreira, L.C.S.; Sa-Rocha, L.C.; Jacintho, L.C.; Santana, V.C.; Sidney, J.; et al. A promiscuous T cell epitope-based HIV vaccine providing redundant population coverage of the HLA class II elicits broad, polyfunctional T cell responses in nonhuman primates. Vaccine 2022, 40, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Guo, T.; Wang, T.; Zhen, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Cai, J.-P.; Mao, W.; Zhu, F.-M.; et al. HLA-B*07, HLA-DRB1*07, HLA-DRB1*12, and HLA-C*03:02 Strongly Associate With BMI: Data From 1.3 Million Healthy Chinese Adults. Diabetes 2018, 67, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, C. Capture and processing of exogenous antigens for presentation on MHC molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997, 15, 821–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudek, N.L.; Perlmutter, P.; Aguilar, M.I.; Croft, N.P.; Purcell, A.W. Epitope discovery and their use in peptide based vaccines. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 3149–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Sha, T.; Chen, Z.; Yu, M.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J. A Multi-Epitope Chitosan Nanoparticles Vaccine of Canine Against Echinococcus granulosus. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 910–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvizpour, S.; Pourseif, M.M.; Razmara, J.; Rafi, M.A.; Omidi, Y. Epitope-based vaccine design: A comprehensive overview of bioinformatics approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ding, J. Design of a Recombinant Multivalent Epitope Vaccine Based on SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants in Immunoinformatics Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 884433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, E.; Klinger, M.; Hou, Y.; Cummings, C.; Ribas, A.; Faham, M.; Fong, L. Improved survival with T cell clonotype stability after anti-CTLA-4 treatment in cancer patients. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 238ra270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Tang, F.; Liu, M.; Su, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, W.; Devenport, M.; Lazarski, C.A.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; et al. A reappraisal of CTLA-4 checkpoint blockade in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rostami-Rad, S.; Jafari, R.; Yousofi Darani, H. Th1/Th2-type cytokine profile in C57 black mice inoculated with live Echinococcus granulosus protoscolices. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottstein, B.; Soboslay, P.; Ortona, E.; Wang, J.; Siracusano, A.; Vuitton, D. Immunology of Alveolar and Cystic Echinococcosis (AE and CE). Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.; Zmolek, A.; Irvine, D.J. Beyond antigens and adjuvants: Formulating future vaccines. J. Clin. Investig 2016, 126, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Category | Software | Protein EgA31 | Protein EgG1Y162 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | Amino Acid Core Sequence | Position | Amino Acid Core Sequence | ||
| T-cell | IEDB | 200–222 | LRRALITQESRNLELQNDLERLQ | 25–35 | FRWIHVGSRSL |
| NetMHCIIpan | 580–599 | LERDLNDMKGLVGFYKAFAK | 52–56 | IKLTANLYTTY | |
| 263–285 | IQVQIQLLRGGYLDLFHDKIGHY | 89–95 | EVVVQAF | ||
| 289–297 | LQESETKLL | ||||
| B-cell | IEDB | 20–29 | AQNNIRTQES | 3–5 | IRV |
| ABCpred | 171–184 | AEKQAMDDSTASSD | 19–20 | TT | |
| 233–235 | RETRDELDEQKAE | 82–84 | LKP | ||
| 399–406 | SKLTESGE | 96–97 | KG | ||
| 492–497 | KKEKDA | 112–118 | APGEDGA | ||
| GOAP Score | GOAP Rank | DFIRE Score | DFIRE Rank | ITScore Score | ITScore Rank | Ranksum Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B7-1 | −45,146.97 | 64 | −40,241.33 | 73 | −21,234.99 | 134 | 271 |
| B7-2 | −29,058.07 | 76 | −33,083.35 | 712 | −17,371.30 | 154 | 942 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; He, Y.; Yin, Z.; Chen, N.; Qi, X.; Ding, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, F. Enhanced Immune Response Against Echinococcus Granulosus Through a CTLA-4/B7 Affinity-Based Vaccine. Vaccines 2024, 12, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121440
Zhu Y, He Y, Yin Z, Chen N, Qi X, Ding J, Li Y, Zhang F. Enhanced Immune Response Against Echinococcus Granulosus Through a CTLA-4/B7 Affinity-Based Vaccine. Vaccines. 2024; 12(12):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121440
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yuejie, Yueyue He, Ziyue Yin, Na Chen, Xingxing Qi, Jianbing Ding, Yujiao Li, and Fengbo Zhang. 2024. "Enhanced Immune Response Against Echinococcus Granulosus Through a CTLA-4/B7 Affinity-Based Vaccine" Vaccines 12, no. 12: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121440
APA StyleZhu, Y., He, Y., Yin, Z., Chen, N., Qi, X., Ding, J., Li, Y., & Zhang, F. (2024). Enhanced Immune Response Against Echinococcus Granulosus Through a CTLA-4/B7 Affinity-Based Vaccine. Vaccines, 12(12), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines12121440






