Using Tourist Diver Photos to Assess the Effects of Marine Heatwaves on Central Red Sea Coral Reefs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Image Surveys
| Region | Country | # Sites | # Survey Dives | Latitudinal Range | Longitudinal Range | Dates Visited |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thuwal | KSA | 7 | 25 | 22°18′–22°26′ N | 38°47′–39°00′ E | 2023: summer–fall 2024: winter–summer |
| Yanbu | KSA | 6 | 9 | 23°06′–24°09′ N | 37°50′–38°02′ E | 2023: summer 2024: spring–summer |
| Qunfudah * | KSA | 2 | 2 | 18°55′–19°15′ N | 40°43′–41°00′ E | 2024: summer only |
| Jeddah * | KSA | 6 | 10 | 21°43′–22°00′ N | 38°49′–39°03′ E | 2024: summer only |
| Rabigh | KSA | 2 | 2 | 22°55′–22°57′ N | 38°05′–38°51′ E | 2024: summer only |
| Marsa Nakari | Egypt | 4 | 4 | 24°51′–24°57′ N | 34°57′–35°08′ E | 2024: summer only |
| Wadi Lahami | Egypt | 7 | 8 | 24°11′–24°15′ N | 35°25′–35°35′ E | 2024: summer only |
| Metric | Value | Notes/Details |
|---|---|---|
| # images taken for informal “tourist diver” analysis | 7173 | |
| # images used in tourist diver CoralNet analysis | 7000 | 173 images failed quality control |
| # images used for initial CoralNet AI training | 450 | Scored 13,500 features manually |
| CoralNet-calculated classification accuracy (%) | 81–83% | See “Classifier Overview” for details |
| # images for post-hoc accuracy verification | 150 | Scored 4500 features manually |
| Manually calculated classification accuracy (%) | 87 ± 9.4% | |
| # images for assessment of FPR and FNR | 150 | Scored 4500 features manually |
| Total # images scored manually for CoralNet training | 750 | |
| Total # images classified automatically by CoralNet | 6250 | |
| Total # features scored by CoralNet | 187,500 | |
| Total # features scored by human and CoralNet | 210,000 | |
| # coral colonies scored for assessment of FPR and FNR | 769 | |
| Overall accuracy of coral bleaching analysis (%) | 90.3% | |
| Bleaching classification FPR (%) | 2.2% | |
| Bleaching classification FNR (%) | 12.6% |
2.2. CoralNet AI Training

3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CoralNet Training
3.2. Temperature Comparison
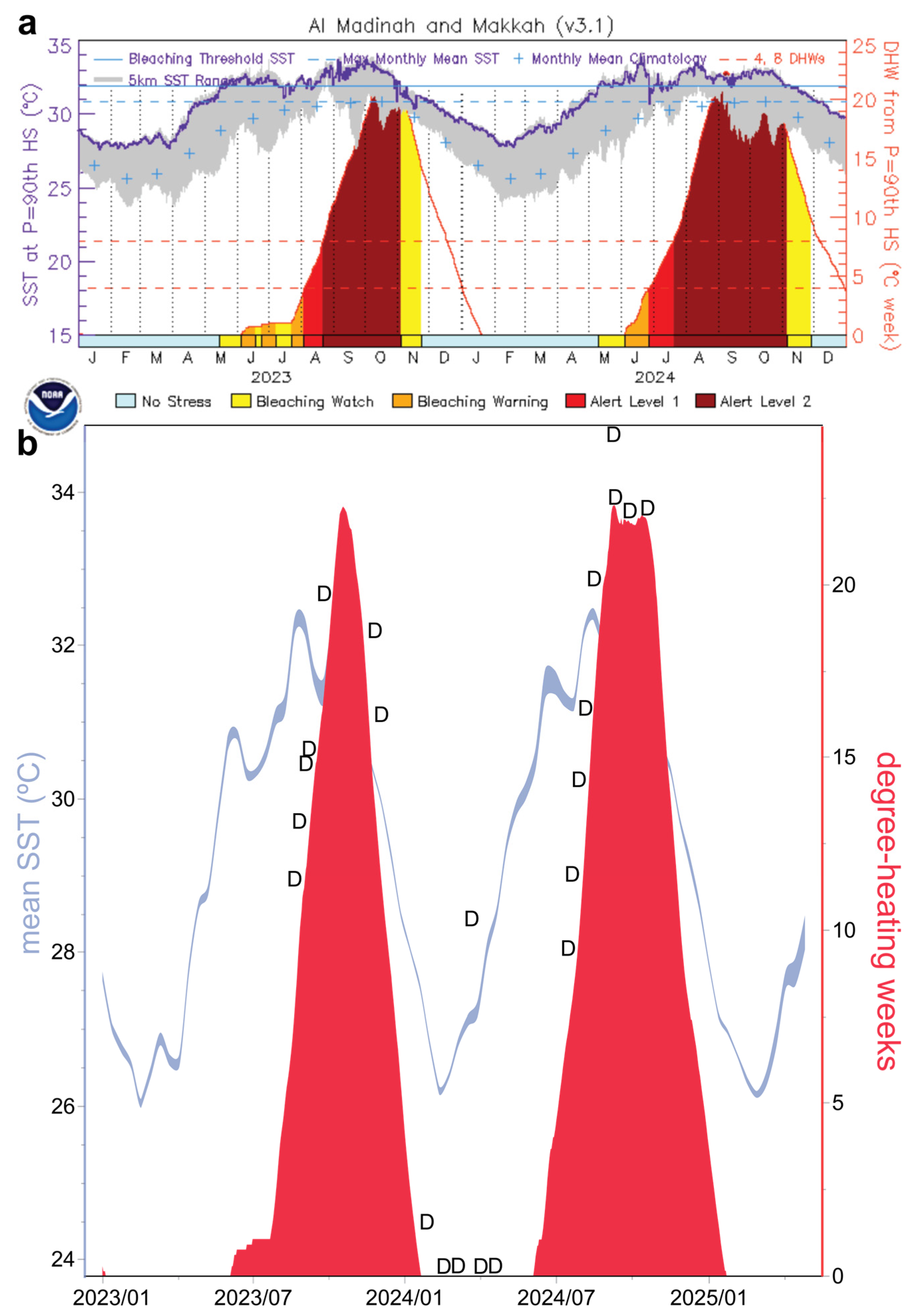

3.3. Coral Cover and Bleaching Dynamics (2023–2024): Thuwal, Saudi Arabia
3.4. Coral Cover and Bleaching Dynamics (2023–2024): Yanbu, Saudi Arabia
3.5. 2024 Coral Bleaching: Remaining Saudi Arabian Sites


| Region, Country | % Healthy (Total) Cover 2023 (Pooled) | % Bleaching Summer 2023 & | % Healthy + (Total) Cover Summer 2024 | % of All Coral Tissues Bleached-Summer 2024 * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thuwal, KSA | 11.2 (17.2) | 34.9–37.6 | 6.0 c (13.6) | 53.9–56.0 |
| Yanbu, KSA | 17.1 (26.1) | 34.0–34.5 | 12.3 b (16.1) | 23.6–25.8 |
| Qunfudah, KSA | NA | NA | 14.7 a (16.5) | 11.1–15.3 |
| Jeddah, KSA | NA | NA | 13.8 a (21.6) | 35.6–36.4 |
| Rabigh, KSA | NA | NA | 8.8 b (23.6) | 62.6–64.8 |
| Marsa Nakari, Egypt | NA | NA | 9.4 b (21.4) | 56.0–57.4 |
| Wadi Lahami, Egypt | NA | NA | 9.2 b (22.1) | 58.4–59.3 |
3.6. Coral Bleaching 2024: Egyptian Sites

4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| DHW | Degree-heating weeks |
| FNR | False-negative rate |
| FPR | False-positive rate |
| SST | Sea surface temperatures |
References
- Hughes, T.P.; Kerry, J.T.; Álvarez-Noriega, M.; Álvarez-Romero, J.G.; Anderson, K.D.; Baird, A.H.; Babcock, R.C.; Beger, M.; Bellwood, D.R.; Berkelmans, R.; et al. Global Warming and Recurrent Mass Bleaching of Corals. Nature 2017, 543, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, J.D.; Peixoto, R.S.; Davies, S.W.; Traylor-Knowles, N.; Short, M.L.; Cabral-Tena, R.A.; Burt, J.A.; Pessoa, I.; Banaszak, A.T.; Winters, R.S.; et al. The Fourth Global Coral Bleaching Event: Where Do We Go from Here? Coral Reefs 2024, 43, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Heron, S.F.; Eakin, C.M.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Vega-Rodriguez, M.; Guild, L.S.; Cour, J.L.; Geiger, E.F.; Skirving, W.J.; Burgess, T.F.R.; et al. Reef-Scale Thermal Stress Monitoring of Coral Ecosystems: New 5-Km Global Products from NOAA Coral Reef Watch. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 11579–11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.B.; Dempsey, A.C.; Chen, C.S. Predicting the Abundance of Corals from Simple Environmental Predictors with a Machine-Learning Approach. Platax 2022, 19, 43–57. [Google Scholar]
- Head, C.E.I.; Bayley, D.T.I.; Rowlands, G.; Roche, R.C.; Tickler, D.M.; Rogers, A.D.; Koldewey, H.; Turner, J.R.; Andradi-Brown, D.A. Coral Bleaching Impacts from Back-to-Back 2015–2016 Thermal Anomalies in the Remote Central Indian Ocean. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, C.J.; Vergés, A.; Poore, A.G.B. A New Resource for Monitoring Reef Ecosystems: The Background of Recreational Diver Photographs Contains Valuable Habitat Data. J. Appl. Ecol. 2023, 60, 2688–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.J.; Kleine, D.A.; Dean, A.J. CoralWatch: Education, Monitoring, and Sustainability through Citizen Science. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licuanan, W.Y.; Mordeno, P.Z.B.; Go, M.V. C30—A Simple, Rapid, Scientifically Valid, and Low-Cost Method for Citizen-Scientists to Monitor Coral Reefs. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Helber, S.B.; Rohde, S.; de Goeij, J.M.; Schupp, P.J. Coral Reef Benthic Community Changes in the Anthropocene: Biogeographic Heterogeneity, Overlooked Configurations, and Methodology. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1956–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.L.; Chartrand, K.M.; Roelfsema, C.M.; Kolluru, A.; Mumby, P.J. Broadscale Reconnaissance of Coral Reefs from Citizen Science and Deep Learning. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Done, T.; Roelfsema, C.; Harvey, A.; Schuller, L.; Hill, J.; Schläppy, M.-L.; Lea, A.; Bauer-Civiello, A.; Loder, J. Reliability and Utility of Citizen Science Reef Monitoring Data Collected by Reef Check Australia, 2002–2015. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 117, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branchini, S.; Pensa, F.; Neri, P.; Tonucci, B.M.; Mattielli, L.; Collavo, A.; Sillingardi, M.E.; Piccinetti, C.; Zaccanti, F.; Goffredo, S. Using a Citizen Science Program to Monitor Coral Reef Biodiversity through Space and Time. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 24, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obura, D.O.; Aeby, G.; Amornthammarong, N.; Appeltans, W.; Bax, N.; Bishop, J.; Brainard, R.E.; Chan, S.; Fletcher, P.; Gordon, T.A.C.; et al. Coral Reef Monitoring, Reef Assessment Technologies, and Ecosystem-Based Management. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters, G.; Holzman, R.; Blekhman, A.; Beer, S.; Loya, Y. Photographic Assessment of Coral Chlorophyll Contents: Implications for Ecophysiological Studies and Coral Monitoring. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2009, 380, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebeck, U.; Marshall, N.; Klüter, A.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Monitoring Coral Bleaching Using a Colour Reference Card. Coral Reefs 2006, 25, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, R.; Dempsey, A.C.; Lubarsky, K.; Akao, I.; Faisal, M.; Purkis, S. Global Reef Expedition: Solomon Islands. Final Report; Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation: Tire Hill, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Beijbom, O.; Edmunds, P.J.; Roelfsema, C.; Smith, J.; Kline, D.I.; Neal, B.P.; Dunlap, M.J.; Moriarty, V.; Fan, T.-Y.; Tan, C.-J.; et al. Towards Automated Annotation of Benthic Survey Images: Variability of Human Experts and Operational Modes of Automation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Hoteit, I. Rapid Red Sea Deep Water Renewals Caused by Volcanic Eruptions and the North Atlantic Oscillation. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCarlo, T.M.; Carvalho, S.; Gajdzik, L.; Hardenstine, R.S.; Tanabe, L.K.; Villalobos, R.; Berumen, M.L. Patterns, Drivers, and Ecological Implications of Upwelling in Coral Reef Habitats of the Southern Red Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2021, 126, e2020JC016493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.B.; Chan, P.H.; Putnam, H.M.; Chen, C.S.; Fan, T.Y. The Effects of a Variable Temperature Regime on the Physiology of the Reef-Building Coral Seriatopora Hystrix: Results from a Laboratory-Based Reciprocal Transplant. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 4183–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeby, G.S.; Shore, A.; Jensen, T.; Ziegler, M.; Work, T.; Voolstra, C.R. A Comparative Baseline of Coral Disease in Three Regions along the Saudi Arabian Coast of the Central Red Sea. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, A.F.; Tietbohl, M.D.; Nuber, C.; Berumen, M.; Jones, B.H. Fish-Mediated Nutrient Flows from Macroalgae Habitats to Coral Reefs in the Red Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 185, 105884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, A.W.; Dempsey, A.C. The Status, Threats, and Resilience of Reef-Building Corals of the Saudi Arabian Red Sea. In The Red Sea: The Formation, Morphology, Oceanography and Environment of a Young Ocean Basin; Rasul, N.M.A., Stewart, I.C.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 471–486. ISBN 978-3-662-45201-1. [Google Scholar]
- Riegl, B.M.; Bruckner, A.W.; Rowlands, G.P.; Purkis, S.J.; Renaud, P. Red Sea Coral Reef Trajectories over 2 Decades Suggest Increasing Community Homogenization and Decline in Coral Size. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, M.D.; Cohen, A.L.; Rotjan, R.D.; Mangubhai, S.; Sandin, S.A.; Smith, J.E.; Thorrold, S.R.; Dissly, L.; Mollica, N.R.; Obura, D. Increasing Coral Reef Resilience through Successive Marine Heatwaves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL094128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, K.; Daraghmeh, N.; Lozano-Cortés, D.; Benzoni, F.; Berumen, M.L.; Carvalho, S. Differential Spatio-Temporal Responses of Red Sea Coral Reef Benthic Communities to a Mass Bleaching Event. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeVantier, L.; Pilcher, N. The Status of Coral Reefs in Saudi Arabia. In Status of Coral Reefs of the World; Australian Institute of Marine Science: Townsville, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner, A.W. Habitat Mapping and Characterization of Coral Reefs of the Saudi Arabian Red Sea: 2006–2009; Final Report Part II, Ras Qisbah, Al Wajh, Yanbu, Farasan Banks and Farasan Islands; Panoramic Press: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dosoky, Y.A.; Ahmed, M.I.; Madkour, F.F.; Hanafy, M.H. Coral Bleaching Occurrence along the Egyptian Coast of the Red Sea during the Summer Heat Stress Period, 2020. Egypt J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2021, 25, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghallab, A.; Hussein, H.N.M.; Madkour, H.; Osman, A.; Mahdy, A. Status of Coral Reefs along the Egyptian Red Sea Coast. In Coral Reefs and Associated Marine Fauna Around the Arabian Peninsula; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; ISBN 978-1-003-32139-2. [Google Scholar]
- Moldrizio, S. Annual Report of RSDS Reef Monitoring Programme. Reef Check. 2012. Available online: https://www.redsea-divingsafari.com/downloads/eco-article/988ed-Reef_Check_Annual_Report_2012.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Sharaka, T.M.A. Scientific Review for the Coral Reef Bleaching Event (2023) along the Egyptian Coast of The Red Sea. Ministry (sp.) Environment Report. 2024. Available online: https://icriforum.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Scientific-Review-for-the-Coral-Reef-Bleaching-Event-2023-along-the-Egyptian-Coast-of-The-Red-Sea.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Furby, K.A.; Bouwmeester, J.; Berumen, M.L. Susceptibility of Central Red Sea Corals during a Major Bleaching Event. Coral Reefs 2013, 32, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, M.; Gildor, H.; Genin, A. A Coral Reef Refuge in the Red Sea. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 3640–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-J.; Heinle, M.J.; Al-Musabeh, A.; Gopalan, J.; Vasanthi, T.D.; Panickan, P.; Hamade, T.; Pulido, B.; Joydas, T.V.; Shepherd, B. Coral Reefs in the Northeastern Saudi Arabian Red Sea Are Resilient to Mass Coral Mortality Events. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, E.O.; Smith, D.J.; Ziegler, M.; Kürten, B.; Conrad, C.; El-Haddad, K.M.; Voolstra, C.R.; Suggett, D.J. Thermal Refugia against Coral Bleaching throughout the Northern Red Sea. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, e474–e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Region | County | # of Photos | % Total Coral Cover ± Std. Dev. | % Healthy Coral Cover ± Std. Dev. | Mean % Bleaching & |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thuwal | Saudi Arabia | 2567 | 16.1 ± 15.2 b | 10.2 ± 12.3 II* | 36.6–37.1 B |
| Yanbu | Saudi Arabia | 1036 | 20.3 ± 15.7 a | 14.3 ± 12.7 I* | 29.5–29.7 C |
| Qunfudah | Saudi Arabia | 210 | 16.5 ± 16.2 b | 14.7 ± 15.6 I | 11.1–15.3 D |
| Jeddah | Saudi Arabia | 1160 | 21.6 ± 16.8 a | 13.8 ± 13.9 I | 35.6–36.4 B |
| Rabigh | Saudi Arabia | 173 | 23.6 ± 16.4 a | 8.8 ± 11.9 II | 62.6–64.8 A |
| Marsa Nakari | Egypt | 674 | 21.4 ± 15.0 a | 9.4 ± 10.3 II | 56.0–57.4 A |
| Wadi Lahami | Egypt | 1180 | 22.1 ± 15.8 a | 9.2 ± 10.3 II | 58.5–59.3 A |
| Mean | 20.2 ± 2.9% | 11.5 ± 2.6% | 42.8–43.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mayfield, A.B. Using Tourist Diver Photos to Assess the Effects of Marine Heatwaves on Central Red Sea Coral Reefs. Environments 2025, 12, 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12070248
Mayfield AB. Using Tourist Diver Photos to Assess the Effects of Marine Heatwaves on Central Red Sea Coral Reefs. Environments. 2025; 12(7):248. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12070248
Chicago/Turabian StyleMayfield, Anderson B. 2025. "Using Tourist Diver Photos to Assess the Effects of Marine Heatwaves on Central Red Sea Coral Reefs" Environments 12, no. 7: 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12070248
APA StyleMayfield, A. B. (2025). Using Tourist Diver Photos to Assess the Effects of Marine Heatwaves on Central Red Sea Coral Reefs. Environments, 12(7), 248. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12070248






