Crosstalk Between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Meat Quality
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
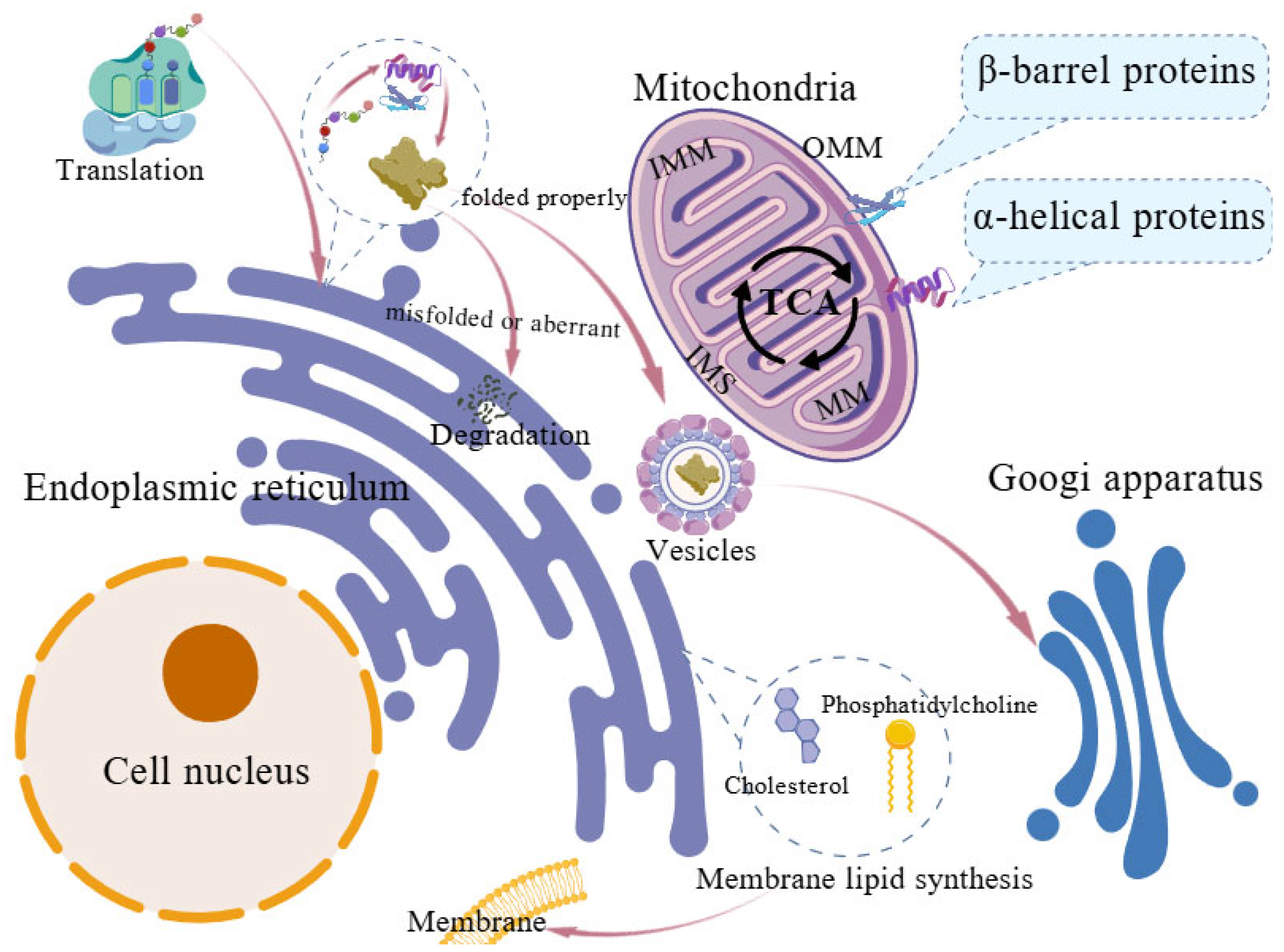
1.1. Structure and Basic Function of Mitochondria and Endoplasmic Reticulum
1.2. Functional Crosstalk Between Mitochondria and ER
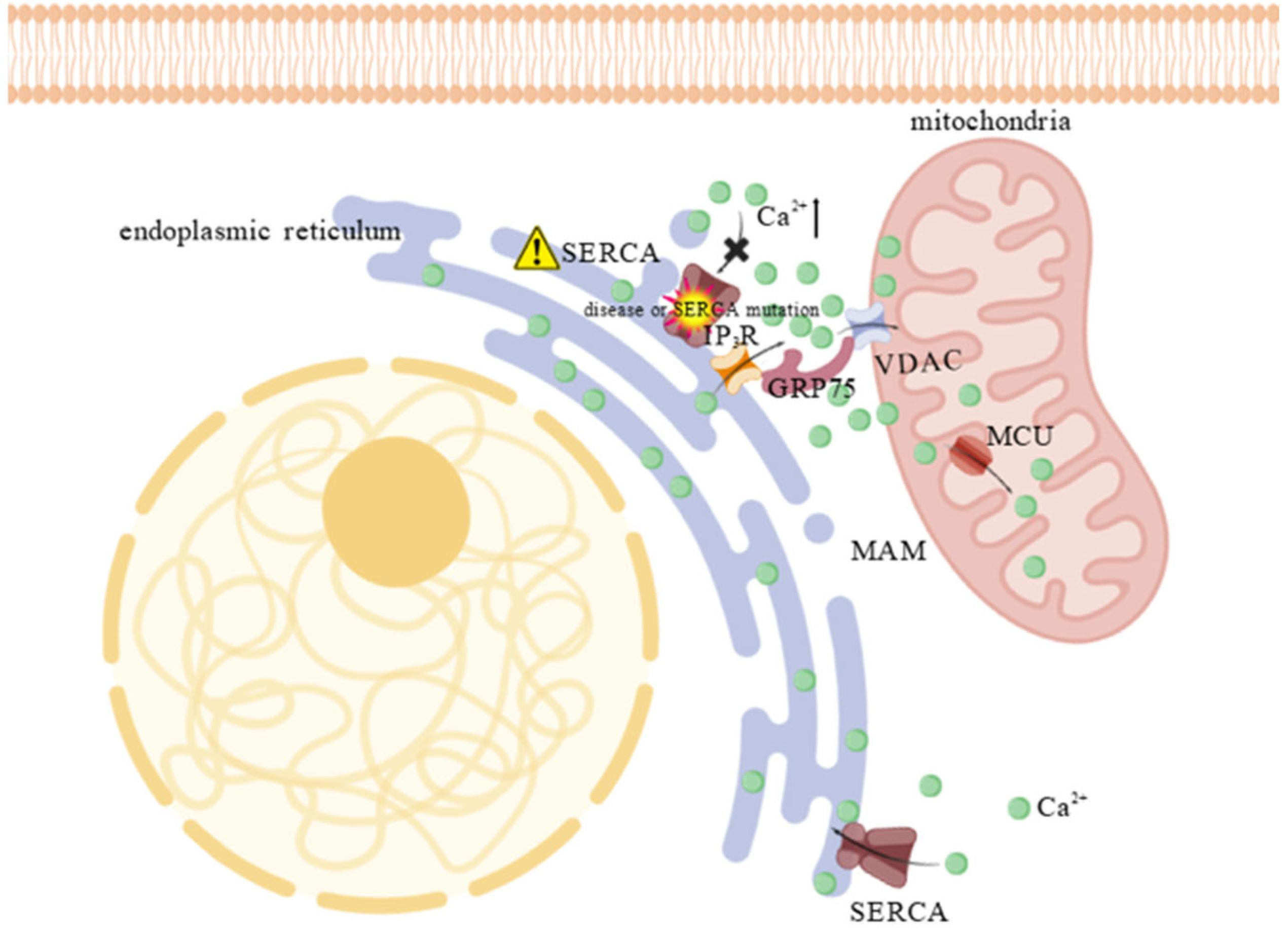
1.2.1. ER-Mitochondrial System and Calcium Transport
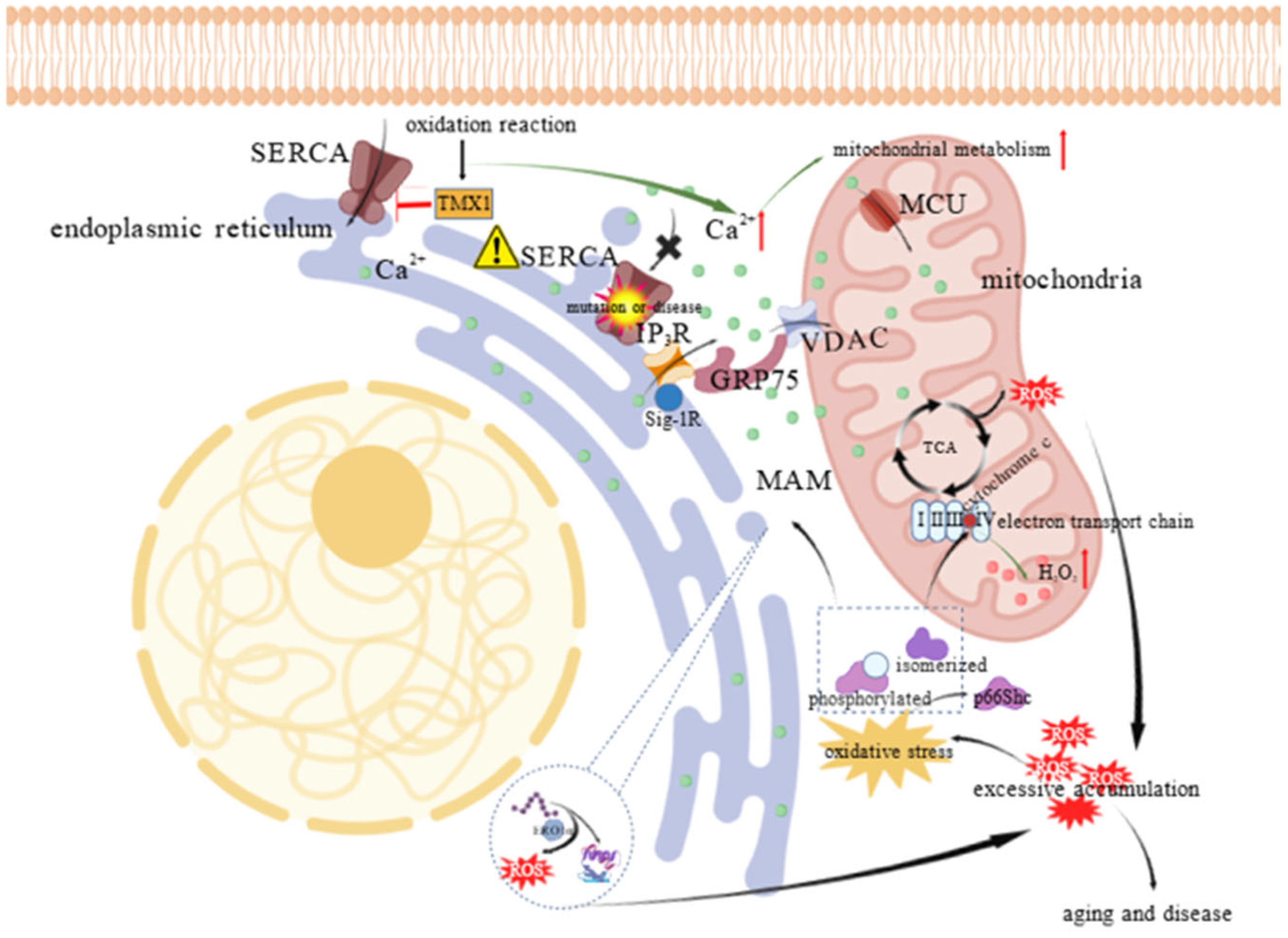
1.2.2. Redox, Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and ER-Mitochondrial System
1.2.3. Stress Responses and Cell Death
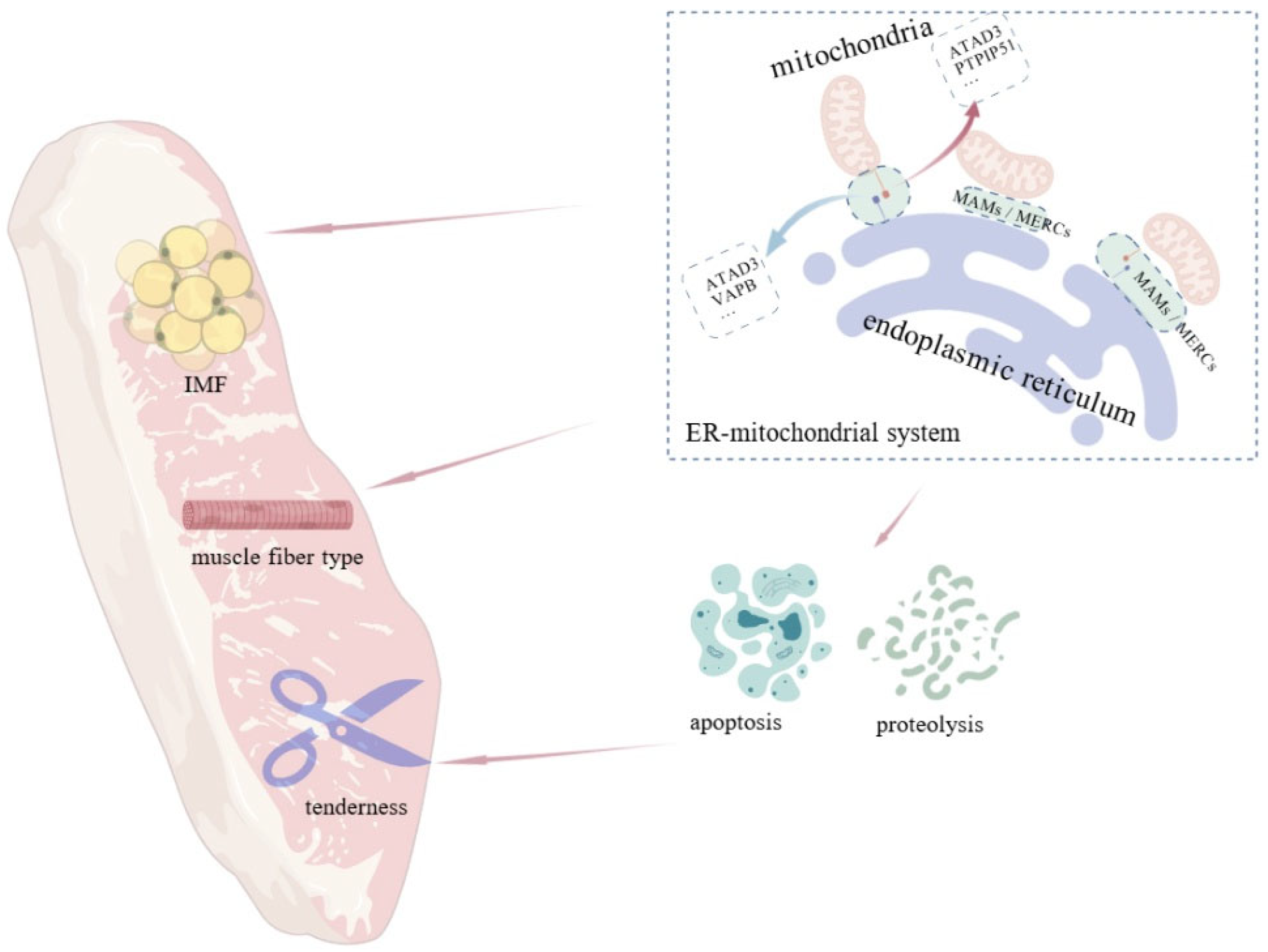
2. Investigation and Application of the ER–Mitochondrial System in Meat Quality
2.1. Intramuscular Fat Content
2.2. Muscle Fiber Type
2.3. Tenderness
2.3.1. The Effects and Mechanisms of the ER–Mitochondrial System on Apoptosis
2.3.2. The Effects and Mechanisms of the ER-Mitochondrial System on Muscle Proteolysis
3. Conclusions and Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| OMM | outer mitochondrial membrane |
| IMM | inner mitochondrial membrane |
| MM | mitochondrial matrix |
| IMS | IMS |
| IBM | inner boundary membrane |
| TCA | tricarboxylic acid |
| MAMs | mitochondria-associated membranes |
| MERCs | mitochondria- endoplasmic reticulum contacts |
| ERS | endoplasmic reticulum stress |
| AAA | ATPase family ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities |
| ATAD3 | ATPase family AAA domain-containing protein 3 |
| VAPB | vesicle-associated membrane protein B |
| PTPIP51 | tyrosine phosphatase-interacting protein–51 |
| SERCA | sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium–ATPase |
| VDACs | voltage–dependent anion channels |
| MCU | mitochondrial calcium uniporter |
| IP3R | inositol 1,4,5–trisphosphate receptors |
| GRP75 | glucose–regulated protein 75 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TMX1 | thioredoxin–related transmembrane proteins 1 |
| Sig–1R | Sigma–1 receptor |
| 4-HNE | 4–hydroxynonenal |
| RIPK1 | receptor–interacting protein kinase 1 |
| RIPK3 | receptor–interacting protein kinase 3 |
| MLKL | mixed lineage kinase domain–like protein |
| PINK1 | phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced kinase 1 |
| CPT1C | palmitoyltransferase 1C |
| DFF45 | DNA fragmentation factor 45 |
| CIDEB | cell death–inducing DNA fragmentation factor 45–like effector b |
| AMPK | AMP–activated protein kinase |
| ACC | Acetyl–CoA Carboxylase |
| miR–148a–3p | microRNA–148a–3p |
| Phosphorylated Acetyl–CoA Carboxylase | p–ACC |
| SIRT1 | silent mating information regulation 2 homolog 1 |
| UPR | unfolded protein response |
| IR | insulin–resistant |
| FFA | free fatty acid |
| lncRNAs | long noncoding RNAs |
| miRNAs | microRNAs |
| PDK4 | pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 |
| JNK | c–Jun N–terminal kinase |
| PGC–1α | PPARγ coactivator 1-alpha |
| MyHC I | myosin heavy chain type I |
| RyRs | ryanodine receptors |
| CaMKK2 | calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase 2 |
| MDFI | MyoD family inhibitor |
| MPTPs | mitochondrial permeability transition pores |
| PERK | protein kinase R–like ER kinase |
| ATF6 | activating transcription factor 6 |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
References
- Harrington, J.S.; Ryter, S.W.; Plataki, M.; Price, D.R.; Choi, A.M.K. Mitochondria in health, disease, and aging. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 2349–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, P.; Galland, R.; Chevrollier, A. Super-resolution microscopies, technological breakthrough to decipher mitochondrial structure and dynamic. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 159, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikstrom, M.; Pecorilla, C.; Sharma, V. The mitochondrial respiratory chain. Enzymes 2023, 54, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suomalainen, A.; Nunnari, J. Mitochondria at the crossroads of health and disease. Cell 2024, 187, 2601–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celik, C.; Lee, S.Y.T.; Yap, W.S.; Thibault, G. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and lipids in health and diseases. Prog. Lipid Res. 2023, 89, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, R.L.; Mesgarzadeh, J.S.; Hendershot, L.M. Reshaping endoplasmic reticulum quality control through the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 1477–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscia, S.M.; Thompson, C.P.; Tang, Q.; Baltrusaitis, E.E.; Rhodenhiser, J.A.; Quintero-Carmona, O.A.; Lakadamyali, M.; Holzbaur, E.L.F. Myo19 tethers mitochondria to endoplasmic reticulum-associated actin to promote mitochondrial fission. J. Cell Sci. 2023, 136, jcs260612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, P.; Schiavon, C.; Cicero, J.; Manor, U.; Germain, M. Mitochondria- and ER-associated actin are required for mitochondrial fusion. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Sheng, R. The correlation between mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes (MAMs) and Ca2+ transport in the pathogenesis of diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2025, 46, 271–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordás, G.; Weaver, D.; Hajnóczky, G. Endoplasmic Reticulum-Mitochondrial Contactology: Structure and Signaling Functions. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirokova, O.M.; Pchelin, P.V.; Mukhina, I.V. MERCs. The Novel Assistant to Neurotransmission? Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 589319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Gang, X.K.; He, G.Y.; Liu, Y.J.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, G.X. The Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane-Induced Insulin Resistance. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 592129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyamurthy, V.H.; Nagarajan, Y.; Parvathi, V.D. Mitochondria-Endoplasmic Reticulum Contact Sites (MERCS): A New Axis in Neuronal Degeneration and Regeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 6528–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Min, K.T. The Interface Between ER and Mitochondria: Molecular Compositions and Functions. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudier, J. ATAD3 proteins: Brokers of a mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum connection in mammalian cells. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 827–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mórotz, G.M.; Martín-Guerrero, S.M.; Markovinovic, A.; Paillusson, S.; Russell, M.R.G.; Machado, P.M.P.; Fleck, R.A.; Noble, W.; Miller, C.C.J. The PTPIP51 coiled-coil domain is important in VAPB binding, formation of ER-mitochondria contacts and IP3 receptor delivery of Ca2+ to mitochondria. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 920947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Wen, Y.J.; Dong, J.; Cao, C.C.; Yuan, S.Q. Systematic In-Depth Proteomic Analysis of Mitochondria-Associated Endoplasmic Reticulum Membranes in Mouse and Human Testes. Proteomics 2018, 18, 1700478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E. Phospholipid synthesis in a membrane fraction associated with mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7248–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzuto, R.; Pinton, P.; Carrington, W.; Fay, F.S.; Fogarty, K.E.; Lifshitz, L.M.; Tuft, R.A.; Pozzan, T. Close contacts with the endoplasmic reticulum as determinants of mitochondrial Ca2+ responses. Science 1998, 280, 1763–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csordas, G.; Thomas, A.P.; Hajnoczky, G. Quasi-synaptic calcium signal transmission between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Murata, Y.; Oka, Y.; Oiwa, K.; Horiuchi, M.; Iguchi, Y.; Komine, O.; Sobue, A.; Katsuno, M.; Ogi, T.; et al. Mitochondria- associated membrane collapse impairs TBK1-mediated proteostatic stress response in ALS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2315347120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.E.; Sowers, J.R.; Hetz, C.; Ren, J. Cell death regulation by MAMs: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications in cardiovascular diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flis, V.V.; Daum, G. Lipid Transport between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a013235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, L.; Sharma, K.; Dodi, L.D.; Rieder, L.S.; Fallier-Becker, P.; Casadei, N.; Fitzgerald, J.C. Miro1 R272Q disrupts mitochondrial calcium handling and neurotransmitter uptake in dopaminergic neurons. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 966209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.J.; Ran, Y.Q.; Xie, H.J.; Deng, L.; Li, C.F.; Ling, C. Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-Transporting ATPase (SERCA) Modulates Autophagic, Inflammatory, and Mitochondrial Responses during Influenza A Virus Infection in Human Lung Cells. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e00217-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, F.H.; Pang, N.; Kessi, M.; Xiong, J.; Chen, S.M.; Peng, J.; Yang, L.; Yin, F. Restoration of Sarco/Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+-ATPase Activity Functions as a Pivotal Therapeutic Target of Anti-Glutamate-Induced Excitotoxicity to Attenuate Endoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Depletion. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 877175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, R.P.; Sickmann, A.; Boehm, A.M.; Winkler, C.; Zufall, N.; Schonfisch, B.; Guiard, B.; Pfanner, N.; Meisinger, C. Proteomic analysis of the yeast mitochondrial outer membrane reveals accumulation of a subclass of preproteins. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 1436–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varughese, J.T.; Buchanan, S.K.; Pitt, A.S. The Role of Voltage-Dependent Anion Channel in Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Human Disease. Cells 2021, 10, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, M.P.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhu, J.J.; Tan, R.; Zhao, J.; Ji, X.Y.; Jin, C.; Jia, Y.F.; Ren, T.T.; et al. MCU-induced mitochondrial calcium uptake promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and colorectal cancer growth. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.C.; Zhou, L.; Jin, Y.J.; Wu, D.L.; Chen, N.; Zhang, C.C.; Liu, H.P.; Li, C.L.; Ning, R.; Yang, X.C.; et al. Calcium bridges built by mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes: Potential targets for neural repair in neurological diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2025, 20, 3349–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atakpa-Adaji, P.; Ivanova, A. IP3R at ER-Mitochondrial Contact Sites: Beyond the IP3R-GRP75-VDAC1 Ca2+ Funnel. Contact 2023, 6, 25152564231181020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Guan, N.; Ren, Y.L.; Wei, Q.J.; Tao, Y.H.; Yang, G.S.; Liu, X.Y.; Bu, D.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, S.N. IP3R-Grp75-VDAC1-MCU calcium regulation axis antagonists protect podocytes from apoptosis and decrease proteinuria in an Adriamycin nephropathy rat model. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.P.; Wang, J.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Yan, Z.Z.; et al. ARTC1-mediated VAPB ADP-ribosylation regulates calcium homeostasis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 15, mjad043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennicke, C.; Cochemé, H.M. Redox metabolism: ROS as specific molecular regulators of cell signaling and function. Mol. Cell 2021, 81, 3691–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.M.; Banik, B.K.; Borah, P.; Jain, A. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Key Components in Cancer Therapies. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, P.; Sarada, D.; Ramkumar, K.M. Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress: Focus on protein disulfide isomerase and endoplasmic reticulum oxidase 1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 892, 173749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.H.; Shan, W.J.; Wan, F.; Luo, J.Y.; Niu, Y.Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.U.; Xu, N.H.; Xie, W.D. Canagliflozin Delays Aging of HUVECs Induced by Palmitic Acid via the ROS/p38/JNK Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, B.R.; Chen, Y.T.; Jia, Z.; Yuan, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.A. Multifunctional mesoporous nanoselenium delivery of metformin breaks the vicious cycle of neuroinflammation and ROS, promotes microglia regulation and alleviates Alzheimer’s disease. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2025, 245, 114300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y. Introducing Thioredoxin-Related Transmembrane Proteins: Emerging Roles of Human TMX and Clinical Implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2022, 36, 984–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.Y.; Yu, X.T.; Zhao, S.; Zhong, X.; Huang, D.; Feng, R.Y.; Li, P.; Fang, Z.Y.; Hu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.T.; et al. SIRT6 deficiency in endothelial cells exacerbates oxidative stress by enhancing HIF1α accumulation and H3K9 acetylation at the Ero1α promoter. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebiedzinska-Arciszewska, M.; Pakula, B.; Bonora, M.; Missiroli, S.; Potes, Y.; Jakubek-Olszewska, P.; Simoes, I.C.M.; Pinton, P.; Wieckowski, M.R. Distribution of the p66Shc Adaptor Protein Among Mitochondrial and Mitochondria-Associated Membranes Fractions in Normal and Oxidative Stress Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebiedzinska-Arciszewska, M.; Oparka, M.; Vega-Naredo, I.; Karkucinska-Wieckowska, A.; Pinton, P.; Duszynski, J.; Wieckowski, M.R. The interplay between p66Shc, reactive oxygen species and cancer cell metabolism. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.X.; Ran, Q.; Qu, C.; Hu, S.; Cui, S.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, B.; Yang, B. Sigma-1 receptor activation attenuates DOX-induced cardiotoxicity by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial calcium overload via PERK and IP3R-VDAC1-MCU signaling pathways. Biol. Direct 2025, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, C.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.M.; Peng, Z.Y. ROS-induced lipid peroxidation modulates cell death outcome: Mechanisms behind apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Guan, Z.; Gao, Y.Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhan, X.Y.; Ji, X.Y.; Xu, J.; Zhou, H.M.; Rao, Z.Q. ER stress promotes mitochondrial calcium overload and activates the ROS/NLRP3 axis to mediate fatty liver ischemic injury. Hepatol. Commun. 2024, 8, e0399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, J.; Area-Gomez, E. Lipidome changes due to accumulation of cholesterol via APP-C99 alters neuronal permeability. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2021, 17 (Suppl. S3), e051164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, A.J.; Chong, K.L.; Gatei, M.; Zou, D.X.; Stewart, R.; Withey, S.; Wolvetang, E.; Parton, R.G.; Brown, A.D.; Kastan, M.B.; et al. Impaired endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondrial signaling in ataxia-telangiectasia. iScience 2021, 24, 101972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, M.; Ahmad, R.; Tantry, I.Q.; Ahmad, W.; Siddiqui, S.; Alam, M.; Abbas, K.; Hassan, M.I.; Habib, S.; Islam, S. Apoptosis: A Comprehensive Overview of Signaling Pathways, Morphological Changes, and Physiological Significance and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2024, 13, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Z.; Yao, S.J.; Yang, H.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, Y.J. Autophagy: Regulator of cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcy, M.S. Cell death: A review of the major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol. Int. 2019, 43, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, K.; Strasser, A.; Kayagaki, N.; Dixit, V.M. Cell death. Cell 2024, 187, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawen, A. Apoptosis-an introduction. Bioessays 2003, 25, 888–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klionsky, D.J. Autophagy. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R282–R283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Meng, L.; Xu, T.; Su, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL-dependent necrosis promotes the aging of mouse male reproductive system. Elife 2017, 6, e27692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.M.; Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Zhang, C.; Huang, L.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, H.; Zhu, J. CIDEB promotes lipid deposition in goat intramuscular adipocytes. Anim. Biosci. 2025, 38, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Wang, H.; Duan, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, R. Identifying the Potential Apoptotic Metabolites in Postmortem Beef Muscle by Targeted Metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 11111–11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Cao, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, X. FNIP1: A key regulator of mitochondrial function. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 117146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.X.; Li, N.N.; Huang, R.L.; Jia, F.J.; He, Z.Y.; Han, W.L.; Liu, W.Z.; Li, S.Q.; Wang, W.Y.; Ren, W.Y.; et al. PINK1 link mitochondria-ER contacts controls deposition of intramuscular fat in pigs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2025, 759, 151672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Li, X.J.; Yang, W. Mitochondrial-Dependent and Independent Functions of PINK1. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10, 954536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, C.A.; Kitada, T.; Shen, J. Loss of PINK1 causes mitochondrial functional defects and increased sensitivity to oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 11364–11369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Ran, D.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.G.; Song, R.L.; Gao, Y.S.; Liu, Z.P. Role of mitochondrial dysfunction and PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in Cd-induced hepatic lipid accumulation in chicken embryos. Life Sci. 2021, 284, 119906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Chen, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Xu, H. Differential regulatory roles of microRNAs during intramuscular adipogenesis in Chinese Guizhou Congjiang Xiang pigs. Epigenetics 2022, 17, 1800–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; He, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Yue, B.; Zhang, M.; Chai, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhong, J.; et al. Functional study and epigenetic targets analyses of SIRT1 in intramuscular preadipocytes via ChIP-seq and mRNA-seq. Epigenetics 2023, 18, 2135194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Haynes, C.M. Mitochondrial dysfunction in cancer: Potential roles of ATF5 and the mitochondrial UPR. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 47, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Q.; Lee, P.R.; Yang, Q.; Moore, A.Z.; Landman, B.A.; Resnick, S.M.; Ferrucci, L. The mediation roles of intermuscular fat and inflammation in muscle mitochondrial associations with cognition and mobility. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, D.; Li, M.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Luo, Y.; Yan, H.; Zheng, P. Dihydromyricetin improves meat quality and promotes skeletal muscle fiber type transformations via AMPK signaling in growing-finishing pigs. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 3649–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.C.; Wang, M.E.; Jiang, Y.F.; Liu, H.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiu, C.H. Long-term feeding of high-fat plus high-fructose diet induces isolated impaired glucose tolerance and skeletal muscle insulin resistance in miniature pigs. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2017, 9, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Liu, T.; Yousuf, S.; Zhang, X.; Huang, W.; Li, A.; Xie, L.; Miao, X. Identification and analysis of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA related to subcutaneous and intramuscular fat in Laiwu pigs. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1081460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, S.N.; Watt, M.J.; Montgomery, M.K. Inter-organelle Communication in the Pathogenesis of Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Insulin Resistance. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2020, 20, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoudam, T.; Ha, C.M.; Leem, J.; Chanda, D.; Park, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, Y.K.; Liangpunsakul, S.; Huh, Y.H.; et al. PDK4 Augments ER-Mitochondria Contact to Dampen Skeletal Muscle Insulin Signaling During Obesity. Diabetes 2019, 68, 571–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Lu, X.-M.; Tuo, X.; Liu, J.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-C.; Song, L.-N.; Cheng, Z.-Q.; Yang, J.-K.; Xin, Z. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial function to preserve skeletal muscle lipid metabolism. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Hung, P.-J.; Wei, Y.-H. Disruption of mitochondria-associated ER membranes impairs insulin sensitivity and thermogenic function of adipocytes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 965523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Kong, X.; Li, F. Serine-to-glycine ratios in low-protein diets regulate intramuscular fat by affecting lipid metabolism and myofiber type transition in the skeletal muscle of growing-finishing pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hu, H.; Liang, X.; Liang, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, X. Gut microbes-muscle axis in muscle function and meat quality. Sci. China Life Sci. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Song, S.; Cheng, H.; Im, C.; Jung, E.Y.; Moon, S.S.; Choi, J.; Hur, S.J.; Joo, S.T.; Kim, G.D. Comparison of Meat Quality and Muscle Fiber Characteristics between Porcine Skeletal Muscles with Different Architectures. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 874–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, K.; Huo, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, G.; Xu, Q. Fiber characteristics and meat quality of different muscular tissues from slow- and fast-growing broilers. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, W.; Zhang, L.; Lin, S. Molecular mechanisms underlying the impact of muscle fiber types on meat quality in livestock and poultry. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1284551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Chen, S.; Zeng, Z.; Xing, S.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, P.; et al. Effects of Cold Exposure on Performance and Skeletal Muscle Fiber in Weaned Piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Hou, L.; Chen, H.; Zuo, B.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, J. Skeletal Muscle-Specific Overexpression of PGC-1alpha Induces Fiber-Type Conversion through Enhanced Mitochondrial Respiration and Fatty Acid Oxidation in Mice and Pigs. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1152–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.; Mo, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Hu, C.Y.; Wang, C. MDFI regulates fast-to-slow muscle fiber type transformation via the calcium signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 671, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, A.; Jollet, M.; Britto, F.A.; Goustard, B.; Bendridi, N.; Rieusset, J.; Ollendorff, V.; Favier, F.B. Endurance exercise decreases protein synthesis and ER-mitochondria contacts in mouse skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 127, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieblas, B.; Pérez-Treviño, P.; García, N. Role of mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes in insulin sensitivity, energy metabolism, and contraction of skeletal muscle. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 959844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltin, C.; Balcerzak, D.; Tilley, R.; Delday, M. Determinants of meat quality: Tenderness. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiang, C.; Roy, B.C.; Bruce, H.L.; Blecker, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Huang, C. Apoptosis and its role in postmortem meat tenderness: A comprehensive review. Meat Sci. 2025, 219, 109652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Han, L.; Yu, Q.; Zhao, S.; Ma, J. Effect of mitochondrial cytochrome c release and its redox state on the mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic cascade reaction and tenderization of yak meat during postmortem aging. Food Res. Int. 2018, 111, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, X.; Yan, N.; Wang, Y.; Jia, M.; Feng, X.; Chen, L. Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways regulate tenderness of post-mortem chicken muscle. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Ding, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, B.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C. Contribution of mitochondria to postmortem muscle tenderization: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J.A.; Zhang, Z.; Svetlov, S.I.; Hayes, R.L.; Wang, K.K.; Larner, S.F. Calpain and caspase processing of caspase-12 contribute to the ER stress-induced cell death pathway in differentiated PC12 cells. Apoptosis 2010, 15, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiang, S.; Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, J.; Feng, X. Endoplasmic reticulum stress improved chicken tenderness, promoted apoptosis and autophagy during postmortem ageing. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2024, 13, 2141–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, L.; Zhu, X.; Guo, X.; Deng, X.; Zhang, J. The effect of caspase-3 in mitochondrial apoptosis activation on degradation of structure proteins of Esox lucius during postmortem storage. Food Chem. 2022, 367, 130767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xie, Y.; Tang, C.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Zhou, H.; Xu, B. New perspective for Calpain-Mediated regulation of meat Quality: Unveiling the impact on mitochondrial pathway apoptosis in post-mortem. Food Chem. 2024, 441, 138287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Mason, S.L.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. Role of calpain system in meat tenderness: A review. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2018, 7, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Huang, F.; Ma, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Preliminary study on the effect of caspase-6 and calpain inhibitors on postmortem proteolysis of myofibrillar proteins in chicken breast muscle. Meat Sci. 2012, 90, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chang, R.; Trivedi, M.; Capetanaki, Y.; Cryns, V.L. Caspase proteolysis of desmin produces a dominant-negative inhibitor of intermediate filaments and promotes apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6848–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koohmaraie, M. Biochemical factors regulating the toughening and tenderization processes of meat. Meat Sci. 1996, 43 (Suppl. S1), 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, V.; Olivan, M. Role of mitochondria on muscle cell death and meat tenderization. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2013, 7, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Ma, G.; Guo, Z.; Yu, Q.; Han, L.; Han, M.; Zhu, Y. Study on the apoptosis mediated by apoptosis-inducing-factor and influencing factors of bovine muscle during postmortem aging. Food Chem. 2018, 266, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ojangba, T.; Nan, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Q. Effects of iron-catalyzed oxidation and methemoglobin oxidation systems on endogenous enzyme activity and myofibrillar protein degradation in yak meat. Food Chem. 2023, 404, 134647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Feng, X.C.; Lu, F.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; Li, Q.Y.; Guo, X.Y. Effects of camptothecin, etoposide and Ca2+ on caspase-3 activity and myofibrillar disruption of chicken during postmortem ageing. Meat Sci. 2011, 87, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.S.; Buhler, J.F.; Davis, H.T.; Thornton, K.J.; Scheffler, T.L.; Matarneh, S.K. Inhibition of mitochondrial calcium uniporter enhances postmortem proteolysis and tenderness in beef cattle. Meat Sci. 2020, 162, 108039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Ge, W. Mechanisms of Mitochondrial Apoptosis-Mediated Meat Tenderization Based on Quantitative Phosphoproteomic Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, W.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Miao, L.; Zhou, X. Crosstalk Between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Meat Quality. Animals 2025, 15, 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233465
Peng W, Guo Y, Wu X, Miao L, Zhou X. Crosstalk Between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Meat Quality. Animals. 2025; 15(23):3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233465
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Wenjin, Yiting Guo, Xiaolin Wu, Liuteng Miao, and Xihong Zhou. 2025. "Crosstalk Between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Meat Quality" Animals 15, no. 23: 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233465
APA StylePeng, W., Guo, Y., Wu, X., Miao, L., & Zhou, X. (2025). Crosstalk Between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle: Implications for Meat Quality. Animals, 15(23), 3465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15233465





