Cluster of Dominant Species and Grazing Jointly Influence the Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Alpine Grasslands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Situation of the Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Selection of Soil Microbial Functional Genes and Nutrient Indicators
2.4. Determination of Soil Microbial Functional Genes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
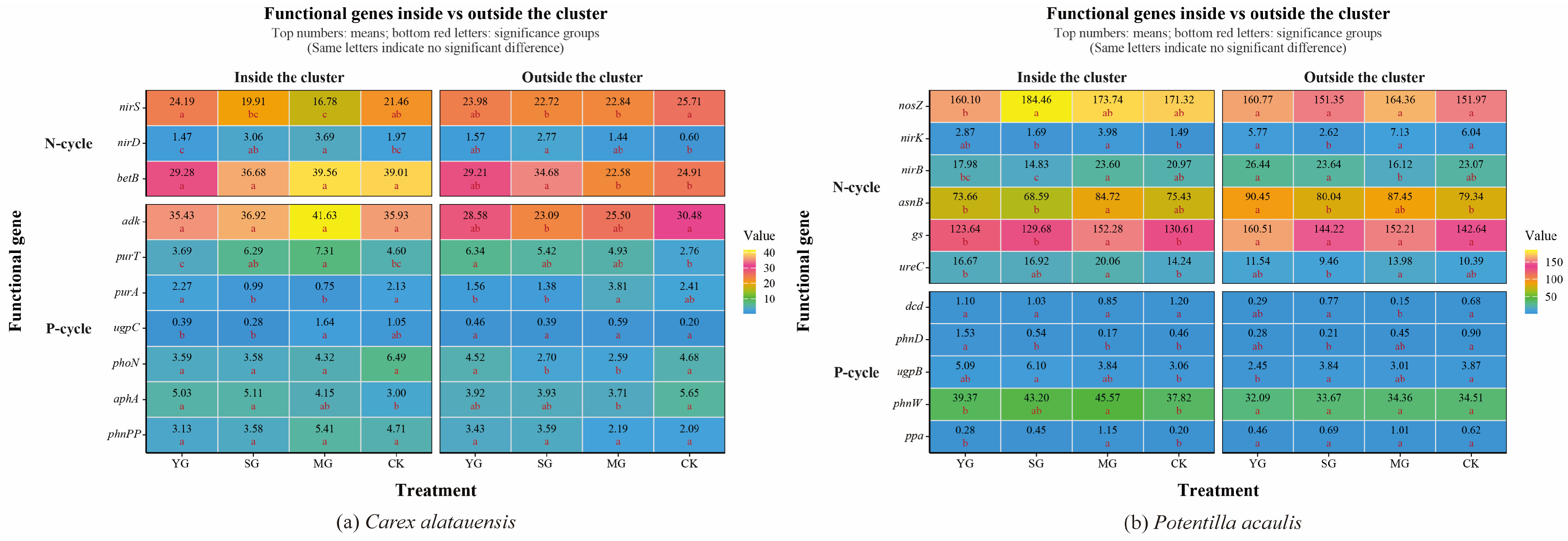
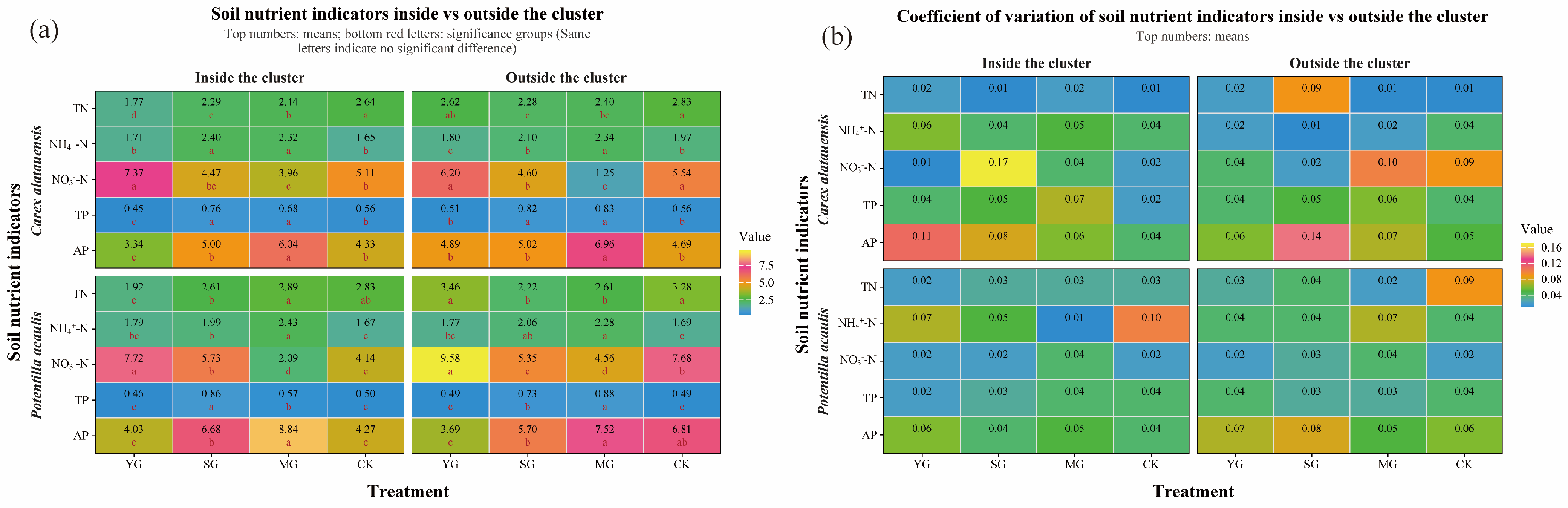
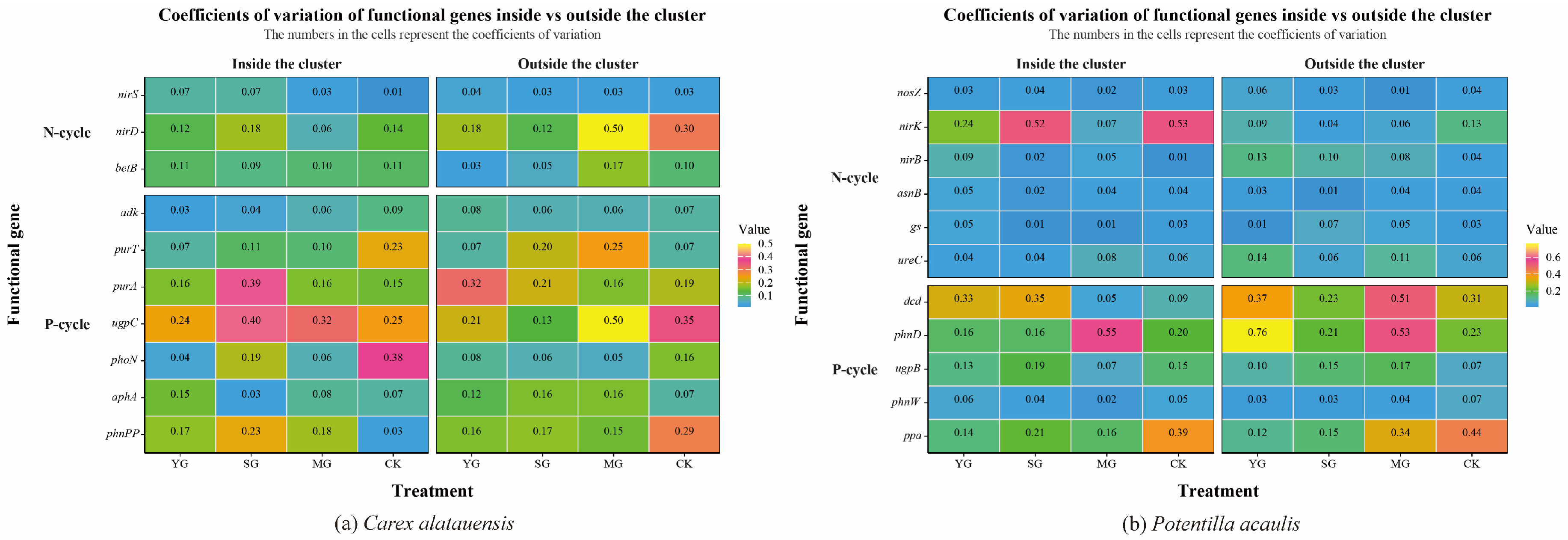
3.1. Overall Effects of and Spatial Variations in Grazing on Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling Genes and Nutrients
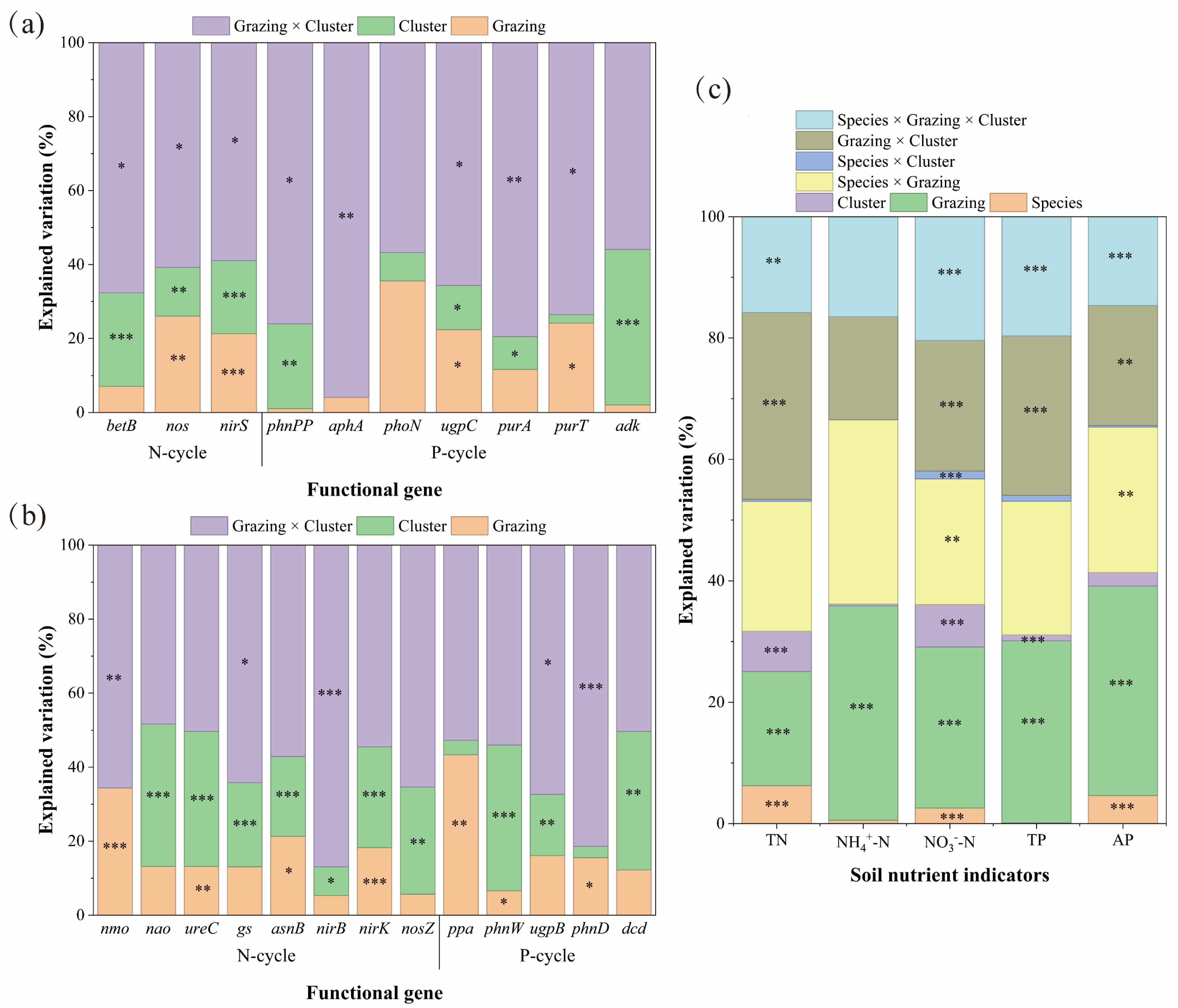
3.2. Regulatory Mechanisms of Grazing, Species, and Clusters on Functional Genes and Nutrient Indicators
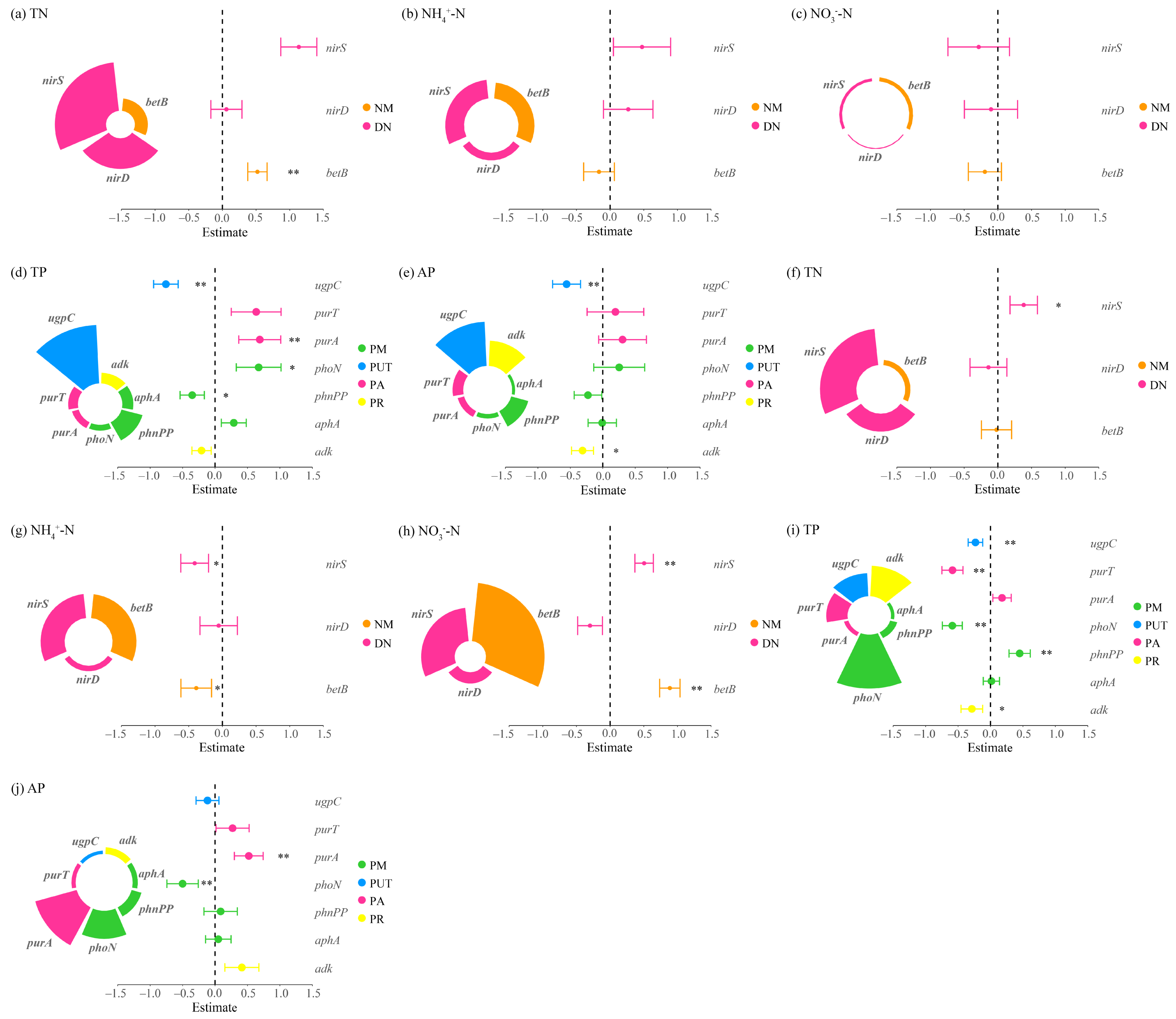
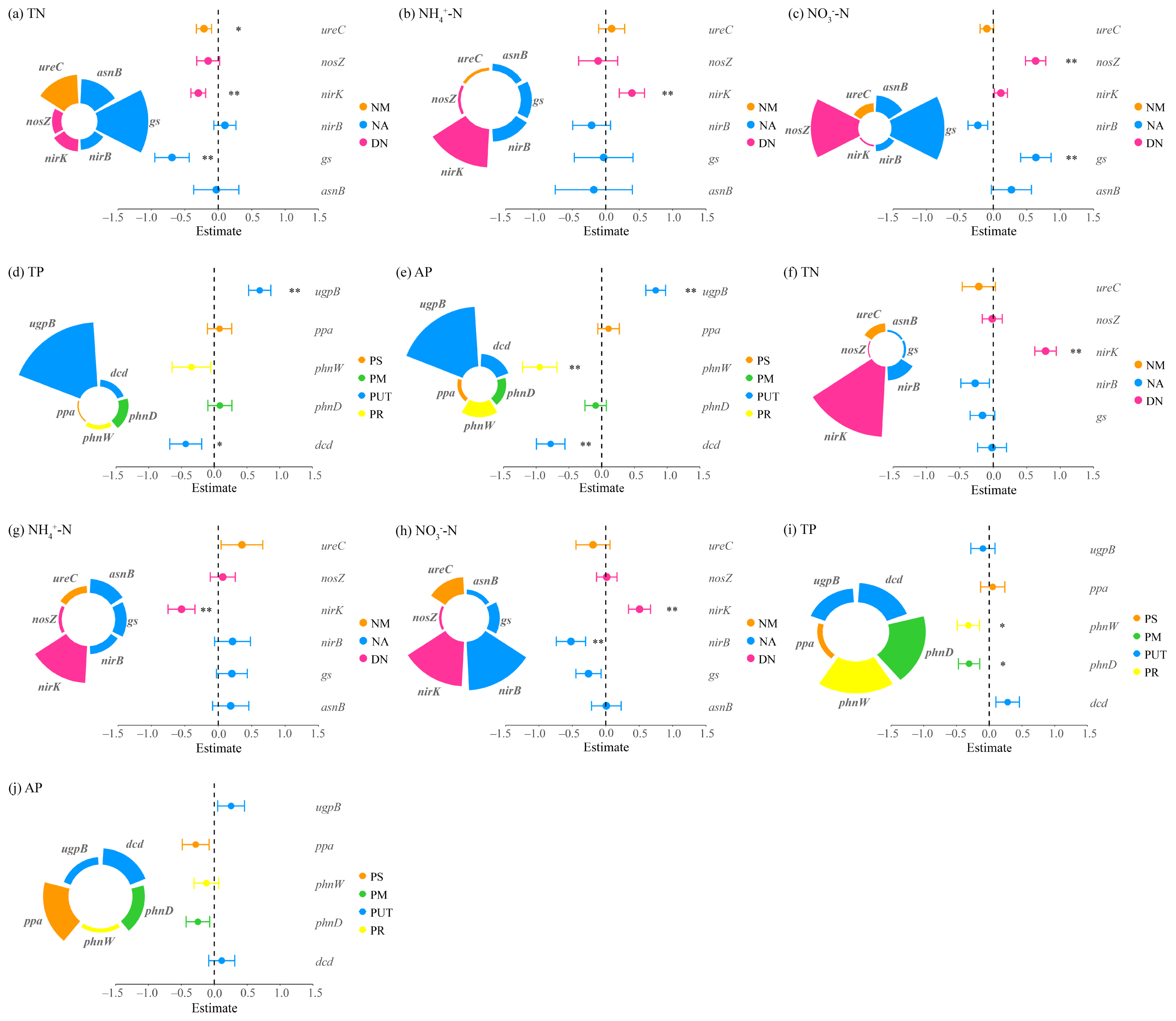
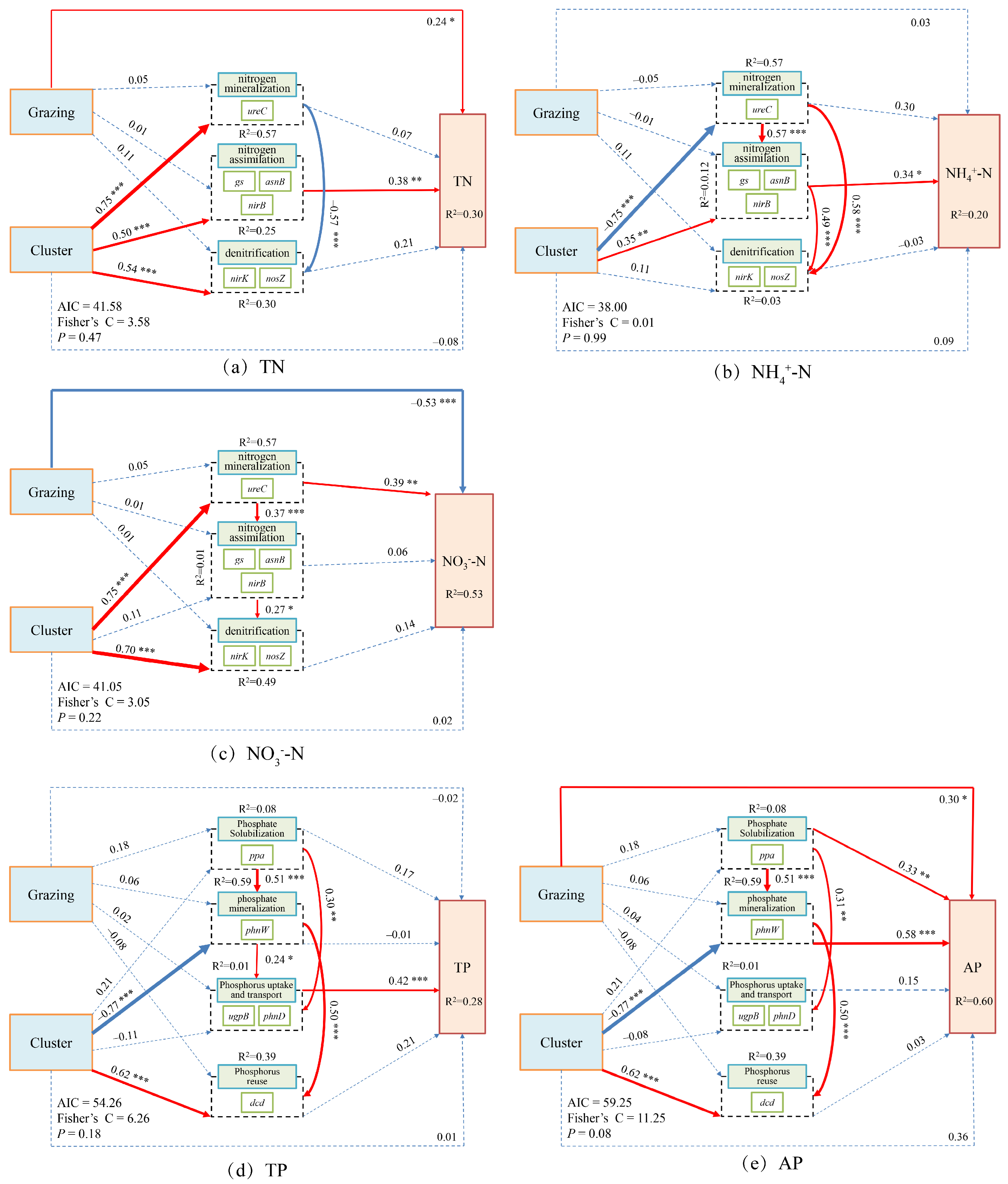
3.2.1. Determinants of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling
3.2.2. Key Processes Influencing Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling
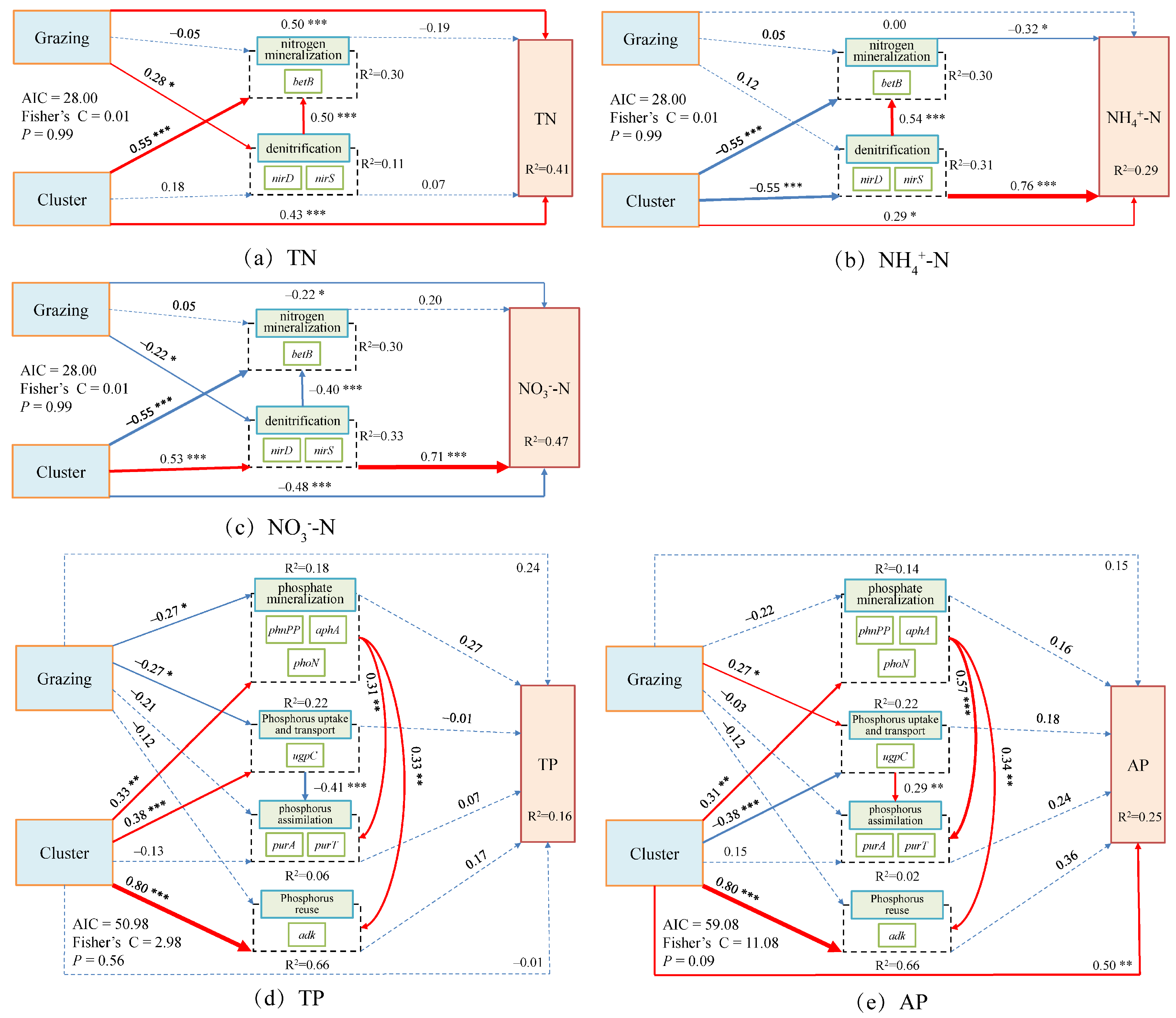
3.3. Intrinsic Regulatory Mechanisms of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling Within Dominant Plant Clusters Under Grazing
4. Discussion
4.1. Response Mechanisms of Soil N- and P-Cycling Functional Genes and Nutrient Indices to Grazing
4.1.1. Changes in N-Cycling Functional Genes and Nutrient Contents
4.1.2. Changes in P-Cycling Functional Genes and Nutrient Contents
4.1.3. Variability and Ecological Adaptability of Functional Genes and Soil Nutrients
4.2. Regulatory Mechanisms of Soil N and P Cycling Under Different Grazing Regimes
4.2.1. Interactive Regulation of Grazing and Dominant Plant Clusters
4.2.2. Differential Regulatory Pathways of N and P Cycling
4.2.3. Intrinsic Regulatory Mechanisms of Soil N and P Cycling
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bagchi, S.; Ritchie, M.E. Introduced grazers can restrict potential soil carbon sequestration through impacts on plant community composition. Ecol. Lett. 2010, 13, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmullina, A.; Rumpel, C.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Chabbi, A. Management of grasslands by mowing versus grazing—Impacts on soil organic matter quality and microbial functioning. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, W.T.; Yang, X.X.; Li, C.D.; Feng, B.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C.P.; Dong, Q.M. Effects of livestock grazing on the C:N:P stoichiometry in global grassland ecosystems: A meta-analysis. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 1251–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, K.; Struik, P.C.; Ashraf, M.N.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, R.; Jin, K.; Li, Y. Alteration of microbial carbon and nitrogen metabolism within the soil metagenome with grazing intensity at semiarid steppe. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Niu, S.; Tian, D.; Wu, Q.; Gao, X.; Schellenberg, M.P.; Han, G. Diversity of plant and soil microbes mediates the response of ecosystem multifunctionality to grazing disturbance. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 776, 145730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; de Goede, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Creamer, R. Unlocking soil health: Are microbial functional genes effective indicators? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 204, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bing, H.; Ficetola, G.F.; Wang, T.; Duan, C.; Qiu, T.; Yang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, Y.; et al. From barren rock to thriving life: How nitrogen fuels microbial carbon fixation in deglaciated landscapes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 21174–21188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, J.P.; Djukic, I.; Bloem, J.; Lehtinen, T.; Hemerik, L.; de Ruiter, P.C.; Lair, G.J. Effects of land use on soil microbial biomass, activity and community structure at different soil depths in the Danube floodplain. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 79, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.Y.; Zhou, S.; Bai, Y.; Rui, Y. Mixed grazing and clipping is beneficial to ecosystem recovery but may increase potential N2O emissions in a semi-arid grassland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Abalos, D.; Luo, Y.; Hui, D.; Hungate, B.A.; García-Palacios, P.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Olesen, J.E.; Jørgensen, U.; et al. Stimulation of ammonia oxidizer and denitrifier abundances by nitrogen loading: Poor predictability for increased soil N2O emission. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 28, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Lang, C.; Nian, H.; Jin, J.; Lian, T. Linking plant functional genes to rhizosphere microbes: A review. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, A.J.; Dumont, B.; Isselstein, J.; Osoro, K.; WallisDeVries, M.F.; Parente, G.; Mills, J. Matching type of livestock to desired biodiversity outcomes in pastures—A review. Biol. Conserv. 2003, 119, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; He, N.; Li, M.; Xu, L.; Sun, O.J. Spatial assembly of grassland communities and interrelationships with productivity. Funct. Ecol. 2023, 37, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, B.; Kéfi, S.; Gounand, I.; Gross, N.; Le Bagousse-Pinguet, Y.; Guerber, J.; Eldridge, D.; Valencia, E.; Plaza, C.; Martínez-Valderrama, J.; et al. Grazing modulates the multiscale spatial structure of dryland vegetation. Glob. Change Biol. 2025, 31, e70345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allington, G.R.H.; Valone, T.J. Islands of fertility: A byproduct of grazing? Ecosystems 2014, 17, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Hueso, R.; Eldridge, D.J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Arredondo, T. Soil fungal abundance and plant functional traits drive fertile island formation in global drylands. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meglioli, P.A.; Aranibar, J.N.; Villagra, P.E.; Vega Riveros, C. Spatial patterns of soil resources under different land use in Prosopis woodlands of the Monte desert. Catena 2017, 149, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behie, S.W.; Bidochka, M.J. Nutrient transfer in plant–fungal symbioses. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Reed, S.C.; Keller, A.B.; Nemergut, D.R.; O’Neill, S.P.; Ostertag, R.; Vitousek, P.M. Litter quality versus soil microbial community controls over decomposition: A quantitative analysis. Oecologia 2014, 174, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.R.; Thomas, A.D.; Hoon, S.R.; Sen, R. Niche partitioning of bacterial communities in biological crusts and soils under grasses, shrubs and trees in the Kalahari. Biodivers. Conserv. 2014, 23, 1709–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Liu, Y.Z.; Liu, W.T.; Lv, W.D.; Sun, C.C.; Yang, Z.Z.; Li, C.D.; Zhou, Q.Y.; Wang, F.C.; Yang, X.X.; et al. Soil physicochemical properties and plant functional traits regulate ecosystem multifunctionality of alpine grassland under different livestock grazing assemblies. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 366, 108947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, B.; Lv, W.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Dong, Q. Plant biomass partitioning in alpine meadows under different herbivores as influenced by soil bulk density and available nutrients. Catena 2024, 240, 108017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Feng, B.; Sun, S.; Dong, Q. Yak and Tibetan sheep mixed grazing enhances plant functional diversity in alpine grassland. J. Integr. Agric. 2025, 24, 936–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.M.; Leung, C.M.; Ting, H.F.; Sadakane, K.; Yamashita, H.; Lam, T.W. MEGAHIT v1.0: A fast and scalable metagenome assembler driven by advanced methodologies and community practices. Methods 2016, 102, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; LoCascio, P.; Land, M.; Larimer, F.; Hauser, L. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Q.; Lin, L.; Cheng, L.; Deng, Y.; He, Z. NCycDB: A curated integrative database for fast and accurate metagenomic profiling of nitrogen cycling genes. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Tang, S.; Li, F.Y. Summer grazing by three livestock species at moderate intensity enhances primary productivity and drives community divergence in a semi-arid steppe. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2022, 25, e12683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefcheck, J.S. piecewiseSEM: Piecewise structural equation modelling in R for ecology, evolution, and systematics. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellado-Vazquez, P.G.; Lange, M.; Bachmann, D.; Gockele, A.; Karlowsky, S.; Milcu, A.; Piel, C.; Roscher, C.; Roy, J.; Gleixner, G. Plant diversity generates enhanced soil microbial access to recently photosynthesized carbon in the rhizosphere. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 94, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Gao, X.; Kuang, W.; Tenuta, M. Soil N2O emissions and functional genes in response to grazing grassland with livestock: A meta-analysis. Geoderma 2023, 436, 116538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirotnak, J.M.; Huntly, N.J. Direct and indirect effects of herbivores on nitrogen dynamics: Voles in riparian areas. Ecology 2000, 81, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, X.; Feng, B.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Y.; Cao, Q.; Sun, S.; Degen, A.A.; et al. Herbivore assemblages affect soil microbial communities by altering root biomass and available nutrients in an alpine meadow. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1117372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Sun, B.; Osman, F.M.; Qi, Z.; Ding, D.; Liu, X.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z. Carboxylic acid accumulation and secretion contribute to the alkali-stress tolerance of halophyte Leymus chinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1366108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, L. Interactions of soil bacteria and fungi with plants during long-term grazing exclusion in semiarid grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tariq, A.; Zeng, F.; Sardans, J.; Peñuelas, J.; Zhang, Z.; Islam, W.; Xu, M. “Fertile islands” beneath three desert vegetation on soil phosphorus fractions, enzymatic activities, and microbial biomass in the desert-oasis transition zone. Catena 2022, 212, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, X.; Jing, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Patch size indirectly influences the distribution characteristics of phosphorus fractions in temperate desert moss crust soils. Catena 2025, 251, 108821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Rahman, M.K.U.; Gao, D.; Wei, Z.; Wu, F.; DiniAndreote, F. Interspecific plant interaction via root exudates structures the disease suppressiveness of rhizosphere microbiomes. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finzi, A.C.; Abramoff, R.Z.; Spiller, K.S.; Brzostek, E.R.; Darby, B.A.; Kramer, M.A.; Phillips, R.P. Rhizosphere processes are quantitatively important components of terrestrial carbon and nutrient cycles. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 2082–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbrich, T.C.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Tiemann, L.K.; Friesen, M.L.; Evans, S.E. Plant root exudates and rhizosphere bacterial communities shift with neighbor context. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhou, G.; Yuan, T.; van Groenigen, K.J.; Shao, J.; Zhou, X. Grazing intensity significantly changes the C:N:P stoichiometry in grassland ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Zhou, X.; He, Y.; Shao, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhou, H.; Hosseinibai, S. Grazing intensity significantly affects belowground carbon and nitrogen cycling in grassland ecosystems: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhu-Barker, X.; Chen, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, N.; Shi, C.; He, L.; Lei, Y. Responses of root exudation and nutrient cycling to grazing intensities and recovery practices in an alpine meadow: An implication for pasture management. Plant Soil 2017, 416, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, S.; Zhalnina, K.; Kosina, S.; Northen, T.R.; Sasse, J. The core metabolome and root exudation dynamics of three phylogenetically distinct plant species. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.B. Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: A review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Liu, M.; Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Gunina, A. Gross mineralization and nitrification in degraded alpine grassland soil. Rhizosphere 2023, 27, 100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, G. Patterns and drivers of atmospheric nitrogen deposition retention in global forests. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
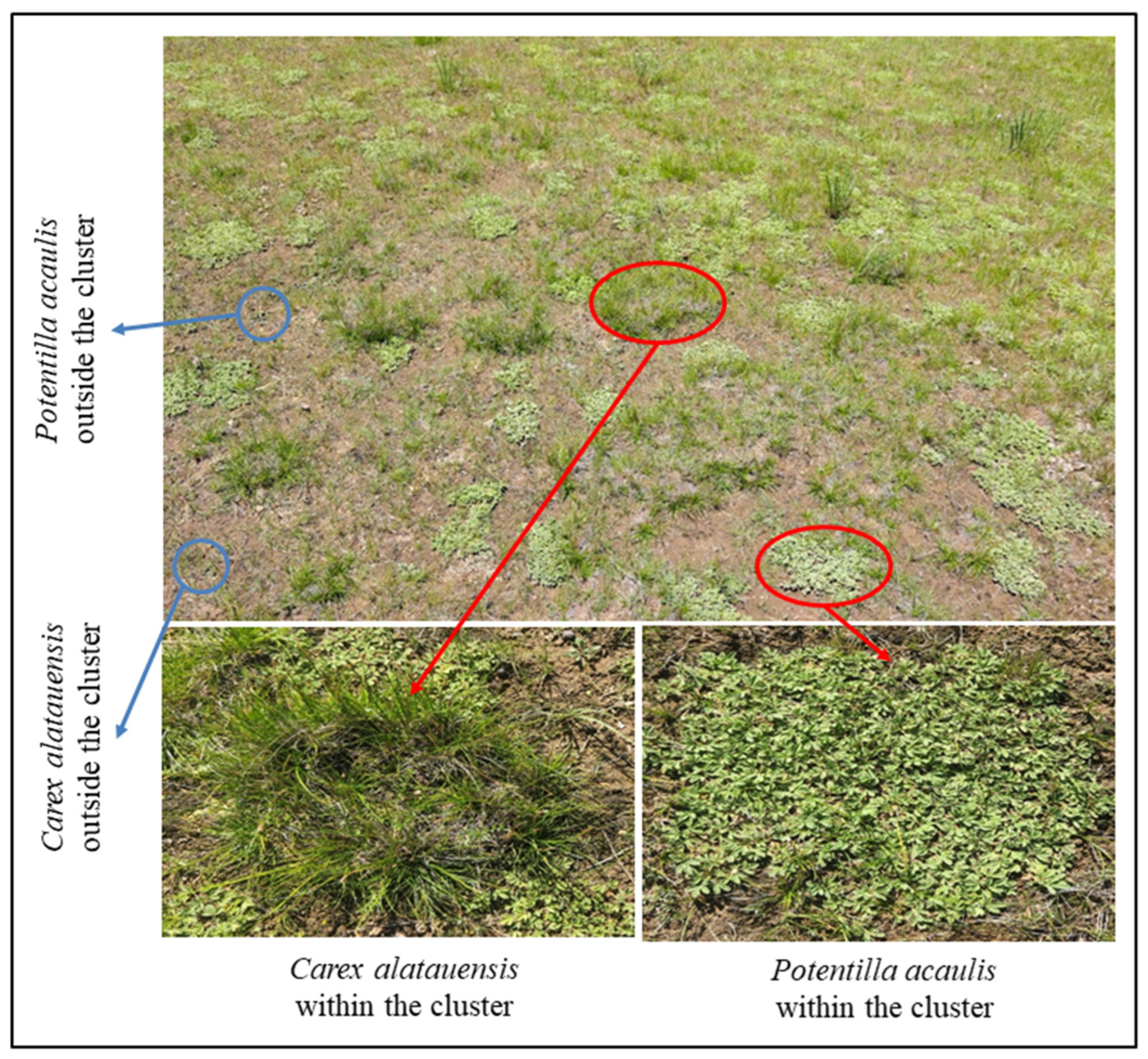
| Treatment | Number of Yaks | Number of Tibetan Sheep | Area of Plot/m2 | Grazing Intensity Sheep Units/ha | Number of Plots |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YG | 1 | 0 | 2.6 × 103 | 3.86 | 3 |
| SG | 0 | 2 | 1.7 × 103 | 3.86 | 3 |
| MG | 1 | 2 | 4.3 × 103 | 3.86 | 3 |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0.5 × 103 | 0 | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, W.; Li, N.; Liu, W.; Lv, W.; Li, M.; Ji, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Dong, Q. Cluster of Dominant Species and Grazing Jointly Influence the Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Alpine Grasslands. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122736
Xu W, Li N, Liu W, Lv W, Li M, Ji H, Liu Y, Yang X, Dong Q. Cluster of Dominant Species and Grazing Jointly Influence the Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Alpine Grasslands. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122736
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Wei, Na Li, Wenting Liu, Weidong Lv, Mengqi Li, Haiming Ji, Yuzhen Liu, Xiaoxia Yang, and Quanmin Dong. 2025. "Cluster of Dominant Species and Grazing Jointly Influence the Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Alpine Grasslands" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122736
APA StyleXu, W., Li, N., Liu, W., Lv, W., Li, M., Ji, H., Liu, Y., Yang, X., & Dong, Q. (2025). Cluster of Dominant Species and Grazing Jointly Influence the Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus Cycling in Alpine Grasslands. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2736. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122736






