Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and PPI Evaluation
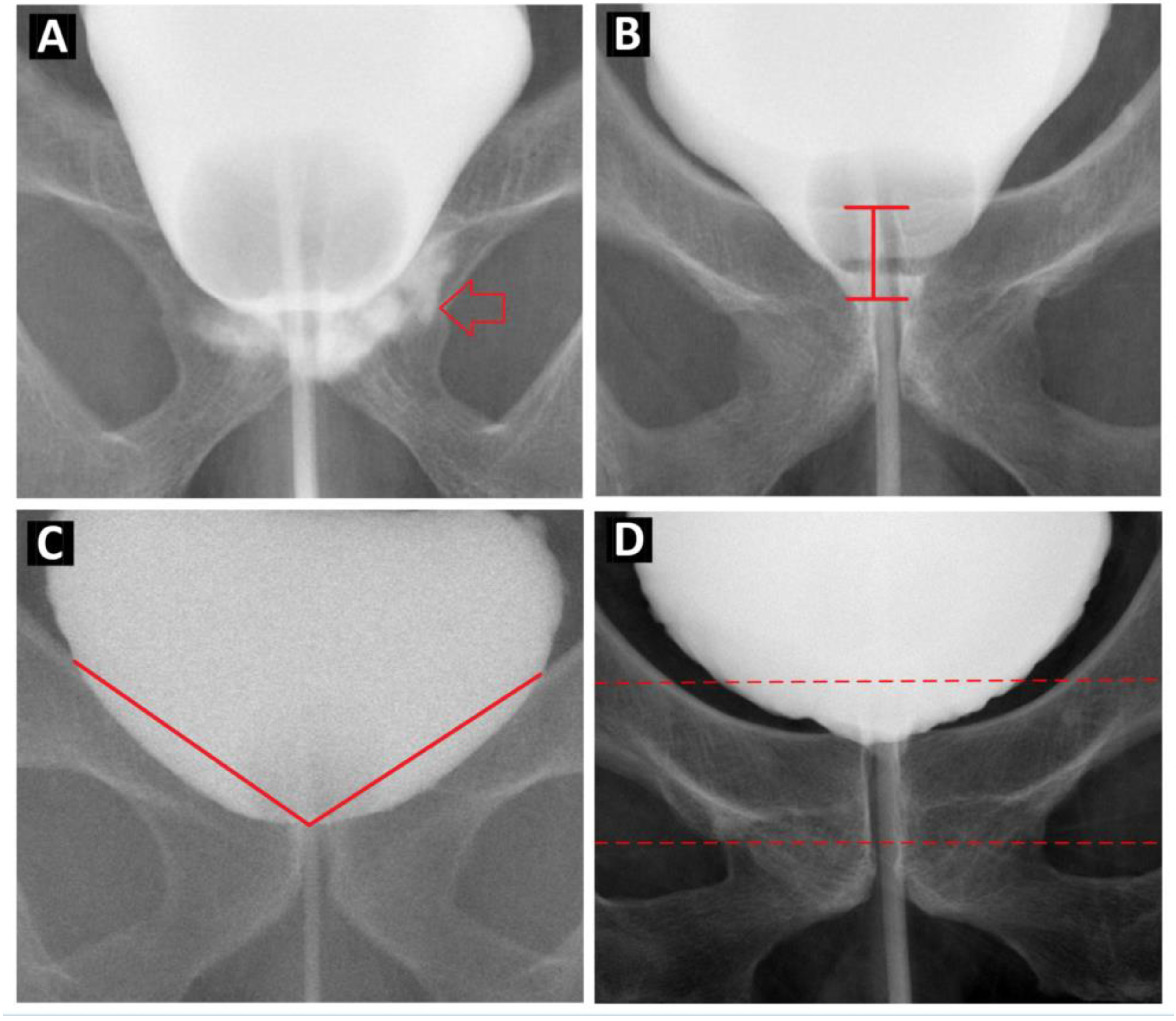
2.2. Cystography Pattern
2.3. Artificial Intelligence Deep Learning Training
2.4. Image Preprocessing
2.5. Datasets Setting
2.6. Establishment of Model and Training Details
2.7. Statistical Analysis
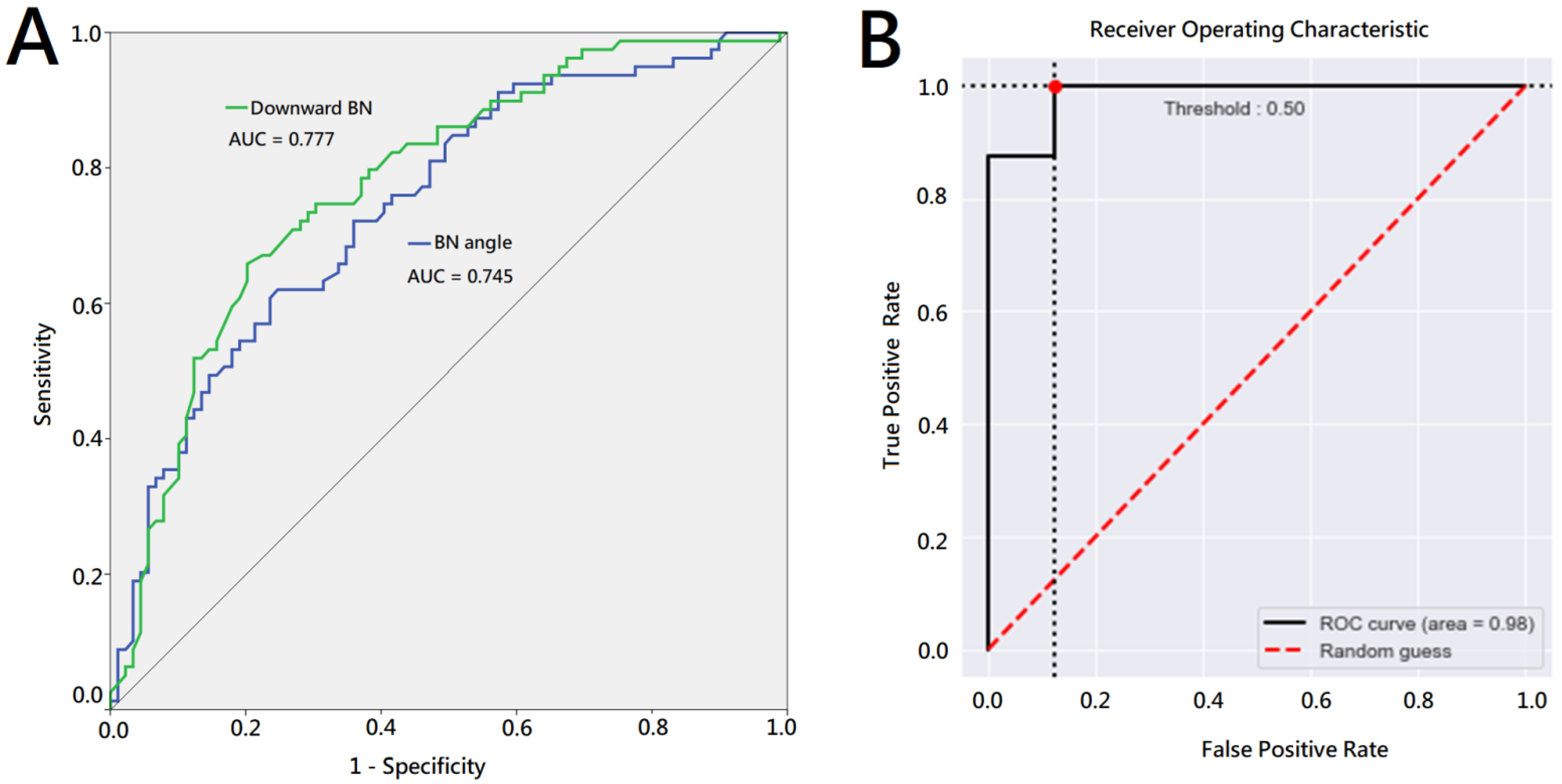
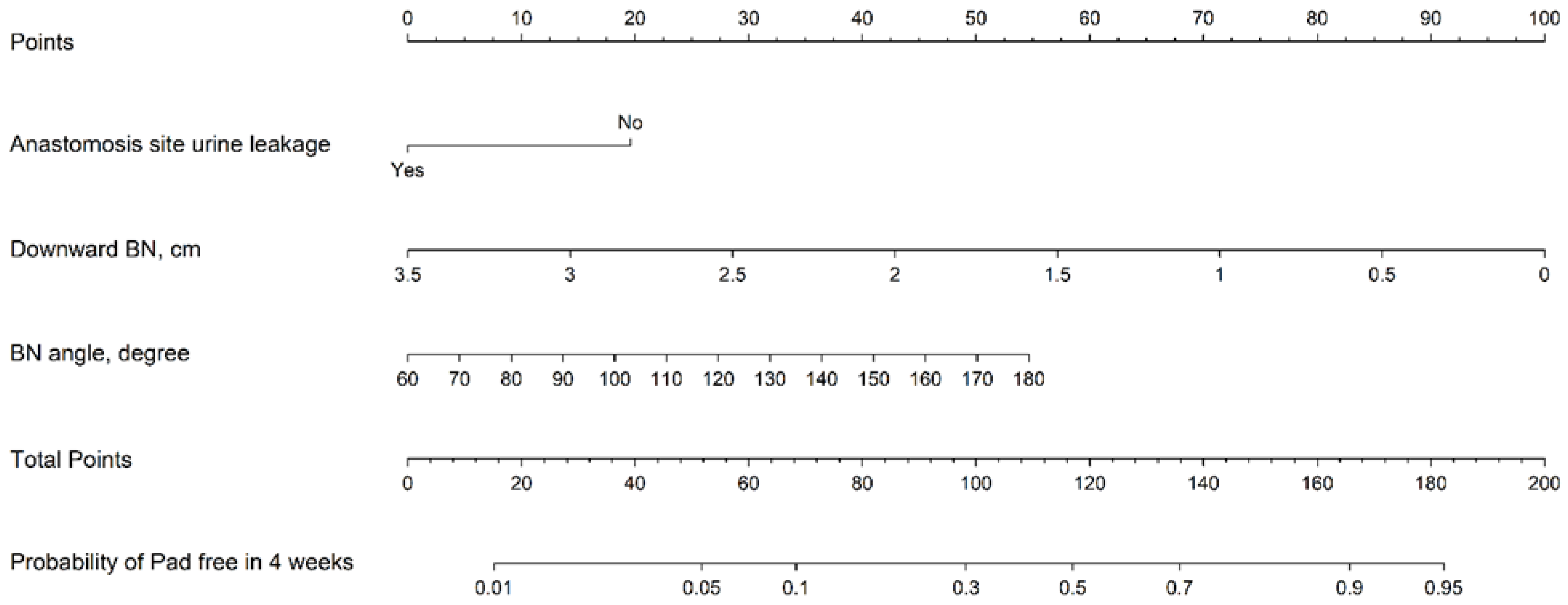
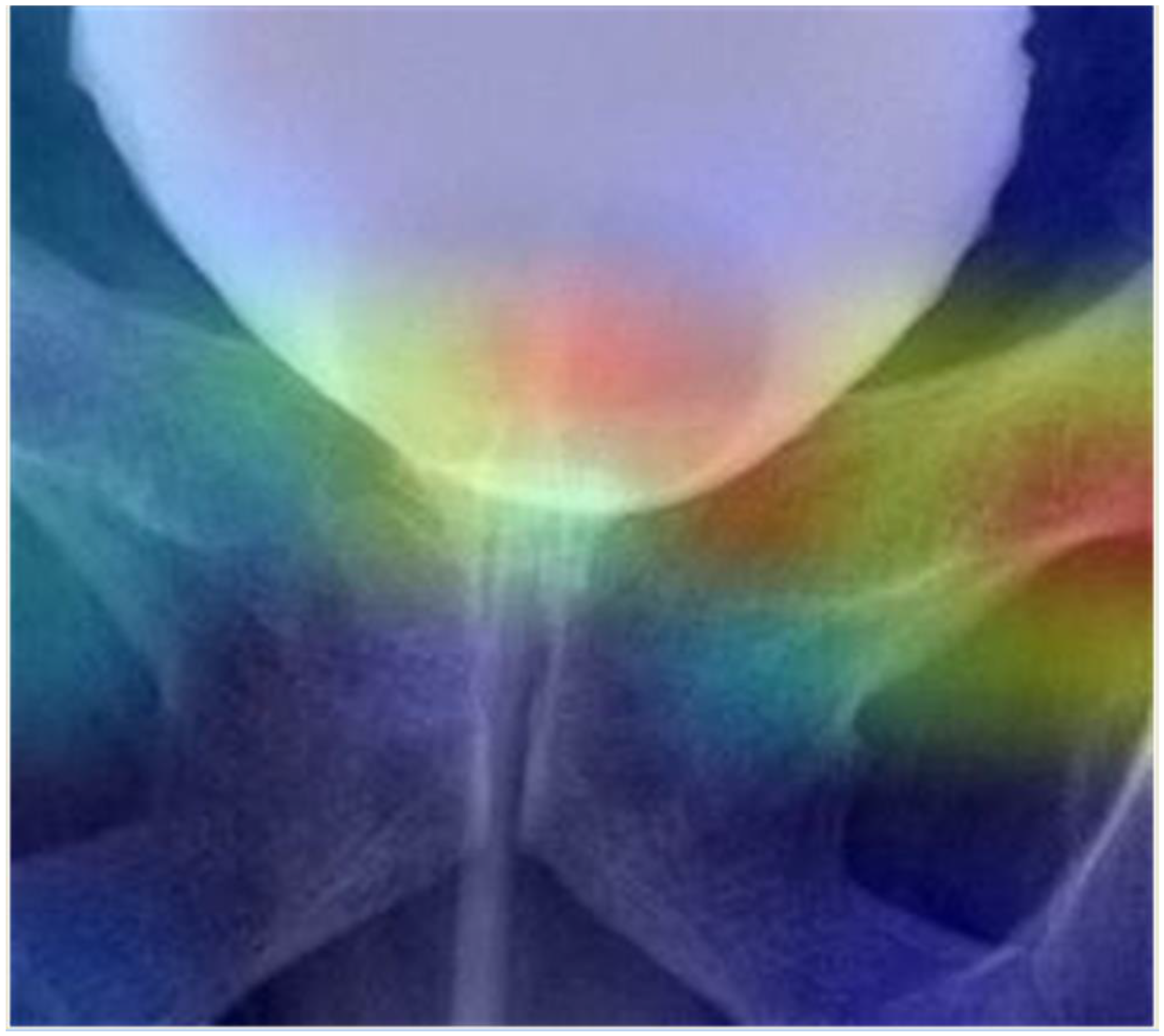
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottet, N.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fanti, S.; Fossati, N.; Gandaglia, G.; Gillessen, S.; et al. EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer-2020 Update. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 243–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciarra, A.; Gentilucci, A.; Salciccia, S.; Von Heland, M.; Ricciuti, G.P.; Marzio, V.; Pierella, F.; Musio, D.; Tombolini, V.; Frantellizzi, V.; et al. Psychological and functional effect of different primary treatments for prostate cancer: A comparative prospective analysis. Urol. Oncol. 2018, 36, 340.e7–340.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Kim, J.K.; Jeong, I.G. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer: A review and update for urologists. Korean J. Urol. 2015, 56, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majoros, A.; Bach, D.; Keszthelyi, A.; Hamvas, A.; Mayer, P.; Riesz, P.; Seidl, E.; Romics, I. Analysis of risk factors for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Urol. Int. 2007, 78, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, P.C.; Partin, A.W.; Epstein, J.I. Cancer control and quality of life following anatomical radical retropubic prostatectomy: Results at 10 years. J. Urol. 1994, 152, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficarra, V.; Novara, G.; Rosen, R.C.; Artibani, W.; Carroll, P.R.; Costello, A.; Menon, M.; Montorsi, F.; Patel, V.R.; Stolzenburg, J.U.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffenberg, G.B.; Qi, J.; Dunn, R.L.; Linsell, S.; Kim, T.; Miller, D.C.; Tosoian, J.; Sarle, R.; Johnston, W.K., 3rd; Kleer, E.; et al. Evaluation of Patient- and Surgeon-Specific Variations in Patient-Reported Urinary Outcomes 3 Months After Radical Prostatectomy From a Statewide Improvement Collaborative. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, e206359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarsono, B.; Jong, J.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Liao, L.; Lee, K.S.; Yoo, T.K.; Liu, S.P.; Chuang, Y.C. The prevalence of urinary incontinence in men and women aged 40 years or over in China, Taiwan and South Korea: A cross-sectional, prevalence-based study. Low Urin. Tract Symptoms 2020, 12, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.; Te, A.E.; Kaplan, S.A.; Sandhu, J.S. Temporal trends in adoption of and indications for the artificial urinary sphincter. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 2622–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Giudice, F.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Sorensen, S.; Enemchukwu, E.; Maggi, M.; Salciccia, S.; Ferro, M.; Crocetto, F.; Pandolfo, S.D.; et al. Contemporary trends in the surgical management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy in the United States. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallami, S. Predictive factors of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: Systematic review. Tunis. Med. 2017, 95, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Rocco, F.; Carmignani, L.; Acquati, P.; Gadda, F.; Dell’Orto, P.; Rocco, B.; Bozzini, G.; Gazzano, G.; Morabito, A. Restoration of posterior aspect of rhabdosphincter shortens continence time after radical retropubic prostatectomy. J. Urol. 2006, 175, 2201–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colarieti, A.; Thiruchelvam, N.; Barrett, T. Evaluation of image-based prognostic parameters of post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: A literature review. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 890–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, I.H.; Chou, C.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, C.F.; Chang, Y.H.; Tseng, H.J.; Wu, C.T. A Specific Cystography Pattern Can Predict Postprostatectomy Incontinence. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22 (Suppl. S3), S1580–S1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.S.; Bak, D.J.; Chung, J.W.; Lee, J.N.; Kwon, S.Y.; Choi, S.H.; Kwon, T.G.; Kim, T.H. Postoperative cystographic findings as an independent predictor of urinary incontinence three months after radical prostatectomy. Minerva Urol. Nefrol. 2017, 69, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.W.; Hung, S.C.; Hu, J.C.; Chiu, K.Y. Retzius-sparing Robotic-assisted Radical Prostatectomy Associated with Less Bladder Neck Descent and Better Early Continence Outcome. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugi, M.; Kinoshita, H.; Yoshida, T.; Taniguchi, H.; Mishima, T.; Yoshida, K.; Yanishi, M.; Komai, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Matsuda, T. The narrow vesicourethral angle measured on postoperative cystography can predict urinary incontinence after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Scand. J. Urol. 2018, 52, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Lin, V.C.; Tsai, Y.C.; Kuo, H.C. Possible predictor of early recovery on urinary continence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy—Bladder neck level and urodynamic parameters. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2019, 118, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kageyama, S.; Yoshida, T.; Nagasawa, M.; Kubota, S.; Tomita, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Murai, R.; Tsuru, T.; Hanada, E.; Johnin, K.; et al. The location of the bladder neck in postoperative cystography predicts continence convalescence after radical prostatectomy. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, S.; Kagebayashi, Y.; Iemura, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Samma, S. Postoperative cystogram findings predict recovery of urinary continence after robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2019, 11, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.D.; Park, K.K. The Effectiveness of Cystography-Measured Bladder Neck Elevation at Predicting the Return of Continence After Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy. Int. Neurourol. J. 2019, 23, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.Y. Association between cystographic anastomotic urinary leakage following retropubic radical prostatectomy and early urinary incontinence. Yeungnam Univ. J. Med. 2021, 38, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossanese, M.; Caloggero, S.; Alario, G.; Mucciardi, G.; Novara, G.; Giannarini, G.; Ficarra, V. Relative position of bladder neck to pubic symphysis on cystogram is a strong and reproducible predictor of early urinary continence recovery following radical prostatectomy. Urologia 2021, 88, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Ha, H.K. Intravesical prostatic protrusion as a predictor of early urinary continence recovery after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 653–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Kim, C.K.; Park, B.K.; Jeon, H.G.; Jeong, B.C.; Seo, S.I.; Jeon, S.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, H.M. Impact of preoperative and postoperative membranous urethral length measured by 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging on urinary continence recovery after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2017, 11, E93–E99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, S.; Kagebayashi, Y.; Iemura, Y.; Matsumura, Y.; Samma, S. Preoperative MRI Parameters Predict Urinary Continence after Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy in Prostatic Cancer Patients. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paparel, P.; Akin, O.; Sandhu, J.S.; Otero, J.R.; Serio, A.M.; Scardino, P.T.; Hricak, H.; Guillonneau, B. Recovery of urinary continence after radical prostatectomy: Association with urethral length and urethral fibrosis measured by preoperative and postoperative endorectal magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; China, T.; Kanayama, M.; Nagata, M.; Isotani, S.; Wakumoto, Y.; Muto, S.; Ide, H.; Horie, S. Significant association between urethral length measured by magnetic resonance imaging and urinary continence recovery after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. Prostate Int. 2019, 7, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.J.; Yi, J.; Chung, M.S.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, W.K.; Park, H.; Yoon, C.Y.; Hong, S.K.; Byun, S.S.; Lee, S.E. Early recovery of urinary continence after radical prostatectomy: Correlation with vesico-urethral anastomosis location in the pelvic cavity measured by postoperative cystography. Int. J. Urol. 2011, 18, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo, J.; González, F.A.; Ramos-Pollán, R.; Oliveira, J.L.; Guevara Lopez, M.A. Representation learning for mammography mass lesion classification with convolutional neural networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2016, 127, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khondker, A.; Kwong, J.C.C.; Rickard, M.; Skreta, M.; Keefe, D.T.; Lorenzo, A.J.; Erdman, L. A machine learning-based approach for quantitative grading of vesicoureteral reflux from voiding cystourethrograms: Methods and proof of concept. J. Pediatr. Urol. 2022, 18, 78.e71–78.e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravina, M.; Spirito, L.; Celentano, G.; Capece, M.; Creta, M.; Califano, G.; Collà Ruvolo, C.; Morra, S.; Imbriaco, M.; Di Bello, F.; et al. Machine Learning and Clinical-Radiological Characteristics for the Classification of Prostate Cancer in PI-RADS 3 Lesions. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, L.Y. Discriminability-Based Transfer between Neural Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1992, 5, 204–211. [Google Scholar]
| Age, Years (SD, Range) | 66.9 (6.1, 51–80) | |
|---|---|---|
| BMI, kg/m2 (SD, range) | 25.2 (3.2, 15.9–36) | |
| Initial PSA, ng/ml (SD, range) | 17.3 (18.3, 2.29–150) | |
| Prostate volume, gm (SD, range) | 40.6 (17.2, 12–116) | |
| D’Amico risk group (%) | Low | 12 (7.1) |
| Intermediate | 29 (17.1) | |
| High | 129 (75.9) | |
| Operative time, mins (SD, range) | 275.1 (49.4, 152–481) | |
| EBL, ml (SD, range) | 108.1 (83.3, 20–550) | |
| Pathological stage (%) | pT2 | 118 (69.4) |
| pT3 | 51 (30.0) | |
| pT4 | 1 (0.6) | |
| Surgical margin (%) | Negative | 116 (68.2) |
| Positive | 54 (31.8) | |
| NVB preservation (%) | Monolateral | 28 (16.5) |
| Bilateral No | 93 (54.7) 49 (28.8) | |
| Bladder neck reconstruction (%) | Yes | 81 (47.7) |
| No | 89 (52.4) | |
| Continence recovery time (%) | Immediate | 53 (31.2) |
| 4 weeks | 81 (47.6) | |
| 12 weeks | 144 (84.7) | |
| 24 weeks | 159 (93.5) |
| Pad Free ≦ 4 Weeks | Not Pad Free in 4 Weeks | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (N = 81) | (N = 89) | p Value | ||
| Anastomosis site urine leakage (%) | * 0.011 | * 0.04 | ||
| Yes | 12 (14.8) | 29 (32.6) | ||
| No | 69 (85.2) | 60 (67.4) | ||
| Bladder height, cm (SD, range) | 8.04 (1.33, 4.6–11.9) | 8.18 (1.37, 5.3–11.4) | 0.501 | |
| Bladder width, cm (SD, range) | 7.21 (1.16, 4.7–11.0) | 7.14 (1.18, 4.3–10.6) | 0.677 | |
| Height to width ratio (SD, range) | 1.13 (0.19, 0.8–1.7) | 1.17 (0.25, 0.6–2.1) | 0.210 | |
| Downward BN, cm (SD, range) | 0.74 (0.49, 0.1–3.5) | 1.31 (0.68, 0.1–3.5) | ** <0.001 | * 0.011 |
| BN angle, degree (SD, range) | 128.37 (18.0, 83.9–170.7) | 110.78 (20.2, 62.6–167.2) | ** <0.001 | 0.122 |
| Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| Fold 2 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 |
| Fold 3 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| Fold 4 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
| Fold 5 | 0.94 | 0.88 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, I.-H.; Kan, H.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Huang, L.-K.; Chu, Y.-C.; Lin, P.-H.; Yu, K.-J.; Chuang, C.-K.; Pang, S.-T.; et al. Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13010126
Shao I-H, Kan H-C, Chen H-Y, Chang Y-H, Huang L-K, Chu Y-C, Lin P-H, Yu K-J, Chuang C-K, Pang S-T, et al. Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(1):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13010126
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, I-Hung, Hung-Cheng Kan, Hung-Yi Chen, Ying-Hsu Chang, Liang-Kang Huang, Yuan-Cheng Chu, Po-Hung Lin, Kai-Jie Yu, Cheng-Keng Chuang, See-Tong Pang, and et al. 2023. "Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 1: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13010126
APA StyleShao, I.-H., Kan, H.-C., Chen, H.-Y., Chang, Y.-H., Huang, L.-K., Chu, Y.-C., Lin, P.-H., Yu, K.-J., Chuang, C.-K., Pang, S.-T., & Wu, C.-T. (2023). Recognition of Postoperative Cystography Features by Artificial Intelligence to Predict Recovery from Postprostatectomy Urinary Incontinence: A Rapid and Easy Way to Predict Functional Outcome. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(1), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13010126






