PHASE: Progressive Hierarchical Adaptation for Sample-Efficient Rebalancing in Long-Tail Classification
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- By combining sample-level difficulty tuning with class-level weight allocation, PHASE systematically reconfigures optimization strategies tailored for long-tailed scenarios. Theoretically, PHASE achieves dynamic adaptation of local weights and equilibrium of global weights, creating a multi-stage, multi-scale adaptive optimization system that enhances learning model performance on long-tailed datasets.
- (2)
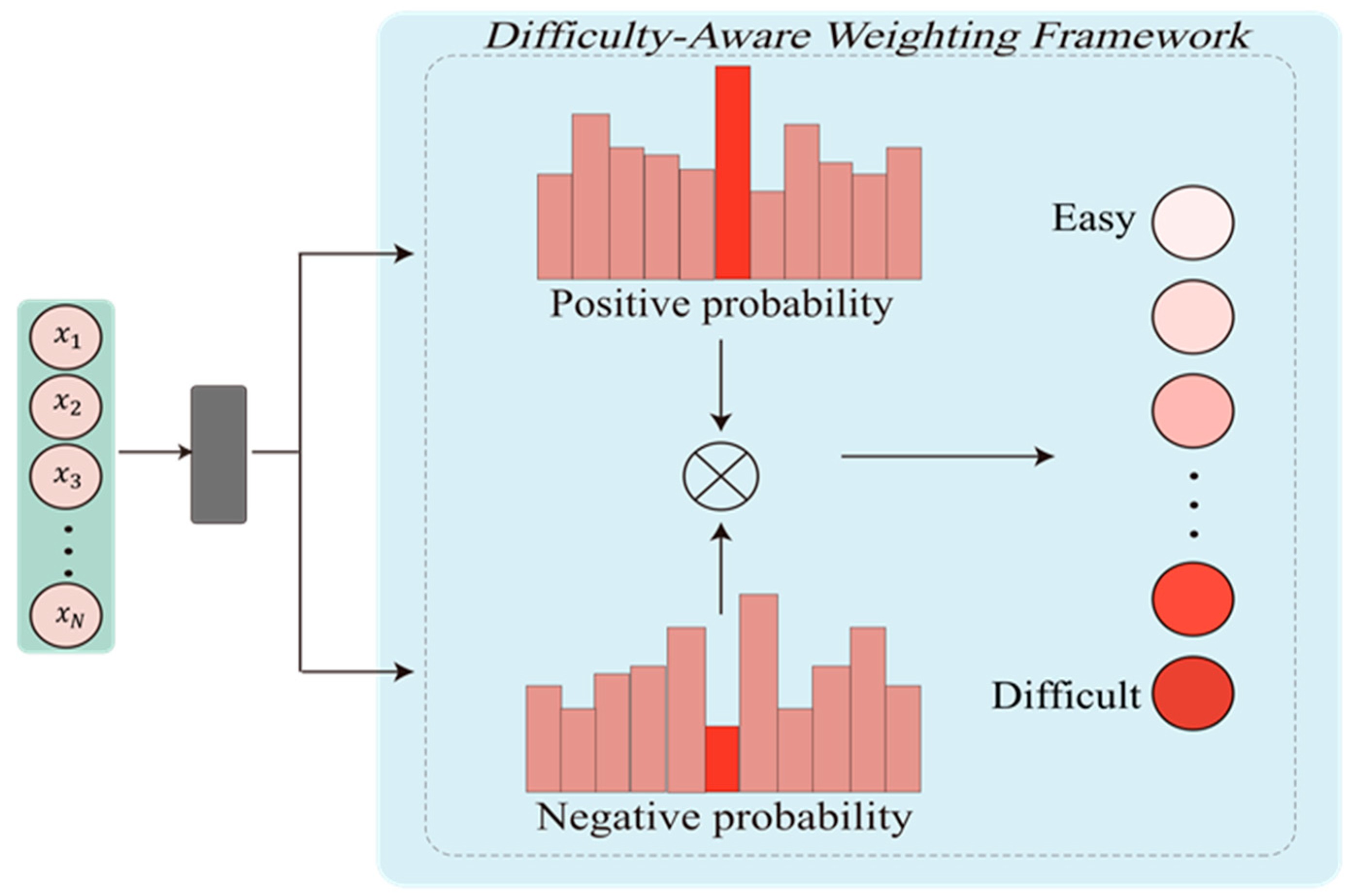
- In the initial phase, PHASE incorporates a dynamic tuning factor utilizing sample prediction probabilities to establish a Difficulty-Aware Weighting (DAW) framework. This framework enables the adjustment of the learning impact of individual samples, enhancing the model’s sensitivity to the intricate sample distributions of tail classes. It actively redirects the trajectory of representation learning, further constructing a more robust feature space. In the second phase, a Multi-Scale Reweighting (MSR) approach is introduced. MSR integrates statistical patterns obtained from class distributions with the intrinsic data characteristics of each class. This approach effectively merges local and global class weight assignments, dynamically balancing the optimization paths of head and tail classes. It alleviates the adverse effects of weight competition-induced negative transfer between classes.
- (3)
- Extensive experiments are performed on three commonly utilized long-tailed datasets: CIFAR10-LT, CIFAR100-LT, and ImageNet-LT. The results indicate that PHASE outperforms existing state-of-the-art long-tailed reweighting approaches in terms of both overall classification accuracy and tail class recognition accuracy. Moreover, when integrated with data augmentation methods, PHASE achieves better or comparable accuracy than/to those of the current state-of-the-art techniques, indicating its efficacy and superiority in addressing tasks involving imbalanced data distributions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Reweighting
2.2. Decoupling Representation
3. Methods
3.1. Preliminaries
3.2. Difficulty-Aware Weighting Framework
| Algorithm 1: DAW |
| Input: Training set , the number of classes C, the positive and negative focusing parameters γ+, γ−, the label smoothing parameter ϵ |
| Output: Optimized feature extractor parameters |
| Procedure: |
| 1. Initialize the model with γ+, γ− and ϵ; |
| 2. Define the log-softmax function for output normalization; |
| 3. For each training instance (xi,yi) (a) Calculate predicted class probabilities p(xi) using softmax; (b) Generate one-hot label vector ti,j; (c) Calculate asymmetric weights A(xi,j) as defined in Equation (3); (d) Apply label smoothing to obtain smoothed labels according to Equation (5); |
| 4. Aggregate the instance-wise losses to obtain the final loss Lfinal; |
| 5. Optimize model parameters by minimizing the expected loss on as defined in Equation (7). |
3.3. Multi-Scale Reweighting
| Algorithm 2: MSR |
| Input: Training set ; the sample counts of each class ; the feature extractor ; the hyper-parameter γ > 0; the tradeoff factor |
| Output: The integrated class-level weights |
Procedure:
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiment Settings
4.2. Long-Tailed Benchmark Results
4.3. Ablation Study
4.4. Comparison with SOTA Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASL | Asymmetric Loss |
| PHASE | Progressive Hierarchical Adaptation for Sample-Efficient rebalancing |
| DAW | Difficulty-Aware Weighting |
| MSR | Multi-Scale Reweighting |
| LDAM | Label-Distribution-Aware Margin |
| VS | Vector-Scaling |
| SGD | Stochastic Gradient Descent |
| SAM | Sharpness-Aware Minimization |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art |
References
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaee, S.; Boykov, Y.; Porikli, F.; Plaza, A.J.; Kehtarnavaz, N.; Terzopoulos, D. Image segmentation using deep learning: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 3523–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Z.; Chen, K.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Y.; Ye, J. Object detection in 20 years: A survey. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 257–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Li, F.F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2014, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 million image database for scene recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayhan, M.S.; Kühlewein, L.; Aliyeva, G.; Inhoffen, W.; Ziemssen, F.; Berens, P. Expert-validated estimation of diagnostic uncertainty for deep neural networks in diabetic retinopathy detection. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 64, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Chun, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.-J. Gaussian YOLOv3: An accurate and fast object detector using localization uncertainty for autonomous driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Cui, Q.; Wei, X.-S.; Chen, Z.-M. BBN: Bilateral-branch network with cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9719–9728. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J.; Yu, C.; Ma, X.; Zhao, H.; Yi, S. Balanced meta-softmax for long-tailed visual recognition. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–12 December 2020; pp. 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jia, M.; Lin, T.Y.; Song, Y.; Belongie, S. Class-balanced loss based on effective number of samples. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9268–9277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.K.; Jayasumana, S.; Rawat, A.S.; Jain, H.; Veit, A.; Kumar, S. Long-tail learning via logit adjustment. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Wei, C.; Gaidon, A.; Arechiga, N.; Ma, T. Learning imbalanced datasets with label-distribution-aware margin loss. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 1567–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Kini, G.R.; Paraskevas, O.; Oymak, S.; Thrampoulidis, C. Label-imbalanced and group-sensitive classification under overparameterization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–14 December 2021; pp. 18970–18983. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, B.; Xie, S.; Rohrbach, M.; Yan, Z.; Gordo, A.; Feng, J.; Kalantidis, Y. Decoupling representation and classifier for long-tailed recognition. arXiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.; Cui, J.; Liu, S.; Jia, J. Improving calibration for long-tailed recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 16489–16498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Kang, B.; Li, J.; Liew, J.; Tang, S.; Hoi, S.; Feng, J. The devil is in classification: A simple framework for long-tail instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2020, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 728–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, D.; Yang, C.; Li, B.; Hu, Q.; Wang, W. Area: Adaptive reweighting via effective area for long-tailed classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 19277–19287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Chen, D.; Shen, X. SURE: Survey recipes for building reliable and robust deep networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 17500–17510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridnik, T.; Ben-Baruch, E.; Zamir, N.; Noy, A.; Friedman, I.; Protter, M.; Zelnik-Manor, L. Asymmetric loss for multi-label classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; pp. 8024–8035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foret, P.; Kleiner, A.; Mobahi, H.; Neyshabur, B. Sharpness-aware minimization for efficiently improving generalization. arXiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Long, M.; Wang, J.; Han, Z.; Wen, Q. Deep quantization network for efficient image retrieval. In Proceedings of the 13th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; pp. 3457–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, P. Accurate, large minibatch SGD: Training ImageNet in 1 hour. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Zeng, W.; Yang, B.; Urtasun, R. Learning to reweight examples for robust deep learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 4334–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lim, J.; Jeon, Y.; Choi, J.Y. Influence-balanced loss for imbalanced visual classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Miao, Z.; Zhan, X.; Wang, J.; Gong, B.; Yu, S.X. Large-scale long-tailed recognition in an open world. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Cao, X.; Huang, Q. A unified generalization analysis of re-weighting and logit-adjustment for imbalanced learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 10–15 December 2024; pp. 48417–48430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Yang, P.; Jia, Q.; Nan, F.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y. Global and local mixture consistency cumulative learning for long-tailed visual recognitions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 15814–15823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangwani, H.; Aithal, S.K.; Mishra, M. Escaping saddle points for effective generalization on class-imbalanced data. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022; pp. 22791–22805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Mane, D.; Vasudevan, V.; Le, Q.V. Autoaugment: Learning augmentation policies from data. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, M.K.; Seo, S.W. Long-tailed recognition by mutual information maximization between latent features and ground-truth labels. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 32770–32782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangwani, H.; Mondal, P.; Mishra, M.; Asokan, A.R.; Babu, R.V. DeiT-LT: Distillation strikes back for vision transformer training on long-tailed datasets. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 23396–23406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Jiang, C.; Hu, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, J. MDCS: More diverse experts with consistency self-distillation for long-tailed recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 11597–11608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Method | Training Paradigm | Focus on Stage 1 | Focus on Stage 2 | Sample-Level Difficulty Awareness? | Intra-Class Characteristic Consideration? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Focal Loss [12] | Single-stage | N/A | N/A | Yes (via modulating factor) | No |
| LDAM-DRW [14] | Two-stage | Minimize class-adjusted margin-based loss | Reweight by class frequency | Indirectly (via margin) | No |
| AREA [19] | Two-stage | Standard cross-entropy loss | Reweight by “effective area” of classes | No | Yes (via class feature distribution) |
| SURE [20] (conceptually) | Single-stage | N/A | N/A | Yes (via loss reweighting) | Implicitly (via robust optimization) |
| PHASE (Ours) | Two-stage | Difficulty-Aware Weighting (DAW) | Multi-Scale Reweighting (MSR) | Yes (explicitly via DAW) | Yes (explicitly via MSR) |
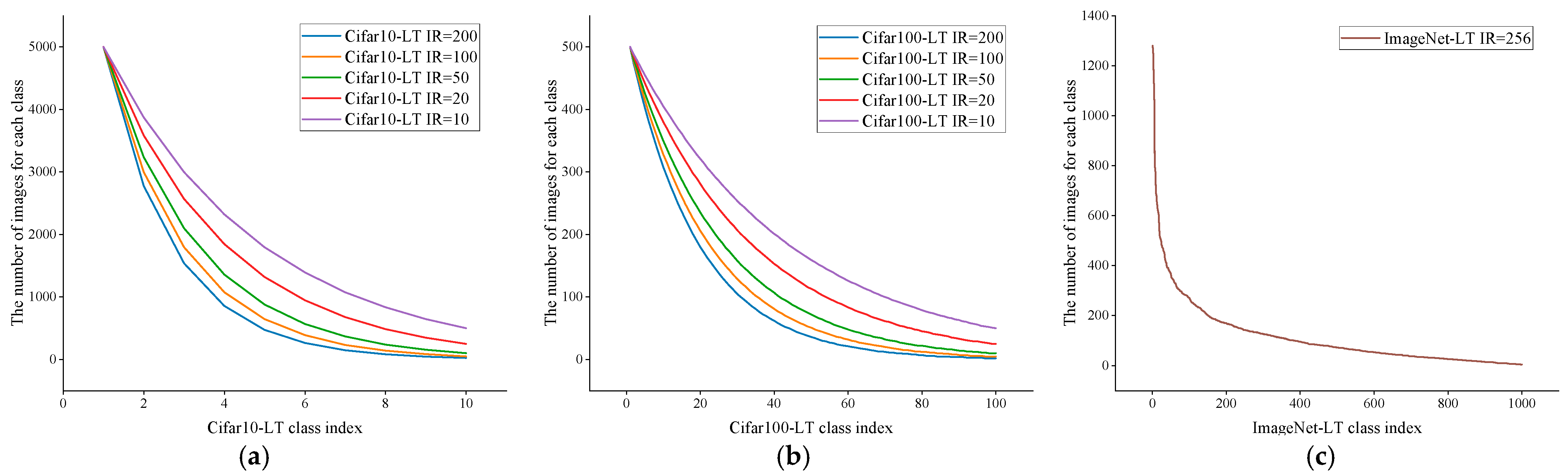
| Dataset | Imbalance Ratio | Number of Training Samples | Number of Testing Samples | Number of Classes | Size of Max Class | Size of Min Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIFAR10-LT | 200, 100, 50, 20, 10 | 11,203~50,000 | 10,000 | 10 | 5000 | 25~500 |
| CIFAR100-LT | 200, 100, 50, 20, 10 | 9502~50,000 | 10,000 | 100 | 500 | 2~500 |
| ImageNet-LT | 256 | 115,846 | 50,000 | 1000 | 1280 | 5 |
| Dataset | CIFAR-10 | CIFAR-100 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IF | 200 | 100 | 50 | 20 | 10 | 200 | 100 | 50 | 20 | 10 |
| Cross-Entropy | 65.68 | 70.36 | 74.81 | 82.23 | 86.39 | 34.84 | 38.32 | 43.85 | 51.14 | 55.71 |
| Focal [12] | 65.29 | 70.38 | 76.71 | 82.76 | 86.66 | 35.62 | 38.41 | 44.32 | 51.95 | 55.78 |
| LDAM [14] | - | 73.35 | - | - | 86.96 | - | 39.6 | - | - | 56.91 |
| L2RW [26] | 66.25 | 72.23 | 76.45 | 81.35 | 82.12 | 33.00 | 38.90 | 43.17 | 50.75 | 52.12 |
| CB [11] | 68.89 | 74.57 | 79.27 | 84.36 | 87.49 | 36.23 | 39.60 | 45.32 | 52.59 | 57.99 |
| LDAM-DRW [14] | 73.52 | 77.03 | 81.03 | - | 88.16 | 38.91 | 42.04 | 47.62 | - | 57.99 |
| IB [27] | 73.96 | 78.26 | 81.70 | 85.80 | 88.25 | 37.31 | 42.14 | 46.22 | 52.63 | 57.13 |
| AREA [19] | 74.99 | 78.88 | 82.68 | 85.99 | 88.71 | 43.85 | 48.83 | 51.77 | 57.02 | 60.77 |
| Our methods | ||||||||||
| DAW | ||||||||||
| +DRW | 74.81 | 78.73 | 82.53 | 86.13 | 88.94 | 44.46 | 48.96 | 52.52 | 57.67 | 61.10 |
| +AREA | 75.70 | 79.32 | 83.08 | 86.19 | 88.86 | 44.52 | 48.97 | 52.60 | 57.73 | 61.11 |
| +MRS | 75.93 | 79.37 | 83.18 | 86.30 | 89.04 | 44.84 | 49.07 | 52.79 | 57.76 | 61.23 |
| Method | Top-1 Accuracy |
|---|---|
| Cross-Entropy | 38.88 |
| Focal Loss [12] | 30.50 |
| Class-Balanced Loss [10] | 40.85 |
| LDAM [14] | 41.86 |
| LDAM-DRW [14] | 45.74 |
| Decoupling [16] | 47.30 |
| VS + TLA + ADRW [29] | 48.21 |
| PHASE | 49.96 |
| DAW | MSR | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|
| × | × | 34.79 |
| √ | × | 37.93 |
| × | √ | 44.02 |
| √ | √ | 44.84 |
| Method | IF = 100 | IF = 50 | IF = 10 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GML [33] | 54.00 | 58.10 | 67.00 |
| DeiT-LT [34] | 55.60 | 60.50 | - |
| MDCS [35] | 56.10 | 60.10 | - |
| GLMC [30] | 57.11 | 62.32 | 72.33 |
| SURE [20] | 57.34 | 63.13 | 73.24 |
| PHASE | 58.00 | 62.51 | 72.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Duan, J.; Shao, C.; Yu, H. PHASE: Progressive Hierarchical Adaptation for Sample-Efficient Rebalancing in Long-Tail Classification. Symmetry 2025, 17, 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122040
Li J, Duan J, Shao C, Yu H. PHASE: Progressive Hierarchical Adaptation for Sample-Efficient Rebalancing in Long-Tail Classification. Symmetry. 2025; 17(12):2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122040
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiale, Jicong Duan, Changbin Shao, and Hualong Yu. 2025. "PHASE: Progressive Hierarchical Adaptation for Sample-Efficient Rebalancing in Long-Tail Classification" Symmetry 17, no. 12: 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122040
APA StyleLi, J., Duan, J., Shao, C., & Yu, H. (2025). PHASE: Progressive Hierarchical Adaptation for Sample-Efficient Rebalancing in Long-Tail Classification. Symmetry, 17(12), 2040. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym17122040








