Sediment Transport into the Saline Western Songnen Basin of NE China from the Late Early Pleistocene to the Early Holocene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Regional Setting
3. Samples and Methods
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Analytical Methods
3.2.1. Dating Methods
3.2.2. Grain Size Analysis
3.2.3. Elemental Analysis
3.2.4. Total Organic Carbon Analysis
3.3. Calculation Methods
3.3.1. Grain Size Parameter Calculation
3.3.2. Sahu Formula Calculation
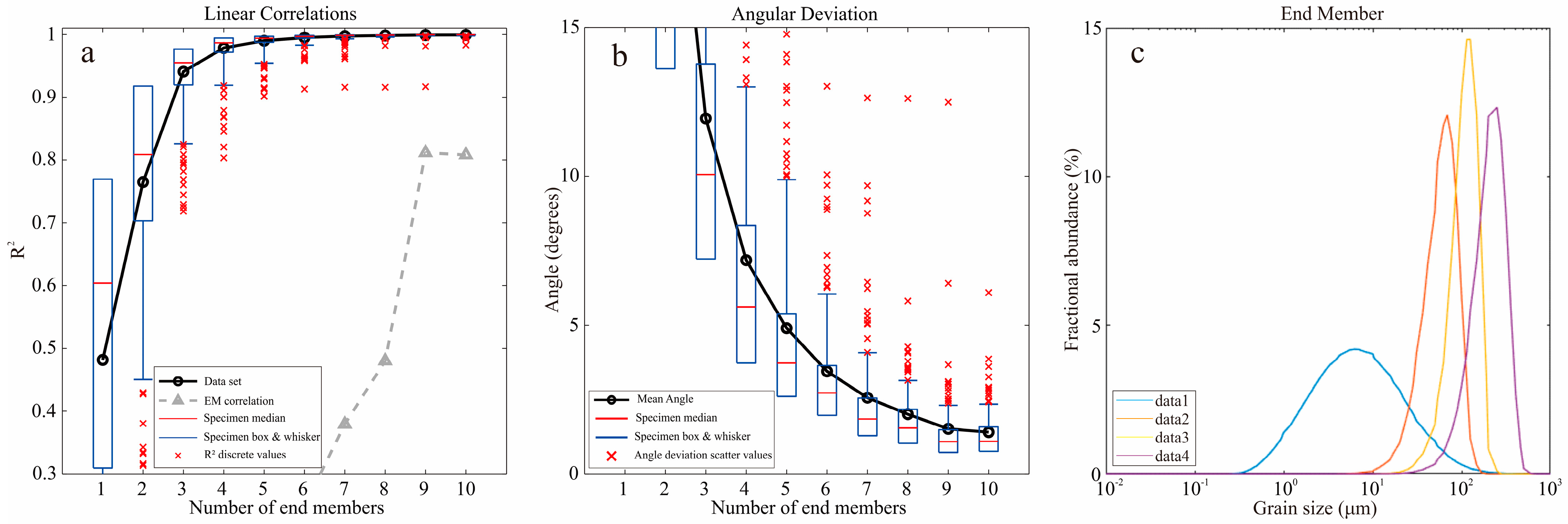
3.3.3. Grain Size End-Member Calculation
4. Results
4.1. Dating Results and Age–Depth Model
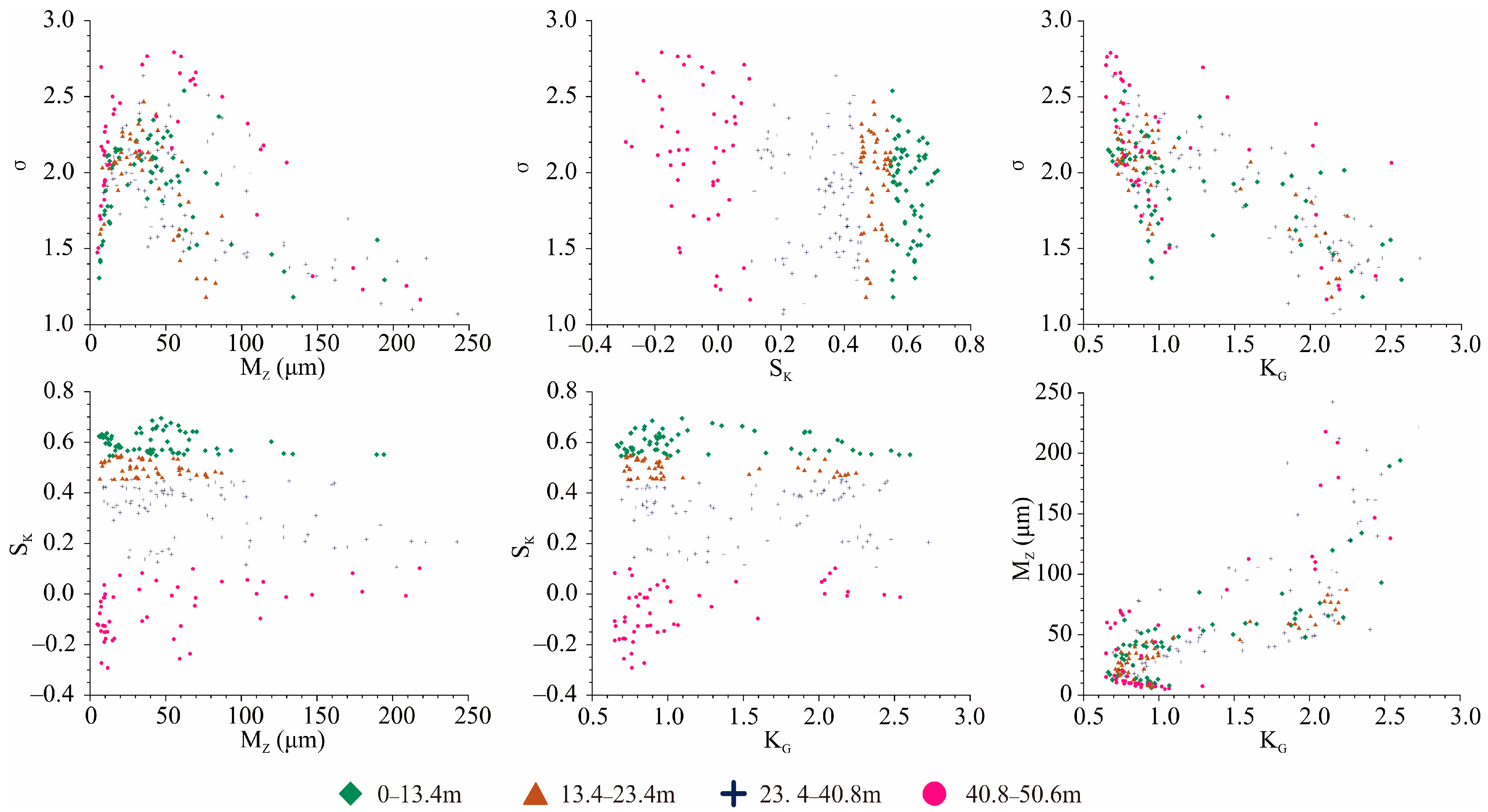
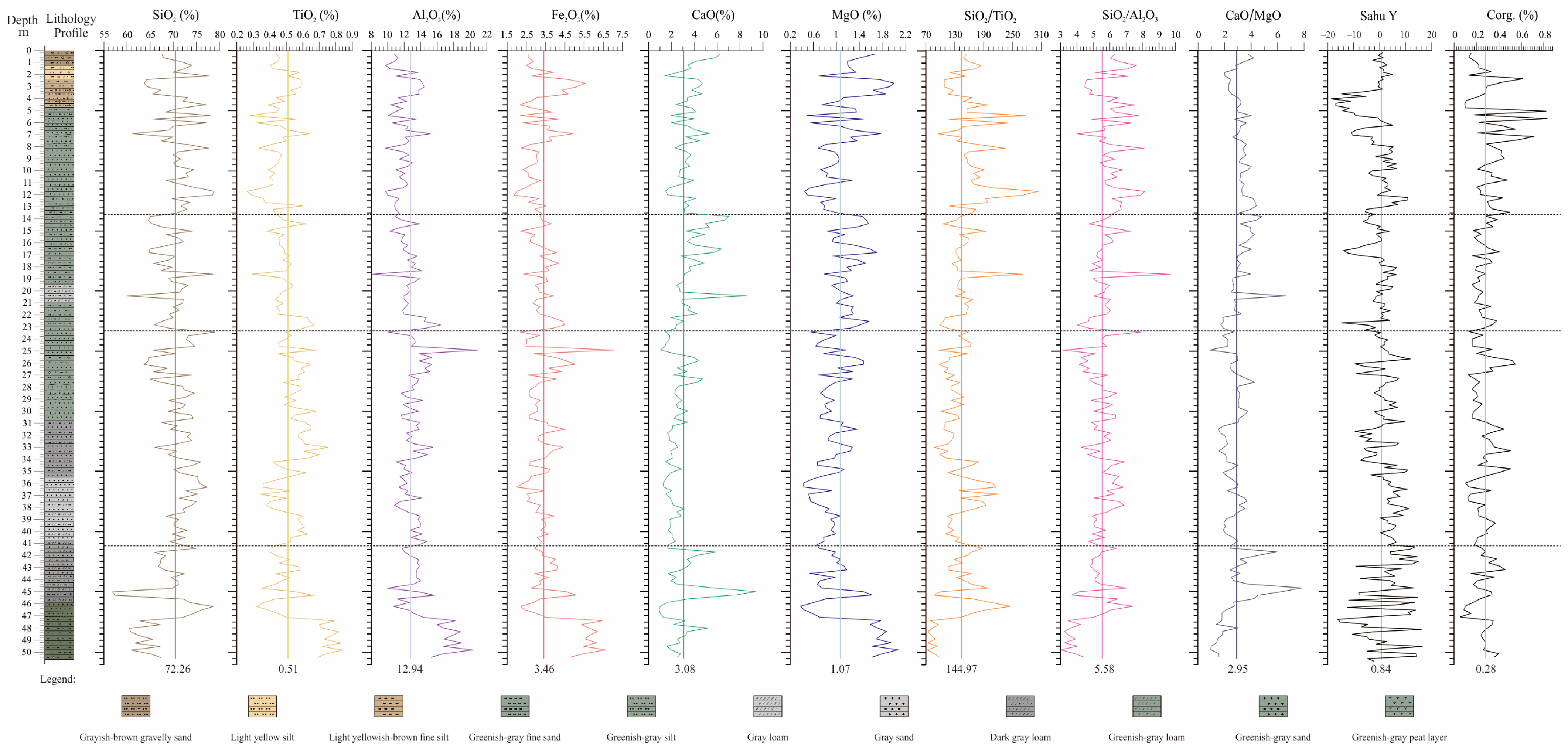
4.2. Grain Size Composition
4.3. Grain Size Parameter Analysis
4.4. Grain Size End-Member Analysis
4.5. Elemental Contents and Ratios
4.6. Sahu Y-Value Characteristics
4.7. Organic Carbon Characteristic
5. Discussion
5.1. Interpretation of Grain Size End Members
5.2. Transport Tracing of Major Elements
5.3. Transport Process Since the Late Early Pleistocene
5.3.1. The Late Early Pleistocene (ca. 885.0–787.6 ka B.P.)
5.3.2. The Early Middle Pleistocene (ca. 787.6–617.7 ka B.P.)
5.3.3. The Mid-Middle Pleistocene (617.7–276.8 ka B.P.)
5.3.4. The Late Middle Pleistocene (276.8–147.2 ka B.P.)
5.3.5. The Late Pleistocene to Early Holocene (147.2–0.6 ka B.P.)
5.4. Paleoclimatic Drivers of Transport Process
6. Conclusions
- The late Early Pleistocene–early Holocene sediment grain size in the drilled core includes four end members: the EM1 aeolian or lacustrine suspended component, the EM2 meltwater or periglacial sediment component, the EM3 dust saltation suspended component caused by wind disturbance, and the EM4 river alluvial component.
- In the saline western Songnen Basin, there were five sediment transport stages from the late Early Pleistocene to the Early Holocene: the late Early Pleistocene transport from weathered volcanic rocks, with minor fluvial–alluvial and proluvial materials; early Middle Pleistocene alluvial–proluvial transport; mid-Middle Pleistocene transport by meltwater and wind; late Middle Pleistocene transport by wind; and late Pleistocene alluvial–proluvial transport.
- The sediment transport process in the saline western Songnen Basin was driven by the local paleoclimate process, which further influenced salt accumulation in the warm humid climate and upward salt migration through capillary action in the cold dry climate, with all of them being controlled by global ice volume cycles.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, X.W.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.T.; Feng, Q.; Xi, H.Y.; Yang, L.S.; Han, T.; Cheng, W.J.; Su, Y.Q. Compounding effects of human activities and climatic changes on coexistence of oasis-desert ecosystems: Prioritizing resilient decision-making for a riskier world. Res. Cold Arid. Reg. 2023, 15, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.M.; Tang, J.; Lin, N.F. Relationship between saline–alkali soil formation and neotectonic movement in Songnen Plain, China. Environ. Geol. 2008, 55, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.F.; Tang, J. Study on the environmental evolution and the analysis of the causes of land salinization and desertification in Songnen plain. Quat. Sci. 2005, 25, 474–483. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.J.; Wang, S.; Qu, X.G.; Wang, L.; Tong, S.Z.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, X.F.; Zhang, W.Q. Impacts of groundwater storage variability on soil salinization in a semi-arid agricultural plain. Geoderma 2025, 454, 117162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Wang, J.D.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Li, C.; Gu, C.Y. Experiments to simulate the salinisation process of loess under a dynamic water cycle. Environ. Res. 2025, 268, 120739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Fu, T.G.; Wang, F.; Zhang, M.; Qi, F.; Liu, J.T. Influence of groundwater table depth on the evolution of saline-alkali land in a coastal area. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 2857–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, G.X.; Yin, X.R.; Liu, Z.J. Field-scale spatial variation of saline-sodic soil and its relation with environmental factors in Western Songnen Plain of China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.J.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, D.S.; Dong, L.S.; Qin, G.H.; Wang, S.F. Impacts of climate change on forest growth in the saline-alkali land of the Yellow River Delta, North China. Dendrochronologia 2022, 74, 125975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.F.; Wang, S.J. Study on the Ecological Geological Environment of Land Salinization in Western Jilin Province. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 2002, 33, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Xu, X.H. Research Progress on Causes, Characteristics and Control Measures of Soda Saline-alkali Land in Songnen Plain. Soil Water Conserv. China 2018, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.G.; Pu, L.J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, R.S. The present situation and hot issues in the salt-affected soil research. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2012, 67, 1233–1245. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.G.; Liu, C.Y. Approaches and prospects of provenance analysis. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2003, 21, 409–415. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.Z. Chinese Sedimentology, 2nd ed.; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Z.; Ling, C.H.; Wan, Z.W.; Jia, Y.L.; Wang, Y.Q. Grain-Size Characteristic of the Regional Sand-Dust Accumulation System in the Southwest of Poyang Lake. Arid. Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 29–37. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/CiFQZXJpb2RpY2FsQ0hJU29scjlTMjAyNTEwMjEwOTUwNDYSDmdocWRsMjAxOTAxMDA0Ggh5bXhsYzZxNQ%3D%3D (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Wang, Z.D.; Huang, C.C.; Zhou, Y.L.; Cha, X.C.; Pang, J.L.; Shang, R.Q. Provenance Analysis of Sediments in the Upper Reaches of the Yinghe River in the Huaihe River Basin. Earth Environ. 2024, 52, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Huang, P.; Sun, J.W.; Yu, Y.H.; Li, A.C. Provenance and controlling factors of major elements in graded components of sediments from the Yalu River. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2019, 39, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.M.; Liu, L.J.; Zhao, H.; Bi, Z.W.; Wang, L.K.; Song, L.; Wang, C.M.; Yang, J.S. Grain-size character and sedimentary environment of Hutuo River paleochannel section. Geoscience 2016, 2, 485–492. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.J. Analysis of grain-size populations with environmentally sensitive components in aeolian deposits and their implications. J. Arid Land Resour. Environ. 2007, 21, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, G.J. Geochemical tracer study of the Asian aeolian dust system. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2011, 41, 1211–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Zhai, S.K. Geochemical Methods for Identification of Sedimentary Provenance. Mar. Sci. 2020, 44, 132–143. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/CiFQZXJpb2RpY2FsQ0hJU29scjlTMjAyNTEwMjEwOTUwNDYSDWh5a3gyMDIwMTIwMTUaCHJmYnVyN3R1 (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Cao, Y.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Xu, T.Y.; Mi, L.S. Application of the ratio of characteristic elements in provenance analysis: A case study from the upper part of the fourth member of the Shahejie Fm. in the W58 area, Dongying Depression. Acta Sediment. Sin. 2007, 25, 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.B.; Wan, S.M. Research progress of tracing sediment sources in Okinawa Trough. Mar. Geol. Front. 2015, 31, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Gao, S. Study on the end-member characteristics of modern clay minerals in the Yangtze River. In Proceedings of the 3rd National Conference on Sedimentology, Chengdu, China, 22–24 September 2005; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.C.; Li, J.B.; Fan, A.P.; Zong, M.; Zhang, T. Research progress and development tendency of provenance analysis on terrigenous sedimentary rocks. Acta Sediment. Sin. 2013, 31, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.B.; He, Q.X.; Yang, S.Y.; Lan, X.H.; Zhang, Z.X. Comparison and application of Shepard’s and Folk’s classifications to the subsurface mapping in the South Yellow Sea. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2008, 28, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, A.M.; Qu, J.J.; Dong, Z.B.; Su, Z.Z.; Wu, B.; Zhang, Z.C.; Qian, G.Q.; Gao, J.L.; Pang, Y.J.; Zhang, C.X. The Characteristic of Grain-Size end Members in Kumtagh Desert and Its Implication for Sediment Source. J. Desert Res. 2020, 40, 33. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/CiFQZXJpb2RpY2FsQ0hJU29scjlTMjAyNTEwMjEwOTUwNDYSDXpnc20yMDIwMDIwMDUaCDZqY2xqZ2xj (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Wang, Z.D.; Huang, C.C.; Zhou, Y.L.; Pang, J.L.; Cha, X.C.; Guo, Y.Q. Environment evolution and provenance characteristics of the loess since the late Pleistocene in Henan Province. Geol. J. China Univ. 2018, 24, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.D.; Huang, C.C.; Yang, H.J.; Pang, J.L.; Cha, X.C.; Zhou, Y.L. Loess Provenance Characteristics and Evolution Indicated by Grain-Size Since the Late Pleistocene at the Eastern Foot of the Liupan Mountains. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 818–826. Available online: https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/CiFQZXJpb2RpY2FsQ0hJU29scjlTMjAyNTEwMjEwOTUwNDYSDWRsa3gyMDE4MDUwMjAaCHJ0eWR3YWYz (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Yang, Y.M.; Zhang, L.Z.; Shen, R.W.; Chu, H.X.; Jiang, Z.L.; Feng, Y.C.; Jiang, W.Q.; Yin, X.B.; Li, J.L.; Wang, P.F.; et al. Characteristics of grain-size and clay mineral distribution of surface sediments and their provenance implication in Tangshan Harbor, Bohai Bay. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2023, 43, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licht, K.J.; Hemming, S.R. Analysis of Antarctic glacigenic sediment provenance through geochemical and petrologic applications. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 164, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.W.; Xia, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.Q. Evolution of the East Asian monsoon and its response to uplift of the Tibetan Plateau since 1.8 Ma recorded by major elements in sediments of the South China Sea. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.F.; Bounlon, V.; Tang, J.; Bian, J.M. Study on the relation between the formation of saline-alkali soil and the neotectonic movement. Glob. Geol. 2005, 24, 282–288+311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.J.; Chi, Y.P.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Wang, Y.H.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Liu, R.N.; Wei, Z.Y.; Liu, H.Q. Variation characteristics and climatic significance of climate proxy indexes of surface sediments in Songnen sandy land. Chin. J. Geol. 2024, 59, 1759–1774. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.S.; Deng, W.; Qian, Z.G. Study on the Formation and Changes of Saline-Alkaline Mire in Songnen Plain. Geogr. Sci. 2000, 20, 362–367. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 695-2014; Soil-Determination of Organic Carbon-Combustion Oxidation Nondispersive Infrared Absorption Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2014; pp. 1–3.
- Krumbein, W.C. Size frequency distributions of sediments. J. Sediment. Res. 1934, 4, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tang, W.W.; Xue, C.F.; Yang, Y.; Gao, W.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Jia, J.J. The Φ Value Expresses Granularity and the Unit Problem of the Sorting Coefficient. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2022, 43, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River bar [Texas]; a study in the significance of grain-size parameters. J. Sediment. Res. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, B.K. Depositional mechanisms from the size analysis of clastic sediments. J. Sediment. Res. 1964, 34, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltje, G.J. End-member modeling of compositional data: Numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem. Math. Geol. 1997, 29, 503–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.H.; An, Z.S.; Su, R.X.; Wu, X.H.; Wang, S.M.; Sun, Q.L.; David, R.; Jan, B. Mathematical methods for separation of sediment grain-size components in paleoenvironment and their applications. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2001, 11, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, G.A.; Heslop, D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain-size data. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2015, 16, 4494–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xie, J. Application of Singular Point Analytical Element Method in Crack Problem. Key Eng. Mater. 2004, 274, 757–762. Available online: https://webofscience.clarivate.cn/wos/alldb/full-record/WOS:000227161500124 (accessed on 3 November 2025).
- Zhang, D.F.; Lin, N.F. A Preliminary Study on the Neotectonism and Climate Cycle Mechanism of Environment Evolvement in the Songnen Plain Since the Quarternary. Glob. Geol. 2000, 19, 73–77. [Google Scholar]
- Shaanxi-Northern Team of Chengdu Institute of Geology. Sedimentary Rock Particle Size Analysis and Its Applications; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1978; p. 147. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.B. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of major elements in surface sediments in Qiongdongnan area. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2007, 27, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, R.Y.; Li, C.C.; Zhang, M.; Sun, C.Q.; Liu, G.N. Analysis of particle characteristics and differentiation processes of glacial sediment in Tianshan and eolian sediment in the Taklimakan Desert. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2012, 48, 744–756. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, N.N.; Pan, B.T.; Wang, J.P.; Hu, Z.B.; Sun, H.; Zhou, T.; Hu, X.F. Grain-size abrupt shift around 0.9 Ma in loess and its environmental effect in Fenwei Basin, China. J. Desert Res. 2008, 28, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.P.; Hao, Y.C.; Wang, Q.K.; Yan, Y.D. Identifying principle of the subsequences for continental fluvial-lacustrine. Daqing Pet. Geol. Dev. 2013, 32, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Remo, J.W.; Heine, R.A.; Ickes, B.S. Particle size distribution of main-channel-bed sediments along the upper Mississippi River, USA. Geomorphology 2016, 264, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J.; Kang, J.C. Quaternary glacial periods, geomorphic periods, and loess records in China. Quat. Res. 1989, 9, 269–278. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.Q.; Gao, H.S.; Zhang, L.K.; Li, Z.M.; Pang, H.L.; Pan, B.T. Grain-size characteristics and evolution of the core sedimentary environment in the Houtao plain reach of the Yellow River. Acta Sedimentol. Sin. 2019, 37, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.J. A misunderstanding in provenance analysis: Sand changes of mineral, roundness, and size in flowing-water transportation. J. Palaeogeogr. 2017, 19, 175–184. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.A.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xiong, D.Q.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J. Geochemical characteristics of major elements in the Wushan Loess. Earth Sci. 2013, 38, 916–922. [Google Scholar]
- Botero, Y.L.; López-Rendón, J.E.; Ramírez, D.; Zapata, D.M.; Jaramillo, F. From clay minerals to Al2O3 nanoparticles: Synthesis and colloidal stabilization for optoelectronic applications. Minerals 2020, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.K.; Li, T.G.; Yu, X.K.; Li, A.C.; Tang, Z.; CHOI, J.Y.; Nan, Q.Y. Major element records of sediment provenance in the West Philippine Sea and the evolution of the East Asian winter monsoon over the past 700 ka. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Hou, H.X.; Wang, W.; Ren, B.Z.; Zhang, G.G.; Li, M.; Qi, L.; Du, X.; Shi, L.F.; Zhan, Z.D.; et al. Geochemical Characteristics of the Ground Substrate Layer in the Black Soil Area of the Northern Songnen Plain and Its Implications for the Provenance of Black Soil. Acta Geosci. Sin. 2025, 46, 827–840. [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt, H.W.; Markovics, G. Weathering of granodioritic crust, long-term storage of elements in weathering profiles, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1997, 61, 1653–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.T.; Huang, Q.H.; Wu, H.B. Soil salinization features in arid areas farmland. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 112–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Z.L.; Derbyshire, E.; Yang, S.L.; Yu, Z.W.; Xiong, S.F.; Liu, T.S. Stacked 2.6-Ma grain-size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record. Paleoceanography 2002, 17, 5-1-5-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.R.; Gong, Y.; Kong, F.P.; Zhao, J.; Ai, C.L.; Pei, Y.D.; He, J.B. Alluvial Plain Evolution and its responds to the paleoclimate indicated by sediment grain-size in the Western Songnen Plain during the Middle–Late Pleistocene. Quaternary, 2025; submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Lisiecki, L.E.; Raymo, M.E. A Pliocene-Pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic δ18O records. Paleoceanography 2005, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, T.; Zeng, F.M.; Yang, Y.; Ge, J.Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Huang, R.F.; Liang, Y.X.; Li, E.; et al. Decreasing summer monsoon precipitation during glacial at ca.900 ka: Evidence from grain-size variation of lacustrine deposits from the Northeast Plain of China. Quat. Sci. 2020, 40, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Chi, Y.P.; Hao, D.M.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Wu, P. Evolution of summer monsoon in Songnen Plain since Middle Pleistocene: Magnetic susceptibility, geochemistry and total organic carbon records from Harbin loess. Chin. J. Geol. 2021, 56, 1279–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.Y.; Xie, Y.Y.; Kang, C.G.; Chi, Y.P.; Sun, L.; Wu, P.; Wei, Z.Y.; Leng, Y.K. Sedimentological, mineralogical, and geochemical characteristics of the Luojiawopeng Fm. in Harbin: Implications for the sedimentary environment. Chin. J. Geol. 2022, 57, 172–189. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, T.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, F.M.; Liang, Y.X.; Ge, J.Y.; Ma, Y.F.; Kong, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, X.; Huang, R.F.; et al. Magnetostratigraphy and magnetic susceptibility of the Dumeng borehole sequence from Northeast China Plain and implications for sedimentary evolution of the Songnen paleo-lake. Chin. J. Geophys. 2023, 66, 673–684. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.L.; Zhang, R.C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.J.; Wang, R.J.; Gao, S.P. Environmental change since 5000cal. a BP in the Anguli-Nuur Lake area based on palynological and geochemical records. Quat. Sci. 2017, 37, 130–142. [Google Scholar]
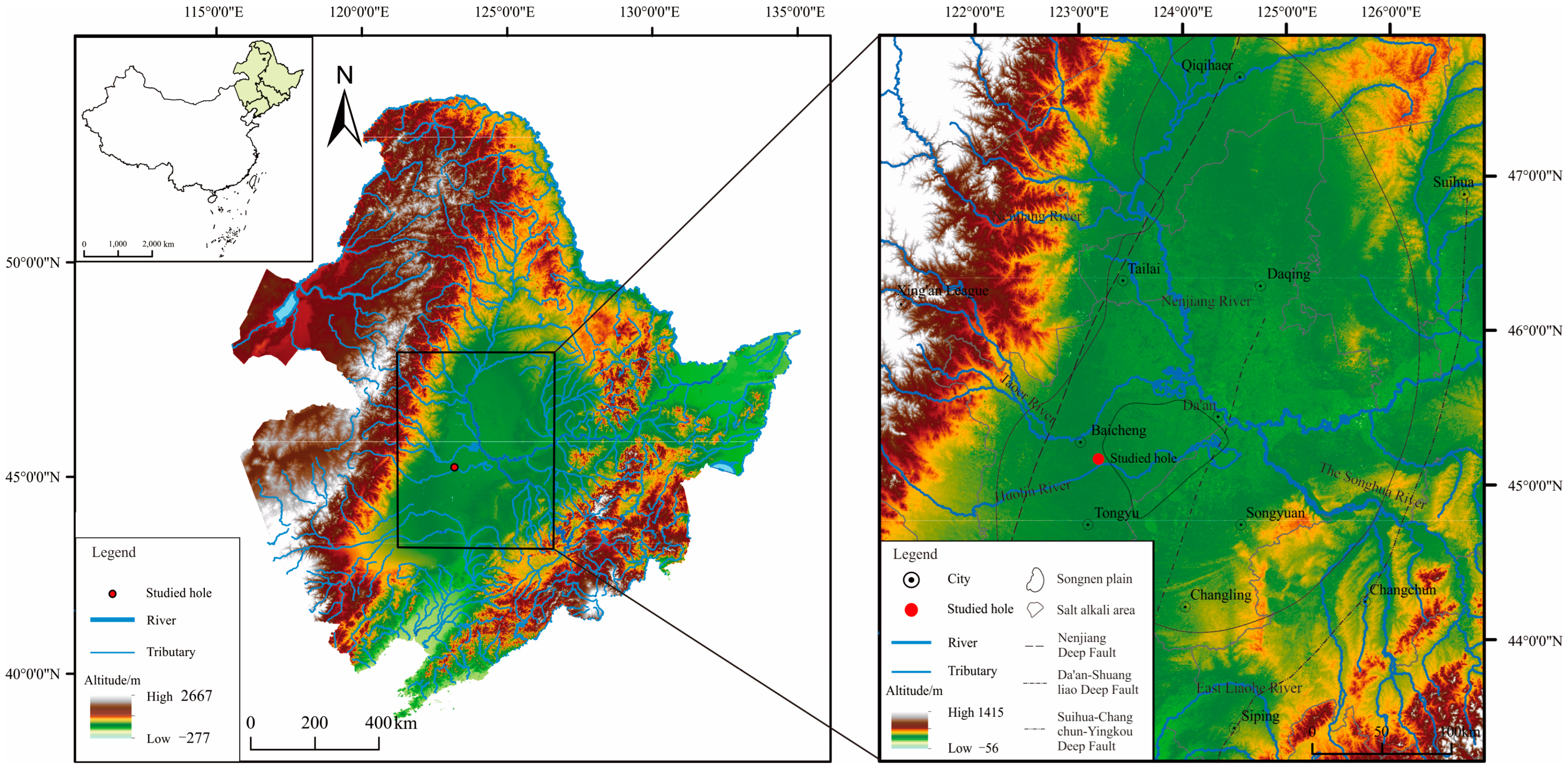
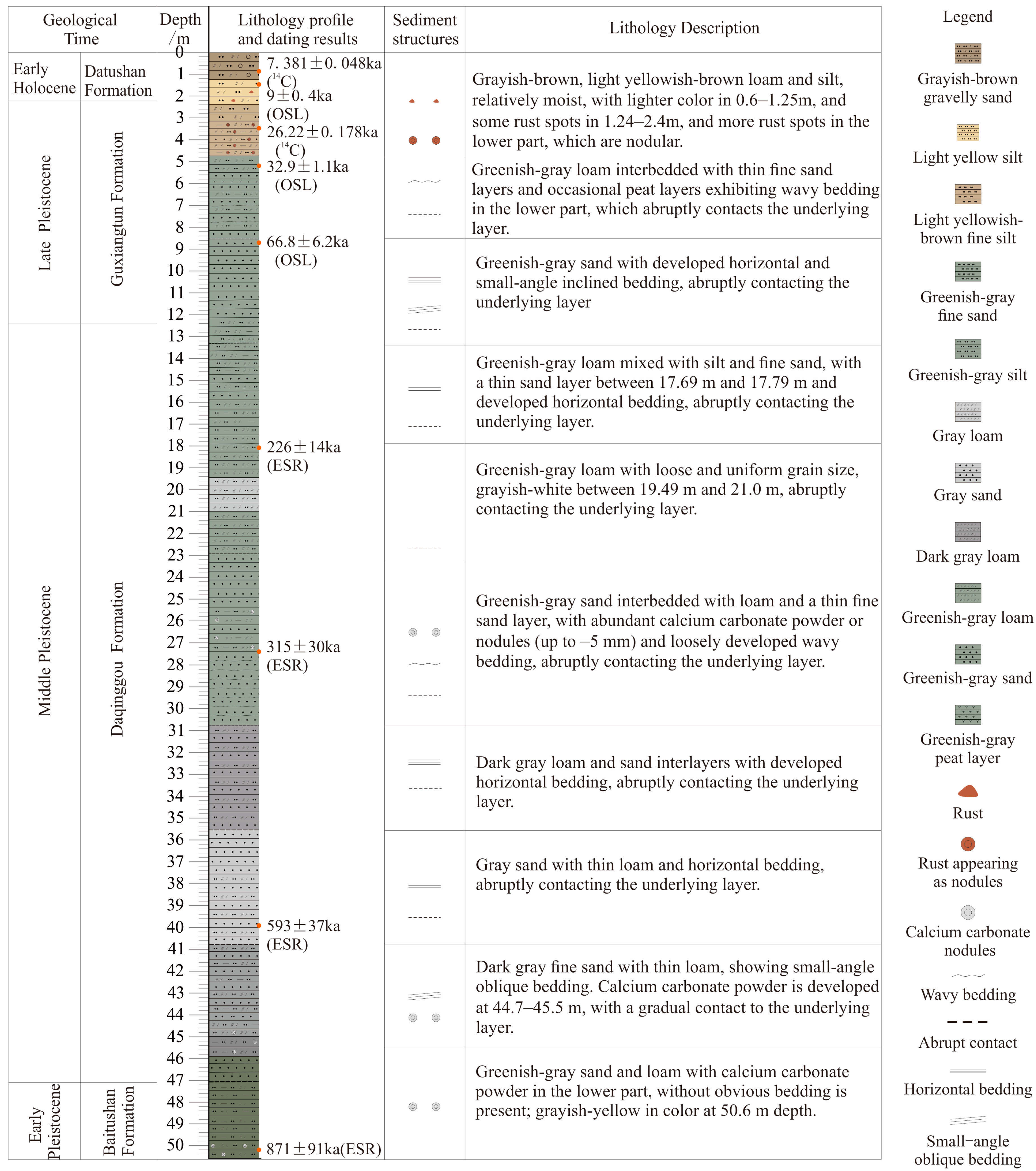
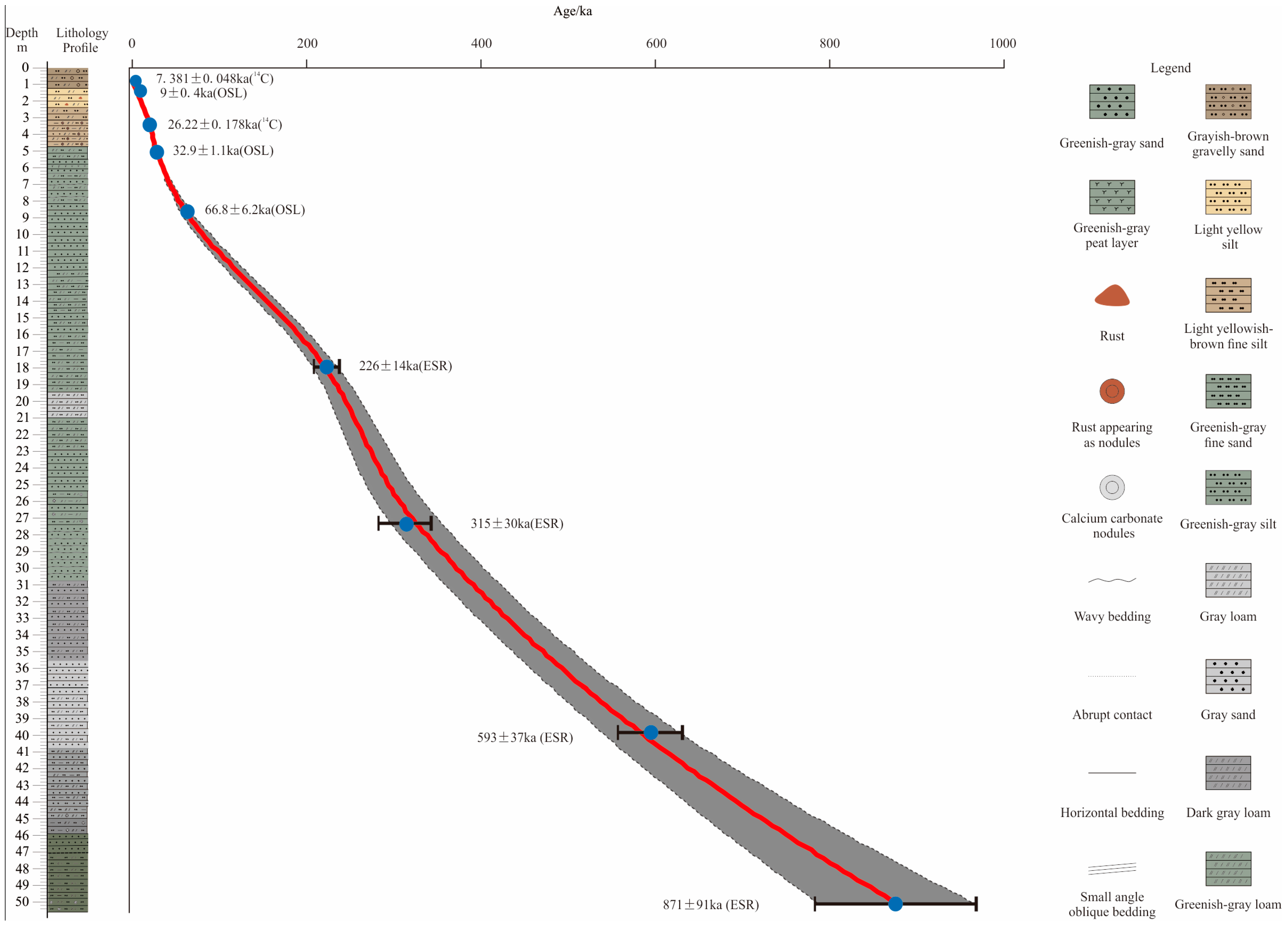


| Lab Code | Sample Number | Sampling Depth (m) | Sample Material | Present Year (a BP) | Tree-Ring Correction (Cal BP) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interval | μ ± σ | |||||
| CG-2024-2084 | TNZK06-14C1 | 0.80 | Total carbon | 6485 ± 45 | 7481 (93.4%) 7305 7300 (2.1%) 7280 | 7381 ± 48 |
| CG-2024-2085 | TNZK06-14C2 | 3.40 | Total carbon | 22,000 ± 140 | 26,747 (1.5%) 26,679 26,490 (93.9%) 25,914 | 26,224 ± 178 |
| Sample Number | Sampling Depth (m) | U (ppm) | K (%) | Th (ppm) | Water Content (%) | Dose Rate (Gy/ka) | Equivalent Dose (Gy) | Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNZK06-G1 | 1.40 | 3.809 | 2.04 | 11.29 | 25.29 | 2.72 | 24.6 ± 1.1 | 9.0 ± 0.4 |
| TNZK06-G2 | 5.10 | 3.416 | 2.36 | 13.55 | 31.63 | 2.72 | 89.6 ± 2.9 | 32.9 ± 1.1 |
| TNZK06-G3 | 8.65 | 3.549 | 2.37 | 9.823 | 24.09 | 2.74 | 183.0 ± 17.1 | 66.8 ± 6.2 |
| Sample Number | Sampling Depth (m) | U (μg/g) | K (%) | Th (μg/g) | Water Content (%) | Dose Rate (Gy/ka) | Equivalent Dose (Gy) | Age (ka) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNZK06-D1 | 18 | 1.86 ± 0.07 | 2.35 ± 0.09 | 10.10 ± 0.20 | 17 ± 5 | 2.77 ± 0.14 | 626 ± 40 | 226 ± 14 |
| TNZK06-D2 | 27.33 | 2.57 ± 0.10 | 2.85 ± 0.11 | 10.90 ± 0.22 | 15 ± 5 | 3.44 ± 0.17 | 1084 ± 104 | 315 ± 30 |
| TNZK06-D3 | 39.85 | 2.81 ± 0.11 | 2.48 ± 0.10 | 10.10 ± 0.20 | 19 ± 5 | 2.97 ± 0.15 | 1764 ± 111 | 593 ± 37 |
| TNZK06-D4 | 50.1 | 22.50 ± 0.90 | 2.18 ± 0.09 | 11.50 ± 0.23 | 19 ± 5 | 2.77 ± 0.14 | 2412 ± 253 | 871 ± 91 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Ai, C.; Kong, F.; Zhao, J.; Gong, Y.; Pei, Y.; He, J. Sediment Transport into the Saline Western Songnen Basin of NE China from the Late Early Pleistocene to the Early Holocene. Land 2025, 14, 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112263
Zhang X, Ai C, Kong F, Zhao J, Gong Y, Pei Y, He J. Sediment Transport into the Saline Western Songnen Basin of NE China from the Late Early Pleistocene to the Early Holocene. Land. 2025; 14(11):2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112263
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinrong, Changli Ai, Fanpeng Kong, Jian Zhao, Yan Gong, Yandong Pei, and Jinbao He. 2025. "Sediment Transport into the Saline Western Songnen Basin of NE China from the Late Early Pleistocene to the Early Holocene" Land 14, no. 11: 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112263
APA StyleZhang, X., Ai, C., Kong, F., Zhao, J., Gong, Y., Pei, Y., & He, J. (2025). Sediment Transport into the Saline Western Songnen Basin of NE China from the Late Early Pleistocene to the Early Holocene. Land, 14(11), 2263. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112263






