Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Mechanisms of Land Surface Temperature in the Urumqi Metropolitan Area Based on Land Use Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
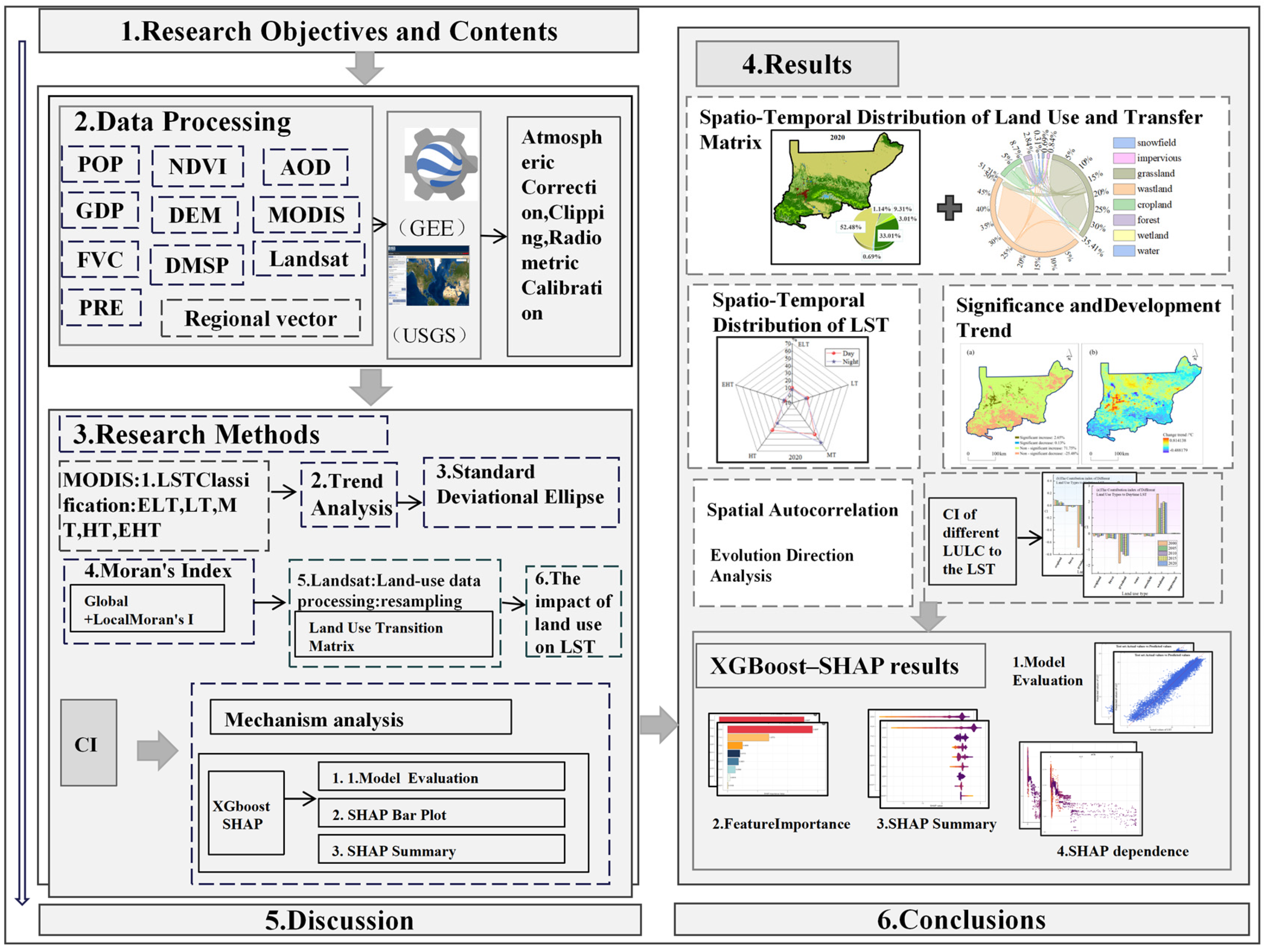
2. Materials and Methods
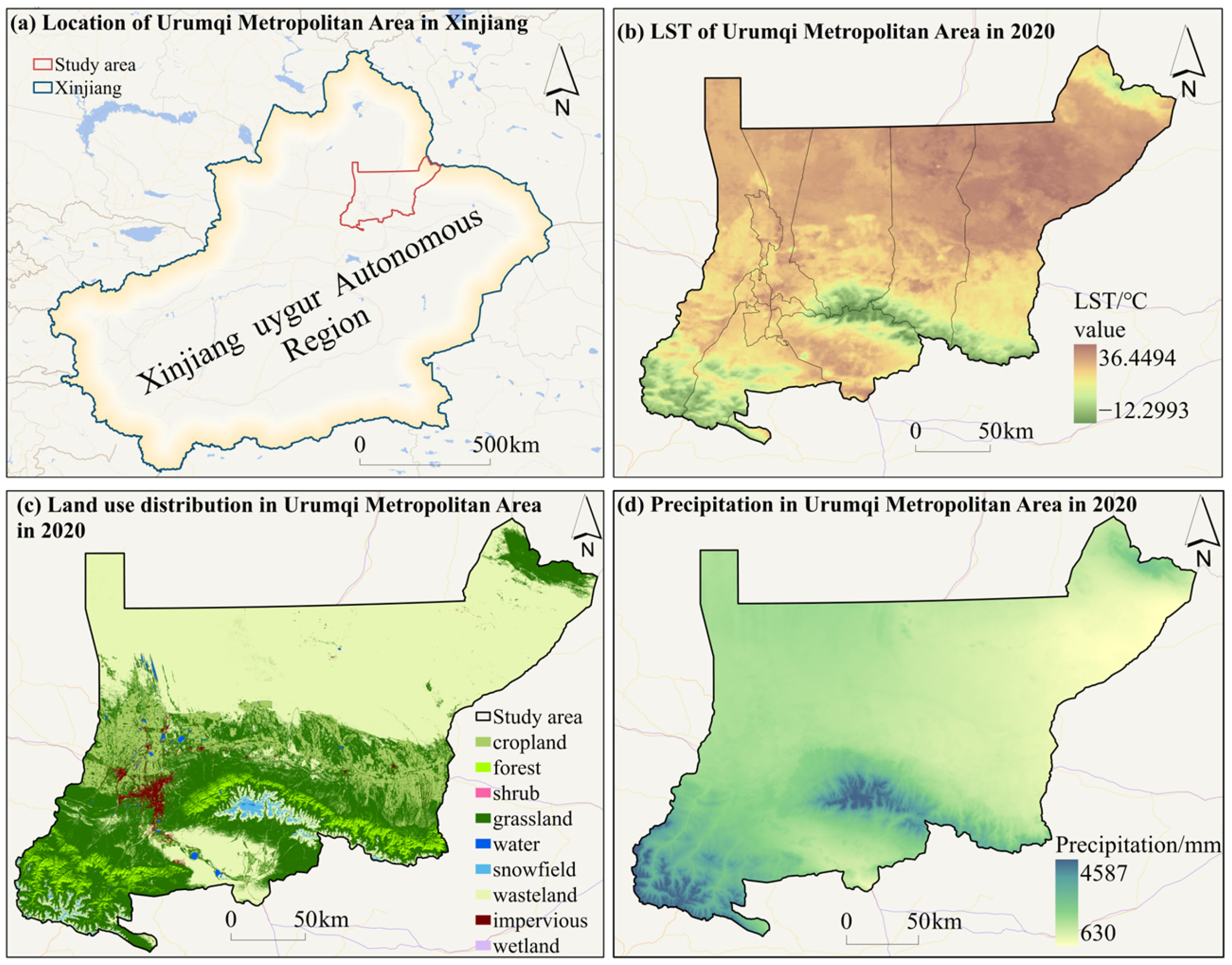
2.1. Study Area Overview
2.2. Data Sources and Research Methods
2.2.1. Data Sources
2.2.2. Research Methods
2.2.3. Classification of LST Grades
2.2.4. Standard Deviation Ellipse (SDE) and Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelation
2.2.5. Calculation of Contribution Index
2.2.6. Analyzing Driving Factors of LST Using XGBoost and SHAP
- XGBoost Regression Model
- 2.
- Model Performance Evaluation
- 3.
- Model Interpretation with SHAP Values
3. Results
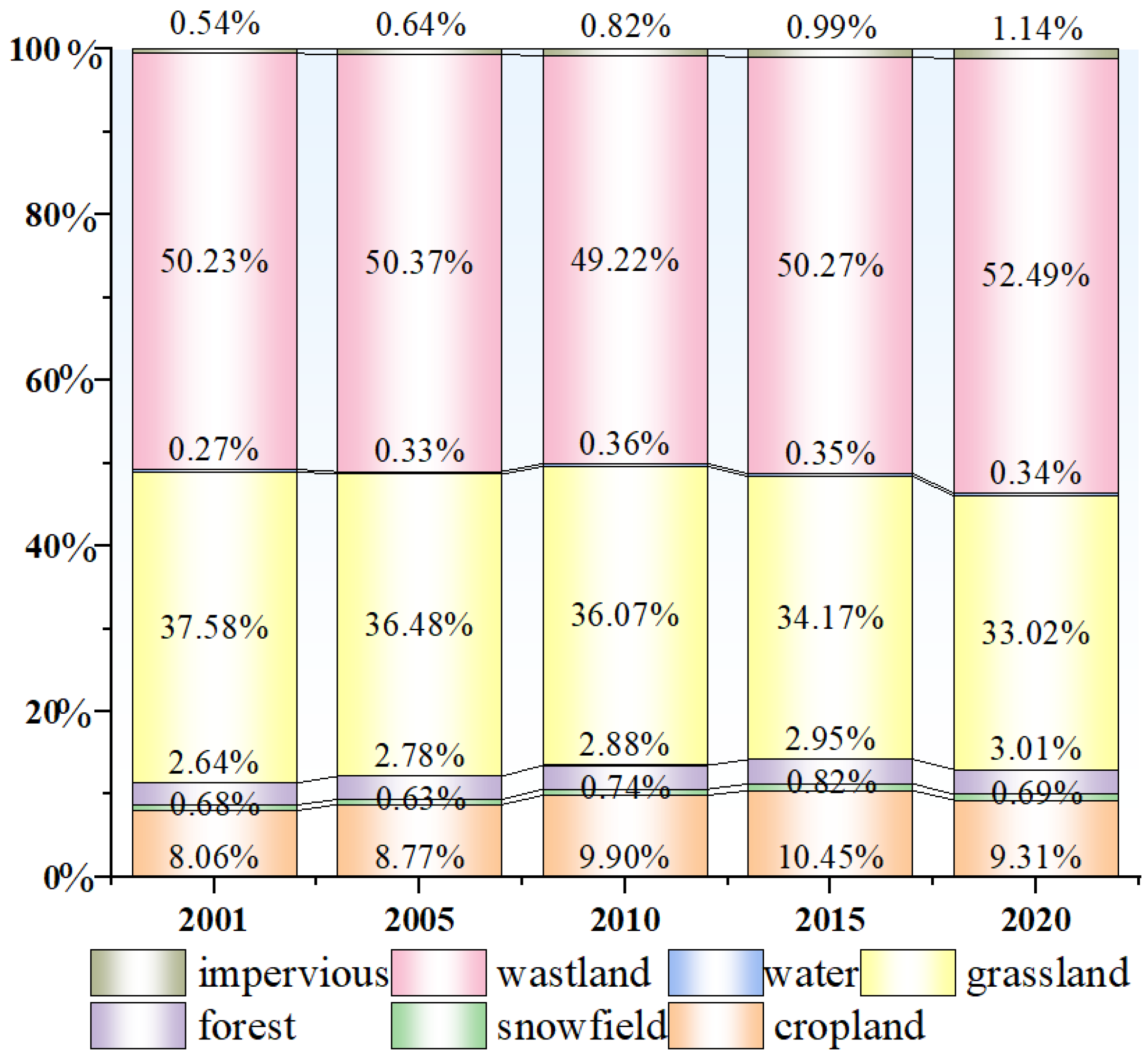
3.1. Land Use Distribution and Transition Characteristics
3.2. Spatiotemporal Characteristics of LST
3.2.1. Daytime and Nighttime LST from 2001 to 2020
3.2.2. Temporal Variation Trend of LST
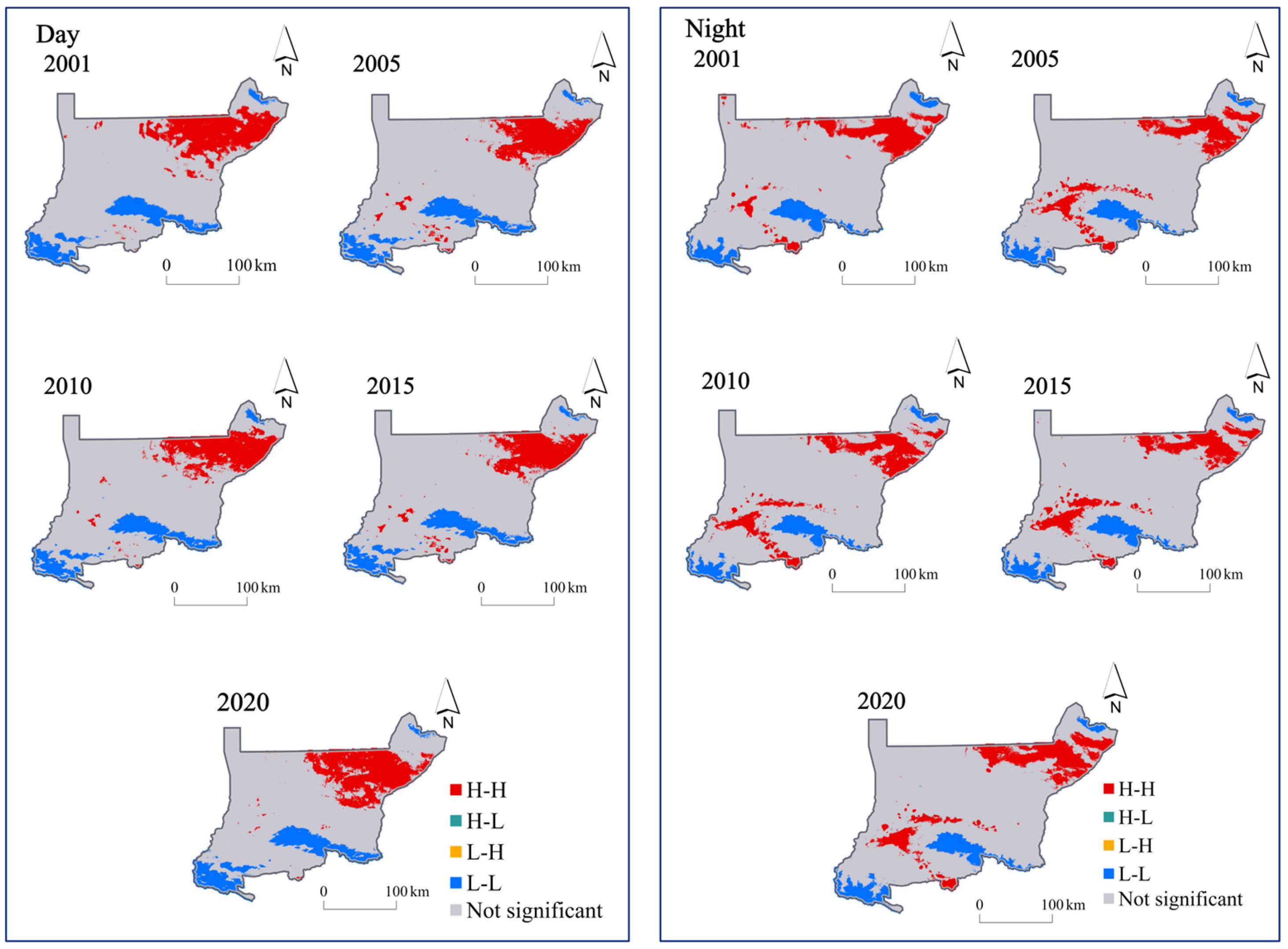
3.2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis of LST
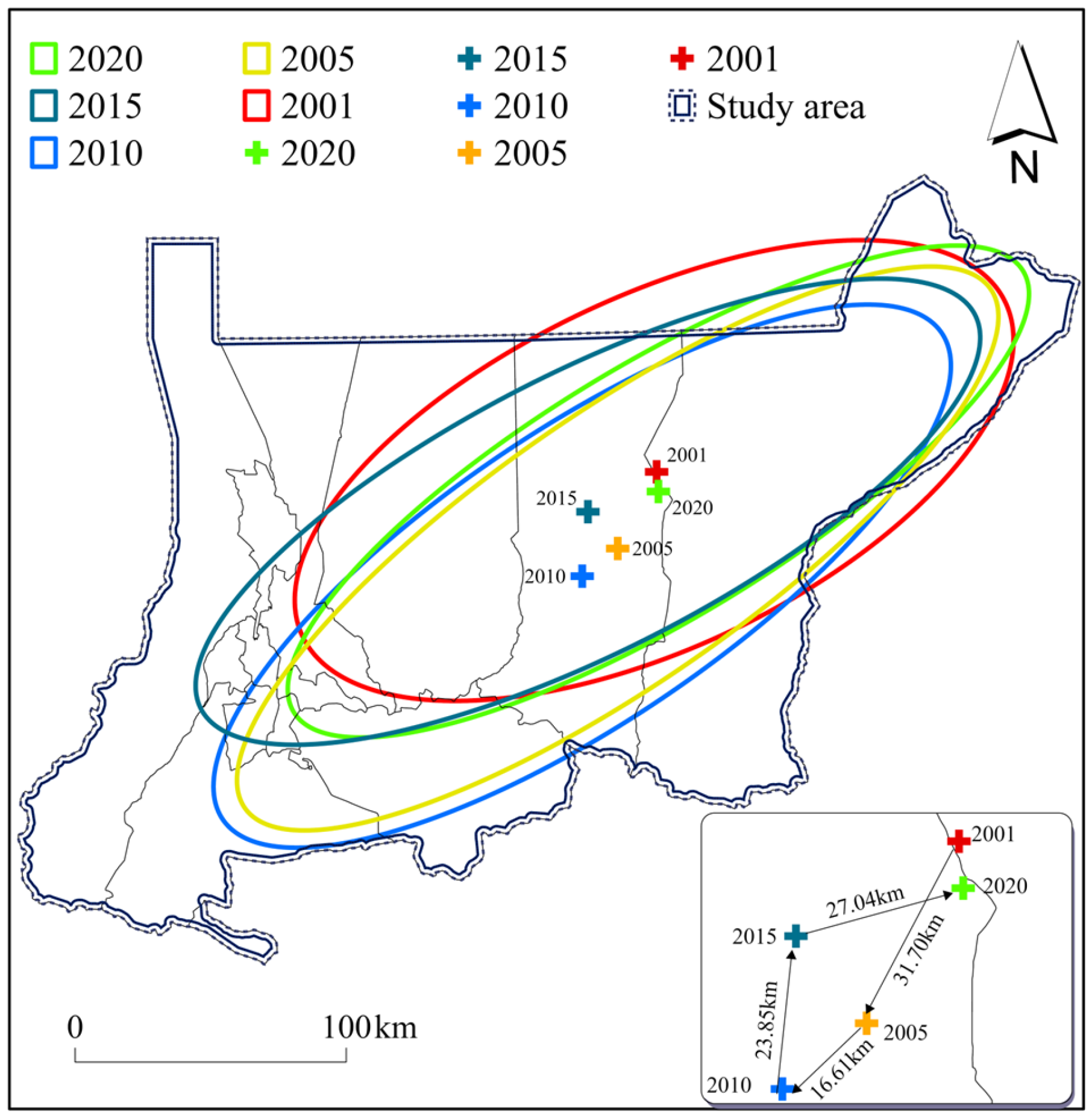
3.2.4. Analysis of LST Evolution Direction
3.2.5. Contribution of Land Use Types to the Regional LST
3.3. Machine Learning-Based Analysis of LST Drivers
3.3.1. Model Performance and Validation
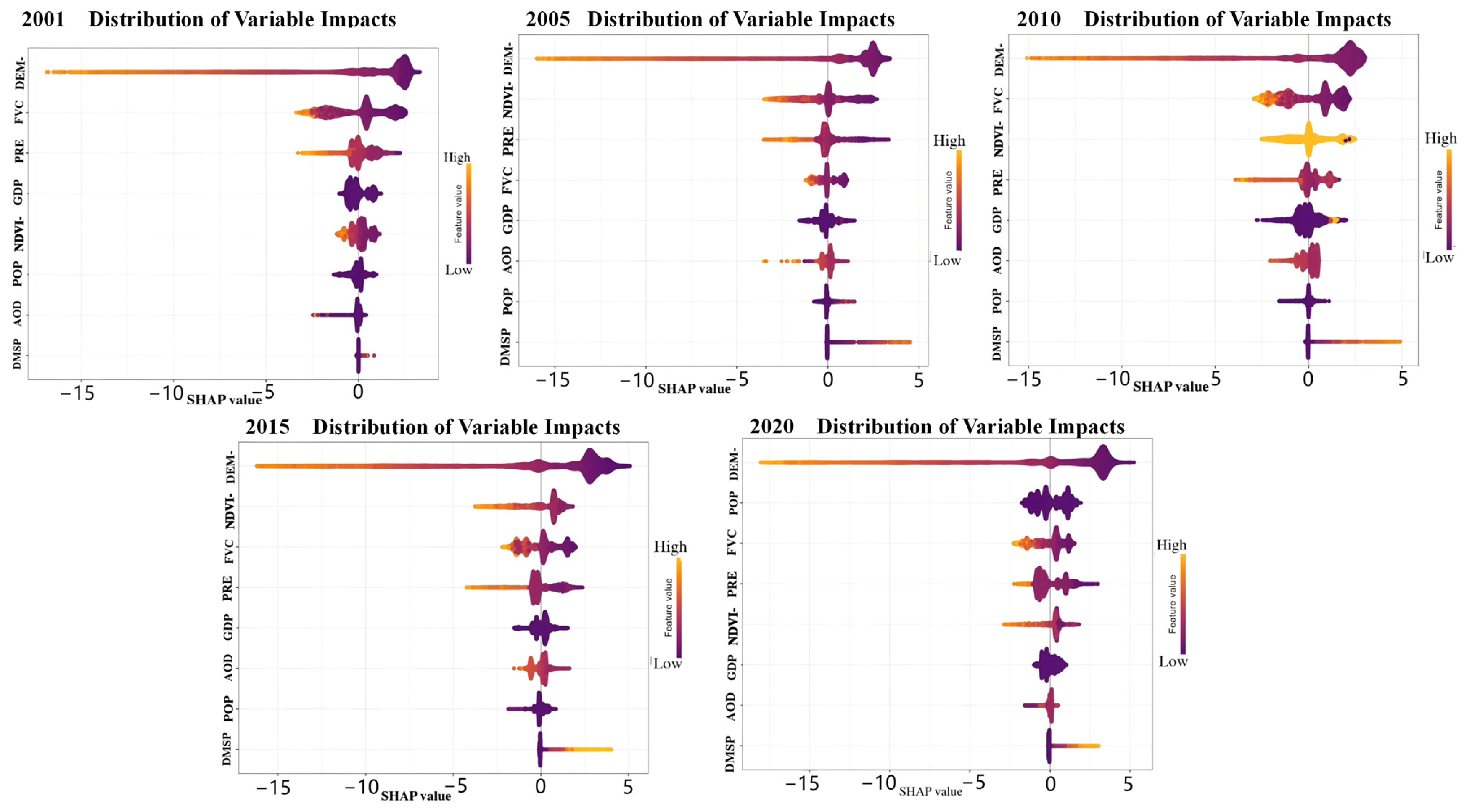
3.3.2. Relative Importance of Driving Factors
3.3.3. Nonlinear Relationships and Threshold Effects
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Variation in Surface Temperature in UMA
4.2. Driving Effects of Land Use Structure Adjustment on Thermal Pattern and Implications for Urban Sustainability
4.3. Machine Learning Interpretation of LST Driving Mechanisms in the UMA
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wenhui, K. Advance and future prospects of urban land use/cover change and ecological regulation of thermal environment. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Oh, K. Developing the urban thermal environment management and planning (UTEMP) system to support urban planning and design. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wei, W.; Zhou, L.; Guo, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Xie, B. Analysis on spatio-temporal evolution of ecological vulnerability in arid areas of northwest China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 4707–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, Z.; Ning, S.; Zhang, X. The decoupling relationship between land use efficiency and carbon emissions in China: An analysis using the socio-ecological systems (SES) framework. Land Use Policy 2024, 138, 107055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, B.; Hu, K. A review of impacts of urbanization on extreme heat events. Prog. Geogr. 2015, 34, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jiang, L.; Liu, B.; Liu, R.; Xiao, Z. Characteristics of drought in China and its effect on vegetation change in recent 40 years. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 7936–7949. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Meng, F.; Wang, Y.; Sa, C.; Bao, Y.; Liu, T. Mutual feedback relationship between vegetation GPP and soil moisture in China under climate change. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2024, 79, 218–239. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.-G.; Guo, A.-Q.; Wu, A.-B.; Wang, Y.-T.; Fan, J. Evolution of urban expansion pattern and its impact on the quality of the ecological environment in the beijing-tianjin-hebei urban agglomeration. Huan Jing Ke Xue = Huanjing Kexue 2025, 46, 3708–3719. [Google Scholar]
- Amindin, A.; Pouyan, S.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Yousefi, S.; Tiefenbacher, J.P. Spatial and temporal analysis of urban heat island using landsat satellite images. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 41439–41450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadizadeh Shorabeh, S.; Hamzeh, S.; Zanganeh Shahraki, S.; Firozjaei, M.K.; Jokar Arsanjani, J. Modelling the intensity of surface urban heat island and predicting the emerging patterns: Landsat multi-temporal images and Tehran as case study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 7400–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lioubimtseva, E.; Cole, R.; Adams, J.; Kapustin, G. Impacts of climate and land-cover changes in arid lands of central asia. J. Arid. Environ. 2005, 62, 285–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, P.; Juanjuan, W.; Shanshan, W.; Liulan, T.; Jie, L.; Zhaopeng, W. Spatiotemporal pattern evolution of land use conflict in urumqi city from the perspective of ecological security. Arid. Land. Geogr. 2024, 47, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tao, H.; Zhu, J.; Mondal, S.K.; Bakhtiyorov, Z. Assessment of ecological vulnerability in xinjiang uygur autonomous region, China. Res. Cold Arid. Reg. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Halik, Ü.; Shi, L.; Fu, W.; Gan, L.; Welp, M. Habitat quality dynamics in urumqi over the last two decades: Evidence of land use and land cover changes. Land 2025, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Kasimu, A.; Reheman, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Aizizi, Y.; Liang, H. Spatiotemporal characteristics and prediction of carbon emissions/absorption from land use change in the urban agglomeration on the northern slope of the tianshan mountains. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhou, L.; Tang, X.; Sun, D.; Dang, X. Spatial influence and prediction of oasis urban expansion on cultivated land in arid areas: A case study of the hexi corridor. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 1008–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumai, M.; Kasimu, A.; Liang, H.; Tang, L.; Aizizi, Y.; Zhang, X. A Study on the Spatial and Temporal Variation of Summer Surface Temperature in the Bosten Lake Basin and Its Influencing Factors. Land 2023, 12, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamattursun, A.; Yang, H.; Ablikim, K.; Obulhasan, N. Spatiotemporal evolution and driving forces of vegetation cover in the Urumqi River Basin. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 15323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zeng, J. Spatial relationship of urban development to land surface temperature in three cities of southern fujian. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2021, 76, 566–583. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.; Yang, J.; Cong, N.; Ren, J.; Yu, H.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. Attribution of urban diurnal thermal environmental change: Importance of global–local effects. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2023, 16, 8087–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhou, S.; Kang, R.; Kaufmann, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Impact of land transformation processes in eastern China on the long-term development of land surface temperatures. Geocarto Int. 2024, 39, 2322063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, G. Examining the relationship between land use/land cover (LULC) and land surface temperature (LST) using explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) models: A case study of Seoul, South Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagi, O.; Rokach, L. Approximating XGBoost with an interpretable decision tree. Inf. Sci. 2021, 572, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subedi, B.; Morneau, A.; LeBel, L.; Gautam, S.; Cyr, G.; Tremblay, R.; Carle, J.-F. An xgboost-based machine learning approach to simulate carbon metrics for forest harvest planning. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takefuji, Y. Beyond xgboost and SHAP: Unveiling true feature importance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 488, 137382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Chen, Q.; Du, M.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, R. Simulation analysis of the cooling effect of urban water bodies on the local thermal environment. Water 2022, 14, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachsen, T.; Ketzler, G.; Knörchen, A.; Schneider, C. Past and future evolution of nighttime urban cooling by suburban cold air drainage in aachen. DIE Erde–J. Geogr. Soc. Berl. 2013, 144, 274–289. [Google Scholar]
- Rochette Cordeiro, A.M.; Ornelas, A.; Silva, D.D. The importance of topography in the formation of cold-air pooling in urban spaces. The example of the city of Coimbra (Portugal). Theor. Appl. Clim. 2023, 152, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abulimiti, A.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Mamtimin, A.; Yao, J.; Zeng, Y.; Abulikemu, A. Urbanization effect on regional thermal environment and its mechanisms in arid zone cities: A case study of urumqi. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Zhou, R.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y. Long-term spatiotemporal patterns and evolution of regional heat islands in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei urban agglomeration. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Zhang, D. Recent advances in understanding urban heat island effects with some future prospects. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2012, 70, 338–353. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xun, X.; Hou, Y.; Gao, S. Analysis on thermal physical properties of different ground types. J. Chang Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2015, 35, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Bindajam, A.A.; Mallick, J.; AlQadhi, S.; Singh, C.K.; Hang, H.T. Impacts of vegetation and topography on land surface temperature variability over the semi-arid mountain cities of Saudi Arabia. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, Y.; Yu, F.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variation of land surface temperature and its driving factors in xinjiang, China. J. Arid. Land 2024, 16, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, L.; Peng, L.; Qiang, L. Study on a model of water surface growth and its driving factors in large cities along the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 3766–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, C.; Shan, B.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Investigating the influence of land cover on land surface temperature. Adv. Space Res. 2025, 75, 2614–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Yu, W.; Ren, J.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J. XGBoost-based analysis of the relationship between urban 2-D/3-D morphology and seasonal gradient land surface temperature. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 4109–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J. Spatial differences and influencing factors of land surface temperature in xinjiang: A county-level study. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2025, 156, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chen, X.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y. Study on the response of the summer land surface temperature to urban morphology in urumqi, china. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyantuyev, A.; Wu, J. Urban heat islands and landscape heterogeneity: Linking spatiotemporal variations in surface temperatures to land-cover and socioeconomic patterns. Landsc. Ecol. 2010, 25, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imhoff, M.L.; Zhang, P.; Wolfe, R.E.; Bounoua, L. Remote sensing of the urban heat island effect across biomes in the continental USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olgun, R.; Karakuş, N.; Selim, S.; Yilmaz, T.; Erdoğan, R.; Aklıbaşında, M.; Dönmez, B.; Çakır, M.; Ardahanlıoğlu, Z.R. Impacts of landscape composition on land surface temperature in expanding desert cities: A case study in arizona, USA. Land 2025, 14, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| ELT | LT | MT | HT | EHT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T < μ − 1.5 std | μ − 1.5 std ≤ T < μ − 0.5 std | μ − 0.5 std ≤ T < μ + 0.5 std | μ + 0.5 std ≤ T < μ + 1.5 std | T > μ + 1.5 std | ||
| 2001 | Day | −10.962~8.893 | 8.894~15.153 | 15.15 ~21.413 | 21.414~27.673 | 27.674~29.553 |
| Night | −25.485~−7.398 | −7.397~−4.131 | −4.13~−0.464 | −0.463~2.434 | 2.435~6.782 | |
| 2005 | Day | −13.101~10.351 | 10.352~16.809 | 16.81~23.267 | 23.268~29.725 | 29.726~34.283 |
| Night | −25.691~−7.921 | −7.92~−4.739 | −4.738~−1.557 | −1.556~1.625 | 1.626~5.636 | |
| 2010 | Day | −13.239~9.474 | 9.475~15.993 | 15.994~22.512 | 22.513~29.031 | 29.032~33.953 |
| Night | −27.173~−7.561 | −7.56~−4.524 | −4.523~−1.487 | −1.486~1.551 | 1.552~5.696 | |
| 2015 | Day | −12.249~10.466 | 10.467~17.521 | 17.522~24.576 | 24.577~31.631 | 31.632~35.122 |
| Night | −22.596~6.314 | −6.313~−3.023 | −3.022~0.07 | 0.071~3.56 | 3.561~6.743 | |
| 2020 | Day | −12.298~11.333 | 11.334~18.397 | 18.398~25.461 | 25.462~32.525 | 32.526~36.449 |
| Night | −25.485~−7.398 | −7.397~−4.131 | −4.13~−0.464 | −0.463~2.434 | 2.435~6.782 | |
| 2001 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Night | Day | Night | Day | Night | Day | Night | Day | Night | |
| Moran’s I | 0.999 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.997 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.998 | 0.997 |
| z | 661.377 | 661.297 | 659.281 | 659.519 | 659.415 | 659.354 | 659.681 | 659.586 | 659.673 | 659.424 |
| p | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.00 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Evaluation Indicators | 2001 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training sets | RMSE | 1.464 | 1.619 | 1.847 | 1.625 | 1.613 |
| MAE | 1.097 | 1.16 | 1.358 | 1.203 | 1.209 | |
| R2 | 0.936 | 0.927 | 0.914 | 0.94 | 0.94 | |
| Test sets | RMSE | 1.508 | 1.625 | 1.87 | 1.668 | 1.637 |
| MAE | 1.125 | 1.175 | 1.374 | 1.234 | 1.224 | |
| R2 | 0.933 | 0.922 | 0.913 | 0.935 | 0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shayiti, B.; Kasimu, A. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Mechanisms of Land Surface Temperature in the Urumqi Metropolitan Area Based on Land Use Change. Land 2025, 14, 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112252
Shayiti B, Kasimu A. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Mechanisms of Land Surface Temperature in the Urumqi Metropolitan Area Based on Land Use Change. Land. 2025; 14(11):2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112252
Chicago/Turabian StyleShayiti, Buwajiaergu, and Alimujiang Kasimu. 2025. "Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Mechanisms of Land Surface Temperature in the Urumqi Metropolitan Area Based on Land Use Change" Land 14, no. 11: 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112252
APA StyleShayiti, B., & Kasimu, A. (2025). Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Mechanisms of Land Surface Temperature in the Urumqi Metropolitan Area Based on Land Use Change. Land, 14(11), 2252. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14112252







