Robust Ensemble-Based Model and Web Application for Nitrogen Content Prediction in Hydrochar from Sewage Sludge
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
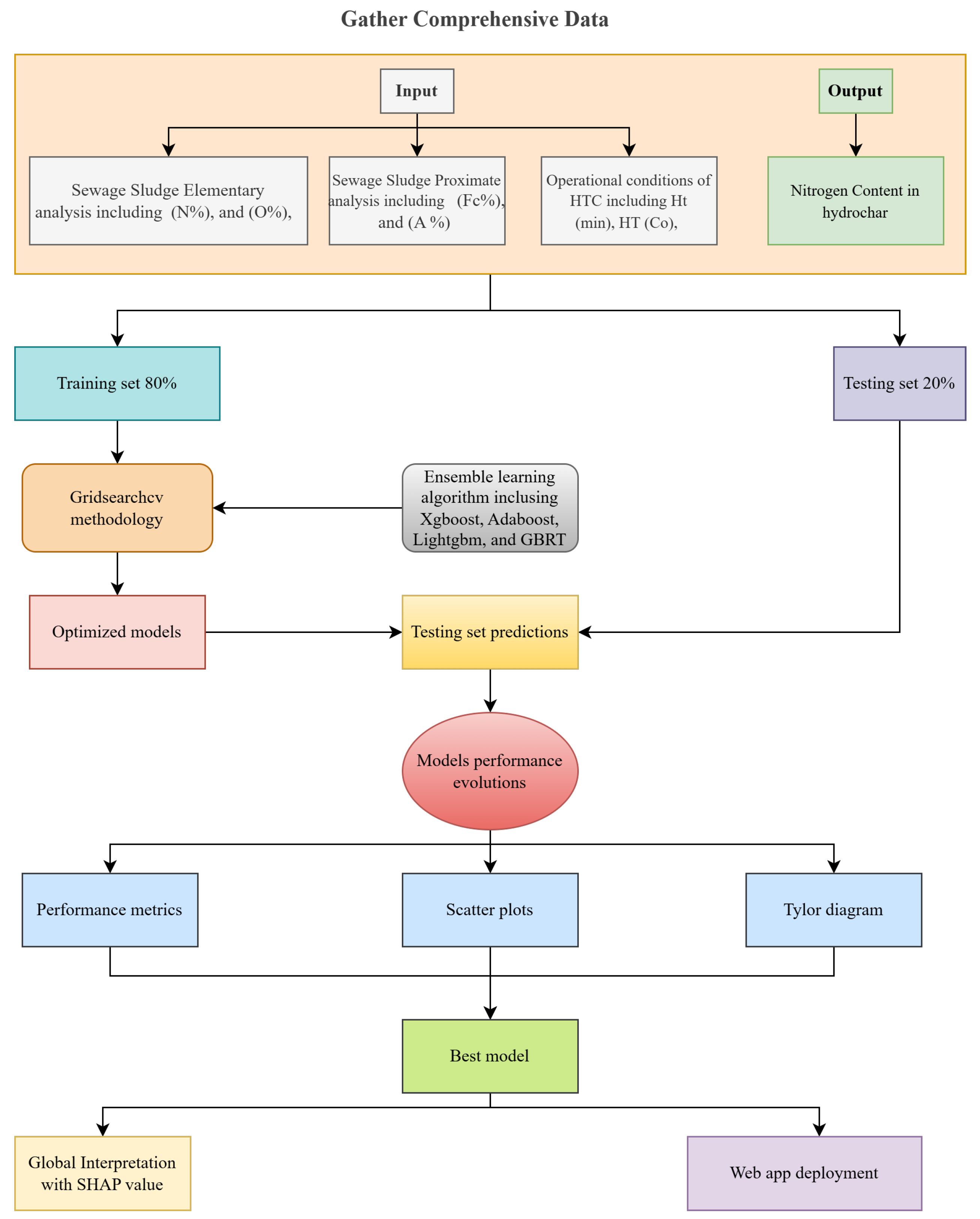
2.1. Research Methodology
2.2. Extreme Gradient Boosting (Xgboost)
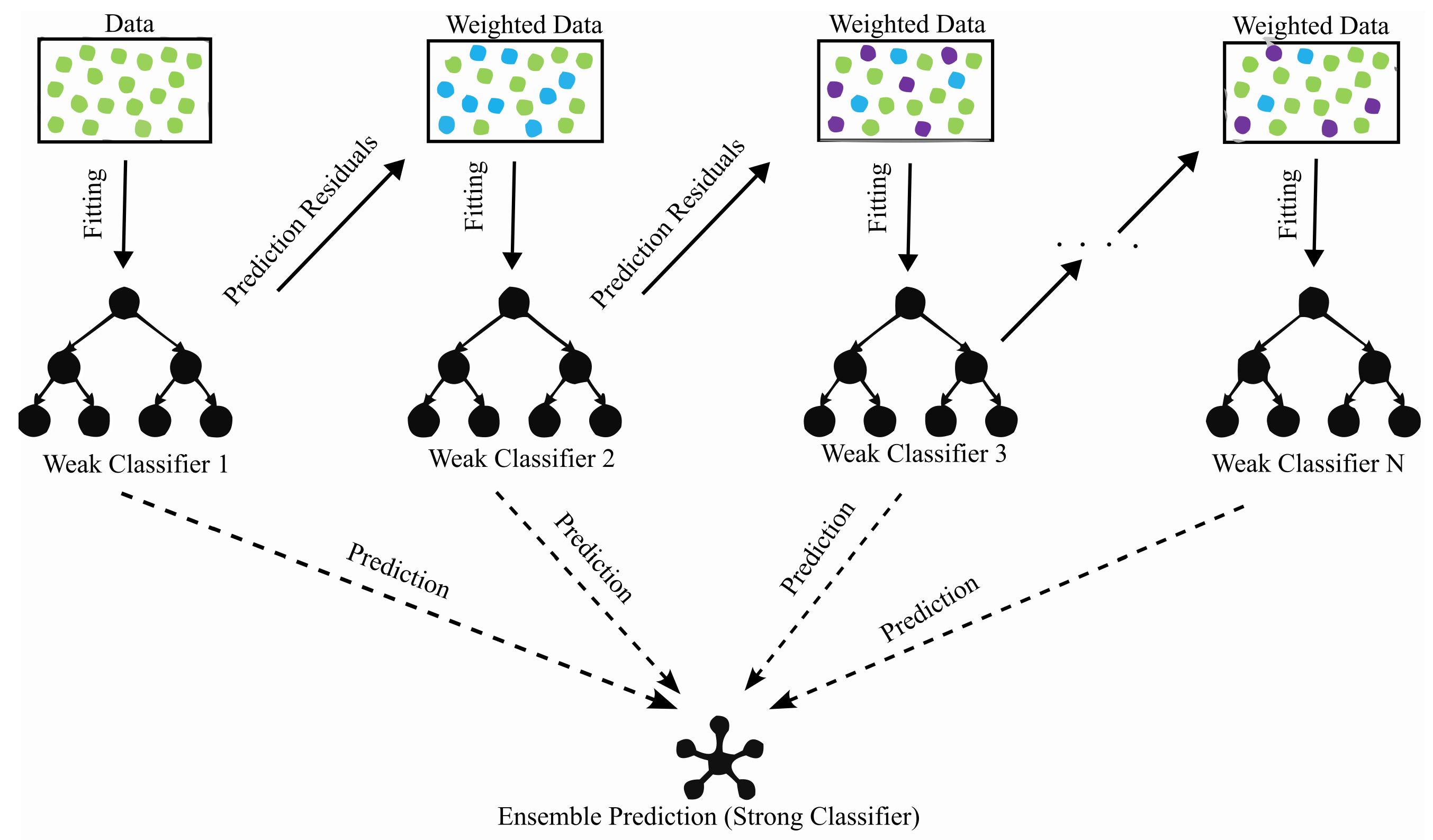
2.3. Adaboost
2.4. Gradient Boosting Regression Trees (GBRTs)
2.5. Light Gradient-Boosting Machine (LightGBM)
2.6. Data Splitting and Normalisation
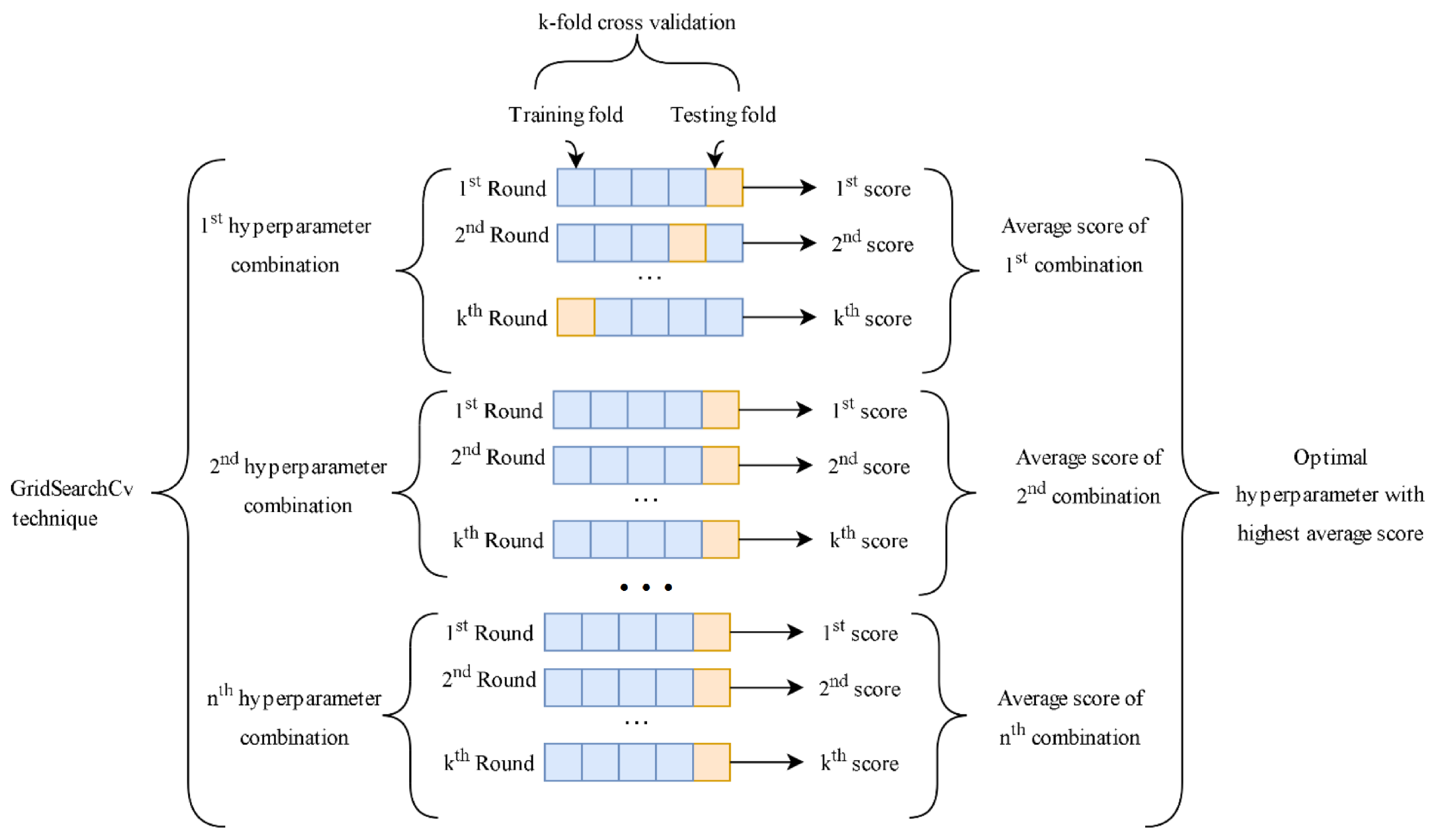
2.7. ML Model Development
2.8. SHapley Additive exPlanations
3. Database
4. Results
4.1. Model Metric Performances Based on Training and Testing Set
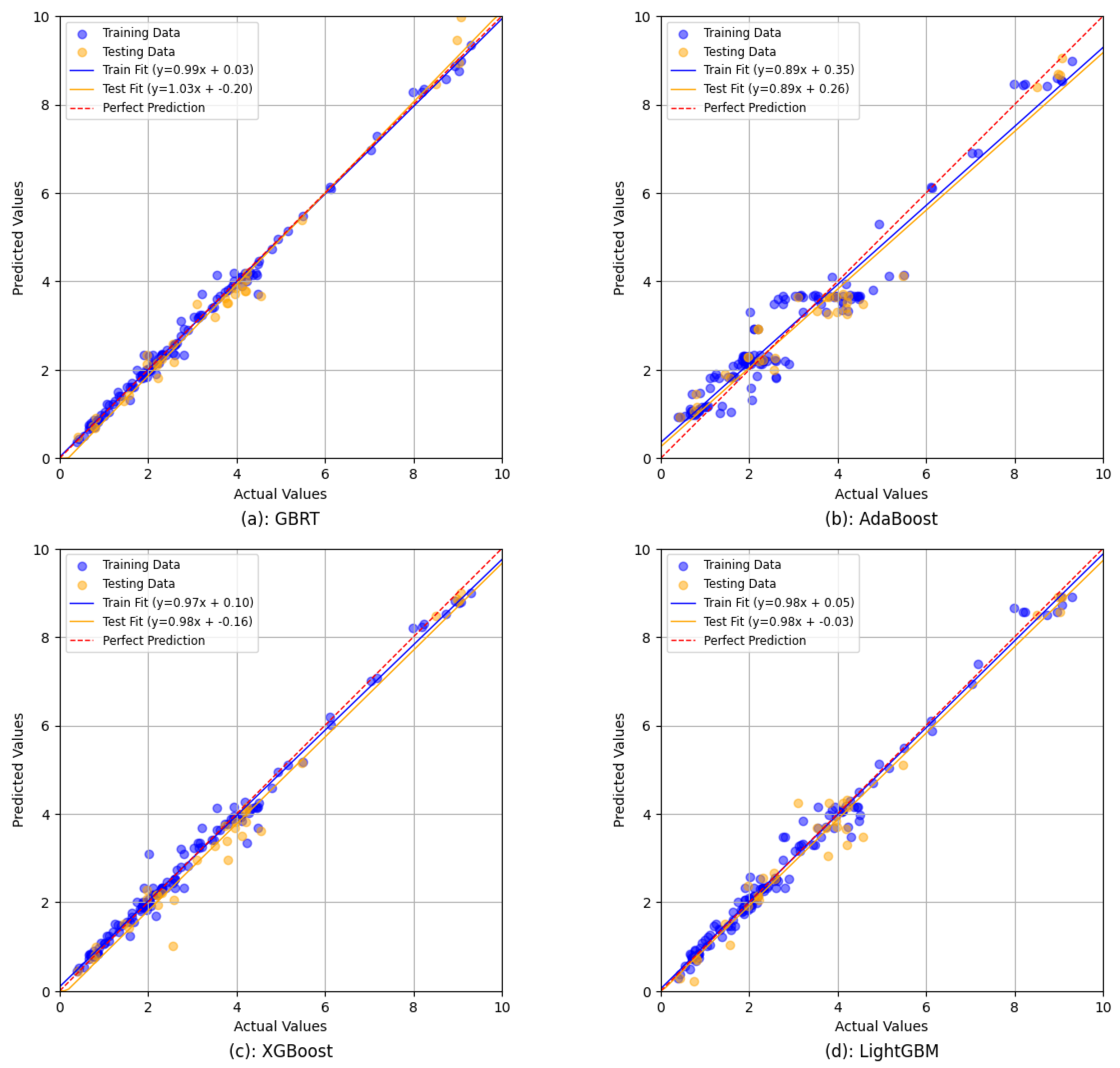
4.2. Scatter Plot Evaluation for Ensemble Models
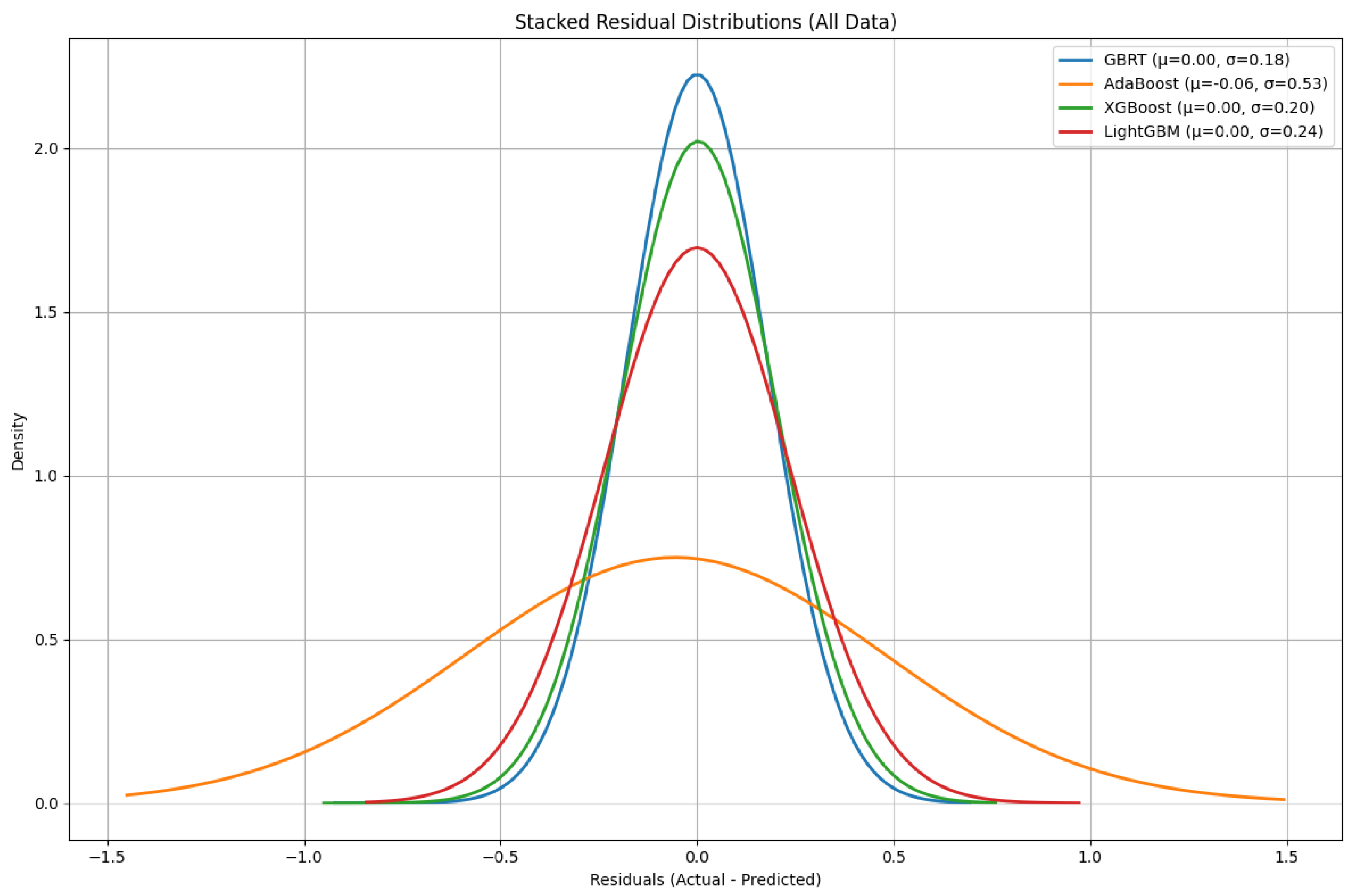
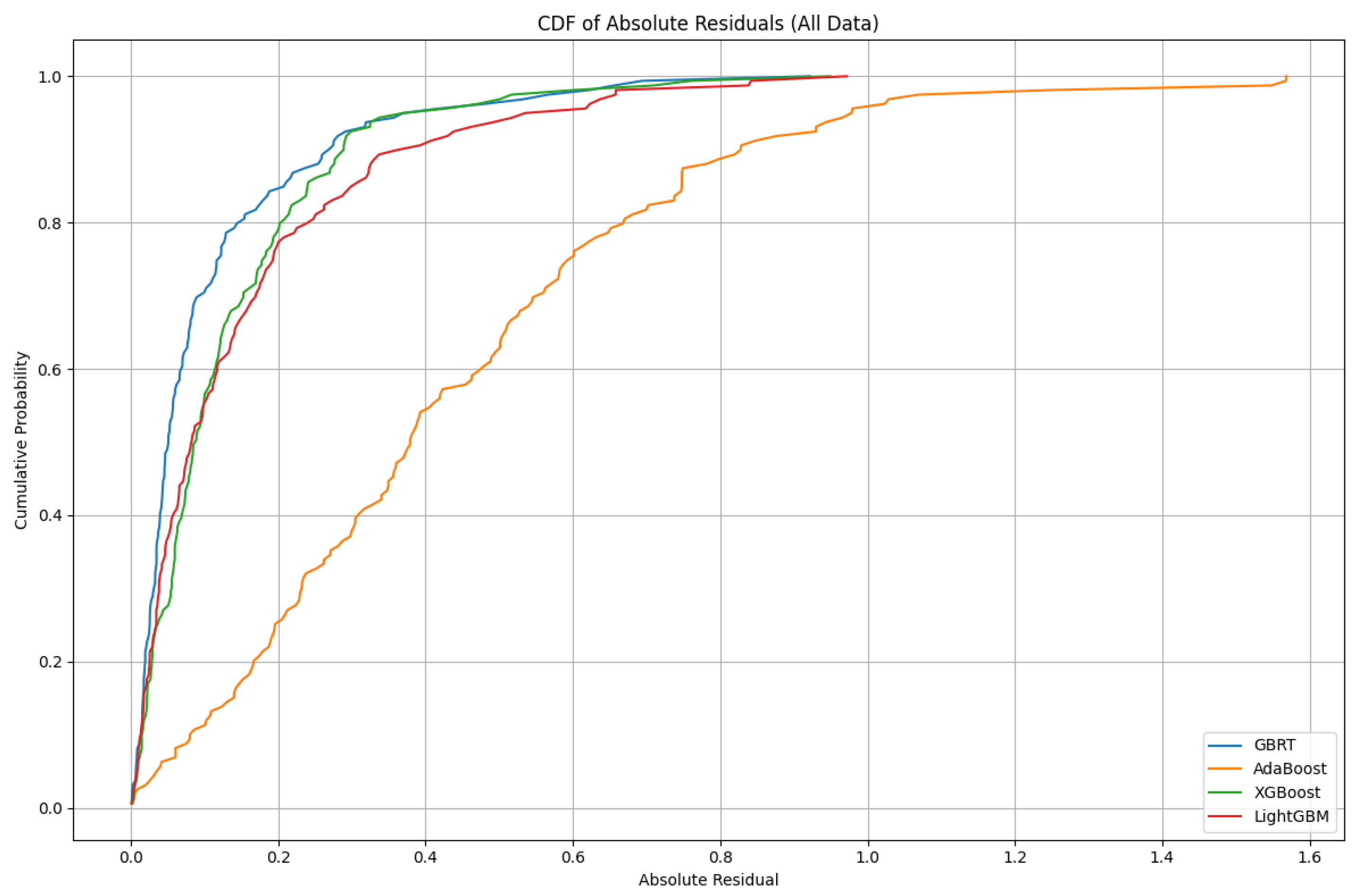
4.3. Error Assessment
4.4. Comparing with Single Learner ML Algorithm
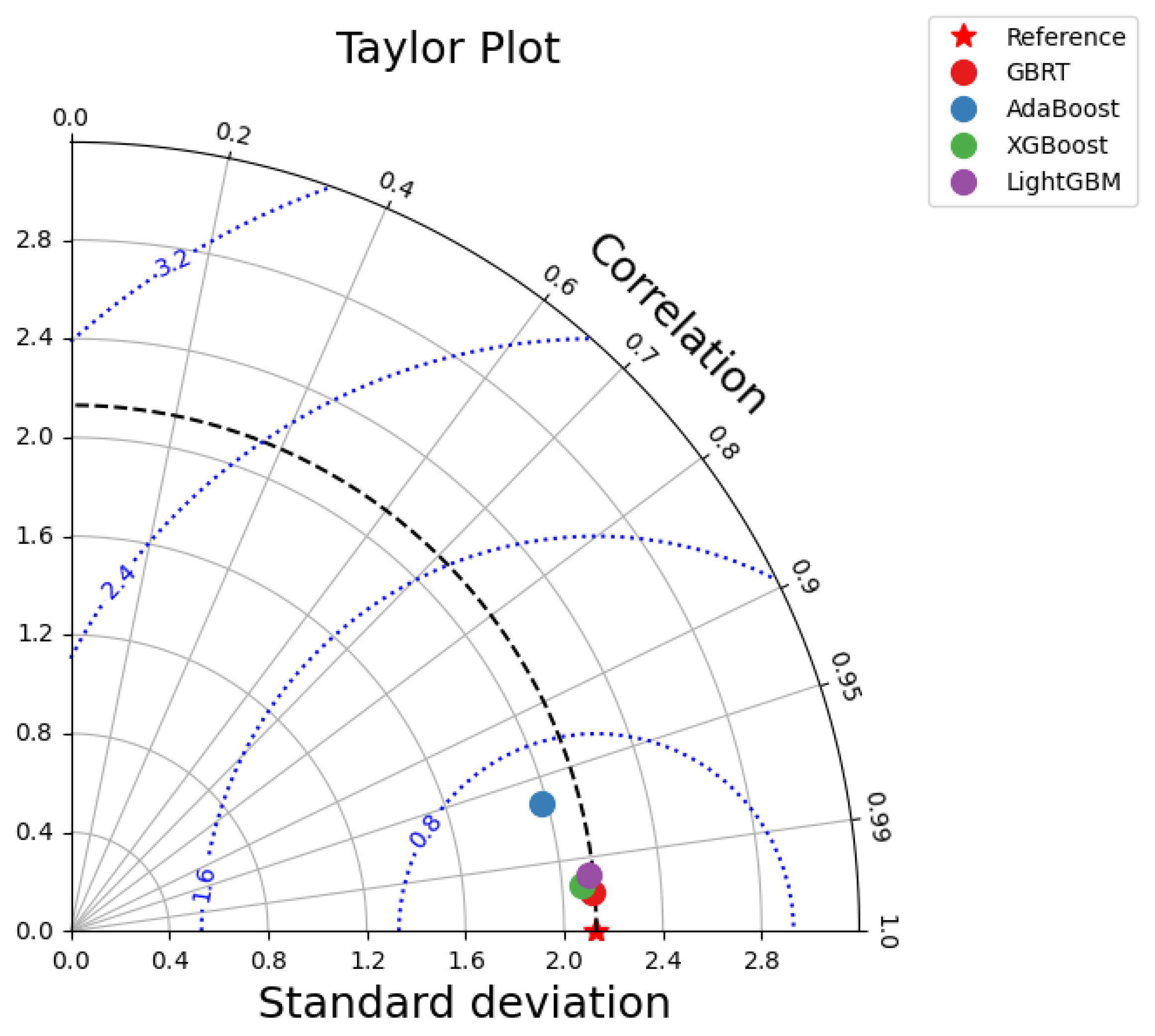
4.5. Taylor Diagram
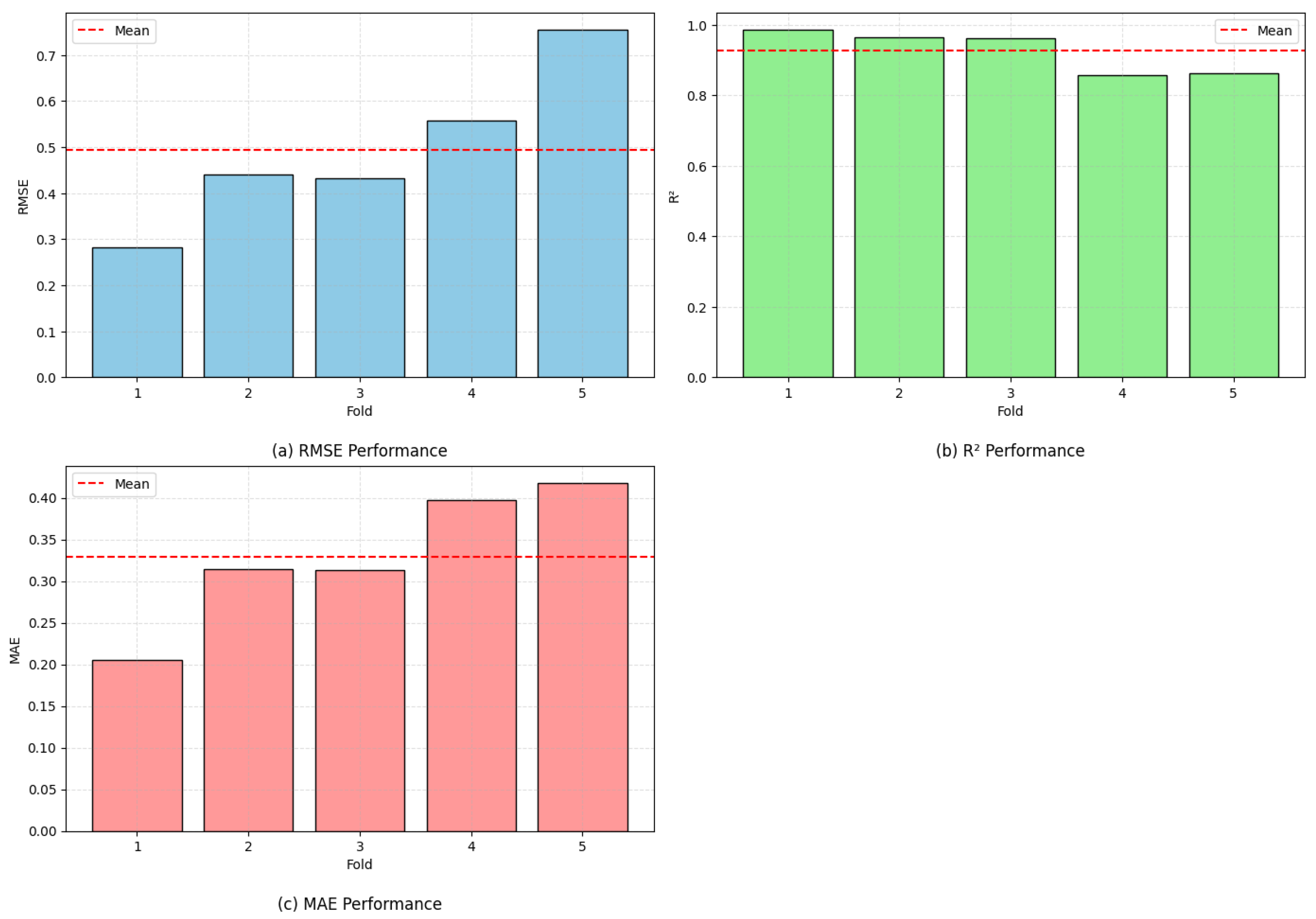
4.6. K-Fold Performance of Optimized GBRT
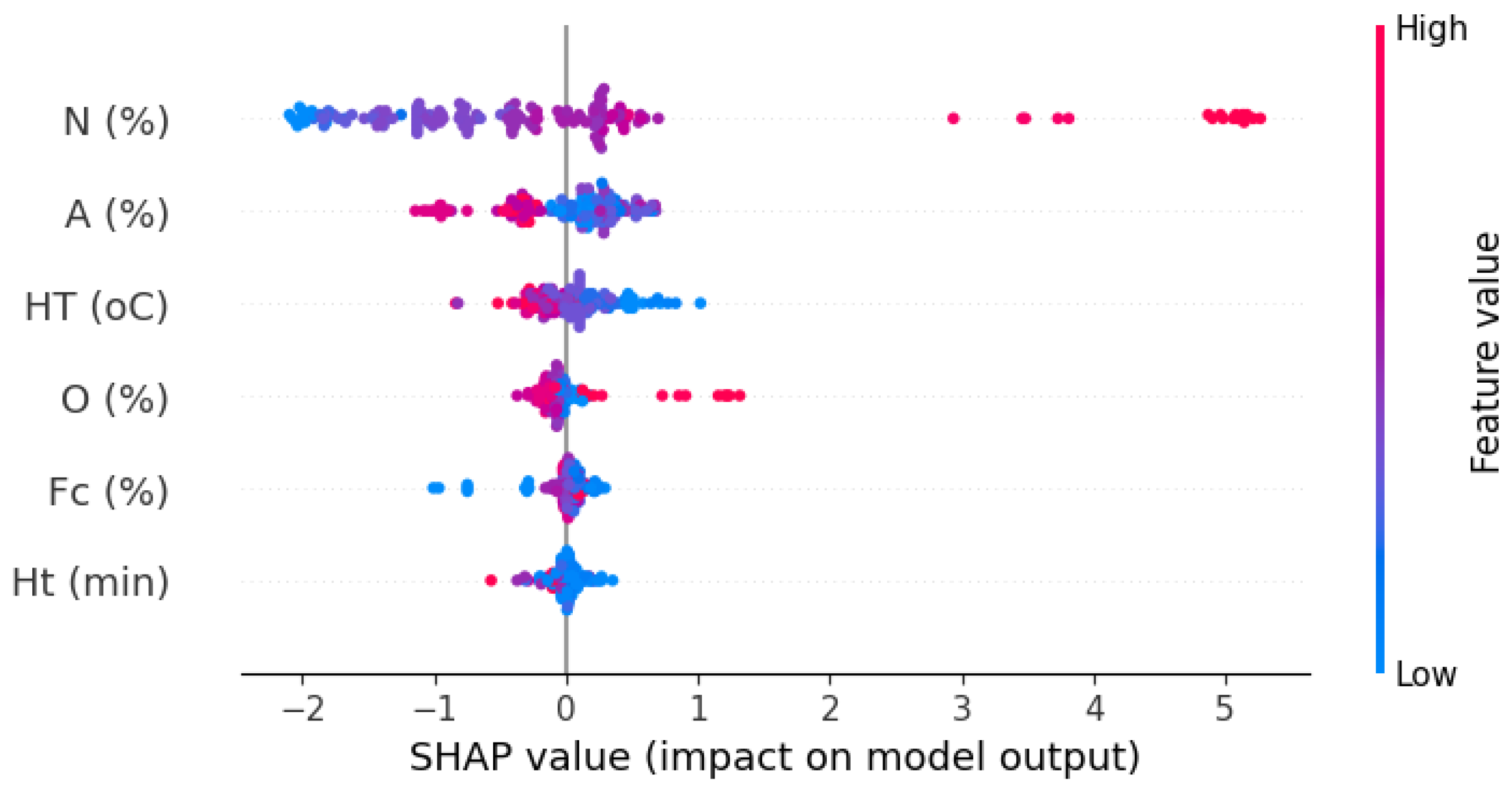
4.7. Shapley Method
4.8. Web App
5. Limitations and Future Studies
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, Q.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Xu, Q.; Ni, B.J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X. Towards hydrogen production from waste activated sludge: Principles, challenges and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.j.; Yang, T.; Lai, F.y.; Wu, G.q. Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and sawdust/rice straw for the production of biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2017, 125, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarpani, R.R.Z.; Alfonsín, C.; Hospido, A.; Azapagic, A. Life cycle environmental impacts of sewage sludge treatment methods for resource recovery considering ecotoxicity of heavy metals and pharmaceutical and personal care products. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 109643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. Statistical Yearbook of Urban and Rural Construction in China; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development: Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.j.; Yuan, X.z. The migration and transformation behaviors of heavy metals during the hydrothermal treatment of sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 200, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.f.; Chang, Y.c.; Lai, F.y.; Fang, H.s.; Zhou, C.f.; Pan, Z.q.; Wang, J.x.; Wang, Y.j.; Yin, X.; Huang, H.j. Effects of rice straw/wood sawdust addition on the transport/conversion behaviors of heavy metals during the liquefaction of sewage sludge. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Cui, D.; Wang, X.; Wu, D.; Bai, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Analysis of fuel properties of hydrochar derived from food waste and biomass: Evaluating varied mixing techniques pre/post-hydrothermal carbonization. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 430, 139660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.I.; Jadamba, C.; Lee, C.G.; Hong, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, S.C.; Park, S.J. Feasibility study of Aesculus turbinata fruit shell-derived biochar for ammonia removal in wastewater and its subsequent use as nitrogen fertilizer. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzari, F.; Goldfarb, J.; Andreottola, G.; Mimmo, T.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L. Hydrothermal carbonization as a strategy for sewage sludge management: Influence of process withdrawal point on hydrochar properties. Energies 2020, 13, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauline, A.L.; Joseph, K. Hydrothermal carbonization of organic wastes to carbonaceous solid fuel–A review of mechanisms and process parameters. Fuel 2020, 279, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrović, J.; Ercegović, M.; Simić, M.; Koprivica, M.; Dimitrijević, J.; Jovanović, A.; Janković Pantić, J. Hydrothermal carbonization of waste biomass: A review of hydrochar preparation and environmental application. Processes 2024, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.W.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, Y.J. A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/biochar nanocomposites: Adsorption behavior and mechanisms for the removal of copper (II) from aqueous media. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsarpali, M.; Kuhn, J.N.; Philippidis, G.P. Hydrothermal carbonization of residual algal biomass for production of hydrochar as a biobased metal adsorbent. Sustainability 2022, 14, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wu, R.; Zhao, F. Migration and conversion of phosphorus in hydrothermal carbonization of municipal sludge with hydrochloric acid. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanakis, T.N.; Vardiambasis, I.O.; Nikolopoulos, C.D.; Konstantaras, A.I.; Trang, T.K.; Khuong, D.A.; Tsubota, T.; Keyikoglu, R.; Khataee, A.; Kalderis, D. Towards engineered hydrochars: Application of artificial neural networks in the hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Energies 2021, 14, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnath, B.; Khanal, S.; Shah, A.; Reza, T. Influence of Hydrothermal Carbonization (HTC) Temperature on Hydrochar and Process Liquid for Poultry, Swine, and Dairy Manure. Environments 2024, 11, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langone, M.; Basso, D. Process waters from hydrothermal carbonization of sludge: Characteristics and possible valorization pathways. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.T.T.; Nadeem, A.; Choe, K. A review of upscaling hydrothermal carbonization. Energies 2024, 17, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.Y.; Huang, W.J. A Practical Case Report on the Node Point of a Butterfly Model Circular Economy: Synthesis of a New Hybrid Mineral–Hydrothermal Fertilizer for Rice Cropping. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Q.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Z. Application of Mg–Al-modified biochar for simultaneous removal of ammonium, nitrate, and phosphate from eutrophic water. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 176, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Gao, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Inyang, M.; Li, Y.; Alva, A.; Yang, L. Engineered carbon (biochar) prepared by direct pyrolysis of Mg-accumulated tomato tissues: Characterization and phosphate removal potential. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 138, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, H.; Zheng, H.; Liu, G.; Chen, L.; Xing, B. Reduced nitrification and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in acidic soil amended with biochar. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; Lei, S.; Xiao, R. Simultaneous capture removal of phosphate, ammonium and organic substances by MgO impregnated biochar and its potential use in swine wastewater treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 147, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Huang, H. Speciation of main nutrients (N/P/K) in hydrochars produced from the hydrothermal carbonization of swine manure under different reaction temperatures. Materials 2021, 14, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roslan, S.Z.; Zainudin, S.F.; Mohd Aris, A.; Chin, K.B.; Musa, M.; Mohamad Daud, A.R.; Syed Hassan, S.S.A. Hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge into solid biofuel: Influences of process conditions on the energetic properties of hydrochar. Energies 2023, 16, 2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Duo, J.; Jin, Z.; Yang, F.; Lai, T.; Collins, E. Effects of Hydrothermal Carbonization Conditions on the Characteristics of Hydrochar and Its Application as a Soil Amendment: A Review. Agronomy 2025, 15, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Yang, L.; Leng, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, H.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, H. A review on nitrogen transformation in hydrochar during hydrothermal carbonization of biomass containing nitrogen. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhnidi, M.J.; Körner, P.; Wüst, D.; Pfersich, J.; Kruse, A. Nitrogen-Containing Hydrochar: The Influence of Nitrogen-Containing Compounds on the Hydrochar Formation. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djandja, O.S.; Salami, A.A.; Wang, Z.C.; Duo, J.; Yin, L.X.; Duan, P.G. Random forest-based modeling for insights on phosphorus content in hydrochar produced from hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Energy 2022, 245, 123295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.; Xu, D.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.; Xu, M.; Wang, S.; Kapusta, K. Machine learning and experiments on hydrothermal liquefaction of sewage sludge: Insight into migration and transformation mechanisms of phosphorus. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Wang, X. Multi-task prediction and optimization of hydrochar properties from high-moisture municipal solid waste: Application of machine learning on waste-to-resource. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Wang, X. Multi-task prediction of fuel properties of hydrochar derived from wet municipal wastes with random forest. In Proceedings of the Applied Energy Symposium, Xiamen, China, 16–18 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Flora, J.R.; Berge, N.D. Predictions of energy recovery from hydrochar generated from the hydrothermal carbonization of organic wastes. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, M.; Xiao, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Naqvi, S.R. Prediction of bio-oil yield and hydrogen contents based on machine learning method: Effect of biomass compositions and pyrolysis conditions. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 11050–11060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Machine learning prediction of biochar yield and carbon contents in biochar based on biomass characteristics and pyrolysis conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 288, 121527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.; Buyukada, M.; Evrendilek, F.; Liu, J. Uncertainty and sensitivity analyses of co-combustion/pyrolysis of textile dyeing sludge and incense sticks: Regression and machine-learning models. Renew. Energy 2019, 288, 121527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djandja, O.S.; Duan, P.G.; Yin, L.X.; Wang, Z.C.; Duo, J. A novel machine learning-based approach for prediction of nitrogen content in hydrochar from hydrothermal carbonization of sewage sludge. Energy 2021, 232, 121010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Jiang, Z.; Ying, Z.; Song, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, B. Role of feedstock properties and hydrothermal carbonization conditions on fuel properties of sewage sludge-derived hydrochar using multiple linear regression technique. Fuel 2020, 271, 117609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, X.; Song, K. A novel gradient boosting regression tree technique optimized by improved sparrow search algorithm for predicting TBM penetration rate. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Taai, S.R.; Azize, N.M.; Thoeny, Z.A.; Imran, H.; Bernardo, L.F.A.; Al-Khafaji, Z. XGBoost prediction model optimized with Bayesian for the compressive strength of eco-friendly concrete containing ground granulated blast furnace slag and recycled coarse aggregate. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.L.; Trinh, H.T.; Pham, T.M. Prediction of punching shear strength in flat slabs: Ensemble learning models and practical implementation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 4207–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab, M.; Taherdangkoo, R.; Butscher, C. Towards reliable barrier systems: A constrained XGBoost model coupled with gray wolf optimization for maximum swelling pressure of bentonite. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 168, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanek, R. Daily streamflow forecasting in mountainous catchment using XGBoost, LightGBM and CatBoost. Hydrology 2022, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraz, A.; Tırınk, C.; Önder, H.; Şen, U.; Ishaq, H.M.; Tauqir, N.A.; Waheed, A.; Nabeel, M.S. Usage of the XGBoost and MARS algorithms for predicting body weight in Kajli sheep breed. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2023, 55, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Pan, S.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, C.; Pan, H.; Zhu, X. Application of the machine learning LightGBM model to the prediction of the water levels of the Lower Columbia River. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, X. Research on Credit Default Prediction Model Based on TabNet-Stacking. Entropy 2024, 26, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, B.; Qi, W.; Wang, J. Service pricing and charging strategy for video platforms considering consumer preferences. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2024, 33, 567–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Geng, M.; Wo, X.; Shi, L.; Zhai, Y.; Ji, P. Development and conceptual design of a sewage sludge-to-fuel hybrid process: Prediction and optimization under analysis of variance and response surface model. Energy Convers. Manag. 2024, 306, 118143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Ojha, C.S.P. Statistical parameters of hydrometeorological variables: Standard deviation, SNR, skewness and kurtosis. In Advances in Water Resources Engineering and Management: Select Proceedings of TRACE 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.C.; Greene, J.A. The wisdom development scale: Translating the conceptual to the concrete. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 2006, 47, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, M.K.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, K.H. Univariate and multivariate skewness and kurtosis for measuring nonnormality: Prevalence, influence and estimation. Behav. Res. Methods 2017, 49, 1716–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puth, M.T.; Neuhäuser, M.; Ruxton, G.D. Effective use of Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient. Anim. Behav. 2014, 93, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, I.; Yang, J.; Javed, M.F.; Iqbal, M.F.; Mahmood, Z.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q.f. Prediction model for compressive arch action capacity of RC frame structures under column removal scenario using gene expression programming. Structures 2020, 25, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K.X. On the criterion that a given system of deviations from the probable in the case of a correlated system of variables is such that it can be reasonably supposed to have arisen from random sampling. London Edinburgh Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1900, 50, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravier, J.; Vignal, V.; Bissey-Breton, S.; Farre, J. The use of linear regression methods and Pearson’s correlation matrix to identify mechanical–physical–chemical parameters controlling the micro-electrochemical behaviour of machined copper. Corros. Sci. 2008, 50, 2885–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.I.; Javed, M.F.; Aslam, F.; Alabduljabbar, H. Machine learning modeling integrating experimental analysis for predicting the properties of sugarcane bagasse ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, G.; Liu, X.; Fan, Y.; Meng, E.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y. Experimental and numerical analysis of seismic behaviour for recycled aggregate concrete filled circular steel tube frames. Comput. Concr. 2023, 31, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.A.; Farooq, F.; Javed, M.F.; Zafar, A.; Ostrowski, K.A.; Aslam, F.; Malazdrewicz, S.; Maślak, M. Simulation of depth of wear of eco-friendly concrete using machine learning based computational approaches. Materials 2021, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Ali, M.; Najeh, T.; Gamil, Y. Computational prediction of workability and mechanical properties of bentonite plastic concrete using multi-expression programming. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Models | Hyperparameters | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max Depth | Learning Rate | Number of Estimators | Num Leaves | |
| XGBoost | 3.0 | 0.10 | 100 | — |
| AdaBoost | — | 1.00 | 100 | — |
| LightGBM | — | 0.20 | 500 | 31 |
| GBRT | 3.0 | 0.10 | 100 | — |
| Variable | Mean | Mode | Median | SE | SD | Variance | Kurtosis | Skewness | Max | Min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 4.80 | 5.29 | 4.75 | 0.139 | 1.753 | 3.073 | 0.938 | 0.466 | 8.85 | 1.21 |
| O (%) | 21.37 | 24.75 | 22.80 | 0.367 | 4.622 | 21.361 | −0.277 | −0.502 | 30.28 | 10.50 |
| Fc (%) | 6.00 | 3.90 | 5.14 | 0.295 | 3.723 | 13.861 | 0.676 | 0.883 | 18.55 | 0.70 |
| A (%) | 35.62 | 27.54 | 33.51 | 1.114 | 14.050 | 197.413 | 0.822 | 0.921 | 80.40 | 14.96 |
| Ht (min) | 99.06 | 30.00 | 45.00 | 11.315 | 142.676 | 20,356.383 | 6.335 | 2.626 | 720.00 | 0.00 |
| HT (°C) | 214.21 | 200.00 | 200.00 | 3.513 | 44.300 | 1962.511 | 1.518 | 0.642 | 380.00 | 100.00 |
| Nhc (%) | 3.07 | 2.10 | 2.40 | 0.170 | 2.137 | 4.569 | 1.478 | 1.355 | 9.29 | 0.39 |
| Variable | N (%) | O (%) | Fc (%) | A (%) | Ht (min) | HT (°C) | Nhc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | 1.000 | ||||||
| O (%) | −0.095 | 1.000 | |||||
| Fc (%) | −0.029 | 0.436 | 1.000 | ||||
| A (%) | −0.529 | −0.197 | −0.078 | 1.000 | |||
| Ht (min) | −0.032 | 0.187 | −0.275 | −0.023 | 1.000 | ||
| HT (°C) | −0.044 | −0.287 | 0.139 | 0.297 | −0.113 | 1.000 | |
| Nhc (%) | 0.865 | −0.107 | −0.055 | −0.601 | −0.178 | −0.206 | 1.000 |
| Phase | Metrics | GBRT | AdaBoost | XGBoost | LightGBM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | 0.993 | 0.933 | 0.989 | 0.987 | |
| RMSE | 0.169 | 0.532 | 0.213 | 0.231 | |
| MAE | 0.100 | 0.434 | 0.140 | 0.155 | |
| Test | 0.973 | 0.935 | 0.979 | 0.960 | |
| RMSE | 0.389 | 0.602 | 0.342 | 0.470 | |
| MAE | 0.276 | 0.486 | 0.242 | 0.323 | |
| All data | 0.988 | 0.934 | 0.987 | 0.981 | |
| RMSE | 0.231 | 0.547 | 0.245 | 0.295 | |
| MAE | 0.135 | 0.444 | 0.160 | 0.189 |
| Model | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
|---|---|---|---|
| KNN | 0.9356 | 0.5966 | 0.3643 |
| SVR | 0.9488 | 0.5322 | 0.3899 |
| GBRT | 0.9722 | 0.3917 | 0.2842 |
| Fold | RMSE | MAE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 0.2815 | 0.2053 | 0.9857 |
| Fold 2 | 0.4413 | 0.3148 | 0.9651 |
| Fold 3 | 0.4316 | 0.3130 | 0.9607 |
| Fold 4 | 0.5574 | 0.3968 | 0.8572 |
| Fold 5 | 0.7549 | 0.4175 | 0.8630 |
| Mean | 0.4933 | 0.3295 | 0.9263 |
| Std. Dev. | 0.1574 | 0.0751 | 0.0548 |
| COV (%) | 31.9 | 22.8 | 5.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shehab, E.Q.; Al-Abdaly, N.M.; Seno, M.E.; Imran, H.; Albuquerque, A. Robust Ensemble-Based Model and Web Application for Nitrogen Content Prediction in Hydrochar from Sewage Sludge. Water 2025, 17, 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243468
Shehab EQ, Al-Abdaly NM, Seno ME, Imran H, Albuquerque A. Robust Ensemble-Based Model and Web Application for Nitrogen Content Prediction in Hydrochar from Sewage Sludge. Water. 2025; 17(24):3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243468
Chicago/Turabian StyleShehab, Esraa Q., Nadia Moneem Al-Abdaly, Mohammed E. Seno, Hamza Imran, and Antonio Albuquerque. 2025. "Robust Ensemble-Based Model and Web Application for Nitrogen Content Prediction in Hydrochar from Sewage Sludge" Water 17, no. 24: 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243468
APA StyleShehab, E. Q., Al-Abdaly, N. M., Seno, M. E., Imran, H., & Albuquerque, A. (2025). Robust Ensemble-Based Model and Web Application for Nitrogen Content Prediction in Hydrochar from Sewage Sludge. Water, 17(24), 3468. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17243468







