Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impacts of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Downstream Daliao River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
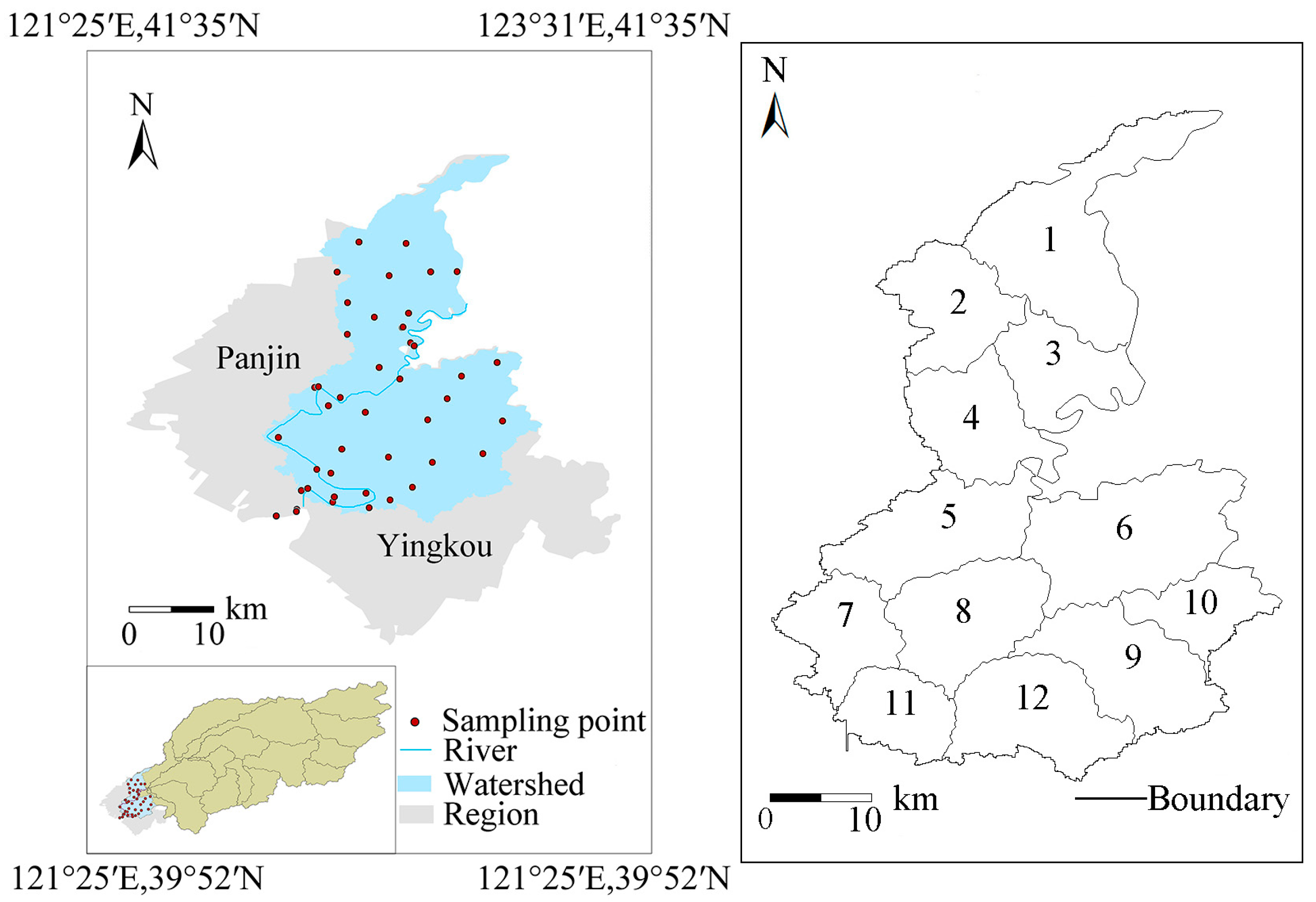
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Export Loads from Soils
2.4. Simulation Experiments
2.4.1. Release Potential of Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Soil and Sediment
2.4.2. Influencing Factors of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Release from Soils and Sediments
3. Results and Discussion
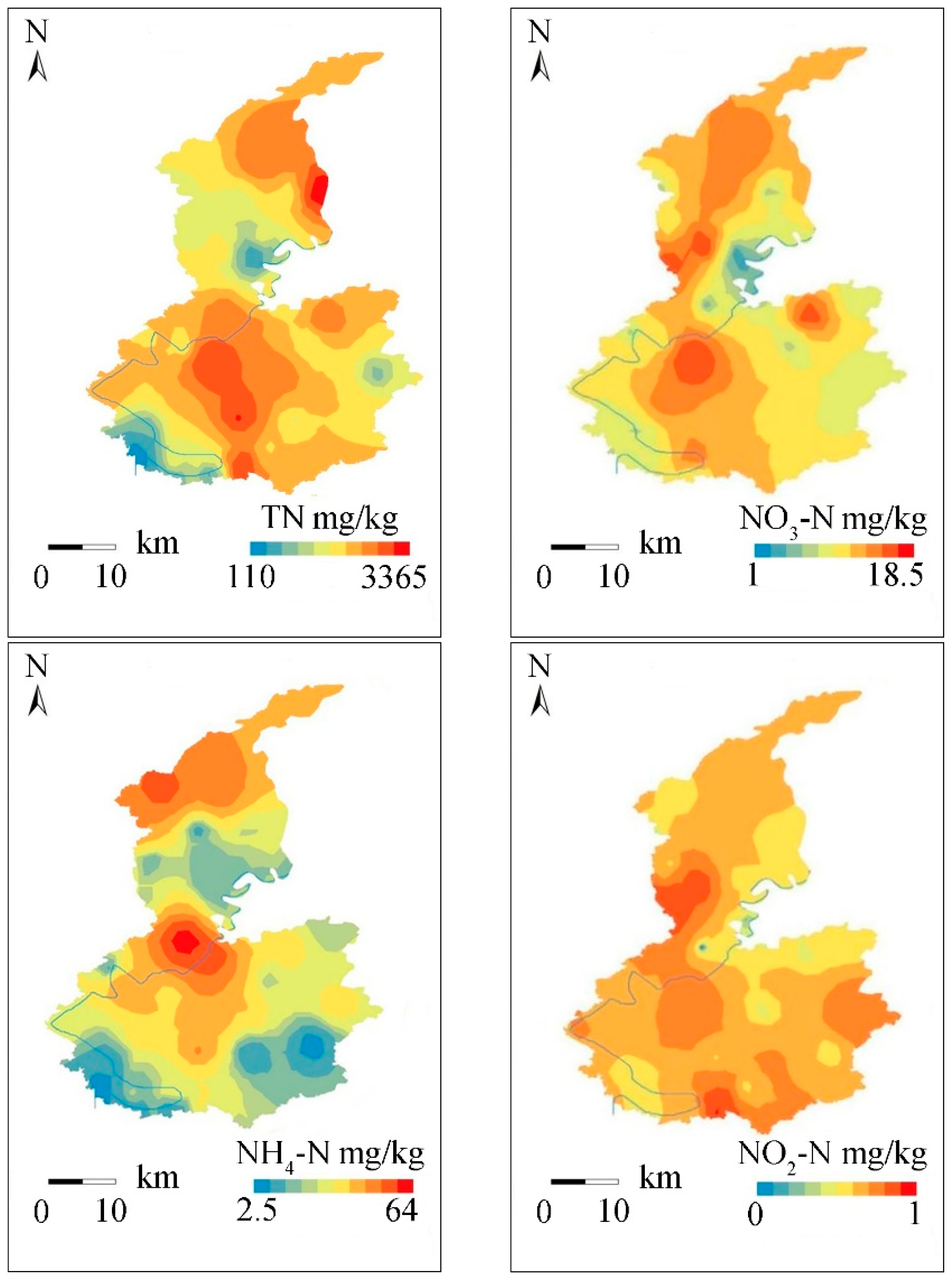
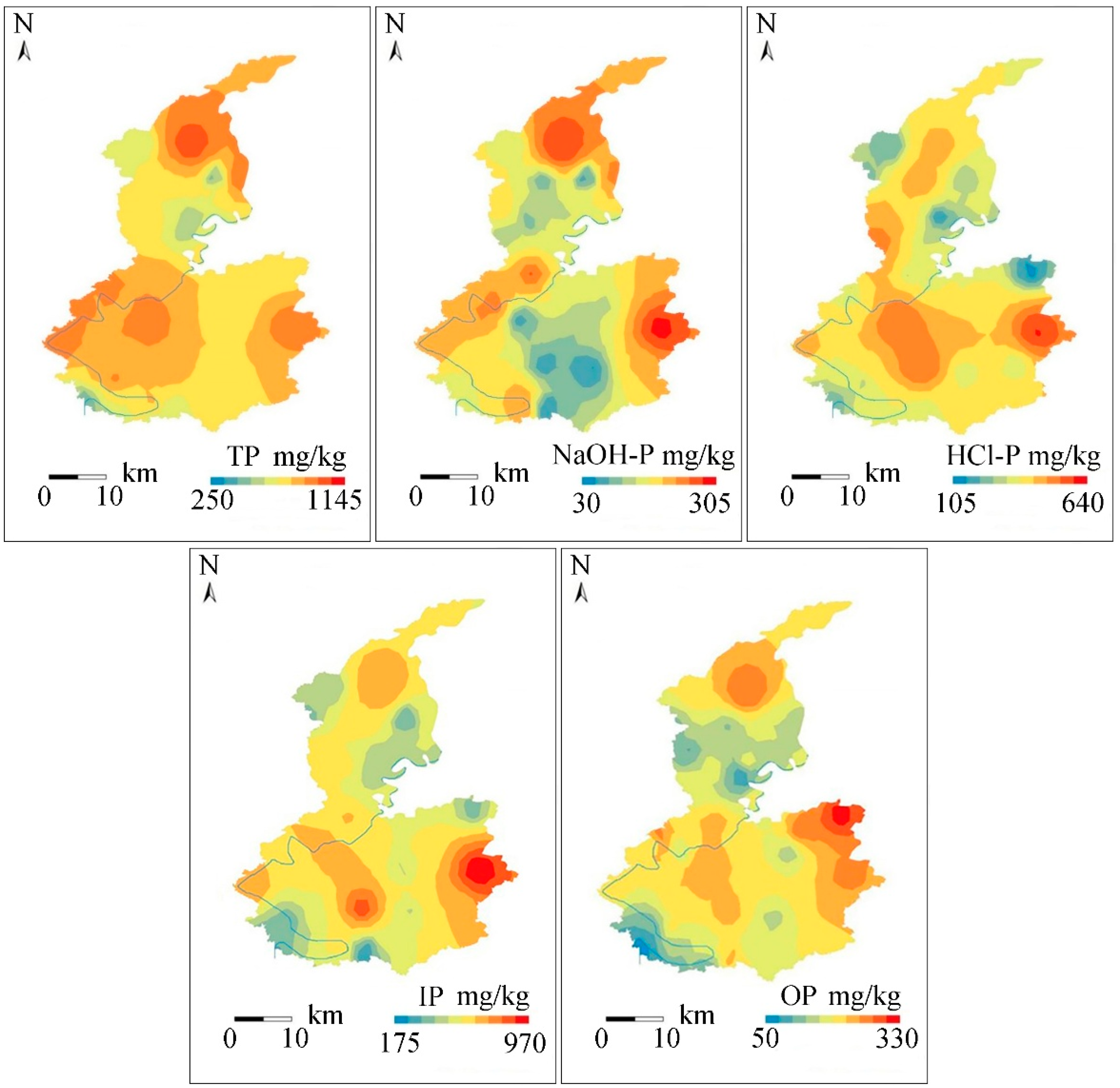
3.1. Spatial Distribution and Fractions
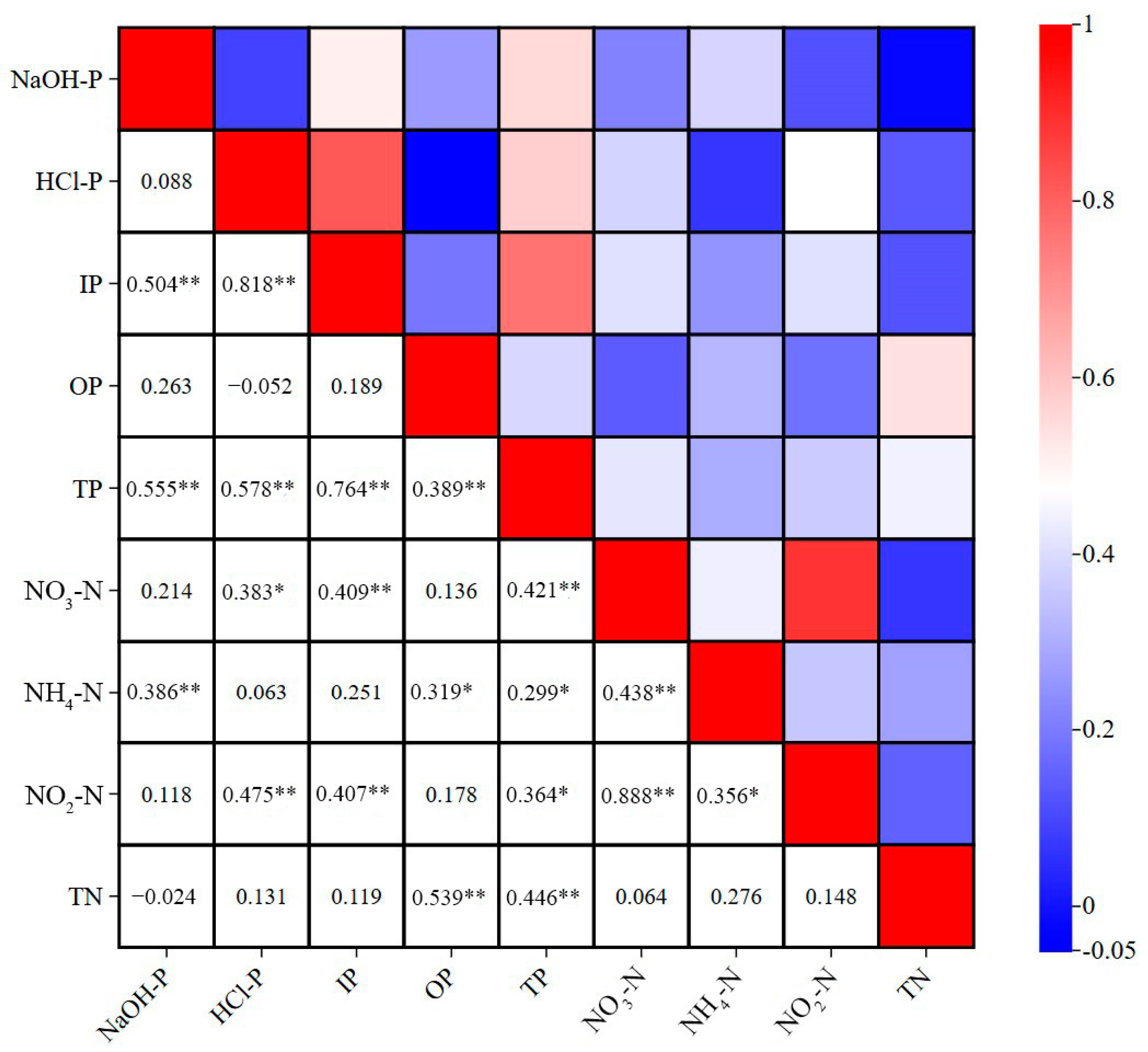
| NaOH-P | HCl-P | IP | OP | TP | NO3-N | NH4-N | NO2-N | TN | |
| NaOH-P | 1 | 0.088 | 0.5040 *** | 0.263 | 0.555 *** | 0.214 | 0.386 *** | 0.118 | −0.024 |
| HCl-P | 0.088 | 1 | 0.818 *** | −0.052 | 0.578 *** | 0.383 ** | 0.063 | 0.475 *** | 0.131 |
| IP | 0.504 *** | 0.818 *** | 1 | 0.189 | 0.764 *** | 0.409 *** | 0.251 | 0.407 *** | 0.119 |
| OP | 0.263 | −0.052 | 0.189 | 1 | 0.389 *** | 0.136 | 0.319 ** | 0.178 | 0.539 *** |
| TP | 0.555 *** | 0.578 *** | 0.764 *** | 0.389 *** | 1 | 0.421 *** | 0.299 ** | 0.364 ** | 0.446 *** |
| NO3-N | 0.214 | 0.383 ** | 0.409 *** | 0.136 | 0.421 *** | 1 | 0.438 *** | 0.888 *** | 0.064 |
| NH4-N | 0.386 *** | 0.063 | 0.251 | 0.319 ** | 0.299 ** | 0.438 *** | 1 | 0.356 ** | 0.276 |
| NO2-N | 0.118 | 0.475 *** | 0.407 *** | 0.178 | 0.364 ** | 0.888 *** | 0.356 ** | 1 | 0.148 |
| TN | −0.024 | 0.131 | 0.119 | 0.539 *** | 0.446 *** | 0.064 | 0.276 | 0.148 | 1 |
| Note: *** and ** represent 1% and 5% significance levels, respectively. | |||||||||
3.2. Release Potential and Influencing Factors
3.2.1. Release Potential
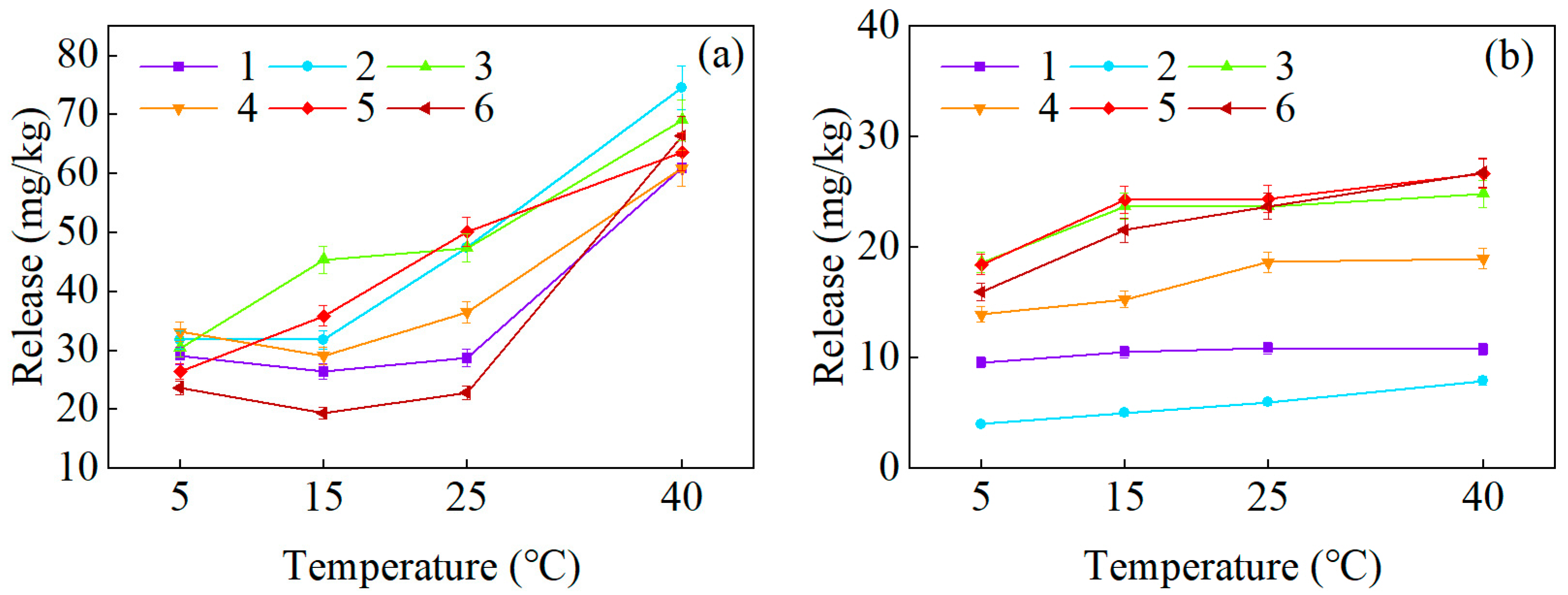
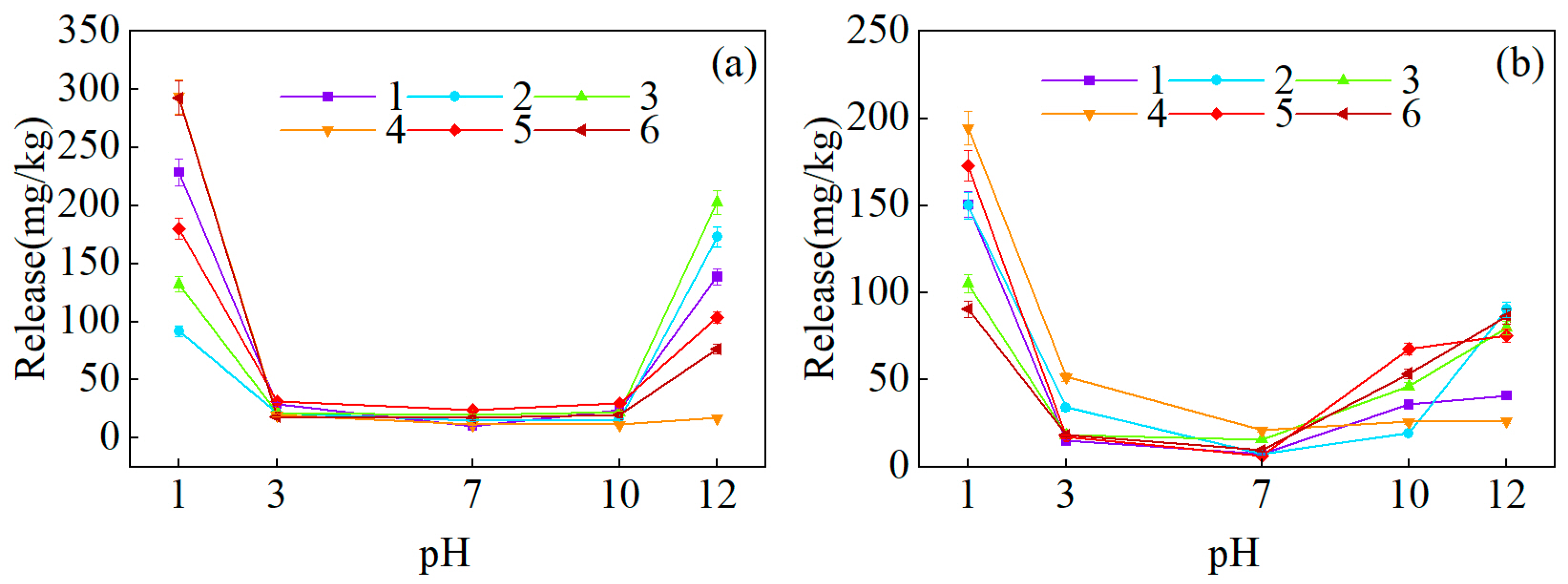
3.2.2. Temperature
3.2.3. pH
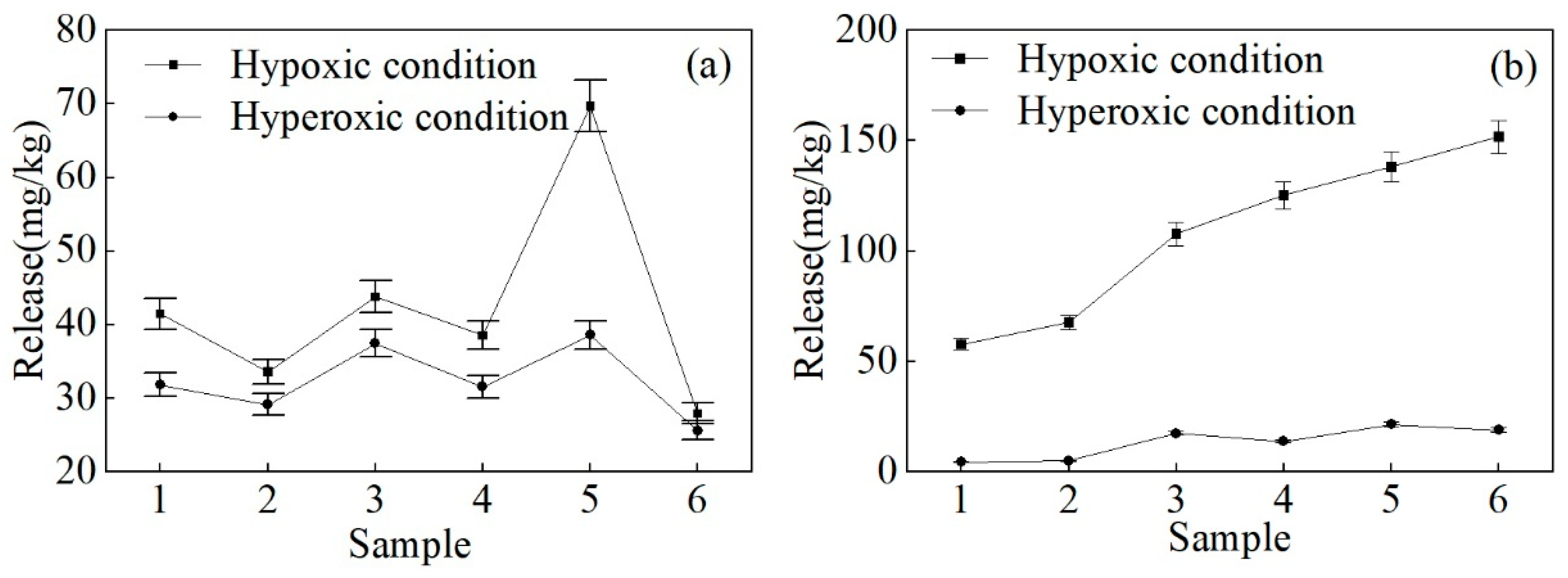
3.2.4. DO
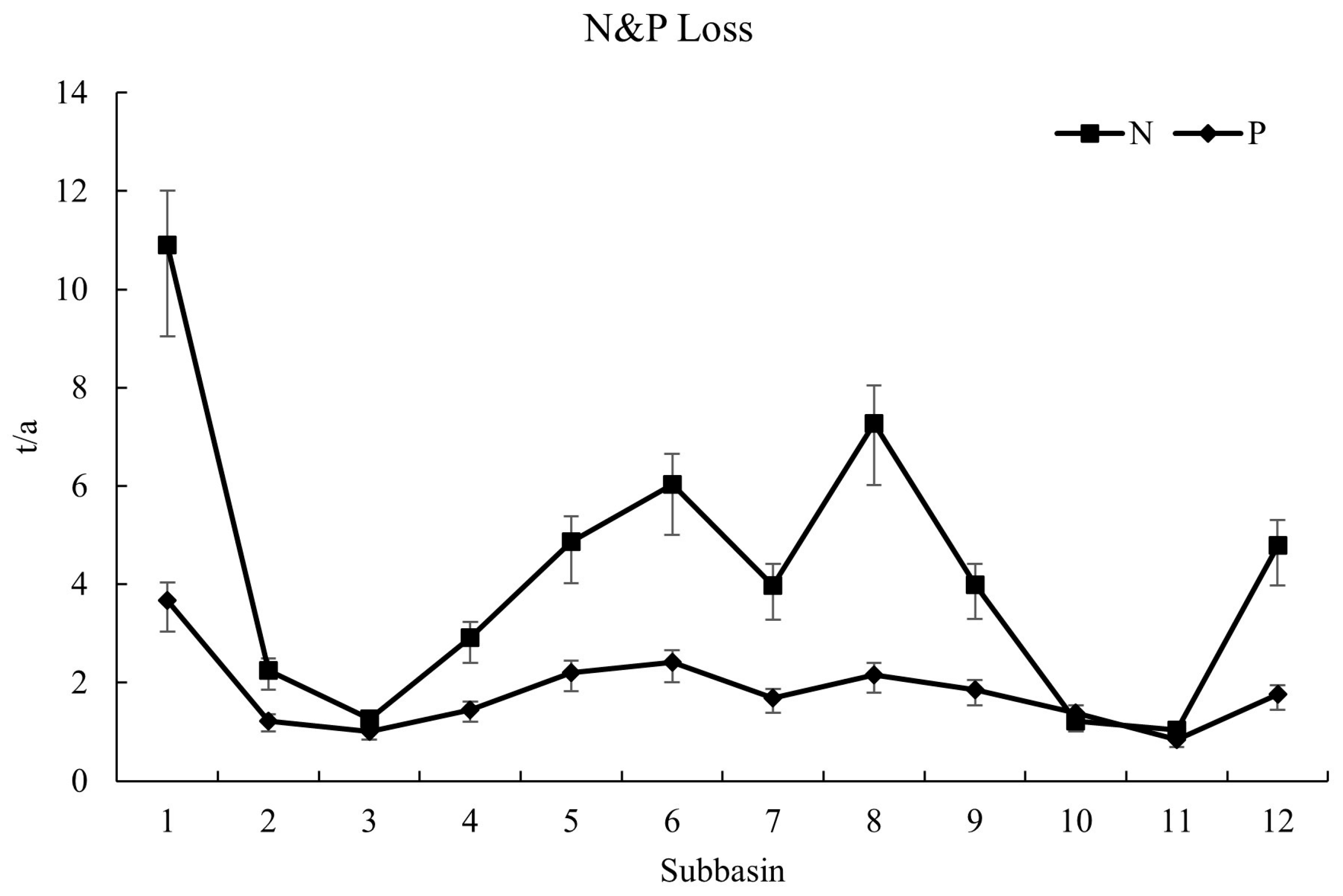
3.3. Impacts of Soil Erosion on the Water Environment
3.4. Management Strategies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Cai, C.; Zhang, H. How to control nitrogen and phosphorus loss during runoff process?—A case study at Fushi Reservoir in Anji County (China). Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Hu, Q.; Wang, C.; Lv, J.; Mi, C.; Shi, R.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W. Exploring the Relationship between Ecosystem Services under Different Socio-Economic Driving Degrees. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Jia, T.; Luo, Y. Influence of natural factors and land use change on changes in the main lake area in China over the past 30 years. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 111005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, L.; Yuan, Z.; Ma, T. Contrasting seasonal variations in riverine nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in China: Implications for N/P imbalances. Water Res. 2025, 287, 124317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, H.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Response of soil structure and fertility to long-term fertilization in alpine grasslands revealed based on fractal theory. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 242, 106167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ai, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Leng, P.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Z.; Tian, C.; Cheng, H.; Chen, G.; Li, F. Impacts of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) fertilizers on maize yields, nutrient use efficiency, and soil nutrient balance: Insights from a long-term diverse NPK omission experiment in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2024, 318, 109616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.; Arya, V.M.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, S.; Popescu, S.M.; Thakur, N.; Iqbal, J.M.; El-Sheikh, M.A.; Baath, G.S. Impact of cropping intensity on soil nitrogen and phosphorus for sustainable agricultural management. J. King Saud Univ.—Sci. 2024, 36, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, M.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Utilizing an 11-year runoff plot dataset to evaluate the regulation of six land management practices on runoff and sediment on Mollisols slopes and the applicability of the WEPP model. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 252, 106601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, L. Agricultural nonpoint source pollutant loads into water bodies in a typical basin in the middle reach of the Yangtze River. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Mao, J.; Zhao, H.; Peng, S.; Hang, X.; Feng, J. Spatiotemporal features and driving factors identification of urban flood-season pollution phenomenon. J. Hydrol. 2025, 661, 133581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Zhao, J.; Huang, Z. The characteristics of nitrogen and phosphorus output in China’s highly urbanized Pearl River Delta region. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Shao, Z.; Fang, S.; Huang, X.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, H. The Evolution of urban agglomerations in China and how it deviates from Zipf’s law. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 27, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Asrar, G.R.; Mao, J.; Li, X.; Li, W. Response of vegetation phenology to urbanization in the conterminous United States. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 2818–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Osterlund, H.; Marsalek, J.; Viklander, M. The pollution conveyed by urban runoff: A review of sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 136125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöman, J.D.; Gill, S.E. Residential runoff—The role of spatial density and surface cover, with a case study in the Höjeå river catchment, southern Sweden. Urban For. Urban Green. 2014, 13, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Osei, F.B.; Dai, S.; Hu, T.; Stein, A. Identifying landscape patterns at different scales as driving factors for urban flooding. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 113614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Long, T.; Liu, X.; Guo, J. Impacts of climate and land-use changes on the migration of non-point source nitrogen and phosphorus during rainfall-runoff in the Jialing River Watershed, China. J. Hydrol. 2012, 475, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaibon, S.; Anderson, S.H.; Kitchen, N.R.; Haruna, S.I. Hydraulic Properties Affected by Topsoil Thickness in Switchgrass and Corn–Soybean Cropping Systems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2016, 80, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, C. Major contributions of agricultural management practices to topsoil organic carbon distribution and accumulation in croplands of East China over three decades. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 359, 108749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, C.; Yu, B. Using soil erosion to locate nonpoint source pollution risks in coastal zones: A case study in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 283, 117117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshan, A.; Biswas, A. Fire-induced geochemical changes in soil: Implication for the element cycling. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 868, 161714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, O.; Bangroo, S.A.; Shafai, S.S.; Senesi, N.; Kader, S.; Alamri, S. Geostatistical modeling approach for studying total soil nitrogen and phosphorus under various land uses of North-Western Himalayas. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Cao, T.; Ji, X.; Yan, J.; Ding, S.; Chen, N. Seasonal hypoxia enhances sediment iron-bound phosphorus release in a subtropical river reservoir. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 936, 173261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Meng, X.; Yue, D. Evaluating the suitability of ecological restoration techniques in distinct ecoregions along the China-Nepal Highway. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 168, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lin, L.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, W.; Pan, X.; Dong, L. Distinct vertical profiles of microbial communities and functional genes between different lake sediment layers mediated by nutrients in the sediments and pore waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 981, 179575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velasquez Hurtado, W.A.; Tapete, D. Monitoring the Recovery Process After Major Hydrological Disasters with GIS, Change Detection and Open and Free Multi-Sensor Satellite Imagery: Demonstration in Haiti After Hurricane Matthew. Water 2025, 17, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronowicka-Mielniczuk, U.; Mielniczuk, J. New indices to quantify patterns of relative errors produced by spatial interpolation models—A comparative study by modelling soil properties. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chakravarty, P.; Davidson, G.R.; Wren, D.G.; Locke, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Brown, G., Jr.; Cizdziel, J.V. Simultaneous determination of mercury and organic carbon in sediment and soils using a direct mercury analyzer based on thermal decomposition-atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 871, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndikuryayo, F.; Gong, X.-Y.; Gan, X.; Yang, W.-C. Assessing emerging contaminants in soils using soil enzyme-based methods: A critical review. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2025, 46, e00260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontes, P.R.M.; Cavalcante, R.B.L.; Salomão, G.N.; Guimarães, J.T.F.; Dall’Agnol, R. Environmental assessment based on soil loss, deforestation in permanent preservation areas, and water quality applied in the Itacaiúnas Watershed, Eastern Amazon. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2025, 13, 248–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaye, Y.; Desta, G.; Molla, E.; Adimassu, Z. Effects of land management practices on runoff and soil and nutrient losses in the rainfed agroecosystem of the Beles River Basin, Ethiopia. Int. J. Sediment. Res. 2025, 40, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Zhou, L.; Fan, H.; Huang, D.; Yang, D.; Liu, H. Effects of freeze–thaw on soil loss under simulated composite upslope inflow and rainfall erosion in the black soil region of northeast China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Deitch, M.J.; Gebremicael, T.G.; Angelini, C.; Ortals, C.J. Identifying critical source areas of non-point source pollution to enhance water quality: Integrated SWAT modeling and multi-variable statistical analysis to reveal key variables and thresholds. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, J.; Ling, M.; Chen, Z.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; You, H.; Wang, F.; Han, X.; et al. A framework for dynamic assessment of soil erosion and detection of driving factors in alpine grassland ecosystems using the RUSLE-InVEST (SDR) model and Geodetector: A case study of the source region of the Yellow River. Ecol. Inform. 2025, 85, 102928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koralay, N.; Kara, Ö. Risk assessment of soil erosion with RUSLE using geographic information system and organic carbon and total nitrogen loadings of suspended sediment in Sogutlu Stream Watershed of Trabzon, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2025, 84, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintos Andreoli, V.; Shimadera, H.; Koga, Y.; Mori, M.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuo, T.; Kondo, A. Inverse estimation of nonpoint source export coefficients for total nitrogen and total phosphorous in the Kako river basin. J. Hydrol. 2023, 620, 129395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, B.; Rachid, H.; Abdeldjalil, B.; Abdessalam, O.; Mohamed, B.; Alfagham, A.T.; Tariq, A. Monitoring and forecasting water erosion in response to climate change effects using the integration of the global RUSLE/SDR model and predictive models. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.J.; Yellen, B.C.; Oyewumi, O.; Ouimet, W.; Richardson, J.B. Accumulation and transport of nutrient and pollutant elements in riparian soils, sediments, and river waters across the Thames River Watershed, Connecticut, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, C.; Qin, B. Water quality improvements and ecological inertia: A basin-wide assessment of ecosystem recovery in the Yangtze River system (2005–2022). Ecol. Indic. 2025, 176, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Han, Y.; Han, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhai, Y. Sewage Vertical Infiltration Introduced Polygenic Multipollutants into Groundwater. Water 2024, 16, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávalos, C.R.; Sosa, G.; Brozón, G.R.; Díaz-Cubilla, M.; Arrúa, A.A.; Ries, A.; Benítez Rodas, G.A. Impact of turbidity, temperature, and total nitrogen on cyanobacterial blooms in Lake Ypacaraí (Paraguay). Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 101027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhu, G. Dual—Functional mechanism for efficient nitrogen removal from water: A hybrid physical system utilizing zero—Valent iron and titanium tannate—Synergistic effect, environmental impact, and kinetics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Z. Release characteristics of sediment phosphorus in all fractions of West Lake, Hang Zhou, China. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendana, M.; Razi Idris, W.M.; Alia, F.; Effendi Rahim, S.; Yamin, M.; Izzudin, M. Relationship between drought and soil erosion based on the normalized differential water index (NDWI) and revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) model. Reg. Sustain. 2024, 5, 100183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, J.; Xiao, X.; Guan, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, E. Exploring the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics and driving factors of water erosion in mountain area based on RUSLE-SDR. J. Hydrol. 2025, 649, 132451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, X.; Lin, R. Integrated study on soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS in Yangtze River Basin of Jiangsu Province (China). Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Tian, F.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; He, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, B. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms regulate the release and transformation of phosphorus in biochar-based slow-release fertilizer. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woznicki, S.A.; Nejadhashemi, A.P. Spatial and Temporal Variabilities of Sediment Delivery Ratio. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2483–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Xie, F. The Adsorption Characteristics and Impact Mechanism of Phosphorus by Surface Sediments in Natural Freshwater Lakes. Water 2025, 17, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Cheng, W.; Kimani, S.M.; Tawaraya, K.; Tokida, T.; Yoshimoto, M.; Sakai, H.; Usui, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Matsushima, M.Y.; et al. The effects of elevated CO2 and temperature on soil organic carbon and total nitrogen contents and mineralization in the 0 to 50 cm paddy soil layer were masked by different land use history. Soil Secur. 2024, 16, 100147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zheng, Q.; Noll, L.; Hu, Y.; Wanek, W. Environmental effects on soil microbial nitrogen use efficiency are controlled by allocation of organic nitrogen to microbial growth and regulate gross N mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Deng, F.; Lv, Q.; Wang, J.; Lv, K.; Xu, J.; Zhou, D.; Feng, Y.; Bai, J. Phosphorus migration during sewage sludge thermal conversion with a focus on the role of temperature and atmosphere. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 376, 124418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wei, L.; Trakal, L.; Wang, S.; Shaheen, S.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Chen, Q. Pyrolytic and hydrothermal carbonization affect the transformation of phosphorus fractions in the biochar and hydrochar derived from organic materials: A meta-analysis study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Li, D. Decomposition of cyanobacterial bloom contributes to the formation and distribution of iron-bound phosphorus (Fe-P): Insight for cycling mechanism of internal phosphorus loading. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, J.; Li, X.; Wang, N.; Lan, Z.; He, J.; Bai, Y. Contrasting effects of nitrogen forms and soil pH on ammonia oxidizing microorganisms and their responses to long-term nitrogen fertilization in a typical steppe ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 107, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiang, H.; Li, K.; Yang, X.; Huang, W. Sediment pH structures the potential of the lake’s internal P pollution involved in different types of P reactivation. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 352, 131576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhou, J.; Sun, S.; Li, H.; Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Li, S. Differential adsorption and degradation of organic phosphorus by different interlayer cationic clay minerals in water-sediment system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 118096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Ma, S.; Cao, M.; Li, J.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Guo, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, F. Recent advances on iron bound phosphorus in wetland sediments: Characteristics, influencing factors, interactions with organic matter and emerging contaminants. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Peng, S.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, H. Effects of dissolved oxygen and nutrient loading on phosphorus fluxes at the sediment-water interface in the Hai River Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 130, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Weng, N.; Zhang, J.; Huo, S. Spatiotemporal patterns and driving factors of dissolved oxygen dynamics in a highly turbid subtropical macrotidal river estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 222, 118732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, M.; He, X.; Li, Q.; Jin, J.; Wu, T.; Shao, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, G.; et al. Seasonal changes-facilitated release of phosphorus and tungsten from the Lake Taihu sediments through reductive dissolution of Fe/Mn (hydr)oxides and competitive adsorption with dissolved organic matter. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 383, 126746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Su, C.; Geng, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, W.; Pan, H.; Xie, X.; Feng, G. Novel insights into the DOM-driven processes affecting nitrogen cycling in shallow aquifers of the West Liao River Plain: Evidence from FT-ICR MS and isotope analyses. J. Hydrol. 2025, 655, 132969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gong, J.; Li, X.; Song, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Dong, J.; Dong, X. Ecological security assessment and ecological management zoning based on ecosystem services in the West Liao River Basin. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 192, 106973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Orsoletta, D.J.; Gatiboni, L.C.; Mumbach, G.L.; Schmitt, D.E.; Boitt, G.; Smyth, T.J. Soil slope and texture as factors of phosphorus exportation from pasture areas receiving pig slurry. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; McConkey, B.G.; Liang, B.C.; Angers, D.A.; Janzen, H.H.; Kröbel, R.; Cerkowniak, D.D.; Smith, W.N. Increasing crop yields and root input make Canadian farmland a large carbon sink. Geoderma 2019, 336, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Yang, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Dong, X.; Zhang, S.; Wang, R.; Yan, C.; Wang, T. Human activities weaken the positive effects of soil abiotic factors and biodiversity on ecosystem multifunctionality more than drought: A case study in China’s West Liao River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
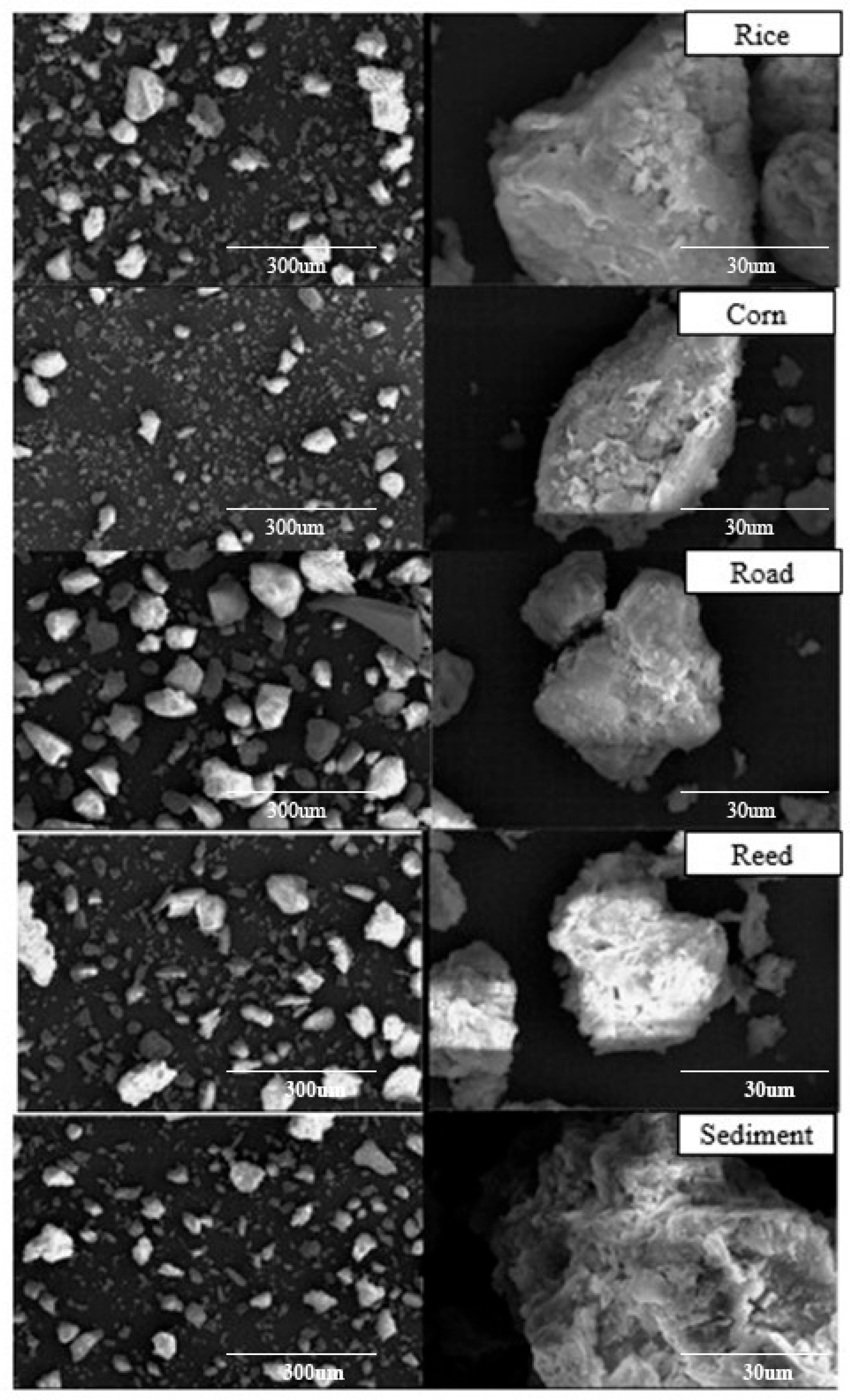

| Sample | Regression Equation | EC0 (mg/L) | NAP | R2 | Land Use Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | q = −72.54C + 54.39 | 0.75 | 54.39 | 0.917 | Rice land |
| 2 | q = −22.53C + 15.77 | 0.70 | 15.77 | 0.921 | Corn land |
| 3 | q = −93.46C + 80.78 | 0.86 | 80.78 | 0.935 | Reed land |
| 4 | q = −90.69C + 784.71 | 8.65 | 784.71 | 0.788 | Road land |
| 5 | q = −46.40C + 44.52 | 0.96 | 44.52 | 0.973 | Sediment |
| 6 | q = −38.32C + 46.29 | 1.21 | 46.29 | 0.988 | Sediment |
| Sample | Regression Equation | EC0 (mg/L) | NAP | R2 | Land Use Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | q = −30.12C + 18.37 | 0.61 | 18.37 | 0.967 | Rice land |
| 2 | q = −22.61C + 22.72 | 1.01 | 22.72 | 0.972 | Corn land |
| 3 | q = −101.86C + 31.48 | 0.31 | 31.48 | 0.978 | Reed land |
| 4 | q = −10.22C + 15.53 | 1.52 | 15.53 | 0.741 | Road land |
| 5 | q = −72.94C + 38.19 | 0.52 | 38.19 | 0.842 | Sediment |
| 6 | q = −84.24C + 37.34 | 0.44 | 37.34 | 0.858 | Sediment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, R.; Ma, R.; Su, G. Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impacts of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Downstream Daliao River Basin. Water 2025, 17, 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223267
Wang T, Liu Y, Wang Z, Wang T, Zhang Z, Cui R, Ma R, Su G. Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impacts of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Downstream Daliao River Basin. Water. 2025; 17(22):3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223267
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianxiang, Yexin Liu, Zixiong Wang, Tianzi Wang, Zipeng Zhang, Runfa Cui, Rongyue Ma, and Guangyu Su. 2025. "Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impacts of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Downstream Daliao River Basin" Water 17, no. 22: 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223267
APA StyleWang, T., Liu, Y., Wang, Z., Wang, T., Zhang, Z., Cui, R., Ma, R., & Su, G. (2025). Spatial Distribution and Environmental Impacts of Soil Nitrogen and Phosphorus in the Downstream Daliao River Basin. Water, 17(22), 3267. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223267







