An Enhanced Machine Learning Approach for Regional Total Suspended Matter Concentration Retrieval Using Multispectral Imagery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Study Area and In Situ Data
2.1.2. Satellite Imagery and Preprocessing
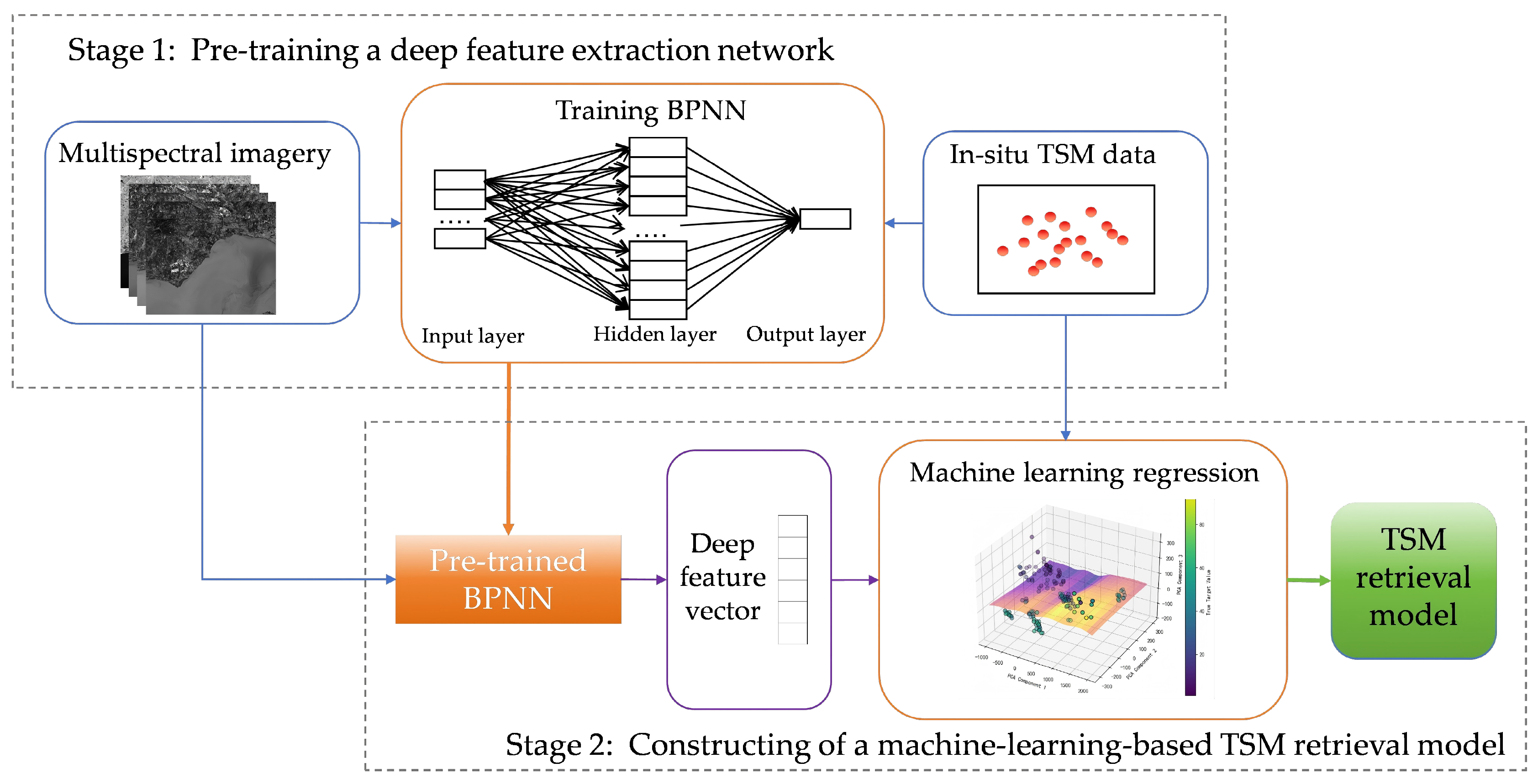
2.2. DFE-ML Framework for TSM Retrieval
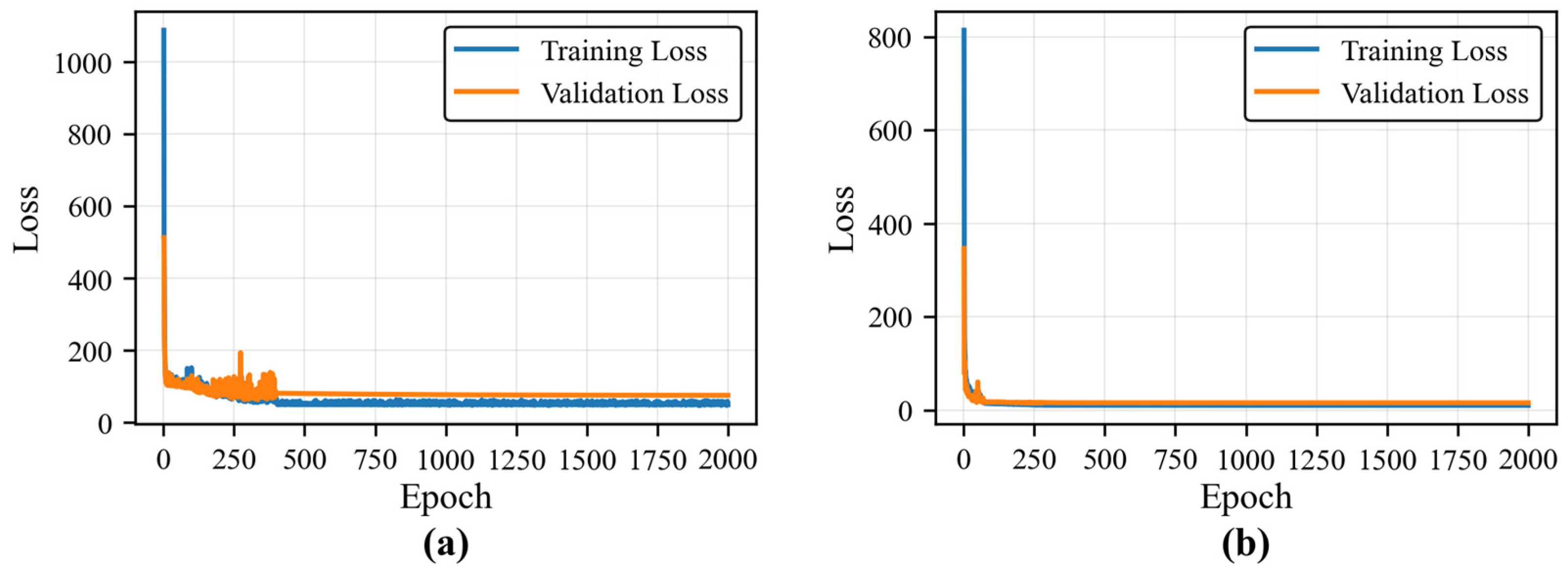
2.2.1. Pre-Training of a Deep Feature Extraction Network
2.2.2. Constructing a Machine-Learning-Based TSM Retrieval Model
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
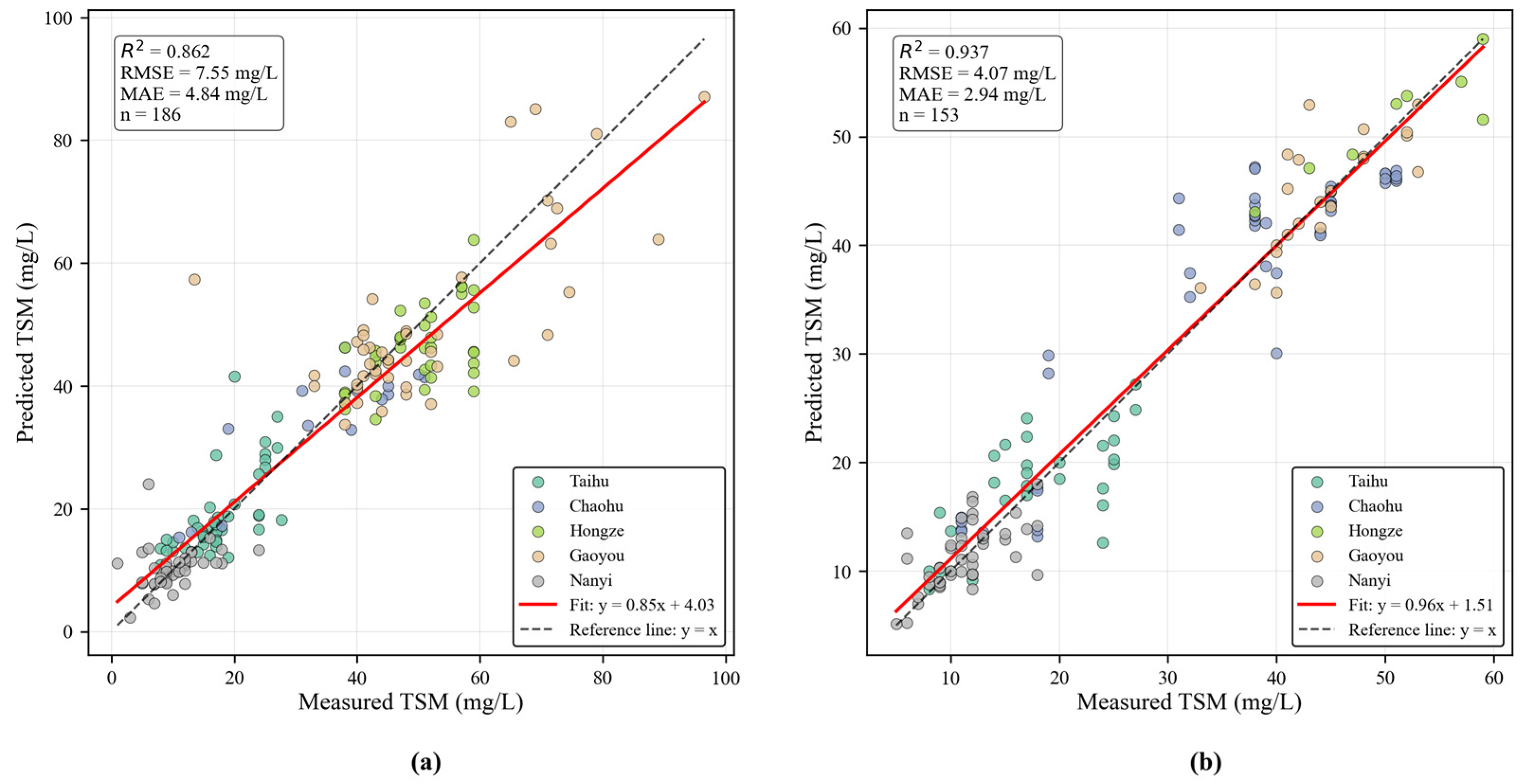
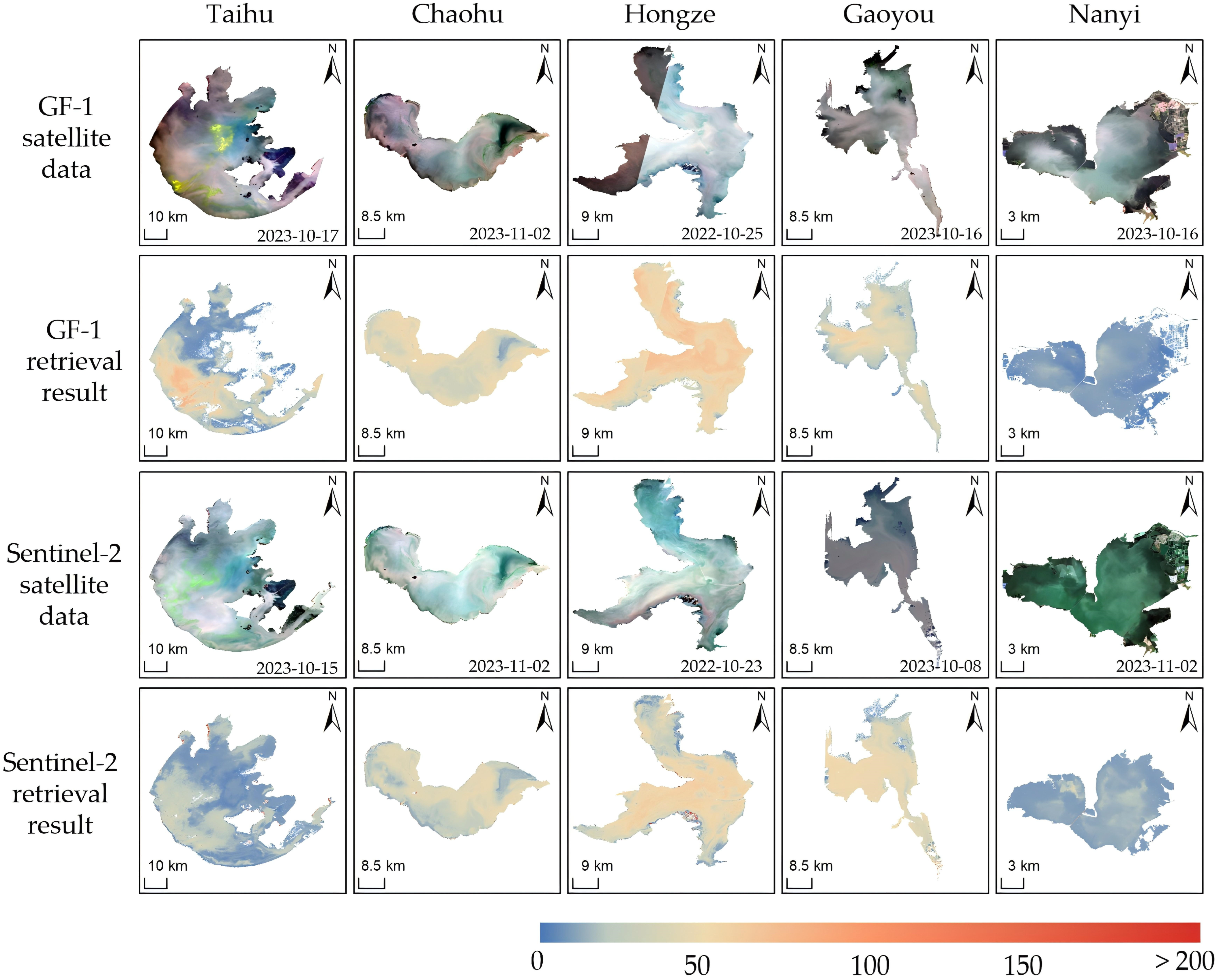
3.1. Results of TSM Retrieval
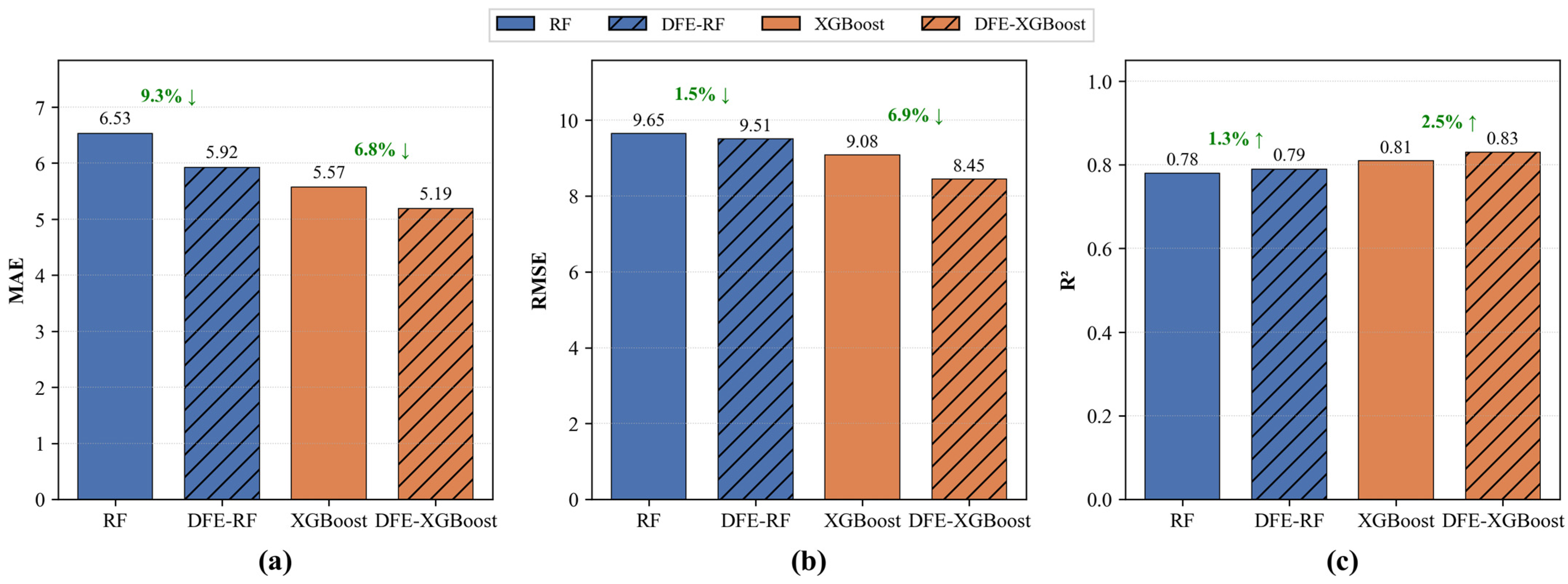
3.2. Validation and Comparison of TSM Retrieval Models
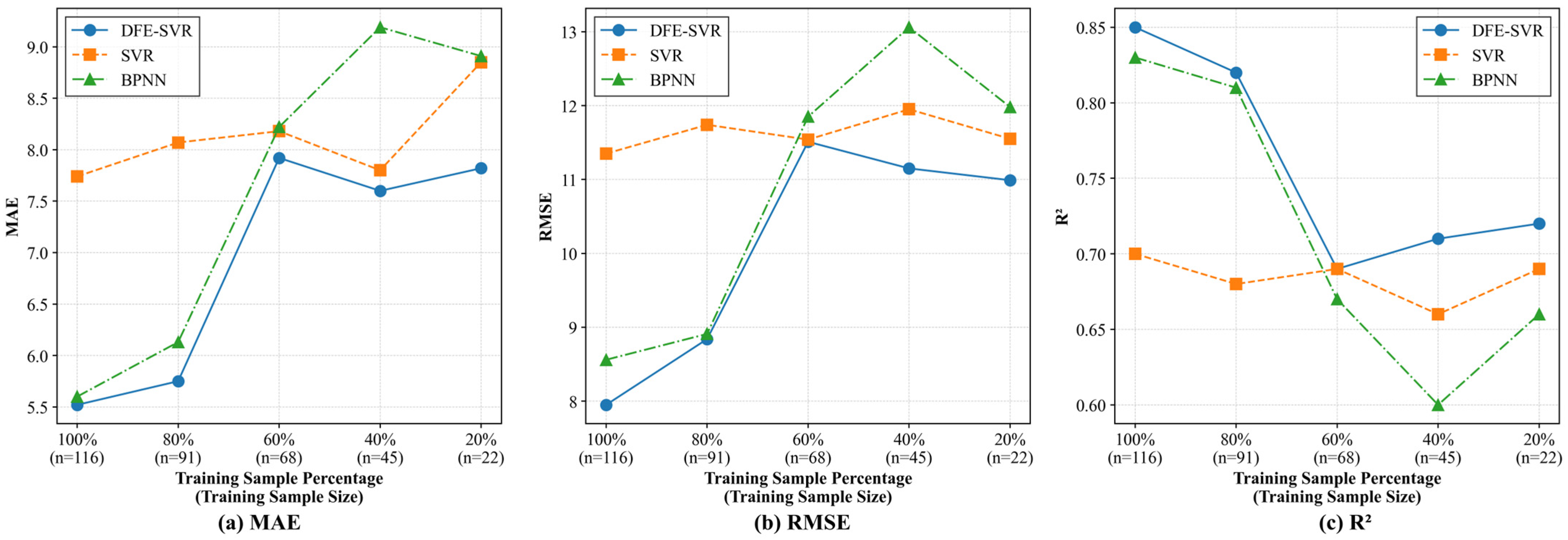
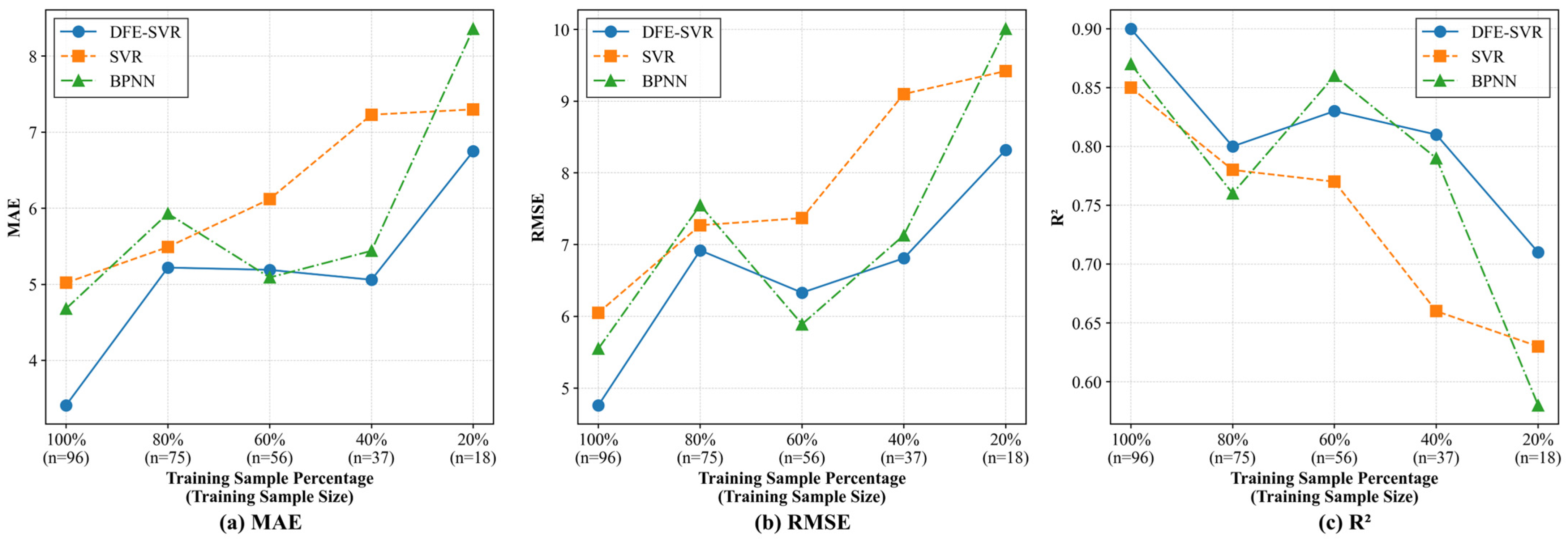
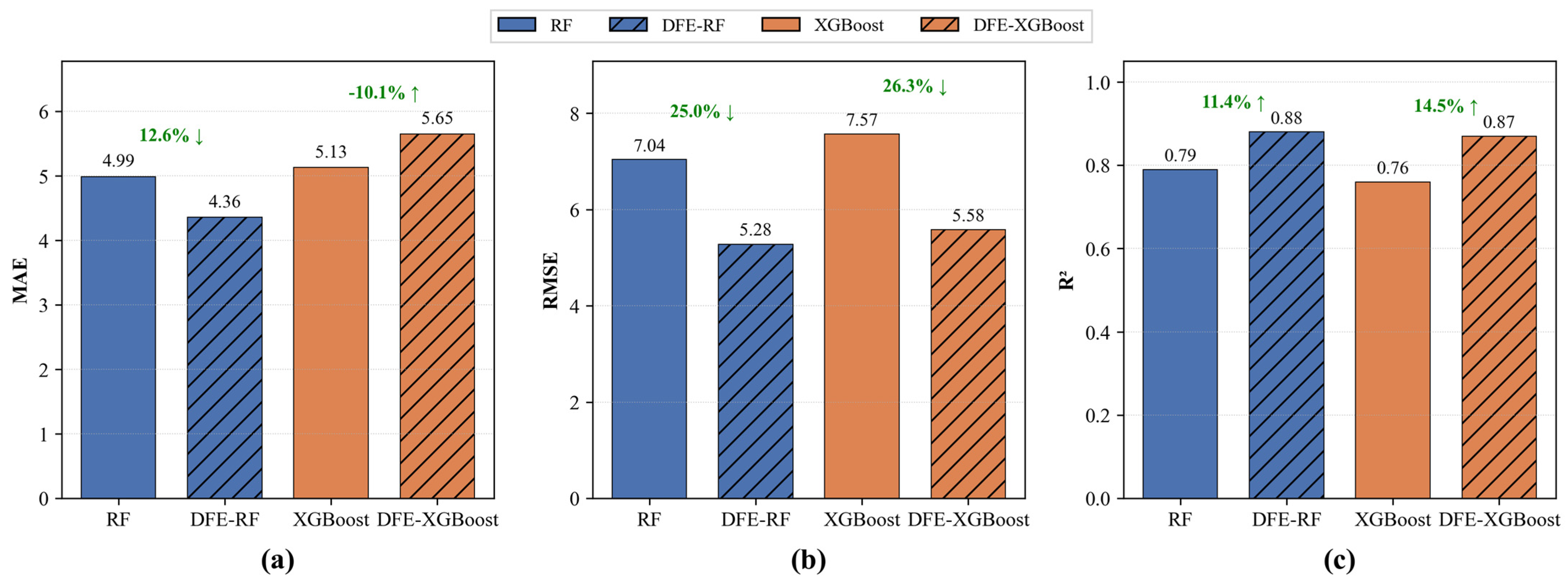
3.3. Effectiveness of the DFE-ML Framework Under Limited Samples
4. Discussion
4.1. Applicability of the DFE-ML Framework to Other Machine Learning Algorithms
4.2. Advantages
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TSM | Total Suspended Matter |
| DFE-ML | Deep Feature Extraction–Machine Learning fusion |
| DFE-SVR | Deep Feature Extraction–Support Vector Regression |
| DFE-RF | Deep Feature Extraction–Random Forest |
| DFE-XGBoost | Deep Feature Extraction–Extreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Giri, S. Water Quality Prospective in Twenty First Century: Status of Water Quality in Major River Basins, Contemporary Strategies and Impediments: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Deng, L.; Ouyang, B. Retrieval of Water Quality Parameters from Hyperspectral Images Using a Hybrid Feedback Deep Factorization Machine Model. Water Res. 2021, 204, 117618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Gao, M. Decline of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations in Lake Taihu from 1984 to 2020: Observations from Landsat TM and OLI. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 22572–22589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on Total Suspended Matters in the Yangtze Estuary and Its Adjacent Coastal Waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. Satellite Observations of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentration in Lake Gaoyou in the Past Four Decades. Water Res. 2024, 254, 121442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blix, K.; Pálffy, K.; Tóth, V.R.; Eltoft, T. Remote Sensing of Water Quality Parameters over Lake Balaton by Using Sentinel-3 OLCI. Water 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.S.; Lv, P.Y. Turbidity Effect on the Fluorescence Determination of Chlorophyll-a in Water. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 522, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, W.; Xu, Z.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W.; Sun, Z. Estimation of Suspended Particulate Matter in Turbid Coastal Waters: Application to Hyperspectral Satellite Imagery. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 10476–10493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, T.J.; Perez-Losada, J.; Schladow, S.G.; Reuter, J.E.; Jassby, A.D.; Goldman, C.R. Water Clarity Modeling in Lake Tahoe: Linking Suspended Matter Characteristics to Secchi Depth. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 68, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Bowers, D.G.; Mitchelson-Jacob, E.G. Estimating Suspended Sediment Concentrations from Ocean Colour Measurements in Moderately Turbid Waters; the Impact of Variable Particle Scattering Properties. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V.-Balogh, K.; Németh, B.; Vörös, L. Specific Attenuation Coefficients of Optically Active Substances and Their Contribution to the Underwater Ultraviolet and Visible Light Climate in Shallow Lakes and Ponds. Hydrobiologia 2009, 632, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, T.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Multiple Machine Learning Methods in Remote Sensing Quantitative Retrieval of Suspended Matter Concentrations: A Case Study of Nansi Lake in North China. J. Spectrosc. 2021, 2021, 5957376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjovu, G.E.; Stephen, H.; James, D.; Ahmad, S. Measurement of Total Dissolved Solids and Total Suspended Solids in Water Systems: A Review of the Issues, Conventional, and Remote Sensing Techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. The Spatial and Temporal Variation of Total Suspended Solid Concentration in Pearl River Estuary during 1987–2015 Based on Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubnova, E.; Bukanova, T.; Kopelevich, O.; Vazyulya, S.; Sahling, I. Spatial-Temporal Variations of the Total Suspended Matter Concentration in the South-Eastern Baltic. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/OES Baltic International Symposium (BALTIC), Klaipeda, Lithuania, 12–15 June 2018; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann, E.; Gleason, C.J.; Feng, D.; Langhorst, T. Estimating Riverine Total Suspended Solids from Spatiotemporal Satellite Sensor Fusion. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 15443–15462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; et al. An Approach for Retrieval of Horizontal and Vertical Distribution of Total Suspended Matter Concentration from GOCI Data over Lake Hongze. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Shi, K. Fifteen-Year Monitoring of the Turbidity Dynamics in Large Lakes and Reservoirs in the Middle and Lower Basin of the Yangtze River, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcântara, E.; Curtarelli, M.; Ogashawara, I.; Rosan, T.; Kampel, M.; Stech, J. Developing QAA-Based Retrieval Model of Total Suspended Matter Concentration in Itumbiara Reservoir, Brazil. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Milan, Italy, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 711–714. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Cui, T.; Qiu, Z.; Lin, C. A Three-Band Semi-Analytical Model for Deriving Total Suspended Sediment Concentration from HJ-1A/CCD Data in Turbid Coastal Waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Weidemann, A.; Kindle, J.; Arnone, R.; Carder, K.L.; Davis, C. Euphotic Zone Depth: Its Derivation and Implication to Ocean-Color Remote Sensing. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2007, 112, C03009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Tao, Z.; Shao, W.; Yang, M. Remote Sensing Inversion of the Total Suspended Matter Concentration in the Nanyi Lake Based on Sentinel-3 OLCI Imagery. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2024, 17, 10380–10389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Optimization and Evaluation of Widely-Used Total Suspended Matter Concentration Retrieval Methods for ZY1-02D’s AHSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, X.; Liao, G.; Gerkema, T. A Physical Perspective of Recurrent Water Quality Degradation: A Case Study in the Jiangsu Coastal Waters, China. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2023, 128, e2022JC019607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between Leaf Pigment Content and Spectral Reflectance across a Wide Range of Species, Leaf Structures and Developmental Stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forget, P.; Ouillon, S.; Lahet, F.; Broche, P. Inversion of Reflectance Spectra of Nonchlorophyllous Turbid Coastal Waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Cao, X.; Du, C.; Dong, W.; Liu, S.; Guo, J.; Xu, M.; Yasir, M. Chl-a Concentration Inversion Methods for Water Bodies With High TSM Concentrations Based on Waterbody Classification and Deep Learning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2025, 18, 5673–5686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalagam, L.; Shepherd, N.; Qi, J.; Barclay, N.; Smith, M. Water Quality Predictions for Urban Streams Using Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the SoutheastCon 2023, Orlando, FL, USA, 14–16 April 2023; pp. 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Alpizar, L.H.; Mejía, J.A.G. Modeling Surface Water Quality Using K-Nearest Neighbors and Random Forest. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 6th International Conference on BioInspired Processing (BIP), Liberia, Costa Rica, 4–6 December 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Tian, S.; Huang, J.J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z. Performance of Deep Learning in Mapping Water Quality of Lake Simcoe with Long-Term Landsat Archive. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 183, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wen, Z.; Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Huang, Y.; Ma, M. Remote Sensing Estimation of Suspended Sediment Concentration Based on Random Forest Regression Model. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2019, 23, 756–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupssinskü, L.S.; Guimarães, T.T.; de Freitas, R.; de Souza, E.M.; Rossa, P.; Marques, A.; Veronez, M.R.; Gonzaga, L.; Cazarin, C.L.; Mauad, F.F. Prediction of Chlorophyll-a and Suspended Solids through Remote Sensing and Artificial Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 13th International Conference on Sensing Technology (ICST), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2–4 December 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Huang, Y. Spatial-Temporal Patterns of Total Suspended Matters (TSM) in the Yellow River Estuary. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2020—2020 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 26 September–2 October 2020; pp. 5773–5776. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Tang, J.; Dong, Q.; Song, Q.; Ding, J. Retrieval of Total Suspended Matter Concentration in the Yellow and East China Seas from MODIS Imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Lu, H.; Xu, Z.; Li, X.; Tian, Y. Research on the Characteristic Spectral Band Determination for Water Quality Parameters Retrieval Based on Satellite Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.; Shin, J.; Seo, I.W.; Noh, H.; Jung, S.H.; You, H. Measurement of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Open Channel Flows Based on Hyperspectral Imagery from UAVs. Adv. Water Resour. 2022, 159, 104076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Shanwei, L.; Mingming, X.; Jianhua, W.; Hui, S.; Nazir, S.; Zhang, X.; Colak, A.T.I. YOLOv8-BYTE: Ship Tracking Algorithm Using Short-Time Sequence SAR Images for Disaster Response Leveraging GeoAI. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 128, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Miao, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lyu, H.; Gong, Z. Remote Sensing Retrieval Method Based on Few-Shot Learning: A Case Study of Surface Dissolved Organic Carbon in Jiangsu Coastal Waters, China. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 3014–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Gao, X.; Wang, W.; Khan, H.O.S.; Pan, B.; Ali, S.; Acharya, K. Wind-Induced Hy-drodynamic Changes Impact on Sediment Resuspension for Large, Shallow Lake Taihu, China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2019, 34, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Cai, S.; Wang, H.; Cui, C.; Cao, X. Hydrodynamics and Water Quality of the Hongze Lake in Response to Human Activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 46215–46232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, W.; Yin, Y.; Jin, X.; Tang, W. Environmental Changes Inferred from Lacustrine Sediments and Historical Literature: A Record from Gaoyou Lake, Eastern China. Quat. Int. 2015, 380–381, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Fan, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhu, S. Nutrient Distribution and Interrelationships in Chaohu Lake, China: Insights from Sedimentary Records. Expo. Health 2025, 17, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, X.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Cai, G.; Luo, K.; Xie, F. Occurrence and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals and Dissolved Organic Matter in Nanyi Lake, Anhui Province. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loisel, H.; Mangin, A.; Vantrepotte, V.; Dessailly, D.; Dinh, D.N.; Garnesson, P.; Ouillon, S.; Lefebvre, J.-P.; Mériaux, X.; Phan, T.M. Variability of Suspended Particulate Matter Concentration in Coastal Waters under the Mekong’s Influence from Ocean Color (MERIS) Remote Sensing over the Last Decade. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 150, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, W.; Yu, Q.; Stramski, D.; Reynolds, R.A.; Woodruff, J.D.; Yellen, B. High Spatial-Resolution Satellite Mapping of Suspended Particulate Matter in Global Coastal Waters Using Particle Composition-Adaptive Algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 323, 114745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Dou, M.; Xia, R.; Li, G.; Shen, L. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Chlorophyll-a Concentration from MODIS Data Inversion in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Hanjiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 38143–38160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Cho, K.H.; Park, J.; Cha, S.M.; Kim, J.H. Development of Early-Warning Protocol for Predicting Chlorophyll-a Concentration Using Machine Learning Models in Freshwater and Estuarine Reservoirs, Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S. An Analysis of The Small Sample Datasets Based on Machine Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering, Xiamen, China, 21–23 October 2022; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 1654–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Seegers, B.N.; Stumpf, R.P.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Loftin, K.A.; Werdell, P.J. Performance Metrics for the Assessment of Satellite Data Products: An Ocean Color Case Study. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 7404–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, K.T.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Cox, A.L.; Martinez, M. Suspended Sediment Concentration Estimation from Landsat Imagery along the Lower Missouri and Middle Mississippi Rivers Using an Extreme Learning Machine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, M.D.; Milas, A.S.; Vincent, R.K.; Evans, J.E. Landsat 8 Monitoring of Multi-Depth Suspended Sediment Concentrations in Lake Erie’s Maumee River Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 4064–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
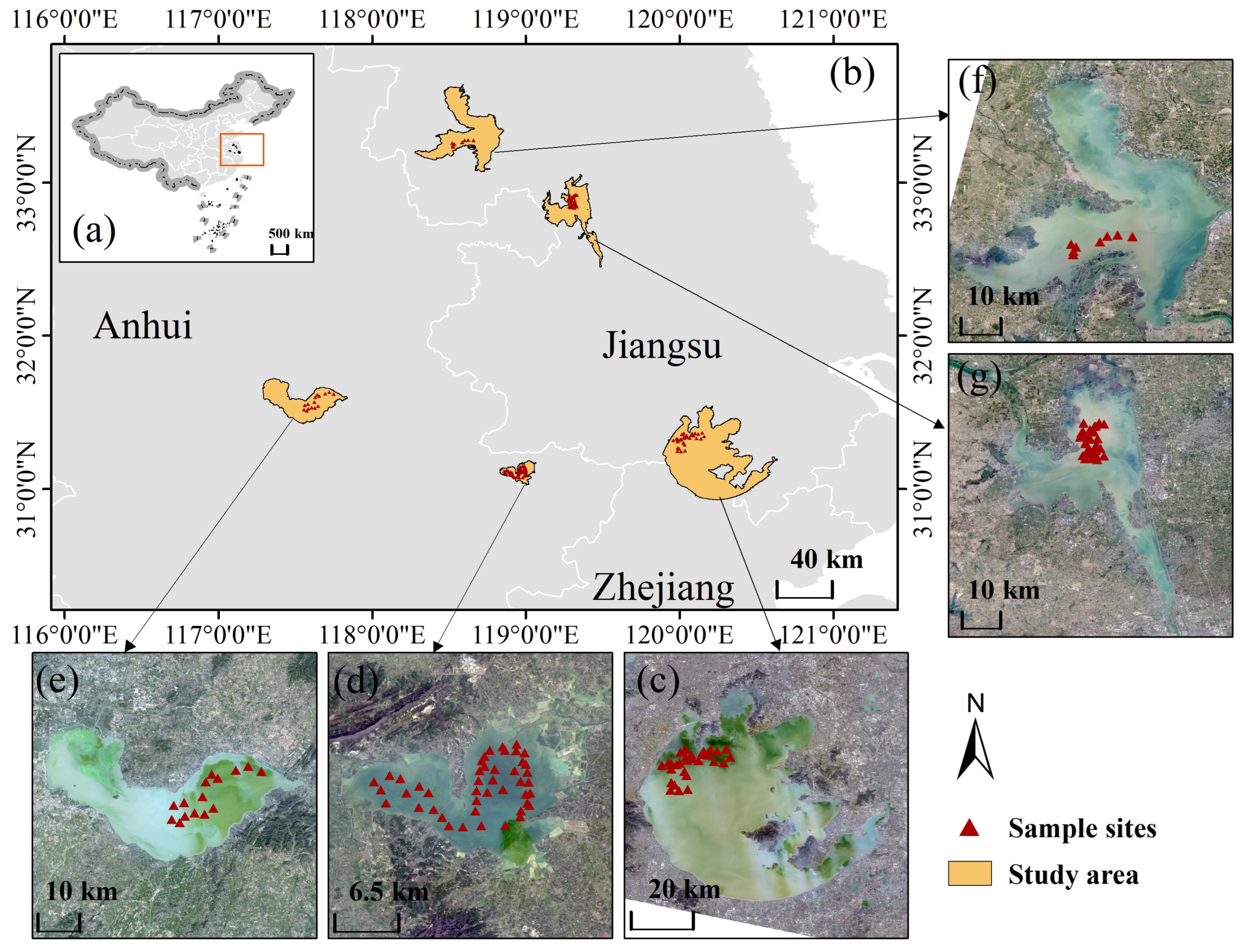
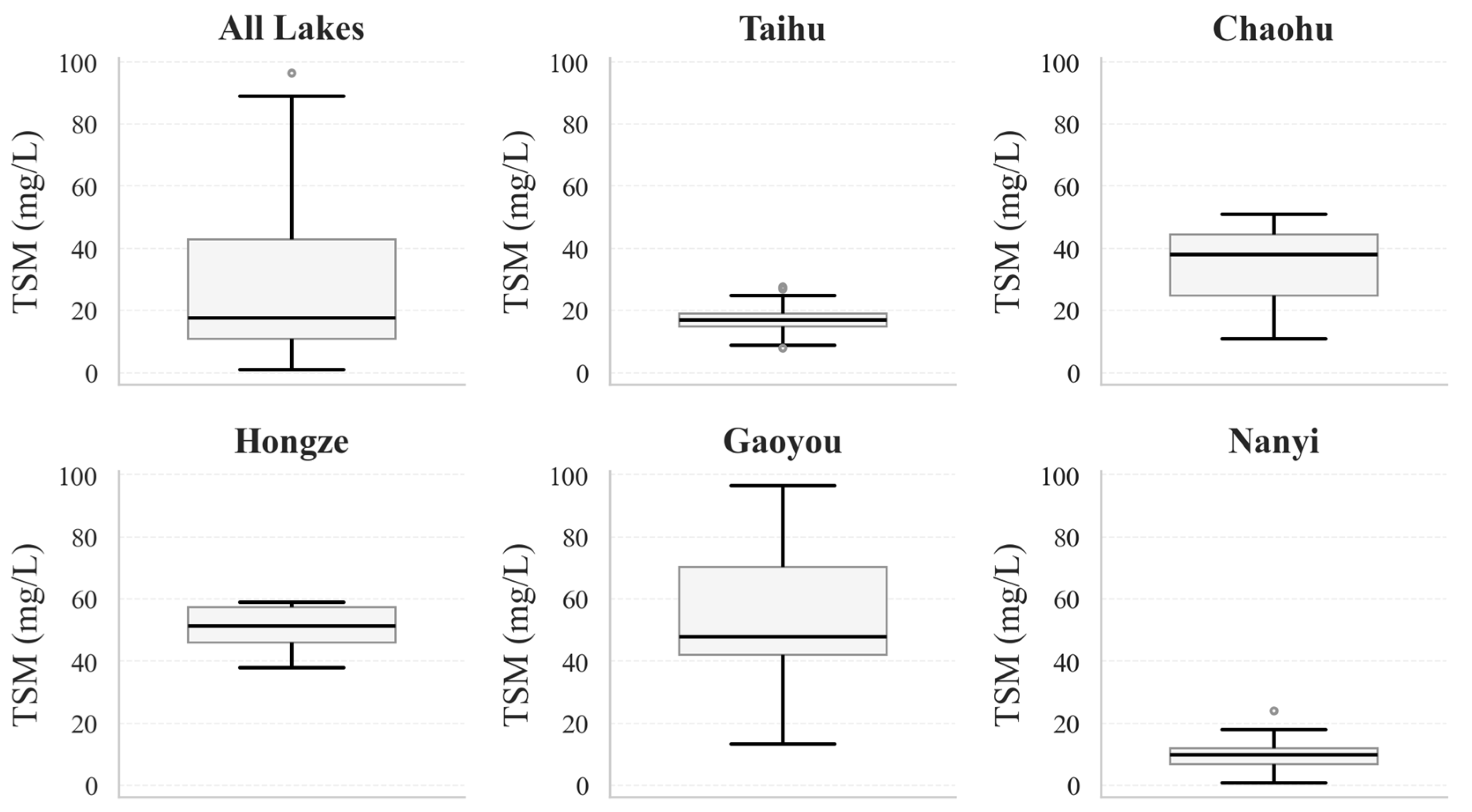
| Lake Name | In Situ Sampling Date(s) | Number of In Situ Sites | Number of GF Scenes | Number of Sentinel-2 Scenes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taihu | 17 October 2023 | 25 | 3 | 2 |
| 16 May 2024 | ||||
| Chaohu | 1 November 2023 | 15 | 1 | 4 |
| Hongze | 23 October 2023 | 8 | 6 | 2 |
| Gaoyou | 14 October 2023 | 25 | 3 | 2 |
| 24 May 2024 | ||||
| Nanyi | 30 October 2023 | 35 | 3 | 3 |
| 15 October 2023 | ||||
| 8 May 2024 |
| Method | Train Set | Test Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | R2 | MAE | RMSE | R2 | |
| DFE-SVR | 3.93 | 6.70 | 0.88 | 5.52 | 7.95 | 0.85 |
| BCR | 8.22 | 11.89 | 0.63 | 10.66 | 14.07 | 0.54 |
| BPNN | 4.94 | 7.22 | 0.86 | 5.60 | 8.56 | 0.83 |
| SVR | 7.65 | 10.64 | 0.71 | 7.74 | 11.35 | 0.70 |
| PCA-SVR | 7.67 | 10.78 | 0.70 | 8.16 | 11.69 | 0.68 |
| BCT10-SVR | 7.39 | 11.60 | 0.65 | 8.11 | 12.11 | 0.66 |
| Method | Train Set | Test Set | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | RMSE | R2 | MAE | RMSE | R2 | |
| DFE-SVR | 2.37 | 3.34 | 0.96 | 3.41 | 4.76 | 0.90 |
| BCR | 4.92 | 6.10 | 0.86 | 5.13 | 6.41 | 0.83 |
| BPNN | 2.51 | 3.23 | 0.96 | 4.68 | 5.55 | 0.87 |
| SVR | 3.70 | 5.13 | 0.90 | 5.02 | 6.05 | 0.85 |
| PCA-SVR | 3.79 | 5.23 | 0.90 | 4.83 | 5.92 | 0.85 |
| BCT10-SVR | 4.86 | 6.12 | 0.86 | 5.33 | 6.91 | 0.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Lou, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Gao, Q.; Tao, C.; Chen, Q. An Enhanced Machine Learning Approach for Regional Total Suspended Matter Concentration Retrieval Using Multispectral Imagery. Water 2025, 17, 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223252
Chen X, Lou G, Li H, Zhang X, Liu S, Gao Q, Tao C, Chen Q. An Enhanced Machine Learning Approach for Regional Total Suspended Matter Concentration Retrieval Using Multispectral Imagery. Water. 2025; 17(22):3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223252
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiuxiu, Ge Lou, Hongbo Li, Xiaoyi Zhang, Shixuan Liu, Qingshan Gao, Conghui Tao, and Qiuxiao Chen. 2025. "An Enhanced Machine Learning Approach for Regional Total Suspended Matter Concentration Retrieval Using Multispectral Imagery" Water 17, no. 22: 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223252
APA StyleChen, X., Lou, G., Li, H., Zhang, X., Liu, S., Gao, Q., Tao, C., & Chen, Q. (2025). An Enhanced Machine Learning Approach for Regional Total Suspended Matter Concentration Retrieval Using Multispectral Imagery. Water, 17(22), 3252. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17223252






