Electrochemical Sensing of Lead Ions Using Ionophore-Modified Raspberry-like Fe3O4–Au Nanostructures via Differential Pulse Voltammetry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of SPCE/Fe3O4@PEI@AuNPs_IONO-Modified Electrodes
2.2.1. Synthesis of Fe3O4@PEI Nanoparticles
2.2.2. Synthesis of Au@PVP Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Attachment of Gold Nanoparticles (AuNPs)
2.2.4. Functionalization with Lead Ionophore IV
2.3. Electrochemical Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Characterization of Raspberry-like Fe3O4@PEI@AuNPs and Ionophore Modification
3.1.1. TEM Images
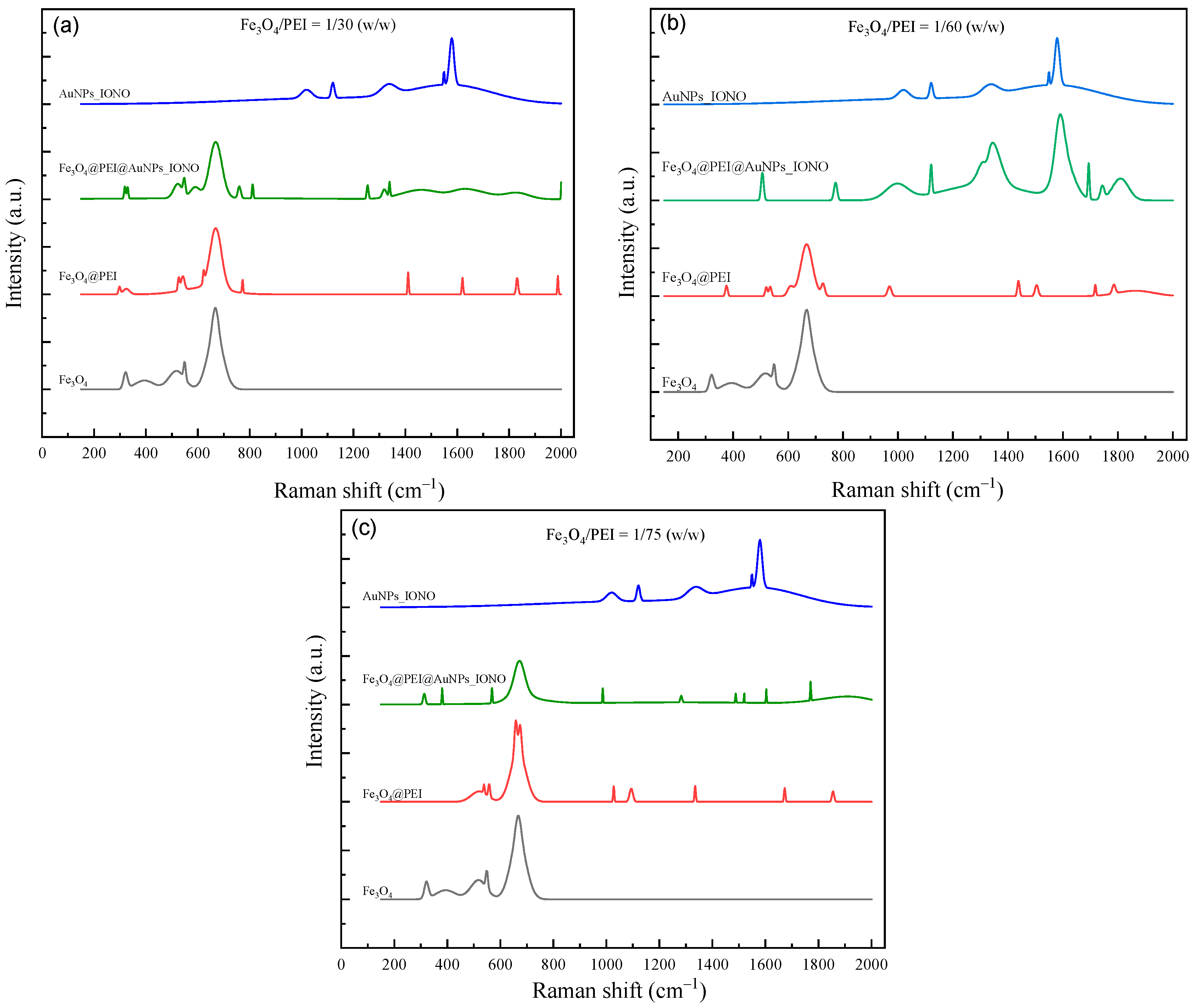
3.1.2. Raman Spectroscopy
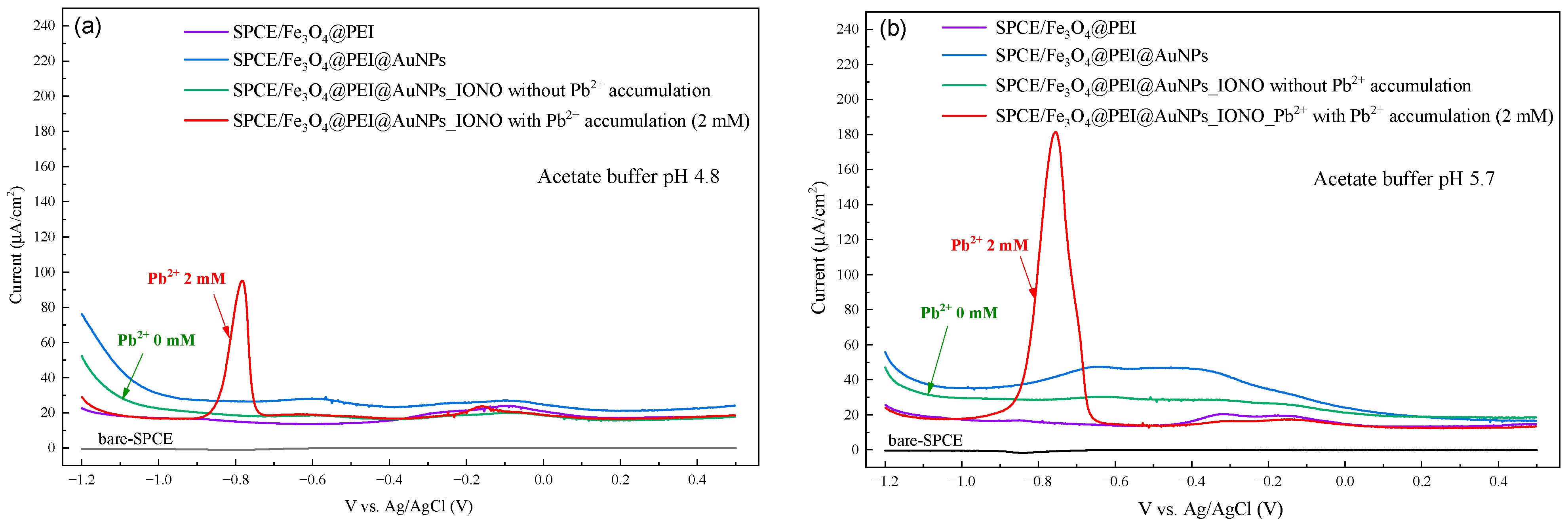
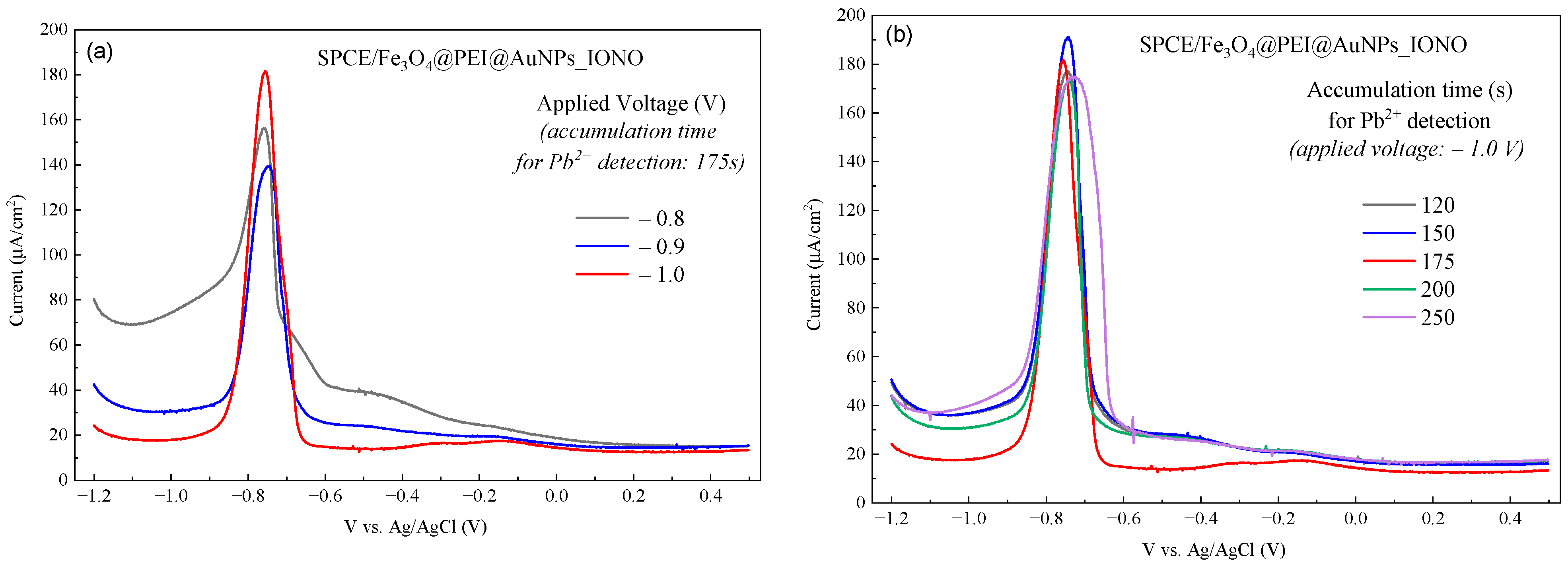
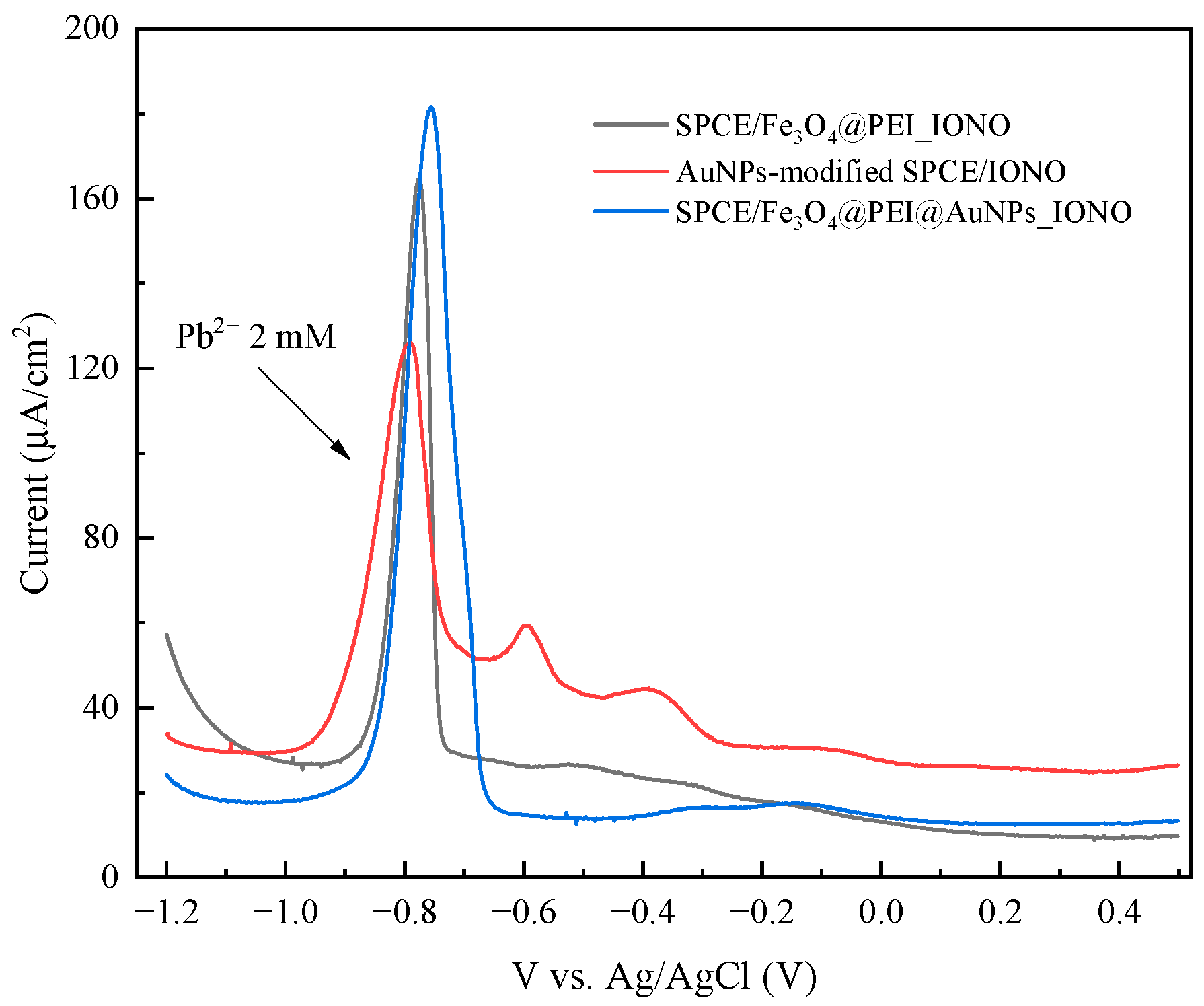
3.2. Optimization of Electrochemical Conditions for Pb2+ Detection
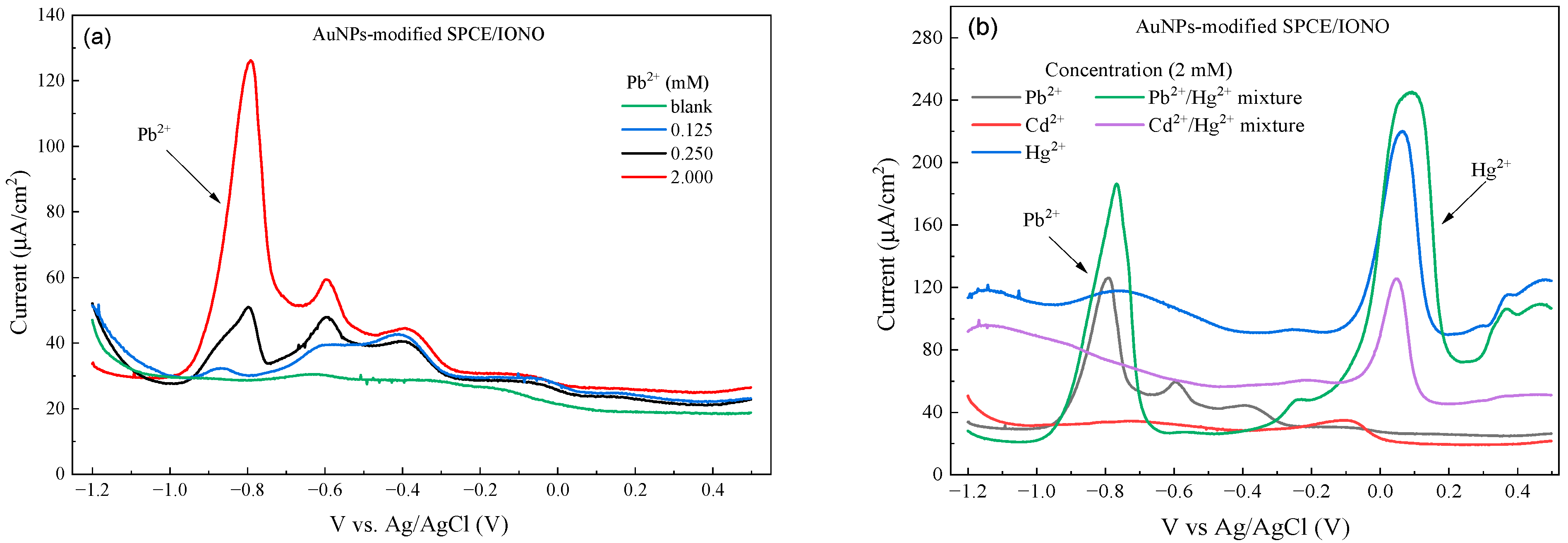
3.3. Analytical Performance and Selectivity of the Developed Sensor
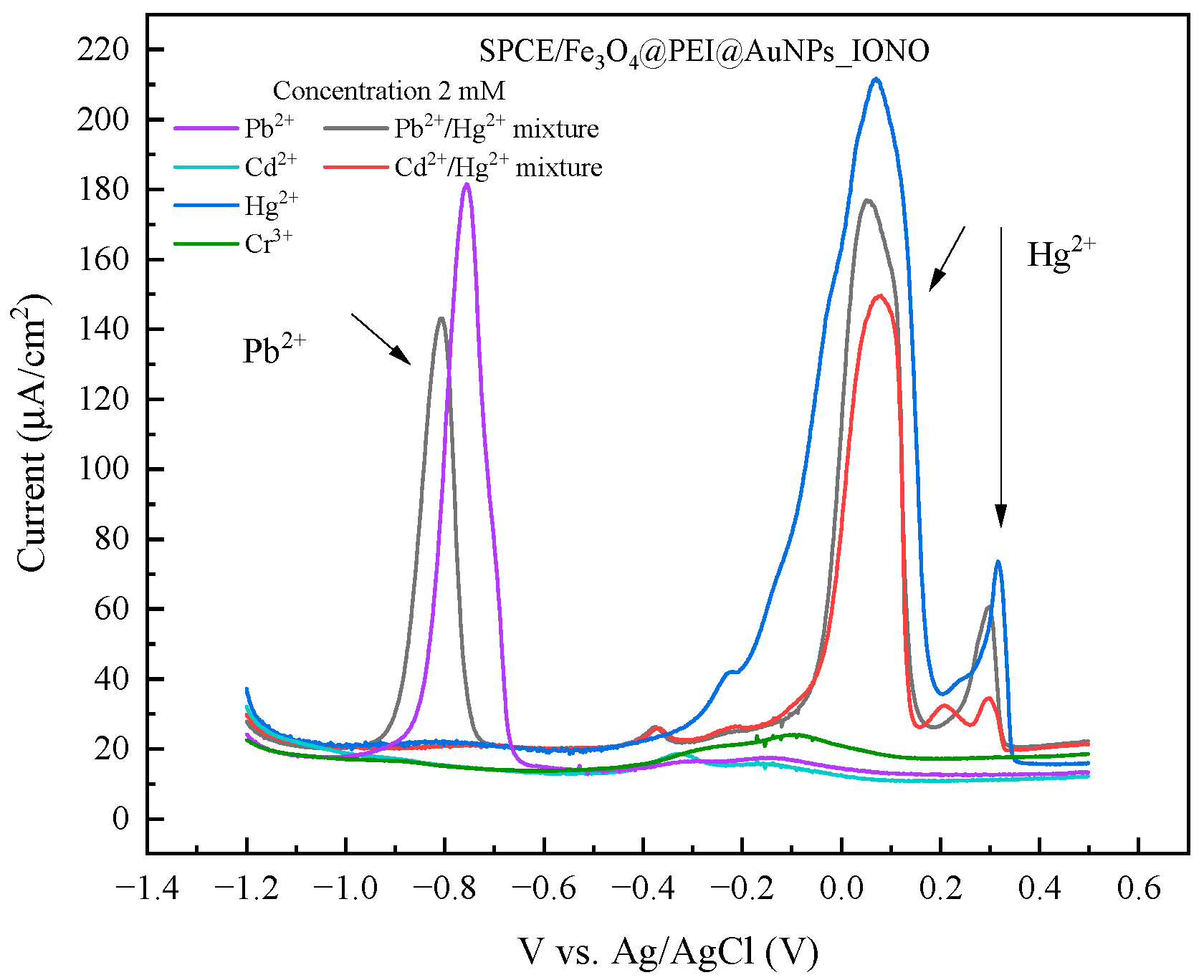
3.4. Selectivity of the Developed Pb2+ Sensor
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HEPES | 2-[4-(2-Hydroxyethyl) piperazin-1-yl] ethane-1-sulfonic acid |
| HAc | Acid Acetic |
| CA | Chronoamperometry |
| DW | Deionized Water |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetry |
| EG | Ethylene Glycol |
| IONO | Lead Ionophore IV |
| PEI | Polyethyleneimine |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| NaAc | Sodium Acetate |
| THF | Tetrahydrofuran |
References
- Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality: Fourth Edition Incorporating the First and Second Addenda. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064 (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Lead and Copper Rule | US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/dwreginfo/lead-and-copper-rule (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Wei, S.; Huang, S.; Zhou, J.; Xiao, C.; Cao, J.; Xiao, J.; Xie, C. Magnetic Carbon Porous Polymer Prepared from a New Suspended Emulsion for the Absorption of Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers 2025, 17, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milikić, J.; Savić, M.; Janošević Ležaić, A.; Šljukić, B.; Ćirić-Marjanović, G. Electrochemical Sensing of Cadmium and Lead Ions in Water by MOF-5/PANI Composites. Polymers 2024, 16, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monir, M.; Elsayed, R.E.; Azzam, R.A.; Madkour, T.M. Novel High-Performance Functionalized and Grafted Bio-Based Chitosan Adsorbents for the Efficient and Selective Removal of Toxic Heavy Metals from Contaminated Water. Polymers 2024, 16, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, J.; Qiao, J.; Ge, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Advancements in Electrochemical SensingTechnology for Heavy Metal Ions Detection. Food Chem. X 2025, 25, 102204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshehri, A.J.; Shetti, M.; Nanomaterial-Based, N.P.; Malode, S.J.; Alshehri, M.A.; Shetti, N.P. Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Pharmaceutical Drugs. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaque, S.; Abubakar, M.; Farid, M.A.; Zia, R.; Nazir, S.; Razzaque, H.; Ali, A.; Ali, Z.; Mahmood, A.; Al-Masry, W.; et al. Detection of Toxic Cypermethrin Pesticides in Drinking Water by Simple Graphitic Electrode Modified with Kraft Lignin@Ni@g-C3N4 Nano-Composite. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 9364–9374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Wei, S.; Gu, M.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L. A Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Immunosensor Using RGO-TEPA-Thi-Au as Sensitive Platform and CMK-3@AuPtNPs as Signal Probe for AFP Detection. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, T.; Fan, D.; Kuang, X.; Ali, A.; Wu, D.; Wei, Q. Triple Amplified Ultrasensitive Electrochemical Immunosensor for Alpha Fetoprotein Detection Based on MoS2@Cu2O-Au Nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavosi, B.; Hallaj, R.; Teymourian, H.; Salimi, A. Au Nanoparticles/PAMAM Dendrimer Functionalized Wired Ethyleneamine-Viologen as Highly Efficient Interface for Ultra-Sensitive α-Fetoprotein Electrochemical Immunosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.C.; Jang, S.-J.; Cho, Y.; Cho, H.; Shin, I.-S.; Kim, T.H. Graphene Quantum Dot-Doped Pedot for the Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 9, e202200557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, L. Recent Advances in Conductive Polymers-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Biomedical and Environmental Applications. Polymers 2024, 16, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepeda-Navarro, A.; Segoviano-Garfias, J.J.N.; Bivián-Castro, E.Y. The Multi-Challenges of the Multi-Ion-Imprinted Polymer Synthesis. Polymers 2024, 16, 2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdorovets, M.V.; Korolkov, I.V.; Yeszhanov, A.B.; Gorin, Y.G. Functionalization of PET Track-Etched Membranes by UV-Induced Graft (Co)Polymerization for Detection of Heavy Metal Ions in Water. Polymers 2019, 11, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, M.; Ali, A.; Jamal, R.; Bakri, T.; Wu, W.; Abdiryim, T. Electrochemical Sensor of Double-Thiol Linked PProDOT@Si Composite for Simultaneous Detection of Cd(II), Pb(II), and Hg(II). Polymers 2019, 11, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Y.; Yu, Y.S.; Chen, T.B.; Chang, C.F.; Tamulevičius, S.; Erts, D.; Wu, K.C.W.; Gu, Y. Fabrication of an Extremely Cheap Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Modified Pencil Lead Electrode for Effective Hydroquinone Sensing. Polymers 2021, 13, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, C.J.; Ahmad, S.A.A.; Mei, C.J.; Ahmad, S.A.A. A Review on the Determination Heavy Metals Ions Using Calixarene-Based Electrochemical Sensors. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 14, 103303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead Ionophore IV | C60H84N4O4S4 | CID 5147889—PubChem. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Lead-ionophore-IV (accessed on 27 October 2025).
- Lu, J.; Chen, R.; He, X. A Lead Ion-Selective Electrode Based on a Calixarene Carboxyphenyl Azo Derivative. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2002, 528, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaftian, M.R.; Rayati, S.; Emadi, D.; Matt, D. A Coated Wire-Type Lead(II) Ion-Selective Electrode Based on a Phosphorylated Calix [4]Arene Derivative. Anal. Sci. 2006, 22, 1075–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qu, W.; Yan, Y.; Wang, P.; Qiu, C. A Planar Disk Electrode Chip Based on MWCNT/CS/Pb2+ Ionophore IV Nanomaterial Membrane for Trace Level Pb2+ Detection. Molecules 2023, 28, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baghayeri, M.; Amiri, A.; Maleki, B.; Alizadeh, Z.; Reiser, O. A Simple Approach for Simultaneous Detection of Cadmium(II) and Lead(II) Based on Glutathione Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Highly Selective Electrochemical Probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1442–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Song, R.; Zhu, Z. Fe3O4/SiO2/CS Surface Ion-Imprinted Polymer Modified Glassy Carbon Electrode for Highly Sensitivity and Selectivity Detection of Toxic Metal Ions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 113, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A.H.; Bashir, A.; Manzoor, T.; Malik, L.A.; Sheikh, F.A. Citrate Coated Magnetite: A Complete Magneto Dielectric, Electrochemical and DFT Study for Detection and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 23, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahaghin, Z.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Mousavi, H.Z. Simultaneous Determination of Lead(II) and Cadmium(II) at a Glassy Carbon Electrode Modified with GO@Fe3O4@benzothiazole-2-Carboxaldehyde Using Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 249, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Qu, W.; Qiu, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Chen, K.; Qu, Y.; Hao, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Su, J. An Electrochemical Sensor for the Simultaneous Detection of Pb2+ and Cd2+ in Contaminated Seawater Based on Intelligent Mobile Detection Devices. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Lou, T.; Qin, W. Nanomaterial/Ionophore-Based Electrode for Anodic Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Lead: An Electrochemical Sensing Platform toward Heavy Metals. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 5088–5094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somerset, V.S.; Hernandez, L.H.; Iwuoha, E.I. Stripping Voltammetric Measurement of Trace Metal Ions Using Screen-Printed Carbon and Modified Carbon Paste Electrodes on River Water from the Eerste-Kuils River System. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2011, 46, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Shen, X.; Nie, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Yin, W.; Hou, C.; Huo, D.; Fa, H. Electrochemical Sensor Using Graphene/Fe3O4 Nanosheets Functionalized with Garlic Extract for the Detection of Lead Ion. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2018, 22, 3515–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


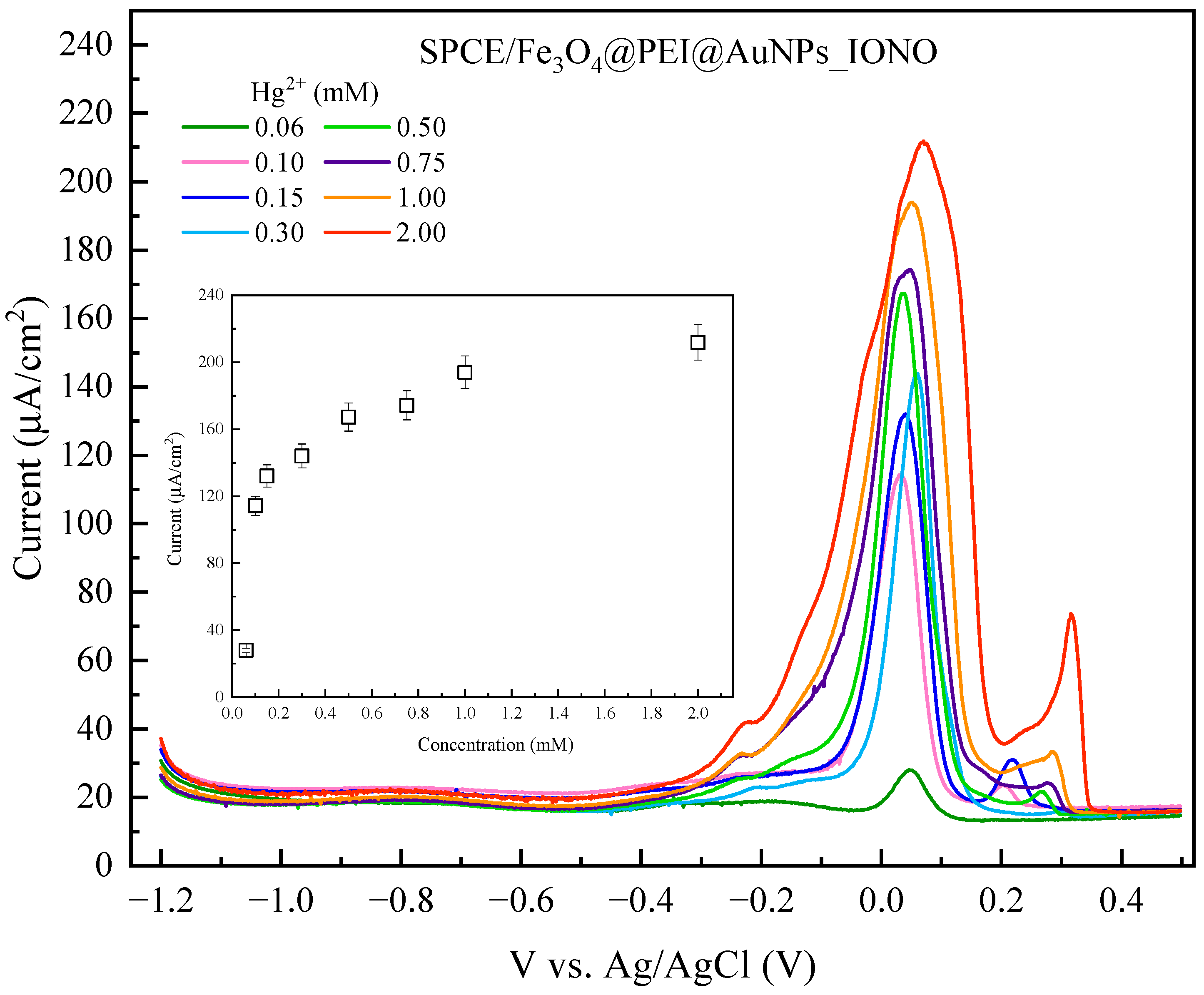
| Pb2+ Concentration (mM) | A/cm2) | Iblank | = Ip − Iblank |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16.49137 | 16.49137 | 0 |
| 0.025 | 22.82193 | 16.49137 | 6.33057 |
| 0.063 | 25.56133 | 16.49137 | 9.06997 |
| 0.250 | 43.6186 | 16.49137 | 27.12723 |
| 0.500 | 54.5018 | 16.49137 | 38.01043 |
| 0.750 | 76.07503 | 16.49137 | 59.58367 |
| 1.000 | 109.756 | 16.49137 | 93.26463 |
| 2.000 | 181.596 | 16.49137 | 165.10463 |
| Electrode | Heavy Metal Ions | LOD (ppm) | Linear Range (ppm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MWCNT/CS/Pb2+ ionophore IV/Au | Pb2+ | 8 × 10−5 | 0.001–0.1 | [22] |
| G-COOH-MWCNTs/ZnO/GCE | Pb2+ Cd2+ | 5.35 × 10−4 3.54 × 10−4 | 0.025–0.45 | [27] |
| GC/NHAP/ionophore/Nafion | Pb2+ | 2.07 × 10−4 | 0.001–0.166 | [28] |
| SPCE/PANI-PDTDA | Pb2+ Cd2+ | 0.0352 0.0601 | 2 × 10−4–207 2 × 10−4–207 | [29] |
| Fe3O4@Citrate/GCE | Pb2+ | 0.0622 | 0.104–3.11 | [25] |
| Fe3O4/GN/GE/GCE | Pb2+ | 2.55 × 10−9 | 2.07 × 10−7–1.04 × 10−4 1.04 × 10−4–0.207 | [30] |
| SPCE/Fe3O4@PEI@AuNPs_IONO | Pb2+ | 11.6 ppm (0.056 mM) | 5.18–414.4 ppm (0.025–2.00 mM) | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dau, G.H.; Nguy, T.P.; Do, T.T.N.; Pham, T.V.; Truong, L.T.N. Electrochemical Sensing of Lead Ions Using Ionophore-Modified Raspberry-like Fe3O4–Au Nanostructures via Differential Pulse Voltammetry. Polymers 2025, 17, 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223015
Dau GH, Nguy TP, Do TTN, Pham TV, Truong LTN. Electrochemical Sensing of Lead Ions Using Ionophore-Modified Raspberry-like Fe3O4–Au Nanostructures via Differential Pulse Voltammetry. Polymers. 2025; 17(22):3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDau, Giang Huong, Tin Phan Nguy, Tram Thi Ngoc Do, Thanh Van Pham, and Lien Thi Ngoc Truong. 2025. "Electrochemical Sensing of Lead Ions Using Ionophore-Modified Raspberry-like Fe3O4–Au Nanostructures via Differential Pulse Voltammetry" Polymers 17, no. 22: 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223015
APA StyleDau, G. H., Nguy, T. P., Do, T. T. N., Pham, T. V., & Truong, L. T. N. (2025). Electrochemical Sensing of Lead Ions Using Ionophore-Modified Raspberry-like Fe3O4–Au Nanostructures via Differential Pulse Voltammetry. Polymers, 17(22), 3015. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym17223015








