Reducing the Induction Time Using Ultrasound and High-Shear Mixing in a Continuous Crystallization Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
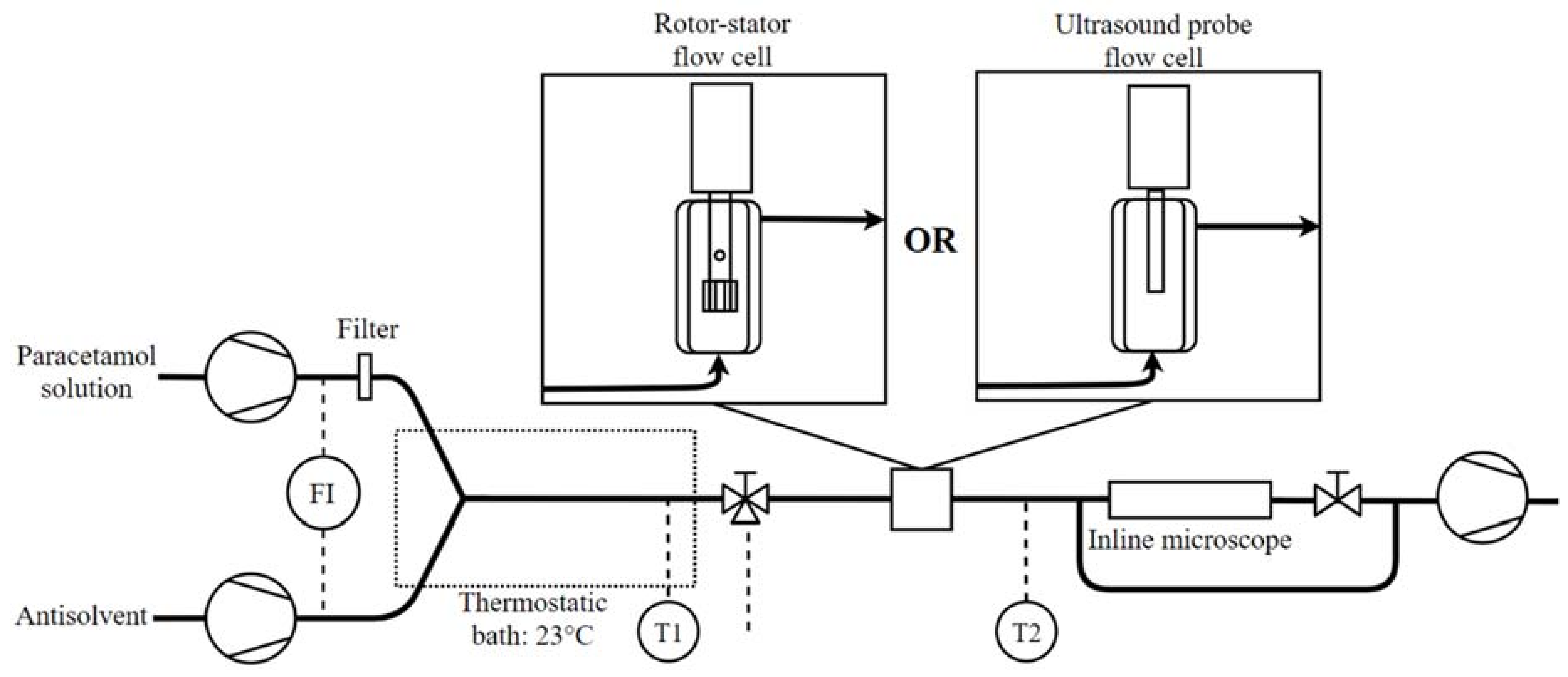
2.2. Experimental Set-Up
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Calorimetric Power Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
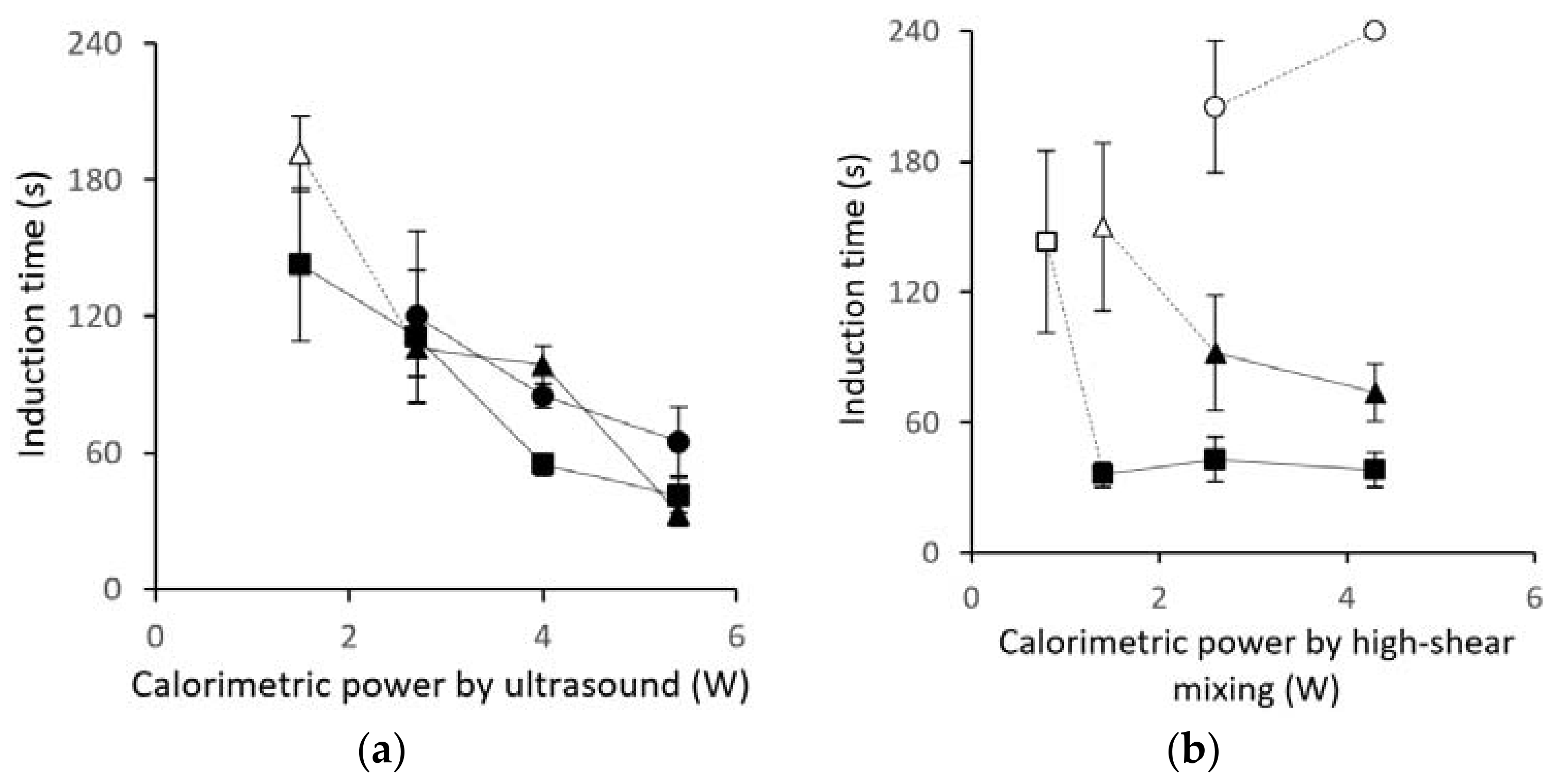
3.1. Induction-Time Measurements
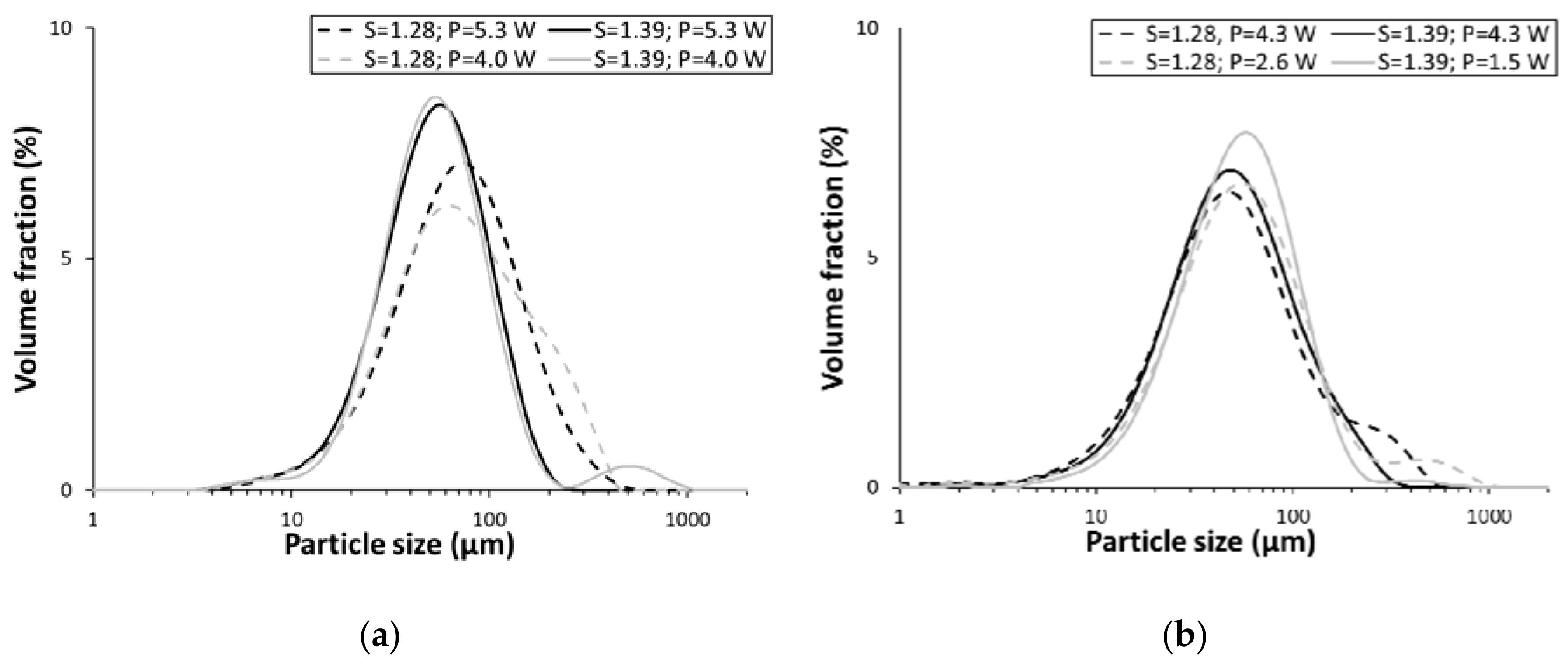
3.2. Particle-Size Measurements
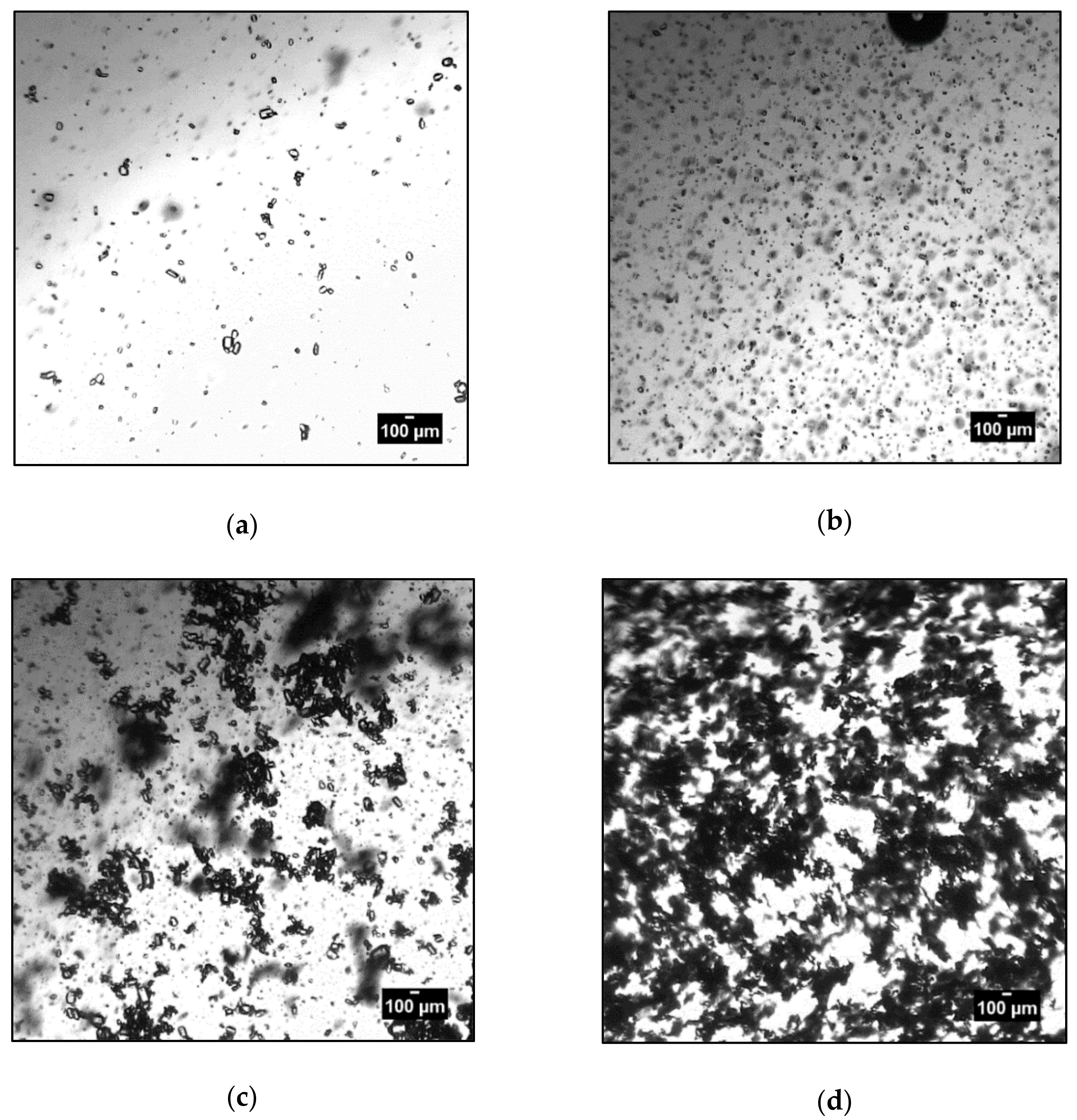
3.3. Agglomeration and Aggregation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, Y.; Hao, H. Recent progress of continuous crystallization. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 54, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Kamaraju, V.K.; Hou, G.; Power, G.; Donnellan, P.; Glennon, B. Kinetic identification and experimental validation of continuous plug flow crystallisation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2015, 133, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsyth, C.; Mulheran, P.A.; Forsyth, C.; Haw, M.D.; Burns, I.S.; Sefcik, J. Influence of controlled fluid shear on nucleation rates in glycine aqueous solutions. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Xu, S.; Du, S.; Wang, J.; Gong, J. Progress of pharmaceutical continuous crystallization. Engineering 2017, 3, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, A.J.; Myerson, A.S. Continuous plug flow crystallization of pharmaceutical compounds. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 2219–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.; Morris, G.; Hao, H.; Barrett, M.; Glennon, B. Characterization of the anti-solvent batch, plug flow and MSMPR crystallization of benzoic acid. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 104, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.; Morris, G.; Hao, H.; Barrett, M.; Glennon, B. In-situ monitoring and characterization of plug flow crystallizers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 77, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, F.; Lakerveld, R. Process intensification for pharmaceutical crystallization. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2018, 127, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaber, S.D.; Gerogiorgis, D.I.; Ramachandran, R.; Evans, J.M.B.; Barton, P.I.; Trout, B.L. Economic analysis of integrated continuous and batch pharmaceutical manufacturing: A case study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 10083–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Jimenez, E.; Papageorgiou, C.D.; Waetzig, J.; Hardy, A.; Langston, M.; Braatz, R.D. Continuous-flow tubular crystallization in slugs spontaneously induced by hydrodynamics. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, R.J.; Back, K.R.; Sullivan, R.A. Crystal nucleation from solutions—Transition states, rate determining steps and complexity. Faraday Discuss. 2015, 179, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez Del Río, J.R.; Rousseau, R.W. Batch and tubular-batch crystallization of paracetamol: Crystal size distribution and polymorph formation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2006, 6, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, M.; Mukai, K.; Cork, D.; Mae, K. Continuous crystallization using a sonicated tubular system for controlling particle size in an API manufacturing process. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2016, 102, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Mustaffar, A.; Phan, A.N.; Zivkovic, V.; Reay, D.; Law, R.; Boodhoo, K. A review of process intensification applied to solids handling. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 118, 78–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur Bhangu, S.; Ashokkumar, M.; Lee, J. Ultrasound assisted crystallization of paracetamol: Crystal size distribution and polymorph control. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordens, J.; Canini, E.; Gielen, B.; Van Gerven, T.; Braeken, L. Ultrasound assisted particle size control by continuous seed generation and batch growth. Crystals 2017, 7, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gielen, B.; Claes, T.; Janssens, J.; Jordens, J.; Thomassen, L.C.J.; Gerven, T.V.; Braeken, L. Particle size control during ultrasonic cooling crystallization of paracetamol. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2017, 40, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, R.J.P.; Schrank, S.; Besenhard, M.O.; Roblegg, E.; Gruber-Woelfler, H.; Khinast, J.G. Continuous sonocrystallization of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA): Control of crystal size. Cryst. Growth Des. 2012, 12, 4733–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Papageorgiou, C.D.; Waetzig, J.; Hardy, A.; Langston, M.; Braatz, R.D. Indirect ultrasonication in continuous slug-flow crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, Y.; Nagy, Z.K. Application of wet milling-based automated direct nucleation control in continuous cooling crystallization processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4987–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, L.; Gao, T.; Nagy, Z.K. Integrated upstream and downstream application of wet milling with continuous mixed suspension mixed product removal crystallization. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 5879–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, T.L.; Cooke, M.; Hall, S.; Pacek, A.W.; Kowalski, A.J. Rotor-stator mixers. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2011, 24, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, J.R.G.; Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonocrystallization and sonofragmentation. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleetz, T.; Funke, F.; Sunderhaus, A.; Schembecker, G.; Wohlgemuth, K. Influence of gassing crystallization parameters on induction time and crystal size distribution. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 6797–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Rasmuson, Å.C. Influence of agitation and fluid shear on primary nucleation in solution. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 4385–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ashokkumar, M.; Kentish, S.E. Influence of mixing and ultrasound frequency on antisolvent crystallisation of sodium chloride. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2014, 21, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granberg, R.A.; Rasmuson, A.C. Solubility of paracetamol in binary and ternary mixtures of water + acetone + toluene. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordens, J.; Gielen, B.; Braeken, L.; Gerven, T.V. Determination of the effect of the ultrasonic frequency on the cooling crystallization of paracetamol. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 84, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kowalski, A.J.; Cooke, M.; Hall, S. Expression for turbulent power draw of an in-line Silverson high shear mixer. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; Li, H.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. Effects of ultrasonic radiation on induction period and nucleation kinetics of sodium sulfate. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurotani, M.; Miyasaka, E.; Ebihara, S.; Hirasawa, I. Effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the behavior of primary nucleation of amino acids in supersaturated solutions. J. Cryst. Growth 2009, 311, 2714–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque de Castro, M.D.; Priego-Capote, F. Ultrasound-assisted crystallization (sonocrystallization). Ultrason. Sonochem. 2007, 14, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, B.; Kusters, P.; Jordens, J.; Thomassen, L.C.J.; Gerven, T.V.; Braeken, L. Energy efficient crystallization of paracetamol using pulsed ultrasound. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2017, 114, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennehy, R.D. Particle Engineering Using Power Ultrasound. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2003, 7, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, R.; Blindt, R.; Chivers, R.; Povey, M. The sonocrystallisation of ice in sucrose solutions: Primary and secondary nucleation. Ultrasonics 2003, 41, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gielen, B.; Jordens, J.; Thomassen, L.; Braeken, L.; Gerven, T.V. Agglomeration control during ultrasonic crystallization of an active pharmaceutical ingredient. Crystals 2017, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Flow Rate of Paracetamol Solution (g/min) | Flow Rate of Anti-Solvent (g/min) | Supersaturation Ratio (S) |
|---|---|---|
| 17.1 | 6.0 | 1.14 |
| 14.9 | 8.4 | 1.28 |
| 13.5 | 10.0 | 1.39 |
| Amplitude (%) | Power Input (W) | Calorimetric Power (W) |
|---|---|---|
| 40 | 20 | 1.5 |
| 60 | 30 | 2.7 |
| 80 | 40 | 4.0 |
| 100 | 50 | 5.4 |
| Rotational Speed (rpm) | Shear Rate (s−1) | Calorimetric Power (W) |
|---|---|---|
| 11,000 | 12,000 | 0.8 |
| 15,500 | 17,000 | 1.4 |
| 20,000 | 22,000 | 2.6 |
| 24,000 | 27,000 | 4.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vancleef, A.; Seurs, S.; Jordens, J.; Van Gerven, T.; Thomassen, L.C.J.; Braeken, L. Reducing the Induction Time Using Ultrasound and High-Shear Mixing in a Continuous Crystallization Process. Crystals 2018, 8, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080326
Vancleef A, Seurs S, Jordens J, Van Gerven T, Thomassen LCJ, Braeken L. Reducing the Induction Time Using Ultrasound and High-Shear Mixing in a Continuous Crystallization Process. Crystals. 2018; 8(8):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080326
Chicago/Turabian StyleVancleef, Arne, Stijn Seurs, Jeroen Jordens, Tom Van Gerven, Leen C. J. Thomassen, and Leen Braeken. 2018. "Reducing the Induction Time Using Ultrasound and High-Shear Mixing in a Continuous Crystallization Process" Crystals 8, no. 8: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080326
APA StyleVancleef, A., Seurs, S., Jordens, J., Van Gerven, T., Thomassen, L. C. J., & Braeken, L. (2018). Reducing the Induction Time Using Ultrasound and High-Shear Mixing in a Continuous Crystallization Process. Crystals, 8(8), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst8080326





