Mechanism of Hydrothermal Zeolite Crystallization from Kaolin in Concentrated NaOH Solutions (1–5 M): Formation of NaP1, NaP2, Analcime, Sodalite and Cancrinite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
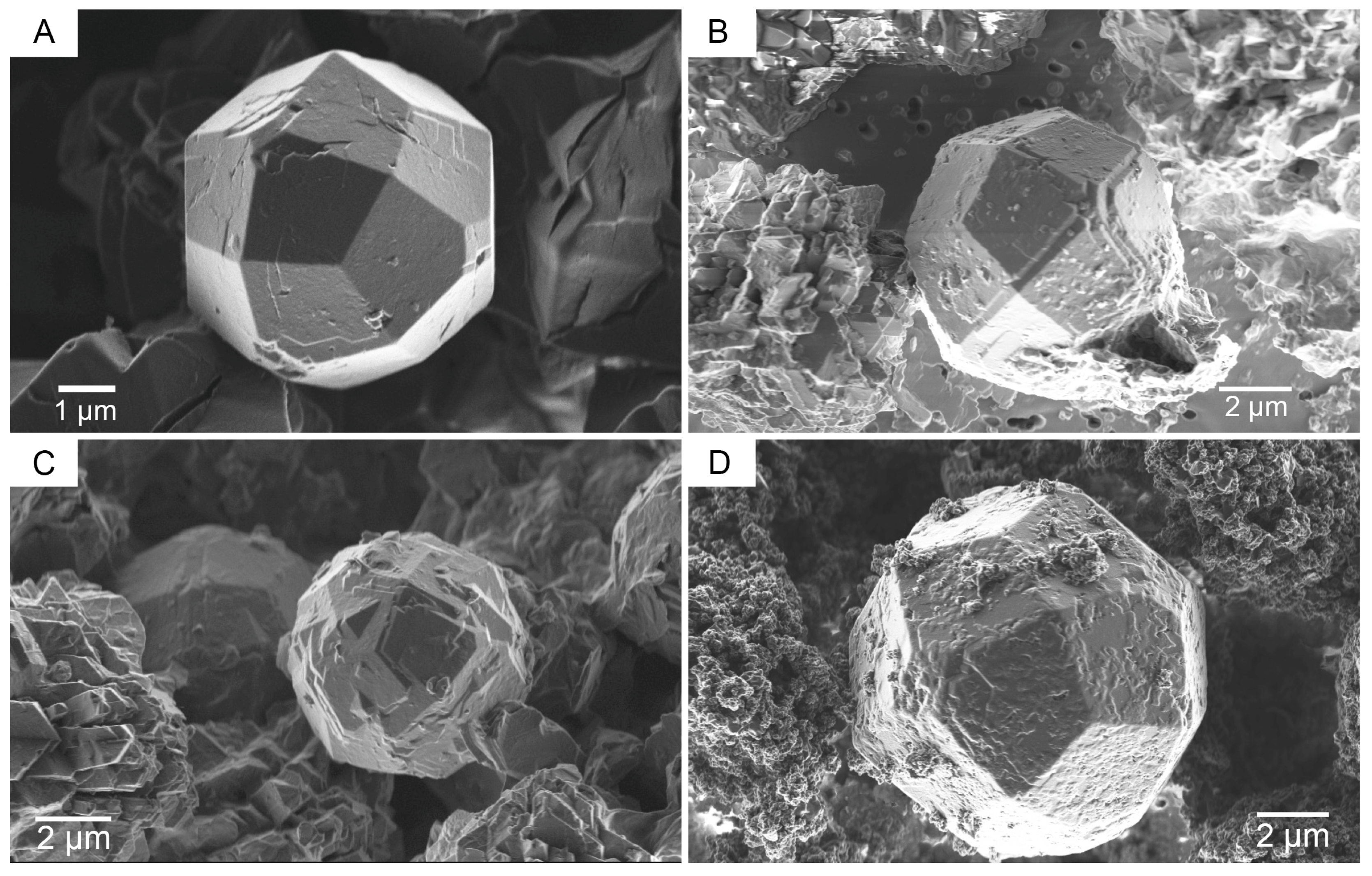
3. Results and Discussion
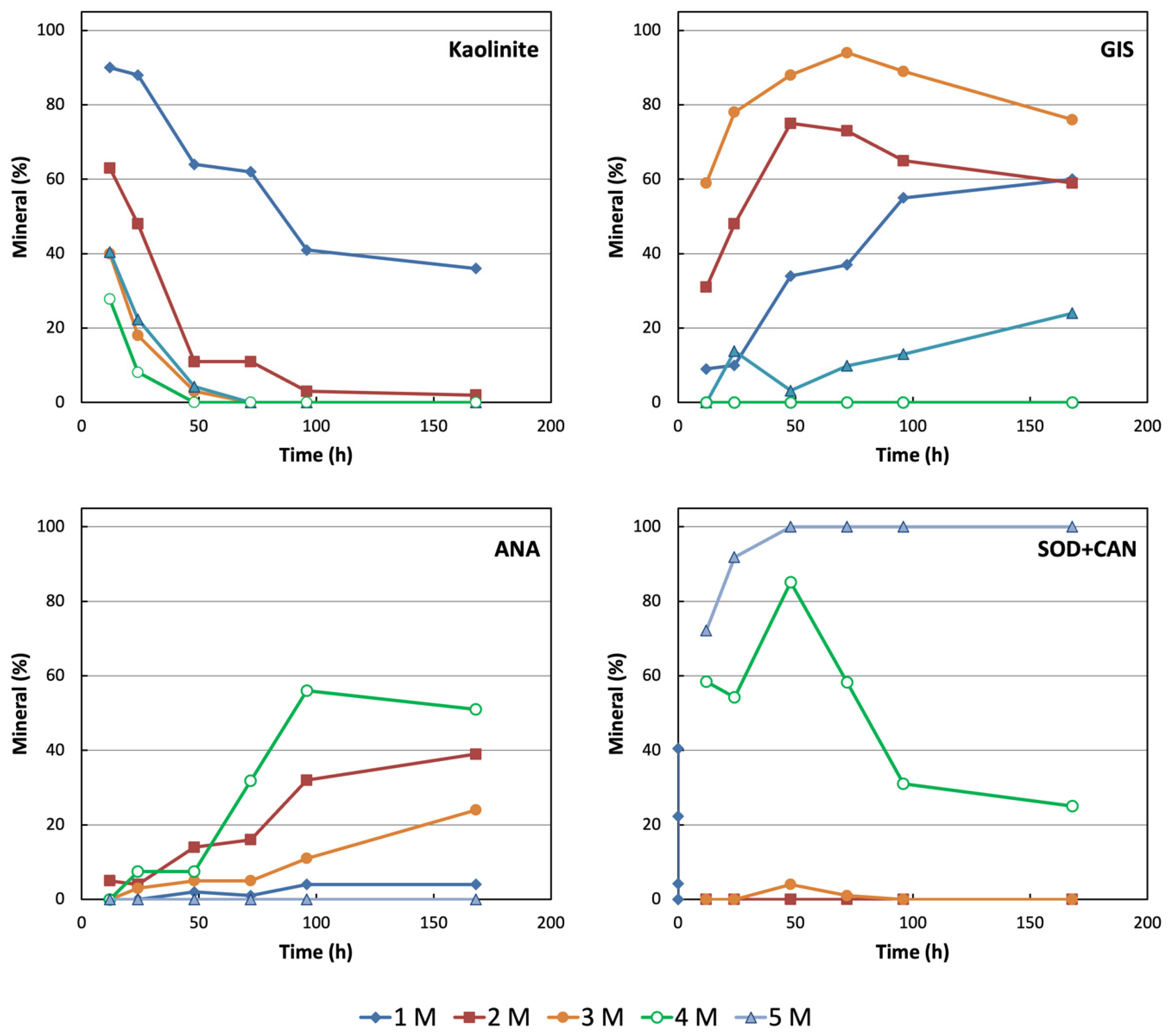
| Ref. # | NaOH (M) | Time (h) | Kln | Qtz | GIS | ANA | SOD + CAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 12 | 90 | Tr | 9 | 0 | - |
| 16 | 1 | 24 | 88 | <3 | 10 | 0 | - |
| 31 | 1 | 48 | 64 | - | 34 | <3 | - |
| 46 | 1 | 72 | 62 | - | 37 | Tr | - |
| 61 | 1 | 96 | 41 | - | 55 | 4 | - |
| 76 | 1 | 168 | 36 | - | 60 | 4 | - |
| 4 | 2 | 12 | 63 | Tr | 31 | 5 | - |
| 19 | 2 | 24 | 47 | - | 48 | 4 | - |
| 34 | 2 | 48 | 11 | - | 75 | 14 | - |
| 49 | 2 | 72 | 11 | - | 73 | 16 | - |
| 64 | 2 | 96 | <3 | - | 65 | 32 | - |
| 79 | 2 | 168 | <3 | - | 59 | 39 | - |
| 7 | 3 | 12 | 40 | - | 60 | Tr | - |
| 22 | 3 | 24 | 18 | - | 78 | <3 | - |
| 37 | 3 | 48 | <3 | - | 88 | 5 | 4 |
| 52 | 3 | 72 | - | - | 94 | 5 | Tr |
| 67 | 3 | 96 | - | - | 89 | 11 | - |
| 82 | 3 | 168 | - | - | 76 | 24 | - |
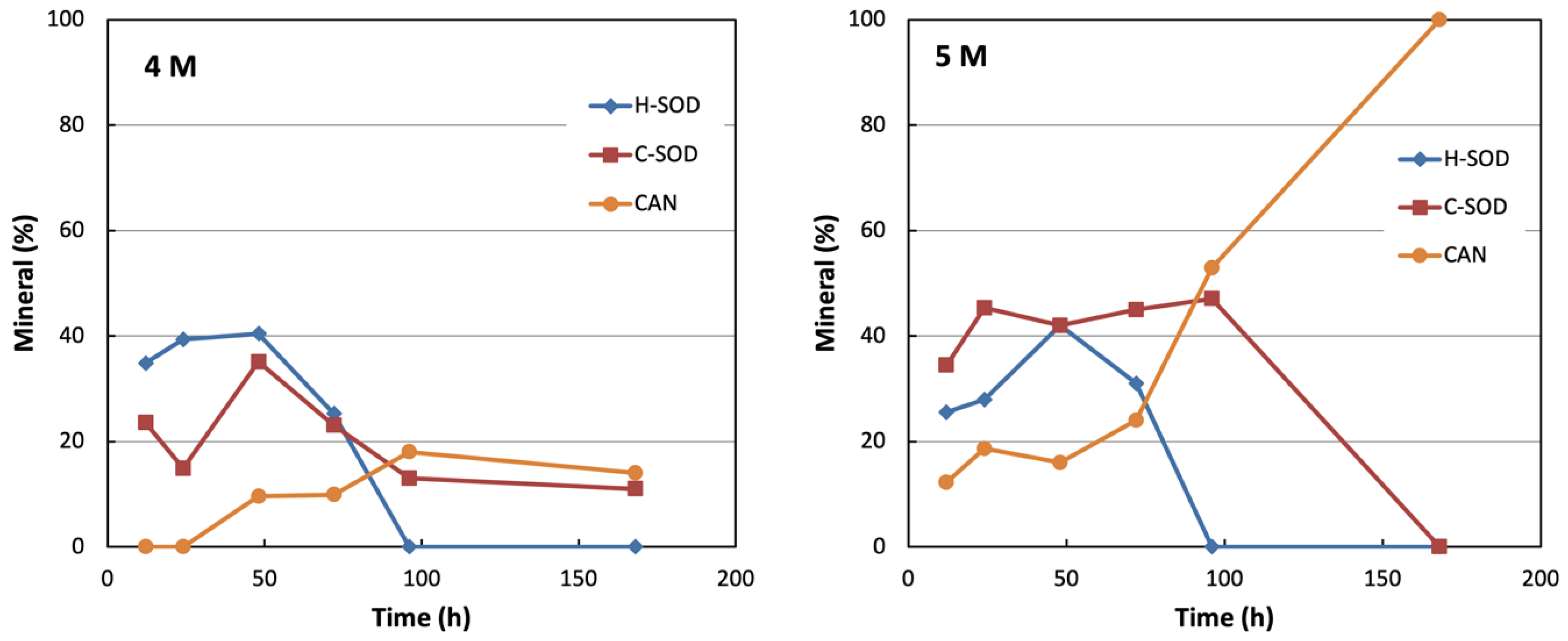
| 10 | 4 | 12 | 41 | - | 0 | - | 59 |
| 25 | 4 | 24 | 23 | - | 14 | 7 | 55 |
| 40 | 4 | 48 | 4 | - | <3 | 7 | 85 |
| 55 | 4 | 72 | - | - | 10 | 32 | 58 |
| 70 | 4 | 96 | - | - | 13 | 56 | 31 |
| 85 | 4 | 168 | - | - | 24 | 51 | 25 |
| 13 | 5 | 12 | 28 | - | - | - | 72 |
| 28 | 5 | 24 | 8 | - | - | - | 92 |
| 43 | 5 | 48 | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| 58 | 5 | 72 | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| 73 | 5 | 96 | - | - | - | - | 100 |
| 88 | 5 | 168 | - | - | - | - | 100 |
Mechanisms of Crystallization
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANA | Analcime |
| CAN | Cancrinite |
| CNMNE | Commission on New Minerals, Nomenclature and Classification |
| EDS | Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectrometer |
| FESEM | Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope |
| GIS | Gismondine |
| HRTEM | High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscope |
| IMA | International Mineralogical Association |
| IZA | International Zeolite Association |
| JCPDS | Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards |
| LOI | Loss on Ignition |
| RIR | Reference Intensity Ratio |
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| SOD | Sodalite |
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| XRF | X-ray Fluorescence |
References
- Colella, C.; Wise, W.S. The IZA Handbook of Natural Zeolites: A tool of knowledge on the most important family of porous minerals. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2014, 149, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IZA (Structure Commission). Database of Zeolite Structures. 2017. Available online: https://www.iza-structure.org/databases/ (accessed on 5 October 2025).
- Breck, D.W. Zeolite Molecular Sieves: Structure, Chemistry and Use; John Wiley & Son: New York, NY, USA, 1974; pp. 1–771. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, J.C. The Preparation of Molecular Sieves. In Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis; Flanigen, E.M., Janse, J.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; Volume 58, pp. 77–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshoeshoe, M.; Nadiye-Tabbiruka, M.S.; Obuseng, V. A review of the chemistry, structure, properties and applications of zeolites. Am. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 7, 196–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, A.; Alam, M.M.; Hoque, M.; Mondal, S.; Haider, J.B.; Johir, M.A.H.; Karmakar, A.K.; Ahmed, M.B.; Moni, M.A. Zeolite synthesis from low-cost materials and environmental applications: A review. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J. Emerging applications of zeolites in catalysis, separation and host–guest assembly. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1156–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Botella, E.; Valencia, S.; Rey, F. Zeolites in adsorption processes: State of the art and future prospects. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17647–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehmani, Y.; Mohammed, B.B.; Oukhrib, R.; Dehbi, A.; Lamhasni, T.; Brahmi, Y.; El-Kordy, A.; Franco, D.S.P.; Georgin, J.; Lima, E.C.; et al. Adsorption of various inorganic and organic pollutants by natural and synthetic zeolites: A critical review. Arab. J. Chem. 2024, 17, 105474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, J.D.C.; Fungaro, D.A.; Cataldo, E. Zeolites synthesized from agro-industrial residues applied in agriculture: A review and future prospects. Soil Use Manag. 2024, 40, e13003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, R. Ammonium removal from aqueous solution by zeolite X synthesized from halloysite mineral. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez, I.; Pérez, G.; Guerrero, A.; Ruiz, B. Mineral phases synthesized by hydro-thermal treatment from biomass ashes. Int. J. Miner. Process 2017, 158, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C. State-of-the-art applications of fly ash from coal and biomass: A focus on zeolite synthesis processes and issues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2018, 65, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoldi, M.; Fuentes-Ordoñez, E.G.; Korili, S.A.; Gil, A. Zeolite synthesis from industrial wastes. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 287, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Peng, W.; Ren, Z.; Li, Y.; Chu, B.; Zhu, Q. Research progress on synthesis of zeolites from coal fly ash and environmental applications. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallette, A.J.; Shilpa, K.; Rimer, J.G. The current understanding of mechanistic pathways in zeolite crystallization. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 3416–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; Cole, J.F.; Sticher, H. Chemistry of soil minerals. Part V. Low temperature hydrothermal transformations of kaolinite. J. Chem. Soc. A 1968, 2475–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M. The Hydrothermal Chemistry of Zeolites; Academic Press: London, UK, 1982; pp. 1–360. [Google Scholar]
- Occelli, M.L.; Robson, H.E. (Eds.) Zeolite Synthesis, ACS Symposium Series; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 1–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, H. (Ed.) Verified Synthesis of Zeolitic Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 1–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Kou, Z.; Tang, C.; Shi, Z.; Tong, Y.; Zhang, K. Recent progress in synthesis of zeolite from natural clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 243, 107087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xiao, F.-S. Green routes for synthesis of zeolites. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 1521–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Moliner, M.; Corma, A. Building zeolites from precystallized units: Nanoscale architecture. Angew.Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15330–15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Mallete, A.; Rimer, J. Controlling nucleation pathways in zeolite crystallization: Seeding conceptual methodologies for advanced materials design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 21446–21460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, S.; Zones, S.I.; Iglesia, E. Synthesis of zeolites via interzeolite transformations without organic structure-directing agents. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devos, J.; Shah, M.A.; Dusselier, M. On the key role of aluminium and other heteroatoms during interzeolite conversion synthesis. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 26188–26210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun-Jon, C.; Martinez, E.; Bertolazzo, A.A.; Banik, S.; Rimer, J.D.; Sankaranarayanan, S.K.R.S.; Molinero, V. Interzeolite transformation through cross-nucleation: A molecular mechanism for seed-assisted synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 33204–33213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pornsetmetakul, P.; Coumans, F.J.A.G.; Heinrichs, J.M.J.J.; Zhang, H.; Wattanakit, C.; Hensen, E.J.M. Accelerated synthesis of nanolayered MWW zeolite by interzeolite transformation. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202302931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, F.; Liang, X.; Han, L.; Han, P. Synthesis of CHA from MFI by three interzeolite transformation strategies and its application in NH3-SCR reaction. J. Porous Mater. 2025, 32, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrer, R.M.; Mainwaring, D.E. Chemistry of soil minerals. Part XIII. Reactions of metakaolinite with single and mixed bases. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton 1972, 12, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Aznar, A.; Sanz, J.; Serratosa, J.M. 29Si and 27Al NMR study of zeolite formation from alkali-leached kaolinites. Influence of thermal preactivation. J. Phys. Chem. 1990, 94, 760–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murat, M.; Amokrane, A.; Bastide, J.P.; Montanaro, L. Synthesis of zeolites from thermally activated kaolinite. Some observations on nucleation and growth. Clay Miner. 1992, 27, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, A.; Colella, C.; Oggiano, G.; Pansini, M.; Vezzalini, G. Zeolite production from waste kaolin-containing materials. Mater. Eng. 1994, 45, 145–158. [Google Scholar]
- Akolekar, D.; Chaffee, A.; Howe, R.F. The transformation of kaolin to low-silica X zeolite. Zeolites 1997, 19, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.; Norby, P.; Artioli, G.; Hanson, J. Kinetics of formation of zeolite Na–A [LTA] from natural kaolinites. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1997, 24, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Pramada, P.N. Investigation on the synthesis of zeolite NaX from Kerala kaolin. J. Porous Mater. 1999, 6, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S.; Pramada, P.N. Sintering behaviour of calcium exchanged low silica zeolites synthesized from kaolin. Ceram. Int. 2001, 27, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, M.; Hopa, C.; Yilmaz, Z.; Guler, H. The effect of alkali concentration and solid/liquid ratio on the hydrothermal synthesis of zeolite NaA from natural kaolinite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 86, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller-Kallai, L.; Lapides, I. Reactions of kaolinites and metakaolinites with NaOH—Comparison of different samples (Part 1). Appl. Clay Sci. 2007, 35, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, H.; Ibrahim, D.; Komarneni, S. Microwave-assisted versus conventional synthesis of zeolite A from metakaolinite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 115, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos, C.A.; Williams, C.D.; Fullen, M.A. Nucleation and growth history of zeolite LTA synthesized from kaolinite by two different methods. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 42, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, I.D.R.; Millar, G.J.; Stolz, W. Low temperature synthesis of zeolite N from kaolinites and montmorillonites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.B.G.; Arshad, S.E. Hydrothermally synthesized zeolites based on kaolinite: A review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 97–98, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meftah, M.; Oueslati, W.; Chorfi, N.; Ben Haj Amara, A. Effect of the raw material type and the reaction time on the synthesis of halloysite based Zeolite Na-P1. Results Phys. 2017, 7, 1475–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsova, M.; Smirnova, E.; Boev, S.; Kotelev, M.; Cherednichenko, K.; Vinokurov, V.; Lvov, Y.; Glotov, A. Nanoarchitectural approach for synthesis of highly crystalline zeolites with a low Si/Al ratio from natural clay nanotubes. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2022, 330, 111622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualtieri, A.; Bellotto, M. Modelling the structure of the metastable phases in the reaction sequence kaolinite-mullite by X-ray scattering experiments. Phys. Chem. Miner. 1998, 25, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, C.E.; Provis, J.L.; Proffen, T.; Riley, D.P.; van Deventer, J.S.J. Density functional modeling of the local structure of kaolinite subjected to thermal dihydroxylation. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 4988–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C.; Giannossa, L.C.; Huertas, F.J.; Lettino, A.; Mangone, A.; Fiore, S. Synthesis of zeolites at low temperatures in fly ash-kaolinite mixtures. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2015, 212, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Torres, J.A.; Espejel-Ayala, F.; Ramirez-Bon, R.; Coutino-Gonzalez, E. Sustainable strategies to synthesize small—Pore NaP zeolites using natural minerals. J. Mater. Sci. 2024, 59, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Diao, H.; Li, B.; Yue, Y.; Bao, X. A quasi-solid-phase approach to activate natural minerals for zeolite synthesis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 3233–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novembre, D.; Gimeno, D. Synthesis and characterization of analcime (ANA) zeolite using a kaolinitic rock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novembre, D.; Gimeno, D.; Del Vecchio, A. Synthesis and characterization of Na-P1 (GIS) zeolite using a kaolinitic rock. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mameli, P. Rilevamento e Caratterizzazione Mineralogica del Caolino della Sardegna Settentrionale e Proposta di Impiego in settori non Convenzionali. Ph.D. Thesis, Università di Sassari, Sassari, Italy, 1999; pp. 1–125. [Google Scholar]
- Mameli, P. Occurrence of halite in kaolin of NW Sardinia: Genetic implications. Water-Rock Interact. 2001, 10, 729–733. [Google Scholar]
- Ligas, P.; Uras, I.; Dondi, M.; Marsigli, M. Kaolinitic materials from Romana (north-west Sardinia, Italy) and their ceramic properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 1997, 12, 145–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oggiano, G.; Mameli, P. Tectonic and litho-stratigraphic controls on kaolin deposits within volcanic successions: Insights from the kaoliniferous district of north-western Sardinia (Italy). Ore Geol. Rev. 2012, 48, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PDF—Powder Diffraction Data, release 2003. In JCPDS, Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards; International Centre for Diffraction Data: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2003.
- Chung, F.H.; IUCr. Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. I. Matrix-flushing method for quantitative multicomponent analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1974, 7, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.H.; IUCr. Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. II. Adiabatic principle of X-ray diffraction analysis of mixtures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1974, 7, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, F.H.; IUCr. Quantitative interpretation of X-ray diffraction patterns of mixtures. III. Simultaneous determination of a set of reference intensities. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1975, 8, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; König, U.; Nénert, G. The HighScore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29, S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baerlocher, C.; McCusker, L.B.; Olson, D.H. Atlas of Zeolite Framework Types, 6th revised ed.; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treacy, M.M.J.; Higgins, J.B. Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites, 5th ed.; Elsevier, B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 1–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, F.J.; Chou, L.; Wollast, R. Mechanism of kaolinite dissolution at room temperature and pressure Part II: Kinetic study. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 3261–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, S.; Håkansson, U.; Fälth, L. Structure of synthetic zeolite Na-P2. Acta Cryst. C 1990, 46, 1361–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksiak, M.D.; Ghorbanpour, A.; Conato, M.T.; McGrail, P.; Grabow, L.C.; Motkuri, R.K.; Rimer, J.D. Synthesis strategies for ultrastable zeolite GIS polymorphs as sorbents for selective separations. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16078–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coombs, D.S.; Alberti, A.; Armbruster, T.; Artioli, G.; Colella, C.; Galli, E.; Grice, J.D.; Liebau, F.; Mandarino, J.A.; Minato, H.; et al. Recommended nomenclature for zeolite minerals: Report of the Subcommittee on Zeolites of the International Mineralogical Association, Commission on New Minerals and Mineral Names. Eur. J. Miner. 1998, 10, 1037–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, B.R.; Cheetham, A.K.; Stuart, J.A.; Adams, C.J. Investigations on P zeolites: Synthesis, characterisation, and structure of highly crystalline low-silica NaP. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 1998, 21, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubowa, H.L.; Kosslick, H.; Müller, D.; Richter, M.; Wilde, L.; Fricke, L. Crystallization of phase-pure zeolite NaP from MCM-22-type gel compositions under microwave radiation. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2008, 109, 542–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Hernández, R.; López-Delgado, A.; Padilla, I.; Galindo, R.; López-Andrés, S. One-step synthesis of NaP1, SOD and ANA from a hazardous aluminum solid waste. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2016, 226, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Wang, Q.; Pan, B.; Ravindra, A.V.; Shaohua, J.; Peng, J. Process regulation of microwave intensified synthesis of Y-type zeolite. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2019, 284, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Song, J.-S.; Han, M.H.; Cho, C.-H. GIS-NaP1 zeolite microspheres as potential water adsorption material: Influence of initial silica concentration on adsorptive and physical/topological properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayraukham, P.; Jantarit, N.; Osakoo, N.; Wittayakun, J. Synthesis of pure phase NaP2 zeolite from the gel of NaY by conventional and microwave-assisted hydrothermal methods. Crystals 2020, 10, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, L.N. IMA–CNMNC approved mineral symbols. Min. Mag. 2021, 85, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.-J.; Xie, X.-Z.; Huang, Y.-X.; Pan, Y.; Mi, J.-X. Phase diagram for hydrothermal alkali activation of kaolin and quartz: Optimal digestion for the synthesis of zeolites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 290, 126570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundy, C.S.; Cox, P.A. The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites: History and development from the earliest days to the present time. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 663–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cundy, C.S.; Cox, P.A. The hydrothermal synthesis of zeolites: Precursors, intermediates and reaction mechanism. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2005, 82, 1–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintova, S.; Olson, N.H.; Valtchev, V.; Bein, T. Mechanism of zeolite A nanocrystal growth from colloids at room temperature. Science 1999, 283, 958–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, S.; Huertas, F.J.; Huertas, F.; Linares, J. Morphology of kaolinite crystals synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. Clays Clay Miner. 1995, 43, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huertas, F.J.; Fiore, S.; Linares, J. In situ transformation of amorphous gels into spherical aggregates of kaolinite: A HRTEM study. Clay Miner. 2004, 39, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.K.; Fedorov, P.P.; Baranchikov, A.E.; Osiko, V.V. Oriented attachment of particles: 100 years of investigations of non-classical crystal growth. Russian Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Yoreo, J.J.; Gilbert, P.U.P.A.; Sommerdijk, N.A.J.M.; Penn, R.L.; Whitelam, S.; Joester, D.; Zhang, H.; Rimer, J.D.; Navrotsky, A.; Banfield, J.F.; et al. Crystallization by particle attachment in synthetic, biogenic, and geologic environments. Science 2015, 349, aaa6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Niu, Z.; Choudhary, M.; Bourji, H.; Palmer, J.C.; Rimer, J.D. In situ imaging of faujasite surface growth reveals unique pathways of zeolite crystallization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valtchev, V.P.; Bozhilov, K.N. Transmission electron microscopy study of the formation of FAU-type zeolite at room temperature. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 15587–15598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.C.; Addai-Mensah, J.; Gerson, A.R. The mechanism of the sodalite-to-cancrinite phase transformation in synthetic spent Bayer liquor. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 1999, 31, 287–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomba, P.; Padalino, G.; Marchi, M. Industrial mineral occurrences associated with Cenozoic volcanic rocks of Sardinia (Italy): Geological, mineralogical, geochemical features and genetic implications. Ore Geol. Rev. 2006, 29, 118–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccerillo, A. Sardinia. In Cenozoic Volcanism in the Tyrrhenian Sea Region, 2nd ed.; Advances in Volcanology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 313–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulon, C.; Dupuy, C. Evolution spatiale des caractères chimiques du volcanisme andésitique de la Sardaigne (Italie). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1975, 25, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccaluva, L.; Brotzu, P.; Morbidelli, L.; Serri, G.; Traversa, G. Cainozoic tectono-magmatic evolution and inferred mantle in the Sardo-Tyrrhenian area. The lithosphere in Italy. Advances in Earth Science Research. Accad. Naz. Lincei 1987, 229–248. [Google Scholar]
- Beccaluva, L.; Bianchini, G.; Mameli, P.; Natali, C. Miocene shoshonite volcanism in Sardinia: Implications for magma sources and geodynamic evolution of the central-western Mediterranean. Lithos 2013, 180–181, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utada, M. Hydrothermal alteration related to igneous acidity in Cretaceous and Neogene formations of Japan. Min. Geol. jpn. Spec. Issue 1980, 8, 67–83. [Google Scholar]
- Berger, G.; Velde, B. Chemical parameters controlling the propylitic and argillic alteration process. Eur. J. Mineral. 1992, 4, 1439–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
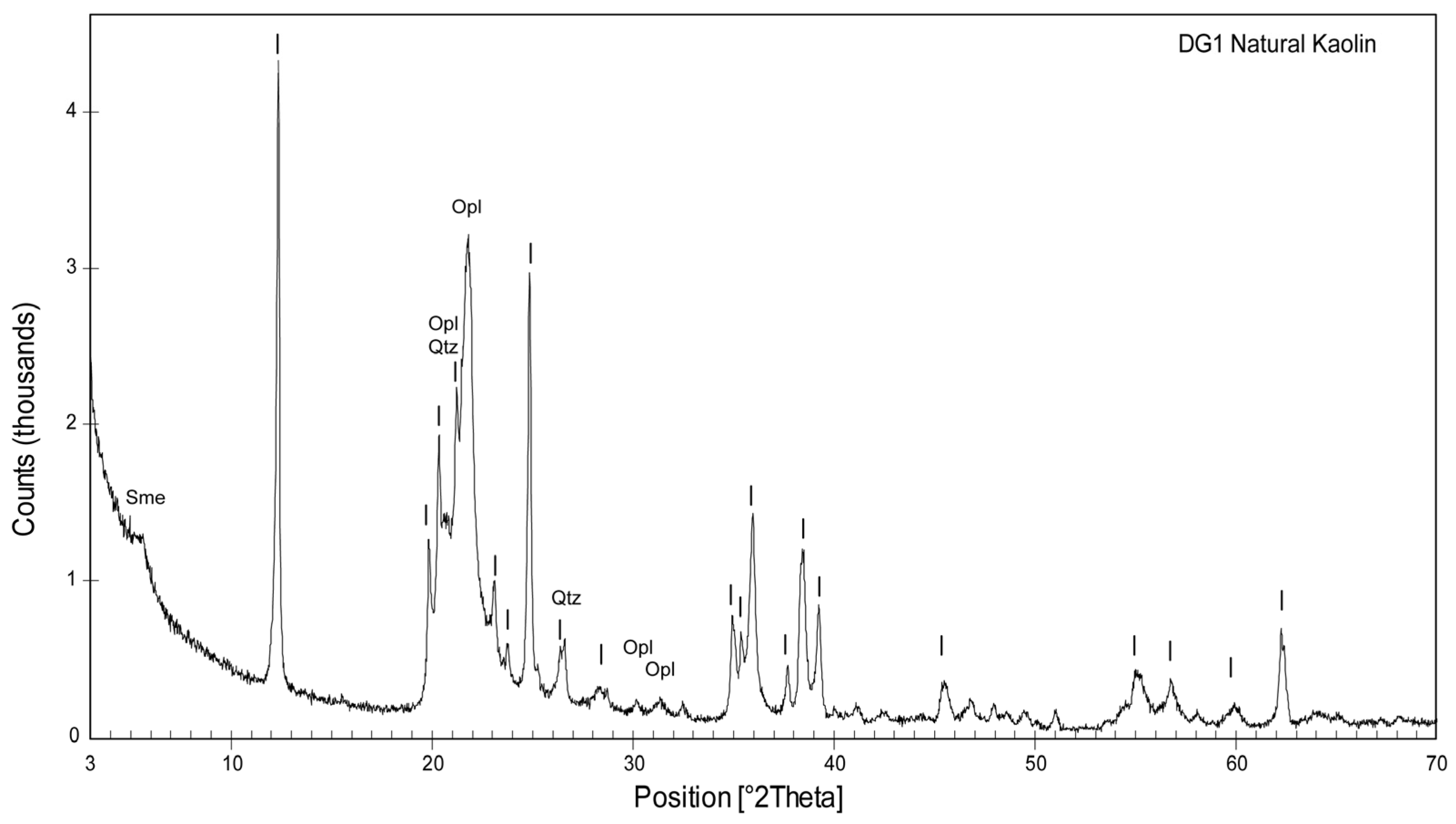
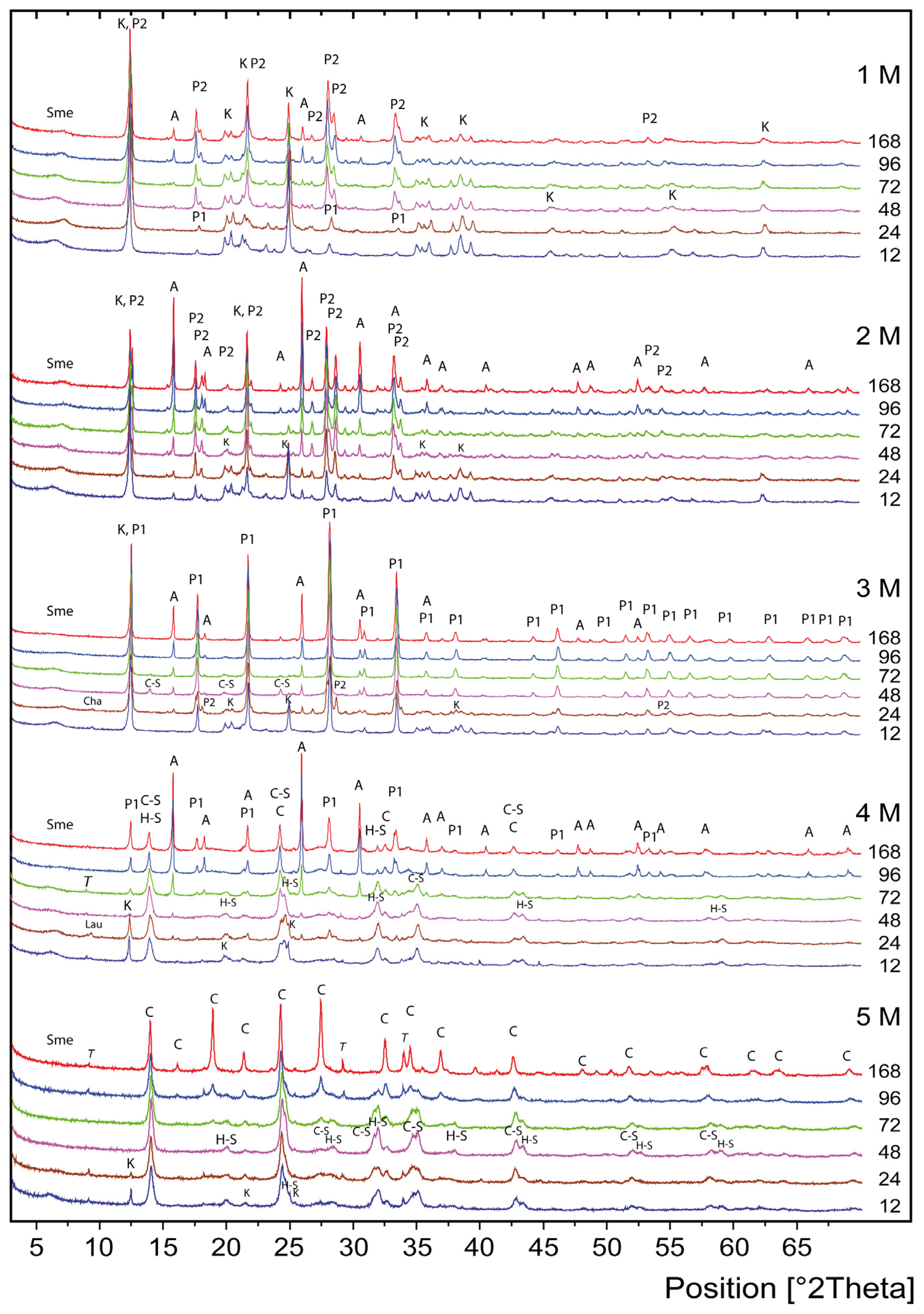

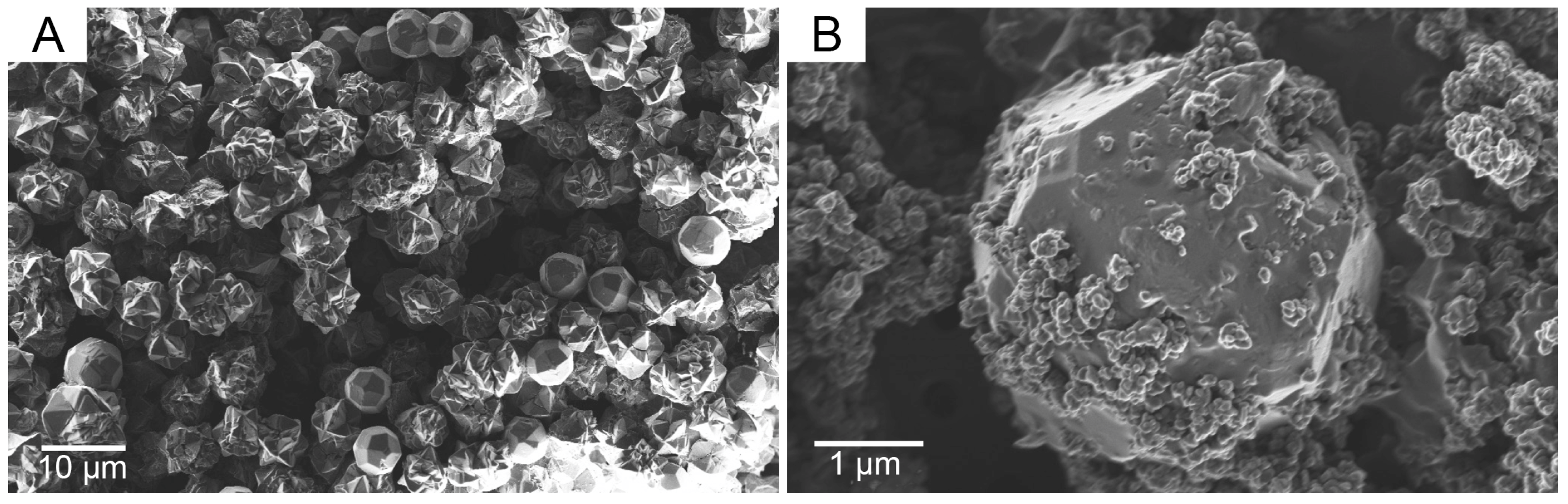
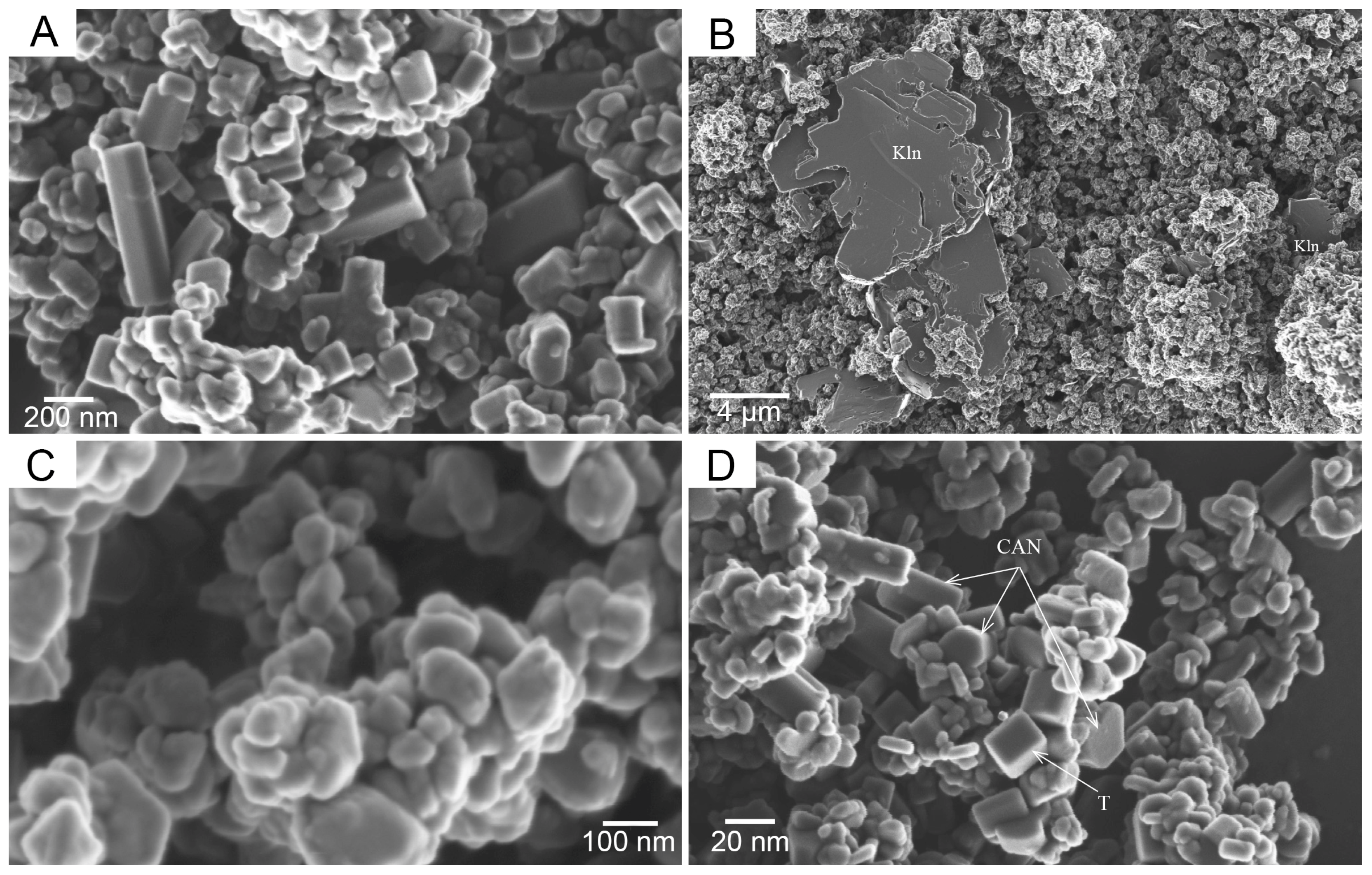
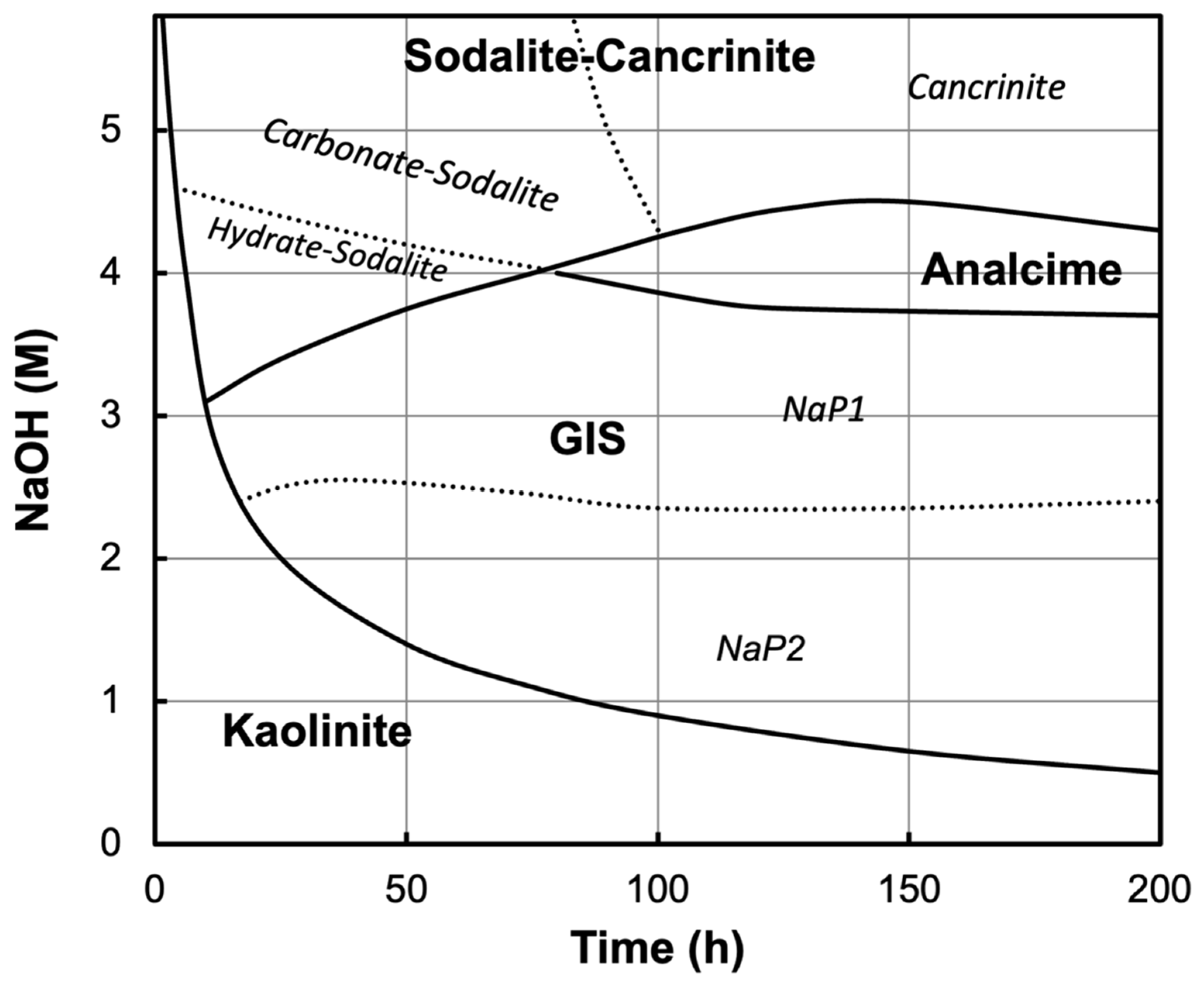
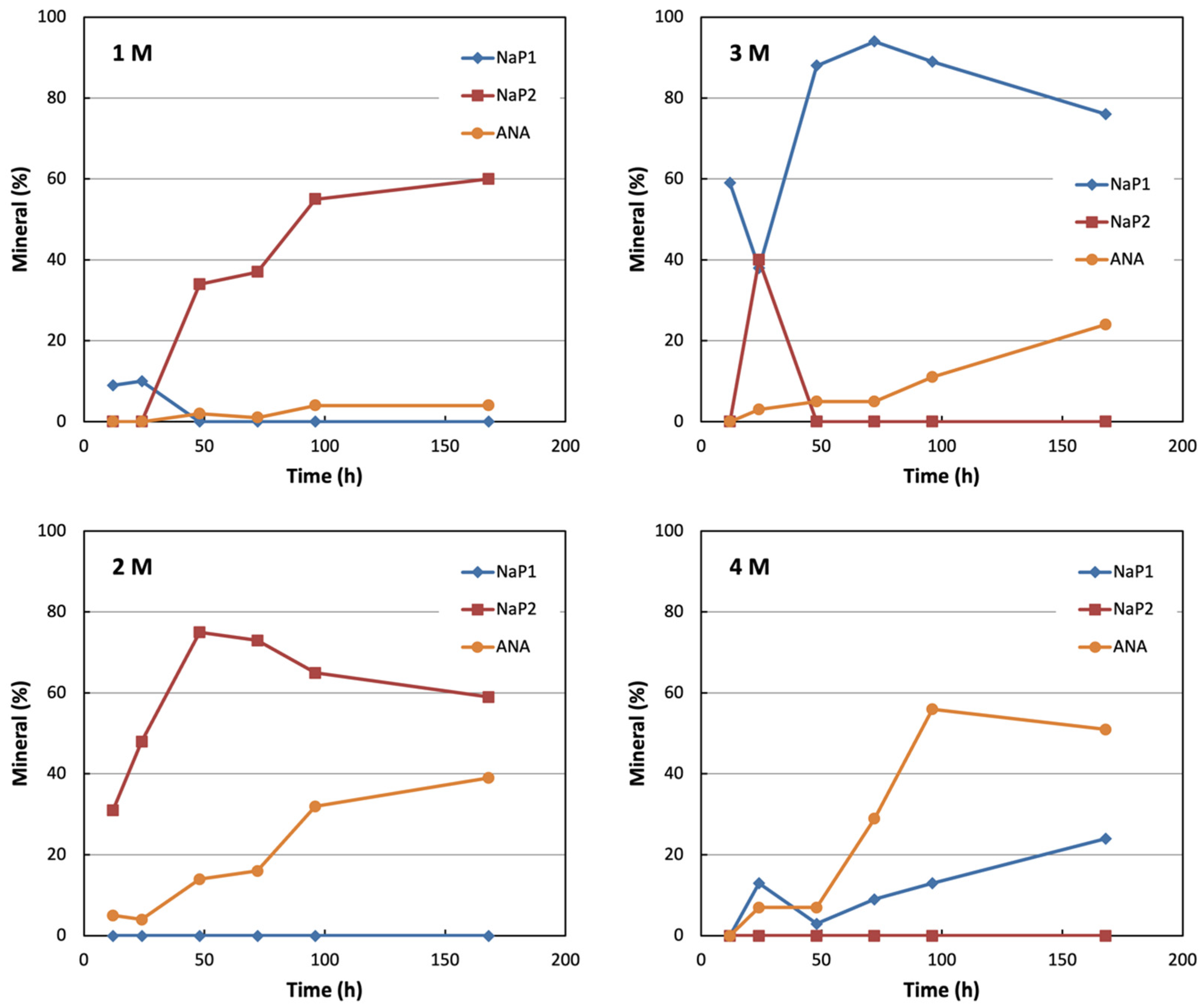
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | TiO2 | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | LOI 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65.22 | 23.86 | 0.27 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.11 | 10.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mameli, P.; Fiore, A.M.; Fiore, S.; Huertas, F.J. Mechanism of Hydrothermal Zeolite Crystallization from Kaolin in Concentrated NaOH Solutions (1–5 M): Formation of NaP1, NaP2, Analcime, Sodalite and Cancrinite. Crystals 2025, 15, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110980
Mameli P, Fiore AM, Fiore S, Huertas FJ. Mechanism of Hydrothermal Zeolite Crystallization from Kaolin in Concentrated NaOH Solutions (1–5 M): Formation of NaP1, NaP2, Analcime, Sodalite and Cancrinite. Crystals. 2025; 15(11):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110980
Chicago/Turabian StyleMameli, Paola, Ambra M. Fiore, Saverio Fiore, and F. Javier Huertas. 2025. "Mechanism of Hydrothermal Zeolite Crystallization from Kaolin in Concentrated NaOH Solutions (1–5 M): Formation of NaP1, NaP2, Analcime, Sodalite and Cancrinite" Crystals 15, no. 11: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110980
APA StyleMameli, P., Fiore, A. M., Fiore, S., & Huertas, F. J. (2025). Mechanism of Hydrothermal Zeolite Crystallization from Kaolin in Concentrated NaOH Solutions (1–5 M): Formation of NaP1, NaP2, Analcime, Sodalite and Cancrinite. Crystals, 15(11), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst15110980







