Accurate Seamless Vertical Handover Prediction Using Peephole LSTM Based on Light-GBM Algorithm in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Using a combination of the PLSTM and LGBM algorithms to provide more accurate predictions for VH decisions with less computational time complexity.
- (2)
- The proposed VH decision model is evaluated through a simulation scenario that mimics real network conditions, effectively demonstrating the model’s robustness, adaptability, and superior performance in ensuring seamless connectivity across heterogeneous wireless networks.
2. Related Works
3. Background
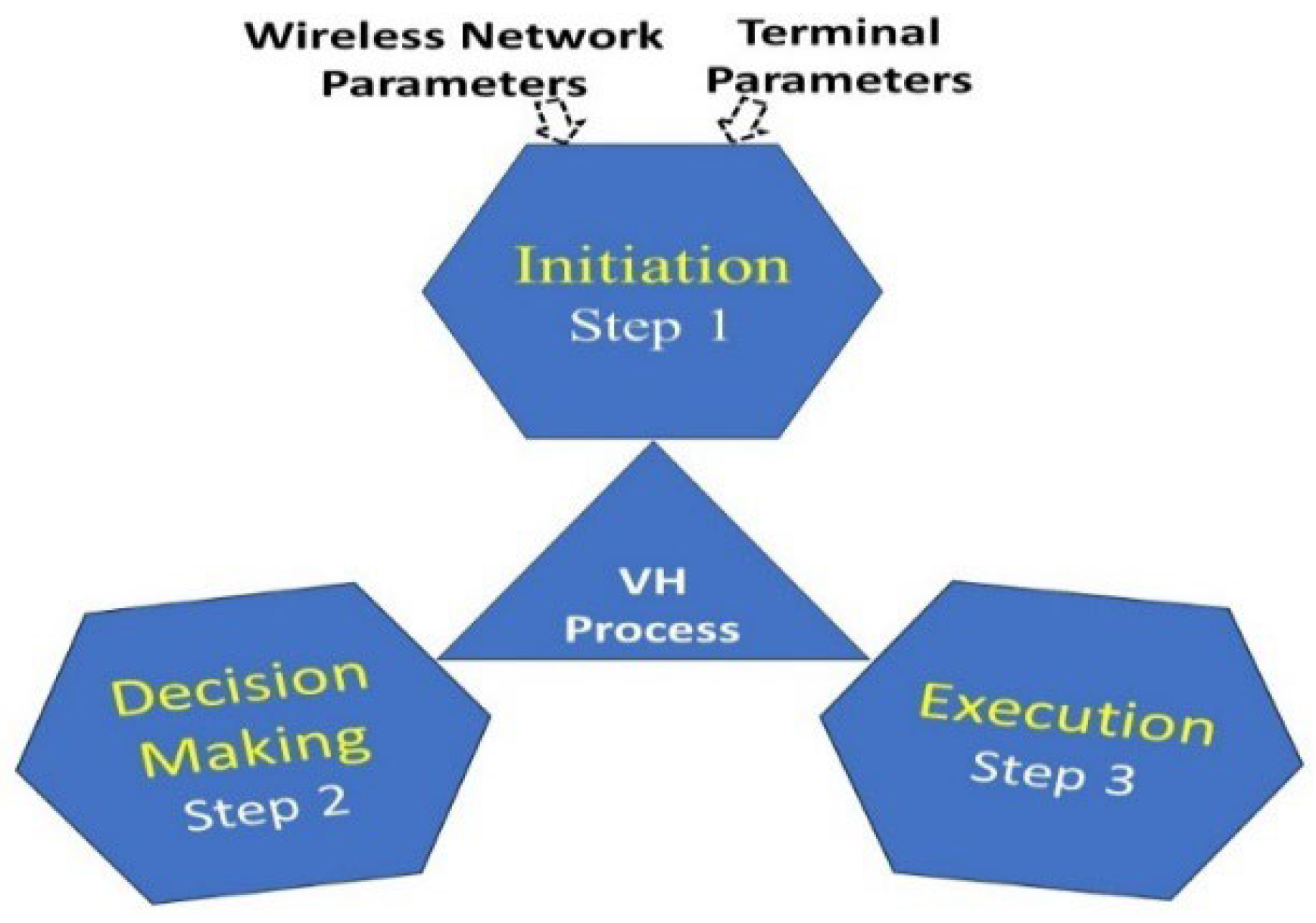
3.1. Vertical Handover Processes
3.2. Feature Selection Using the LGBM Algorithm
- Step 1: Initialize LGBM model parameters
- Step 2: Iterate to build decision trees to compute the gradients (1st order and 2nd order)
- Step 3: Find the best feature by calculating the right and left child nodes, then find the gain for split nodes.
- Step 4: Updating the importance feature to obtain the best feature.
- Step 5: Adding the recently trained tree to the model.
- Step 6: Choosing features and considering their importance based on thresholding or ranking.
- Step 7: Return the chosen features and their importance accordingly.
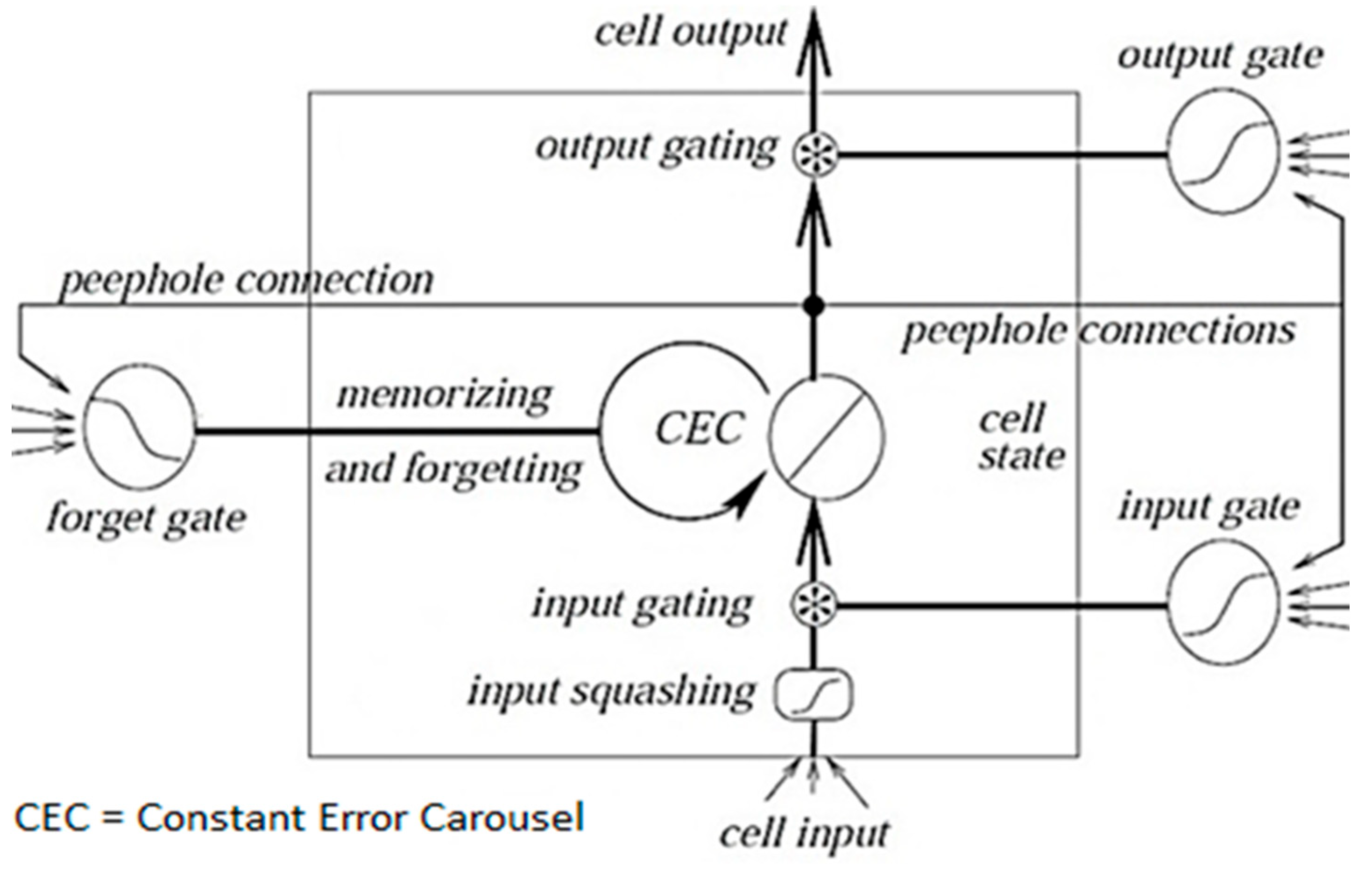
3.3. Peephole LSTM Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: (Peephole LSTM) [49] | |
| Input = network initialization: = , ; forward pass: current external input, , = ; B = no. of memory blocks; = no. of memory cells per block. | |
| Output = VH Occurrence | |
| 1: | For j = 1 to B |
| 2: | { |
| 3: | Input gates calculations according to Equation (A1) |
| 4: | Forget gates calculations according to Equation (A2) |
| 5: | Cell states calculations using Equations (A3) and (A4) |
| 6: | Activation of output gate calculation according to Equation (A5) |
| 7: | For = 1 to |
| 8: | { |
| 9: | Cell output calculations according to Equation (A6) |
| 10: | Output unit calculations according to Equation (A7) |
| 11: | Partial derivatives for input and forget gates using Equations (8) and (9) |
| 12: | } //end loop of cells |
| 13: | } //end loop of memory blocks |
| 14: | End |
4. Dataset Description
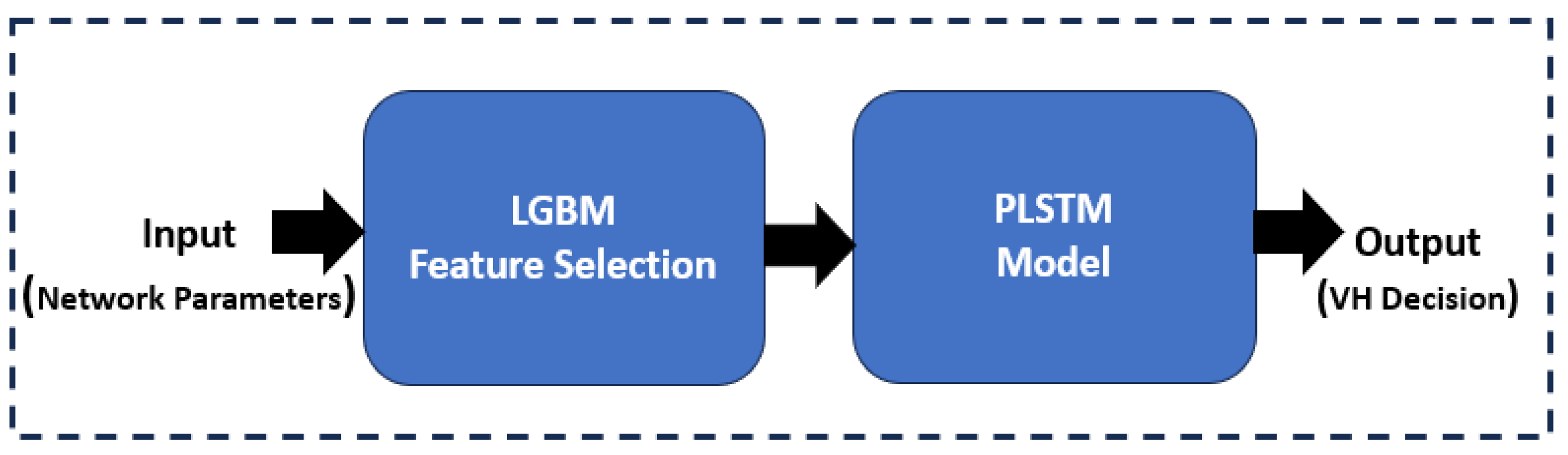
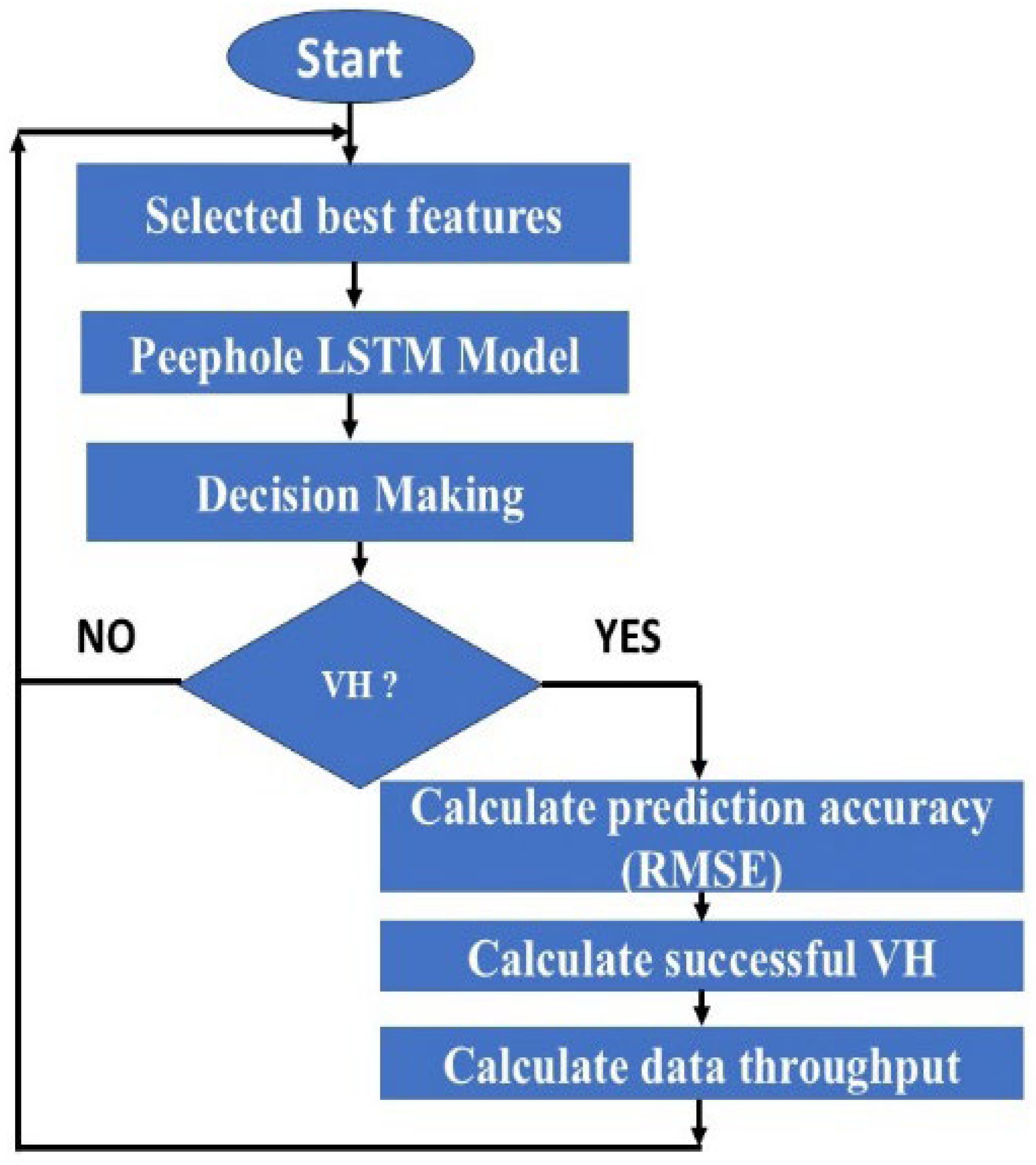
5. The Proposed VH Prediction Using Plstm and Lgbm Algorithms
| Algorithm 2: RSS-based VH. | |
| Input = network initialization: , , . | |
| Output = Decision [Trigger_VH, No_VH] | |
| 1: | //Calculate time difference |
| 2: | If ) |
| 3: | Return No_VH |
| 4: | Else |
| 5: | Calculate dwell time ()//Equation (6) |
| 6: | If ( ) //Check RSS condition |
| 7: | If ( ,) |
| 8: | Return Trigger_VH |
| 9: | Else |
| 10: | Return No_VH |
| 11: | Else |
| 12: | Return No_VH |
| 13: | End |
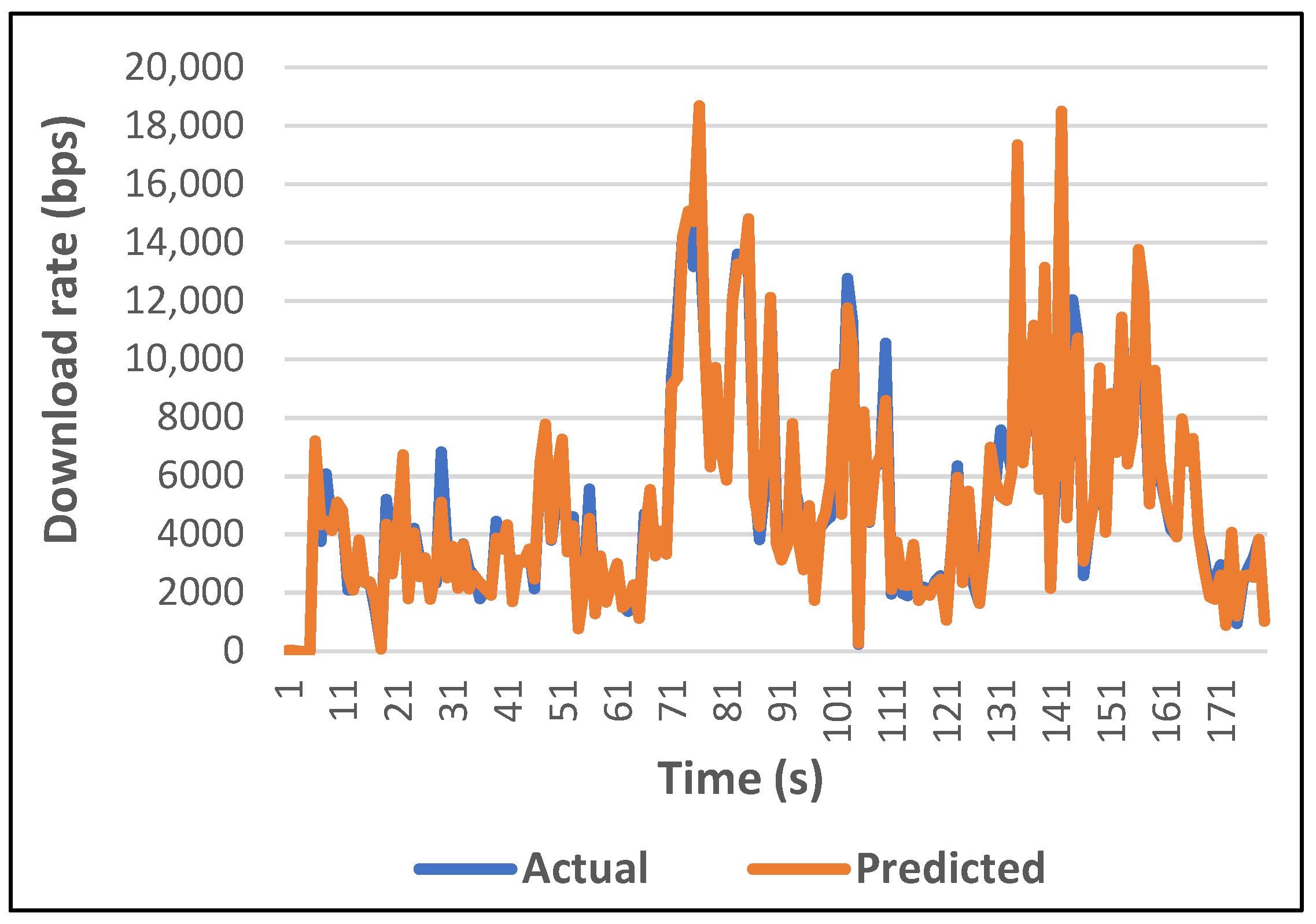
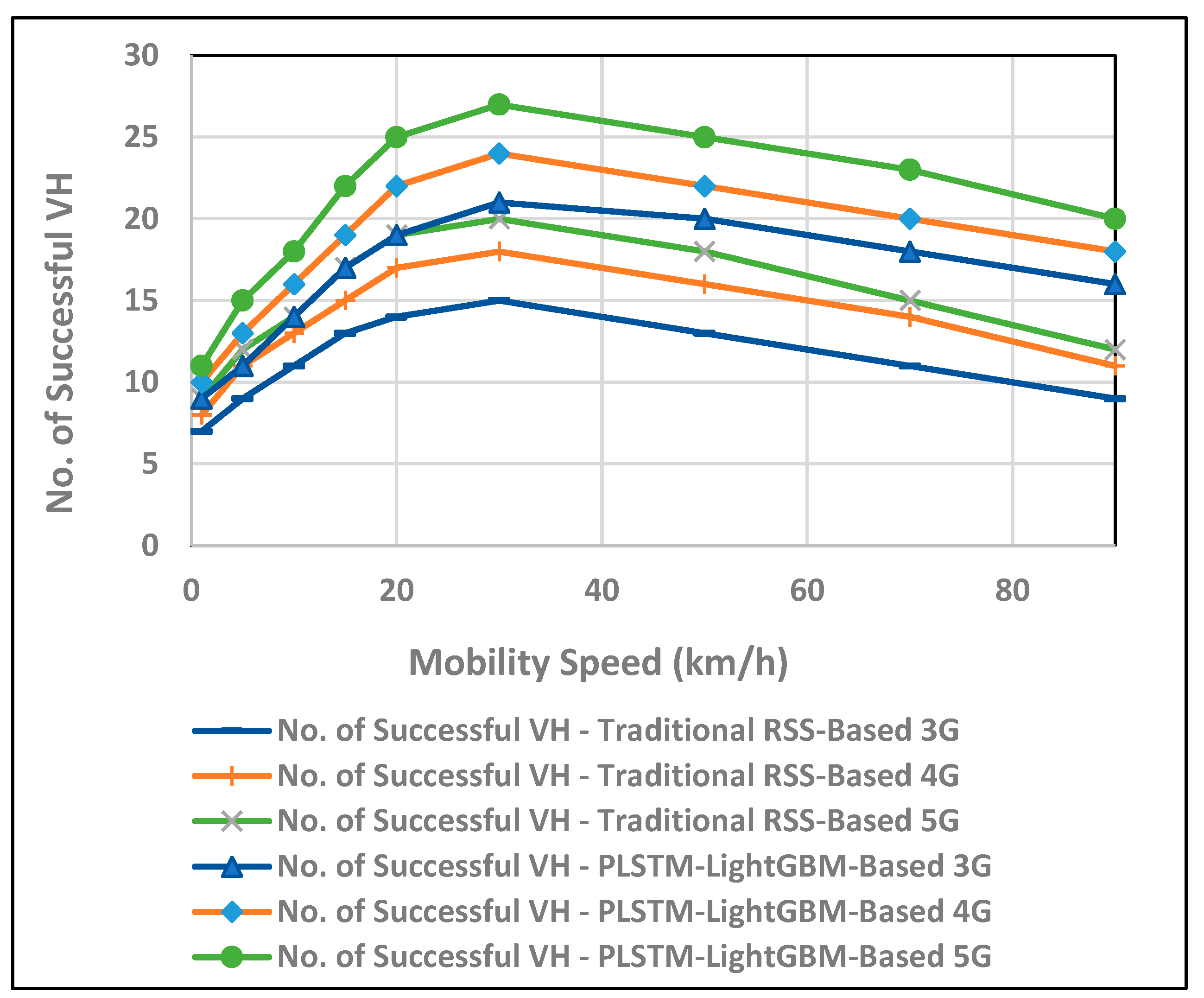
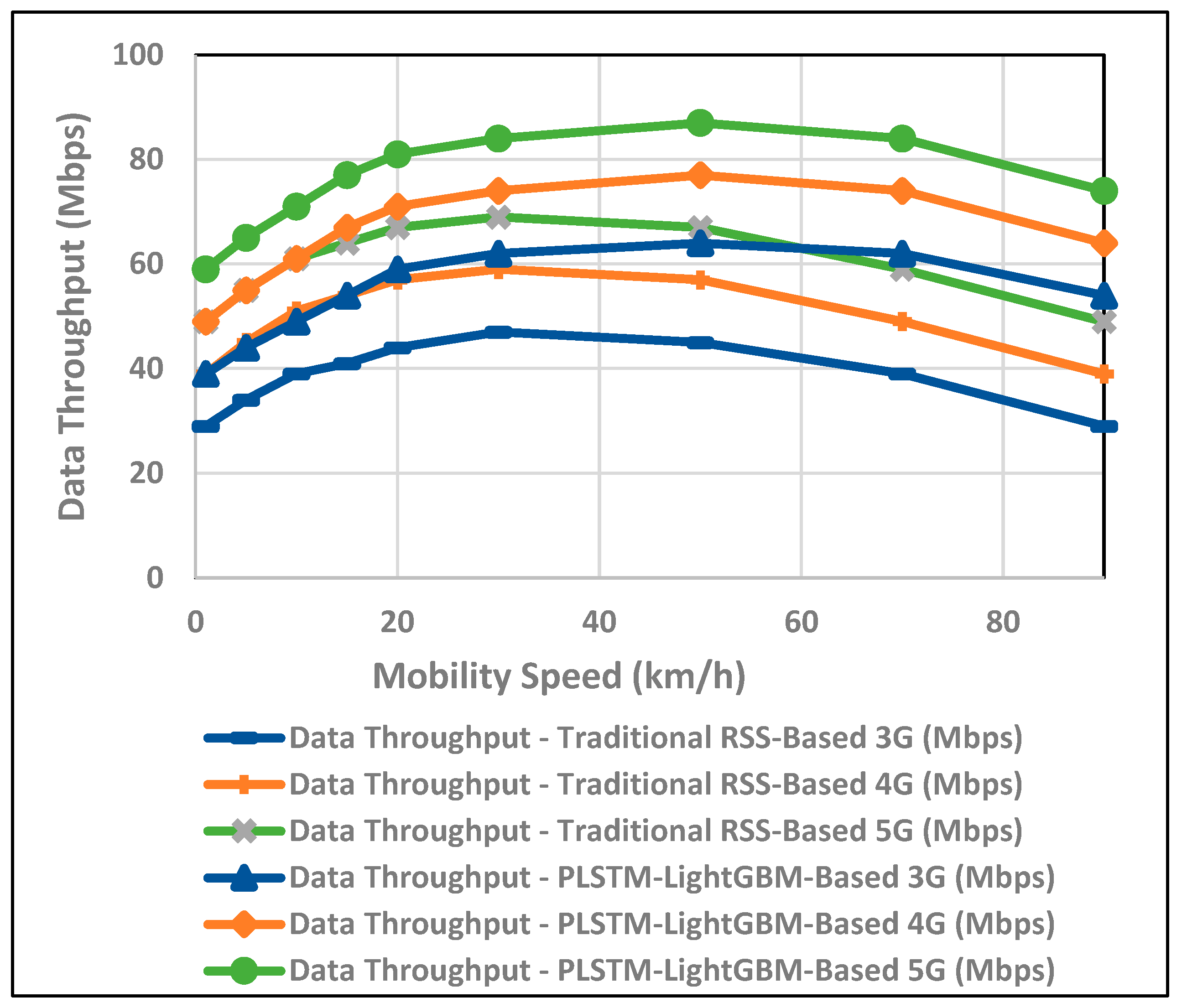
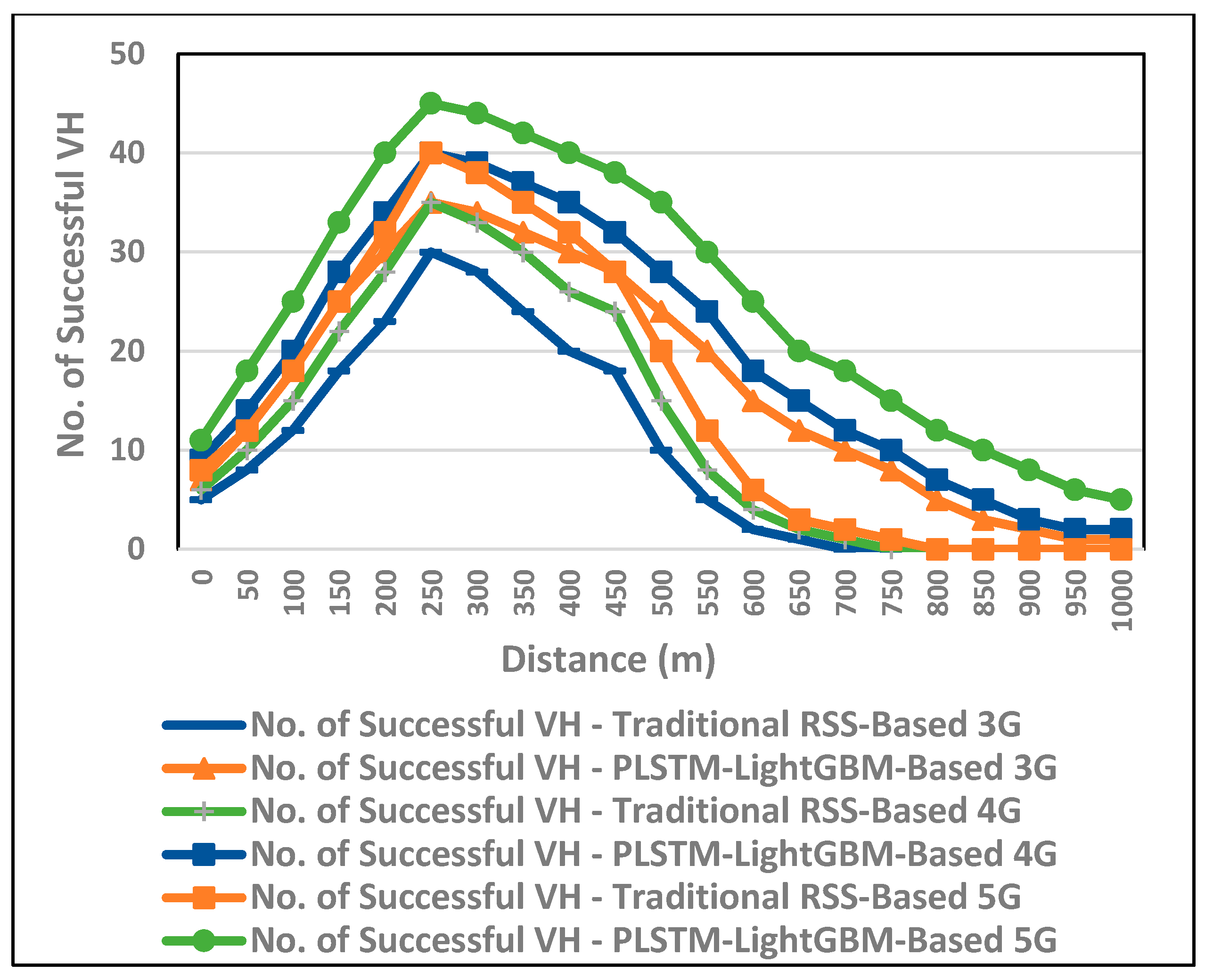
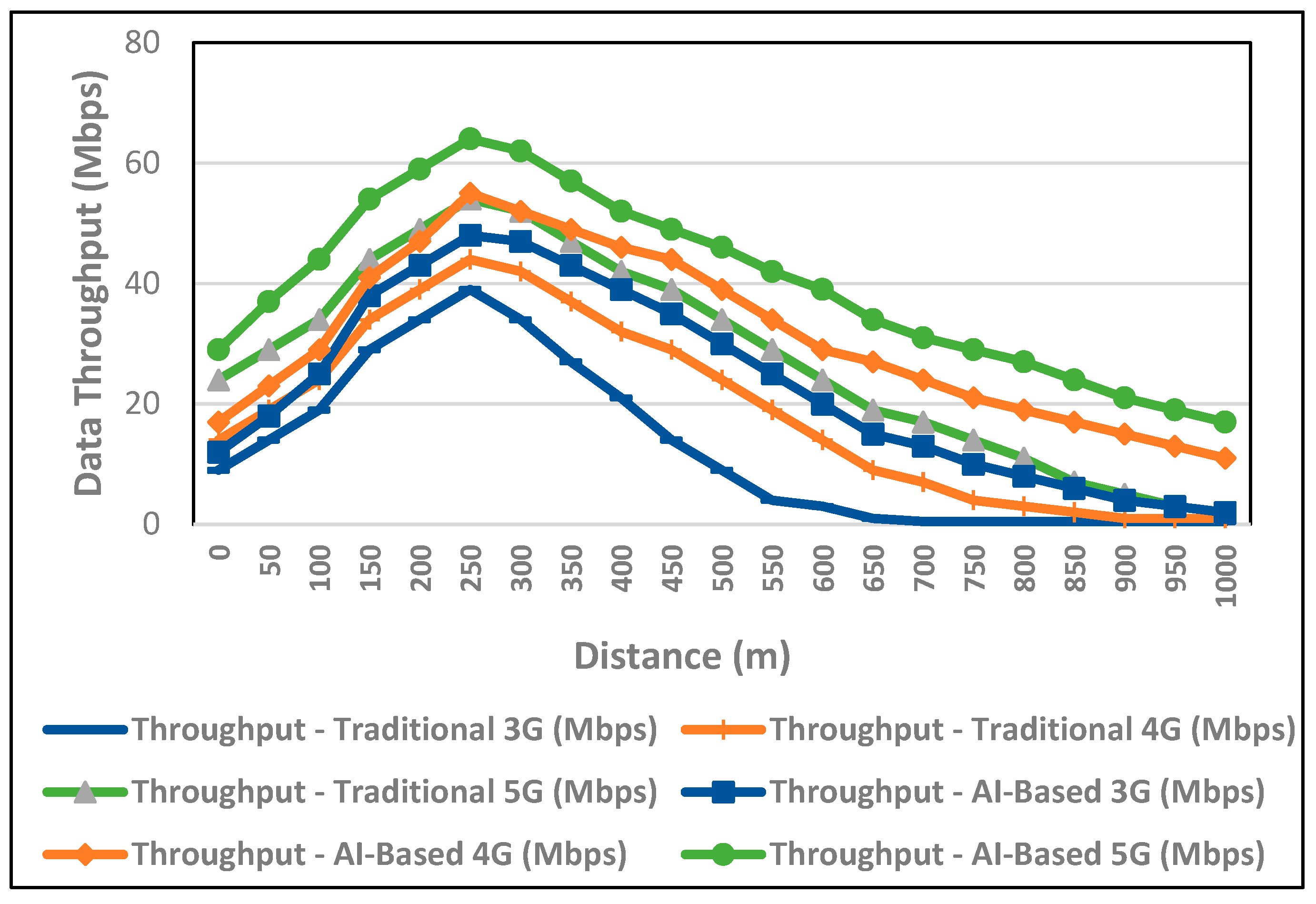
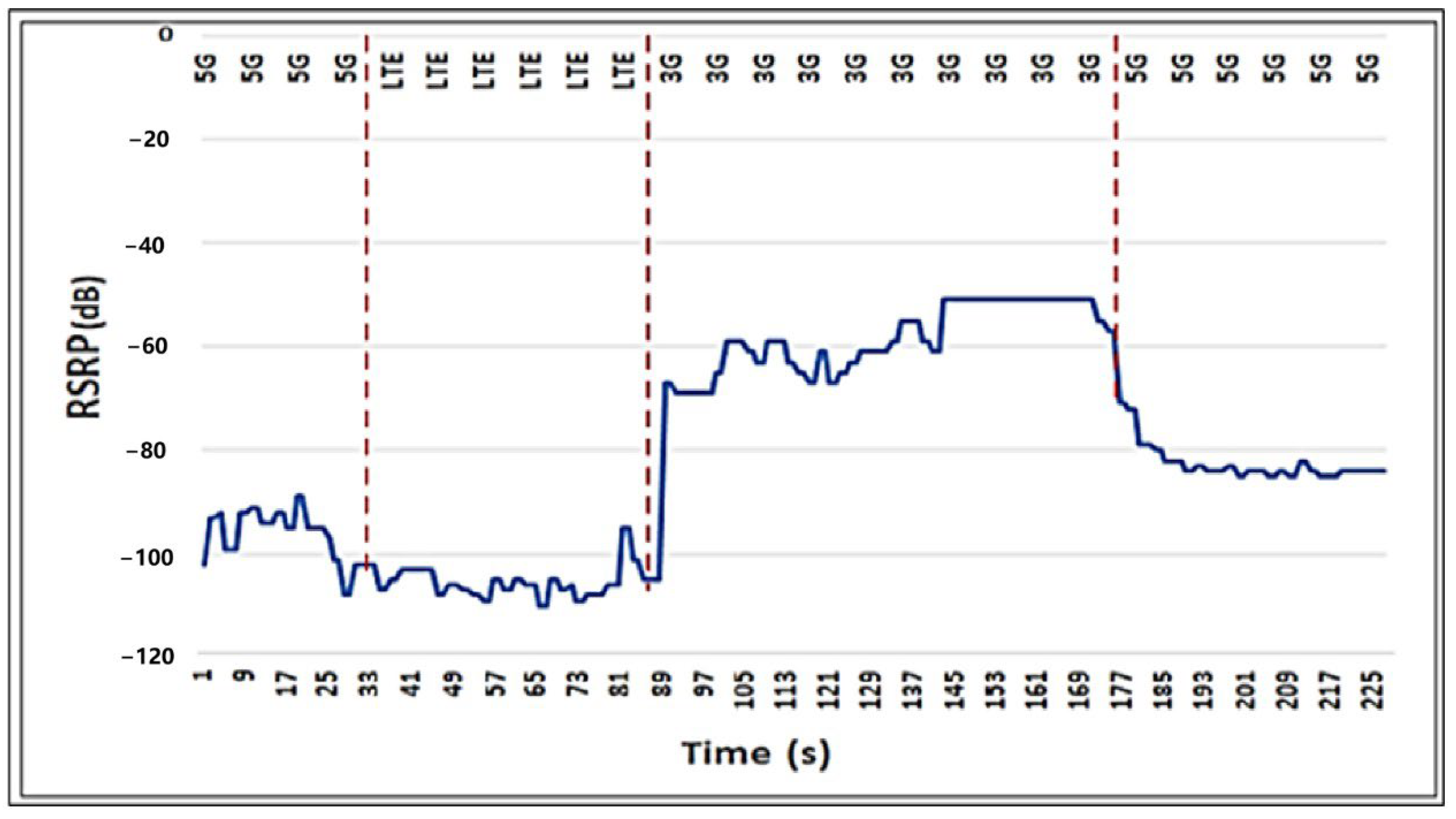
6. Performance Evaluation and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| Activation of the input gate | |
| Squashing function of the logistic sigmoid | |
| The net input of the gate, | |
| The logistic sigmoid function | |
| Memory cells in the block | |
| The cell state | |
| The cell output | |
| The activation of the output gate | |
| Total units that feed the output units | |
| Squashing function for the output |
References
- Gzar, D.A.; Mahmood, A.M.; Al-Adilee, M.K.A. Recent trends of smart agricultural systems based on Internet of Things technology: A survey. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 104, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O.Y.K. The impact of base station antennas configuration on the performance of millimetre wave 5G networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Ninth International Conference on Ubiquitous and Future Networks (ICUFN), Milan, Italy, 4–7 July 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2017; pp. 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albonda, H.D. Distributed Reinforcement Learning-based Seamless Multi-Connectivity Solution for Heterogeneous 5GNR and Wi-Fi Networks. Int. J. Intell. Eng. Syst. 2024, 17, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.A.; Jamshed, M.A.; Nauman, A.; Iqbal, A.; Shakeel, A.; Hussain, R. Performance evaluation of handover triggering condition estimation using mobility models in heterogeneous mobile networks. IET Netw. 2024, 13, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.R.; Mahmood, A.M.; Al-Falahy, N. Performance Evaluation of IPTV Zapping Time Reduction Using Edge Processing of Fog RAN. Math. Model. Eng. Probl. 2022, 9, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, K.M.; Khashaba, M.M.; Khedr, W.I.; Amer, F.A. New vertical handover prediction schemes for LTE-WLAN heterogeneous networks. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, S.P.; Werner, S. Distributed Kalman filtering: Consensus, diffusion, and mixed. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Control Technology and Applications (CCTA), Copenhagen, Denmark, 21–24 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2018; pp. 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchi, M.M.; Motameni, H. Evaluation of the improved particle swarm optimization algorithm efficiency inward peer to peer video streaming. Comput. Netw. 2018, 142, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhao, J.; Qu, H. A user mobility pattern based vertical handoff decision algorithm in cellular-WLAN integrated networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC), Chengdu, China, 14–17 October 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2016; pp. 1550–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, A.; Jeyakumar, A.; Pareek, N. Comparison between vertical handoff algorithms for heterogeneous wireless networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Melmaruvathur, India, 6–8 April 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2016; pp. 1370–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.S.; Budakoti, J.; Lung, C.H. Vertical handover decision for mobile IoT edge gateway using multi-criteria and fuzzy logic techniques. Adv. Internet Things 2020, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.B.; Patil, R. A network controlled vertical handoff mechanism for heterogeneous wireless network using optimized support vector neural network. Int. J. Pervasive Comput. Commun. 2023, 19, 23–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilakazi, M.; Olwal, T.O.; Mfupe, L.P.; Lysko, A.A. Vertical handover algorithm in OpenAirInterface and neural network for 4G and 5G base stations. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Information Networking (ICOIN), Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 17–19 January 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2024; pp. 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Chen, G.; Sun, H. Vertical handover algorithm based on multi-attribute and neural network in heterogeneous integrated network. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2020, 2020, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, O.; Semenov, A.; Voitsekhovska, O. Neuro-fuzzy controller for handover operation in 5G heterogeneous networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International Conference on Advanced Information and Communications Technologies (AICT), Lviv, Ukraine, 2–6 July 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2019; pp. 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, K.; Rao, D.R. Analytical review and study on various vertical handover management technologies in 5G heterogeneous network. Infocommun. J. 2022, 14, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Başaran, M.; Durak-Ata, L. Handover-enabled dynamic computation offloading for vehicular edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 9394–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaabi, S.R.; Gregory, M.A.; Li, S. Multi-access edge computing handover strategies, management, and challenges: A review. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 4660–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, M.I.; Mbulwa, A.I.; Yew, H.T.; Kiring, A.; Chung, S.K.; Farzamnia, A.; Chekima, A.; Haldar, M.K. Handover decision-making algorithm for 5G heterogeneous networks. Electronics 2023, 12, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.M.; Al-Yasiri, A.; Alani, O.Y. A new processing approach for reducing computational complexity in cloud-RAN mobile networks. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 6927–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, T.M.; Kwon, S. Vertical handover analysis for randomly deployed small cells in heterogeneous networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Liang, B. Stochastic geometric analysis of user mobility in heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 2212–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.U.; Roslee, M.B.; Jun Jiat, T. A survey of handover management in mobile HetNets: Current challenges and future directions. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Parthiban, R.; Karmakar, N. An artificial neural network-based handover scheme for hybrid lifi networks. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 130350–130358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Bazán, J.V.; Cuevas-Rasgado, A.D.; Rojas-Cárdenas, L.M.; Lazcano-Salas, S.; García-Lamont, F.; Soriano, L.A.; Rubio, J.d.J.; Pacheco, J. Proactive cross-layer framework based on classification techniques for handover decision on WLAN environments. Electronics 2022, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höchst, J.; Sterz, A.; Frömmgen, A.; Stohr, D.; Steinmetz, R.; Freisleben, B. Learning Wi-Fi connection loss predictions for seamless vertical handovers using multipath TCP. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 44th Conference on Local Computer Networks (LCN), Osnabrueck, Germany, 14–17 October 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2019; pp. 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paropkari, R.A.; Thantharate, A.; Beard, C. Deep-mobility: A deep learning approach for an efficient and reliable 5g handover. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Wireless Communications Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 24–26 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2022; pp. 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, P.; Seet, B.C. Multi-Tier Cellular Handover with Multi-Access Edge Computing and Deep Learning. Telecom 2021, 2, 446–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapadia, P. 5G Multi-Tier Handover with Multi-Access Edge Computing: A Deep Learning Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Hui, P.S.; Sun, C. Deep Learning Based Handover for High-Speed Connected Vehicles in Ultra-Dense Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference (VNC), Kobe, Japan, 29–31 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2024; pp. 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.N.; Takizawa, K. Deep Learning-Based Proactive Physical Layer Handover using Cameras for Indoor Environment. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 21st Consumer Communications & Networking Conference (CCNC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 6–9 January 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2024; pp. 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikci, S.; Unnisa, N.; Das, A.; Kanna, S.R.; Murthy, M.Y.B.; Preetha, N.N.; Brammya, G. Deep learning with game theory assisted vertical handover optimization in a heterogeneous network. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2023, 32, 2350012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollel, M.S.; Abubakar, A.I.; Ozturk, M.; Kaijage, S.; Kisangiri, M.; Zoha, A.; Imran, M.A.; Abbasi, Q.H. Intelligent handover decision scheme using double deep reinforcement learning. Phys. Commun. 2020, 42, 101133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, D.; Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z. Deep reinforcement learning-based adaptive handover mechanism for VLC in a hybrid 6G network architecture. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 87241–87250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoder, R.; Naja, R.; Ismail, S.; Mouawad, N.; Tohme, S. Vertical Handover Decision using Machine Learning in Vehicular Platooning. In Proceedings of the 2021 3rd IEEE Middle East and North Africa COMMunications Conference (MENACOMM), Agadir, Morocco, 3–5 December 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2021; pp. 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitnala, V.N.; Reed, M.J.; Kegel, I.; Bicknell, J. Avoiding handover interruptions in pervasive communication applications through machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference and Expo on Real Time Communications at IIT (RTC), Chicago, IL, USA, 12–14 October 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2021; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, A.; Gauthamarayathirumal, P.; Chandrasekar, C. Machine learning algorithms in proactive decision making for handover management from 5G & beyond 5G. Egypt. Inform. J. 2023, 24, 100389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, T.; Rodosek, G.D. Machine Learning Based Predictive Handover in Unmanned Aerial Systems Communication. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/AIAA 42nd Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), Barcelona, Spain, 1–5 October 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; Hossain, M.S.; Atiquzzaman, M. A testbed implementation of hybrid decision model based seamless lightweight vertical handover. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rubaye, A. Vertical Handover Management with Quality of Service Support. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Ilmenau, Ilmenau, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Khattab, O.; Alani, O. I am 4 vho: New approach to improve seamless vertical hanover in heterogeneous wireless networks. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1306.1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Meng, Q.; Finley, T.; Wang, T.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Ye, Q.; Liu, T.Y. LGBM: A highly efficient gradient boosting decision tree. Advances in neural information processing systems. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, B.B.; Ahsan, M.; Dhanalakshmi, R. LGBM empowered by whale optimization for thyroid disease detection. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023, 15, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X. The role of LGBM model in management efficiency enhancement of listed agricultural companies. Appl. Math. Nonlinear Sci. 2023, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, C.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, H. LGBM: An efficient and accurate method for predicting pregnancy diseases. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2022, 42, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florek, P.; Zagdański, A. Benchmarking state-of-the-art gradient boosting algorithms for classification. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.17094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldini, D.; Grisoni, F.; Kuhn, D.; Friedrich, L.; Sieber, S.A. Practical guidelines for the use of gradient boosting for molecular property prediction. J. Cheminformatics 2023, 15, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essai Ali, M.H.; Abdellah, A.R.; Atallah, H.A.; Ahmed, G.S.; Muthanna, A.; Koucheryavy, A. Deep learning peephole LSTM neural network-based channel state estimators for OFDM 5G and beyond networks. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gers, F.A.; Schraudolph, N.N.; Schmidhuber, J. Learning precise timing with LSTM recurrent networks. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2002, 3, 115–143. [Google Scholar]
- Greff, K.; Srivastava, R.K.; Koutník, J.; Steunebrink, B.R.; Schmidhuber, J. LSTM: A search space odyssey. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 28, 2222–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Liang, Y.; Cong, M.; Yao, N.; Wang, K. Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on LSTM with Peephole for PEMFC. SAE Tech. Paper 2022, 2022-01-7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raca, D.; Leahy, D.; Sreenan, C.J.; Quinlan, J.J. Beyond throughput, the next generation: A 5G dataset with channel and context metrics. In Proceedings of the 11th ACM Multimedia Systems Conference, Istanbul, Turkey, 8–11 June 2020; pp. 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yew, H.T.; Chekima, A.; Kiring, A.; Mbulwa, A.I.; Dargham, J.A.; Chung, S.K. RSS based vertical handover schemes in heterogeneous wireless networks: Past, present & future. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Engineering and Technology (IICAIET), Kota Kinabalu, Malaysia, 26–27 September 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NI, USA, 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Gavali, V.S.; Patil, J.K. A study of RSS based vertical handover decision algorithms. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2015, 4, 825–827. [Google Scholar]
- Nasser, A.R.; Alani, O.Y. Investigation of Multiple Hybrid Deep Learning Models for Accurate and Optimized Network Slicing. Computers 2025, 14, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, G. Accurate confidence intervals for proportion in studies with clustered binary outcome. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 2020, 29, 3006–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Feature | GBM | XGBoost | LGBM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed of evaluation | Relatively slow | Slower than LGBM | Very fast due to the use of histogram splitting |
| Accuracy of feature ranking | Medium to low | High | High, especially for large data |
| Flexibility in handling redundant features | Weak | Good | Very good |
| Support for missing values | Does not automatically support | Good | Excellent |
| Custom scoring control | Limited | Flexible | Flexible |
| Stability across folds | Unstable | Good | Stable with imbalanced data |
| Best suited for feature selection in big data | Not suitable | Very good | Best |
| Feature | LSTM | Peephole LSTM |
|---|---|---|
| Structure of Gates | Input Gate, Forget Gate, Output Gate | Input Gate, Forget Gate, Output Gate with peephole connections |
| Connections of Peephole | No peephole connections | Peephole connections allow gates to access the current cell state directly |
| Interaction of cell state | Gates do not directly access the cell state | Gates have direct access to the cell state, enhancing feedback |
| Computation Complexity | Less complex with fewer parameters | Slightly more complex due to additional parameters introduced by peephole connections |
| Uses | General sequence prediction tasks (NLP, time series) | Useful in tasks requiring precise timing and control (e.g., speech recognition) |
| Performance | Effective for most tasks with long-term dependencies | Can potentially improve performance where finer control over gates is beneficial |
| No. | Feature | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Longitude | Mobile device’s GPS coordinates |
| 2 | Latitude | Mobile device’s GPS coordinates |
| 3 | Speed | The Mobility speed of a mobile device |
| 4 | Cell-Id | Serving as a mobile device’s cell |
| 5 | UL_bitrate | Uplink bitrate (UL_bitrate) the device’s (application layer) measurement of the uplink rate |
| 6 | State | The state in which the download is happening. It can have one of two values: D (downloading) or I (idle). |
| 7 | ServingCell_Distance | Distance to the serving cell |
| 8 | SNR | The Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) value |
| 9 | RSRQ | Reference Signal Received Quality (RSRQ) represents a ratio between RSRP and Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). |
| 10 | RSRP (Reference Signal Received Power) | Value for RSRP. |
| 11 | RSSI | value for RSSI. |
| 12 | CQI | value for a mobile device’s Channel Quality Indicator (CQI). |
| 13 | NRxRSRQ | RSRQ and RSRP values for the neighboring cell, where NR denotes 5G New Radio. |
| 14 | NRxRSRP |
| Parameter | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Directions for data transmission | Downlink |
| Type of network | 3G, 4G, 5G |
| Bandwidth | 5 MHz, 20 MHz, 100 MHz |
| Frequency | 1.9 GHz, 2.3 GHz, 4.8 GHz |
| User mobility | 0–100 km/h |
| Type of areas | Urban |
| System specifications | Processor: 2.3 GHz Intel Core i7, 8 GB of DDR4 RAM, Framework: Python, 64-bit Windows 10 |
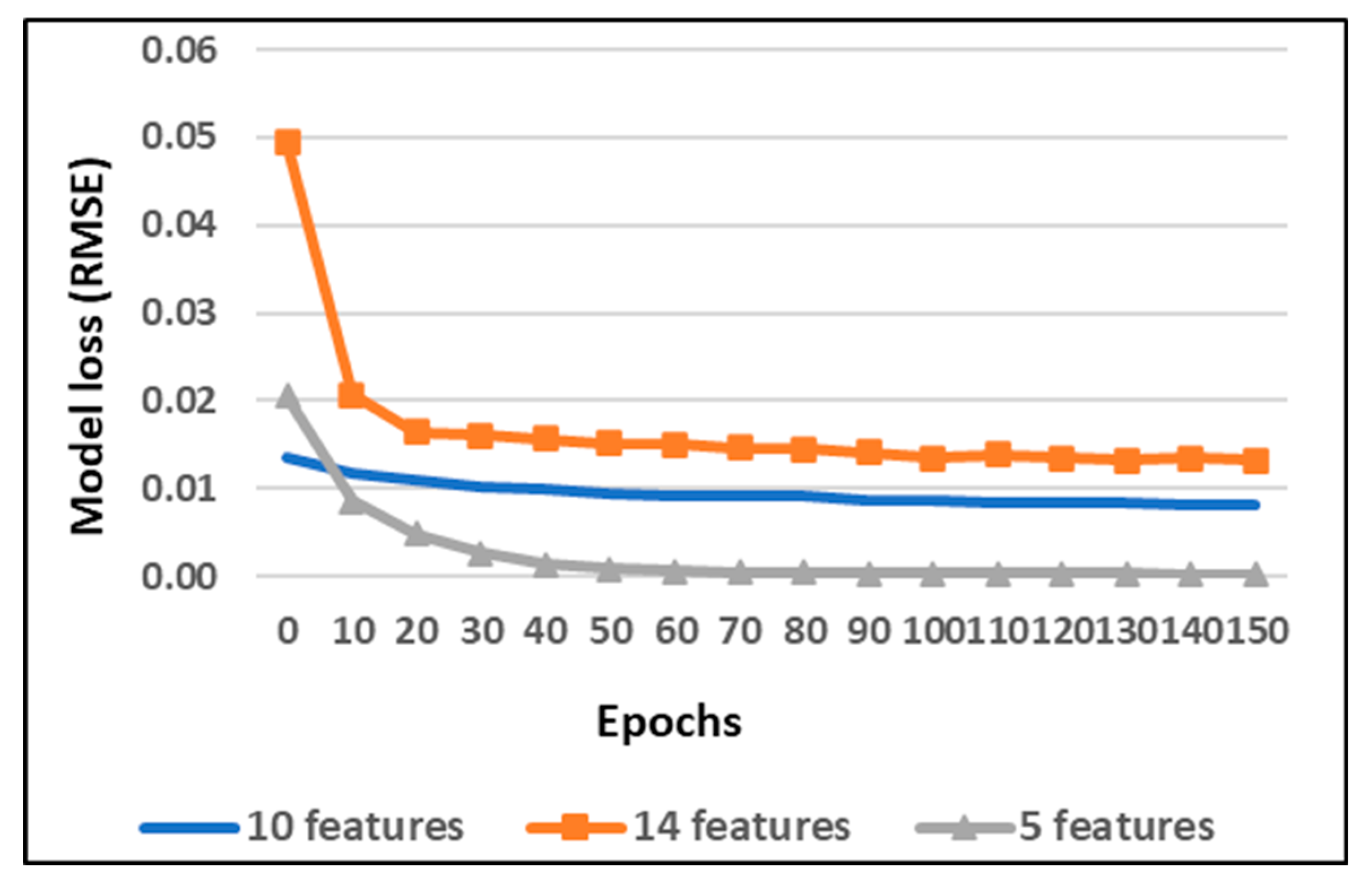
| Threshold | Number of Features |
|---|---|
| >250 | 5 |
| >150 | 10 |
| >0 | 14 |
| Hyperparameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of PLSTM Layers | 2 |
| Hidden Units | 64 |
| Dropout Rate | 0.2 |
| Sequence Length | 10 |
| Batch Size | 32 |
| Learning Rate | 0.001 |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Number of Epochs | 150 |
| Activation function | Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) |
| Loss function | RMSE |
| Features | RMSE | MAE | R2 | Confidence Interval (95%) | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 (ALL) | 9.86 | 8.37 | 0.76 | 8.87, 10.85 | 0.0032 |
| 10 | 8.47 | 7.4 | 0.82 | 7.62, 9.32 | 0.00001 |
| 5 | 5.54 | 4.69 | 0.91 | 4.99, 6.09 | 0.00001 |
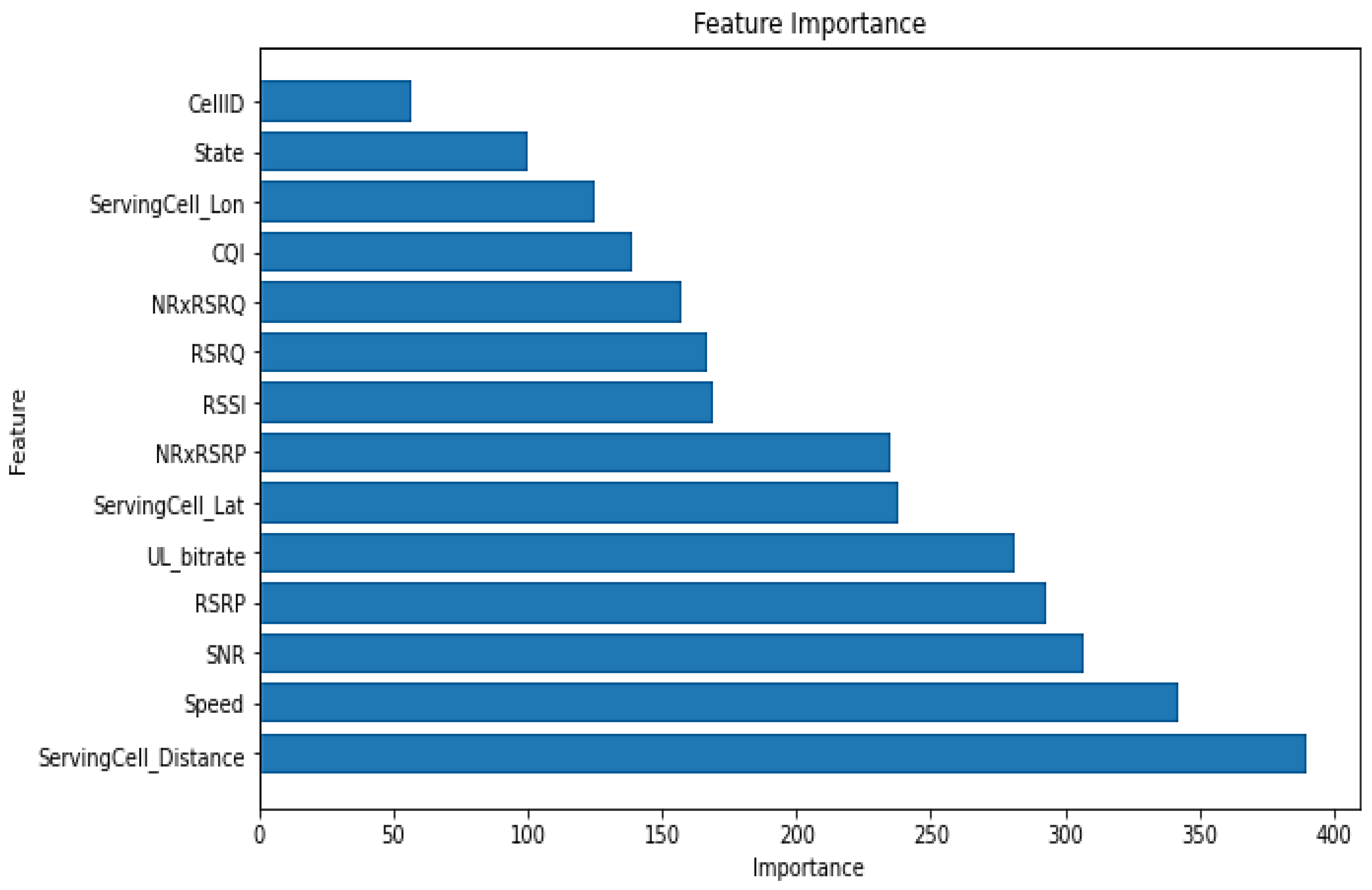
| No. | Feature | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ServingCell_Distance | 390 |
| 2 | Speed | 340 |
| 3 | SNR | 310 |
| 4 | RSRP | 290 |
| 5 | UL_bitrate | 280 |
| Method | No. Features | Decision Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|
| PLSTM | 14 | 37 |
| PLSTM-LGBM | 5 | 18 |
| BS-Location (m) | BS-Type | Coverage Range (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5G-BS1 | 300 |
| 300 | 4G-BS1 | 400 |
| 500 | 5G-BS2 | 300 |
| 700 | 4G-BS2 | 400 |
| 1000 | 3G-BS1 | 600 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmood, A.M.; Alani, O.Y. Accurate Seamless Vertical Handover Prediction Using Peephole LSTM Based on Light-GBM Algorithm in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks. Computers 2025, 14, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120522
Mahmood AM, Alani OY. Accurate Seamless Vertical Handover Prediction Using Peephole LSTM Based on Light-GBM Algorithm in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks. Computers. 2025; 14(12):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120522
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmood, Ali M., and Omar Younis Alani. 2025. "Accurate Seamless Vertical Handover Prediction Using Peephole LSTM Based on Light-GBM Algorithm in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks" Computers 14, no. 12: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120522
APA StyleMahmood, A. M., & Alani, O. Y. (2025). Accurate Seamless Vertical Handover Prediction Using Peephole LSTM Based on Light-GBM Algorithm in Heterogeneous Cellular Networks. Computers, 14(12), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14120522







