Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Is Primarily Caused by PSMα Peptides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Hla Is Important for Hemolysis of Sheep Erythrocytes but Not Human Erythrocytes
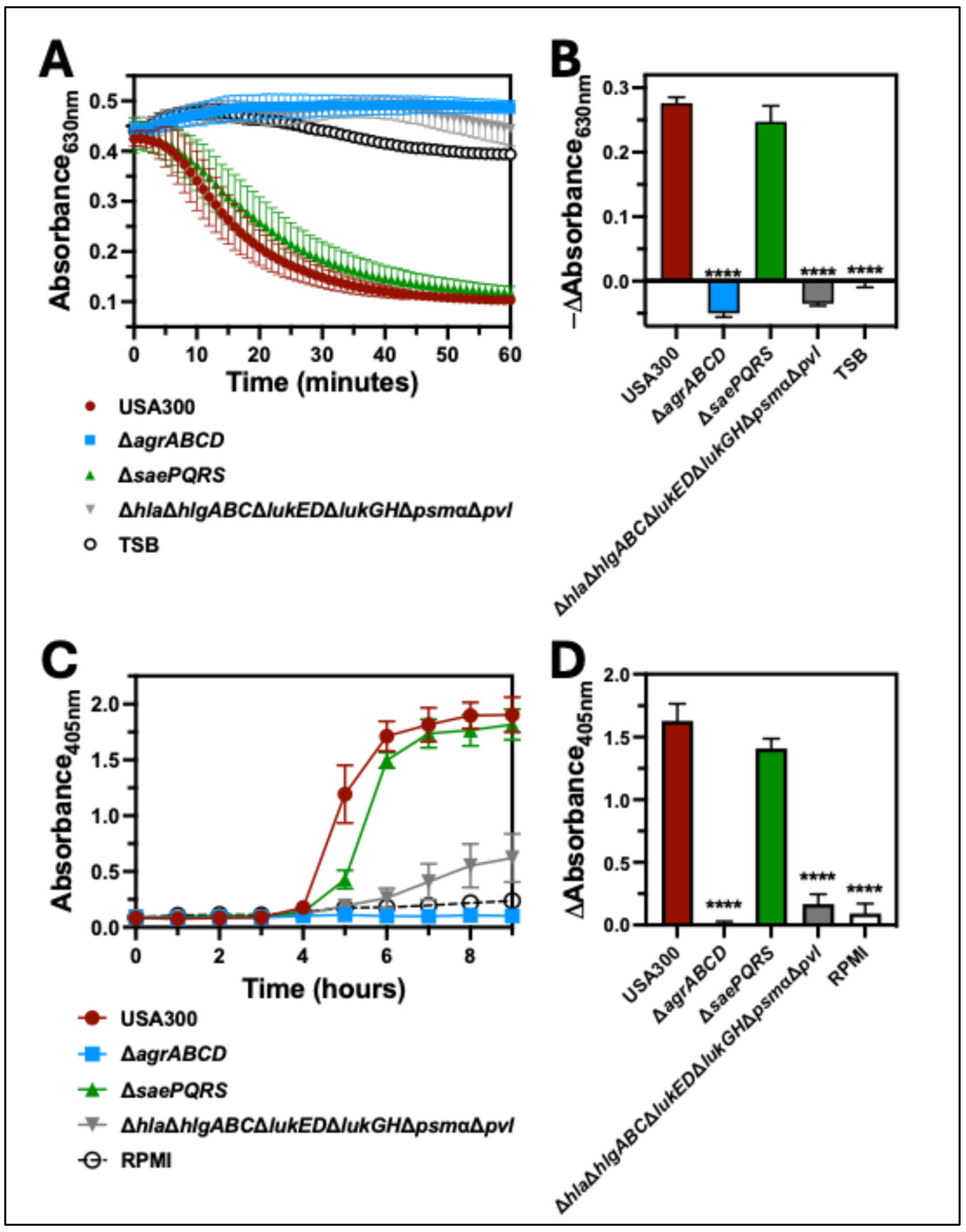
2.2. The Agr Two-Component System Is Required for Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes
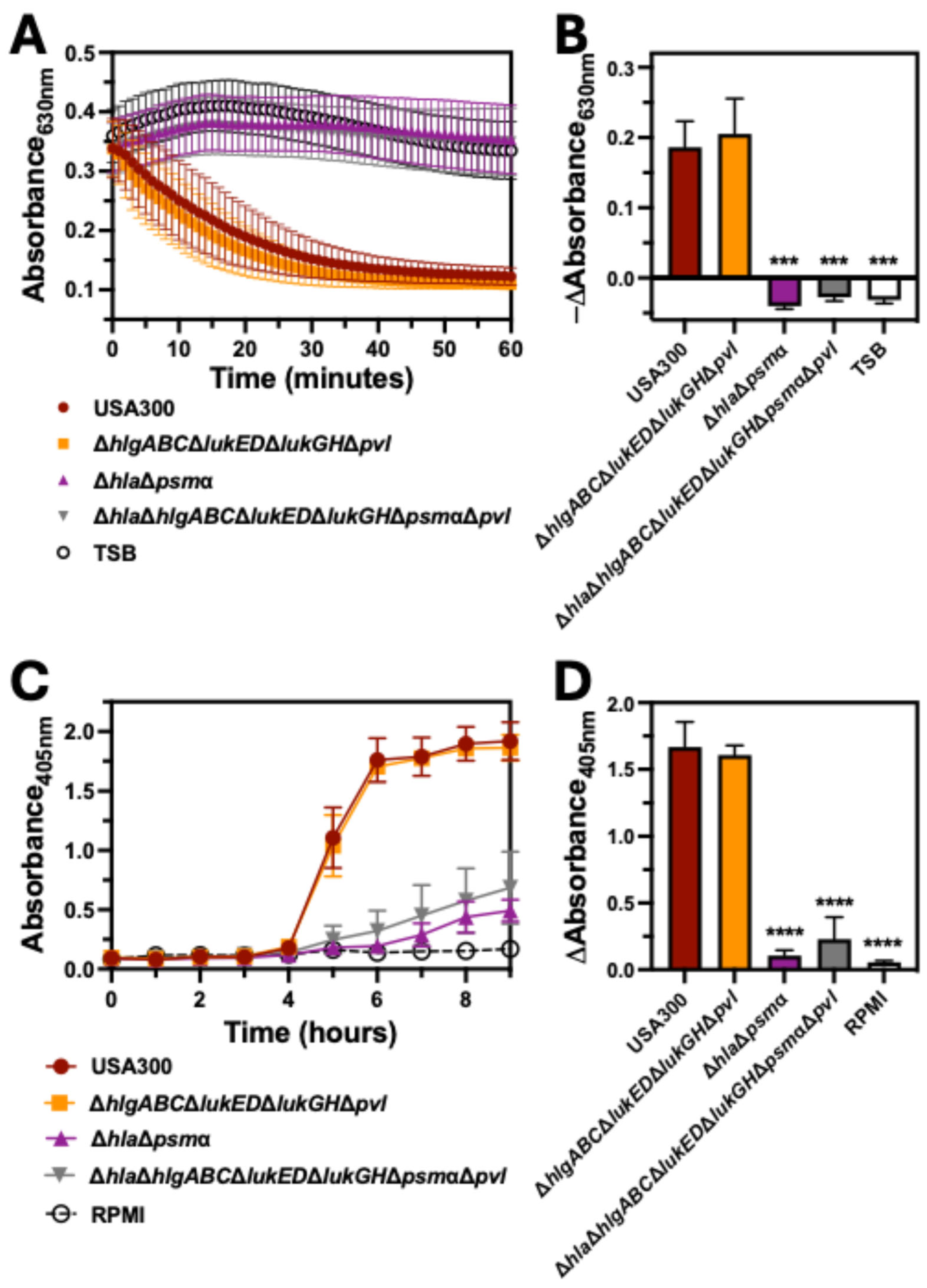
2.3. Bicomponent Leukocidins Are Not Necessary for Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes
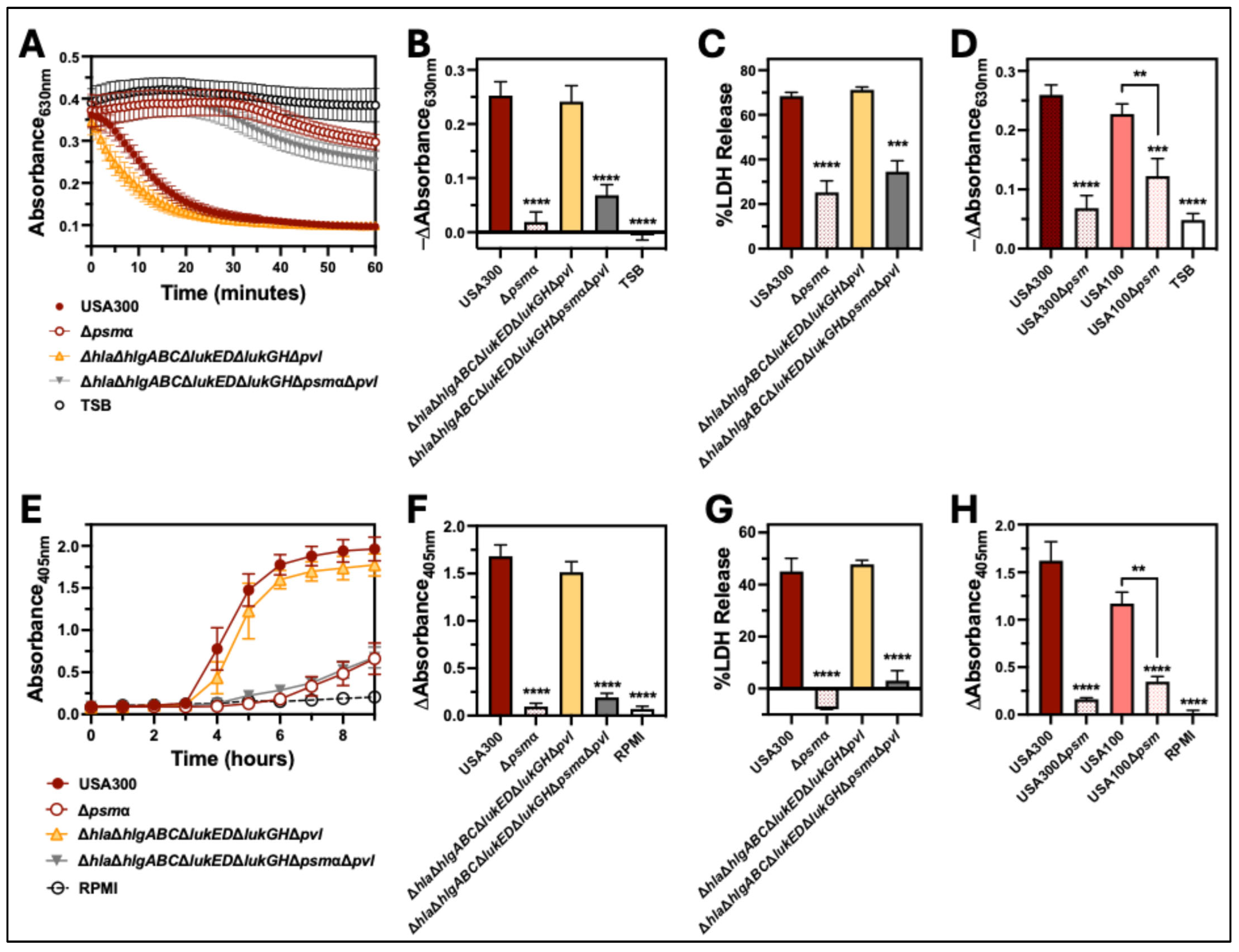
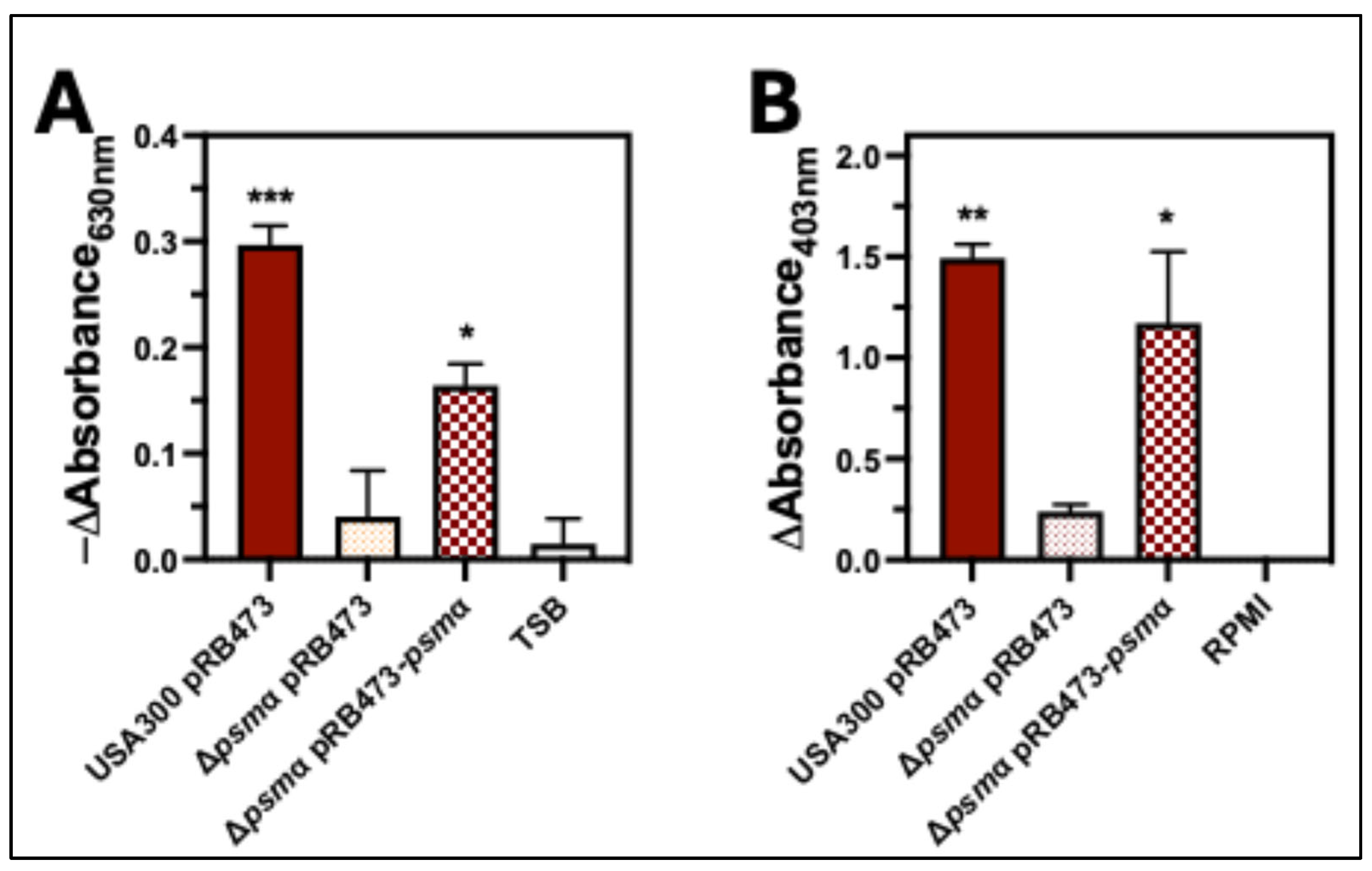
2.4. PSMα Is the Major Hemolytic Factor Produced by S. aureus Against Human Erythrocytes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.2. Human Erythrocyte Preparation
4.3. Blood Agar Hemolysis Assays
4.4. Intoxication Assays
4.5. Co-Culture Assays
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Staphylococcus aureus infections: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.B.; Mourad, A.; Conlon, B.P.; Kielian, T.; Fowler, V.G. Methicillin-resistant and susceptible Staphylococcus aureus: Tolerance, immune evasion and treatment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrand, A.; Pohl, M.; Bhakdi, S. Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. Dual mechanism of binding to target cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 17195–17200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, L.Z.; Madoff, M.A.; Weinstein, L. Heat Stability and Species Range of Purified Staphylococcal α-Toxin. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 91, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenesch, F.; Lina, G.; Henry, T. Staphylococcus aureus Hemolysins, bi-component Leukocidins, and Cytolytic Peptides: A Redundant Arsenal of Membrane-Damaging Virulence Factors? Front. Cell. Inf. Microbiol. 2012, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, A.N.; van Strijp, J.A.G.; Torres, V.J. Leukocidins: Staphylococcal bi-component pore-forming toxins find their receptors. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.; Torres, V.J. Staphylococcus aureus Secreted Toxins and Extracellular Enzymes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonzo, F.; Torres, V.J. The bicomponent pore-forming leucocidins of Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 199–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freer, J.H.; Arbuthnottt, J.P. Toxins Of Staphylococcus aureus. Pharmacol. Ther. 1982, 19, 55–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mrochen, D.M.; Fernandes De Oliveira, L.M.; Raafat, D.; Holtfreter, S. Staphylococcus aureus Host Tropism and Its Implications for Murine Infection Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiseman, G.M. The Hemolysins of Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteriol. Rev. 1975, 39, 317–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elek, S.D.; Levy, E. Distribution of hæmolysins in pathogenic and non-pathogenic staphylococci. J. Pathol. 1950, 62, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malachowa, N.; Kobayashi, S.D.; Braughton, K.R.; Whitney, A.R.; Parnell, M.J.; Gardner, D.J.; Deleo, F.R. Staphylococcus aureus leukotoxin GH promotes inflammation. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löffler, B.; Hussain, M.; Grundmeier, M.; Brück, M.; Holzinger, D.; Varga, G.; Roth, J.; Kahl, B.C.; Proctor, R.A.; Peters, G. Staphylococcus aureus panton-valentine leukocidin is a very potent cytotoxic factor for human neutrophils. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trstenjak, N.; Milić, D.; Graewert, M.A.; Rouha, H.; Svergun, D.; Djinović-Carugo, K.; Nagy, E.; Badarau, A. Molecular mechanism of leukocidin GH-integrin CD11b/CD18 recognition and species specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Voyich, J.M. The Susceptibility Profiles of Human Peripheral Blood Cells to Staphylococcus aureus Cytotoxins. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, C.L.; Malachowa, N.; Hammer, C.H.; Nardone, G.A.; Robinson, M.A.; Kobayashi, S.D.; DeLeo, F.R. Identification of a novel Staphylococcus aureus two-component leukotoxin using cell surface proteomics. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, A.L.; Nygaard, T.K.; Watkins, R.L.; Smith, A.; Kozhaya, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Shopsin, B.; Unutmaz, D.; Voyich, J.M.; Torres, V.J. Characterization of a new cytotoxin that contributes to Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2011, 79, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, A.F.; Bagnoli, F. The Role of Two-Component Signal Transduction Systems in Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Regulation. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 409, 145–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleul, L.; Francois, P.; Wolz, C. Two-Component Systems of S. aureus: Signaling and Sensing Mechanisms. Genes 2021, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Joo, H.-S.; Chatterjee, S.S.; Otto, M. Phenol-soluble modulins—Critical determinants of staphylococcal virulence. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 698–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queck, S.Y.; Jameson-Lee, M.; Villaruz, A.E.; Bach, T.-H.L.; Khan, B.A.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Ricklefs, S.M.; Li, M.; Otto, M. RNAIII-independent target gene control by the agr quorum-sensing system: Insight into the evolution of virulence regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinska, A.K.; Beenken, K.E.; Joo, H.-S.; Mrak, L.N.; Griffin, L.M.; Luong, T.T.; Lee, C.Y.; Otto, M.; Shaw, L.N.; Smeltzer, M.S. Defining the Strain-Dependent Impact of the Staphylococcal Accessory Regulator (sarA) on the Alpha-Toxin Phenotype of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2948–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münzenmayer, L.; Geiger, T.; Daiber, E.; Schulte, B.; Autenrieth, S.E.; Fraunholz, M.; Wolz, C. Influence of Sae-regulated and Agr-regulated factors on the escape of Staphylococcus aureus from human macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, N.D.; Skaar, E.P. Molecular mechanisms of Staphylococcus aureus iron acquisition. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, V.J.; Pishchany, G.; Humayun, M.; Schneewind, O.; Skaar, E.P. Staphylococcus aureus IsdB is a hemoglobin receptor required for heme iron utilization. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 8421–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaar, E.P.; Humayun, M.; Bae, T.; DeBord, K.L.; Schneewind, O. Iron-source preference of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Science 2004, 305, 1626–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaan, A.N.; Reyes-Robles, T.; Badiou, C.; Cochet, S.; Boguslawski, K.M.; Yoong, P.; Day, C.J.; de Haas, C.J.C.; van Kessel, K.P.M.; Vandenesch, F.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Targets the Duffy Antigen Receptor for Chemokines (DARC) to Lyse Erythrocytes. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 18, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreras, M.; Höper, F.; Dalla Serra, M.; Colin, D.A.; Prévost, G.; Menestrina, G. The interaction of Staphylococcus aureus bi-component gamma-hemolysins and leucocidins with cells and lipid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1414, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, J.; Ozawa, T.; Tomita, T.; Kamio, Y. Sequential binding of Staphylococcal gamma-hemolysin to human erythrocytes and complex formation of the hemolysin on the cell surface. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 61, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Takeshita, M.; Shibata, N.; Tada, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kaneko, J. Rim domain loops of staphylococcal β-pore forming bi-component toxin S-components recognize target human erythrocytes in a coordinated manner. J. Biochem. 2018, 164, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, G.Y.C.; Duong, A.C.; Otto, M. Direct and synergistic hemolysis caused by Staphylococcus phenol-soluble modulins: Implications for diagnosis and pathogenesis. Microbes Infect. 2012, 14, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, G.A.; Wardenburg, J.B. Role of a disintegrin and metalloprotease 10 in Staphylococcus aureus α-hemolysin–mediated cellular injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13473–13478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Pallister, K.B.; Ruzevich, P.; Griffith, S.; Vuong, C.; Voyich, J.M. SaeR Binds a Consensus Sequence within Virulence Gene Promoters to Advance USA300 Pathogenesis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voyich, J.M.; Vuong, C.; DeWald, M.; Nygaard, T.K.; Kocianova, S.; Griffith, S.; Jones, J.; Iverson, C.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Braughton, K.R.; et al. The SaeR/S gene regulatory system is essential for innate immune evasion by Staphylococcus aureus. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 1698–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yeo, W.-S.; Bae, T. The SaeRS Two-Component System of Staphylococcus aureus. Genes 2016, 7, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, C.-L.; Tan, V.Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hong, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, T.; et al. Virulence determinants associated with the Asian community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus lineage ST59. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, T.; Wang, Y.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Z. New insight into the virulence and inflammatory response of Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from diabetic foot ulcers. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1234994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatasubramaniam, A.; Kanipakala, T.; Ganjbaksh, N.; Mehr, R.; Mukherjee, I.; Krishnan, S.; Bae, T.; Aman, M.J.; Adhikari, R.P. A Critical Role for HlgA in Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenesis Revealed by A Switch in the SaeRS Two-Component Regulatory System. Toxins 2018, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, T.; Goerke, C.; Mainiero, M.; Kraus, D.; Wolz, C. The Virulence Regulator Sae of Staphylococcus aureus: Promoter Activities and Response to Phagocytosis-Related Signals. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 3419–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainiero, M.; Goerke, C.; Geiger, T.; Gonser, C.; Herbert, S.; Wolz, C. Differential Target Gene Activation by the Staphylococcus aureus Two-Component System saeRS. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hébert, G.A.; Hancock, G.A. Synergistic hemolysis exhibited by species of staphylococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1985, 22, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berube, B.J.; Sampedro, G.R.; Otto, M.; Bubeck Wardenburg, J. The psm α Locus Regulates Production of Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin during Infection. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 3350–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, R.; Race, R.R.; Jack, J. The Duffy Blood Groups of New York Negroes: The Phenotype Fy (a−b−). Br. J. Haematol. 1955, 1, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.H.; Mason, S.J.; Clyde, D.F.; McGinniss, M.H. The Resistance Factor to Plasmodium vivax in Blacks. N. Engl. J. Med. 1976, 295, 302–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malachowa, N.; Whitney, A.R.; Kobayashi, S.D.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Kennedy, A.D.; Braughton, K.R.; Shabb, D.W.; Diep, B.A.; Chambers, H.F.; Otto, M.; et al. Global Changes in Staphylococcus aureus Gene Expression in Human Blood. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlipala, G.E.; Lei, Z.A.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Kunstman, K.; Okamoto, K.; Green, S.J.; Popovich, K.J. Complete Genome Sequence of a USA100 Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8, e00006-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diep, B.A.; Gill, S.R.; Chang, R.F.; Phan, T.H.; Chen, J.H.; Davidson, M.G.; Lin, F.; Lin, J.; Carleton, H.A.; Mongodin, E.F.; et al. Complete genome sequence of USA300, an epidemic clone of community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet 2006, 367, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, T.; Schneewind, O. Allelic replacement in Staphylococcus aureus with inducible counter-selection. Plasmid 2006, 55, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Borgogna, T.R.; Sward, E.W.; Guerra, F.E.; Dankoff, J.G.; Collins, M.M.; Pallister, K.B.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Voyich, J.M. Aspartic Acid Residue 51 of SaeR Is Essential for Staphylococcus aureus Virulence. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.M.; Behera, R.K.; Pallister, K.B.; Evans, T.J.; Burroughs, O.; Flack, C.; Guerra, F.E.; Pullman, W.; Cone, B.; Dankoff, J.G.; et al. The Accessory Gene saeP of the SaeR/S Two-Component Gene Regulatory System Impacts Staphylococcus aureus Virulence During Neutrophil Interaction. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Pallister, K.B.; DuMont, A.L.; DeWald, M.; Watkins, R.L.; Pallister, E.Q.; Malone, C.; Griffith, S.; Horswill, A.R.; Torres, V.J.; et al. Alpha-Toxin Induces Programmed Cell Death of Human T cells, B cells, and Monocytes during USA300 Infection. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nygaard, T.K.; Borgogna, T.R.; Pallister, K.B.; Predtechenskaya, M.; Burroughs, O.S.; Gao, A.; Lubick, E.G.; Voyich, J.M. The Relative Importance of Cytotoxins Produced by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Strain USA300 for Causing Human PMN Destruction. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strain | Reference |
|---|---|
| USA300 | [47] |
| USA300Δhla | [52] |
| USA300ΔagrABCD | [53] |
| USA300ΔsaePQRS | [53] |
| USA300ΔhlaΔhlgABCΔlukEDΔlukGHΔpsmαΔpvl | [53] |
| USA300ΔhlgABCΔlukEDΔlukGHΔpvl | [53] |
| USA300ΔhlaΔpsmα | [53] |
| USA300Δpsmα | this study |
| USA300ΔhlaΔhlgABCΔlukEDΔlukGHΔpvl | this study |
| USA100 | [48] |
| USA100Δpsmα | this study |
| USA300 pRB473 | this study |
| USA300Δpsmα pRB473 | this study |
| USA300Δpsmα pRB473-psmα | this study |
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| psmα-Top_fwd | 5′-GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CGT CGT CTA CCT TTC CAT GC-3′ |
| psmα-SphI-Top_rvs | 5′-GGT GGT GCA TGC CTC AGG CCA CTA TAC CAA TAG-3′ |
| psmα-SphI-Bot_fwd | 5′-GGT GGT GCA TGC CAG CGA TGA TAC CCA TTA AGA TTA CC-3′ |
| psmα-Bot_rvs | 5′-GGG GAC CAC TTT GTA CAA GAA AGC TGG GTC GAA TGC AAG CCA ACC AC-3′ |
| hla-Top_fwd | 5′-GGG GAC AAG TTT GTA CAA AAA AGC AGG CGA AGT CCA TAC AAA ATC CGC ATC-3′ |
| hla-BamHI-Top_rvs | 5′-GGT GGT GGA TCC CTA TCT ACT TGA TTT GCT TTC CTG AC-3′ |
| hla-BamHI-Bot_fwd | 5′-GGT GGT GGA TCC CAA TTT CGA GGG TTA GTC AAA GTT G-3′ |
| hla-Bot_rvs | 5′-GGG GAC CAC TTT GTA CAA GAA AGC TGG GTG CAA TAC TTT ATT GTC CCA TGA TTA GTG-3′ |
| psmα-comp-SacI_fwd | 5′-CCA CCA GAG CTC CTA GAC GAG ACC TAA CGT G-3′ |
| psmα-comp-BamHI_rvs | 5′-GGT GGT GGA TCC CTA TTG GTA TAG TGG CCT GAG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nygaard, T.K.; Gao, A.; LaTray, E.; Voyich, J.M. Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Is Primarily Caused by PSMα Peptides. Toxins 2025, 17, 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110529
Nygaard TK, Gao A, LaTray E, Voyich JM. Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Is Primarily Caused by PSMα Peptides. Toxins. 2025; 17(11):529. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110529
Chicago/Turabian StyleNygaard, Tyler K., Annika Gao, Eliot LaTray, and Jovanka M. Voyich. 2025. "Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Is Primarily Caused by PSMα Peptides" Toxins 17, no. 11: 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110529
APA StyleNygaard, T. K., Gao, A., LaTray, E., & Voyich, J. M. (2025). Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Is Primarily Caused by PSMα Peptides. Toxins, 17(11), 529. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins17110529




