Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Predicting the Concentration of Air Pollutants in Urban Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
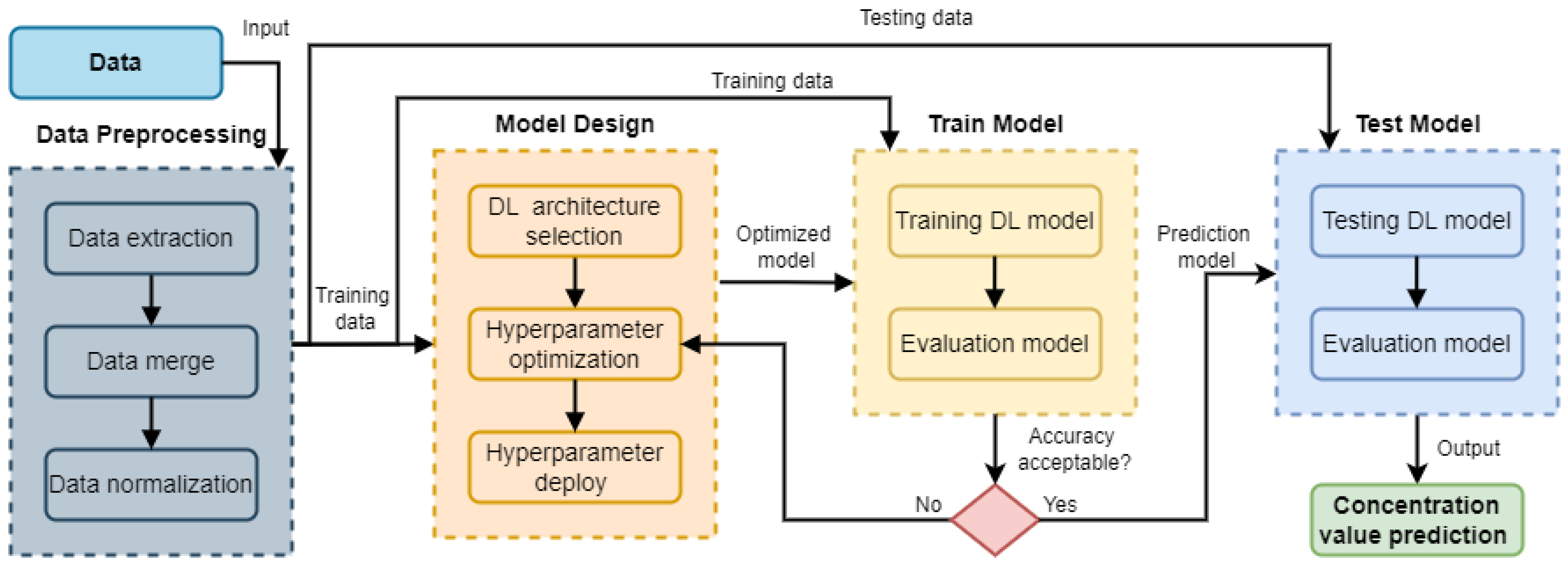
3.1. Methodology
3.1.1. Data Preprocessing
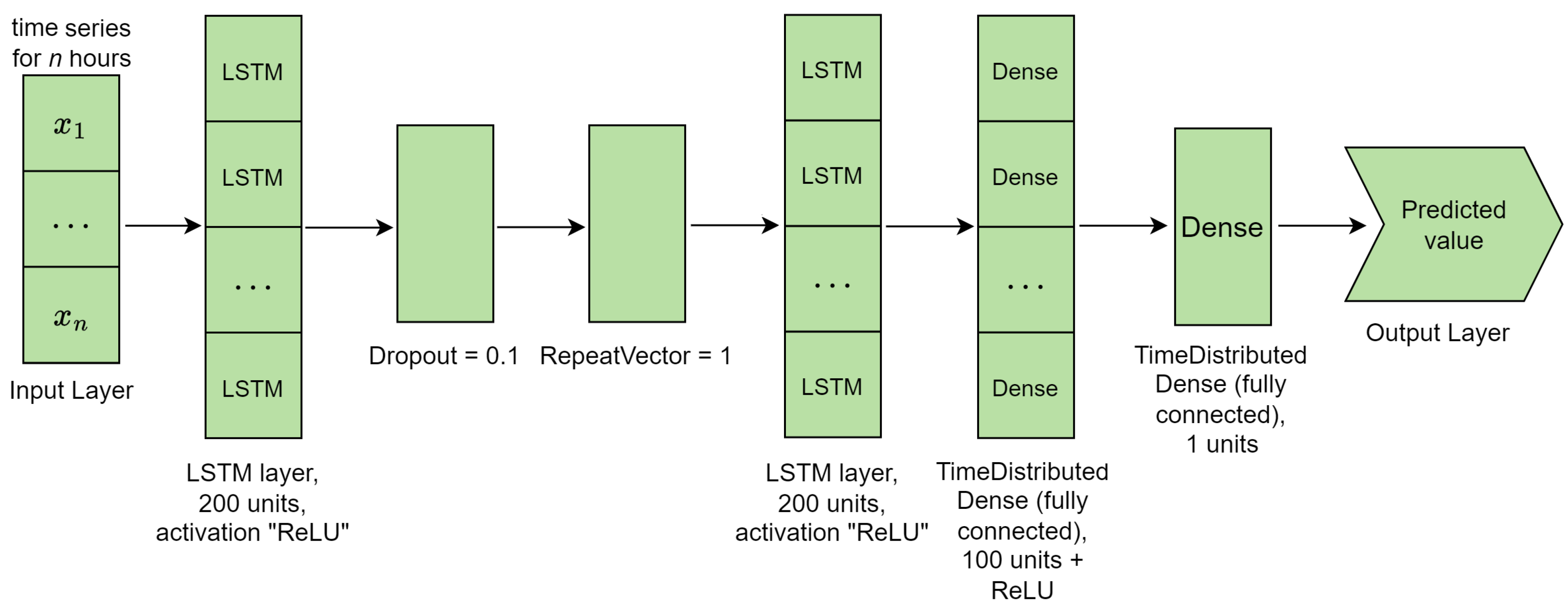
3.1.2. Model Design
3.1.3. Train Model
3.1.4. Test Model
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Measurement
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DL | Deep learning |
| LSTM | Long short-term memory |
| Bi-LSTM | Bidirectional long short-term memory |
| RNN | Recurrent neural networks |
| RMSE | Root mean square error |
| MAE | Mean absolute error |
| MSE | Mean square error |
| MAPE | Mean absolute percentage error |
| R2 | Determination coefficient |
| PM2.5 | Particulate matter < 10 μm |
| PM10 | Particulate matter < 2.5 μm |
| CO | Carbon monoxide |
References
- Delavar, M.A.; Jahani, M.A.; Sepidarkish, M.; Alidoost, S.; Mehdinezhad, H.; Farhadi, Z. Relationship between fine particulate matter (PM2.5) concentration and risk of hospitalization due to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anenberg, S.C.; Mohegh, A.; Goldberg, D.L.; Kerr, G.H.; Brauer, M.; Burkart, K.; Hystad, P.; Larkin, A.; Wozniak, S.; Lamsal, L. Long-term trends in urban NO2 concentrations and associated pediatric asthma incidence: Estimates from global datasets. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e49–e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreão, W.L.; Toledo de Almeida Albuquerque, T. Avoidable mortality by implementing more restrictive fine particles standards in Brazil: An estimation using satellite surface data. Environ. Res. 2021, 192, 110288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, J.L.; Rovira, J. Effects of air pollutants on the transmission and severity of respiratory viral infections. Environ. Res. 2020, 187, 109650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutman, L.; Pauly, V.; Orleans, V.; Piga, D.; Channac, Y.; Armengaud, A.; Boyer, L.; Papazian, L. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollution is associated with an increased incidence and mortality of acute respiratory distress syndrome in a large French region. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yin, P.; Chen, R.; Meng, X.; Wang, L.; Niu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; et al. Ambient carbon monoxide and cardiovascular mortality: A nationwide time-series analysis in 272 cities in China. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, e12–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; You, J.; Dong, J.; Wang, J.; Bao, H. Ambient carbon monoxide and relative risk of daily hospital outpatient visits for respiratory diseases in Lanzhou, China. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2023, 67, 1913–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.; Nouri, F.; Ziaddini, M.; Rabiei, K.; Pourmoghaddas, A.; Islam, S.M.S.; Sarrafzadegan, N. Ambient carbon monoxide and cardiovascular-related hospital admissions: A time-series analysis. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsborough, E.; Gopal, M.; McEvoy, J.W.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Jacobsen, A.P. Pollution and cardiovascular health: A contemporary review of morbidity and implications for planetary health. Am. Heart J. Plus Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2023, 25, 100231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chillrud, S.N.; Ae-Ngibise, K.A.; Gould, C.F.; Owusu-Agyei, S.; Mujtaba, M.; Manu, G.; Burkart, K.; Kinney, P.L.; Quinn, A.; Jack, D.W.; et al. The effect of clean cooking interventions on mother and child personal exposure to air pollution: Results from the Ghana Randomized Air Pollution and Health Study (GRAPHS). J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaali, S.; Jack, D.W.; Mujtaba, M.N.; Chillrud, S.N.; Ae-Ngibise, K.A.; Kinney, P.L.; Boamah Kaali, E.; Gennings, C.; Colicino, E.; Osei, M.; et al. Identifying sensitive windows of prenatal household air pollution on birth weight and infant pneumonia risk to inform future interventions. Environ. Int. 2023, 178, 108062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, D.A.; Northcross, A.; Karrison, T.; Morhasson-Bello, O.; Wilson, N.; Atalabi, O.M.; Dutta, A.; Adu, D.; Ibigbami, T.; Olamijulo, J.; et al. Pregnancy outcomes and ethanol cook stove intervention: A randomized-controlled trial in Ibadan, Nigeria. Environ. Int. 2018, 111, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, B.J.; Kishashu, Y.; Matechi, E.; Zhou, Z.; Coull, B.; Abioye, A.I.; Dionisio, K.L.; Mugusi, F.; Premji, Z.; Fawzi, W.; et al. Maternal exposure to carbon monoxide and fine particulate matter during pregnancy in an urban Tanzanian cohort. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez, M.; Merayo, M.G.; Núñez, M. Machine learning algorithms to forecast air quality: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 10031–10066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekkar, A.; Hssina, B.; Douzi, S.; Douzi, K. Air-pollution prediction in smart city, deep learning approach. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalajdjieski, J.; Zdravevski, E.; Corizzo, R.; Lameski, P.; Kalajdziski, S.; Pires, I.M.; Garcia, N.M.; Trajkovik, V. Air Pollution Prediction with Multi-Modal Data and Deep Neural Networks. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhu, W.; Liao, B.; Chen, M.; Cai, L.; Huang, L. Novel architecture for long short-term memory used in question classification. Neurocomputing 2018, 299, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, M.; Han, H.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.S. Development of a Deep Learning-Based Prediction Model for Water Consumption at the Household Level. Water 2022, 14, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu, S.; Altan, A. Crude oil time series prediction model based on LSTM network with chaotic Henry gas solubility optimization. Energy 2022, 242, 122964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Dai, G.; Zhou, J. Short-Term Traffic Flow Prediction for Urban Road Sections Based on Time Series Analysis and LSTM_BILSTM Method. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 5615–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, L.; Ilk, N.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y. Multi-disease prediction using LSTM recurrent neural networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 177, 114905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.S.; Chiao, H.T.; Abimannan, S.; Huang, Y.P.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lin, K.M. An LSTM-based aggregated model for air pollution forecasting. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiani, E.; Lin, H.; Lin, J.R.; Chuang, Y.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Yang, C.T. Short-Term Prediction of PM2.5 Using LSTM Deep Learning Methods. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.; Dursun, Ö.O.; Toraman, S. Prediction of air pollutants for air quality using deep learning methods in a metropolitan city. Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaini, N.; Ahmed, A.N.; Ean, L.W.; Chow, M.F.; Malek, M.A. Forecasting of fine particulate matter based on LSTM and optimization algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 427, 139233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-B.; Park, S.B.; Lee, S.; Park, Y.K. Comparison of PM2.5 prediction performance of the three deep learning models: A case study of Seoul, Daejeon, and Busan. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 120, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, B.; Aksangür, İ; Erden, C. Predicting next hour fine particulate matter (PM2.5) in the Istanbul Metropolitan City using deep learning algorithms with time windowing strategy. Urban Clim. 2023, 48, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J. Air quality predictions with a semi-supervised bidirectional LSTM neural network. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, Y.; Xia, B.; Liu, K.; Li, H. Prediction of atmospheric pollutants in urban environment based on coupled deep learning model and sensitivity analysis. Chemosphere 2023, 331, 138830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilik, A.; Ogrenci, A.S.; Ozmen, A. Air quality prediction using CNN+LSTM-based hybrid deep learning architecture. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 11920–11938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Lee, H.; Lee, G. A Hybrid Deep Learning Model to Forecast Particulate Matter Concentration Levels in Seoul, South Korea. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Santos, V.; Costa Rocha, P.A.; Scott, J.; Van Griensven Thé, J.; Gharabaghi, B. Spatiotemporal Air Pollution Forecasting in Houston-TX: A Case Study for Ozone Using Deep Graph Neural Networks. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, M.; Li, S.; Xing, J.; Fan, C.; Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Song, G.; Ding, Y.; Dong, J.; Wang, S. 72-hour real-time forecasting of ambient PM2.5 by hybrid graph deep neural network with aggregated neighborhood spatiotemporal information. Environ. Int. 2023, 176, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dun, A.; Yang, Y.; Lei, F. Dynamic graph convolution neural network based on spatial-temporal correlation for air quality prediction. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shen, W. A long-term prediction method for PM2.5 concentration based on spatiotemporal graph attention recurrent neural network and grey wolf optimization algorithm. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Jiao, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Tong, X.; Zhao, S. A hybrid integrated deep learning model for predicting various air pollutants. GISci. Remote Sens. 2021, 58, 1395–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Kong, J.L.; Bai, Y.T.; Su, T.L.; Ma, H.J.; Chakrabarti, P. Deep Spatio-Temporal Graph Network with Self-Optimization for Air Quality Prediction. Entropy 2023, 25, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Ying, J.J.C.; Tseng, V.S. Spatio-attention embedded recurrent neural network for air quality prediction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 233, 107416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, C.; Husi, L. A Spatial-Temporal Interpretable Deep Learning Model for improving interpretability and predictive accuracy of satellite-based PM2.5. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Guo, H.; Gu, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Mi, X.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, D. High-Resolution PM2.5 Concentrations Estimation Based on Stacked Ensemble Learning Model Using Multi-Source Satellite TOA Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, P.; Hu, B.; Gao, Y.; Si, Y. The Ground-Level Particulate Matter Concentration Estimation Based on the New Generation of FengYun Geostationary Meteorological Satellite. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello-Leal, E.; Macías-Hernández, B.A. Association of environmental and meteorological factors on the spread of COVID-19 in Victoria, Mexico, and air quality during the lockdown. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Alcocer, U.M.; Tello-Leal, E.; Macías-Hernández, B.A.; Hernandez-Resendiz, J.D. Data-Driven Prediction of COVID-19 Daily New Cases through a Hybrid Approach of Machine Learning Unsupervised and Deep Learning. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobierno de México—SEMARNAT. Normas Oficiales Mexicanas (NOM) de Calidad del Aire Ambiente. 2024. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/cof\protect\discretionary{\char\hyphenchar\font}{}{}epris/acciones-y-programas/4-normas-oficiales-mexicanas-nom-de-calidad-del-aire-ambiente (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Criteria Air Pollutants. 2024. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/criteria-air-pollutants/naaqs-table (accessed on 31 July 2024).
- Chicco, D.; Warrens, M.J.; Jurman, G. The coefficient of determination R-squared is more informative than SMAPE, MAE, MAPE, MSE and RMSE in regression analysis evaluation. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabie, R.; Asghari, M.; Nosrati, H.; Emami Niri, M.; Karimi, S. Spatially resolved air quality index prediction in megacities with a CNN-Bi-LSTM hybrid framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 109, 105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Gupta, Y. Comparative analysis of Air Quality Index prediction using deep learning algorithms. Spat. Inf. Res. 2024, 32, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanga, R.; Tang, J.; Xia, H.; Pan, X.; Yu, W.; Qiao, J. CO emission predictions in municipal solid waste incineration based on reduced depth features and long short-term memory optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 5473–5498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Sorooshian, A.; Goudarzi, G.; Baboli, Z.; Birgani, Y.T.; Rahmati, M. Air pollution prediction by using an artificial neural network model. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2019, 21, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Liu, S.; Yao, X.; Peng, L.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Chi, T. A novel spatiotemporal convolutional long short-term neural network for air pollution prediction. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 654, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Li, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, A. A novel hybrid model for six main pollutant concentrations forecasting based on improved LSTM neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, S.; Thakur, M. A city-based PM2.5 forecasting framework using Spatially Attentive Cluster-based Graph Neural Network model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 137036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navares, R.; Aznarte, J.L. Predicting air quality with deep learning LSTM: Towards comprehensive models. Ecol. Inform. 2020, 55, 101019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Woo, S.H.; Lim, C. Predicting PM10 and PM2.5 concentration in container ports: A deep learning approach. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2023, 115, 103601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kujawska, J.; Kulisz, M.; Oleszczuk, P.; Cel, W. Machine Learning Methods to Forecast the Concentration of PM10 in Lublin, Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariff, N.M.; Bakar, M.A.A.; Lim, H.Y. Prediction of PM10 Concentration in Malaysia Using K-Means Clustering and LSTM Hybrid Model. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Chen, P.H.; Wu, C.H.; Yang, C.S.; Chuang, L.Y. Deep learning-based air pollution analysis on carbon monoxide in Taiwan. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 80, 102477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizi, H.; Sattari, M.T.; Prasad, R.; Apaydin, H. Comparative analysis of deep and machine learning approaches for daily carbon monoxide pollutant concentration estimation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 1753–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, E.D.; Tsoulos, I.; Stylios, C. Applying and Comparing LSTM and ARIMA to Predict CO Levels for a Time-Series Measurements in a Port Area. Signals 2022, 3, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Model | RMSE | MAE | MSE | MAPE | MBE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNN | 3.5125 | 2.3465 | 12.3379 | 26.9229 | −0.0118 | 0.8955 |
| Vanilla LSTM | 3.4647 | 2.2554 | 12.0047 | 24.7679 | −0.1806 | 0.8977 |
| Stacked LSTM | 3.4538 | 2.2478 | 11.9289 | 23.5741 | 0.0232 | 0.8991 |
| Bi-LSTM | 3.4766 | 2.2908 | 12.0873 | 24.1854 | −0.1561 | 0.8967 |
| Encoder–decoder LSTM | 3.4731 | 2.2883 | 12.0626 | 22.5815 | 0.0144 | 0.8969 |
| Model | RMSE | MAE | MSE | MAPE | MBE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNN | 3.3925 | 2.2448 | 11.5097 | 19.0679 | −0.3805 | 0.8894 |
| Vanilla LSTM | 3.2873 | 2.1284 | 10.8064 | 16.6895 | −0.1460 | 0.8962 |
| Stacked LSTM | 3.3144 | 2.1336 | 10.9857 | 16.3813 | −0.0313 | 0.8945 |
| Bi-LSTM | 3.3103 | 2.1579 | 10.9584 | 16.9279 | 0.1929 | 0.8947 |
| Encoder–decoder LSTM | 3.2606 | 2.1074 | 10.6318 | 16.6577 | −0.0227 | 0.8979 |
| Model | RMSE | MAE | MSE | MAPE | MBE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RNN | 0.1222 | 0.0708 | 0.0149 | 14.2915 | 0.0239 | 0.9754 |
| Vanilla LSTM | 0.1330 | 0.0957 | 0.0177 | 21.3912 | −0.0575 | 0.9717 |
| Stacked LSTM | 0.1246 | 0.0840 | 0.0155 | 17.7031 | −0.0485 | 0.9743 |
| Bi-LSTM | 0.1262 | 0.0848 | 0.0159 | 17.4148 | −0.0451 | 0.9739 |
| Encoder–decoder LSTM | 0.1117 | 0.0556 | 0.0124 | 9.915 | 0.0186 | 0.9799 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tello-Leal, E.; Ramirez-Alcocer, U.M.; Macías-Hernández, B.A.; Hernandez-Resendiz, J.D. Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Predicting the Concentration of Air Pollutants in Urban Environments. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167062
Tello-Leal E, Ramirez-Alcocer UM, Macías-Hernández BA, Hernandez-Resendiz JD. Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Predicting the Concentration of Air Pollutants in Urban Environments. Sustainability. 2024; 16(16):7062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167062
Chicago/Turabian StyleTello-Leal, Edgar, Ulises Manuel Ramirez-Alcocer, Bárbara A. Macías-Hernández, and Jaciel David Hernandez-Resendiz. 2024. "Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Predicting the Concentration of Air Pollutants in Urban Environments" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167062
APA StyleTello-Leal, E., Ramirez-Alcocer, U. M., Macías-Hernández, B. A., & Hernandez-Resendiz, J. D. (2024). Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Predicting the Concentration of Air Pollutants in Urban Environments. Sustainability, 16(16), 7062. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167062








