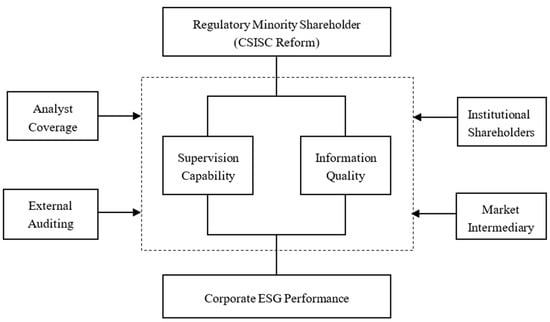
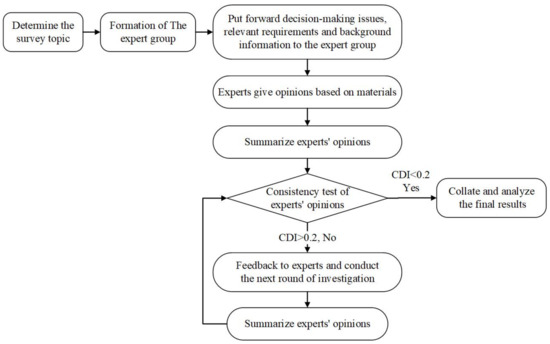
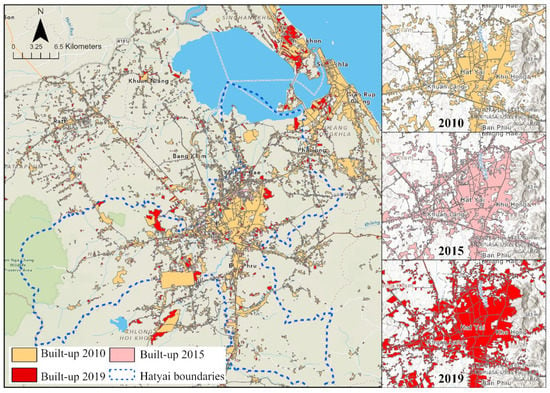
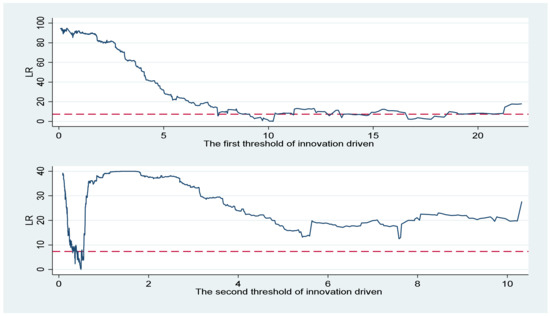
Sustainability 2023, 15(7), 6326; https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076326 - 6 Apr 2023
Cited by 25 | Viewed by 3361
Abstract
►
Show Figures
The increase in population has increased the need for agricultural and food products, and thus agricultural production should be increased. This goal may cause increases in emissions and environmental impacts by increasing the consumption of agricultural inputs. The prediction of environmental impacts plays
[...] Read more.
The increase in population has increased the need for agricultural and food products, and thus agricultural production should be increased. This goal may cause increases in emissions and environmental impacts by increasing the consumption of agricultural inputs. The prediction of environmental impacts plays an important role in evaluating pollutant emissions in crop production. This study employed two artificial intelligence (AI) methods: the adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system–fuzzy c-means (ANFIS–FCM) algorithm as a novel computational method, and an artificial neural network (ANN) as a conventional computational method to predict the environmental impacts of soybean production in different scenarios (i.e., soybean cultivation after rapeseed (R-S), wheat (W-S), and fallow (F-S)). The life cycle of soybean production was assessed in terms of environmental impacts through the IMPACT2002+ method in SimaPro. In the present study, the production of one ton of soybeans was considered the functional unit, and the boundary of the system was considered the gate of the field. According to the results, the production of each ton of soybean in the defined scenarios resulted in 0.0009 to 0.0016 DALY, 5476.18 to 8799.80 MJ primary, 1033.68 to 1840.70 PDF × m2 × yr, and 563.55 to 880.61 kg CO2-eq damage to human health, resources, ecosystem quality, and climate change, respectively. Moreover, the weighted analysis indicated that various soybean production scenarios led to 293.87–503.73 mPt damage to the environment, in which the R-S scenario had the best environmental performance. According to the results, the ANFIS–FCM algorithm acted as the best prediction model of environmental indicators for soybean cultivation in all cases related to the ANN. The range of calculated R2 for the ANFIS-FCM and ANN models were between 0.9967 to 0.9989 and 0.9269 to 0.9870, respectively. It can be concluded that the proposed ANFIS–FCM model is an efficient technique for obtaining accurate environmental prediction parameters of soybean cultivation.
Full article