Immunotoxicity of Heavy Metals (Silver, Cadmium, Mercury and Lead) on Marine Bivalve Mytilus edulis: In Vitro Exposure of Hemocytes †
Abstract
:Introduction
Industrial revolutions and ecotoxicity: historical background
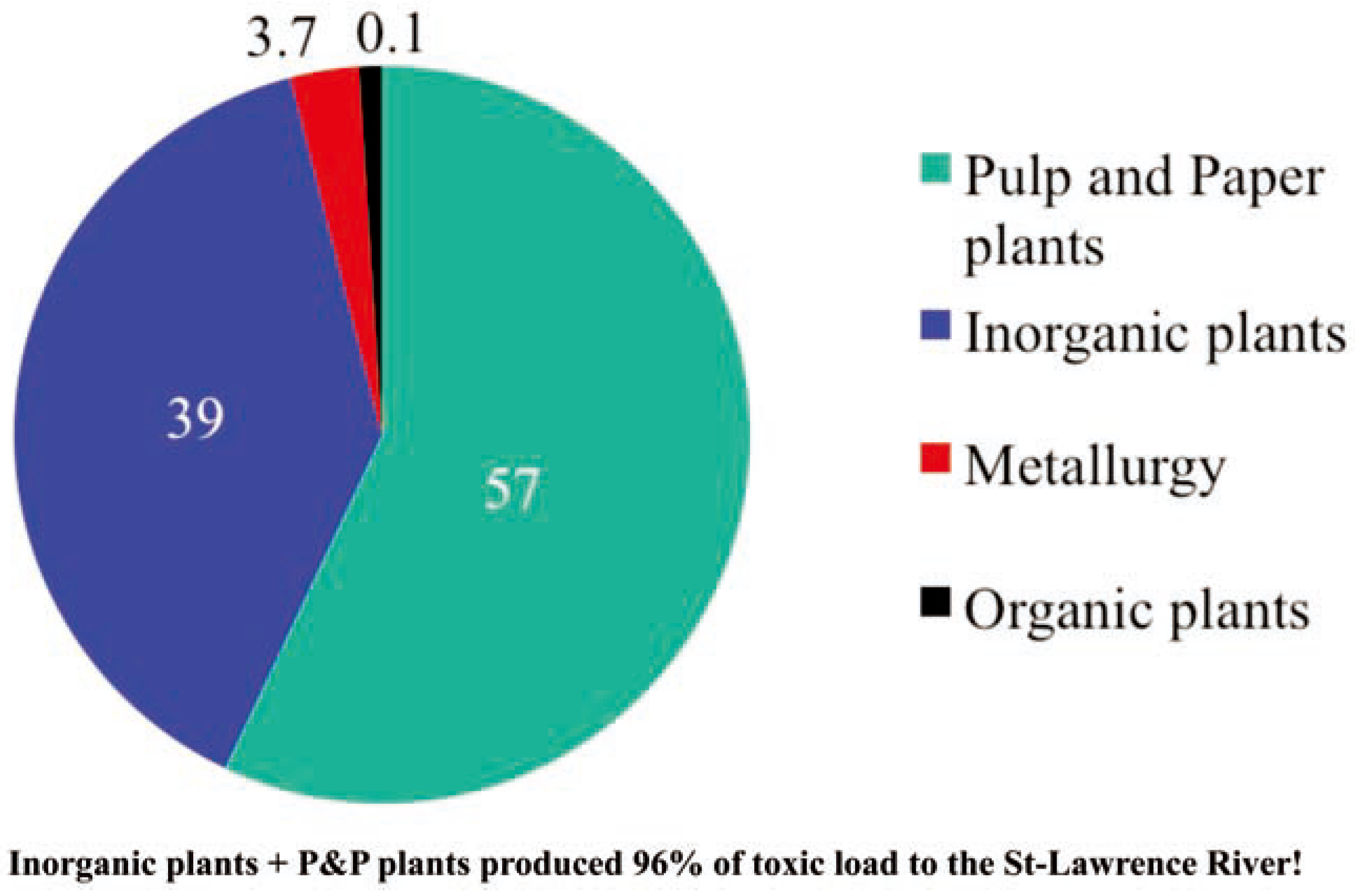
The St-Lawrence River Action Plan: trying to solve a whale of a problem! ...or integrating bioassays as an aid to decision-making
A few words on sediment assessment
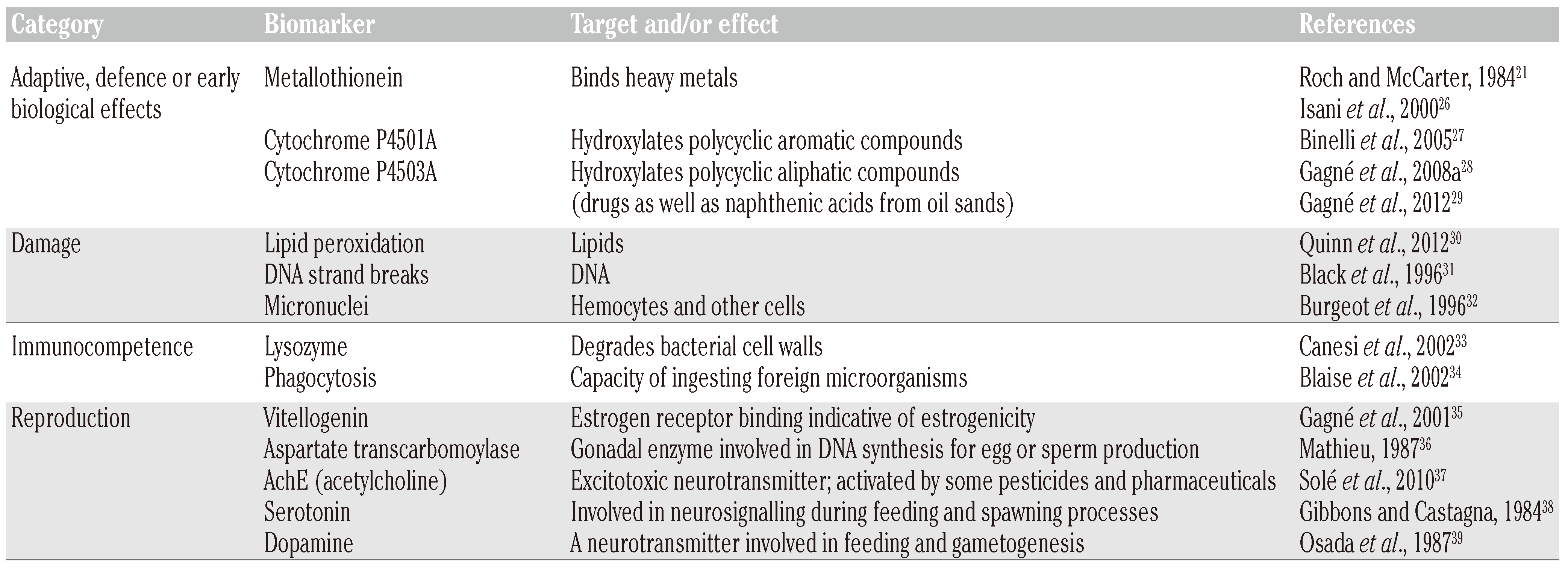
Biomarkers
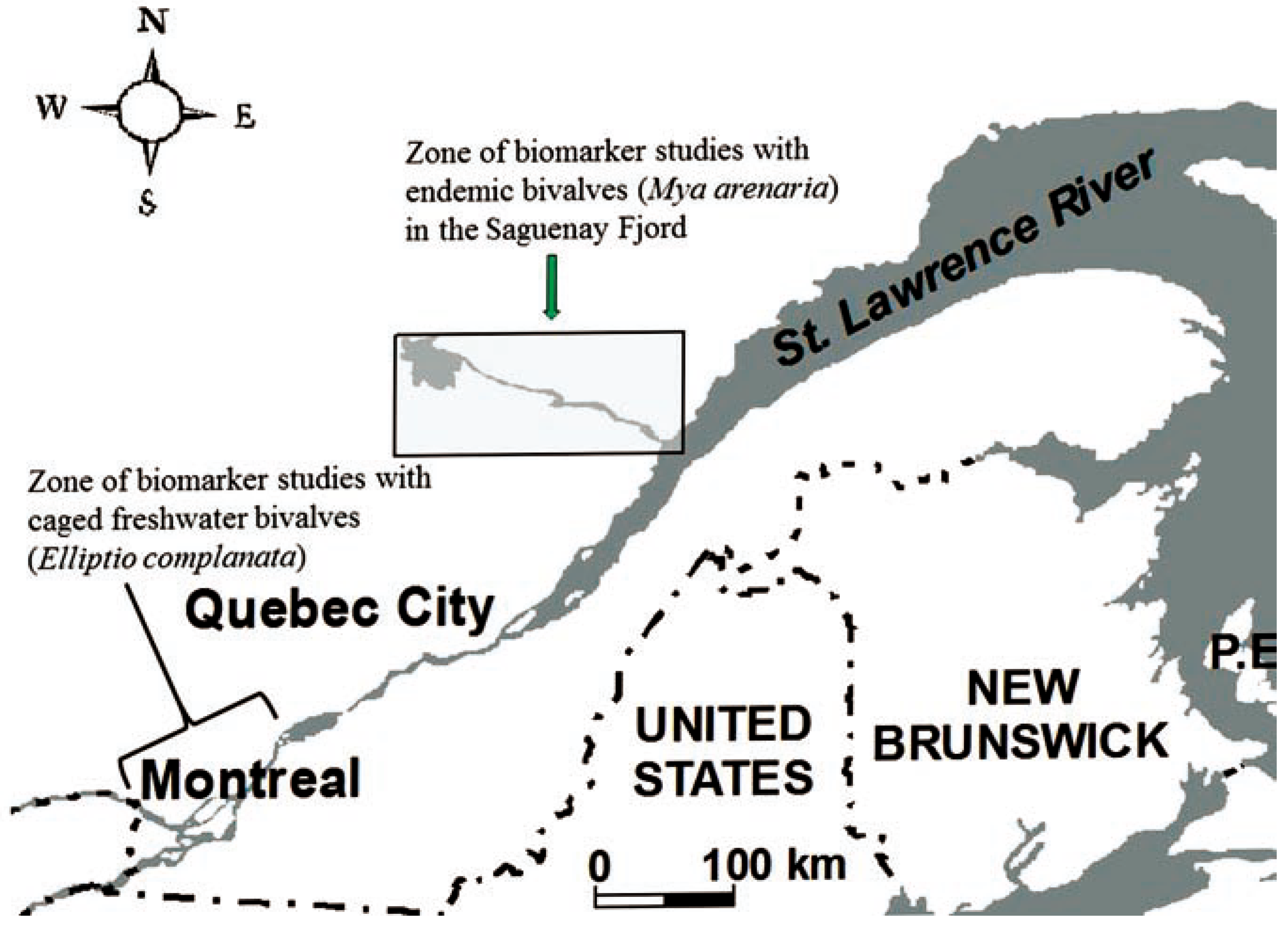
Biomarker studies in Eastern Canada
Emerging substances: pharmaceuticals
Emerging substances: nanoparticles
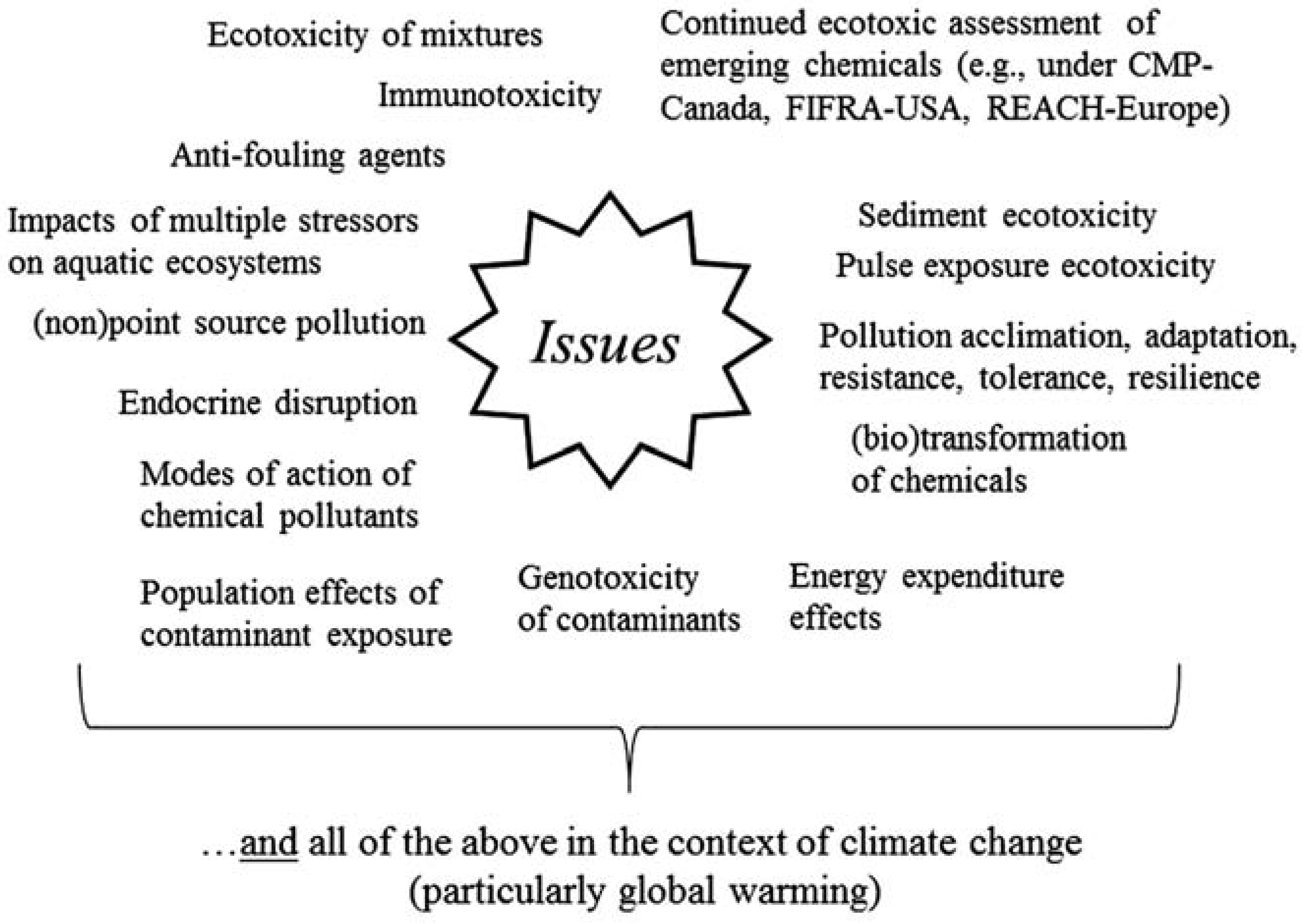
Issues and needs confronting ecotoxicology today
General conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
References
- Blaise, C.; Sergy, G.; Wells, P.; Bermigham, N.; van Coillie, R. Biological testing develop- ment, application and trends in Canadian environmental protection laboratories. Toxicity Assess 1988, 3, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Costan, G. La toxicité létale aiguë des effluents industriels au Québec vis-à- vis de la truite arc-en-ciel. Water Poll Res J Canada 1987, 22, 385–402. [Google Scholar]
- Jouany, J.M. Nuisances et ecologie. Actualités Pharmaceutiques 1971, 69, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C.; Wells, P.; Lee, K. Microscale testing in aquatic toxicology: introduction, histor- ical perspective, and context. In Microscale testing in Aquatic Toxicology Advances, Techniques and Practice; Wells, P., Lee, K., Blaise, C., Eds.; CRC Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C.; Forghani, R.; Legault, R.; Guzzo, J.; Dubow, M. A bacterial toxicity assay per- formed with microplates, microluminome- try and MicrotoxR reagent. Biotechniques 1994, 16, 932–937. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Validation of the rain- bow trout hepatocyte model for the ecotox- icity evaluation of industrial wastewaters. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 1997, 12, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.R.; Mitchell, E. Catch history and initial population of white whales, Delphinapterus leucas, in the River and Gulf of St-Lawrence, Eastern Canada. Le Naturaliste Canadien 1984, 111, 63–121. [Google Scholar]
- Martineau, D. Beluga whales and ecotoxic- ity. In Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology. Vol. I-II; Férard, J.F., Blaise, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, 2013; pp. 151–168. [Google Scholar]
- Costan, G.; Bermingham, N.; Blaise, C.; Férard, J.F. Potential ecotoxic effects probe (PEEP): a novel index to assess and com- pare the toxic potential of industrial efflu- ents. Environ Toxicol Water Qual 1993, 8, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Férard, J.F. Effluent assessment with the PEEP (potential ecotoxic effects probe) index. In Small-scale freshwater toxicity investiga- tions. Vol. 2; Blaise, C., Férard, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, 2005; pp. 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Thériault, F. La réduction des rejets liq- uides toxiques des 50 établissements industriels prioritaires du Plan d’action Saint-Laurent, Rapport-synthèse 1988-1995. Environnement Canada, Montréal, région du Québec, Direction de la protec- tion de l’environnement / Ministère de l’Environnement et de la Faune du Québec, Direction régionale de la Montérégie. Saint-Laurent Vision 2000 – volet Protection; 1996. 12 pp + tables and appendices.
- Gosselin, J.F.; Hammill, M.; Lesage, V. Comparison of photographic and visual abundance indices of belugas in the St. Lawrence Estuary in 2003 and 2005. C. S. A. S. C. S. A. Report 2007; Secretariat. Mont-Joli: Maurice Lamontagne Institute; 2007.
- Bombardier, M.; Blaise, C. Comparative study of the sediment toxicity index, ben- thic community metrics and contaminant concentrations. Water Qual Res J Canada 2000, 4, 753–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardier, M. Développement d’outils écotoxicologiques pour l’évaluation de sédiments. Doctoral thesis, Université Paul Verlaine, Metz, France. [In French].
- Depledge, M.H.; Amaral-Mendes, J.J.; Daniel, B.; Halbrook, R.S.; Loepper-Sams, P.; Moore, M.N.; et al. The conceptual basis of the bio- marker approach. In Biomarkers: research and applica- tion in the assessment of environmental health. Vol. 68; Peakall, D.B., Shugart, L.R., Eds.; NATO ASI Series H: Cell Biology. Berlin: Springer Verlag; 1993. pp 15-29.
- Lagadic, L.; Caquet, T.; Amiard, J.C.; Ramade, F. (Eds.) . Biomarqueurs en écotoxicologie. Aspects fondamentaux. Collection Écolo- gie; Masson: Paris, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Benford, D.J.; Hanley, A.B.; Bottrill, K.; Oehlschlager, S.; Balls, M.; Branca, F. , et al. Biomarkers as predictive tools in toxicity testing. The Report and Recommendations of ECVAM Workshop 40. ATLA 2000, 28, 119–131. [Google Scholar]
- Hébert N, Gagné F, Cejka P, Bouchard B, Hausler R, Cyr DG, et al. Effects of ozone, ultraviolet and peracetic acid disinfection of a primary-treated municipal effluent on the Immune system of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 2008, 148, 122–127. [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; André, C.; Cejka, P.; Blaise, C.; Hausler, R. Reduction of alkali-labile phos- phates in mussels exposed to primary- treated wastewaters undergoing ozone and ultraviolet disinfection: a pilot study. Water Qual Res J Canada 2009, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Marcogliese, D.; Pietrock, M. Combined effects of parasites and contaminants on animal health: parasites do matter. Trends Parasitol 2011, 27, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roch, M.; McCarter, J.A. Hepatic metalloth- ionein production and resistance to heavy metals by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) Exposed to an artificial mixture of zinc, copper and cadmium. Comp Biochem Physiol C 1984, 77, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, P.D.; Addison, R.F. The use of mixed function oxidases (MFO) to support bio- logical effects monitoring in the sea. ICES CM/E1990; 33; International Council for the Exploration of the Sea (ICES): Copenhagen, 1190. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C.; Pellerin, J.; Fournier, M.; Durand, M.J.; Talbot, A. Relationships between intertidal clam population and health status of the soft-shell clam Mya arenaria in the St. Lawrence Estuary and Saguenay Fjord (Québec, Canada). Environment Intern 2008, 34, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné F, Blaise C, Pellerin J, Fournier M, Gagnon C, Sherry J, et al. Impacts of pollu- tion in feral Mya arenaria populations: The effects of clam bed distance from the shore. Sci Total Environ 2009, 407, 5844–5854. [CrossRef]
- Dagnino A, Sforzini S, Dondero F, Fenoglio S, Bona E, Jensen J, et al. ‘Weight-of-evi- dence’ approach for the integration of environmental ‘triad’ data to assess eco- logical risk and biological vulnerability. Integrat Environ Assess Manag 2008, 4, 314–326. [CrossRef]
- Isani, G.; Andreani, G.; Kindt, M.; Carpene, E. Metallothioneins (MTs) in marine mol- luscs. Cell Molec Biol 2000, 46, 311–330. [Google Scholar]
- Binelli, A.; Ricciardi, F.; Riva, C.; Provini, A. New evidences for old biomarkers: effects of several xenobiotics on EROD and AChE activities in Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Chemosphere 2005, 62, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C.; André, C. Occurrence of pharmaceutical products in a municipal effluent and toxicity to rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatocytes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 2008, 64, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné F, Douville M, André C, Debenest T, Talbot A, Sherry J, et al. Differential changes in gene expression in rainbow trout hepatocytes exposed to extracts of oil sands process-affected water and the Athabasca River. Comp Biochem Physiol C 2012, 155, 551–559.
- Quinn B, Schmidt W, O’Rourke K, Hernan, R. Effects of the pharmaceuticals gemfi- brozil and diclofenac on biomarker expres- sion in the zebra mussel (Dreissena poly- morpha) and their comparison with stan- dardised toxicity tests. Chemosphere 2012, 84, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Black MC, Ferrell JR, Horning RC, Martin LK. DNA strand breakage in freshwater mussels (Anodonta grandis) exposed to lead in the laboratory and field. Environ Toxicol Chem 1996, 15, 802–808. [CrossRef]
- Burgeot, T.; Woll, S.; Galgani, F. Evaluation of the micronucleus test on Mytilus gallo- provincialis for monitoring applications along the French coast. Mar Poll Bull 1996, 32, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesi, L.; Gallo, G.; Gavioli, M.; Pruzzo, C. Bacteria-hemocyte interactions and phagocytosis in marine bivalves. Microsc Res Techn 2002, 15, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Trottier, S.; Gagné, F.; Lallement, C.; Hansen, P.-D. Immunocompetence of bivalve hemocytes by a miniaturized phagocytosis assay. Environ Toxicol 2002, 17, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C.; Salazar, S.; Hansen, P.D. Evaluation of estrogenic effects of munici- pal effluents to the freshwater mussel Elliptio complanata. Comp Biochem Physiol-Part C: Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 2001, 128, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, M. Utilization of aspartate tran- scarbamylase activity in the study of neu- roendocrinal control of gametogenesis in Mytilus edulis. J Explor Biol 1987, 241, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Solé, M.; Shaw, J.P.; Frickers, P.E.; Readman, J.W.; Hutchinson, T.H. Effects on feeding rate and biomarker responses of marine mus- sels experimentally exposed to propranolol and acetaminophen. Anal Bioanal Chem 2010, 396, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, M.C.; Castagna, M. Serotonin as an inducer of spawning in six bivalve species. Aquaculture 1984, 40, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, M.; Matsutami, T.; Nomura, T. Implication of catecholamines during spawning in marine bivalve molluscs. Intern J Invertebr Repr Dev 1987, 12, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Salazar, M.; Salazar, S.; Trottier, S.; Hansen, P.-D. Experimentally- induced feminisation of freshwater mus- sels after long-term exposure to a munici- pal effluent. Fresenius Environ Bull 2003, 12, 865–870. [Google Scholar]
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Pellerin, J. Bivalve popu- lation status and biomarker responses in Mya arenaria clams (Saguenay Fjord, Québec, Canada). Fresenius Environ Bull 2003, 12, 956–960. [Google Scholar]
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C. Immunotoxic effects of selected pharmaceutical products and municipal effluents to Elliptio complanata hemocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol C 2006, 143, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Holeton, C.; Chambers, P.A.; Grace, L. Wastewater release and its impacts on Canadian waters. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 2011, 68, 1836–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kestemont, P.; Depiereux, S. Sewage treat- ment plant effluents and aquatic ecotoxi- cology. In: Férard JF, Blaise C, eds. Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology. Vol. I-II. Dordrecht: Springer; 2013. pp 1047-1062.
- Salazar, M.H.; Salazar, S.M. Standard guide for conducting in situ field bioassays with marine, estuarine and freshwater bivalves, E2122-01. In: Annual book of ASTM standards. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM); 2001; P30.
- Gagné, F.; Blaise, C.; Pellerin, J.; Fournier, M. Etudes de biomarqueurs chez la mye com-mune (Mya arenaria) du fjord du Saguenay: bilan de recherches (1997 à 2006)/Biomarker studies of the soft-shell clam (Mya arenaria) in the Saguenay Fjord: research results (1997-2006). Rev Sci Eau 2009, 22, 253–259. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, S.F. A data-based perspective on the environmental risk assessment of Human pharmaceuticals I – collation of available ecotoxicity data. In: Kümmerer K, ed. Pharmaceuticals in the environment, sources, fate, effects and risks. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer; 2004. pp 317-361.
- Metcalfe, C.D.; Koenig, B.G.; Bennie, D.T.; Servos, M.; Ternes, T.A.; Hirsch, R. Occurrence of neutral and acidic drugs in the effluents of Canadian sewage treatment plants. Environ Toxicol Chem 2003, 22, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Eullaffroy, P.; Férard, J.F. Ecotoxicity of selected pharmaceuticals of urban origin discharged to the Saint- Lawrence River (Québec, Canada): a review. Braz J Aquat Sci Technol 2006, 10, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garric, J. Emerging issues in ecotoxicolo- gy: pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs). In: Férard JF, Blaise C, eds. Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology. Vol. I-II. Dordrecht: Springer; 2013. pp 407-427.
- Vernouillet, G.; Eullaffroy, P.; Lajeunesse, A.; Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Juneau, P. Toxic effects and bioaccumulation of carbamazepine evaluated by biomarkers measured in organisms of different trophic levels. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.N. Do nanoparticles present eco- toxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environ Intern 2006, 32, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovern, S.B.; Klaper, R. Daphnia magna mor- tality when exposed to titanium dioxide and fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 2006, 25, 1132–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, E.; Zhu, S.; Blickley McClellan- Green, P.; Haasch, M.L. Ecotoxicology of car- bon-based engineered nanoparticles: effects of fullerene (C-60) on aquatic organisms. Carbon 2006, 44, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma C, Sarkar S, Periyakaruppan A, Barr J, Wise K, Thomas R, et al. Single- walled carbon nanotubes induce oxidative stress in rat lung epithelial cells. J Nanosci Nanotech 2007, 7, 2466–2472. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, Meng H, Xing G, Chen C, Zhao Y, Jia G et al. Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Toxicol Lett 2006, 163, 109–120. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Meng, H.; Xing, G.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y. Toxicological and biological effects of nanoparticles. Int J Nanotech 2007, 4, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, Meng H, Xing G, Chen C, Zhao Y, Jia G et al. Acute toxicological effects of copper nanoparticles in vivo. Sci Total Environ 2007, 387, 155–165.
- Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Férard, J.F.; Eullaffroy, P. Ecotoxicity of selected nano-materials to aquatic organisms. Environ Toxicol 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.A.; Monteiro, R.T.R.; Blaise, C.; Gagné, F.; Bull, K.; Férard, J.F. Influence of sediment grain size on elutriate toxicity of inorgan- ic nano-materials. Water Qual Res J Canada 2009, 44, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; Gagnon, C.; Blaise, C. Aquatic nan- otoxicology: a review. Res Trends 2008, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kawata, K.; Osawa, M.; Okabe, S. In vitro tox- icity of silver nanoparticles at noncytotox- ic doses to HepG2 human hepatoma cells. Environ Sci Technol 2009, 43, 6046–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagné, F.; Maysinger, D.; André, C.; Blaise, C. Cytotoxicity of aged cadmium-telluride quantum dots to rainbow trout hepato- cytes. Nanotoxicol 2008, 2, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, B.P.; Neupane, K.P. Metallothioneins initiate semiconducting nanoparticle cel- lular toxicity. Small 2006, 2, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, A.-N.; Debenest, T.; Gagné, F. Dendrimers increase glyphosate formula- tion toxicity to Chlamydomonas rein- hardtii. Fresenius Environ Bull 2012, 21, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bulté, G.; Robinson, S.A.; Forbes, M.R.; Marcogliese, D.M. Is there such thing as a parasite free lunch? the direct and indirect consequences of eating invasive prey. EcoHealth 2012, 9, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha LPhoto-toxicity in ice In: Férard, J.F.; Blaise, C.; (Eds.). Encyclopedia of aquatic eco- toxicology. Vol. I-II. Dordrecht: Springer; 2013. pp 845-850.
- Breitholtz, M.; Ruden, C.; Hansson, S.O.; Bengtsson, B.E. Ten challenges for improved ecotoxicological testing in envi- ronmental risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety 2006, 63, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas J, Arts G, Babut M, Barra Caracciolo A, Charles S, Chaumot A, et al. Towards a renewed research agenda in ecotoxicology. Environ Poll 2012, 160, 201–206.
- Vindimian, E. Environmental research needs (in ecotoxicology) in relation to public policies. In: Férard JF, Blaise C, eds. Encyclopedia of aquatic ecotoxicology. Vol. I-II. Dordrecht: Springer; 2013. pp 437-442.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2013 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rault, P.; Fortier, M.; Pédelucq, J.; Lacaze, E.; Brousseau, P.; Auffret, M.; Fournier, M. Immunotoxicity of Heavy Metals (Silver, Cadmium, Mercury and Lead) on Marine Bivalve Mytilus edulis: In Vitro Exposure of Hemocytes. J. Xenobiot. 2013, 3, e8. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.s1.e8
Rault P, Fortier M, Pédelucq J, Lacaze E, Brousseau P, Auffret M, Fournier M. Immunotoxicity of Heavy Metals (Silver, Cadmium, Mercury and Lead) on Marine Bivalve Mytilus edulis: In Vitro Exposure of Hemocytes. Journal of Xenobiotics. 2013; 3(s1):e8. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.s1.e8
Chicago/Turabian StyleRault, P., M. Fortier, J. Pédelucq, E. Lacaze, P. Brousseau, M. Auffret, and M. Fournier. 2013. "Immunotoxicity of Heavy Metals (Silver, Cadmium, Mercury and Lead) on Marine Bivalve Mytilus edulis: In Vitro Exposure of Hemocytes" Journal of Xenobiotics 3, no. s1: e8. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.s1.e8
APA StyleRault, P., Fortier, M., Pédelucq, J., Lacaze, E., Brousseau, P., Auffret, M., & Fournier, M. (2013). Immunotoxicity of Heavy Metals (Silver, Cadmium, Mercury and Lead) on Marine Bivalve Mytilus edulis: In Vitro Exposure of Hemocytes. Journal of Xenobiotics, 3(s1), e8. https://doi.org/10.4081/xeno.2013.s1.e8




