Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Drug Release of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs of Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of Drug-Containing Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs)
2.3. Drug Release from Drug-Containing LDHs
2.4. Characterisations
2.5. Computational Simulation
3. Results and Discussion
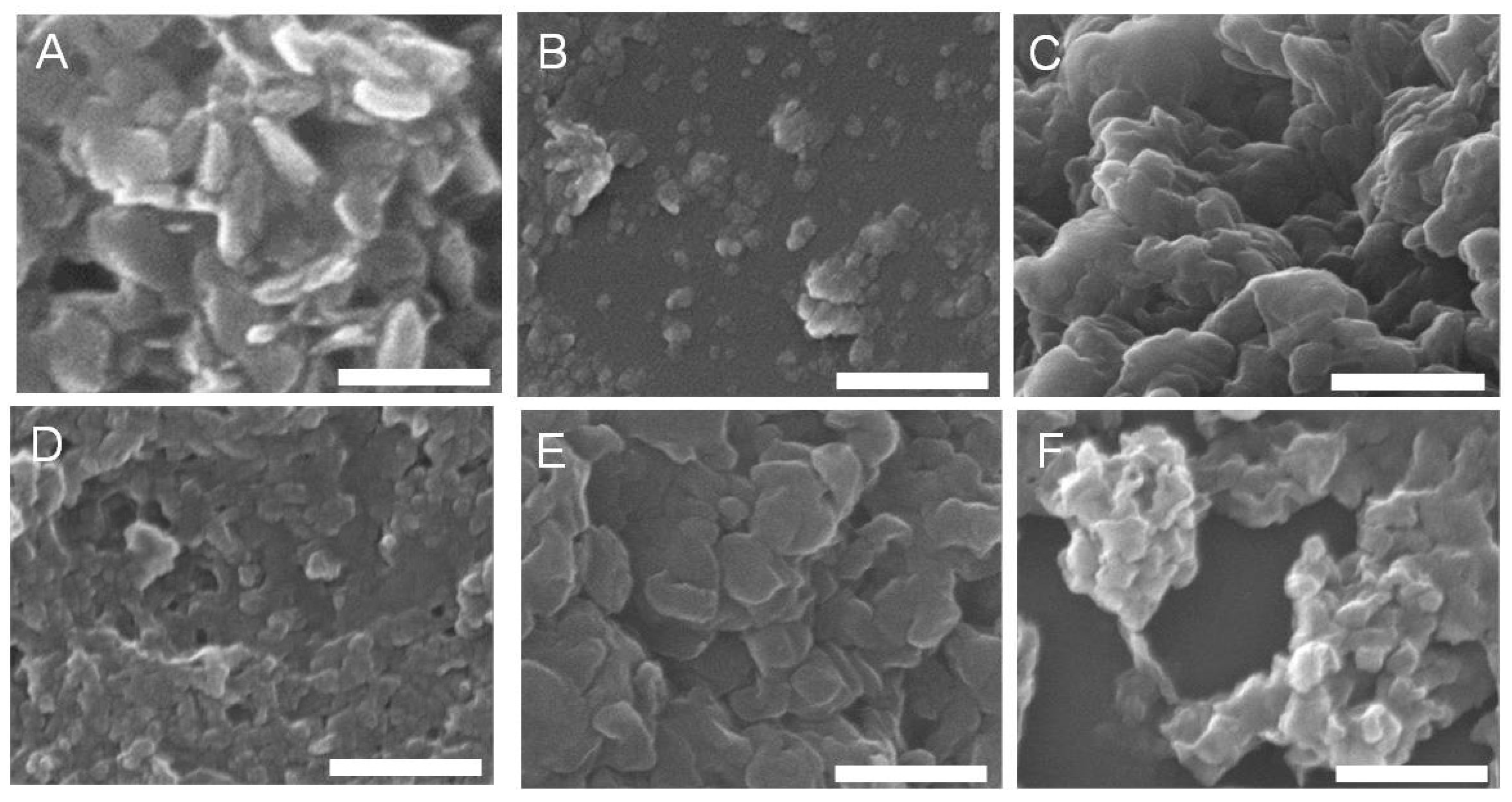
3.1. LDH–Drug Particle Size
| Sample | Source of data | HT (nm) | FP (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDH–NAP | DLS | 332 ± 36/0.19 ± 0.04 | 172 ± 12/0.26 ± 0.02 |
| SEM | 230 ± 60 | 58 ± 22 * | |
| LDH–DIC | DLS | 194 ± 11/0.28 ± 0.02 | 159 ± 18/0.20 ± 0.02 |
| SEM | 168 ± 34 | 54 ± 13 * | |
| LDH–IBU | DLS | 342 ± 14/0.09 ± 0.00 | 272 ± 44/0.25 ± 0.06 |
| SEM | 270 ± 71 | 88 ± 19 * |
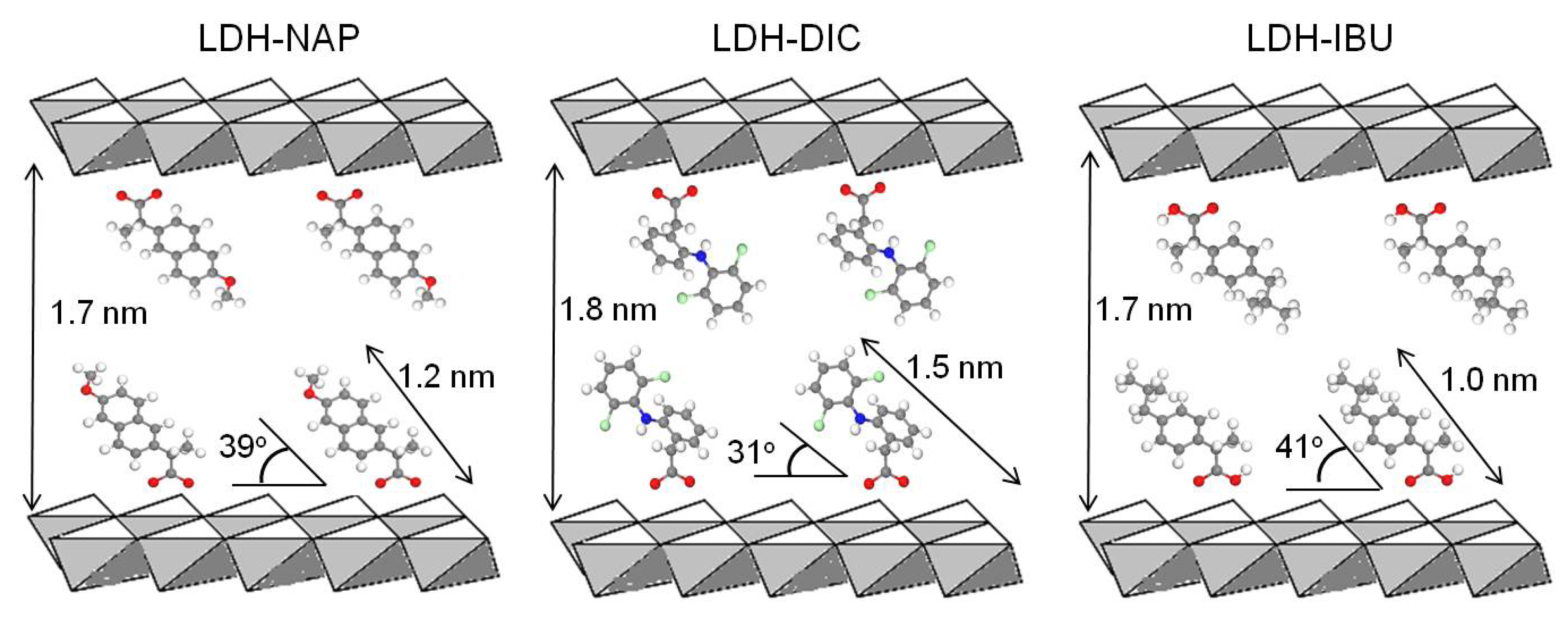
3.2. LDH–Drug Structure and Composition

| Sample | FWHM (003) (°) | d003 (nm) | d006 (nm) | d009 (nm) | d spacing (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH–NAP–HT | 0.46 | 2.10 | 1.06 | 0.71 | 2.12 |
| LDH–NAP–FP | 0.88 | 2.16 | 1.09 | 0.74 | 2.19 |
| LDH–DIC–HT | 0.50 | 2.24 | 1.13 | 0.76 | 2.26 |
| LDH–DIC–FP | 0.80 | 2.23 | 1.12 | 0.76 | 2.25 |
| LDH–IBU–HT | 0.48 | 2.12 | 1.08 | 0.72 | 2.15 |
| LDH–IBU–FP | 0.76 | 2.10 | 1.09 | 0.71 | 2.14 |
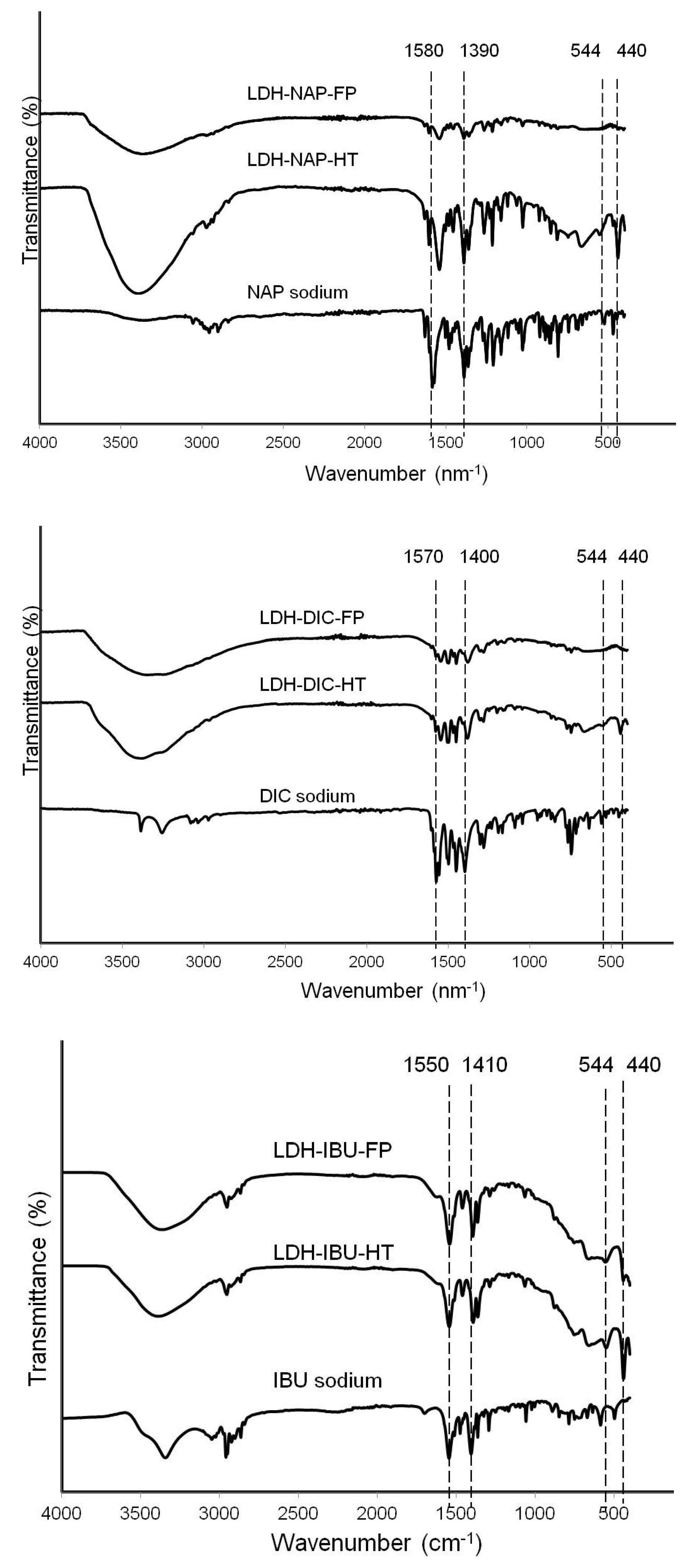
| Sample | Mg (wt%) | Al (wt%) | N (wt%) | C (wt%) | H (wt%) | Mg/Al molar ratio | Drug loading capacity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH–NAP–HT | 10.2 | 6.26 | 0 | 36.5 | 5.09 | 1.81 | 42.1 |
| LDH–NAP–FP | 7.75 | 4.10 | 0 | 32.0 | 4.89 | 2.10 | 39.0 |
| LDH–DIC–HT | 11.0 | 5.75 | 2.44 | 32.1 | 4.04 | 2.12 | 45.9 |
| LDH–DIC–FP | 7.51 | 3.85 | 2.98 | 31.4 | 3.88 | 2.17 | 45.4 |
| LDH–IBU–HT | 11.1 | 6.98 | 0 | 33.0 | 6.10 | 1.76 | 47.4 |
| LDH–IBU–FP | 10.4 | 5.97 | 0 | 34.3 | 6.05 | 1.93 | 41.1 |
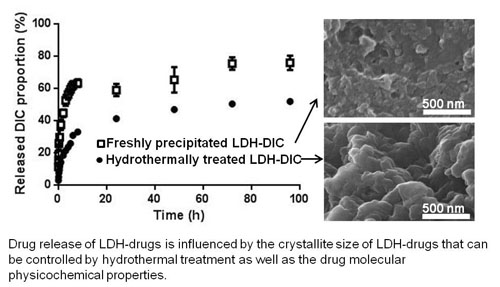
3.3. Drug Release Behaviours

| Sample | T50 (h) | T90 (h) | log P of drug | Molecular weight of drug |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH–NAP–HT | 2.5 | 8 | 3.2 | 230 |
| LDH–NAP–FP | 6 | 15 | ||
| LDH–DIC–HT | >96 | >96 | 4.75 | 295 |
| LDH–DIC–FP | 56 | >96 | ||
| LDH–IBU–HT | 1 | 48 | 3.5 | 206 |
| LDH–IBU–FP | 0.5 | 1 |
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Braterman, P.S.; Xu, Z.P.; Yarberry, F. Handbook of Layered Materials; Auerbach, S.M., Carrado, K.A., Dutta, P.K., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 373–474. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.P.; Lu, G.Q. Layered double hydroxide nanomaterials as potential cellular drug delivery agents. Pure Appl. Chem. 2006, 78, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.P.; Zeng, Q.H.; Lu, G.Q.; Yu, A.B. Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers for efficient cellular delivery. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Niebert, M.; Porazik, K.; Walker, T.L.; Cooper, H.M.; Middelberg, A.P.J.; Gray, P.P.; Bartlett, P.F.; Lu, G.Q. Subcellular compartment targeting of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2008, 130, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Barua, S.; Sharma, G.; Dey, S.K.; Rege, K. Inorganic nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy. J. Control. Release 2011, 155, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Qin, L.L.; Wang, W.R.; Zhu, R.R.; Yu, Y.C.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.L. The use of layered double hydroxides as DNA vaccine delivery vector for enhancement of anti-melanoma immune response. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.M.; Park, M.; Kim, S.T.; Jung, J.Y.; Kang, Y.G.; Choy, J.H. Efficient delivery of anticancer drug MTX through MTX–LDH nanohybrid system. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Rolfe, B.E.; Xu, Z.P.; Thomas, A.C.; Campbell, J.H.; Lu, G.Q. Enhanced effects of low molecular weight heparin intercalated with layered double hydroxide nanoparticles on rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5455–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Thomas, A.C.; Xu, Z.P.; Campbell, J.H.; Lu, G.Q. In vitro sustained release of LMWH from MgAl-layered double hydroxide nanohybrids. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Rolfe, B.E.; Thomas, A.C.; Campbell, J.H.; Lu, G.Q.; Xu, Z.P. Cellular trafficking of low molecular weight heparin incorporated in layered double hydroxide nanoparticles in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7234–7240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Rolfe, B.E.; Xu, Z.P.; Campbell, J.H.; Lu, G.Q.; Thomas, A.C. Antibody-targeted drug delivery to injured arteries using layered double hydroxide nanoparticles. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonina, F.P.; Giannossi, M.L.; Medici, L.; Puglia, C.; Summa, V.; Tateo, F. Diclofenac-hydrotalcite: In vitro and in vivo release experiments. Appl. Clay Sci. 2008, 41, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriazo, D.; del Arco, M.; Martin, C.; Ramos, C.; Rives, V. Influence of the inorganic matrix nature on the sustained release of naproxen. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2010, 130, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Arco, M.; Gutierrez, S.; Martin, C.; Rives, V.; Rocha, J. Synthesis and characterization of layered double hydroxides (LDH) intercalated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 3954–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.X.; He, J.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Inorganic layered double hydroxides as a drug delivery system-intercalation and in vitro release of fenbufen. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 27, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Stevenson, G.; Lu, C.Q.; Lu, G.Q. Dispersion and size control of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles in aqueous solutions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16923–16929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labajos, F.M.; Rives, V.; Ulibarri, M.A. Effect of hydrothermal and thermal treatments on the physicochemical properties of Mg–Al hydrotalcite-like materials. J. Mater. Sci. 1992, 27, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, W.; Sham, L.J. Self-consistent equations including exchange and correlation effects. Phys. Rev. 1965, 140, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Ernzerhof, M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 3865–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delley, B. An all-electron numerical method for solving the local density functional for polyatomic molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1990, 92, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delley, B. From molecules to solids with the DMol(3) approach. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 113, 7756–7764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Stevenson, G.S.; Lu, C.Q.; Lu, G.Q.; Bartlett, P.F.; Gray, P.P. Stable suspension of layered double hydroxide nanoparticles in aqueous solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Musumeci, A.W.; Xu, Z.P.; Smith, S.V.; Minchin, R.F.; Martin, D.J. Layered double hydroxide nanoparticles incorporating terbium: Applicability as a fluorescent probe and morphology modifier. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 111–120. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.P.; Braterman, P.S. Synthesis, structure and morphology of organic layered double hydroxide (LDH) hybrids: Comparison between aliphatic anions and their oxygenated analogs. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 48, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, P.; Xu, R. Direct control of drug release behavior from layered double hydroxides through particle interactions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4367–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Shi, S.X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Duan, X. Studies on the intercalation of naproxen into layered double hydroxide and its thermal decomposition by in situ FT-IR and in situ HT-XRD. J. Solid State Chem. 2004, 177, 2534–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Fardella, G.; Grandolini, G.; Perioli, L.; Tiralti, M.C. Intercalation compounds of hydrotalcite-like anionic clays with anti-inflammatory agents, II: Uptake of diclofenac for a controlled release formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2002, 3, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Perioli, L.; Posati, T.; Nocchetti, M.; Bellezza, F.; Costantino, U.; Cipiciani, A. Intercalation and release of antiinflammatory drug diclofenac into nanosized ZnAl hydrotalcite-like compound. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, U.; Ambrogi, V.; Nocchetti, M.; Perioli, L. Hydrotalcite-like compounds: Versatile layered hosts of molecular anions with biological activity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 107, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogi, V.; Fardella, G.; Grandolini, G.; Perioli, L. Intercalation compounds of hydrotalcite-like anionic clays with antiinflammatory agents—I. Intercalation and in vitro release of ibuprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 220, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drezdzon, M.A. Synthesis of isopolymetalate-pillared hydrotalcite via organic-anion-pillared precursors. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 4628–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, Z.; Sarkarat, M. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic composites: Intercalation of naproxen into Mg–Al layered double hydroxides coated on Fe3O4. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2012, 638, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Lei, L.X.; Norquist, A.J.; O’Hare, D. Intercalation and controlled release of pharmaceutically active compounds from a layered double hydroxide. Chem. Commun. 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, A.; Fazio, G.; Feroci, G. Solubility and solubilization properties of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 126, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Paavola, A.; Yliruusi, J.; Rosenberg, P. Controlled release and dura mater permeability of lidocaine and ibuprofen from injectable poloxamer-based gels. J. Control. Release 1998, 52, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.P.; Braterman, P.S. High affinity of dodecylbenzene sulfonate for layered double hydroxide and resulting morphological changes. J. Mater. Chem. 2003, 13, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamura, A.; Jones, M.I.; Kanezaki, E.; Metson, J.B. Complete desporption of interlayer hydrogen phosphate in Mg/Al-layered double hydroxides by means of anion exchange with 1-octanesulfonate. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, Z.; Wu, A.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.P. Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Drug Release of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs of Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 235-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics6020235
Gu Z, Wu A, Li L, Xu ZP. Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Drug Release of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs of Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics. 2014; 6(2):235-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics6020235
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Zi, Aihua Wu, Li Li, and Zhi Ping Xu. 2014. "Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Drug Release of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs of Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles" Pharmaceutics 6, no. 2: 235-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics6020235
APA StyleGu, Z., Wu, A., Li, L., & Xu, Z. P. (2014). Influence of Hydrothermal Treatment on Physicochemical Properties and Drug Release of Anti-Inflammatory Drugs of Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxide Nanoparticles. Pharmaceutics, 6(2), 235-248. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics6020235