3D-Printed Oral Disintegrating Films of Brain-Targeted Acetyl Salicylic Acid Nanoparticles for Enhanced CNS Delivery in Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
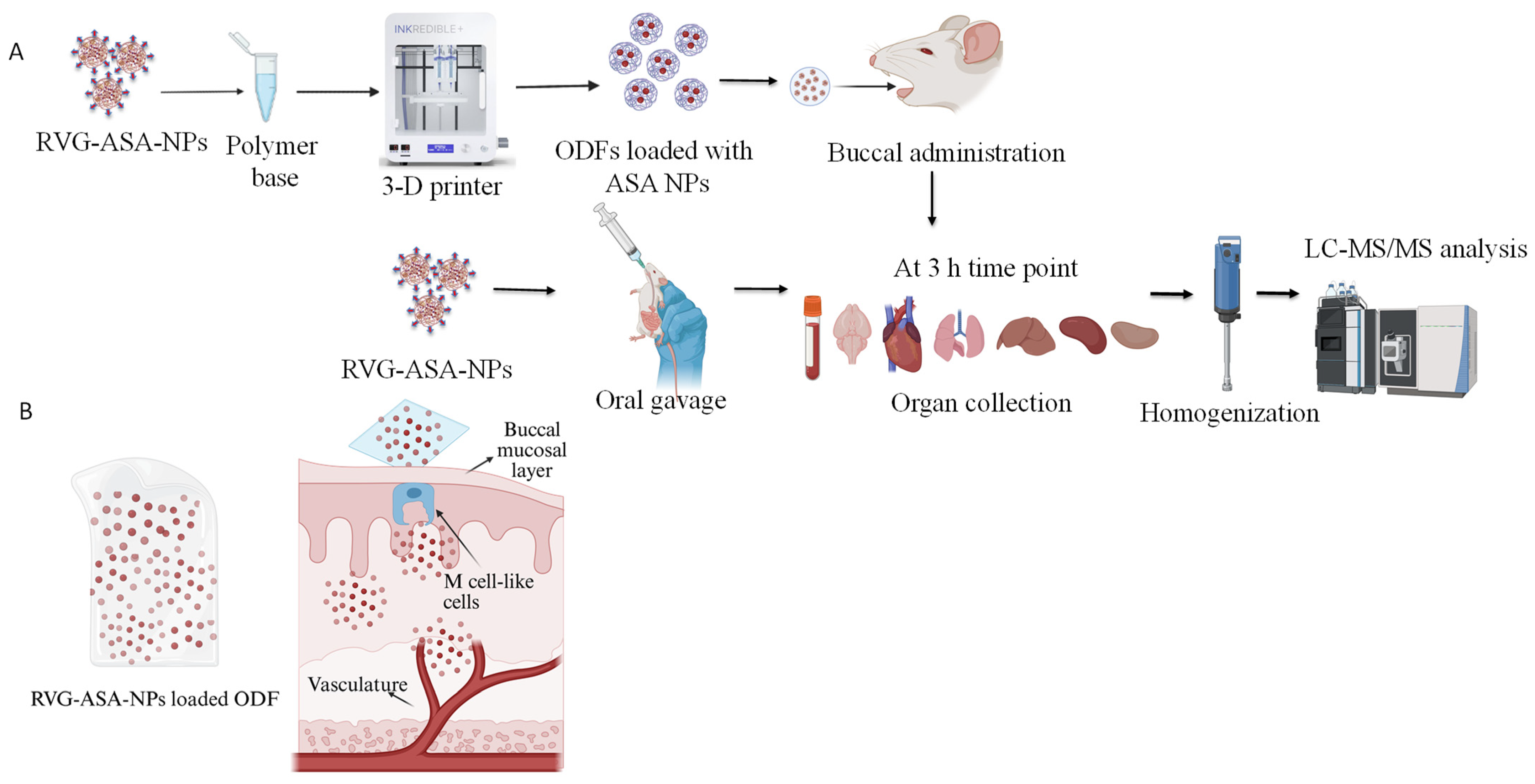
2.2. Formulation of RVG-ASA-NPs Using a 5-Input Chip-Based Microfluidics System
2.3. Formulation of ASA Nanoparticles Loaded Oral Dissolving Films Using 3-D Bioprinter
2.4. Characterization of Oral Dissolving Films Containing ASA Nanoparticles
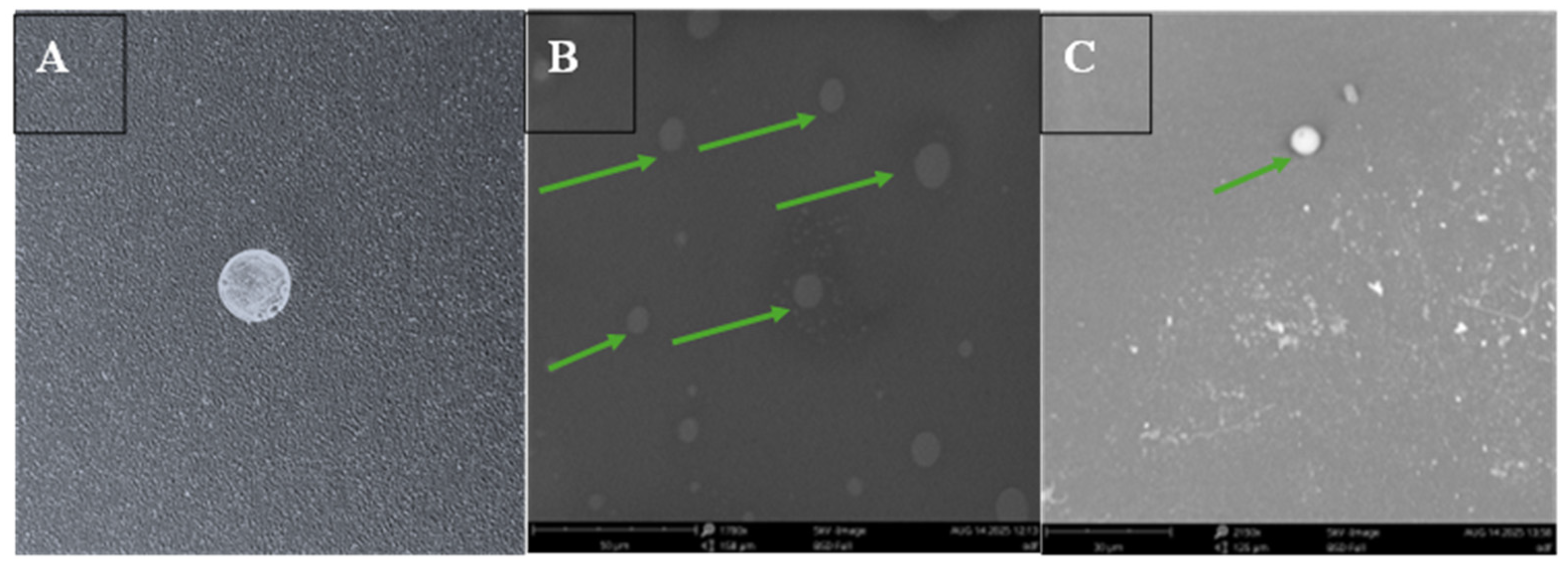
2.4.1. Morphological Evaluation of the ASA NP-Loaded Oral Dissolving Films
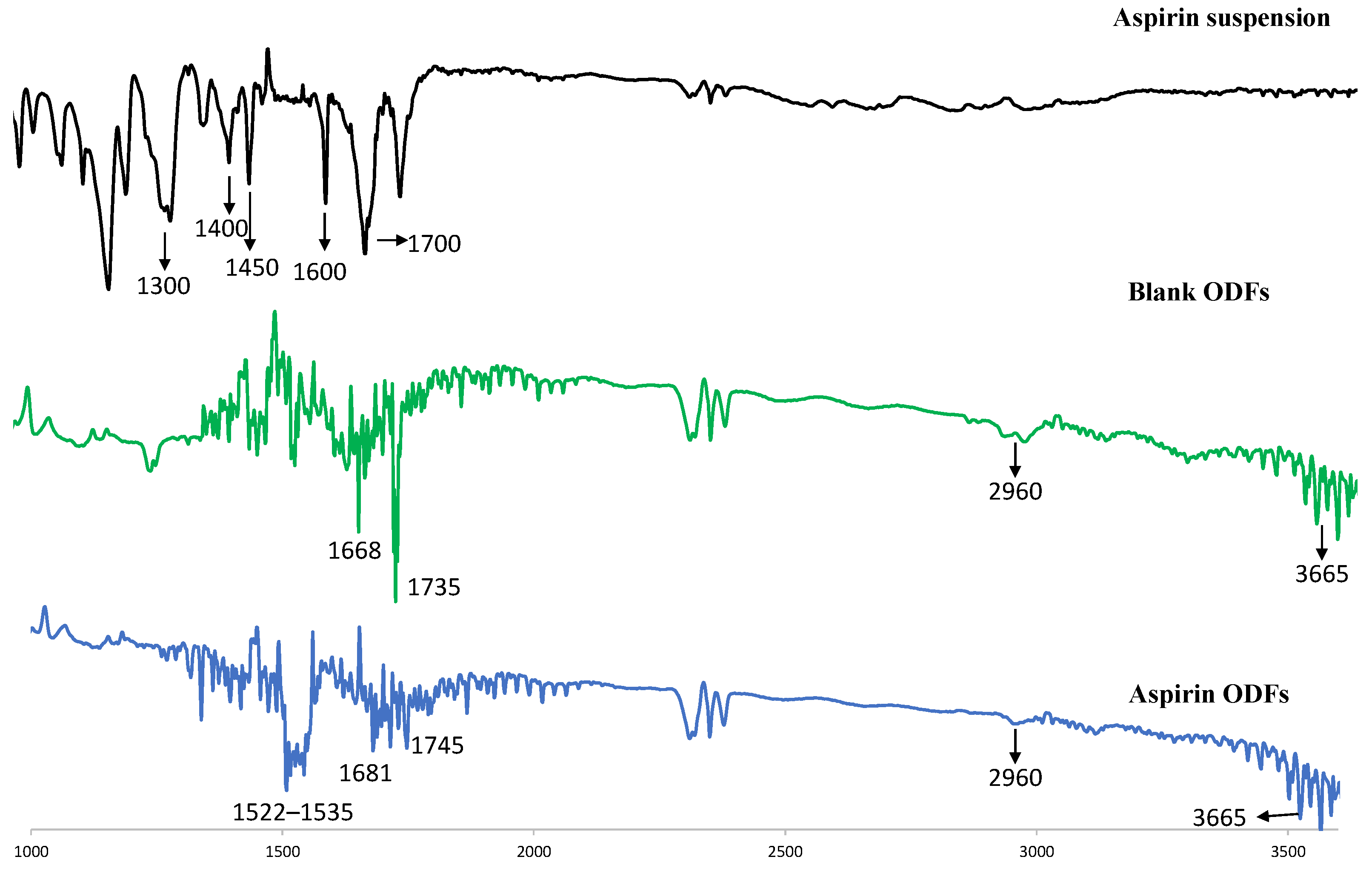
2.4.2. Evaluation of Oral Dissolving Films Containing ASA Nanoparticles Using Fourier Transform Infrared Microscopy (FTIR)
2.4.3. Physicochemical Characterization
Weight Variation and Diameter
Diameter
Average Thickness of the Film
Surface pH of the ODFs
Disintegration Test
Tensile Strength
Swelling Index
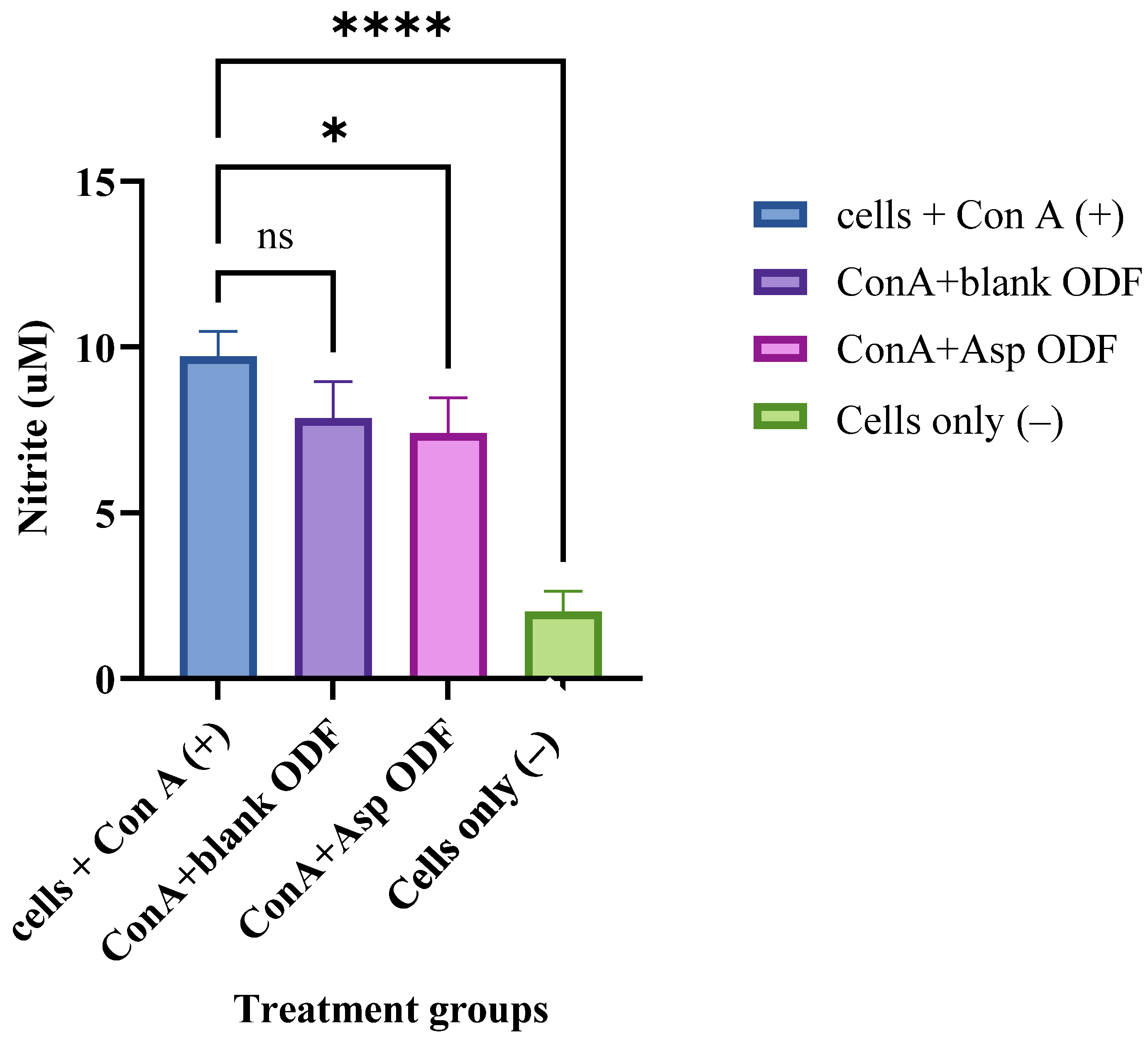
2.4.4. Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the ASA NPs in ODFs
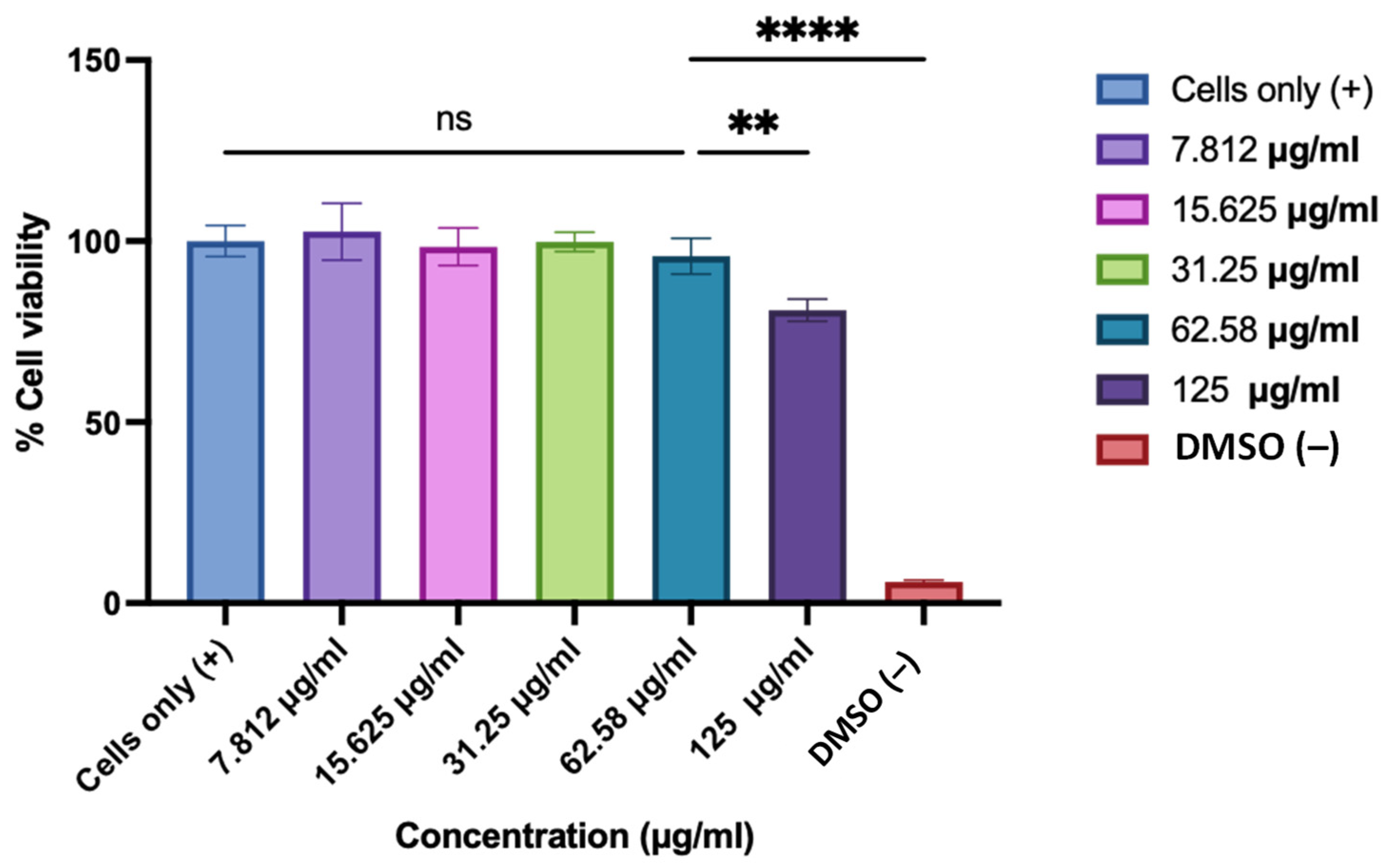
2.4.5. Determination of Cytotoxicity of the ASA NP-Loaded ODFs Using BEND3 Cells
2.4.6. Tracking Study Using Indocyanine Green (ICG) Encapsulated BSA Nanoparticles Conjugated with Brain Targeting Ligand RVG, Loaded ODFs to Evaluate the Drug Delivery via Buccal Delivery
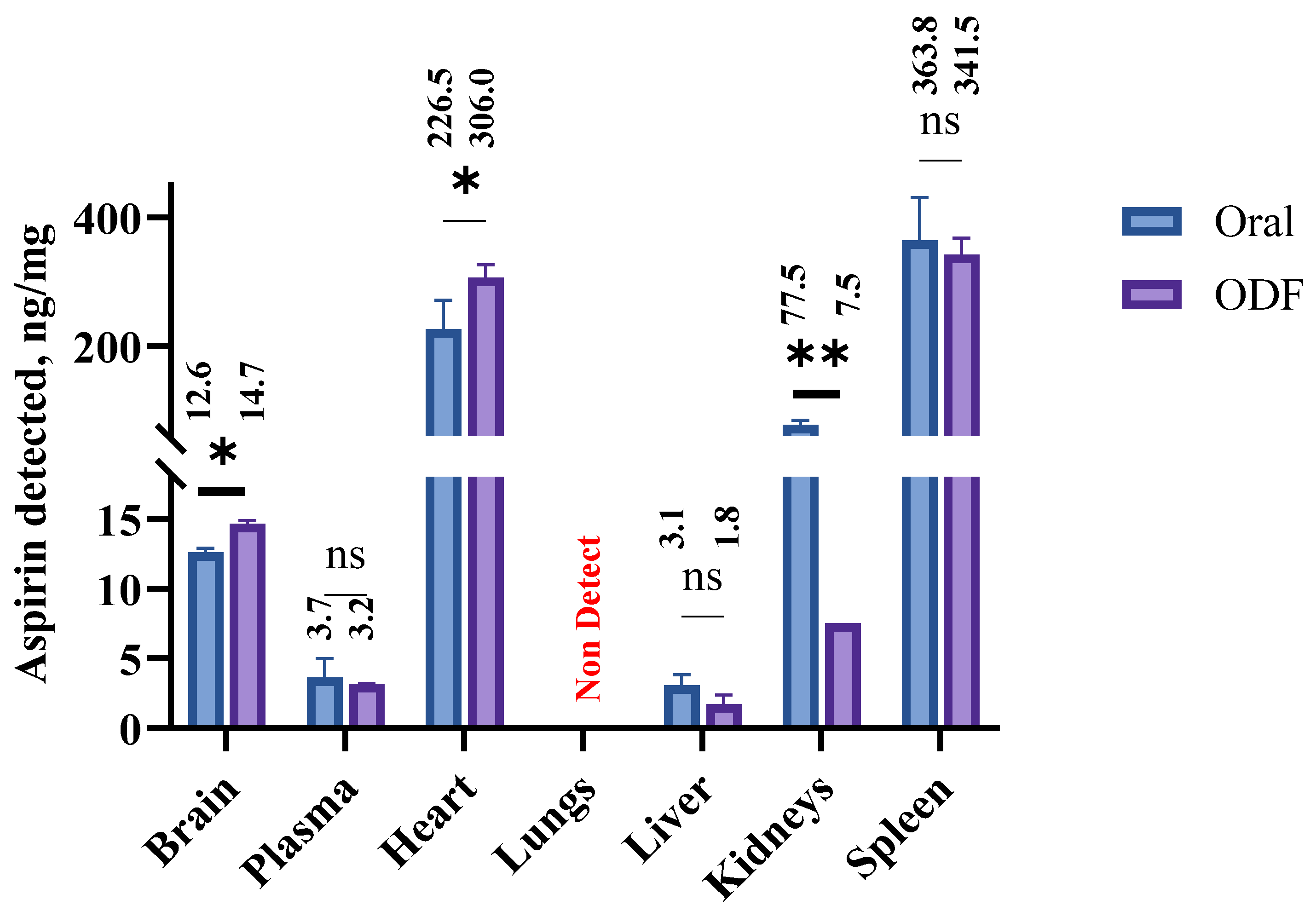
2.4.7. Assessment of Biodistribution of ASA in Mice Tissues Following Buccal Delivery of Oral Disintegrating Films
2.4.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Formulation of ASA NP-Loaded with Oral Dissolving Films
3.2. Physical Characterization of ASA NP-Loaded ODFs
Morphological Examination of the ODFs Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.3. FTIR
3.4. Physicochemical Evaluation of the Oral Dissolving Films
3.5. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the ASA Nanoparticles ODFs
3.6. Evaluation of the Toxicity of the ASA NP-Loaded ODFs Using MTT Assay
3.7. ICG Tracking Study to Evaluate the Nanoparticle Delivery to the Brain Using Bioimager in a Murine Model
3.8. Quantitative Determination of the Biodistribution of ASA upon Buccal Administration in a Murine Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Q.; Fu, Y.; Kao, W.J.; Janigro, D.; Yang, H. Transbuccal Delivery of CNS Therapeutic Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vitro Permeation Studies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaei, S.; Omidian, H. Mucoadhesion and Mechanical Assessment of Oral Films. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 159, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.V.; Cabrera, P.; Ramírez-Lecaros, C.; Jara, M.O.; Brayden, D.J.; Morales, J.O. Buccal delivery of small molecules and biologics: Of mucoadhesive polymers, films, and nanoparticles—An update. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 636, 122789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Weyers, M.; Steenekamp, J.H.; Steyn, J.D.; Gouws, C.; Hamman, J.H. Drug Bioavailability Enhancing Agents of Natural Origin (Bioenhancers) that Modulate Drug Membrane Permeation and Pre-Systemic Metabolism. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Hamid, H.M.; Darwish, Z.E.; Elsheikh, S.M.; Mourad, G.M.; Donia, H.M.; Afifi, M.M. Following cytotoxic nanoconjugates from injection to halting the cell cycle machinery and its therapeutic implications in oral cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivard, A.B.; Kortz, M.W.; Burns, B. Anatomy, Head and Neck: Internal Jugular Vein. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; An, S.; Li, J.; Kuang, Y.; He, X.; Guo, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, B.; Jiang, C. Brain-targeted co-delivery of therapeutic gene and peptide by multifunctional nanoparticles in Alzheimer’s disease mice. Biomaterials 2016, 80, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakka, L.R.J.; Chede, S. 3D printing of pharmaceuticals for disease treatment. Front. Med. Technol. 2022, 4, 1040052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Orlu, M.; Woerdenbag, H.J.; Scarpa, M.; Kiefer, O.; Kottke, D.; Sjöholm, E.; Öblom, H.; Sandler, N.; Hinrichs, W.L.J.; et al. Oromucosal films: From patient centricity to production by printing techniques. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.A.M.; Goz, A.; Voronov, R. Geometrical Modifications for Reliable 3D Printing of Microvalves in Multi-Plane Microfluidic Devices. engrXiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, M.; Petrović, M.; Cvijić, S.; Tomić, N.; Stojanović, D.; Ibrić, S.; Uskoković, P. 3D Printed Buccal Films for Prolonged-Release of Propranolol Hydrochloride: Development, Characterization and Bioavailability Prediction. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozon, E.A.; Sarbu, I.; Popovici, V.; Mitu, M.A.; Musuc, A.M.; Karampelas, O.; Velescu, B.S. Three-Dimensional Printing Technologies in Oral Films Manufacturing—A Minireview. Processes 2023, 11, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, L.; Liu, F.; Kerai-Varsani, L.; Okwuosa, T.C. Buccal films: A review of therapeutic opportunities, formulations & relevant evaluation approaches. J. Control. Release 2022, 352, 1071–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Patel, P.; Ferguson, A.; Bagwe, P.; Kale, A.; Adediran, E.; Singh, R.; Arte, T.; Pasupuleti, D.; Uddin, M.; et al. Buccal Administration of a Zika Virus Vaccine Utilizing 3D-Printed Oral Dissolving Films in a Mouse Model. Vaccines 2024, 12, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, P.D.; Durai, R.D.; Veluri, S.; B Narayanan, V.H. Semisolid extrusion 3D printing of Dolutegravir-Chitosan nanoparticles laden polymeric buccal films: Personalized solution for pediatric treatment. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 19, 025046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zong, M.; Suo, C.; Man, Q.; Xiong, L. Global Burden, Risk Factor Analysis, and Prediction Study of Ischemic Stroke, 1990–2030. Neurology 2023, 101, e137–e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.S.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Barone Gibbs, B.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; et al. 2024 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics: A Report of US and Global Data From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 149, e347–e913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Koh, Y.; Choi, H.A.; Lee, K. Critical care for patients with massive ischemic stroke. J. Stroke 2014, 16, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, D.; Tao, W.; Dong, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, M. Early consciousness disorder in acute ischemic stroke: Incidence, risk factors and outcome. BMC Neurol. 2016, 16, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.C.; Amarenco, P.; Denison, H.; Evans, S.R.; Himmelmann, A.; James, S.; Knutsson, M.; Ladenvall, P.; Molina, C.A.; Wang, Y. Ticagrelor and Aspirin or Aspirin Alone in Acute Ischemic Stroke or TIA. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansara, A.J.; Nisly, S.A.; Arif, S.A.; Koehler, J.M.; Nordmeyer, S.T. Aspirin Dosing for the Prevention and Treatment of Ischemic Stroke: An Indication-Specific Review of the Literature. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhajj, L.; Ovenseri Airemwen, C.; Pozharani, L.B. Formulation of aspirin nanoparticles using solvent evaporation method and in vivo evaluation of its antithrombotic effect. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 36, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tung, Y.-T.; Wei, C.-H.; Yen, C.-C.; Lee, P.-Y.; Ware, L.B.; Huang, H.-E.; Chen, W.; Chen, C.-M. Aspirin Attenuates Hyperoxia-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) by Suppressing Pulmonary Inflammation via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 793107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorani, R.; Bhatt, A.N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, U.N. COX-2, aspirin and metabolism of arachidonic, eicosapentaenoic and docosahexaenoic acids and their physiological and clinical significance. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 785, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.; Sangha, K.S.; Khatri, P. Drug treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2013, 13, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazali, H.S.; Askari, E.; Seyfoori, A.; Naghib, S.M. A high-absorbance water-soluble photoinitiator nanoparticle for hydrogel 3D printing: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, C.; Song, I.-O.; Lee, B.-J.; Kang, C.-Y.; Park, J.-B. Investigation of Patient-Centric 3D-Printed Orodispersible Films Containing Amorphous Aripiprazole. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarpa, M.; Paudel, A.; Kloprogge, F.; Hsiao, W.K.; Bresciani, M.; Gaisford, S.; Orlu, M. Key acceptability attributes of orodispersible films. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 125, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grilc, B.; Felicijan, T.; Parfant, T.P.; Planinšek, O. Formulation and Characterization of Buccal Films Containing Valsartan with Additional Support from Image Analysis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2023, 24, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’vov, V.; Procaccia, I. Exact resummations in the theory of hydrodynamic turbulence. II. A ladder to anomalous scaling. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 52, 3858–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamar, S.K.; Frank, H.K.; La Flamme, A.; Gartrell, B.; Ormsby, D.; Nelson, N. The effects of annual cycle, source population, and body condition on leukocyte profile and immune challenge in a basal reptile, the tuatara (Sphenodon punctatus). J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2024, 341, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braz Gomes, K.; D’Souza, B.; Vijayanand, S.; Menon, I.; D’Souza, M.J. A dual-delivery platform for vaccination using antigen-loaded nanoparticles in dissolving microneedles. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 613, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, A.; Joshi, D.; Menon, I.; Bagwe, P.; Patil, S.; Vijayanand, S.; Braz Gomes, K.; Uddin, M.; D’Souza, M. Zika Vaccine Microparticles (MPs)-Loaded Dissolving Microneedles (MNs) Elicit a Significant Immune Response in a Pre-Clinical Murine Model. Vaccines 2023, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayanand, S.; Patil, S.; Menon, I.; Braz Gomes, K.; Kale, A.; Bagwe, P.; Uddin, M.N.; Zughaier, S.M.; D’Souza, M.J. An Adjuvanted Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Microparticulate Vaccine Delivered Using Microneedles Induces a Robust Immune Response in Vaccinated Mice. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, R.U.; Mulla, N.S.; Braz Gomes, K.; D’Souza, C.; Murnane, K.S.; D’Souza, M.J. Nanoparticle formulations that allow for sustained delivery and brain targeting of the neuropeptide oxytocin. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 548, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejugam, N.K.; Gayakwad, S.G.; Uddin, A.N.; D’souza, M.J. Microencapsulation of protein into biodegradable matrix: A smart solution cross-linking technique. J. Microencapsul. 2013, 30, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xie, Q.; Sun, Y. Advances in nanomaterial-based targeted drug delivery systems. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1177151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltaib, L. Polymeric Nanoparticles in Targeted Drug Delivery: Unveiling the Impact of Polymer Characterization and Fabrication. Polymers 2025, 17, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.J.; Billingsley, M.M.; Haley, R.M.; Wechsler, M.E.; Peppas, N.A.; Langer, R. Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulicherla, K.K.; Verma, M.K. Targeting Therapeutics Across the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB), Prerequisite Towards Thrombolytic Therapy for Cerebrovascular Disorders—An Overview and Advancements. AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 16, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, R.; Hawthorne, S.; McCarron, P. The potential use of rabies virus glycoprotein-derived peptides to facilitate drug delivery into the central nervous system: A mini review. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. Treatment of Parkinson’s disease with biologics that penetrate the blood–brain barrier via receptor-mediated transport. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1276376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.R.; Canjels, A.; Miyauchi, R.; Kwon, E.J. Impact of Conjugation Chemistry on the Pharmacokinetics of Peptide–Polymer Conjugates in a Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Bioconjugate Chem. 2025, 36, 1483–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Singh, M. Angiopep-2-Modified Nanoparticles for Brain-Directed Delivery of Therapeutics: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppong-Damoah, A.; Zaman, R.U.; D’Souza, M.J.; Murnane, K.S. Nanoparticle encapsulation increases the brain penetrance and duration of action of intranasal oxytocin. Horm. Behav. 2019, 108, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R.; You, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Targeted delivery of neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriadis, G.K.; Kantarelis, E.; Monou, P.K.; Andriotis, E.G.; Bouropoulos, N.; Tzimtzimis, E.K.; Tzetzis, D.; Rantanen, J.; Fatouros, D.G. Automated digital design for 3D-printed individualized therapies. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 599, 120437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbl, J.; Veselý, M.; Blaháčková, D.; Ondruš, J.; Kulich, P.; Mašková, E.; Mašek, J.; Gajdziok, J. Development of 3D Printed Multi-Layered Orodispersible Films with Porous Structure Applicable as a Substrate for Inkjet Printing. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamróz, W.; Szafraniec, J.; Kurek, M.; Jachowicz, R. 3D Printing in Pharmaceutical and Medical Applications—Recent Achievements and Challenges. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, S.; Nair, A.B.; Boddu, S.H.S.; Gorain, B.; Sreeharsha, N.; Shah, J. An Updated Overview of the Emerging Role of Patch and Film-Based Buccal Delivery Systems. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachlioutaki, K.; Iordanopoulou, A.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Tsitsos, A.; Koltsakidis, S.; Anastasiadou, P.; Andreadis, D.; Economou, V.; Ritzoulis, C.; Tzetzis, D.; et al. Tailored Sticky Solutions: 3D-Printed Miconazole Buccal Films for Pediatric Oral Candidiasis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2024, 25, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadach, B.; Misek, M.; Ferlak, J. Comparison of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose and Alginate Gel Films with Meloxicam as Fast Orodispersible Drug Delivery. Gels 2023, 9, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, K.; Takei, M.; Watanabe, J. Gastrointestinal and hepatic first-pass metabolism of aspirin in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 34, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vllasaliu, D. Grand challenges in oral drug delivery. Front. Drug Deliv. 2025, 5, 1571982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Kapoor, D.; Kapil, R.; Chhabra, N.; Dhawan, S. Design and development of paclitaxel-loaded bovine serum albumin nanoparticles for brain targeting. Acta Pharm. 2011, 61, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karachaliou, M.; Moncunill, G.; Espinosa, A.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Rubio, R.; Vidal, M.; Jiménez, A.; Prados, E.; Carreras, A.; Cortés, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection, vaccination, and antibody response trajectories in adults: A cohort study in Catalonia. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roblegg, E.; Fröhlich, E.; Meindl, C.; Teubl, B.; Zaversky, M.; Zimmer, A. Evaluation of a physiological in vitro system to study the transport of nanoparticles through the buccal mucosa. Nanotoxicology 2012, 6, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gala, R.P.; Popescu, C.; Knipp, G.T.; McCain, R.R.; Ubale, R.V.; Addo, R.; Bhowmik, T.; Kulczar, C.D.; D’Souza, M.J. Physicochemical and Preclinical Evaluation of a Novel Buccal Measles Vaccine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2017, 18, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, A.S.; Castro, P.M.; Roque, L.; Thomé, N.G.; Reis, C.P.; Pintado, M.E.; Fonte, P. Novel and revisited approaches in nanoparticle systems for buccal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 320, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Choi, W.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G. Brain-targeted delivery of protein using chitosan- and RVG peptide-conjugated, pluronic-based nano-carrier. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1170–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, S.M.; Schneider, M.; Türeli, A.E.; Günday Türeli, N. Key for crossing the BBB with nanoparticles: The rational design. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 11, 866–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, N.W.; Petrucci, G.; Rocca, B. Aspirin, stroke and drug-drug interactions. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 87, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrono, C.; Baigent, C.; Hirsh, J.; Roth, G. Antiplatelet Drugs. Chest 2008, 133, 199S–233S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, J.; Hou, Y.; Huang, S.; Pei, G. Alzheimer’s Amyloid-β Accelerates Human Neuronal Cell Senescence Which Could Be Rescued by Sirtuin-1 and Aspirin. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 906270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Ding, M.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; Ye, J.; Wang, S.; Leonard, S.S.; Castronova, V.; Vallyathan, V. Antioxidant properties of aspirin: Characterization of the ability of aspirin to inhibit silica-induced lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, NF-kappaB activation, and TNF-alpha production. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 199, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrignani, P.; Filabozzi, P.; Patrono, C. Selective Cumulative Inhibition of Platelet Thromboxane Production by Low-dose Aspirin in Healthy Subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1982, 69, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Yoshimoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Sakabe, M.; Funaki, H.; Ikegaya, H. Oral administration of ethanol with aspirin increases the concentration of salicylic acid in plasma and organs, especially the brain, in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 635, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakic, K.; Selc, M.; Razga, F.; Nemethova, V.; Mazancova, P.; Havel, F.; Sramek, M.; Zarska, M.; Proska, J.; Masanova, V.; et al. Long-Term Accumulation, Biological Effects and Toxicity of BSA-Coated Gold Nanoparticles in the Mouse Liver, Spleen, and Kidneys. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 4103–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyauchi, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Kurachi, T.; Sakamoto, K.; Sakai, H. Oral Absorption across Organotypic Culture Models of the Human Buccal Epithelium after E-cigarette Aerosol Exposure. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 45574–45581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tronde, A. Pulmonary Drug Absorption: In Vitro and In Vivo Investigations of Drug Absorption Across the Lung Barrier and Its Relation to Drug Physicochemical Properties; Acta Universitatis Upsaliensis: Uppsala, Sweden, 2002; ISBN 978-91-554-5373-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Fu, F.; Han, B.; Zhu, M.; Yu, X.; Zhang, L. Aspirin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemic Injury in Diabetic Rats. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2008, 117, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kollidon 90F (g) | 4.9 | 3 | 4.9 | - | ||||
| Kollidon VA64 (g) | 0.32 | 1 | - | 0.32 | ||||
| PEG 2000 (g) | 0.18 | 1 | 0.18 | 0.18 | ||||
| Ethanol (mL) | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | ||||
| PCL (g) | - | 3 | 0.3 | 4.9 | ||||
| Glycerin (50%) mL | 5 | - | - | - | ||||
| citric acid (g) | 1 | 1 | 0.25 | 0.25 | ||||
| HPMC 1 (g) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | ||||
| Sucrose (mL) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| Soluplus (mL) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.1 | ||||
| Water (mL) | 80 | 30 | 20 | 60 |
| S. No. | Parameter | Blank Polymer ODFs | Blank NP Loaded ODFs | ASA NP Loaded ODFs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Weight variation (mg) | 8.43 ± 0.74 | 10.73 ± 0.46 | 10.86 ± 0.28 |
| 2 | Diameter (mm) | 0.4 ± 0.03 | 0.4 ± 0.01 | 0.4 ± 0.01 |
| 3 | Thickness (mm) | 0.33 ± 0.10 | 0.47 ± 0.24 | 0.47 ± 0.26 |
| 4 | Disintegration Test (min) | 1.38 ± 0.29 | 2.24 ± 0.24 | 2.38 ± 0.28 |
| 5 | pH | 7.5 | 8 | 7.5 |
| 6 | Tensile Strength (N/cm2) | 2.67 ± 0.06 | 2.28 ± 0.5 | 2.30 ± 0.10 |
| 7 | Swelling Index (%) | 48 ± 0.8 | 56 ± 0.7 | 63 ± 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasupuleti, D.; D’Souza, M.; Ferguson, A.; Gulani, M.A.; Patel, P.; Singh, R.; Adediran, E.; Vijayanand, S.; Arte, T.M.; D’Souza, M. 3D-Printed Oral Disintegrating Films of Brain-Targeted Acetyl Salicylic Acid Nanoparticles for Enhanced CNS Delivery in Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121547
Pasupuleti D, D’Souza M, Ferguson A, Gulani MA, Patel P, Singh R, Adediran E, Vijayanand S, Arte TM, D’Souza M. 3D-Printed Oral Disintegrating Films of Brain-Targeted Acetyl Salicylic Acid Nanoparticles for Enhanced CNS Delivery in Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121547
Chicago/Turabian StylePasupuleti, Dedeepya, Marissa D’Souza, Amarae Ferguson, Mahek Anil Gulani, Parth Patel, Revanth Singh, Emmanuel Adediran, Sharon Vijayanand, Tanisha Manoj Arte, and Martin D’Souza. 2025. "3D-Printed Oral Disintegrating Films of Brain-Targeted Acetyl Salicylic Acid Nanoparticles for Enhanced CNS Delivery in Ischemic Stroke" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121547
APA StylePasupuleti, D., D’Souza, M., Ferguson, A., Gulani, M. A., Patel, P., Singh, R., Adediran, E., Vijayanand, S., Arte, T. M., & D’Souza, M. (2025). 3D-Printed Oral Disintegrating Films of Brain-Targeted Acetyl Salicylic Acid Nanoparticles for Enhanced CNS Delivery in Ischemic Stroke. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1547. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121547










