The Absorption, Distribution, Excretion, and In Vitro Hepatic Microsomal Metabolism of the Novel CDK Compound XMD12 in Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Materials and Reagents
2.2. Animal Studies
2.3. Instrumentation and Analytical Conditions
2.4. Preparation of Standard and Quality Control Samples
2.5. Sample Preparation
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Liver Microsomes In Vitro
2.8. Collection of Animal Specimens
2.8.1. Plasma Exposure Study
2.8.2. Tissue Distribution Study
2.8.3. Urine and Feces Excretion Studies
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Method Validation
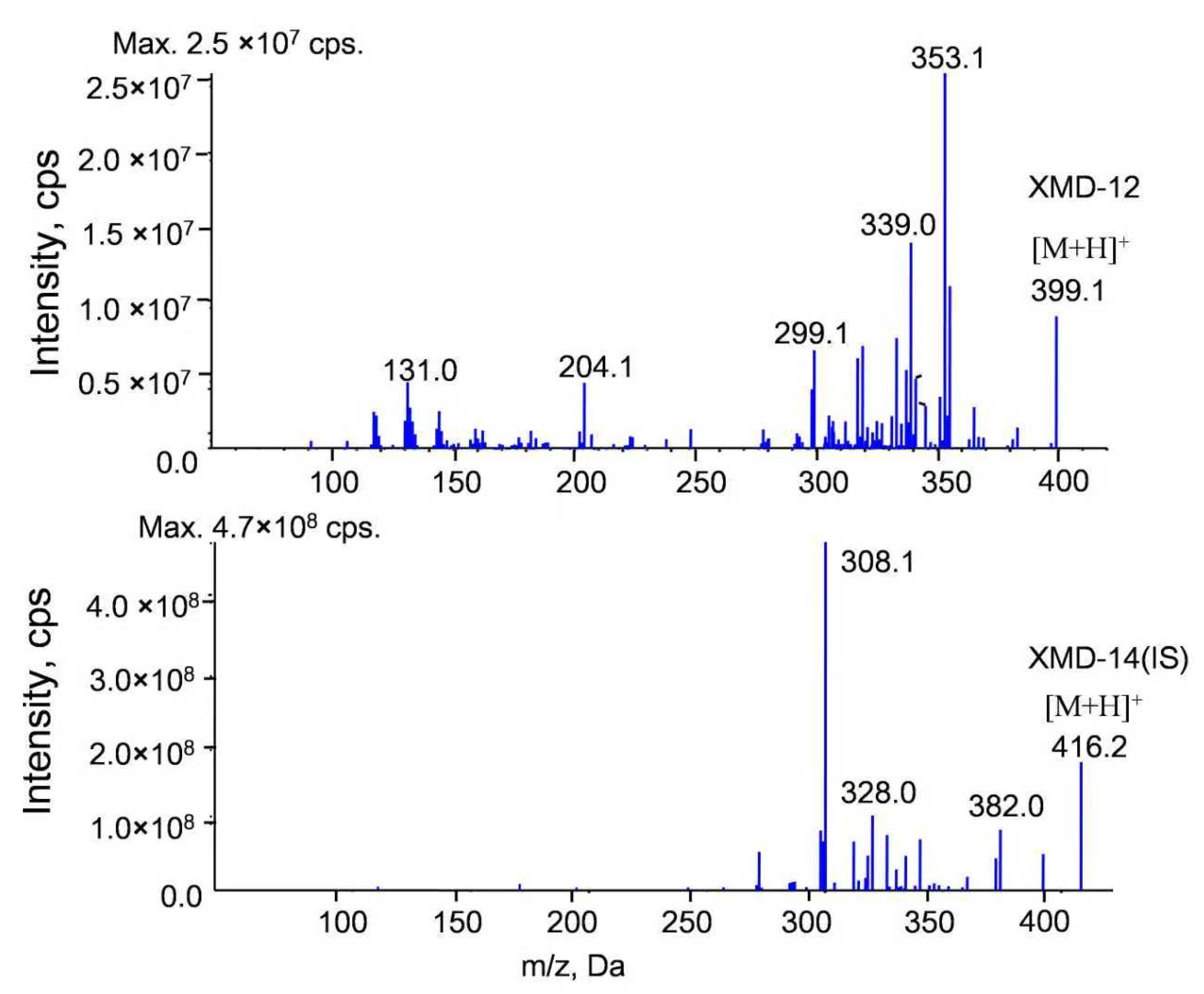
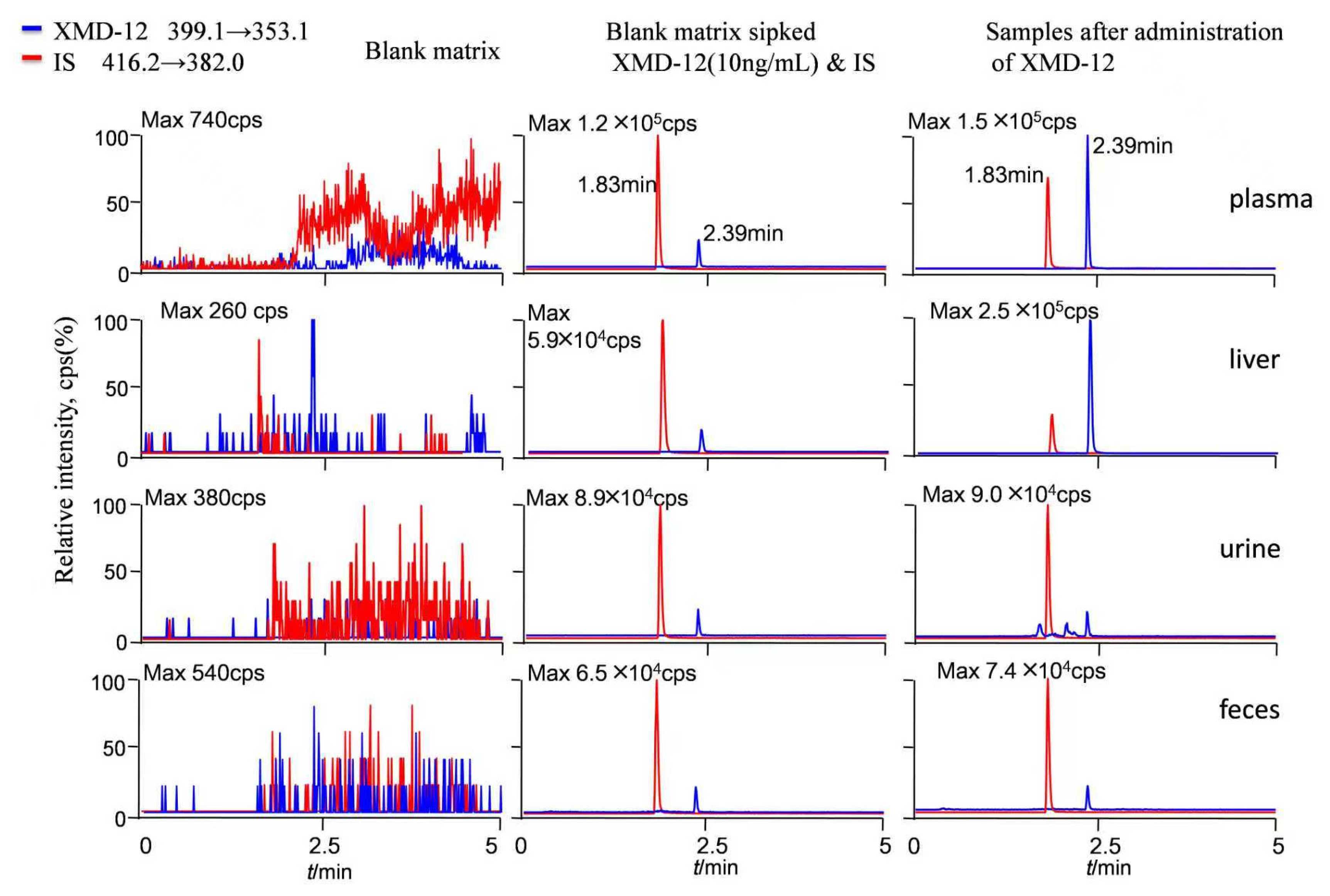
3.1.1. Specificity and Carryover
3.1.2. Linearity
3.1.3. Precision, Accuracy and Stability
3.1.4. Extraction Recovery and Matrix Effect
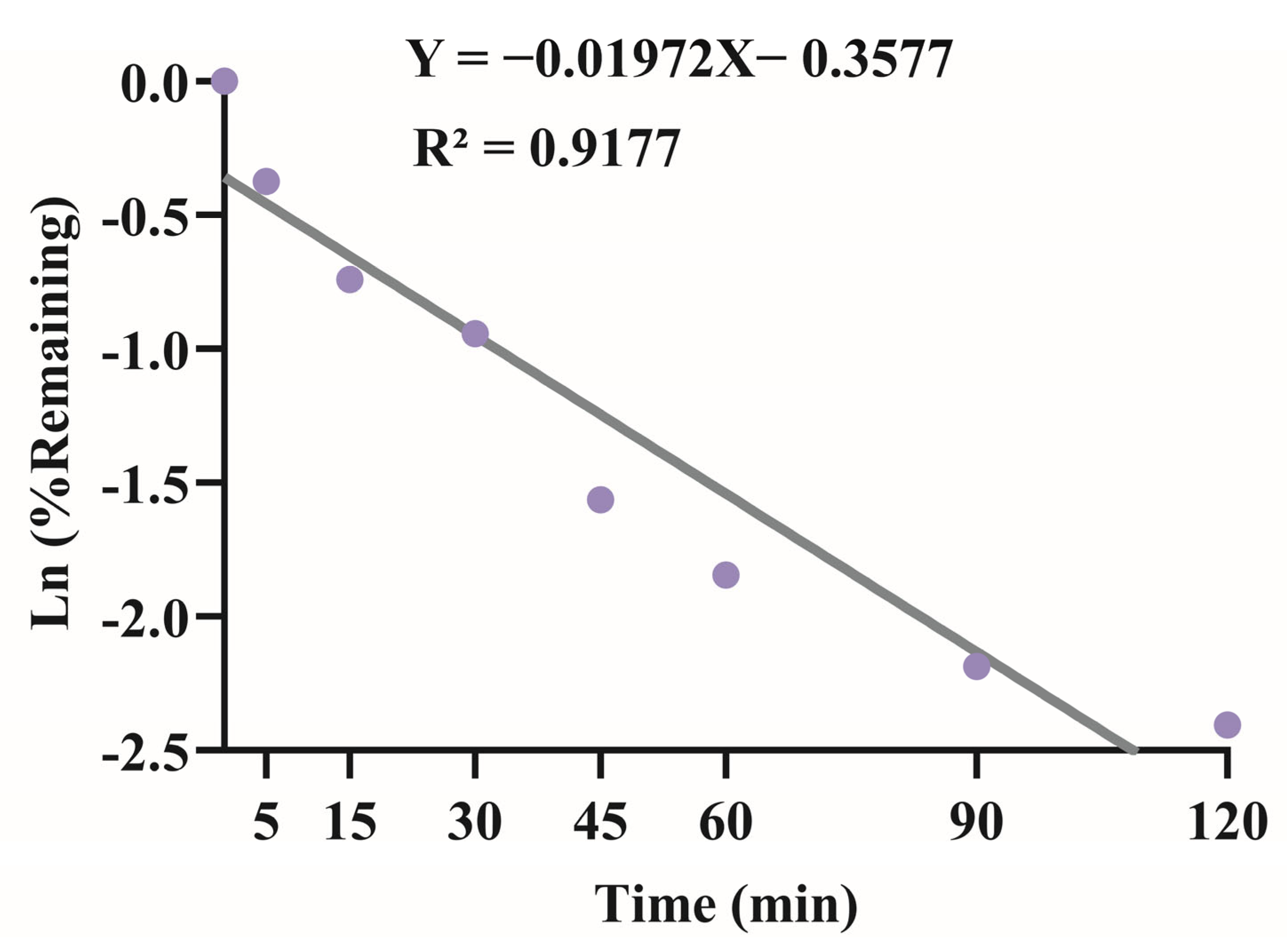
3.2. Liver Microsomes In Vitro
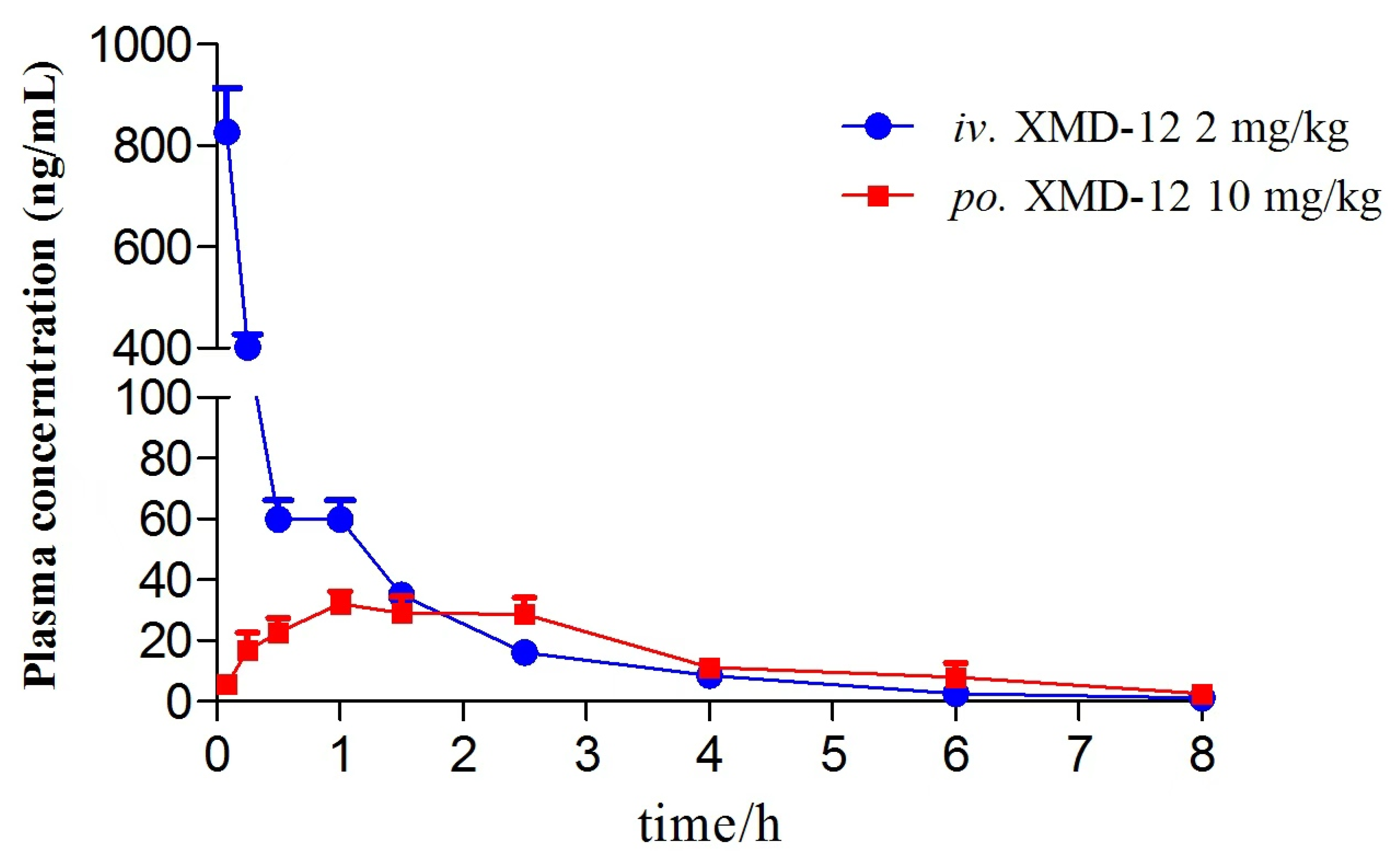
3.3. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Bioavailability
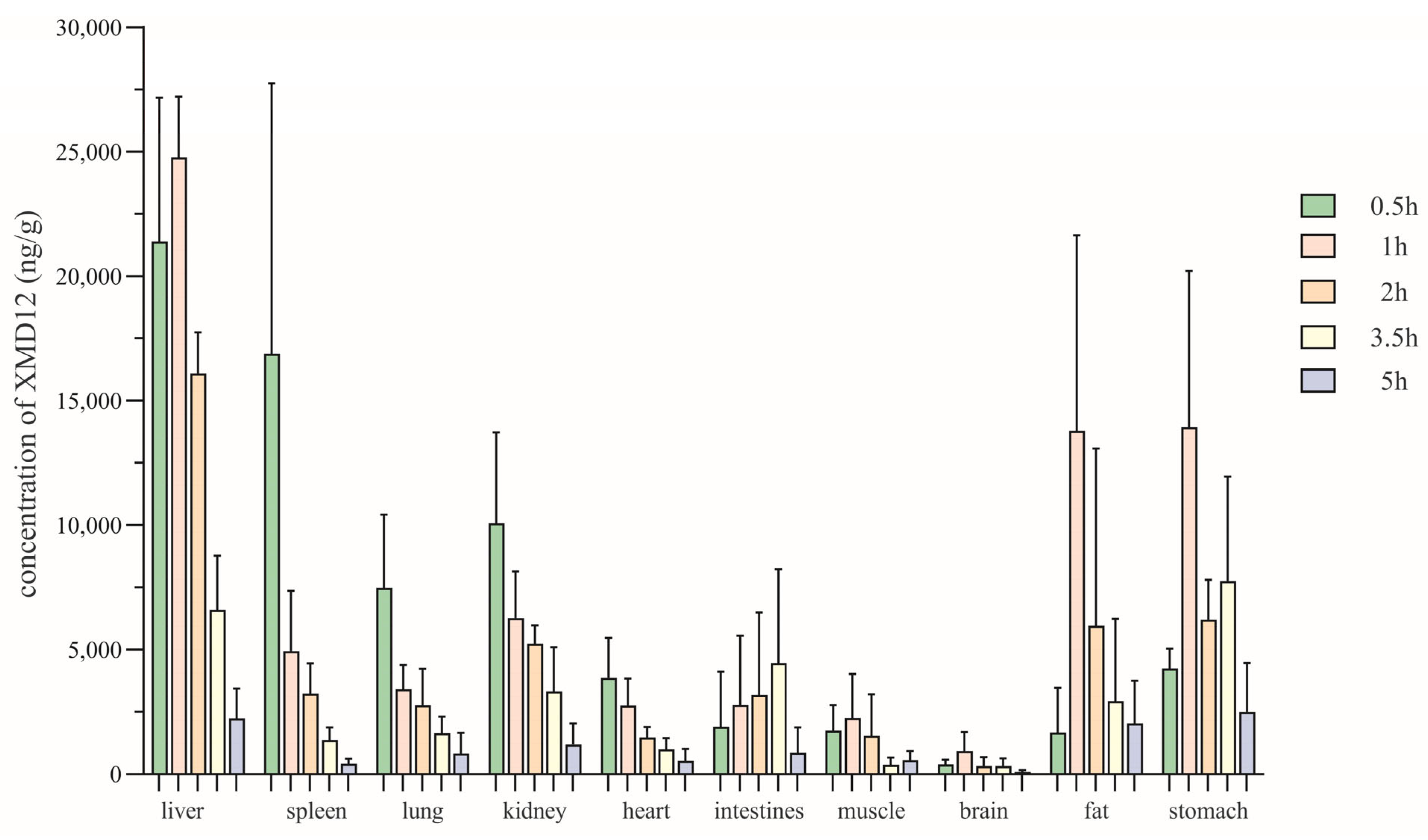
3.4. Tissue Distribution Study
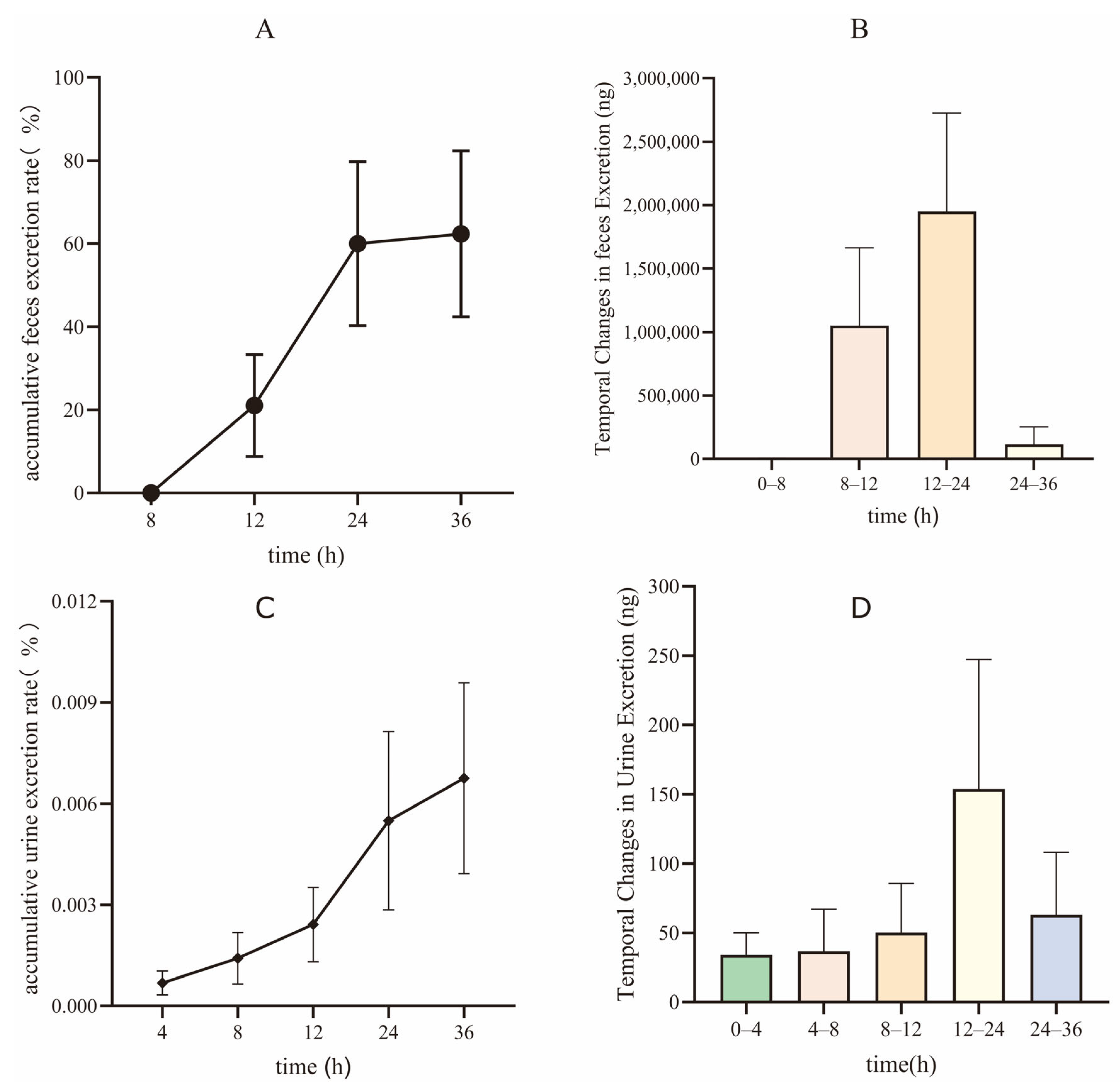
3.5. Excretory Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as first-line therapy for HR-positive, advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.-A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, G.W.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women with HR+/HER2− advanced breast cancer who had progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piezzo, M.; Chiodini, P.; Riemma, M.; Cocco, S.; Caputo, R.; Cianniello, D.; Di Gioia, G.; Di Lauro, V.; Rella, F.D.; Fusco, G.; et al. Progression-free survival and overall survival of CDK 4/6 inhibitors plus endocrine therapy in metastatic breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Approves Abemaciclib for HR-Positive, HER2-Negative Breast Cancer. FDA. 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/fda-approves-abemaciclib-hr-positive-her2-negative-breast-cancer (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Ribociclib (kisqali). FDA. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/ribociclib-kisqali (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Palbociclib (IBRANCE). FDA. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/palbociclib-ibrance (accessed on 25 October 2025).
- Elmallah, S. Computational optimization and in silico analysis for the discovery of new HER2 and CDK4/6 drug candidates for breast cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2025, 26, 77–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, G.R.; Harris, R.Z.; Lau, D.T. Pharmacokinetics and its role in small molecule drug discovery research. Med. Res. Rev. 2001, 21, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakne, P.; Sahu, A.K.; Sharma, M.K.; Sengupta, P. Simultaneous quantification of abemaciclib and letrozole in rat plasma: Method development, validation and pharmacokinetic application. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2020, 34, e4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Maiello, M.R.; D’Alessio, A.; Frezzetti, D.; Gallo, M.; Carotenuto, M.; Normanno, N. Pharmacokinetic drug evaluation of palbociclib for the treatment of breast cancer. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshogran, O.Y.; Al-Shdefat, R.; Hailat, M. Simple and rapid quantification of ribociclib in rat plasma by protein precipitation and LC-MS/MS: An application to pharmacokinetics of ribociclib nanoparticles in rats. J. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 58, e4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braal, C.L.; Jongbloed, E.M.; Wilting, S.M.; Mathijssen, R.H.J.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Jager, A. Inhibiting CDK4/6 in breast cancer with palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib: Similarities and differences. Drugs 2021, 81, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenland, S.L.; Martínez-Chávez, A.; van Dongen, M.G.J.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schinkel, A.H.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Steeghs, N. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 inhibitors palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 1501–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Abdelhady, A.M.; Samant, T.S.; Yang, S.; Rodriguez Lorenc, K. Evaluation of absolute oral bioavailability and bioequivalence of ribociclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor, in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Drug Dev. 2020, 9, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Zheng, D.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; et al. A potential anti-glioblastoma compound LH20 induces apoptosis and arrest of human glioblastoma cells via CDK4/6 inhibition. Molecules 2023, 28, 5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesters, R.J.; Voswinkel, S. Bioanalytical method development and validation: From the USFDA 2001 to the USFDA 2018 guidance for industry. J. Appl. Bioanal. 2018, 4, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Matrix | Equation (1/x2, Weighting Index) | Range (ng/mL) | LLOQ/(ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | y = 0.00306x + 0.00342 (r = 0.9985) | 2.5–1000 | 2.5 |
| Liver | y = 316x + 21,300 (r = 0.9936) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Spleen | y = 400x + 1710 (r = 0.9919) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Heart | y = 374x + 507 (r = 0.9955) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Kidney | y = 379x + 1370 (r = 0.9989) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Lung | y = 375x + 1490 (r = 0.9959) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Brain | y = 459x + 399 (r = 0.9924) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Muscle | y = 414x + 2710 (r = 0.9954) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Stomach | y = 485x + 4640 (r = 0.9931) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Fat | y = 439x + 965 (r = 0.9924) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| intestines | y = 453x + 1250 (r = 0.9946) | 10–2000 | 10 |
| Urine | y = 0.00582x + 0.00438 (r = 0.9963) | 2.5–1000 | 2.5 |
| Feces | y = 0.00662x + 0.00437 (r = 0.9952) | 2.5–1000 | 2.5 |
| Microsome | y = 1200x – 7790 (r = 0.9952) | 100–2000 | 100 |
| Matrix | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Intra-Day (n = 5) | Inter-Day (n = 15) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Precision (RSD,%) | Accuracy (%) | Measured Concentration (ng/mL) | Precision (RSD,%) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Plasma | 2.5 | 2.49 ± 0.23 | 9.20 | 99.76 | 2.41 ± 0.21 | 8.80 | 96.22 |
| 5 | 5.35 ± 0.31 | 5.80 | 107.20 | 5.08 ± 0.37 | 7.38 | 101.76 | |
| 90 | 83.70 ± 2.67 | 3.19 | 93.00 | 86.96 ± 8.37 | 9.63 | 96.68 | |
| 800 | 733.60 ± 11.01 | 1.50 | 91.74 | 772.27 ± 69.39 | 8.99 | 96.56 | |
| Liver | 30.0 | 29.5 ± 2.6 | 8.95 | 98.3 | 30.0 ± 2.2 | 7.43 | 100.05 |
| 800.0 | 802.8 ± 27.9 | 3.48 | 100.4 | 815.1 ± 40.8 | 5.00 | 101.84 | |
| 1600.0 | 1582.5 ± 92.5 | 5.85 | 90.06 | 1582.2 ± 87.6 | 5.54 | 95.85 | |
| Matrix | Nominal Concentration (ng∙mL−1) | 6 h at Room Temperature | Freeze–Thaw (3 Circles) | 15 d,−80 °C (15 Days and −80 °C) | Autosample (at Ambient Temperature for 6 h) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (%, RSD) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%, RSD) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%, RSD) | Accuracy (%) | Precision (%, RSD) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| Plasma | 5 | 6.46 | 105.58 | 8.12 | 97.10 | 3.93 | 94.20 | 5.22 | 92.16 |
| 90 | 2.35 | 108.60 | 6.38 | 107.22 | 5.81 | 93.76 | 3.06 | 92.44 | |
| 800 | 5.05 | 110.80 | 5.18 | 106.80 | 5.72 | 102.22 | 4.39 | 90.02 | |
| Liver | 30.0 | 3.67 | 100.93 | 6.44 | 100.47 | 1.61 | 97.53 | 3.01 | 100.80 |
| 800.0 | 4.28 | 101.93 | 3.69 | 99.78 | 3.12 | 99.40 | 2.70 | 103.;10 | |
| 1600.0 | 5.72 | 101.56 | 7.64 | 97.75 | 5.70 | 101.63 | 6.12 | 100.94 | |
| Matrix | Nominal Concentration (ng/mL) | Matrix Effect (%, Mean) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | 5 | 93.93 ± 7.07 | 7.53 |
| 800 | 92.87 ± 4.61 | 4.96 | |
| Liver | 30 | 104.17 ± 7.22 | 6.93 |
| 1600 | 94.03 ± 5.50 | 5.85 | |
| Spleen | 15 | 101.13 ± 4.81 | 4.76 |
| 1600 | 100.37 ± 5.88 | 5.86 | |
| Heart | 30 | 92.28 ± 3.78 | 4.09 |
| 1600 | 87.05 ± 3.57 | 4.10 | |
| Kidney | 30 | 96.21 ± 6.22 | 6.46 |
| 1600 | 91.88 ± 4.37 | 4.76 | |
| Lung | 30 | 90.56 ± 2.53 | 2.79 |
| 1600 | 94.83 ± 4.53 | 4.78 | |
| Brain | 30 | 87.33 ± 1.36 | 1.56 |
| 1600 | 91.92 ± 2.40 | 2.61 | |
| Muscle | 30 | 102.21 ± 5.32 | 5.20 |
| 1600 | 101.31 ± 6.37 | 6.29 | |
| Stomach | 30 | 91.38 ± 3.85 | 4.21 |
| 1600 | 97.06 ± 6.87 | 7.08 | |
| Intestines | 30 | 107.38 ± 5.83 | 5.43 |
| 1600 | 109.37 ± 3.74 | 3.42 |
| Matrix | Nominal Concentration (ng∙mL−1) | Mean ± SD (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma | 5 | 84.52 ± 9.46 | 11.19 |
| 90 | 87.99 ± 4.79 | 5.45 | |
| 800 | 88.27 ± 7.47 | 8.46 | |
| Liver | 30 | 90.25 ± 6.07 | 6.73 |
| 800 | 95.17 ± 5.36 | 5.63 | |
| 1600 | 94.26 ± 3.14 | 3.33 |
| Parameters | i.v. (2 mg∙kg−1) | p.o. (10 mg∙kg−1) |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (ng∙mL−1) | 827.00 ± 191.30 | 38.26 ± 10.90 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.083 | 1.300 ± 0.758 |
| AUC0-t (h∙ng∙mL−1) | 357.21 ± 66.60 | 117.78 ± 28.97 |
| AUC0-∞ (h∙ng∙mL−1) | 360.03 ± 66.00 | 120.06 ± 30.19 |
| t1/2 (h) | 1.47 ± 0.29 | 1.21 ± 0.16 |
| MRT0-t (h) | 0.74 ± 0.08 | 2.475 ± 0.344 |
| CL (L∙h−1∙kg−1) | 5.69 ± 0.95 | 86.64 ± 16.72 |
| V (L∙kg−1) | 12.29 ± 3.98 | 150.59 ± 34.37 |
| F (%) | - | 6.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.-H.; Chang, Y.-C.; Li, Y.-H.; He, Y.-X.; Zhao, P.-X.; Wang, F.-F.; Xu, J.-Y.; Tan, Y.-F. The Absorption, Distribution, Excretion, and In Vitro Hepatic Microsomal Metabolism of the Novel CDK Compound XMD12 in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121545
Zheng X-H, Chang Y-C, Li Y-H, He Y-X, Zhao P-X, Wang F-F, Xu J-Y, Tan Y-F. The Absorption, Distribution, Excretion, and In Vitro Hepatic Microsomal Metabolism of the Novel CDK Compound XMD12 in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Pharmaceutics. 2025; 17(12):1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121545
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xue-Hai, Yan-Chun Chang, Yong-Hui Li, Yu-Xia He, Pei-Xiong Zhao, Fei-Fei Wang, Jun-Yu Xu, and Yin-Feng Tan. 2025. "The Absorption, Distribution, Excretion, and In Vitro Hepatic Microsomal Metabolism of the Novel CDK Compound XMD12 in Sprague-Dawley Rats" Pharmaceutics 17, no. 12: 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121545
APA StyleZheng, X.-H., Chang, Y.-C., Li, Y.-H., He, Y.-X., Zhao, P.-X., Wang, F.-F., Xu, J.-Y., & Tan, Y.-F. (2025). The Absorption, Distribution, Excretion, and In Vitro Hepatic Microsomal Metabolism of the Novel CDK Compound XMD12 in Sprague-Dawley Rats. Pharmaceutics, 17(12), 1545. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17121545










