The Interaction Network of NSm and Its Role as a Movement Protein in the Tomato Zonate Spot Virus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus and Plant Material
2.2. Preparation of Plasmids
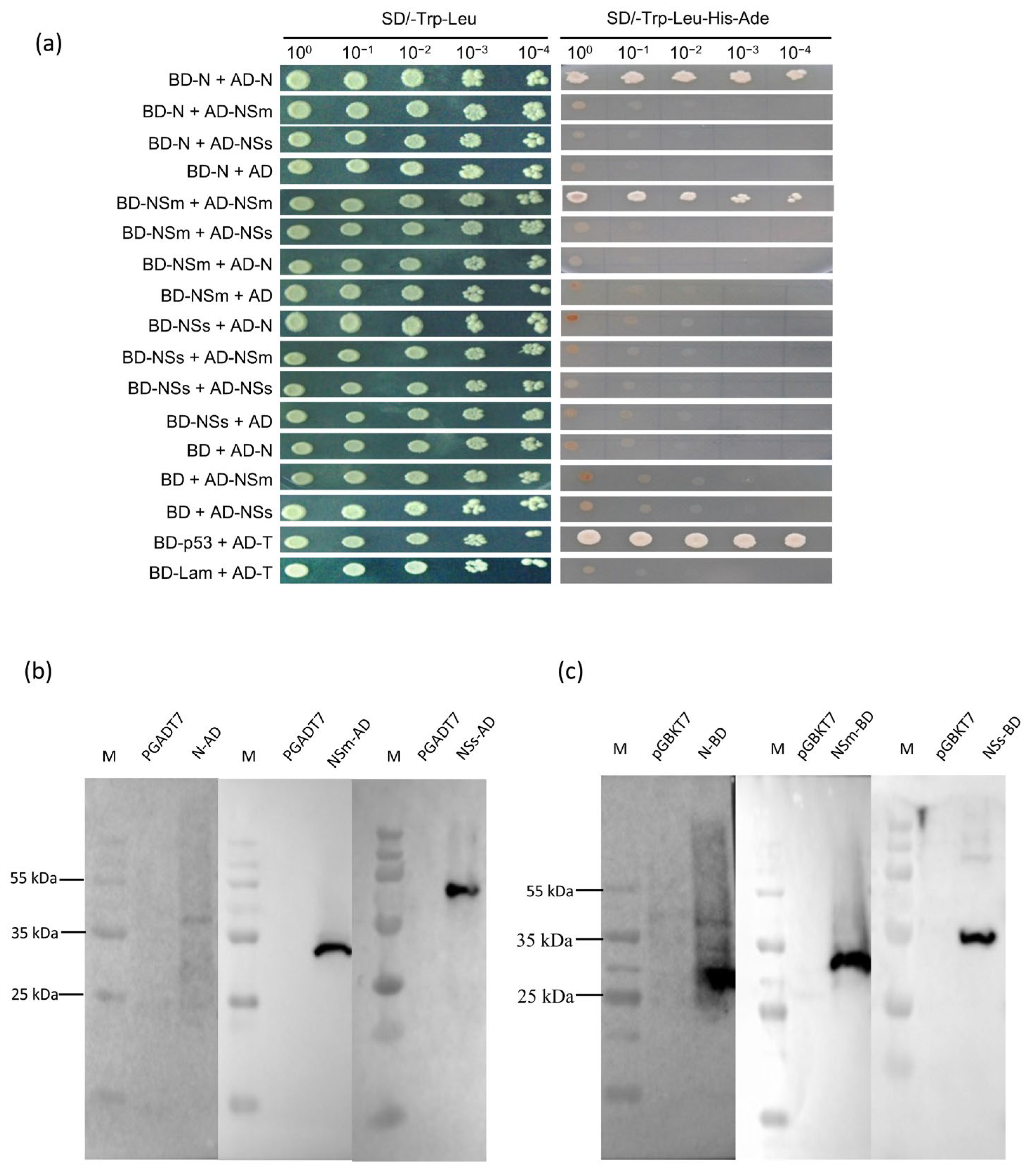
2.3. Yeast Two-Hybrid (Y2H) Assays
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
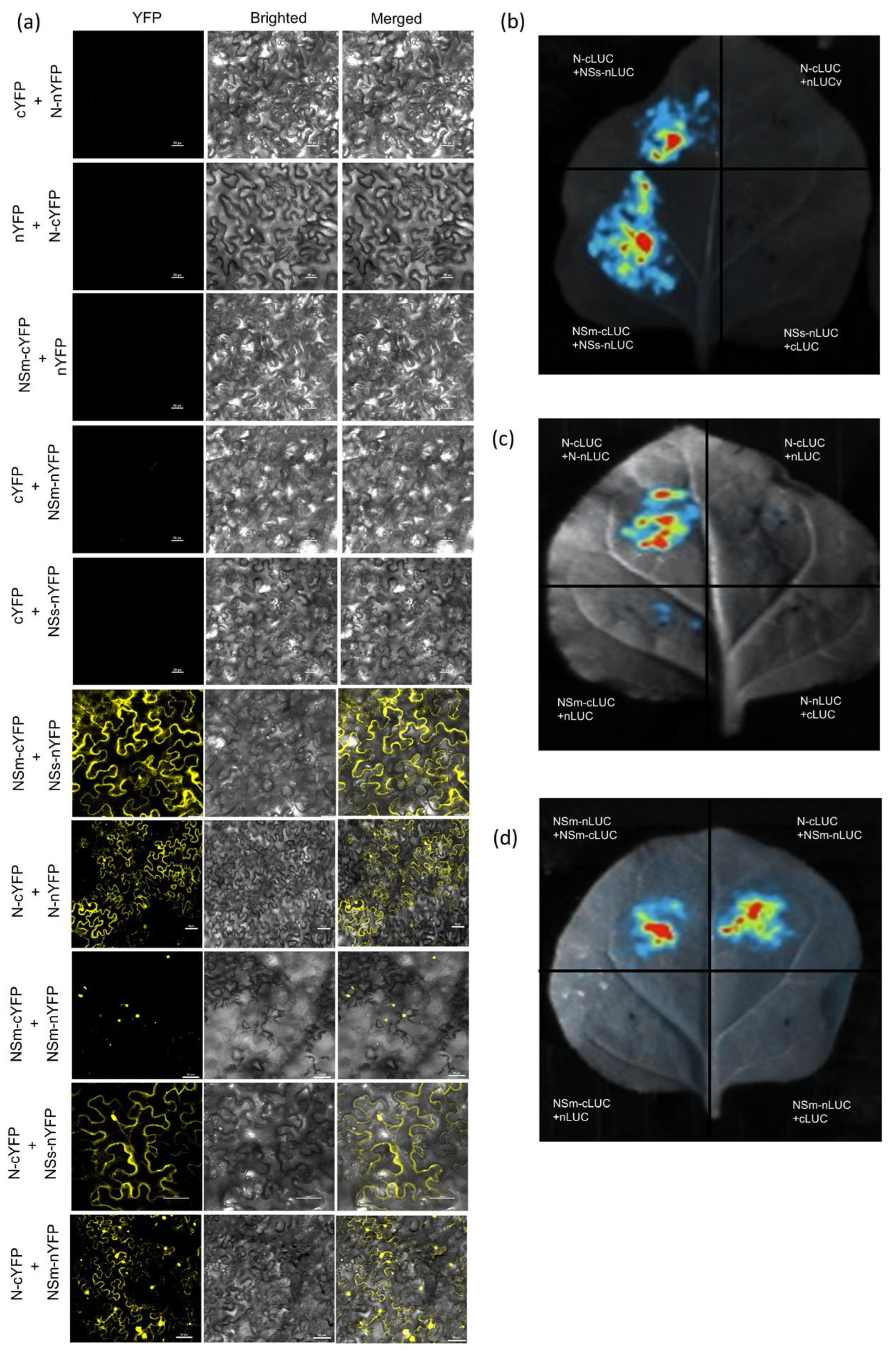
2.5. BiFC Assays
2.6. Luciferase Complementation (LCI) Assay
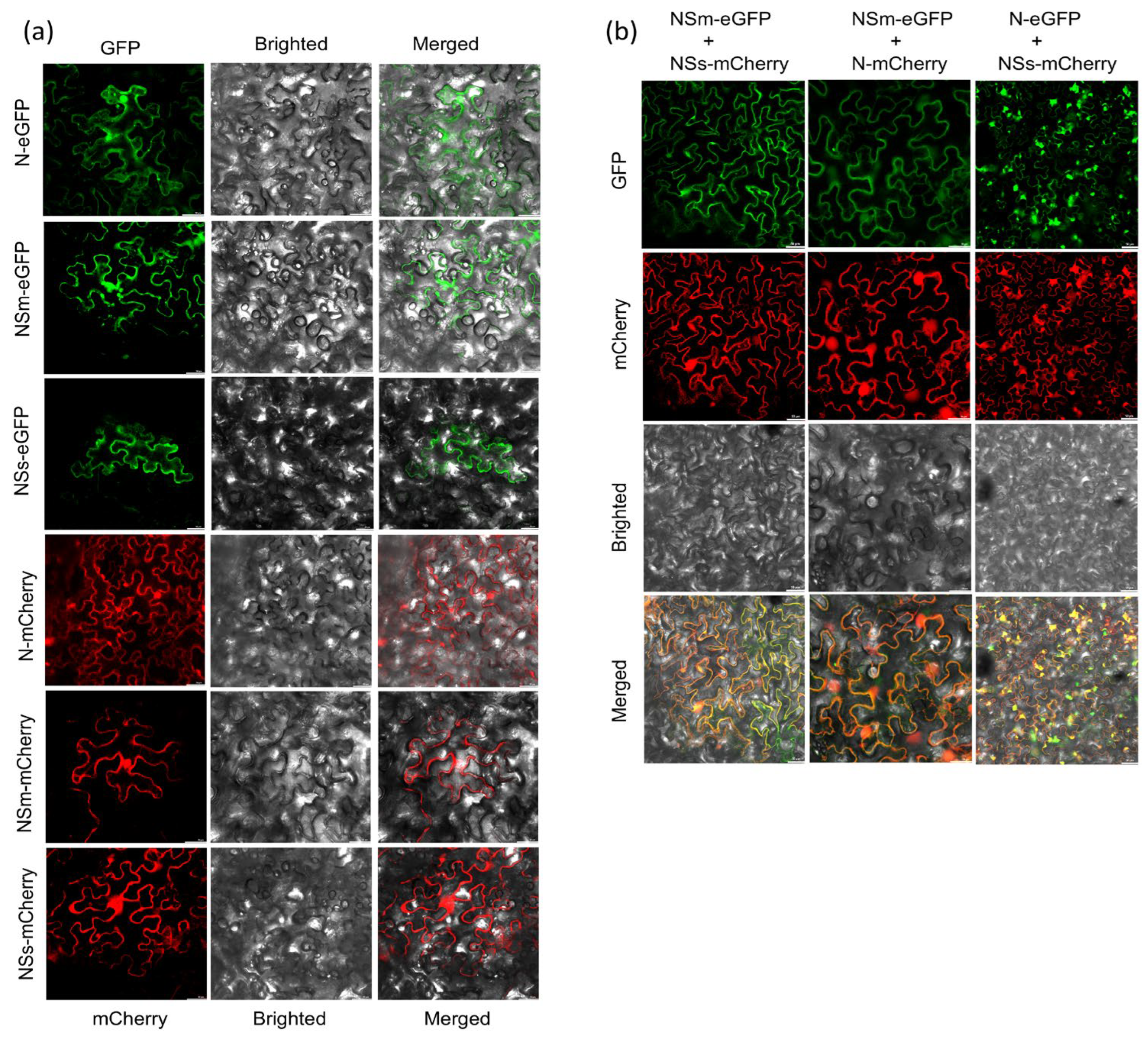
2.7. Subcellular Localization
2.8. Complementation Assay of the NSm Protein with a CMV Movement Protein Deletion Mutant
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. N, NSm and NSs Interact with Each Other In Vitro
3.2. N, NSm and NSs Interact with Each Other in N. benthamiana
3.3. Subcellular Localization and Co-Localization Analysis of TZSV N, NSm and NSs Proteins in N. benthamiana
3.4. The TZSV NSm Protein Functions as a Movement Protein
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pappu, H.R.; Jones, R.A.C.; Jain, R.K. Global status of tospovirus epidemics in diverse cropping systems: Successes achieved and challenges ahead. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholthof, K.B.G.; Adkins, S.; Czosnek, H.; Palukaitis, P.; Jacquot, E.; Hohn, T.; Hohn, B.; Saunders, K.; Candresse, T.; Ahlquist, P.; et al. Top 10 plant viruses in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2011, 12, 938–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.R. Plant Viruses Transmitted by Thrips. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2005, 113, 119–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.H.; Cheng, X.F.; Yin, Y.Y.; Fang, Q.; Ding, M.; Li, T.T.; Zhang, L.Z.; Su, X.X.; McBeath, J.H.; Zhang, Z.K. Characterization of tomato zonate spot virus, a new tospovirus in China. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Dong, J.; Fang, Q.; Ding, M.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Su, X.; Zhang, Z. A Preliminary Study on the Occurrence and Epidemic Characteristics of Tomato Ringspot Disease. In Proceedings of the 2008 Annual Academic Meeting of the Chinese Society for Plant Protection, Beijing, China, 29–31 October 2008; pp. 358–359. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.; Tian, H.; Lin, S.; Wang, L.; Linghu, T.; Zheng, X.; Wei, H.; Fan, X.; et al. Chemosensory protein regulates the behavioural response of Frankliniella intonsa and Frankliniella occidentalis to tomato zonate spot virus-Infected pepper (Capsicum annuum). PLoS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wei, H.; Chen, Y.D.; Zheng, K.Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhao, L.H.; Gao, Y.L.; Zheng, L.M.; et al. A plant virus mediates interspecific competition between its insect vectors in Capsicuum annuum. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 94, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.H.; Zhang, Z.K.; Yin, Y.Y.; Cheng, X.F.; Ding, M.; Fang, Q. Natural host ranges of Tomato zonate spot virus in Yunnan. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 12–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, K.Y.; Dong, J.; Yin, Y.; Fang, Q.; Su, X.; Zhang, Z. Prokaryotic expression and antiserum preparation of non-structural protein NSs of Tomato zonate spot virus. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 28, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, R.M. Molecular biology of Bunyaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 1990, 71, 501–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, T. Tospoviruses: Diagnosis, molecular biology, phylogeny, and vector relationships. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1992, 30, 315–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haan, P.; Kormelink, R.; De, O.R.; Van Poelwijk, R.F.; Peters, D.; Goldbach, R. Tomato spotted wilt virus L RNA encodes a putative RNA polymerase. J. Gen. Virol. 1991, 72, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormelink, R.; Haan, P.D.; Meurs, C.; Peters, D. The nucleotide sequence of the M RNA segment of tomato spotted wilt virus, a bunyavirus with two ambisense RNA segments. J. Gen. Virol. 1992, 73, 2795–2804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, P.J.; Siddell, S.G.; Lefkowitz, E.J.; Mushegian, A.R.; Adriaenssens, E.M.; Alfenas-Zerbini, P.; Davison, A.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dutilh, B.E.; García, M.L.; et al. Changes to virus taxonomy and to the International Code of Virus Classification and Nomenclature ratified by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2633–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Shi, X.; Zhang, S.; Tan, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, B.; Ye, Q.; Miao, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. The nonstructural protein NSs encoded by tomato zonate spot virus suppresses RNA silencing by interacting with NbSGS3. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2022, 23, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrig, J.F.; Soellick, T.R.; Minke, C.J.; Philipp, C.; Kellmann, J.W.; Schreier, P.H. Homotypic interaction and multimerization of nucleocapsid protein of tomato spotted wilt tospovirus: Identification and characterization of two interacting domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soellick, T.R.; Uhrig, J.F.; Bucher, G.L.; Kellmann, J.W.; Schreier, P.H. The movement protein NSm of tomato spotted wilt tospovirus (TSWV): RNA binding, interaction with the TSWV N protein, and identification of interacting plant proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2373–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snippe, M.; Borst, J.W.; Goldbach, R.; Kormelink, R. The use of fluorescence microscopy to visualise homotypic interactions of tomato spotted wilt virus nucleocapsid protein in living cells. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 125, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilian, E.; Maiss, E. An optimized mRFP-based bimolecular fluorescence complementation system for the detection of protein–protein interactions in planta. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 174, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzgen, R.G.; Martin, K.M.; Anderson, G.; Goodin, M.M. In planta localization and interactions of impatiens necrotic spot tospovirus proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2490–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widana Gamage, S.M.K.; Dietzgen, R.G. Intracellular Localization, Interactions and Functions of Capsicum Chlorosis Virus Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, D.; Raikhy, G.; Goodin, M.M.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Pappu, H.R. In vivo localization of iris yellow spot tospovirus (Bunyaviridae)-encoded proteins and identification of interacting regions of nucleocapsid and movement proteins. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leastro, M.O.; Pallás, V.; Resende, R.O.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.A. The movement proteins (NSm) of distinct tospoviruses peripherally associate with cellular membranes and interact with homologous and heterologous NSm and nucleocapsid proteins. Virology 2015, 478, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.M.; Chen, Y.; Mayfield, M.A.; Montero-Astua, M.; Whitfield, A.E. Visualizing Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus Protein Localization: Cross-Kingdom Comparisons of Protein-Protein Interactions. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2025, 38, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, D.J.; Adkins, S. The tubule-forming NSm protein from Tomato spotted wilt virus complements cell-to-cell and long-distance movement of Tobacco mosaic virus hybrids. Virology 2005, 342, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Yao, M.; Li, C.; Miriam, K.; Zhang, X.; Tao, X.R. A versatile complementation assay for cell-to-cell and long distance movements by cucumber mosaic virus based agro-infiltration. Virus Res. 2014, 190, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Su, X.; Luo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Du, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.O.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. First evidence showing that Pepper vein yellows virus P4 protein is a movement protein. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amari, K.; Emmanuel Boutant, E.; Hofmann, C.; Schmitt-Keichinger, C.; Fernandez-Calvino, L.; Didier, P.; Lerich, A.; Mutterer, J.; Thomas, C.; Heinlein, M.; et al. A family of plasmodesmal proteins with receptor-like properties for plant viral movement proteins. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, H.; Liao, Q.; Chen, J.; Carr, J.P.; Du, Z. Self-interaction of the cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein plays a vital role in the suppression of RNA silencing and the induction of viral symptoms. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, S.; Cho, W.K.; Jo, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.H. Interaction study of rice stripe virus proteins reveals a region of the nucleocapsid protein (NP) required for NP self-interaction and nuclear localization. Virus Res. 2014, 183, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukhovitskaya, N.I.; Cowan, G.H.; Vetukuri, R.R.; Tilsner, J.; Torrance, L.; Savenkov, E.I. Importin-α-mediated nucleolar localization of potato mop-top virus TRIPLE GENE BLOCK1 (TGB1) protein facilitates virus systemic movement, whereas TGB1 self-interaction is required for cell-to-cell movement in Nicotiana benthamiana. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cho, W.K.; Lian, S.; Kim, K.H. Identification of residues or motif(s) of the rice stripe virus NS3 protein required for self-interaction and for silencing suppressor activity. Virus Res. 2017, 235, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.H.; Foo, M.H.; Raja, J.A.J.; Tan, Y.R.; Lin, T.T.; Lin, S.S.; Yeh, S.D. A Conserved Helix in the C-Terminal Region of Watermelon Silver Mottle Virus Nonstructural Protein S Is Imperative for Protein Stability Affecting Self-Interaction, RNA Silencing Suppression, and Pathogenicity. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2020, 33, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomchan, P.; Li, S.F.; Shirako, Y. Rice Grassy Stunt Tenuivirus Nonstructural Protein p5 Interacts with Itself to Form Oligomeric Complexes In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.j.; Wu, K.C.; Zheng, L.P.; Ding, Z.M.; Li, F.; Zou, P.; Yang, L.; Wu, J.G.; Wu, Z.J. Rice grassy stunt virus nonstructural protein p5 serves as a viral suppressor of RNA silencing and interacts with nonstructural protein p3. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2769–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormelink, R.; Storms, M.; Van Lent, J.; Peters, D.; Goldbach, R. Expression and subcellular location of the NSM protein of tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV), a putative viral movement protein. Virology 1994, 200, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappu, H.R.; Du Toit, L.J.; Schwartz, H.F.; Mohan, S.K. Sequence diversity of the nucleoprotein gene of Iris yellow spot virus (genus Tospovirus, family Bunyaviridae) isolates from the western region of the United States. Arch. Virol. 2006, 151, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kormelink, R.; Garcia, M.L.; Goodin, M.; Sasaya, T.; Haenni, A.L. Negative-strand RNA viruses: The plant-infecting counterparts. Virus Res. 2011, 162, 184–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poelwijk, F.; Haan, P.; Kikkert, M.; Prins, M.; Kormelink, R.; Storms, M.; Lent, J.; Peters, D.; Goldbach, R. Replication and expression of the tospoviral genome. Tospoviruses Thrips Flor. Veg. Crops 1995, 431, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldbach, R.; Peters, D. Molecular and biological aspects of tospoviruses. In The Bunyaviridae; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 129–157. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.T.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.J.; Zhang, H.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, G.P.; Hong, N. Protein P5 of pear chlorotic leaf spot-associated virus is a pathogenic factor that suppresses RNA silencing and enhances virus movement. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2024, 25, e70015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xue, F.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; Zhao, W.; Garcia-Murria, M.J.; Mingarro, I.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lei, J.; et al. The ER-Membrane Transport System Is Critical for Intercellular Trafficking of the NSm Movement Protein and Tomato Spotted Wilt Tospovirus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
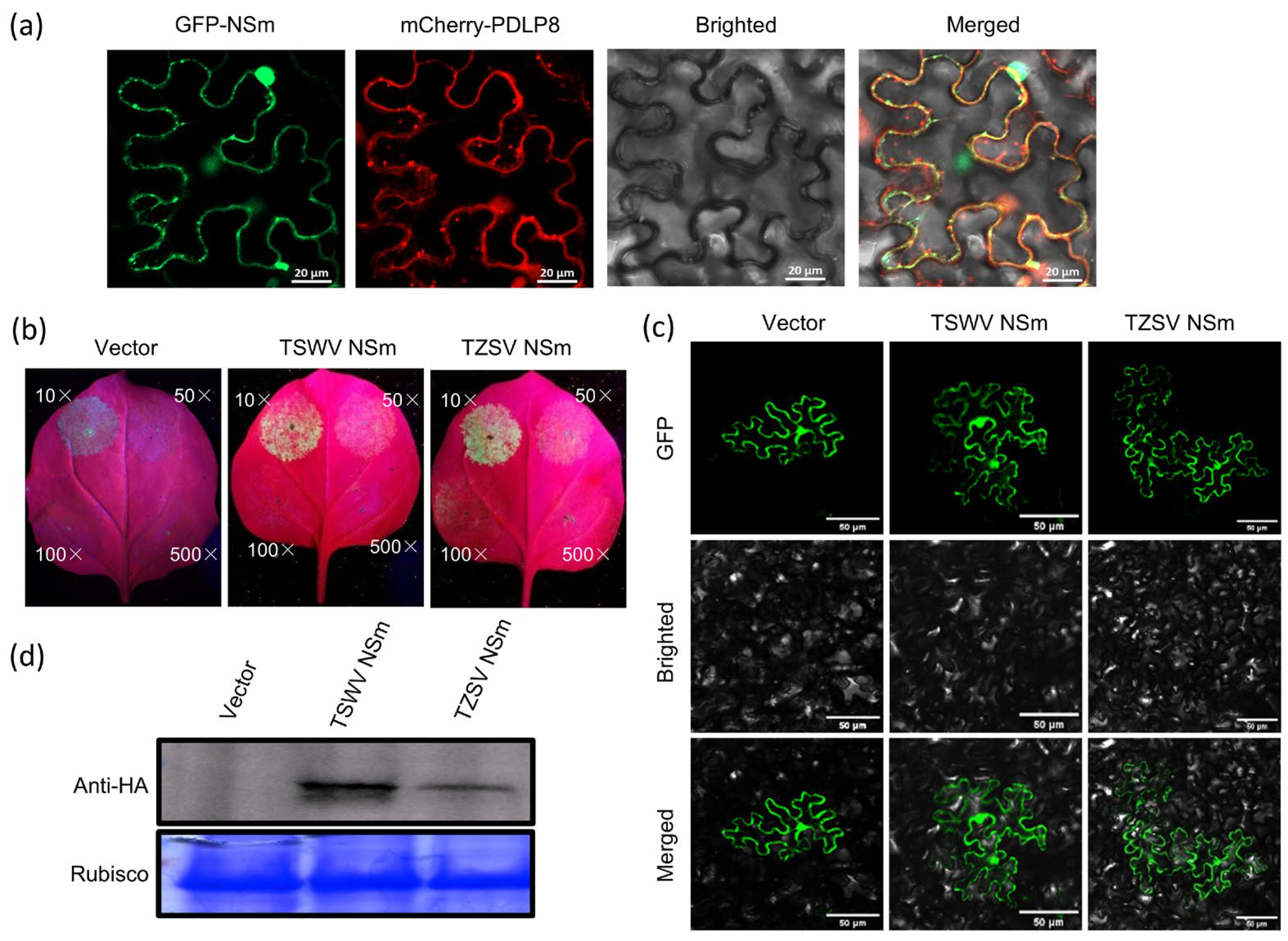
| Constructs | No. of Loci Examined | No. of Loci with a Single Cell | No. of Loci with More Than 2 Cells | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vector | 50 | 50 a | 0 | |
| TSWV NSm | 50 | 4 | 46 | p < 0.05 b |
| TZSV NSm | 50 | 5 | 45 | p < 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Tu, J.; Wang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; et al. The Interaction Network of NSm and Its Role as a Movement Protein in the Tomato Zonate Spot Virus. Viruses 2025, 17, 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121570
Zhao X, Chen J, Zheng L, Tu J, Wang X, Shi X, Zhang Y, Sun S, Zhang J, Zheng X, et al. The Interaction Network of NSm and Its Role as a Movement Protein in the Tomato Zonate Spot Virus. Viruses. 2025; 17(12):1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121570
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xingyue, Jianbin Chen, Limin Zheng, Jiajia Tu, Xin Wang, Xiaobin Shi, Yu Zhang, Shue Sun, Jie Zhang, Xue Zheng, and et al. 2025. "The Interaction Network of NSm and Its Role as a Movement Protein in the Tomato Zonate Spot Virus" Viruses 17, no. 12: 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121570
APA StyleZhao, X., Chen, J., Zheng, L., Tu, J., Wang, X., Shi, X., Zhang, Y., Sun, S., Zhang, J., Zheng, X., & Zhang, D. (2025). The Interaction Network of NSm and Its Role as a Movement Protein in the Tomato Zonate Spot Virus. Viruses, 17(12), 1570. https://doi.org/10.3390/v17121570





