The Potential Role of COVID-19 in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis—A Preliminary Report
Abstract
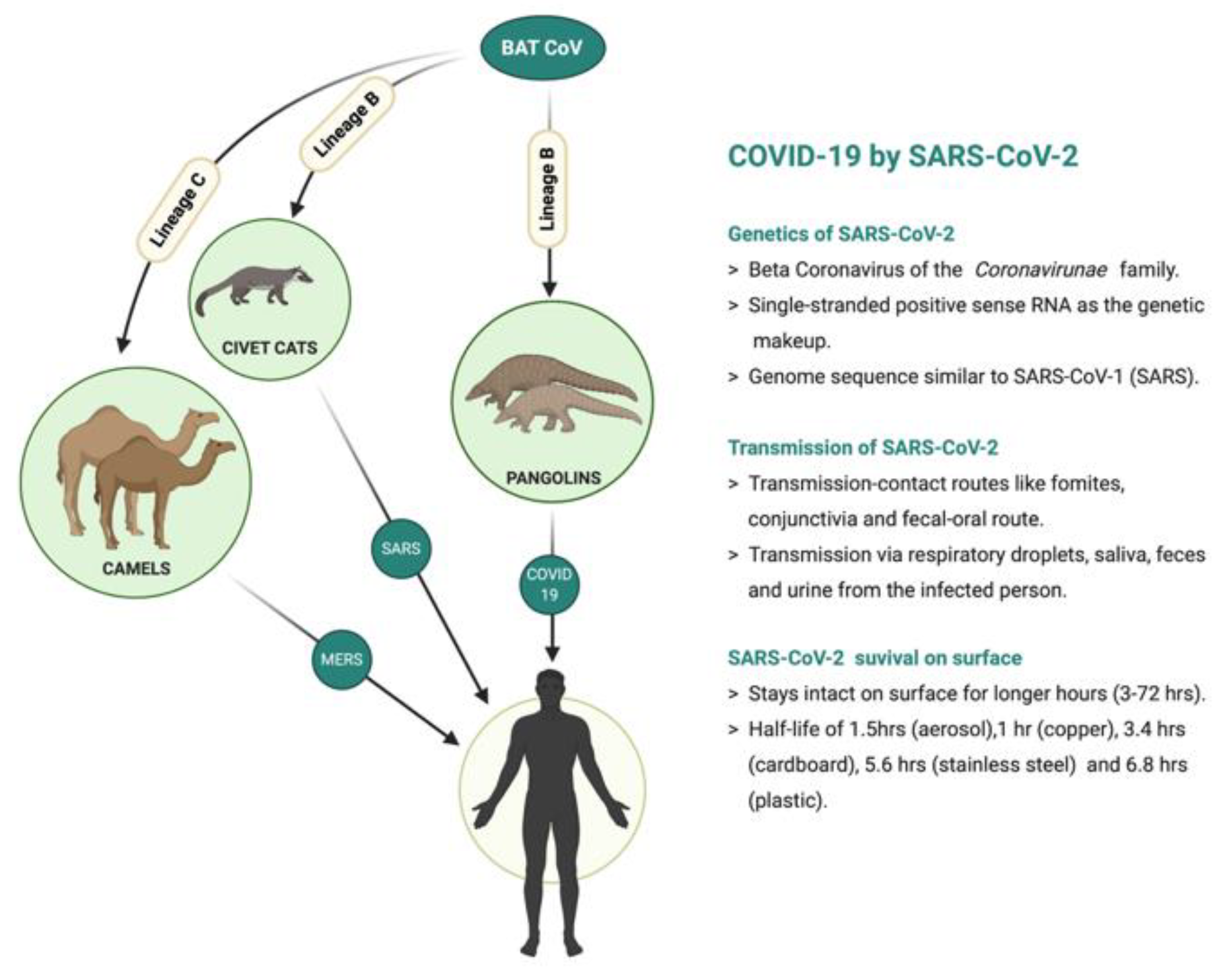
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Invasion and the Effects on the Nervous System
3. MS and Coronavirus Infection
4. Possible Mechanisms for Viral/SARS-CoV-2 Infection-Mediated MS Development
4.1. Cytokine Storm and Neuroinflammation
4.2. Hypoxia Mediated Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Neurodegeneration
4.3. Altering the Phagocytotic Capability of Microglia/Macrophage
- (a)
- Phagocytosis of myelin and extracellular aggregates such as amyloid-β particles;
- (b)
- Release of growth factor, neurotrophic factors, and anti-inflammatory cytokines would stimulate axon branching and repair myelin sheaths;
- (c)
- Recruitment of stem cells and other precursor cells and the triggering of astrocytes to release trophic factors that would neurons to develop and maintain synaptic connections.
5. Conclusions
Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE2 | Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 |
| ADEM | Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis |
| ARDS | Acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| BBB | Blood-brain barrier |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| BMEC | Brain microvascular endothelium cells |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CCL-CXCL | Chemokines |
| CLR | C-type lectin receptors |
| CD8+ | T cells Cytotoxic T cells |
| CD4+ | T cells T-helper cells |
| FLAIR | Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery |
| LIF | Leukaemia inhibitory factor |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MHV | Mouse Hepatitis Virus |
| MS | Multiple Sclerosis |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor |
| NG2 | Nerve/glial antigen 2 |
| PAMP | Pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PRR | Pattern recognition receptors |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus |
| Th | Helper T-cells |
| TJ | Tight junctions |
| TLR | Toll-like receptors |
| Treg | Regulatory T cells |
| TNF | Tumour necrosis factor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. 12 June 2021. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/# (accessed on 13 June 2021).
- Song, Z.; Xu, Y.; Bao, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, P.; Qu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhao, W.; Han, Y.; Qin, C. From SARS to MERS, Thrusting Coronaviruses into the Spotlight. Viruses 2019, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandhi, M.; Yokoe, D.S.; Havlir, D.V. Asymptomatic Transmission, the Achilles’ Heel of Current Strategies to Control Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2158–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarner, J. Three Emerging Coronaviruses in Two Decades. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 153, 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuki, K.; Fujiogi, M.; Koutsogiannaki, S. COVID-19 pathophysiology: A review. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 215, 108427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Yang, H.; Ji, W.; Wu, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Duan, G. Virology, Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Control of COVID-19. Viruses 2020, 12, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lake, M.A. What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research. Clin. Med. 2020, 20, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Needham, E.J.; Chou, S.H.-Y.; Coles, A.J.; Menon, D.K. Neurological Implications of COVID-19 Infections. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 32, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornstein, S.R.; Voit-Bak, K.; Donate, T.; Rodionov, R.N.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Tselmin, S.; Kanczkowski, W.; Müller, G.M.; Achleitner, M.; Wang, J.; et al. Chronic post-COVID-19 syndrome and chronic fatigue syndrome: Is there a role for extracorporeal apheresis? Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.C.; Kern, F.; Losada, P.M.; Agam, M.R.; Maat, C.A.; Schmartz, G.P.; Fehlmann, T.; Stein, J.A.; Schaum, N.; Lee, D.P.; et al. Dysregulation of brain and choroid plexus cell types in severe COVID-19. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 595, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taquet, M.; Geddes, J.R.; Husain, M.; Luciano, S.; Harrison, P.J. 6-month neurological and psychiatric outcomes in 236 379 survivors of COVID-19: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. Lancet Psychiatry 2021, 8, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Ren, Y.; Lv, T. Encephalitis as a clinical manifestation of COVID-19. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 88, 945–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriguchi, T.; Harii, N.; Goto, J.; Harada, D.; Sugawara, H.; Takamino, J.; Ueno, M.; Sakata, H.; Kondo, K.; Myose, N.; et al. A first case of meningitis/encephalitis associated with SARS-Coronavirus-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.-W.; Yuan, S.; Yuen, K.-S.; Fung, S.-Y.; Chan, C.P.; Jin, D.-Y. Zoonotic origins of human coronaviruses. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verdecchia, P.; Cavallini, C.; Spanevello, A.; Angeli, F. The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 76, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, K.G.; Rambaut, A.; Lipkin, W.I.; Holmes, E.C.; Garry, R.F. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sungnak, W.; Huang, N.; Bécavin, C.; Berg, M.; Queen, R.; Litvinukova, M.; Talavera-López, C.; Maatz, H.; Reichart, D.; Sampaziotis, F.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are highly expressed in nasal epithelial cells together with innate immune genes. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche1, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, M.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Chang, J.; Hong, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; et al. Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baig, A.M. Neurological manifestations in COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2020, 26, 499–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pallanti, S. Importance of SARs-Cov-2 anosmia: From phenomenology to neurobiology. Compr. Psychiatry 2020, 100, 152184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carod-Artal, F.J. Neurological complications of coronavirus and COVID-19. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 70, 311–322. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.; Jakimovski, D.; Ramanathan, M.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Zivadinov, R. The role of Epstein-Barr virus in multiple sclerosis: From molecular pathophysiology to in vivo imaging. Neural Regener. Res. 2019, 14, 373. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Duan, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, C. Nervous system involvement after infection with COVID-19 and other coronaviruses. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanin, L.; Saraceno, G.; Panciani, P.P.; Renisi, G.; Signorini, L.; Migliorati, K.; Fontanella, M.M. SARS-CoV-2 can induce brain and spine demyelinating lesions. Acta Neurochir. 2020, 162, 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellul, M.; Solomon, A.T. Acute encephalitis—Diagnosis and management. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, T.; Banks, S.; Bae, C.; Gelber, J.; Alahmadi, H.; Tichauer, M. COVID-19-associated acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM). J. Neurol. 2020, 267, 2799–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, A.; Khan, O. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 123, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Anilkumar, A.C.; Foris, L.A.; Tadi, P. Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Poyiadji, N.; Shahin, G.; Noujaim, D.; Stone, M.; Patel, S.; Griffith, B. COVID-19-associated Acute Hemorrhagic Necrotizing Encephalopathy: CT and MRI Features. Radiology 2020, 2020, 01187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filatov, A.; Sharma, P.; Hindi, F.; Espinosa, P.S. Neurological Complications of Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Encephalopathy. Cureus 2020, 12, e7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bohmwald, K.; Gálvez, N.M.S.; Ríos, M.; Kalergis, A.M. Neurologic Alterations Due to Respiratory Virus Infections. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulgar, V.M. Transcytosis to Cross the Blood Brain Barrier, New Advancements and Challenges. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.A.; Rhea, E.M.; Knopp, R.C.; Banks, W.A. Interactions of SARS-CoV-2 with the Blood–Brain Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, P.G.; Nani, J.V.; Oses, J.P.; Brietzke, E.; Hayashi, M.A. Neuroinflammation and glial cell activation in mental disorders. Brain, Behav. Immun.-Heal. 2020, 2, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulzova, L.; Bhide, M.R.; Andrej, K. Pathogen translocation across the blood-brain barrier. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 57, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde Cardona, G.; Quintana Pájaro, L.D.; Quintero Marzola, I.D.; Ramos Villegas, Y.; Moscote Salazar, L.R. Neurotropism of SARS-CoV 2: Mechanisms and manifestations. J. Neurol. Sci. 2020, 412, 116824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netland, J.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Moore, S.; Cassell, M.; Perlman, S. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Infection Causes Neuronal Death in the Absence of Encephalitis in Mice Transgenic for Human ACE2. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 7264–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubé, M.; Le Coupanec, A.; Wong, A.H.; Rini, J.M.; Desforges, M.; Talbot, P.J. Axonal Transport Enables Neuron-to-Neuron Propagation of Human Coronavirus OC43. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 00404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swanson, P.A., 2nd; McGavern, D.B. Viral diseases of the central nervous system. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 11, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baig, A.M.; Khaleeq, A.; Ali, U.; Syeda, H. Evidence of the COVID-19 Virus Targeting the CNS: Tissue Distribution, Host–Virus Interaction, and Proposed Neurotropic Mechanisms. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dale, R.; Branson, J. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis or multiple sclerosis: Can the initial presentation help in establishing a correct diagnosis? Arch. Dis. Child. 2005, 90, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Cerdá, F.; Sánchez-Gómez, M.V.; Matute, C. The link of inflammation and neurodegeneration in progressive multiple sclerosis. Multiple Scler. Demyelinating Disord. 2016, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donati, D. Viral infections and multiple sclerosis. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Models 2020, 32, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Federoff, H.J. Immune responses in Parkinson’s disease: Interplay between central and peripheral immune systems. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 275178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musella, A.; Gentile, A.; Rizzo, F.R.; De Vito, F.; Fresegna, D.; Bullitta, S.; Vanni, V.; Guadalupi, L.; Bassi, M.A.U.S.; Buttari, F.; et al. Interplay Between Age and Neuroinflammation in Multiple Sclerosis: Effects on Motor and Cognitive Functions. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisticò, R.; Mori, F.; Feligioni, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Centonze, D. Synaptic plasticity in multiple sclerosis and in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, S.; Furlan, R.; De Chiara, V.; Motta, C.; Studer, V.; Mori, F.; Musella, A.; Bergami, A.; Muzio, L.; Bernardi, G.; et al. Interleukin-1β causes synaptic hyperexcitability in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 71, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, S. Demyelinating diseases. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.; Gritti, L.; Crooks, D.; Dombrowski, Y. Oligodendrocytes in Development, Myelin Generation and Beyond. Cells 2019, 8, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Owens, G.P.; Gilden, D.; Burgoon, M.P.; Yu, X.; Bennett, Y.L. Viruses and multiple sclerosis. Neuroscientist 2011, 17, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burks, J.S.; DeVald, B.L.; Jankovsky, L.D.; Gerdes, J.C. Two Coronaviruses Isolated from Central Nervous System Tissue of Two Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Science 1980, 209, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, J.N.; Mounir, S.; Talbot, P.J. Human coronavirus gene expression in the brains of multiple sclerosis patients. Virology 1992, 191, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matías-Guiu, J.; Gomez-Pinedo, U.; Montero-Escribano, P.; Gomez-Iglesias, P.; Porta-Etessam, J.; .Matias-Guiu, J.A. Should we expect neurological symptoms in the SARS-CoV-2 epidemic? Neurologia 2020, 35, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, M.N.; Schaumburg, C.S.; Lane, T.E.; Keirstead, H.S. Endogenous remyelination is induced by transplant rejection in a viral model of multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 212, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, J.; Kremer, S.; Merdji, H.; Clere-Jehl, R.; Schenck, M.; Kummerlen, C.; Collange, O.; Boulay, C.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Ohana, M.; et al. Neurologic Features in Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2268–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palao, M.; Fernández-Díaz, E.; Gracia-Gil, J.; Romero-Sánchez, C.; Díaz-Maroto, I.; Segura, T. Multiple sclerosis following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 45, 102377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novi, G.; Rossi, T.; Pedemonte, E.; Saitta, L.; Rolla, C.; Roccatagliata, L.; Inglese, M.; Farinini, D. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichard, R.R.; Kashani, K.B.; Boire, N.A.; Constantopoulos, E.; Guo, Y.; Lucchinetti, C.F. Neuropathology of COVID-19: A spectrum of vascular and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM)-like pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyk, D.S.; Alexander, A.K.; Walker, M.; Walker, M. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis progressing to multiple sclerosis: Are infectious triggers involved? Immunol. Res. 2014, 60, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children: Differential diagnosis from multiple sclerosis on the basis of clinical course. Korean J. Pediatr. 2011, 54, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, D.; Biswas, K.; Nag, S.; Ramachandra, S.G.; Das Sarma, J. Microglia Play a Major Role in Direct Viral-Induced Demyelination. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayo, L.; Quintana, F.J.; Weiner, H.L. The innate immune system in demyelinating disease. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 248, 170–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielian, T. Toll-like receptors in central nervous system glial inflammation and homeostasis. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 83, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, J.; Smeyne, R.; Jang, H.; Miller, B.; Okun, M. Parkinsonism and neurological manifestations of influenza throughout the 20th and 21st centuries. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marrodan, M.; Alessandro, L.; Farez, M.F.; CORREALE, J. The role of infections in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 25, 891–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlinton, R.E.; Martynova, E.; Rizvanov, A.A.; Khaiboullina, S.; Verma, S. Role of viruses in the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis. Viruses 2020, 12, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Cai, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liao, H.; Zhi, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Cytokine storm intervention in the early stages of COVID-19 pneumonia. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020, 53, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, P.; McAuley, D.; Brown, M.; Sanchez, E.; Tattersall, R.S.; Manson, J.J. COVID-19: Consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet 2020, 395, 1033–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Moosavi, A.M. Cytokine-targeted therapy in severely ill COVID-19 patients: Options and cautions. Mortality 2020, 4, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, N.; Razavi, S.; Nikzad, E. Multiple Sclerosis: Pathogenesis, Symptoms, Diagnoses and Cell-Based Therapy. Cell J. 2017, 19, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, K. Regulatory T cells in multiple sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Neuroimmunol. 2020, 11, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peferoen, L.; Kipp, M.; Van Der Valk, P.; van Noort, J.; Amor, S. Oligodendrocyte-microglia cross-talk in the central nervous system. Immunology 2014, 141, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponath, G.; Park, C.; Pitt, D. The Role of Astrocytes in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutma, E.; Van Gent, D.; Amor, S.; Peferoen, L.A.N. Astrocyte and Oligodendrocyte Cross-Talk in the Central Nervous System. Cells 2020, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henstridge, C.M.; Tzioras, M.; Paolicelli, R.C. Glial Contribution to Excitatory and Inhibitory Synapse Loss in Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghatak, N.R. Occurrence of oligodendrocytes within astrocytes in demyelinating lesions. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1992, 51, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furer, M.; Hartloper, V.; Wilkins, J.; Nath, A. Lymphocyte Emperipolesis in Human Glial Cells. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1993, 1, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, H.L.; Willenbring, R.C.; Jin, F.; Manhart, W.A.; Lafrance, S.J.; Pirko, I.; Johnson, A.J. Perforin Competent CD8 T Cells Are Sufficient to Cause Immune-Mediated Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e111401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balabanov, R.; Strand, K.; Goswami, R.; McMahon, E.; Begolka, W.; Miller, S.D.; Popko, B. Interferon-gamma-oligodendrocyte interactions in the regulation of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kostianovsky, A.M.; Maier, L.M.; Anderson, R.C.; Bruce, J.N.; Anderson, D.E. Astrocytic Regulation of Human Monocytic/Microglial Activation. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5425–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, D.; López-Rodas, G.; Casanova, B.; Burgal Marti, M. Perturbed glucose metabolism: Insights into multiple sclerosis pathogenesis. Front. Neurol. 2014, 5, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regenold, W.T.; Phataka, P.; Makley, M.J.; Stone, R.D.; Klinge, M.A. Cerebrospinal fluid evidence of increased extra-mitochondrial glucose metabolism implicates mitochondrial dysfunction in multiple sclerosis disease progression. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 275, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Almeida, A.; Esteban, M.D.; Bolanos, J.; Medina, J.M. Oxygen and glucose deprivation induces mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurones but not in astrocytes in primary culture. J. Neurochem. 2002, 81, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barcelos, I.P.; Troxell, R.M.; Graves, J.S. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Multiple Sclerosis. Biology 2019, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, K.; Bourdette, D.; Forte, M. Mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, A.H.; Tavitian, B. Noninvasive molecular imaging of neuroinflammation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1393–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, H.; Kotter, M.R.; Franklin, R.J. Debris clearance by microglia: An essential link between degeneration and regeneration. Brain 2009, 132 Pt 2, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotter, M.; Setzu, A.; Sim, F.; Van Rooijen, N.; Franklin, R.J. Macrophage depletion impairs oligodendrocyte remyelination following lysolecithin-induced demyelination. Glia 2001, 35, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawji, K.S.; Mishra, M.K.; Yong, V.W. Regenerative Capacity of Macrophages for Remyelination. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Genome | Virus Family | Virus Type | Specifics | Targets | Association with MS | CNS Entry | [REF] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dsDNA | Herpes viridae | Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) | Alpha herpesvirus | neuronal | VZV is frequently detected during the active disease phases of MS | ORN | (Sotelo and Corona, 2011, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) |
| Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 and 2) | Viral encephalitis and demyelinating encephalitis | ORN | (Boukhvalova et al., 2020, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) | ||||
| Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | Beta herpesvirus | non-neuronal (macrophages and B cells) | -CMV seropositivity and MS diagnosis expansion -T-cell driven responses, pneumonia | BBB and BMVEC | (Langer-Gould et al., 2017, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) | ||
| Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) | non-neuronal (macrophages and B cells) | -HHV-6 antibody and DNA positivity and MS -HHV-6 proteins have cross reactivity with myelin basic protein, which could contribute to CD8+ T cell-mediated oligodendrocyte death | unknown | (Leibovitch and Jacobson, 2014, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) | |||
| Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) | Gamma herpesvirus | non-neuronal (macrophages and B cells) | -Infectious mononucleosis, which is caused by delayed primary EBV infection, predisposes MS. -EBV may also contribute to MS pathogenesis indirectly by activating silent human endogenous retrovirus-W. | BBB and BMVEC | (Guan et al., 2019, Langer-Gould et al., 2017, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) | ||
| dsDNA | Polyomaviridae | Human polyomavirus 2 or John Cunningham virus (JCV) | neuronal | -Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy -Risk assessment and monitoring of patients based on JCV seropositivity and antibody titer is necessary in treatment decision for MS | BBB and BMVEC | (Paz et al., 2018, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) | |
| ssRNA | Retroviridae | Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs-H and W) | Gammaretrovirus | non-neuronal (immune cells) | Inflammation, aberrant immune reaction and dysregulated gene expression cellular immune responses | BBB | (Christensen, 2017, Marrodan et al., 2019, Tarlinton et al., 2020) |
| Name | MS Associated Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| IL-2 | Plays a role in the loss of immune tolerance. Helps in the proliferation of autoreactive T cells. | (Göbel et al., 2018, Osherov and Milo, 2017) |
| IL-6 | T cell expansion, pro-inflammatory | (Göbel et al., 2018, Ireland et al., 2015, Fiedler et al., 2017) |
| IL-17 | Reduced lesion activity, demyelination in MS | (Göbel et al., 2018, Ghaffari et al., 2017) |
| IL-10 | Anti-inflammatory, Decreases antigen presentation of monocytes and macrophages; Neuroprotective, Decreases prior to relapse and increased during remission | (Göbel et al., 2018, Wei et al., 2019) |
| IL-7 | Lymphocyte development, Increased risk of MS | (Wu et al., 2016, Ghaffari et al., 2017) |
| IL-8/CXCL8 | Chemo-attractant for neutrophils and monocytes, In MS, monocyte recruitment to the CNS | (Lund et al., 2004) |
| IL-1 | Pro-inflammatory, pathogenic role in MS | (Fiedler et al., 2017, Lin and Edelson, 2017, Ghaffari et al., 2017) |
| GM-CSF | Regulation of microglial functions, stimulation of microglial priming for antigen presentation, pathogenic action in MS | (Aram et al., 2019) |
| IFN-gamma | Drives inflammation | (Arellano et al., 2015) |
| TNF-α | Pro-inflammatory | (Fiedler et al., 2017) |
| TGF-β | Lymphocyte proliferation, differentiation, and survival, protective effect in MS | (Mirshafiey and Mohsenzadegan, 2009) |
| IP-10/CXCL10 | Pathogenesis in MS | (Franciotta et al., 2001) |
| NO | Dual role- immunomodulatory, Disrupts BBB, demyelination, axonal degeneration | (Smith and Lassmann, 2002) |
| MCP-1 | Pathogenesis in MS | (Franciotta et al., 2001) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Satheesh, N.J.; Salloum-Asfar, S.; Abdulla, S.A. The Potential Role of COVID-19 in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis—A Preliminary Report. Viruses 2021, 13, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102091
Satheesh NJ, Salloum-Asfar S, Abdulla SA. The Potential Role of COVID-19 in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis—A Preliminary Report. Viruses. 2021; 13(10):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102091
Chicago/Turabian StyleSatheesh, Noothan J., Salam Salloum-Asfar, and Sara A. Abdulla. 2021. "The Potential Role of COVID-19 in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis—A Preliminary Report" Viruses 13, no. 10: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102091
APA StyleSatheesh, N. J., Salloum-Asfar, S., & Abdulla, S. A. (2021). The Potential Role of COVID-19 in the Pathogenesis of Multiple Sclerosis—A Preliminary Report. Viruses, 13(10), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13102091






