Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Breast Cancer: A Case Report
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
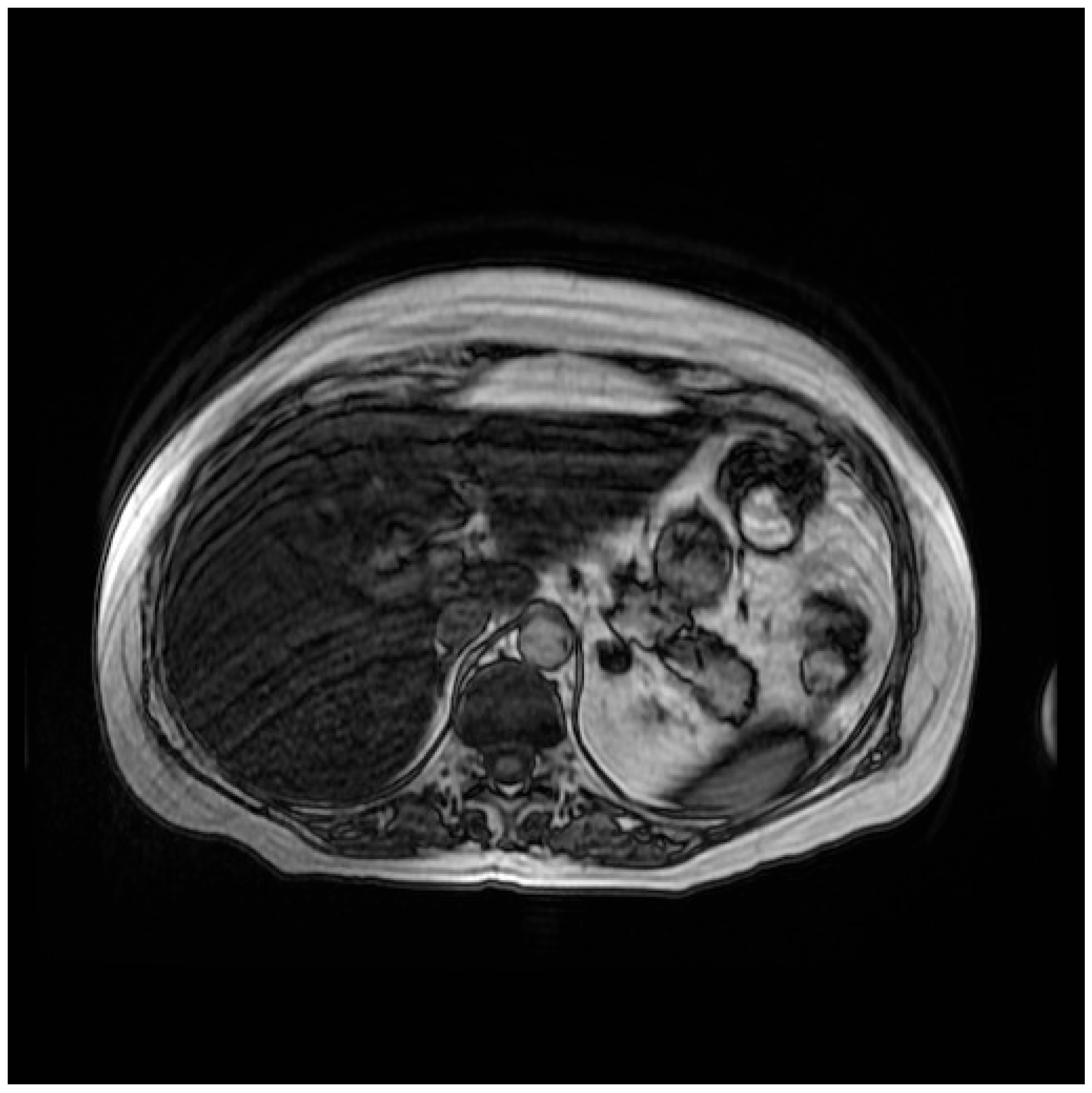
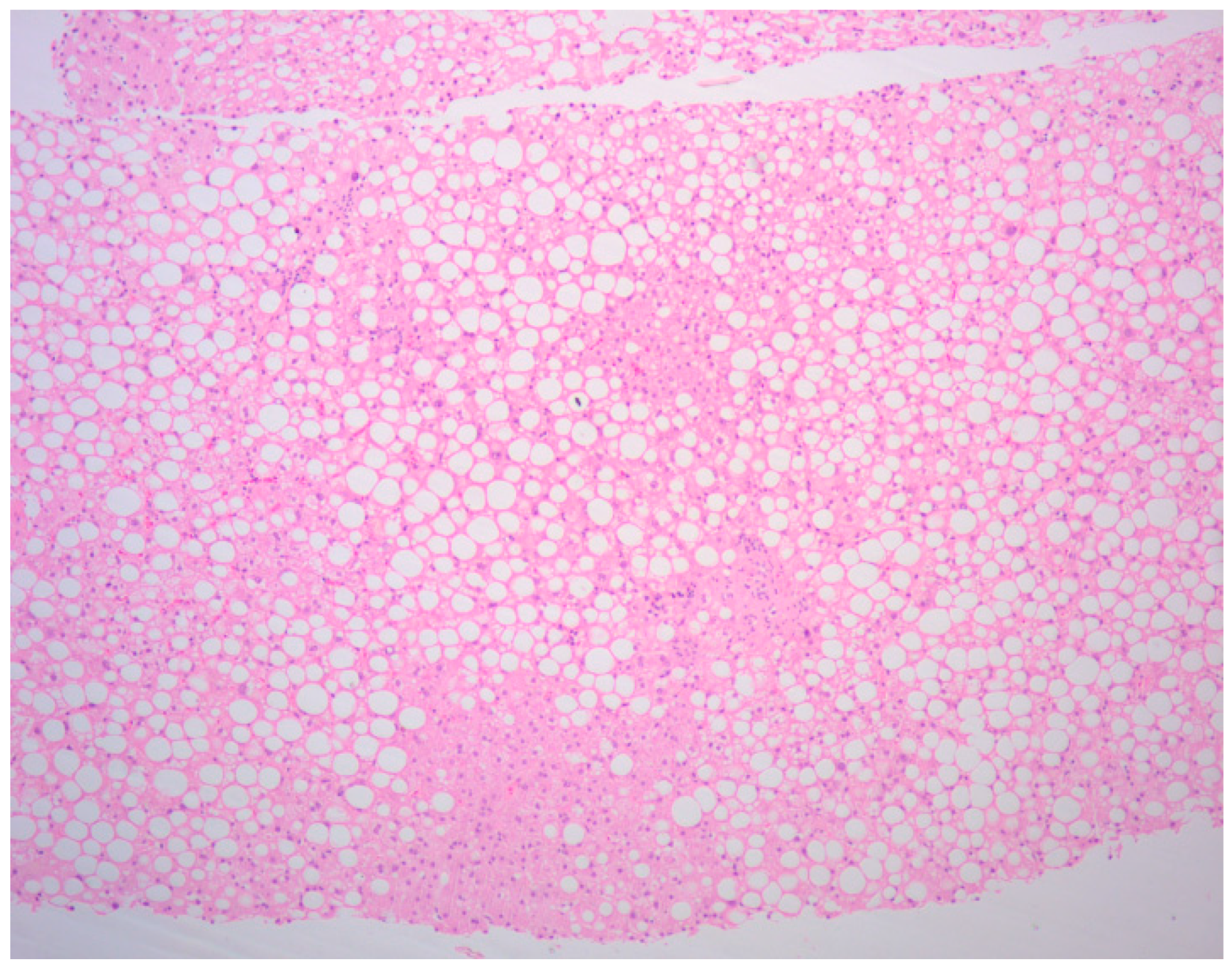
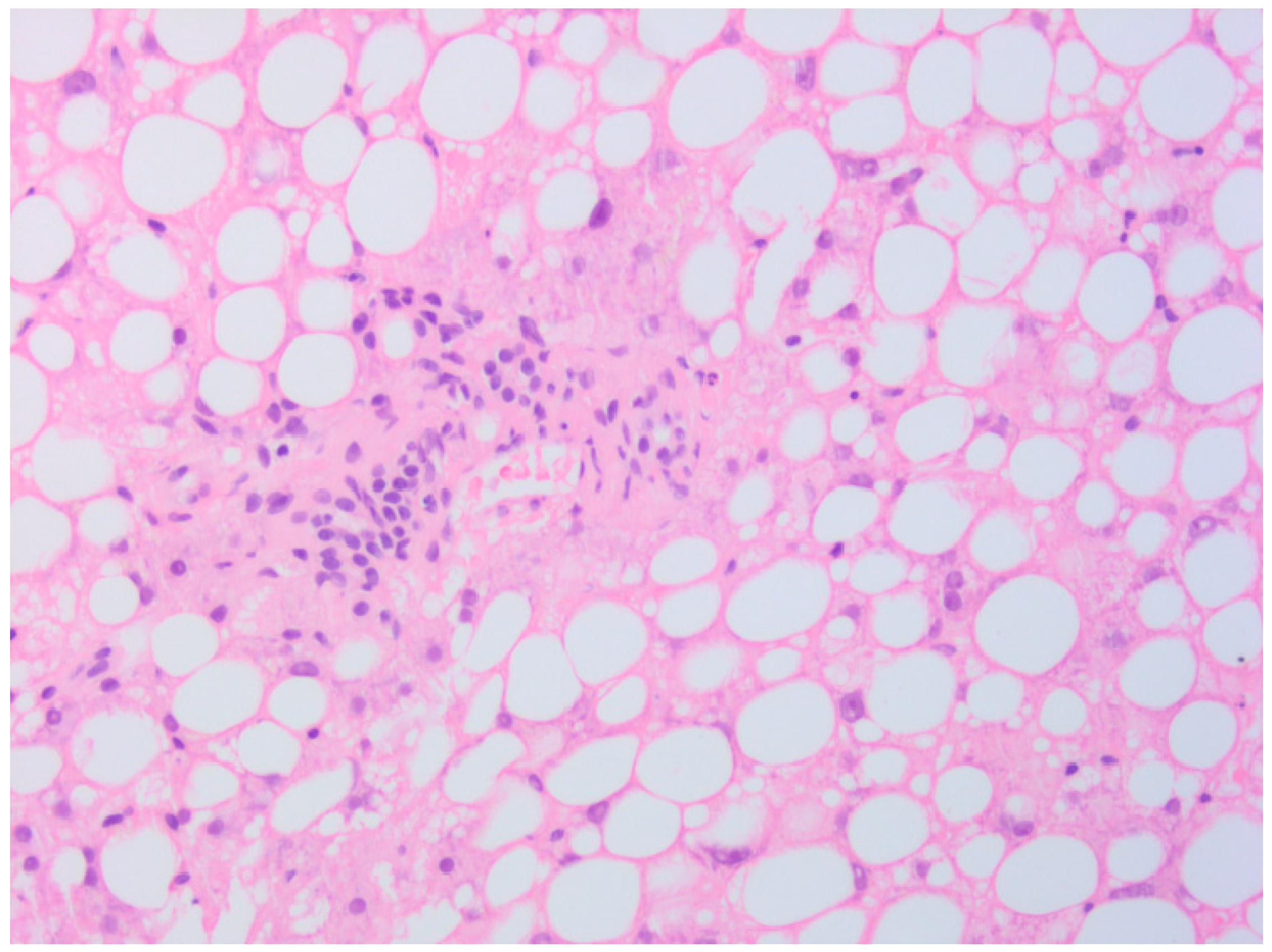
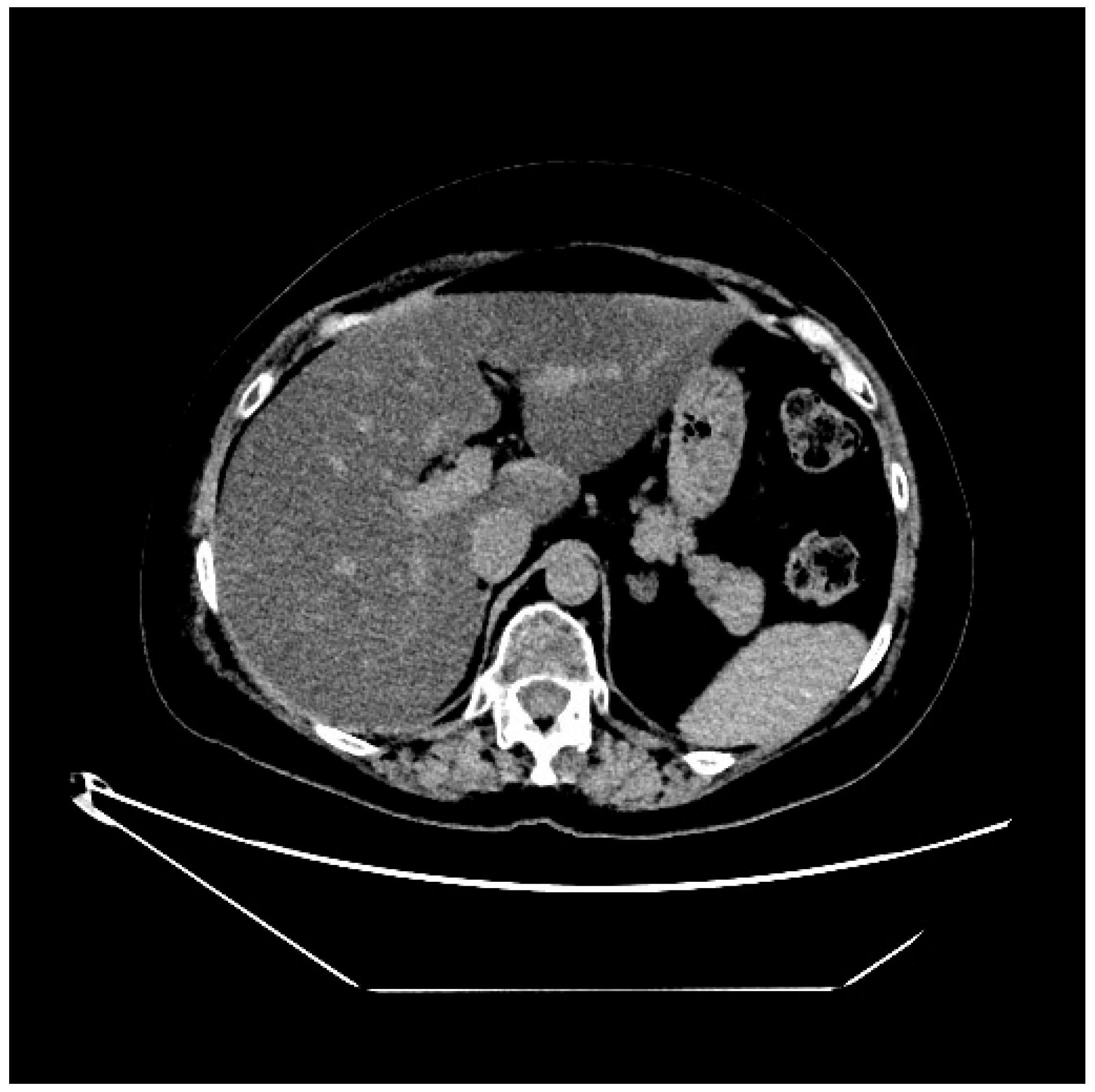
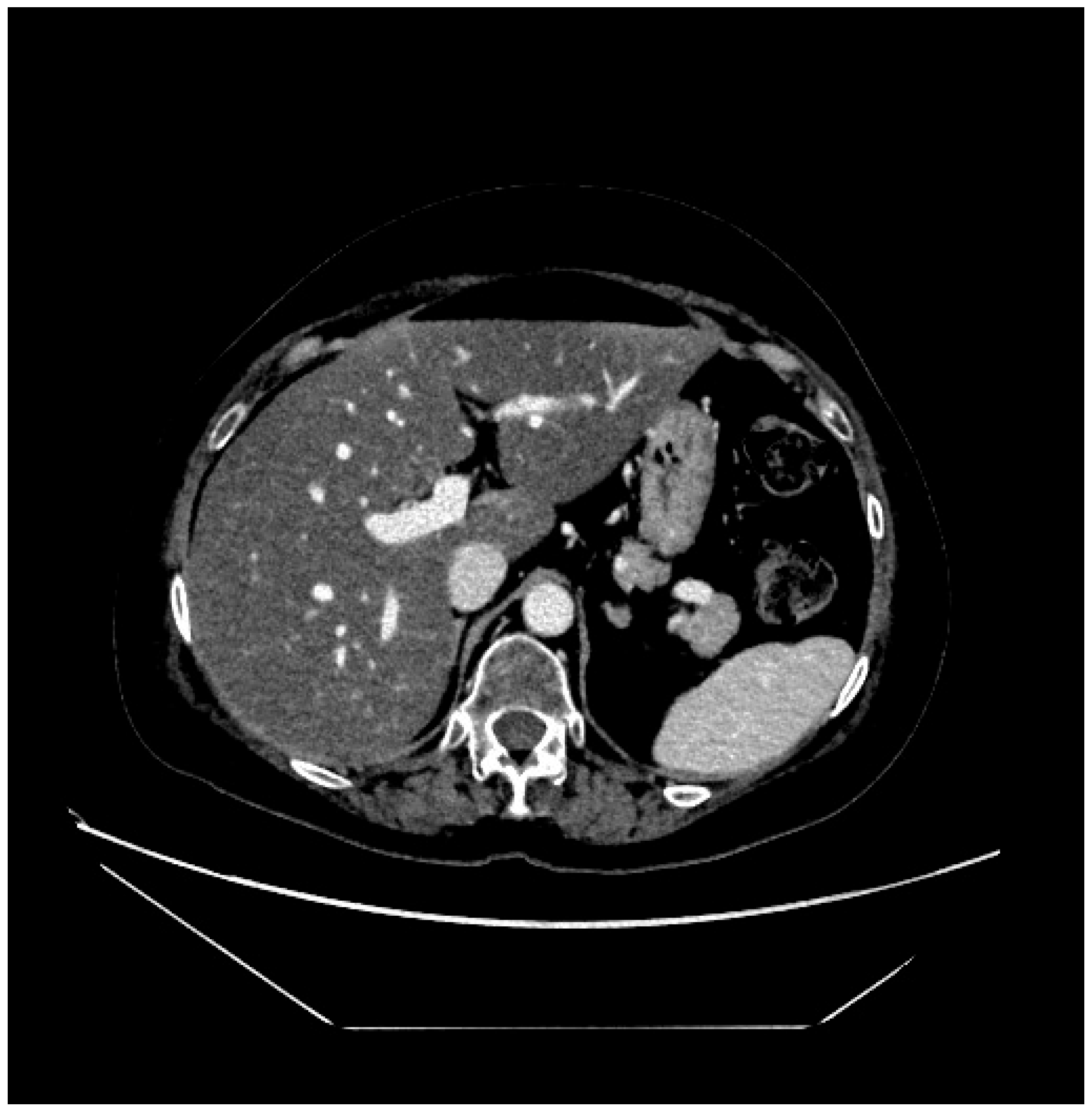
2. Case Presentation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T-DXd | Trastuzumab deruxtecan |
| DILI | Drug-induced liver injury |
| ADC | Antibody–drug conjugate |
| DB-01 | DESTINY-Breast01 |
| mBC | Metastatic breast cancer |
| mPFS | Median progression-free survival |
| mDoR | Median duration of response |
| DB-03 | DESTINY-Breast03 |
| T-DM1 | Trastuzumab emtansine |
| OS | Overall survival |
| DB-02 | DESTINY-Breast02 |
| DB-09 | DESTINY-Breast09 |
| DB-04 | DESTINY-Breast04 |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| DB-06 | DESTINY-Breast06 |
| ILD | Interstitial lung disease |
| HR | Hormone receptors |
| 18F-FDG PET/CT | 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| G | Grade |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| AST | Aspartate transaminase |
| ALT | Alanine transaminase |
| TEAEs | Treatment-emergent adverse events |
| FAERS | FDA Adverse Event Reporting System |
| ULN | Upper limit of normal |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| RUCAM | Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method |
References
- Zouein, J.; Karam, E.; Strickler, J.H.; Kourie, H.R. Trastuzumab-Deruxtecan: Redefining HER2 as a Tumor Agnostic Biomarker. Target. Oncol. 2024, 19, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Saura, C.; Yamashita, T.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S.-B.; Tamura, K.; Andre, F.; Iwata, H.; Ito, Y.; Tsurutani, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Positive Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Hurvitz, S.; Hegg, R.; Chung, W.-P.; Im, S.-A.; Jacot, W.; Ganju, V.; Chiu, J.W.Y.; Xu, B.; Hamilton, E.; Madhusudan, S.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer: Updated results from DESTINY-Breast03, a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, F.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, S.-B.; Takano, T.; Im, S.-A.; Borges, G.; Lima, J.P.; Aksoy, S.; Gregori, J.G.; De Laurentiis, M.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus treatment of physician’s choice in patients with HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer (DESTINY-Breast02): A randomised, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolaney, S.M.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Park, Y.H.; Rimawi, M.F.; Manich, C.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Toi, M.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) + pertuzumab (P) vs taxane + trastuzumab + pertuzumab (THP) for first-line (1L) treatment of patients (pts) with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–positive (HER2+) advanced/metastatic breast cancer (a/mBC): Interim results from DESTINY-Breast09. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, LBA1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Hu, X.; Dent, R.; Yonemori, K.; Barrios, C.H.; O’shaughnessy, J.A.; Wildiers, H.; Pierga, J.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Saura, C.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan after Endocrine Therapy in Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 2110–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Hamilton, J.P. Drug-induced Liver Injury. US Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Rev. 2010, 6, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Slamon, D.J.; Clark, G.M.; Wong, S.G.; Levin, W.J.; Ullrich, A.; McGuire, W.L. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science 1987, 235, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onitilo, A.A.; Engel, J.M.; Greenlee, R.T.; Mukesh, B.N. Breast Cancer Subtypes Based on ER/PR and Her2 Expression: Comparison of Clinicopathologic Features and Survival. Clin. Med. Res. 2009, 7, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, J.; Kim, S.-B.; Chung, W.-P.; Im, S.-A.; Park, Y.H.; Hegg, R.; Kim, M.H.; Tseng, L.-M.; Petry, V.; Chung, C.-F.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan versus Trastuzumab Emtansine for Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Yang, X.; Tang, L.; Chen, J. A pharmacovigilance study on drug-induced liver injury associated with antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) based on the food and drug administration adverse event reporting system. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2024, 23, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.J.; Aithal, G.P.; Björnsson, E.S.; Kaplowitz, N.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Larrey, D.; Karlsen, T.H. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1222–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, B.H. Drug Induced Liver Injury (DILI). Mechanisms and Medicinal Chemistry Avoidance/Mitigation Strategies. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11397–11419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.J. Pathogenesis of Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Clinical Perspectives. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 914–928.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, R.A.; Luyendyk, J.P.; Maddox, J.F.; Ganey, P.E. Inflammation and Drug Idiosyncrasy—Is There a Connection? J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 307, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknahad, H.; Heidari, R.; Firuzi, R.; Abazari, F.; Ramezani, M.; Azarpira, N.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Najibi, A.; Saeedi, A. Concurrent Inflammation Augments Antimalarial Drugs-Induced Liver Injury in Rats. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, H.; Björnsson, E. Drug-induced liver injury: Pathogenesis, epidemiology, clinical features, and practical management. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 97, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricart, A.D. Drug-induced liver injury in Oncology. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2013–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danan, G.; Teschke, R. RUCAM in Drug and Herb Induced Liver Injury: The Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, G.P.; Watkins, P.B.; Andrade, R.J.; Larrey, D.; Molokhia, M.; Takikawa, H.; Hunt, C.M.; A Wilke, R.; Avigan, M.; Kaplowitz, N.; et al. Case Definition and Phenotype Standardization in Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Goodman, Z.; Brunt, E.; Avigan, M.I.; Regev, A.; Hayashi, P.H.; Lewis, J.H.; Mehta, R.; Harrison, S.A.; et al. Liver biopsy for assessment of suspected drug-induced liver injury in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis clinical trials: Expert consensus from the Liver Forum. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 59, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettiplace, A.; Marcinak, J.; Merz, M.; Zhang, H.; Kikuchi, L.; Regev, A.; Palmer, M.; Rockey, D.; Fontana, R.; Hayashi, P.H.; et al. Review article: Recommendations for detection, assessment and management of suspected drug-induced liver injury during clinical trials in oncology patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 60, 1293–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Barnhart, H.X.; Bonacini, M.; Ghabril, M.; Hayashi, P.H.; Odin, J.A.; Rockey, D.C.; Rossi, S.; Serrano, J.; Tillmann, H.L.; et al. Value of liver biopsy in the diagnosis of drug-induced liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E. Role of liver biopsy in the management of idiosyncratic DILI. Liver Int. 2025, 45, e16097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsson, E.S.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Categorization of drugs implicated in causing liver injury: Critical assessment based on published case reports. Hepatology 2016, 63, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuna, K.; Ninomiya, J.; Ogawa, T.; Tsuji, E. Hepatotoxicity induced by trastuzumab used for breast cancer adjuvant therapy: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2014, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, A.; Carrera, S.; Ferreiro, J.; de Lobera, A.R.; Mañé, J.M.; López-Vivanco, G. Reversible liver toxicity with adjuvant trastuzumab for localized breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 2045–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucicevic, D.; Carey, E.J.; Karlin, N.J. Trastuzumab-Induced Hepatotoxicity: A Case Report. Breast Care 2013, 8, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, S.; Parsa, V.; Liu, C.Y.; A Fontana, J. Trastuzumab-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Ann. Pharmacother. 2008, 42, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hey-Hadavi, J.; Seekins, D.; Palmer, M.; Coffey, D.; Caminis, J.; Abdullaev, S.; Patwardhan, M.; Tyler, H.; Raheja, R.; Stanley, A.M.; et al. Overview of Causality Assessment for Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) in Clinical Trials. Drug Saf. 2021, 44, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnsson, E.S.; Vucic, V.; Stirnimann, G.; Robles-Díaz, M. Role of Corticosteroids in Drug-Induced Liver Injury. A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 820724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Disease | Trial ° | Control Arm | Enzymes | aG Exp Arm | ≥G3 exp arm | aG ctrl Arm | ≥G3 Ctrl Arm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | DB-03 | T-DM1 | AST | 23.3 | 0.8 | 37.2 | 5.0 |
| ALT | 19.5 | 1.6 | 27.2 | 4.6 | |||
| DB-04 | TPC | TA | 34.0 | 6.7 | 31.4 | 13.4 | |
| DB-06 | TPC | TA | 29.5 | 2.3 | 11.8 | 0 | |
| DB-09 | THP | TA | 36.0 | 4.5 | 18.8 | 2.1 | |
| Gastric | DG-01 | TPC | TA | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| DG-02 | - | AST | 15.2 | 1.3 | |||
| ALT | 8.9 | 1.3 | |||||
| DG-04 | RAM + PTX | TA | 21.7 | 2.0 | 9.4 | 0.4 | |
| Lung | DL-01 * | - | AST | 7.3 | 0 | ||
| ALT | 98 | 0 | |||||
| DL-02 ** | - | TA | 21.8 | 3.8 | |||
| Colon | CRC-01 | - | AST | 7.7 | 2.6 | ||
| ALT | 7.7 | 1.3 | |||||
| CRC-02 | - | AST | 8.4 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lisanti, C.; Della Rossa, S.; Zottarelli, E.; Vida, R.; Bolzonello, S.; Da Ros, L.; Zdjelar, A.; Cecchin, E.; Perin, T.; Puglisi, F. Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Breast Cancer: A Case Report. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110606
Lisanti C, Della Rossa S, Zottarelli E, Vida R, Bolzonello S, Da Ros L, Zdjelar A, Cecchin E, Perin T, Puglisi F. Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Breast Cancer: A Case Report. Current Oncology. 2025; 32(11):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110606
Chicago/Turabian StyleLisanti, Camilla, Serena Della Rossa, Emma Zottarelli, Riccardo Vida, Silvia Bolzonello, Lucia Da Ros, Adrian Zdjelar, Erika Cecchin, Tiziana Perin, and Fabio Puglisi. 2025. "Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Breast Cancer: A Case Report" Current Oncology 32, no. 11: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110606
APA StyleLisanti, C., Della Rossa, S., Zottarelli, E., Vida, R., Bolzonello, S., Da Ros, L., Zdjelar, A., Cecchin, E., Perin, T., & Puglisi, F. (2025). Idiosyncratic Drug-Induced Liver Injury and Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Breast Cancer: A Case Report. Current Oncology, 32(11), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol32110606







