HC-Pro Disrupts miR319–TCP Regulatory Pathways to Induce Sterility in Transgenic Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
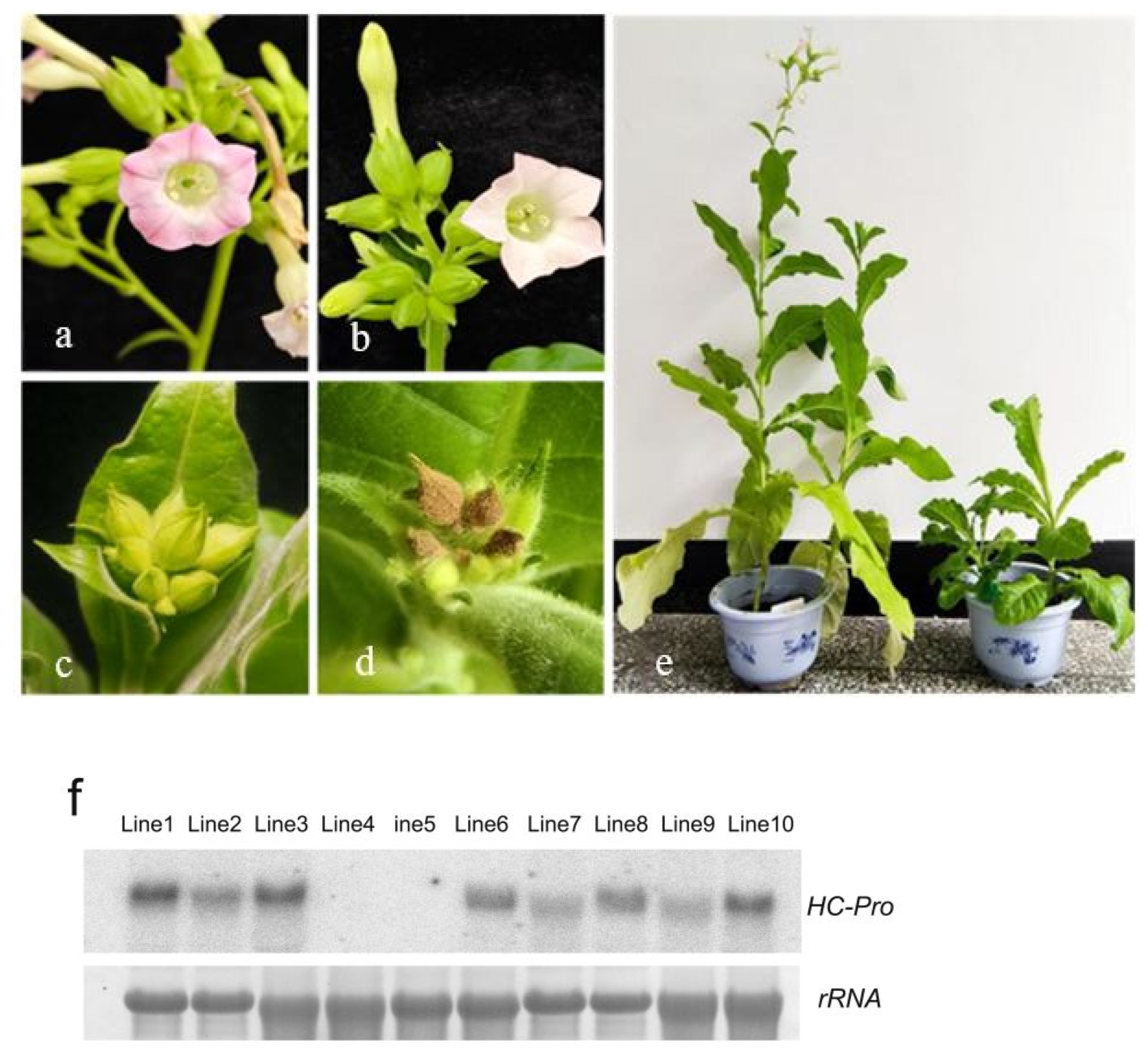
2.1. Abnormal Development of Floral Organs in Transgenic Tobacco Plants Expressing HC-Pro
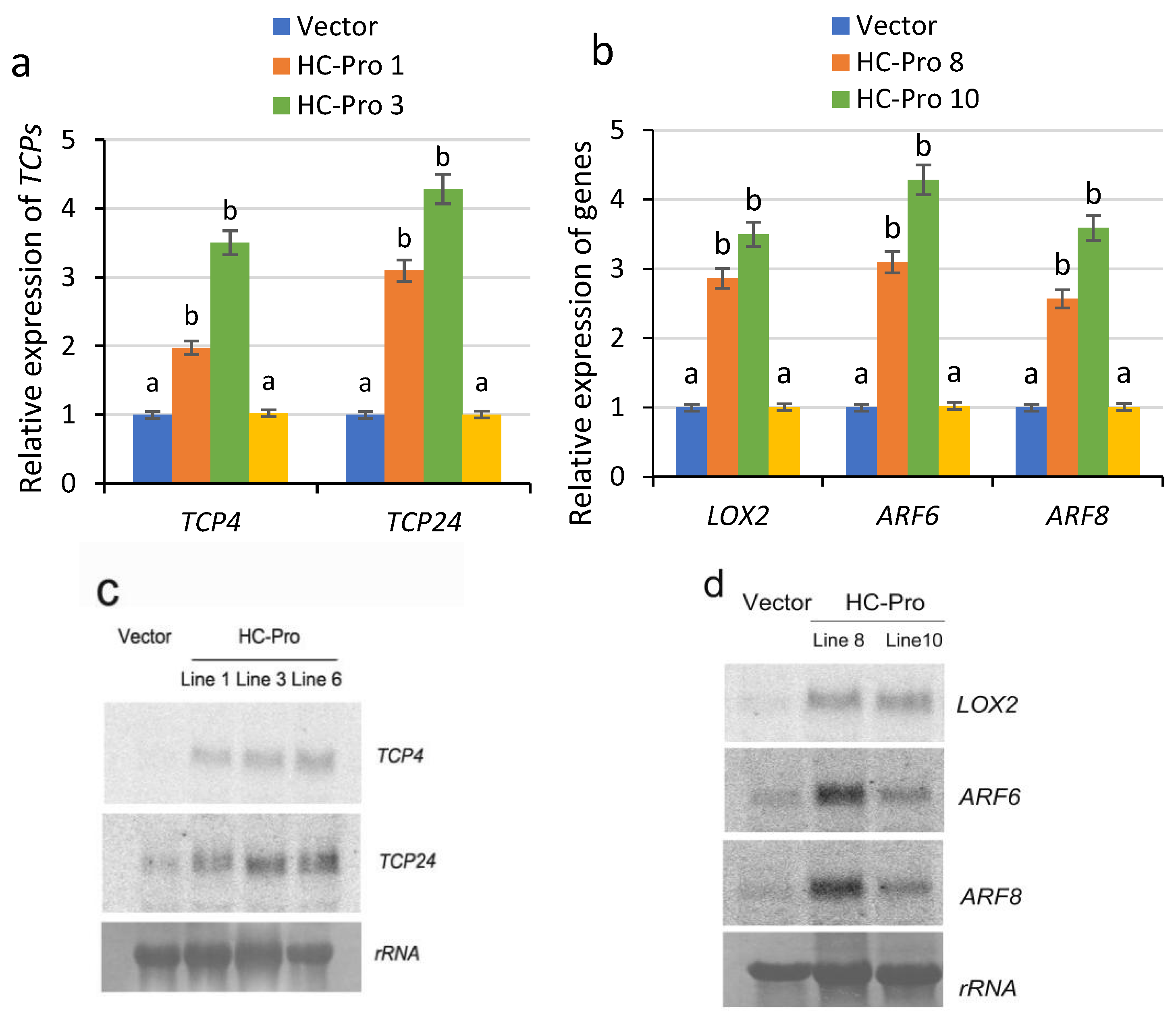
2.2. Abnormal Development of Floral Organs in Transgenic Tobacco Plants Expressing HC-Pro Is Associated with Abnormal Gene Expression
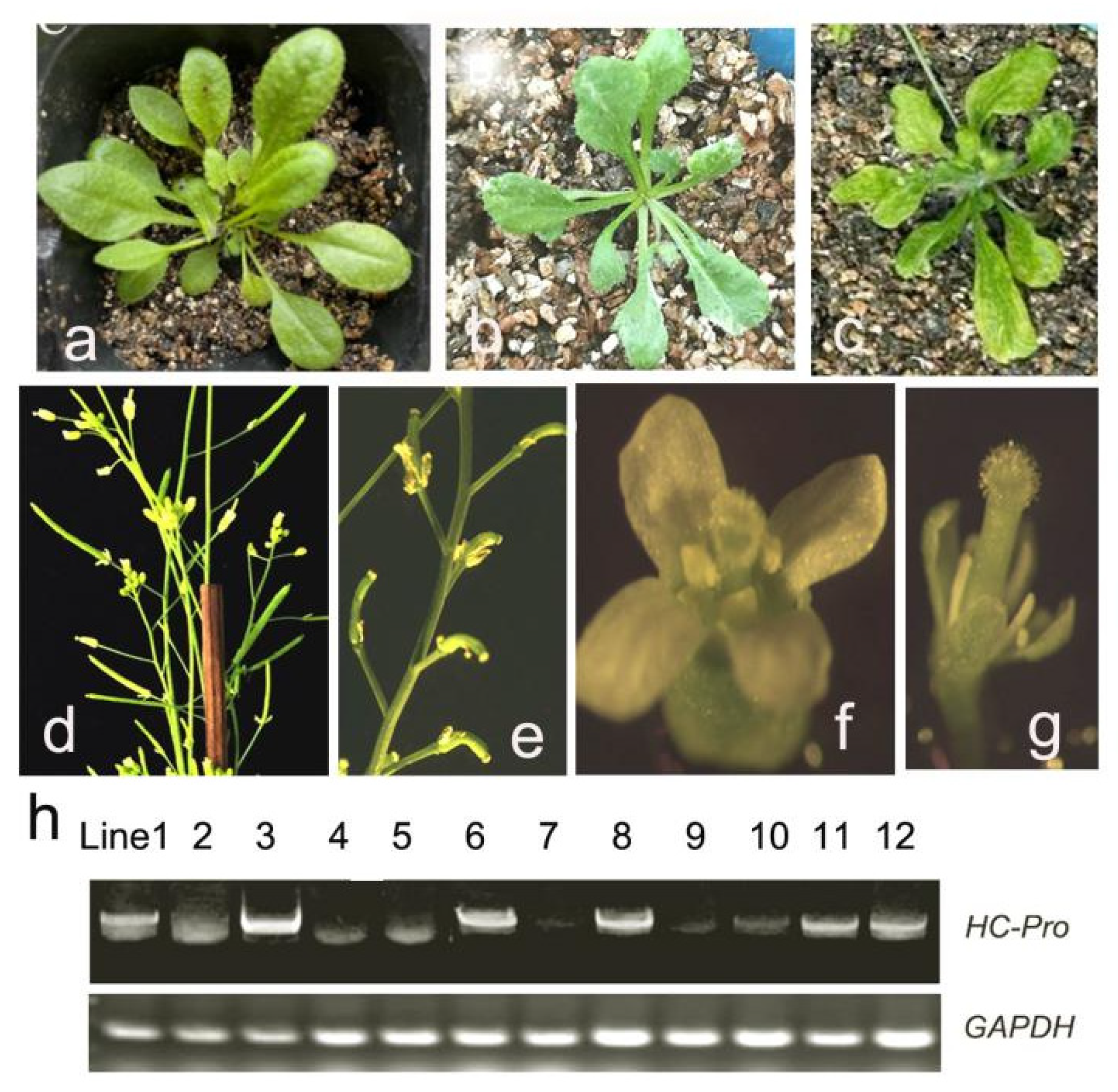
2.3. Aberrant Phenotype and Identification of HC-Pro Transgenic A. thaliana
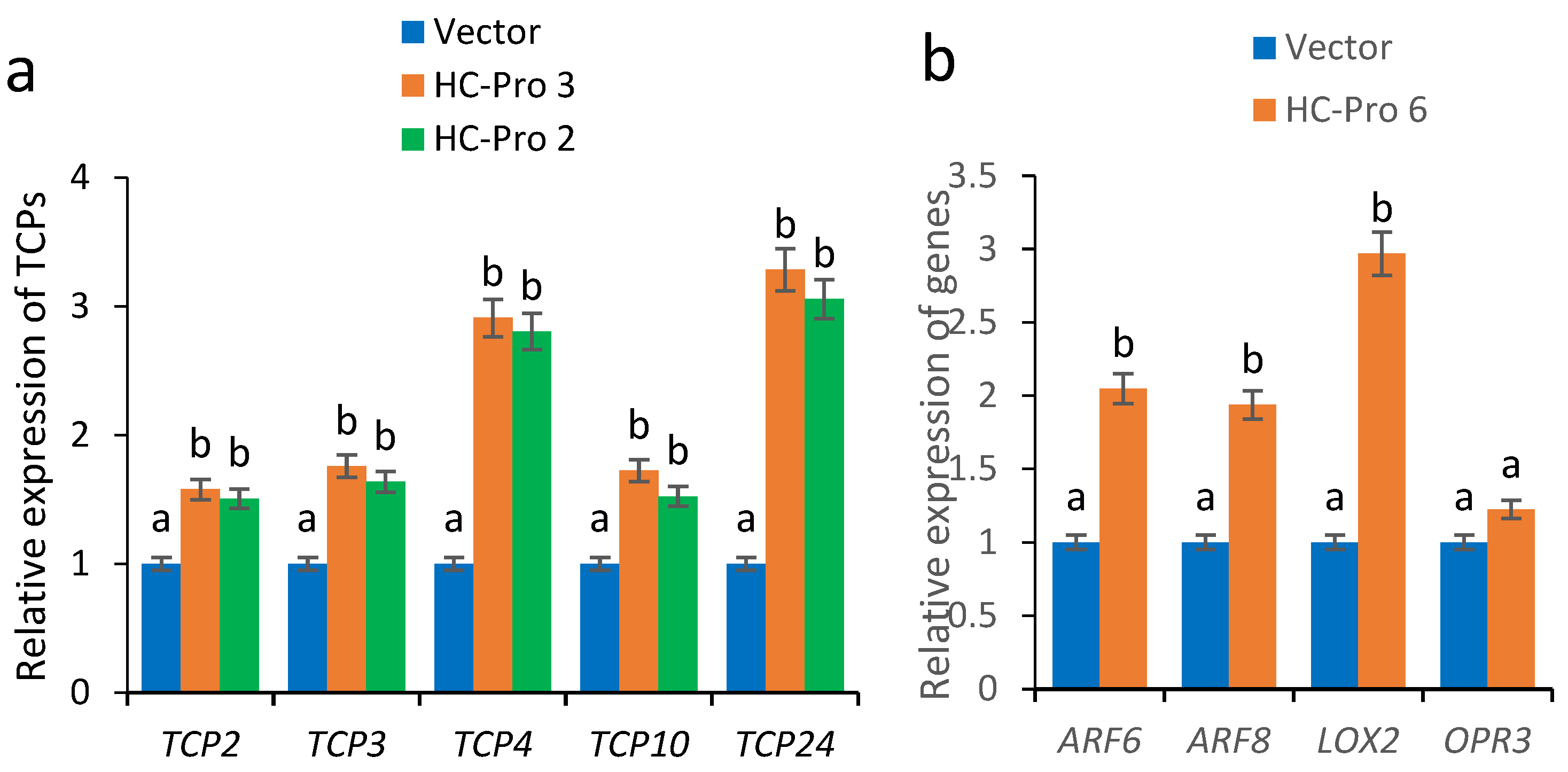
2.4. Expression Analysis of Fertility-Related Genes in HC-Pro Transgenic A. thaliana
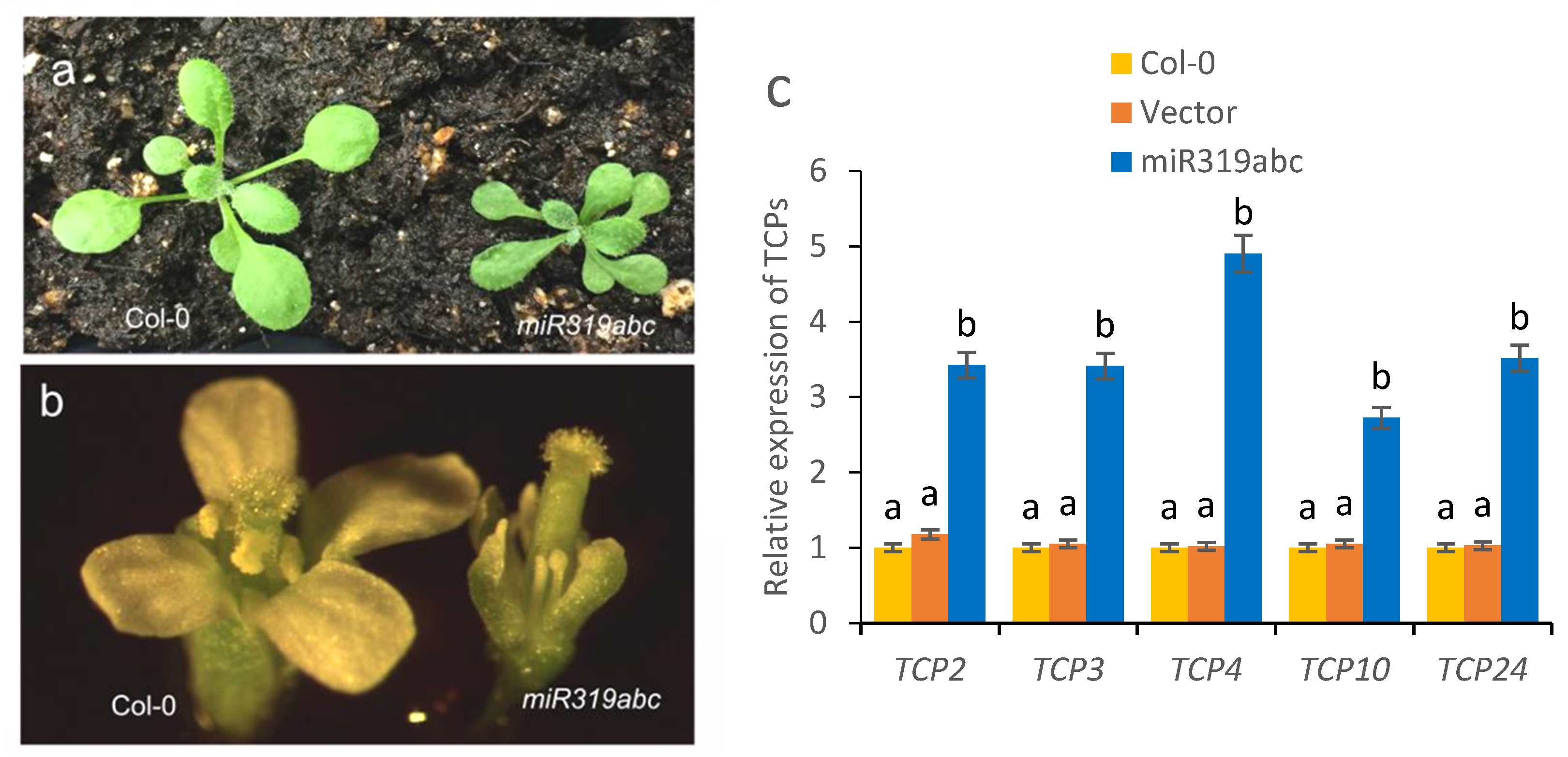
2.5. Recovery of Fertile Phenotypes in Plants Harbouring the miR319abc Deletion Mutant
3. Discussion
3.1. Abortion in HC-Pro Transgenic Plants Is Associated with Abnormal Expression of Fertility-Related Genes
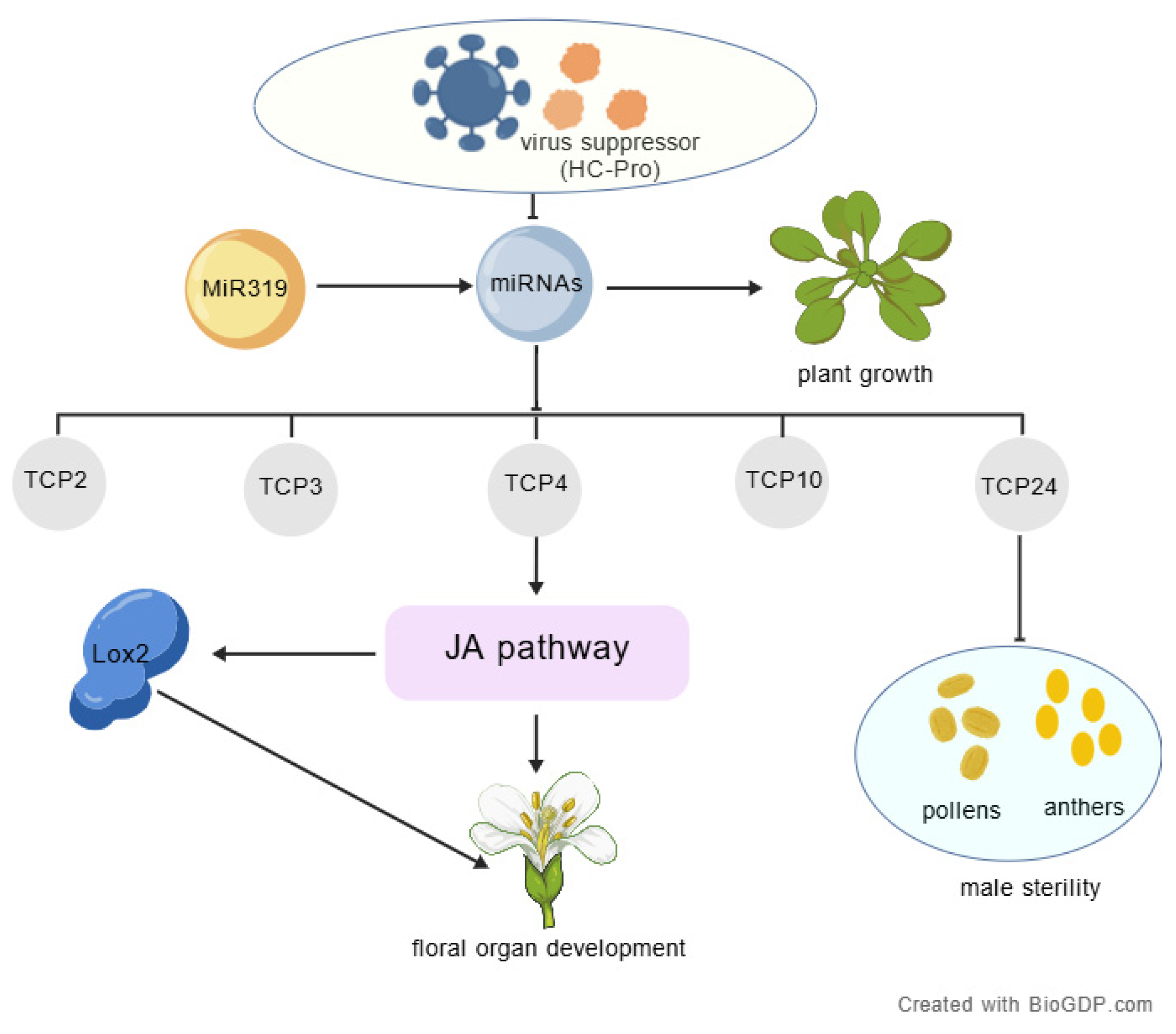
3.2. The Viral Suppressor HC-Pro Interferes with miR319–TCP Regulatory Pathways
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Agrobacterium-Mediated Leaf Disc Transformation of Tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.)
4.2. Northern Blotting Identification of HC-Pro Transgenic Plants
4.3. RT–qPCR Analysis of the Expression of Relevant Genes in HC-Pro Transgenic Plants
4.4. Obtaining Mutants via CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Efroni, I.; Han, S.K.; Kim, H.J.; Wu, M.F.; Steiner, E.; Birnbaum, K.D.; Hong, J.C.; Eshed, Y.; Wagner, D. Regulation of leaf maturation by chromatin-mediated modulation of cytokinin responses. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.S.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. RNA interference pathways in fungi: Mechanisms and functions. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, B.M.; Pruss, G.J.; Vance, V.B. Plant viral suppressors of RNA silencing. Virus Res. 2004, 102, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poque, S.; Wu, H.W.; Huang, C.H.; Cheng, H.W.; Hu, W.C.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, D.; Yeh, S.D. Potyviral gene-silencing suppressor HCPro interacts with salicylic acid (SA)-binding protein 3 to weaken SA-mediated defense responses. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.F.; Wei, W.L.; Hong, S.F.; Fang, R.Y.; Wu, H.Y.; Lin, P.C.; Sanobar, N.; Wang, H.P.; Sulistio, M.; Wu, C.T.; et al. Investigation of the effects of P1 on HC-pro-mediated gene silencing suppression through genetics and omics approaches. Bot. Stud. 2020, 61, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasschau, K.D.; Xie, Z.; Allen, E.; Llave, C.; Chapman, E.J.; Krizan, K.A.; Carrington, J.C. P1/HC-Pro, a viral suppressor of RNA silencing, interferes with Arabidopsis development and miRNA function. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.P.; Meng, D.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, Y.J.; Lang, C.J.; Jin, T.C.; Zhou, X.F. The viral suppressor HCPro decreases DNA methylation and activates auxin biosynthesis genes. Virology 2020, 546, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.P.; Xu, Y.N.; Liu, Y.Q.; Meng, D.W.; Jin, T.C.; Zhou, X.F. HC-Pro viral suppressor from tobacco vein banding mosaic virus interferes with DNA methylation and activates the salicylic acid pathway. Virology 2016, 497, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.C.; Li, Y.S.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.D.; Xiao, Z.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Yu, J.X.; Yang, L.P. DNA Demethylase ROS1 Interferes with DNA Methylation and Activates Stress Response Genes in Plants Infected with Beet Severe Curly Top Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.Y.; Li, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Mao, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Genschik, P.; Wang, L.L.; Yan, S.P. The polymerase-associated factor 1 complex modulates the growth-defense tradeoff in Arabidopsis. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eady5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Zhao, S.S.; Liu, N.L.; Wu, F.; Huang, S.T.; Li, D.Y.; Li, B.Y.; Miao, Y.T.; Guan, H.X.; Wu, M.; et al. A virulence protein activates SERK4 and degrades RNA polymerase IV protein to suppress rice antiviral immunity. Dev. Cell. 2025, 60, 2348–2362.e7. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Shi, T.; Ni, X.; Xu, Y.; Qu, S.; Gao, Z. The role of miR319a and its target gene TCP4 in the regulation of pistil development in Prunus mume. Genome 2018, 61, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannenberg, G.; Martínez, M.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Diversity of the enzymatic activity in the lipoxygenase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Lipids 2009, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauser, G.; Dubugnon, L.; Mousavi, S.A.; Rudaz, S.; Wolfender, J.L.; Farmer, E.E. Velocity estimates for signal propagation leading to systemic jasmonic acid accumulation in wounded Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 34506–34513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, A.; King, S.; Jack, T. miR319a targeting of TCP4 is critical for petal growth and development in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22534–22539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Somoza, I.; Weigel, D. Coordination of flower maturation by a regulatory circuit of 384 three microRNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003374. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Xiang, N.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Du, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Y. Activation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis by miR319-targeted TCP 4 transcription factor. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1284–1294. [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal, P.; Ellis, C.M.; Weber, H.; Ploense, S.E.; Barkawi, L.S.; Guilfoyle, T.J.; Hagen, G.; Alonso, J.M.; Cohen, J.D.; Farmer, E.E.; et al. Auxin response factors ARF6 and ARF8 promote jasmonic acid production and flower maturation. Development 2005, 132, 4107–4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Mao, Y.; Yang, J.; He, Y.K. TCP24 modulates secondary cell wall thickening and anther endothecium development. Front. Plant. Sci. 2015, 6, 436. [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik, J.F.; Allen, E.; Wu, X.; Schommer, C.; Schwab, R.; Carrington, J.C.; Weigel, D. Control of leaf morphogenesis by micro-RNAs. Nature 2003, 425, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.; Wolf, J.N.; Bisaro, D.M. RNA silencing directed against geminiviruses: Post-transcriptional and epigenetic components. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1799, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnussat, G.C.; Yu, H.J.; Ngo, Q.A.; Rajani, S.; Mayalagu, S.; Johnson, C.S.; Capron, A.; Xie, L.F.; Ye, D.; Sundaresan, V. Genetic and molecular identification of genes required for female gametophyte development and function in Arabidopsis. Development 2005, 132, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vick, B.A.; Zimmerman, D.C. The biosynthesis of jasmonic acid: A physiological role for plant lipoxygenase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1983, 111, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarvepalli, K.; Nath, U. Hyper-activation of the TCP4 transcription factor in Arabidopsis thaliana accelerates multiple aspects of plant maturation. Plant J. 2011, 67, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, F.; Martin, V.; Colaneri, A.; Gonzalez-Schain, N.; Perales, M.; Martin, M.; Lombardo, C.; Braun, H.P.; Bartoli, C.; Zabaleta, E. Ectopic expression of mitochondrial gamma carbonic anhydrase 2 causes male sterility by anther indehiscence. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 70, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, I.L.; Gonzalez, D.H. TCP Transcription Factors in Plant Reproductive Development: Juggling Multiple Roles. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.Y.; Hwarari, D.; Ma, H.Y.; Xu, H.B.; Yang, L.M.; Luo, Y.M. Genomic survey of TCP transcription factors in plants: Phylogenomics, evolution and their biology. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1060546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.P.; Lang, C.J.; Wu, Y.J.; Meng, D.W.; Yang, T.B.; Li, D.Q.; Jin, T.C.; Zhou, X.F. ROS1-mediated decrease in DNA methylation and increase in expression of defense genes and stress response genes in Arabidopsis thaliana due to abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, T.; Wang, W.; Yu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, X.; Yang, L. HC-Pro Disrupts miR319–TCP Regulatory Pathways to Induce Sterility in Transgenic Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 10551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110551
Jin T, Wang W, Yu J, Xiao Z, Li Y, Sun X, Yang L. HC-Pro Disrupts miR319–TCP Regulatory Pathways to Induce Sterility in Transgenic Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(21):10551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110551
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Taicheng, Weiyan Wang, Jiaxue Yu, Zhuyi Xiao, Yushuo Li, Xu Sun, and Liping Yang. 2025. "HC-Pro Disrupts miR319–TCP Regulatory Pathways to Induce Sterility in Transgenic Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 21: 10551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110551
APA StyleJin, T., Wang, W., Yu, J., Xiao, Z., Li, Y., Sun, X., & Yang, L. (2025). HC-Pro Disrupts miR319–TCP Regulatory Pathways to Induce Sterility in Transgenic Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(21), 10551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262110551




