Potential of Pandan Root and Teak Leaf Extracts in Managing Maternal Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy: Comparative Efficacy and Mechanistic Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
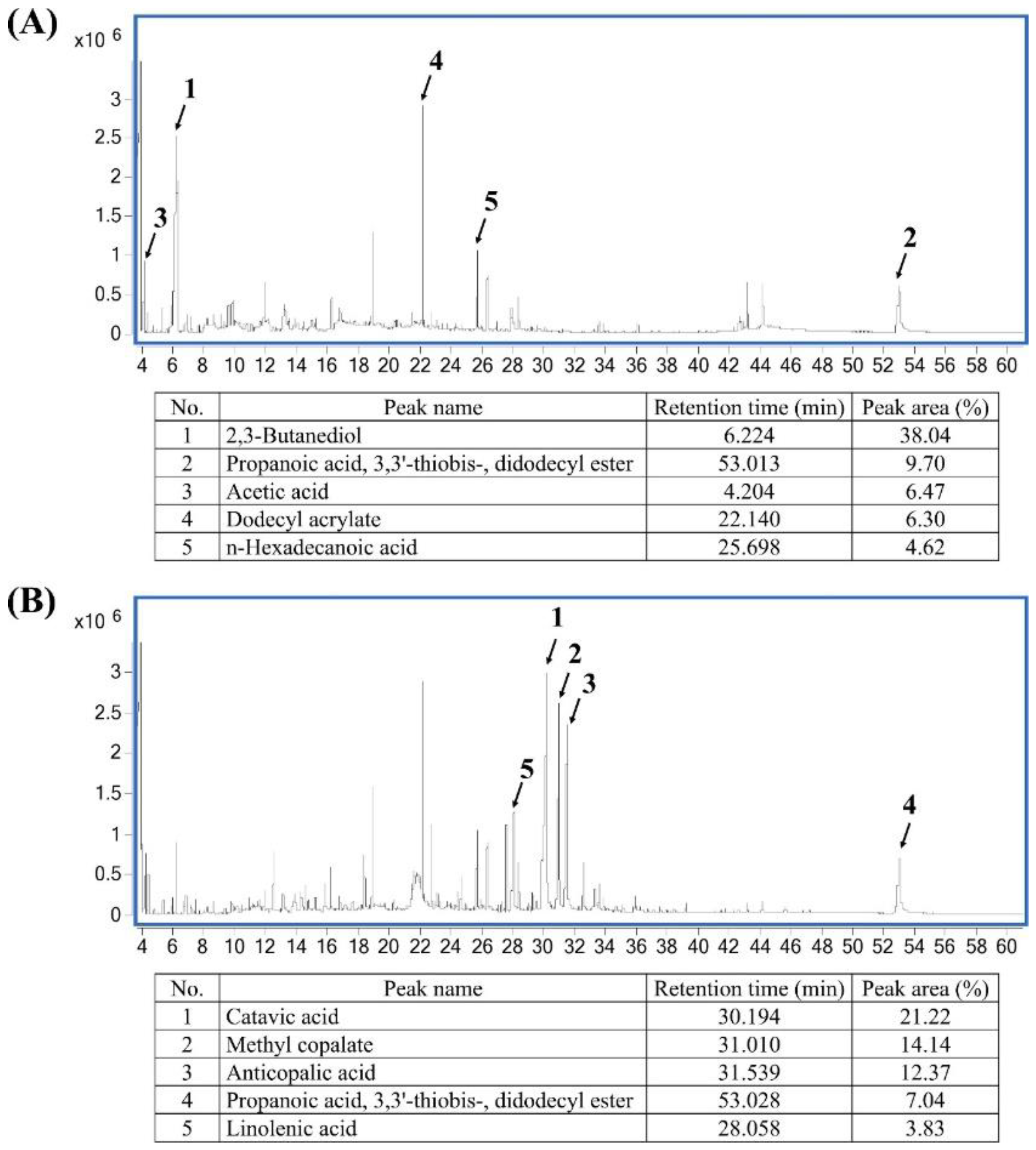
2.1. Phytochemical Composition of Pandan and Teak Extracts
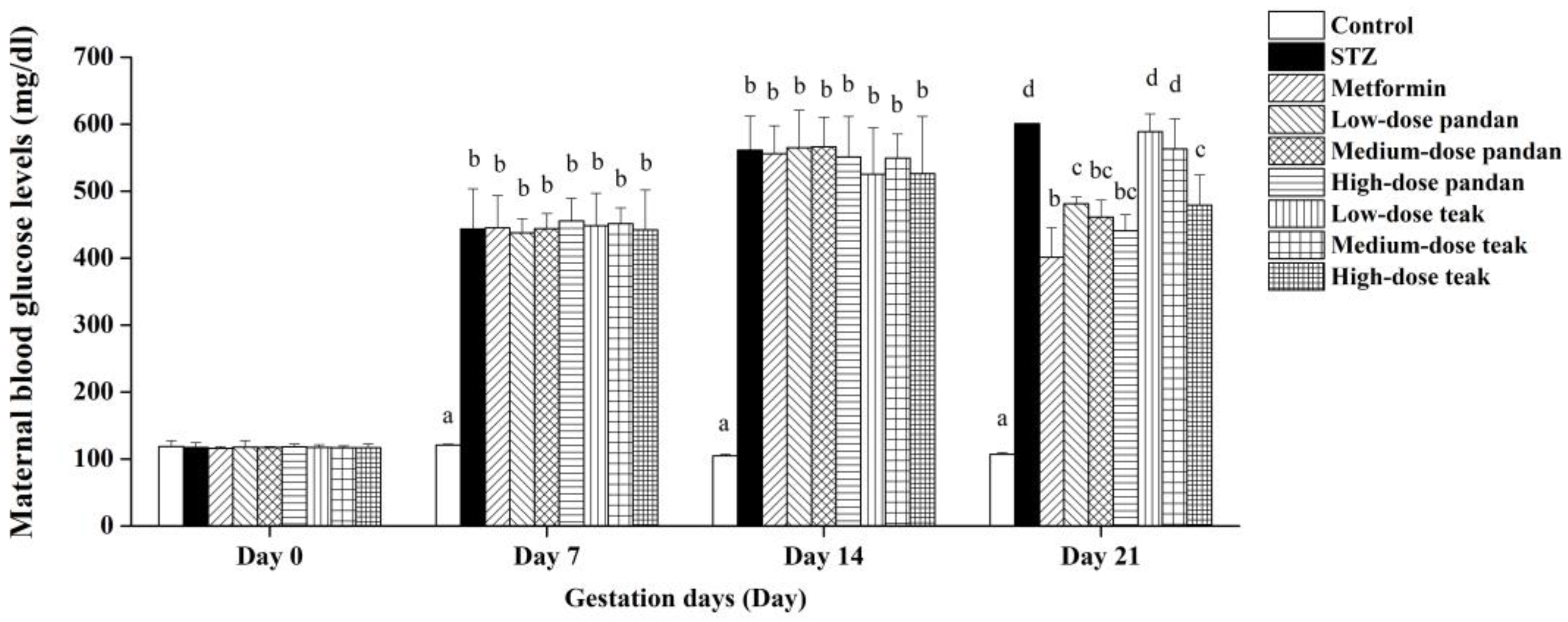
2.2. Induction of Maternal Hyperglycemia
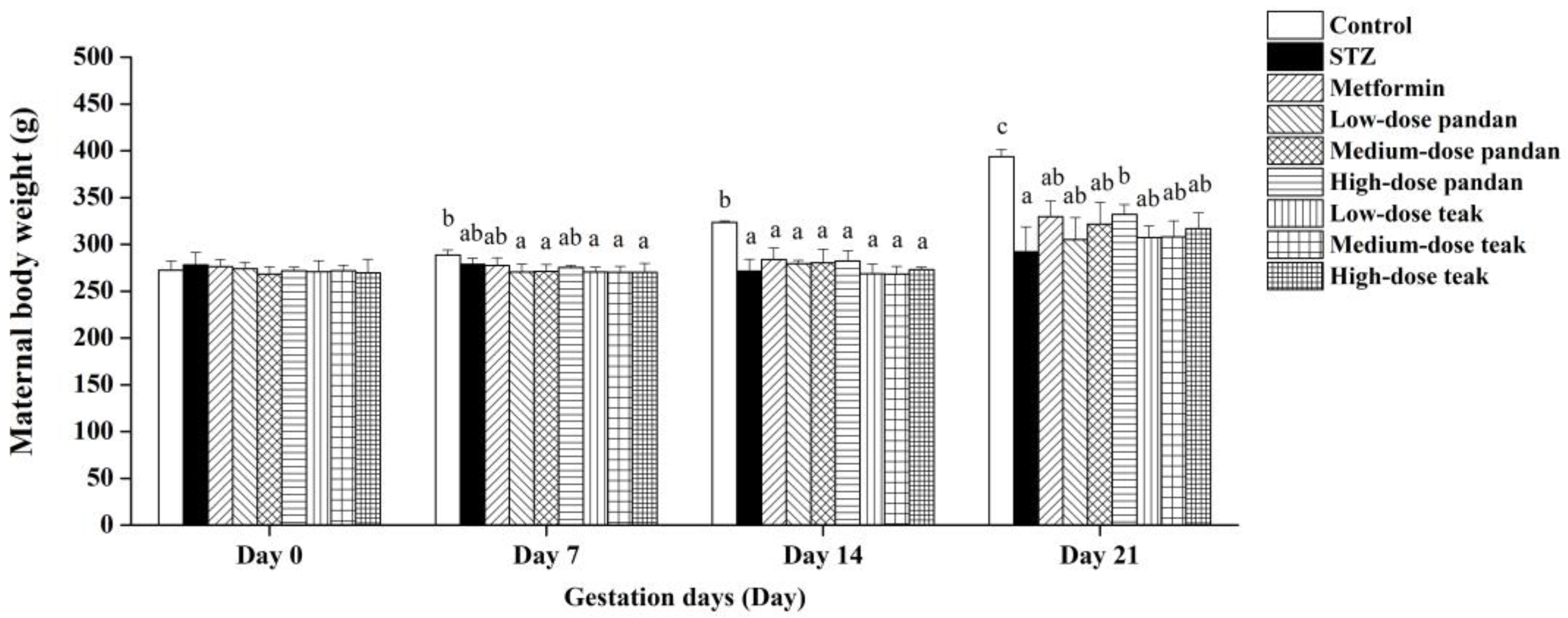
2.3. Maternal Body Weight
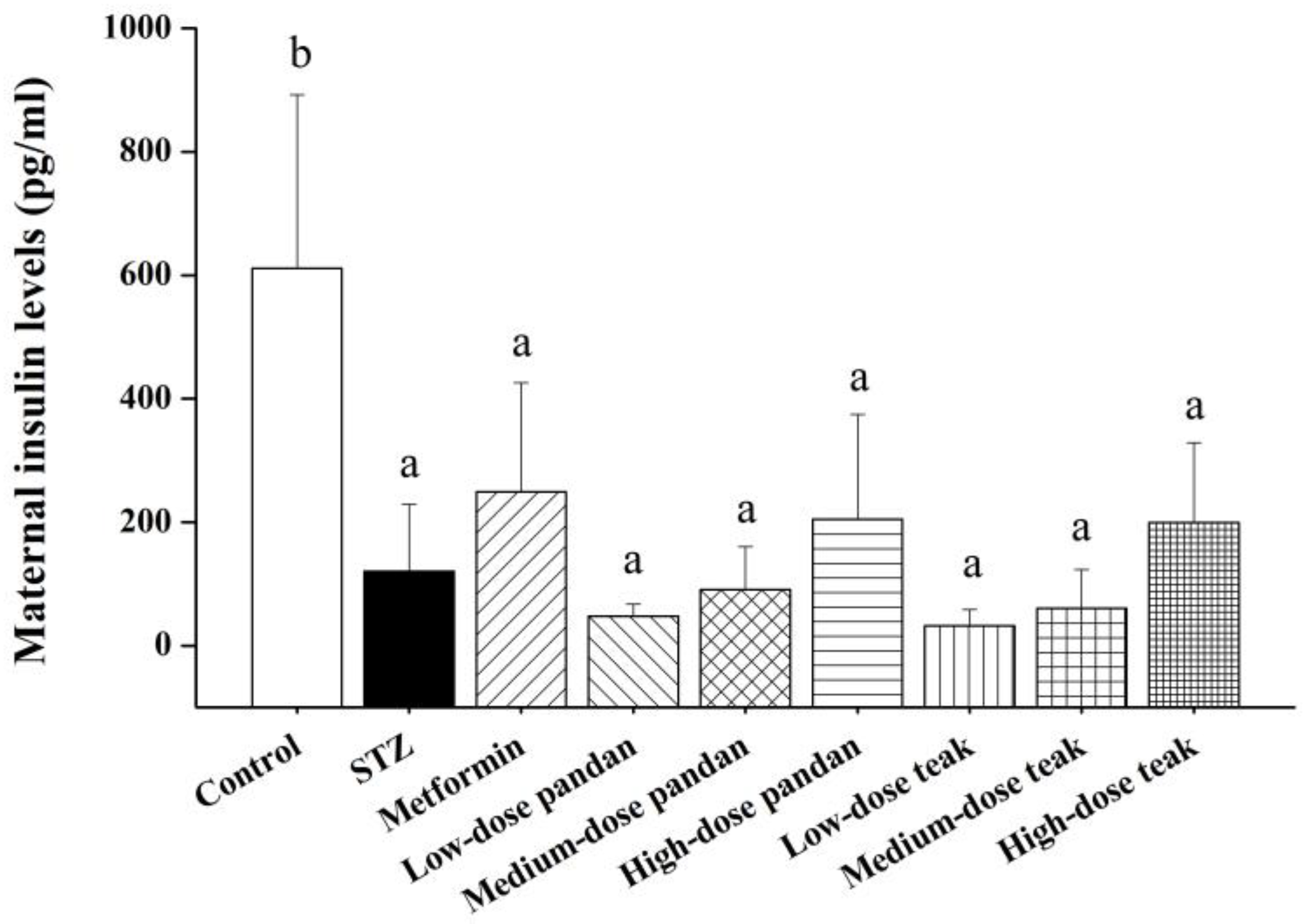
2.4. Maternal Insulin Levels
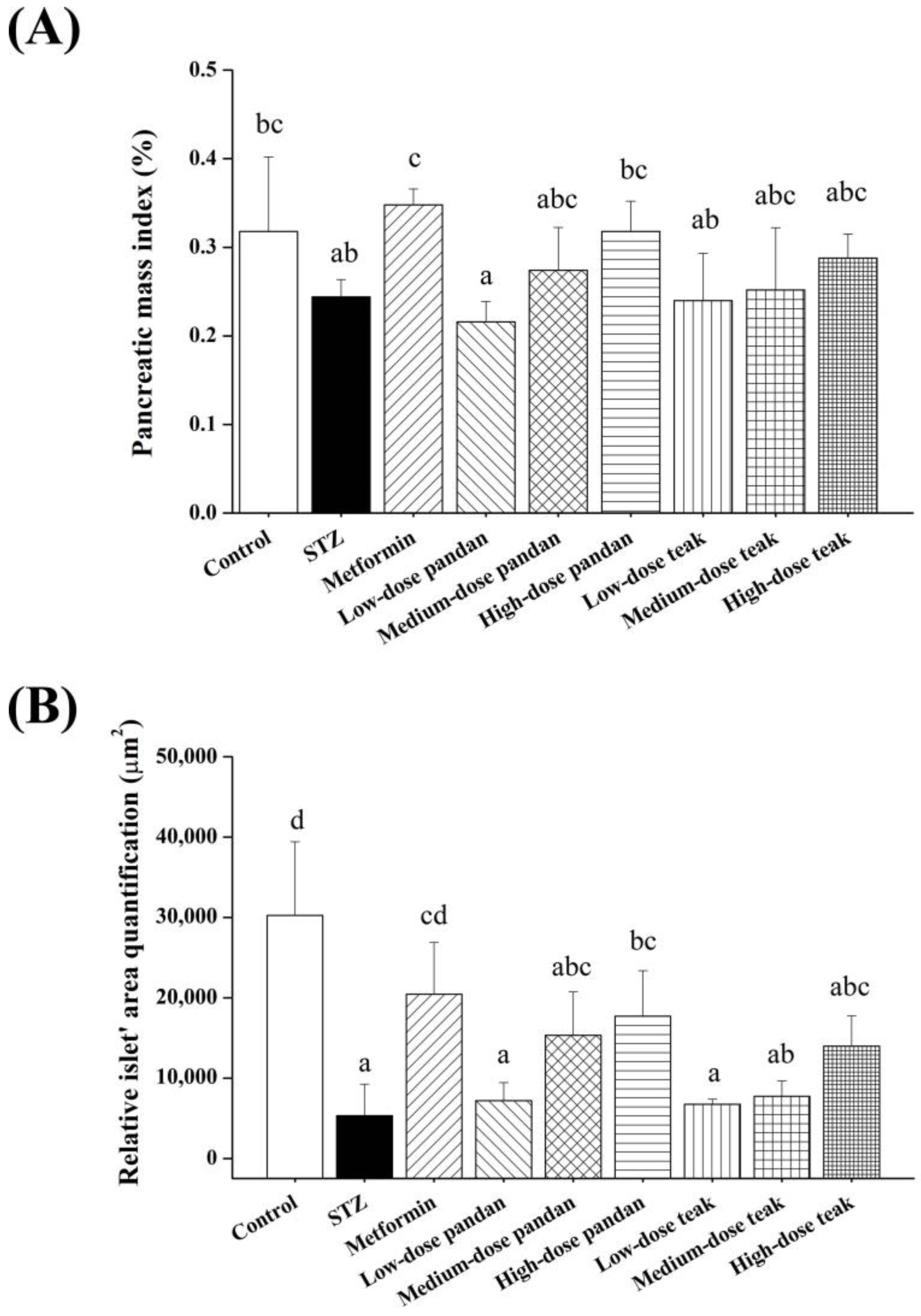
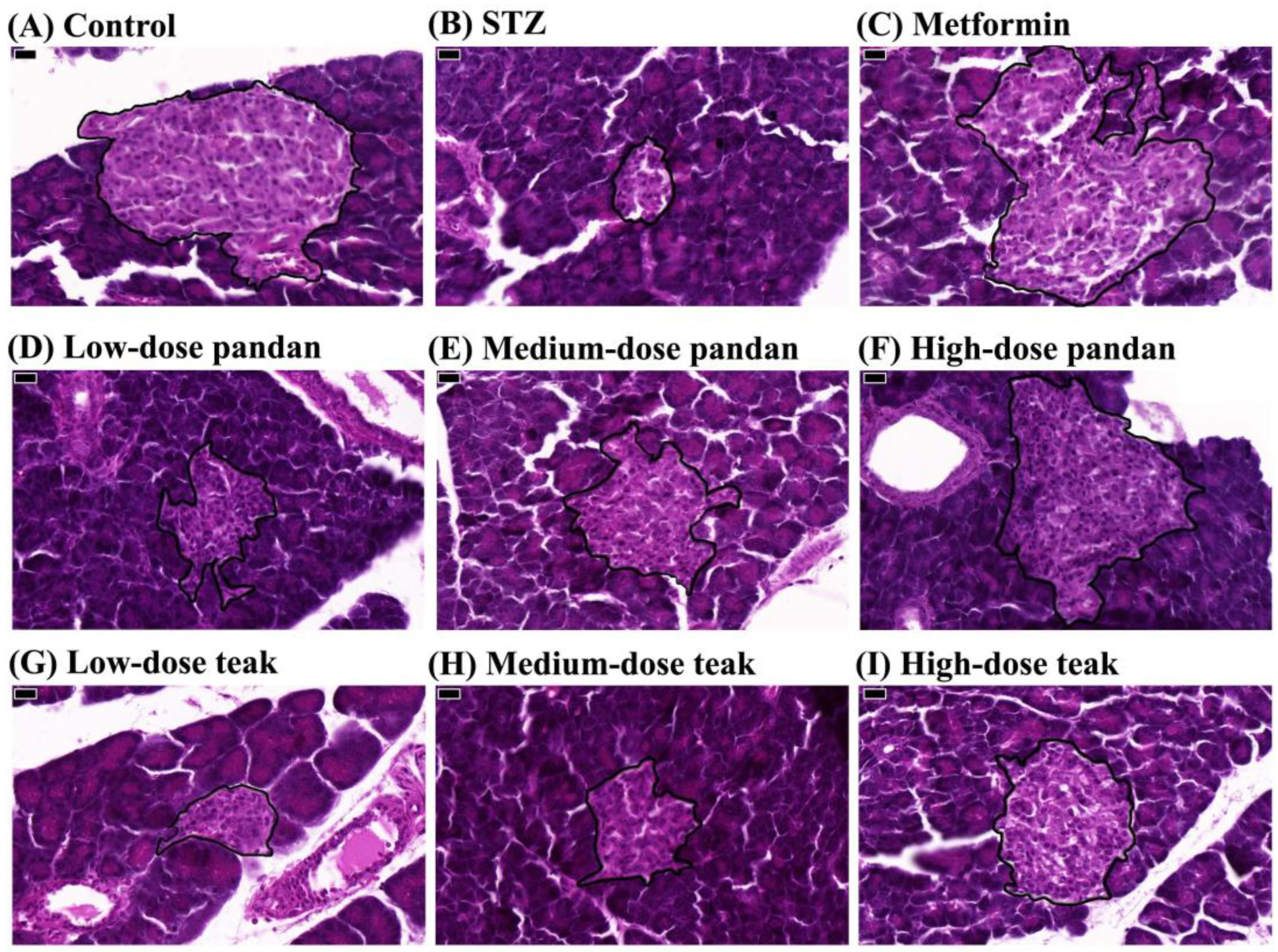
2.5. Effects on Pancreatic Morphology
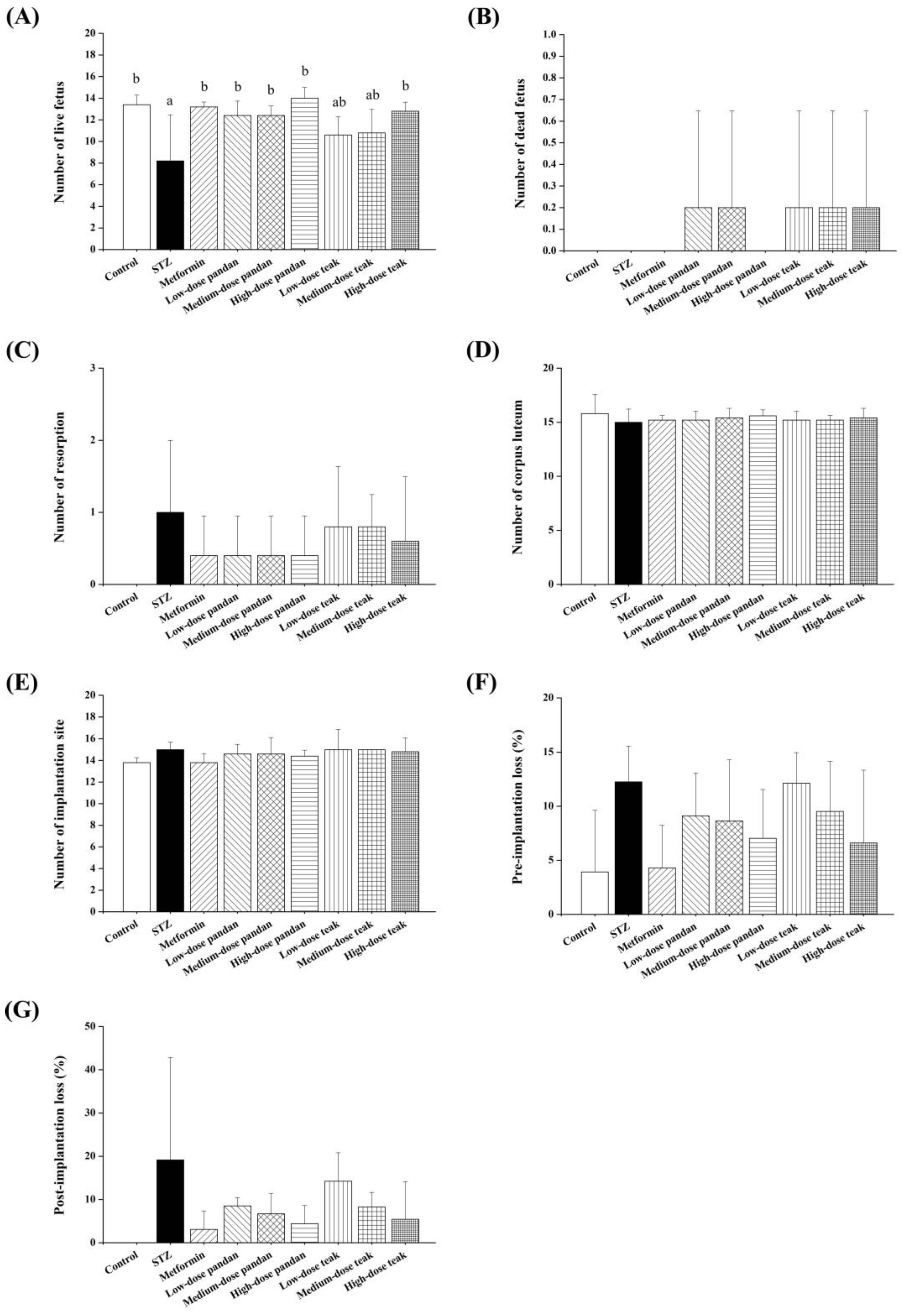
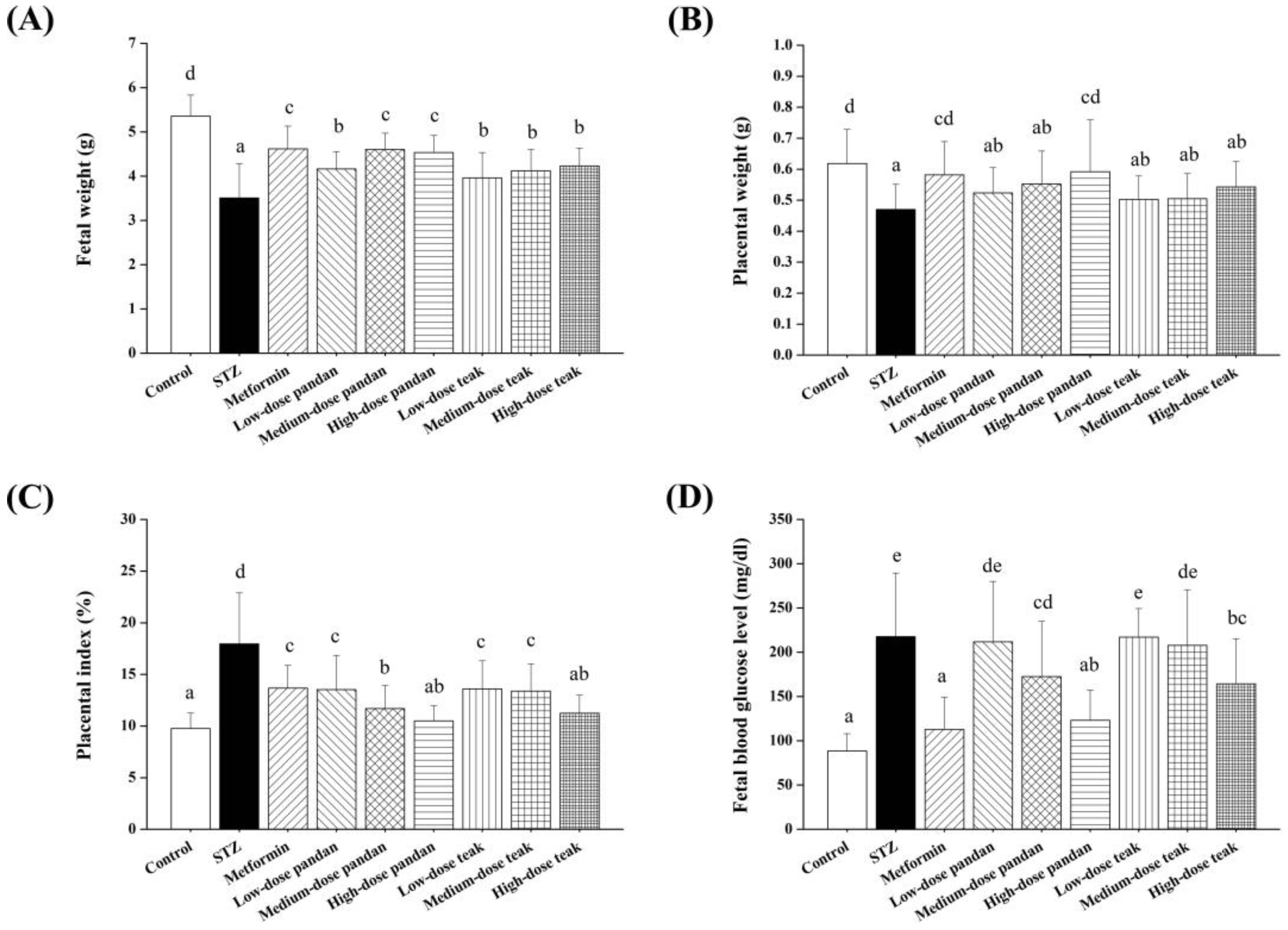
2.6. Fetal and Placental Outcomes
2.7. Blood Glucose Levels in Newborns
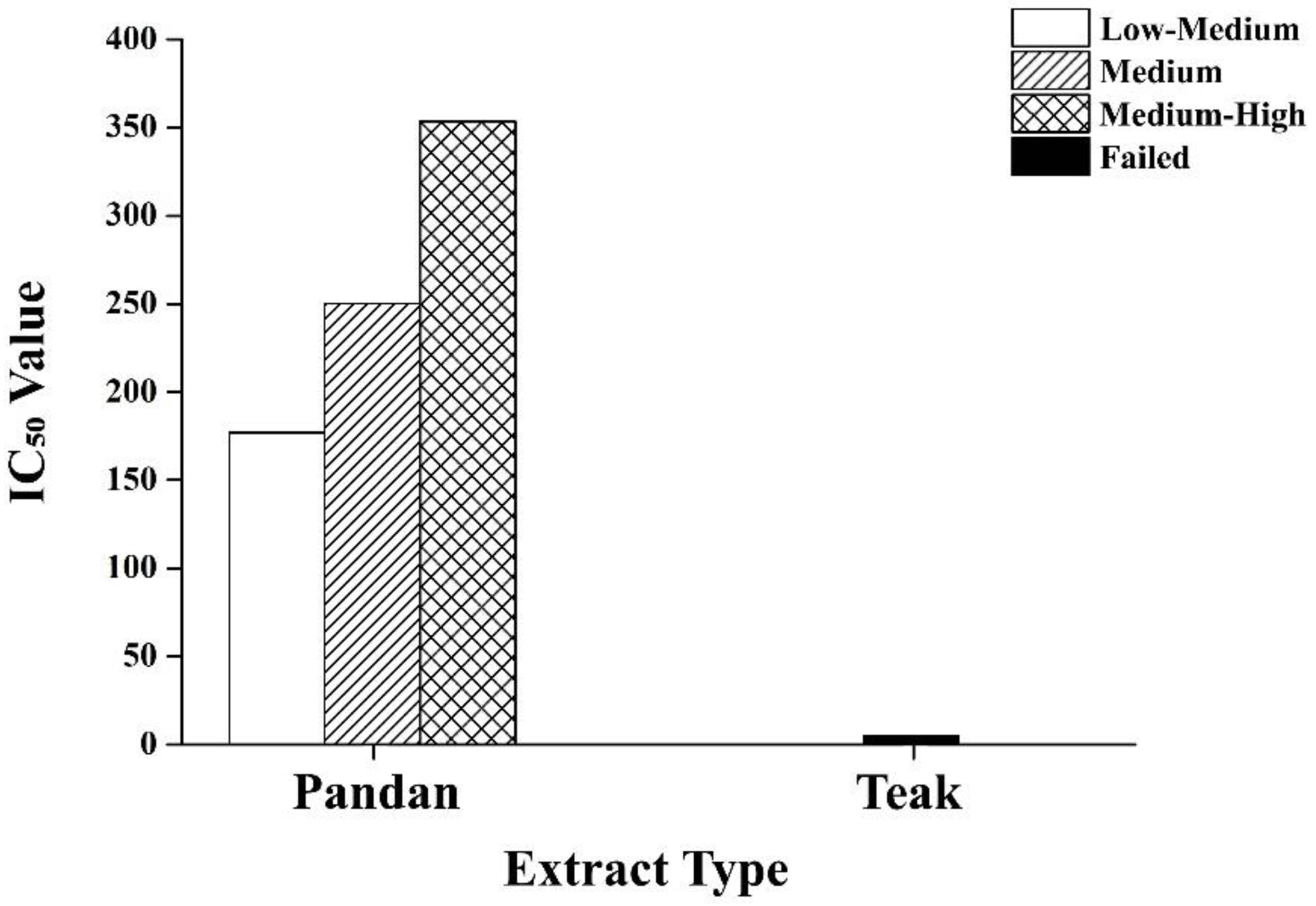
2.8. Dose–Response Analysis of Pandan and Teak Extracts
3. Discussion
3.1. Efficacy of Metformin and Plant Extracts
3.2. Insulin Levels and Pancreatic Morphology
3.3. Fetal and Placental Outcomes
3.4. Blood Glucose Levels in Newborns
3.5. Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Extracts
4.2. Chemical Analysis of Extracts
4.3. Animal Ethics Statement
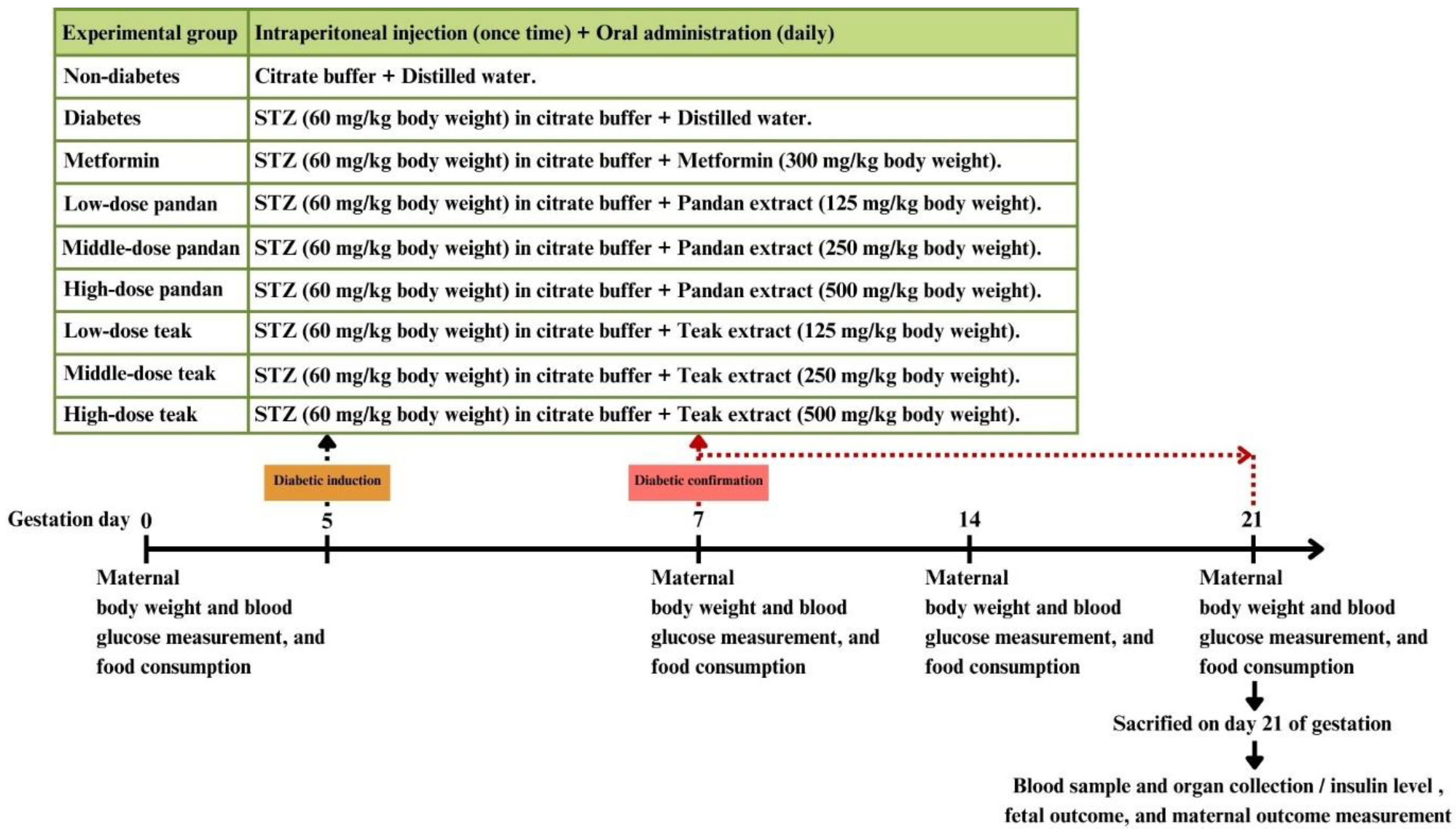
4.4. Preparation of Experimental Animals
4.5. Animal Experimentation
4.6. Blood Glucose Measurement
4.7. Maternal and Fetal Outcome Measurement
4.8. Maternal Serum Collection and Insulin Level Measurement
4.9. Pancreas Collection and Histopathological Examination
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GDM | Gestational diabetes mellitus |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| GC/MS | Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| BW | Body weight |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| IC50 | Half-maximal inhibitory concentration |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| CRSPG SUT | Center for Plant Genetic Conservation Project Under the Royal Initiative of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn of Suranaree University of Technology |
| SUT | Suranaree University of Technology |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| IACUC | Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee |
| CL | Corpora lutea |
| OD | Optical density |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
References
- Lende, M.; Rijhsinghani, A. Gestational Diabetes: Overview with Emphasis on Medical Management. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xiao, Y. The Association Between Trimester-Specific Weight Gain and Severe Preeclampsia/Adverse Perinatal Outcome in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Complicated by Preeclampsia: A Retrospective Case Study. Diabetes Ther. 2019, 10, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, S.K.; Das Gupta, R.; Alam, S.; Kaur, K.; Shamim, A.A.; Puthussery, S. Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) and adverse pregnancy outcome in South Asia: A systematic review. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picón-César, M.J.; Molina-Vega, M.; Suárez-Arana, M.; González-Mesa, E.; Sola-Moyano, A.P.; Roldan-López, R.; Romero-Narbona, F.; Olveira, G.; Tinahones, F.J.; González-Romero, S. Metformin for gestational diabetes study: Metformin vs insulin in gestational diabetes: Glycemic control and obstetrical and perinatal outcomes: Randomized prospective trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 225, 517.e1–517.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercado-Méndez, S.; González-Sepúlveda, L.; Romaguera, J.; González-Rodríguez, L.A. The Use of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents during Pregnancy: An Alternative to Insulin? Puerto Rico Health Sci. J. 2021, 40, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Gao, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Jia, X. Comparison of the effectiveness and safety of insulin and oral hypoglycemic drugs in the treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of 26 randomized controlled trials. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2022, 38, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjou, C.G.; Grigsby, J.; Mbemi, A.; Nelson, D.; Mildort, B.; Latinwo, L.; Tchounwou, P.B. The Management of Diabetes Mellitus Using Medicinal Plants and Vitamins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, P. Antidiabetic effect on some medicinal plants. Int. J. Curr. Res. Life Sci. 2021, 10, 3392–3395. [Google Scholar]
- Chiabchalard, A.; Nooron, N. Antihyperglycemic effects of Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. leaf extract. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sida, N.A.; Mahmudah, R.A.; Trinovitasari, N.; Shofa, N.; Parawansah; Nuralifah; Rafid, A.; Risma. Tectona grandis Linn.: Antidiabetic activity of the fractions using an in vivo approach. Med. Sains J. Ilm. Kefarmasian 2024, 9, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, T.S.; Le, P.U.; Ngo, D.H. In Vitro Hypoglycemic and Radical Scavenging Activities of Certain Medicinal Plants. Exp. Appl. Biomed. Res. 2022, 23, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, B.; Sonowal, R. An overview of Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. exLindl. and its potential impact on health. Curr. Trends Pharm. Res. 2021, 8, 138–157. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Ren, Z.; Zheng, S.; Wu, H.; Li, P.; Peng, W.; Su, W.; Wang, Y. Botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and applications of Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb.: A review. Fitoterapia 2024, 177, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, W.; Sulistyani; Swasono, F.D.H. The effect of Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. extract addition and cooling period on the preference levels, chemical properties and glycemic index of Cr and Mg fortified—Parboiled rice. Food Res. 2021, 5, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poowanna, R.; Hodruecha, N.; Kumchoo, P.; Prathumtet, J.; Poonsawat, J. Influence of Duration Times of Storage on the Caffeic Acid Contents in Pandanus amaryllifolius Root Decoction. Isan J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 13, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ordas, J.A.D.; Nonato, M.G.; Moran, C.B. Ethnobotanical Uses of Pandanaceae Species in Selected Rural Communities in the Philippines. Econ. Bot. 2020, 74, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asdaq, S.M.B.; Nayeem, N.; Abida; Alam, M.T.; Alaqel, S.I.; Imran, M.; Hassan, E.E.; Rabbani, S.I. Tectona grandis L.f: A comprehensive review on its patents, chemical constituents, and biological activities. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1456–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balslev, H.; Phumthum, M. Thai Ethnomedicinal Plants Used for Diabetes Treatment. OBM Integr. Complement. Med. 2018, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahroh, R.; Istiroha; Suwanto; Rohmah, D.Z. The influence boiling of fragrant pandan and cinnamon to reducing blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus. Lux Mensana J. Sci. Health 2023, 2, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Petres, E.R.; Sferruzzi-Perri, A.N. Pregnancy-induced changes in β-cell function: What are the key players? J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1089–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningtiyas, E.N.; Widyaningsih, T.D.; Sutrisno, A. Optimization of the Formulation of Antidiabetic Functional Drinks According to Sorghum, Red Ginger, and Aromatic Pandan Leaves in Type II Diabetes Rats. Int. Res. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. 2019, 4, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Saenthaweesuk, S.; Naowaboot, J.; Somparn, N. Pandanus amaryllifolius leaf extract increases insulin sensitivity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2016, 6, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Jiang, S.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, D. STZ-induced gestational diabetes exposure alters PTEN/AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy signaling pathway leading to increase the risk of neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Reprod. Toxicol. 2024, 123, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Gao, F.; Hou, J.; Li, T.; Tan, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Metformin inhibits MAPK signaling and rescues pancreatic aquaporin 7 expression to induce insulin secretion in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, M.E.; Brown, S.J.; Satrom, K.M.; Scheurer, J.M.; Ramel, S.E.; Rao, R.B. Long-term outcomes after early neonatal hyperglycemia in VLBW infants: A systematic review. Neonatology 2021, 118, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Reichetzeder, C.; Li, J.; Hocher, B. Low birth weight, a risk factor for diseases in later life, is a surrogate of insulin resistance at birth. J. Hypertens. 2019, 37, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavati, N.; Smies, M.; Ganzevoort, W.; Charles, A.K.; Erwich, J.J.; Plösch, T.; Gordijn, S.J. The Possible Role of Placental Morphometry in the Detection of Fetal Growth Restriction. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshidan, N.H.; Abd Muid, S.; Mamikutty, N. The effects of Pandanus amaryllifolius (Roxb.) leaf water extracts on fructose-induced metabolic syndrome rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusnadi, J.; Arumingtyas, E.L.; Ningtyas, D.W.; Setiawan, E.C. Antioxidant activity of MAE extracted teak (Tectona grandis LF) leaves collected from different plantation site at Java Island. Indones. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2016, 7, 154–160. [Google Scholar]
- Pasek, R.C.; Gannon, M. Advancements and challenges in generating accurate animal models of gestational diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, E1327–E1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, F.V.; Segabinazi, E.; de Meireles, A.L.F.; Mega, F.; Spindler, C.D.F.; Augustin, O.A.; Salvalaggio, G.D.S.; Achaval, M.; Kruse, M.S.; Coirini, H.; et al. Severe Uncontrolled Maternal Hyperglycemia Induces Microsomia and Neurodevelopment Delay Accompanied by Apoptosis, Cellular Survival, and Neuroinflammatory Deregulation in Rat Offspring Hippocampus. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 39, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, A.; Sinzato, Y.K.; Volpato, G.T.; Gallego, F.Q.; Perecin, F.; Rodrigues, T.; Damasceno, D.C. Severity of prepregnancy diabetes on the fetal malformations and viability associated with early embryos in rats. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 103, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Shukor, N.A.B. Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity of Pandanus amaryllifolius Roxb. Master’s Thesis, University of malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdin, C.D.; Prasedya, E.; Utami, S.; Galanova, D.; Cahyo Saputro, D.; Nurrochmad, A.; Murwanti, R.; Jupri, A.; Sunarpi, H. Acute Toxicity of Indonesian Natural Food Colorant Tectona grandis Leaf Extract in Wistar Rats. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 19, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals. Section 4, Test No 415: One-Generation Reproduction Toxicity Study; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, G.; Echiburú, B.; Crisosto, N.; Sotomayor-Zárate, R.; Maliqueo, M.; Cruz, G. Metformin during Pregnancy: Effects on Offspring Development and Metabolic Function. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngo, C.; Salomon, C.; Quak, S.; Lai, A.; Willcox, J.C.; Lappas, M. Nobiletin exerts anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects in an in vitro human model and in vivo murine model of gestational diabetes. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 571–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes-Souza, R.Q.; Sinzato, Y.K.; Antunes, B.T.; Umeoka, E.H.L.; Oliveira, J.A.C.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Karki, B.; Volpato, G.T.; Damasceno, D.C. Evaluation of Maternal Reproductive Outcomes and Biochemical Analysis from Wistar Audiogenic Rats (WAR) and Repercussions in Their Offspring. Reprod. Sci. 2020, 27, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusin, A.H.A.; Ghani, N.I.A.; Ahmad, N. Pancreatic islet regenerative capability of Dillenia excelsa in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 11, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerdsuknirund, S.; Khunkaewla, P.; Kupittayanant, P.; Chanlun, S.; Tongdee, P.; Nimkuntod, P.; Kupittayanant, S. Potential of Pandan Root and Teak Leaf Extracts in Managing Maternal Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy: Comparative Efficacy and Mechanistic Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125506
Kerdsuknirund S, Khunkaewla P, Kupittayanant P, Chanlun S, Tongdee P, Nimkuntod P, Kupittayanant S. Potential of Pandan Root and Teak Leaf Extracts in Managing Maternal Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy: Comparative Efficacy and Mechanistic Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125506
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerdsuknirund, Sasitorn, Panida Khunkaewla, Pakanit Kupittayanant, Suthida Chanlun, Pattama Tongdee, Porntip Nimkuntod, and Sajeera Kupittayanant. 2025. "Potential of Pandan Root and Teak Leaf Extracts in Managing Maternal Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy: Comparative Efficacy and Mechanistic Insights" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125506
APA StyleKerdsuknirund, S., Khunkaewla, P., Kupittayanant, P., Chanlun, S., Tongdee, P., Nimkuntod, P., & Kupittayanant, S. (2025). Potential of Pandan Root and Teak Leaf Extracts in Managing Maternal Hyperglycemia During Pregnancy: Comparative Efficacy and Mechanistic Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5506. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125506





