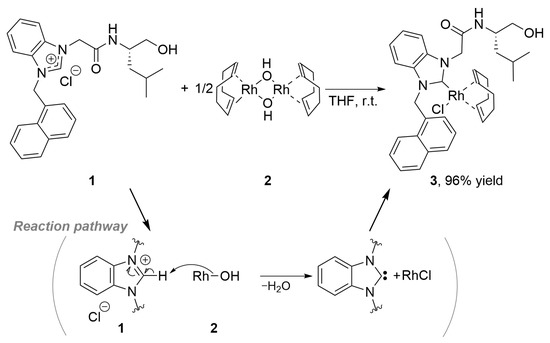
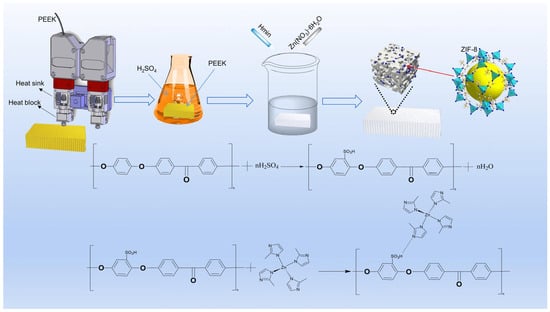
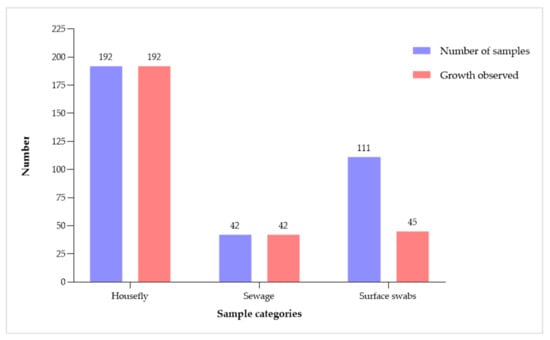
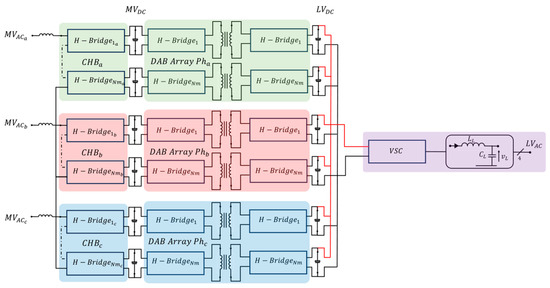
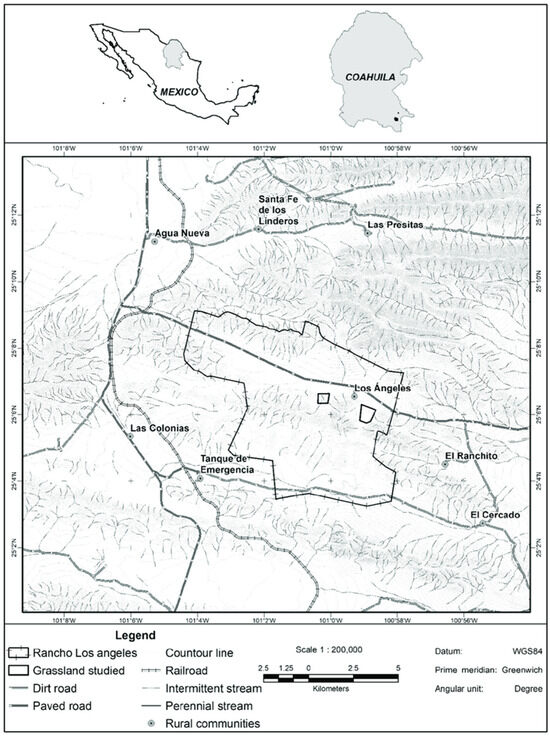
Mammary cancer is a frequent disease in female dogs, where a high proportion of cases correspond to malignant tumors that may exhibit drug resistance. Within the mammary tumor microenvironment, there is a cell subpopulation called cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are capable of
[...] Read more.
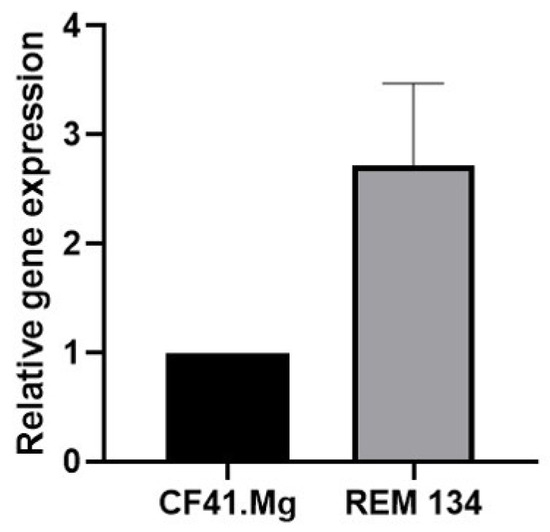
Mammary cancer is a frequent disease in female dogs, where a high proportion of cases correspond to malignant tumors that may exhibit drug resistance. Within the mammary tumor microenvironment, there is a cell subpopulation called cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are capable of forming spheres in vitro and resisting anti-tumor treatments, partly explaining the recurrence of some tumors. Previously, it has been described that spheres derived from canine mammary carcinoma cells CF41.Mg and REM 134 exhibit stemness characteristics. Melatonin has shown anti-tumor effects on mammary tumor cells; however, its effects have been poorly evaluated in canine mammary CSCs. This study aimed to analyze the effect of melatonin on the chemoresistance exhibited by stem-like neoplastic cells derived from canine mammary carcinoma to cytotoxic drugs such as doxorubicin and mitoxantrone. CF41.Mg and REM 134 cells were cultured in high-glucose DMEM supplemented with fetal bovine serum and L-glutamine. The spheres were cultured in ultra-low attachment plates in DMEM/F12 medium without fetal bovine serum and with different growth factors. The CD44
+/CD24
−/low phenotype was analyzed by flow cytometry. The viability of sphere-derived cells (MTS reduction) was studied in the presence of melatonin (0.1 or 1 mM), doxorubicin, mitoxantrone, and luzindole. In addition, the gene (RT-qPCR) of the multidrug resistance bombs
MDR1 and
ABCG2 were analyzed in the presence of melatonin. Both cell types expressed the
MT1 gene, which encodes the melatonin receptor MT1. Melatonin 1 mM does not modify the CD44
+/CD24
−/low phenotype; however, the hormone reduced viability (
p < 0.0001) only in CF41.Mg spheres, without inducing an additive effect when co-incubated with cytotoxic drugs. These effects were independent of the binding of the hormone to its receptor MT1, since, by pharmacologically inhibiting them, the effect of melatonin was not blocked. In CF41.Mg spheres, the relative gene expression of
ABCG2 and
MDR1 was decreased in response to the hormone (
p < 0.001). These results indicate that melatonin negatively modulates the cell survival of spheres derived from CF41.Mg cells, in a way that is independent of its MT1 receptor. These effects did not counteract the resistance to doxorubicin and mitoxantrone, even though the hormone negatively regulates the gene expression of
MDR1 and
ABCG2.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT