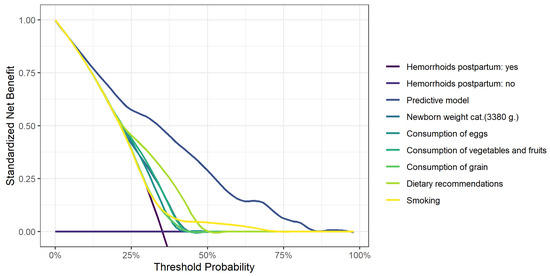
Objective: We aimed to identify the incidence and risk factors of perianal pathology during pregnancy and the postpartum period. Methods: A prospective cohort study was conducted in three institutions in Lithuania. A total of 190 patients were examined and interviewed three times (<12, 18–20 weeks of gestation, and during the first 2 months after delivery). They completed a questionnaire including demographic, obstetric, coloproctological, and birth data. Results: A total of 73 (34.59%) women developed hemorrhoidal disease after delivery, and 120 (56.87%) developed perianal pathology. Multivariate analysis identified a neonatal birth weight ≥3380 g (OR 4.22; 95% CI 1.83–9.71,
p < 0.001) and consumption of eggs (OR 3.10; 95% CI 1.13–8.53,
p = 0.028) or cereals (OR 2.87; 95% CI 1.32–6.25,
p = 0.008) several times per week as significant risk factors for hemorrhoidal disease. Neonatal birth weight ≥3380 g (OR 3.95; 95% CI 1.47–10.59,
p = 0.006), maternal BMI ≥ 21.48 (OR 3.58; 95% CI 1.51–8.47,
p = 0.004), the duration of the second labor period ≥38 min (OR 2.81; 95% CI 1.09–7.23,
p = 0.032), and consumption of flour products several times per week (OR 2.77; 95% CI 1.10–6.98,
p = 0.030) were associated with a higher risk of perianal pathology. Daily consumption of fruits and vegetables (OR 0.35; 95% CI 0.15–0.81,
p = 0.014) and less frequent consumption of eggs were protective factors (OR 0.18; 95% CI 0.06–0.56,
p = 0.003). Conclusions: Perianal diseases, especially hemorrhoidal disease, are common during pregnancy and the postpartum period. A neonatal birth weight ≥ 3380 g, a maternal BMI of ≥21.48, duration of the second labor period of ≥38 min, and consumption of flour products and cereals several times a week are risk factors for developing these diseases.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT