Decaying Dark Energy in Light of the Latest Cosmological Dataset
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
3. Methodology and Data
3.1. Supernovae Type Ia
3.2. Differential Ages,
3.3. Baryonic Acoustic Oscillation
3.4. Gamma Ray Burst
3.5. –Redshift Relation
3.6. PlanckTT + LowP
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAO | Baryon Acoustic Oscillation |
| DE | Dark Energy |
| DM | Dark Matter |
| FRW | Friedman–Robertson–Walker |
| GR | General Relativity |
| GRB | Gamma Ray Burst |
| MCMC | Monte Carlo Markov Chain |
| SNIa | Supernovae Type Ia |
| SPT | South Pole Telescope |
References
- Perlmutter, S.; Gabi, S.; Goldhaber, G.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; Hook, I.M.; Kim, A.G.; Kim, M.Y.; Lee, J.C.; Pain, R.; et al. Measurements of the Cosmological Parameters Omega and Lambda from the First Seven Supernovae at z ≥ 0.35. Astrophys. J. 1997, 483, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Strolger, L.G.; Tonry, J.; Casertano, S.; Ferguson, H.C.; Mobasher, B.; Challis, P.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jha, S.; Li, W.; et al. Type Ia Supernova Discoveries at z > 1 from the Hubble Space Telescope: Evidence for Past Deceleration and Constraints on Dark Energy Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 665–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astier, P.; Guy, J.; Regnault, N.; Pain, R.; Aubourg, E.; Balam, D.; Basa, S.; Carlberg, R.G.; Fabbro, S.; Fouchez, D.; et al. The Supernova Legacy Survey: Measurement of ΩM, ΩΛ and w from the first year data set. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 447, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Rubin, D.; Lidman, C.; Aldering, G.; Amanullah, R.; Barbary, K.; Barrientos, L.F.; Botyanszki, J.; Brodwin, M.; Connolly, N.; et al. The Hubble Space Telescope Cluster Supernova Survey. V. Improving the Dark-energy Constraints above z > 1 and Building an Early-type-hosted Supernova Sample. Astrophys. J. 2012, 746, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, A.C.; Matsubara, T.; Szalay, A.S.; Blanton, M.R.; Eisenstein, D.J.; Gray, J.; Jain, B.; Bahcall, N.A.; Brinkmann, J.; Budavari, T.; et al. Cosmological Parameters from Eigenmode Analysis of Sloan Digital Sky Survey Galaxy Redshifts. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percival, W.J.; Baugh, C.M.; Bland-Hawthorn, J.; Bridges, T.; Cannon, R.; Cole, S.; Colless, M.; Collins, C.; Couch, W.; Dalton, G.; et al. The 2dF Galaxy Redshift Survey: The power spectrum and the matter content of the Universe. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2001, 327, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegmark, M.; Blanton, M.R.; Strauss, M.A.; Hoyle, F.; Schlegel, D.; Scoccimarro, R.; Vogeley, M.S.; Weinberg, D.H.; Zehavi, I.; Berlind, M.S.; et al. The Three-Dimensional Power Spectrum of Galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Astrophys. J. 2004, 606, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinshaw, G.; Larson, D.; Komatsu, E.; Spergel, D.N.; Bennett, C.L.; Dunkley, J.; Nolta, M.R.; Halpern, M.; Hill, R.S.; Odegard, N.; et al. Nine-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Cosmological Parameter Results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 208, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Kazin, E.A.; Beutler, F.; Davis, T.M.; Parkinson, D.; Brough, S.; Colless, M.; Contreras, C.; Couch, W.; Croom, S.; et al. The WiggleZ Dark Energy Survey: Mapping the distance-redshift relation with baryon acoustic oscillations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 418, 1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2018 results. VI. Cosmological parameters. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1807.06209. [Google Scholar]
- de Martino, I.; Génova-Santos, R.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Ebeling, H.; Kashlinsky, A.; Kocevski, D.; Martins, C.J.A.P. Constraining the Redshift Evolution of the Cosmic Microwave Background Blackbody Temperature with PLANCK Data. Astrophys. J. 2015, 808, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; Martins, C.J.A.P.; Ebeling, H.; Kocevski, D. Constraining spatial variations of the fine structure constant using clusters of galaxies and Planck data. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 083008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peebles, P.J.E.; Ratra, B. Cosmology with a time-variable cosmological ’constant’. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1988, 325, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratra, B.; Peebles, P.J.E. Cosmological consequences of a rolling homogeneous scalar field. Phys. Rev. D 1988, 37, 3406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Starobinsky, A.A. The Case for a Positive Cosmological Λ-Term. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2000, D9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.R. A phantom menace? Cosmological consequences of a dark energy component with super-negative equation of state. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 545, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T. Cosmological constant-the weight of the vacuum. Phys. Rep. 2003, 380, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P.J.E.; Ratra, B. The cosmological constant and dark energy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demianski, M.; Piedipalumbo, E.; Rubano, C.; Tortora, C. Two viable quintessence models of the Universe: Confrontation of theoretical predictions with observational data. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 431, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardone, V.F.; Tortora, C.; Troisi, A.; Capozziello, S. Beyond the perfect fluid hypothesis for the dark energy equation of state. Phys. Rev. D 2006, 73, 043508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, A. Dark matter and dark energy induced by condensates. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capolupo, A. Quantum vacuum, dark matter, dark energy and spontaneous supersymmetry breaking. Adv. High Energy Phys. 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidis, K.; Spyrou, N.K. A conventional approach to the dark energy concept. Astron. Astrophys. 2011, 529, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidis, K.; Spyrou, N.K. A conventional form of dark energy. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2011, 283, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleidis, K.; Spyrou, N.K. Polytropic dark matter flows illuminate dark energy and accelerated expansion. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 576, A23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidis, K.; Spyrou, N.K. Dark energy: The shadowy reflection of dark matter? Entropy 2016, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidis, K.; Spyrou, N.K. Cosmological perturbations in the ΛCDM-like limit of a polytropic dark matter model. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 606, A116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldwell, R.; Kamionkowski, M. The Physics of Cosmic Acceleration. Ann. Rev. Nuclear Part. Sci. 2009, 59, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Abdalla, E.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Pavón, D. Dark Matter and Dark Energy Interactions: Theoretical Challenges, Cosmological Implications and Observational Signatures. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozziello, S.; de Laurentis, M.; Francaviglia, M.; Mercadante, S. From Dark Energy & Dark Matter to Dark Metric. Found. Phys. 2009, 39, 1161. [Google Scholar]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified cosmic history in modified gravity: From F(R) theory to Lorentz non-invariant models. Phys. Rep. 2011, 505, 59–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Martino, I.; De Laurentis, M.; Capozziello, S. Constraining f(R) gravity by the Large Scale Structure. Universe 2015, 1, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Modified gravity theories on a nutshell: Inflation, bounce and late-time evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Introduction to modified gravity and gravitational alternative for dark energy. Int. J. Geom. Meth. Mod. Phys. 2007, 4, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. Extended Theories of Gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraut, I. The graviton Higgs mechanism. Europhys. Letter 2015, 111, 61001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arraut, I.; Chelabi, K. Non-linear massive gravity as a gravitational σ-model. Europhys. Letter 2016, 115, 31001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arraut, I.; Chelabi, K. Vacuum degeneracy in massive gravity: Multiplicity of fundamental scales. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2017, 32, 1750112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, J.A.S. Thermodynamics of decaying vacuum cosmologies. Phys. Rev. D 1996, 54, 2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, J.A.S.; Alcaniz, J.A.S. Flat Friedmann-Robertson-Walker cosmologies with adiabatic matter creation: kinematic tests. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 348, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, J.A.S.; Silva, A.I.; Viegas, S.M. Is the radiation temperature-redshift relation of the standard cosmology in accordance with the data? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2000, 312, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puy, D. Thermal balance in decaying Λ cosmologies. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 422, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Variable cosmological constant model: The reconstruction equations and constraints from current observational data. Nuclear Phys. B 2008, 804, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jetzer, P.; Puy, D.; Signore, M.; Tortora, C. Limits on decaying dark energy density models from the CMB temperature-redshift relation. Gen. Relat. Grav. 2011, 43, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jetzer, P.; Tortora, C. Constraints from the CMB temperature and other common observational data sets on variable dark energy density models. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 84, 043517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fixsen, D.J. The Temperature of the Cosmic Microwave Background. Astrophys. J. 2009, 707, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcall, J.N.; Wolf, R.A. Fine-Structure Transitions. Astrophys. J. 1968, 152, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, R.; Melchiorri, F.; Natale, V. The Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect in the millimetric region. Astrophys. Space Sci. 1978, 59, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rephaeli, Y. On the determination of the degree of cosmological Compton distortions and the temperature of the cosmic blackbody radiation. Astrophys. J. 1980, 241, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyaev, R.A.; Zeldovich, Y.B. The Observations of Relic Radiation as a Test of the Nature of X-Ray Radiation from the Clusters of Galaxies. Comment Astrophys. Space Phys. 1972, 4, 173. [Google Scholar]
- Avgoustidis, A.; Génova-Santos, R.T.; Luzzi, G.; Martins, C.J.A.P. Subpercent constraints on the cosmological temperature evolution. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 043521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luzzi, G.; Shimon, M.; Lamagna, L.; Rephaeli, Y.; De Petris, M.; Conte, A.; De Gregori, S.; Battistelli, E.S. Redshift Dependence of the Cosmic Microwave Background Temperature from Sunyaev-Zeldovich Measurements. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzzi, G.; Génova-Santos, R.T.; Martins, C.J.A.P.; De Petris, M.; Lamagna, L. Constraining the evolution of the CMB temperature with SZ measurements from Planck data. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2015, 1509, 011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurier, G.; Aghanim, N.; Douspis, M.; Pointecouteau, E. Measurement of the TCMB evolution from the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 561, A143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saro, A.; Liu, J.; Mohr, J.J.; Aird, K.A.; Ashby, M.L.N.; Bayliss, M.; Benson, B.A.; Bleem, L.E.; Bocquet, S.; Brodwin, M.; et al. Constraints on the CMB temperature evolution using multiband measurements of the Sunyaev-Zel’dovich effect with the South Pole Telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 440, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; da Silva, A.; Ebeling, H.; Kashlinsky, A.; Kocevski, D.; Martins, C.J.A.P. Measuring the Redshift Dependence of the Cosmic Microwave Background Monopole Temperature with Planck Data. Astrophys. J. 2012, 757, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Gravitation and Cosmology: Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Hastings, W.K. Monte Carlo Sampling Methods using Markov Chains and their Applications. Biometrika 1970, 57, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metropolis, N.; Rosenbluth, A.W.; Rosenbluth, M.N.; Teller, A.H.; Teller, E. Equation of State Calculations by Fast Computing Machines. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Roberts, G.O.; Gilks, W.R. Efficient Metropolis jumping rule. Bayesian Stat. 1996, 5, 599. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, G.O.; Gelman, A.; Gilks, W.R. Weak convergence and optimal scaling of random walk Metropolis algorithms. Ann. Appl. Probab. 1997, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelman, A.; Rubin, D.B. Inference from Iterative Simulation Using Multiple Sequences. Stat. Sci. 1992, 7, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.N.; Verde, L.; Peiris, H.V.; Komatsu, E.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Halpern, M.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Kogut, A.; et al. First-Year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) Observations: Determination of Cosmological Parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2003, 148, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amanullah, R.; Lidman, C.; Rubin, D.; Aldering, G.; Astier, P.; Barbary, K.; Burns, M.S.; Conley, A.; Dawson, K.S.; Deustua, S.E.; et al. Spectra and Hubble Space Telescope Light Curves of Six Type Ia Supernovae at 0.511 < z < 1.12 and the Union2 Compilation. Astrophys. J. 2010, 716, 712. [Google Scholar]
- Di Pietro, E.; Claeskens, J.F. Future supernovae data and quintessence models. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2003, 341, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesseris, S.; Perivolaropoulos, L. Comparison of the Legacy and Gold SnIa Dataset Constraints on Dark Energy Models. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 123519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perivolaropoulos, L. Constraints on linear negative potentials in quintessence and phantom models from recent supernova data. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 063503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H. Constraints on linear negative potentials in quintessence and phantom models from recent supernova data. Phys. Lett. B 2010, 687, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luković, V.V.; D’Agostino, R.; Vittorio, N. Is there a concordance value for H0? Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, R.; Loeb, A. Constraining Cosmological Parameters Based on Relative Galaxy Ages. Astrophys. J. 2005, 573, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Verde, L.; Jimenez, R. Constraints on the redshift dependence of the dark energy potential. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, D.; Jimenez, R.; Verde, L.; Stanford, S.A.; Kamionkowski, M. Cosmic Chronometers: Constraining the Equation of State of Dark Energy. II. A Spectroscopic Catalog of Red Galaxies in Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2010, 188, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.J.; Sun, Y.C. Four new observational H(z) data from luminous red galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey data release seven. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M. Raising the bar: New constraints on the Hubble parameter with cosmic chronometers at z∼2. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 450, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Pozzetti, L.; Zamorani, G.; Bolzonella, M.; Dunlop, J.; Lamareille, F.; Mignoli, M.; Pearce, H.; et al. Improved constraints on the expansion rate of the Universe up to z∼1.1 from the spectroscopic evolution of cosmic chronometers. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Pozzetti, L.; Cimatti, A.; Jimenez, R.; Maraston, C.; Verde, L.; Thomas, D.; Citro, A.; Tojeiro, R.; Wilkinson, D. A 6% measurement of the Hubble parameter at z∼0.45: Direct evidence of the epoch of cosmic re-acceleration. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, M.; Verde, L.; Pozzetti, L.; Jimenez, R.; Cimatti, A. New constraints on cosmological parameters and neutrino properties using the expansion rate of the Universe to z∼1.75. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstein, D.J.; Hu, W.; Tegmark, M. Cosmic Complementarity: H0 and Ωm from Combining Cosmic Microwave Background Experiments and Redshift Surveys. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1998, 504, L57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenstein, D.J.; Zehavi, I.; Hogg, D.W.; Scoccimarro, R.; Blanton, M.R.; Nichol, R.C.; Scranton, R.; Seo, H.; Tegmark, M.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Detection of the Baryon Acoustic Peak in the Large-Scale Correlation Function of SDSS Luminous Red Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2005, 633, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutler, F.; Blake, C.; Colless, M.; Jones, D.H.; Staveley-Smith, L.; Campbell, L.; Parker, Q.; Saunders, W.; Watson, F. The 6dF Galaxy Survey: baryon acoustic oscillations and the local Hubble constant. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2011, 416, 3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.J.; Samushia, L.; Howlett, C.; Percival, W.J.; Burden, A.; Manera, M. The clustering of the SDSS DR7 main Galaxy sample - I. A 4 per cent distance measure at z = 0.15. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 449, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.; Aubourg, E.; Bailey, S.; Beutler, F.; Bhardwaj, V.; Blanton, M.; Bolton, A.S.; Brinkmann, J.; Brownstein, J.R.; Burden, A.; et al. The clustering of galaxies in the SDSS-III Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey: baryon acoustic oscillations in the Data Releases 10 and 11 Galaxy samples. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 441, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delubac, T.; Bautista, J.E.; Busca, N.G.; Rich, J.; Kirkby, D.; Bailey, S.; Font-Ribera, A.; Slosar, A.; Lee, K.G.; Pieri, M.M.; et al. Baryon acoustic oscillations in the Lyα forest of BOSS DR11 quasars. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 574, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Font-Ribera, A.; Kirkby, D.; Busca, N.; Miralda-Escudé, J.; Ross, N.P.; Slosar, A.; Rich, J.; Aubourg, E.; Bailey, S.; Bhardwaj, V.; et al. Quasar-Lyman α forest cross-correlation from BOSS DR11: Baryon Acoustic Oscillations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 5, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H. Observational constraints on cosmological models with the updated long gamma-ray bursts. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 1008, 020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haridasu, B.S.; Luković, V.V.; D’Agostino, R.; Vittorio, N. Strong evidence for an accelerating Universe. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 600, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Frontera, F.; Guidorzi, C. Extremely energetic Fermi gamma-ray bursts obey spectral energy correlations. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 508, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Frontera, F.; Tavani, M.; in’t Zand, J.J.M.; Antonelli, A.; Costa, E.; Feroci, M.; Guidorzi, C.; Heise, J.; Masetti, N.; et al. Intrinsic spectra and energetics of BeppoSAX Gamma-Ray Bursts with known redshifts. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 390, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Guidorzi, C.; Frontera, F.; Della Valle, M.; Finelli, F.; Landi, R.; Montanari, E. Measuring the cosmological parameters with the Ep,i − Eiso correlation of gamma-ray bursts. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 391, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosowsky, A.; Milosavljevic, M.; Jimenez, R. Efficient cosmological parameter estimation from microwave background anisotropies. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 063007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Mukherjee, P. Observational Constraints on Dark Energy and Cosmic Curvature. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 103533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planck Collaboration. Planck 2015 results. XIV. Dark energy and modified gravity. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 594, A14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.L. A 2.4% Determination of the Local Value of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.; Anderson, J.; MacKenty, J.W.; Bowers, J.B.; Clubb, K.I.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jones, D.O.; et al. New Parallaxes of Galactic Cepheids from Spatially Scanning the Hubble Space Telescope: Implications for the Hubble Constant. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1801.01120. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Ratra, B.; Wang, F.Y. Hubble Parameter and Baryon Acoustic Oscillation Measurement Constraints on the Hubble Constant, the Deviation from the Spatially Flat ΛCDM Model, the Deceleration-Acceleration Transition Redshift, and Spatial Curvature. Astrophys. J. 2018, 856, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Amendola, L. H0 from cosmic chronometers and Type Ia supernovae, with Gaussian Processes and the novel Weighted Polynomial Regression method. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 2018, 051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, W. Machine Learning Cosmic Expansion History. arXiv, 2018; arXiv:1712.09208. [Google Scholar]
- LSST Science Collaborations and LSST Project. LSST Science Book, 2nd ed.; LSST Science Collaborations and LSST Project: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Laureijs, R.; Amiaux, J.; Arduini, S.; Auguères, J.L.; Brinchmann, J.; Cole, R.; Cropper, M.; Dabin, C.; Duvet, L.; Ealet, A.; et al. Euclid Definition Study Report ESA/SRE(2011)12. arXiv, 2011; arXiv:1110.3193. [Google Scholar]
- Spergel, D.; Gehrels, N.; Baltay, C.; Bennett, D.; Breckinridge, J.; Donahue, M.; Dressler, A.; Gaudi, B.S.; Greene, T.; Guyon, O.; et al. Wide-Field InfrarRed Survey Telescope-Astrophysics Focused Telescope Assets WFIRST-AFTA 2015 Report. arXiv, 2015; arXiv:1503.03757. [Google Scholar]
- Kashlinsky, A.; Arendt, R.G.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Helgason, K. Lyman-tomography of cosmic infrared background fluctuations with Euclid: Probing emissions and baryonic acoustic oscillations at z > 10. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 813, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
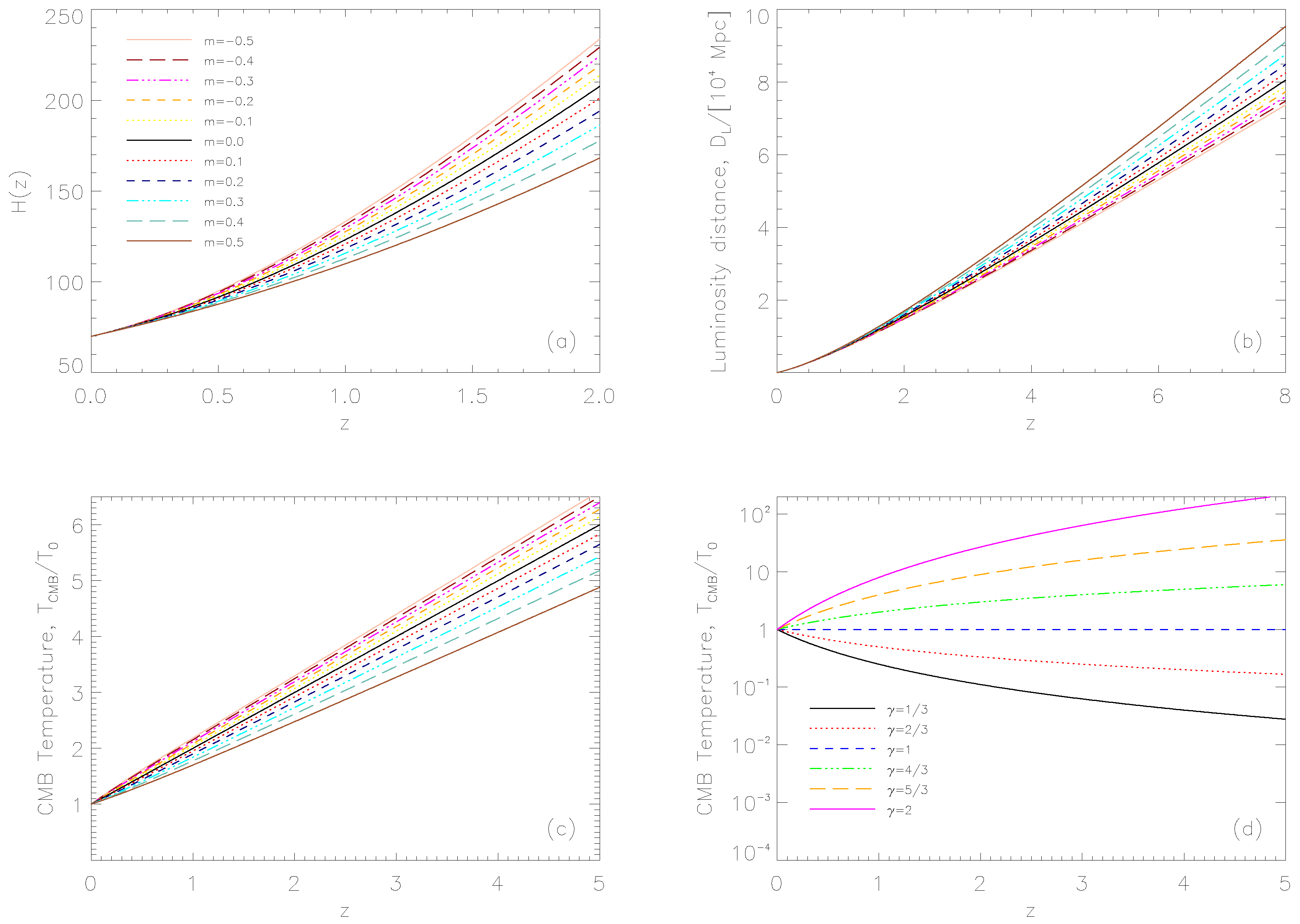
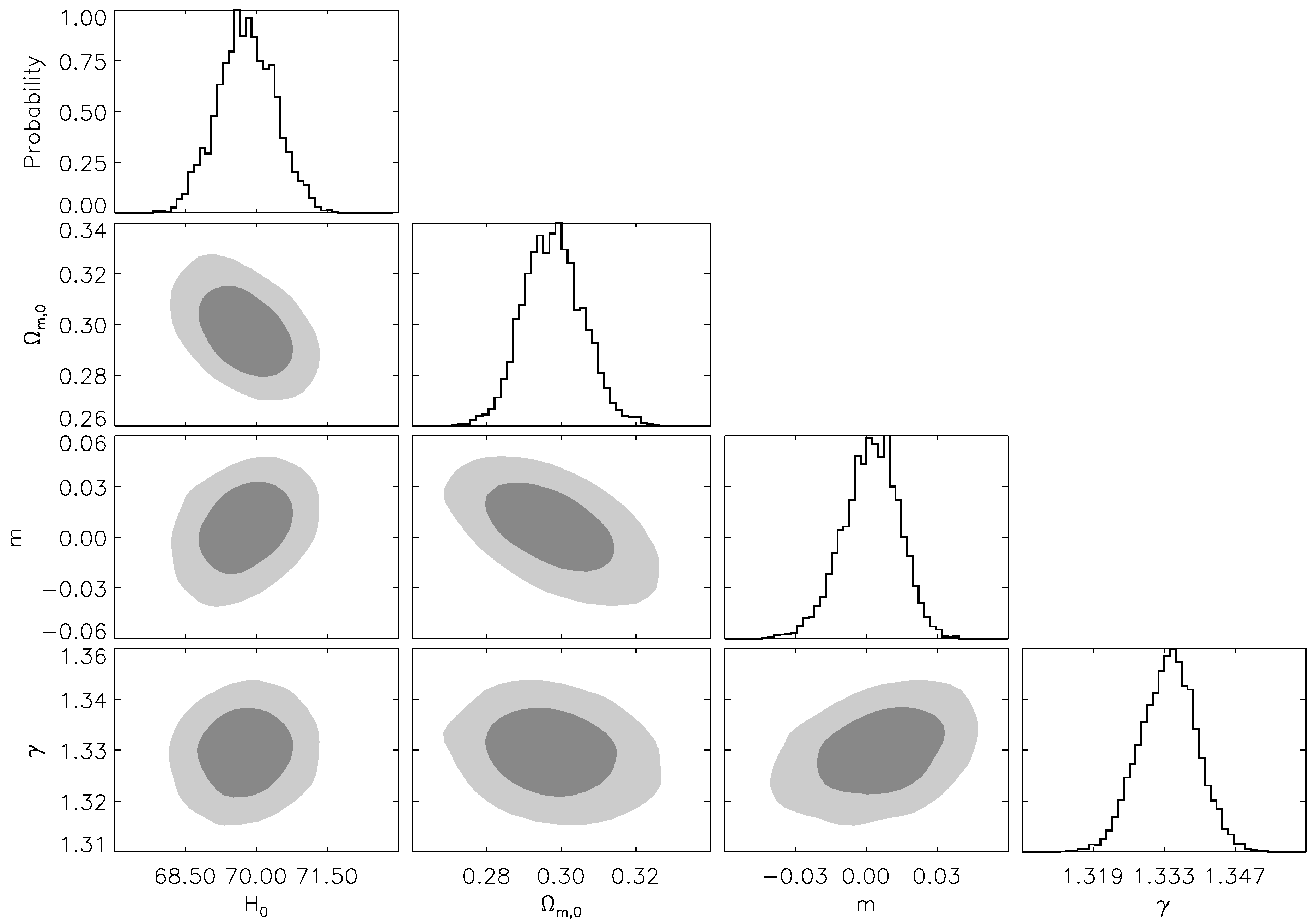
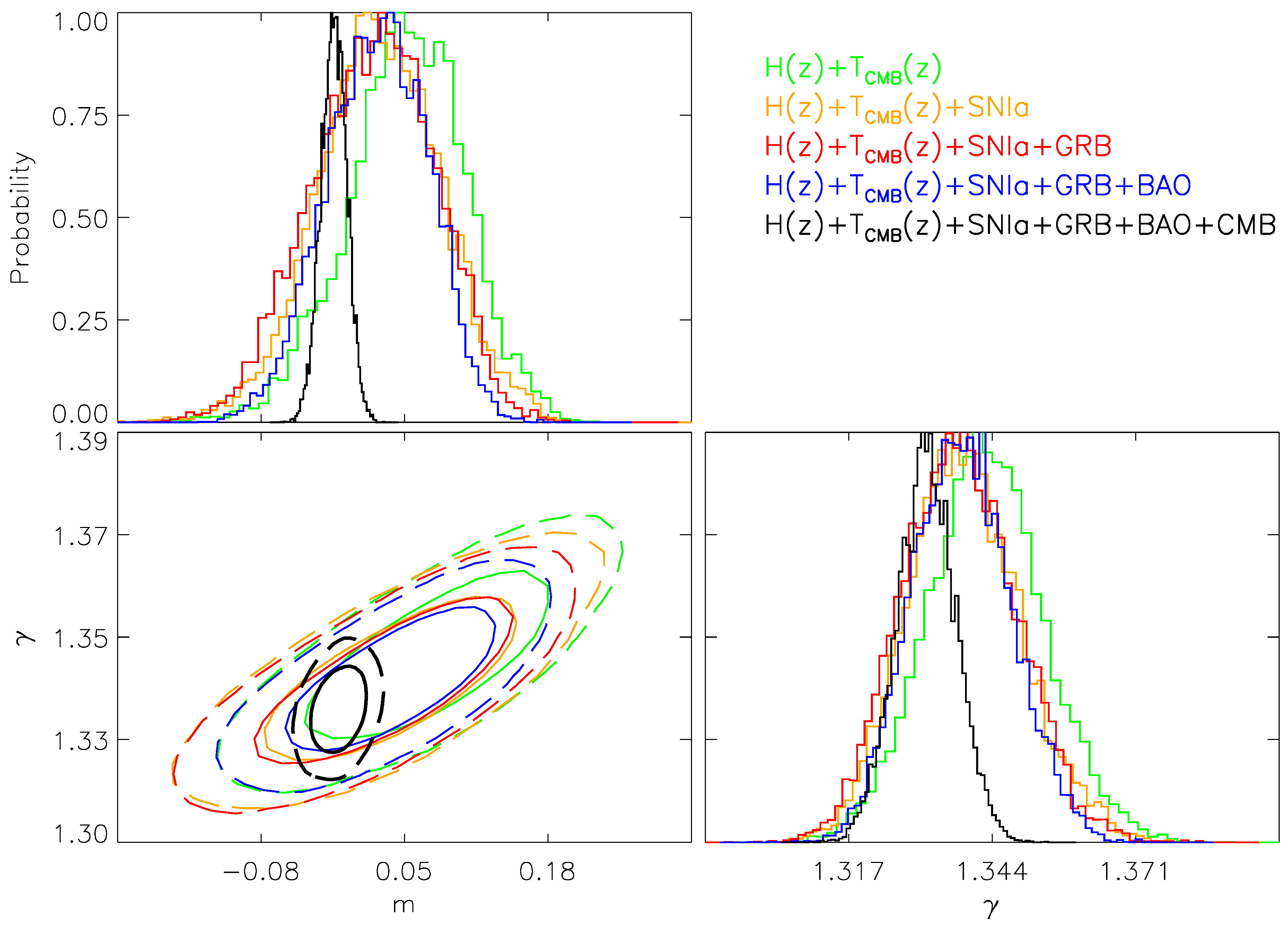
| Parameter | Priors |
|---|---|
| m | [−1, 1] |
| Dataset | Free | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | ||||
| SNIa++ | ||||
| SNIa+GRB++ | ||||
| SNIa+GRB++BAO+ | ||||
| SNIa+GRB++BAO++CMB | ||||
| + | ||||
| SNIa++ | ||||
| SNIa+GRB++ | ||||
| SNIa+GRB++BAO+ | ||||
| SNIa+GRB++BAO++CMB | ||||
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Martino, I. Decaying Dark Energy in Light of the Latest Cosmological Dataset. Symmetry 2018, 10, 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090372
De Martino I. Decaying Dark Energy in Light of the Latest Cosmological Dataset. Symmetry. 2018; 10(9):372. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090372
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Martino, Ivan. 2018. "Decaying Dark Energy in Light of the Latest Cosmological Dataset" Symmetry 10, no. 9: 372. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym10090372





