Evaluation of a Modified Monod Model for Predicting Algal Dynamics in Lake Tai
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
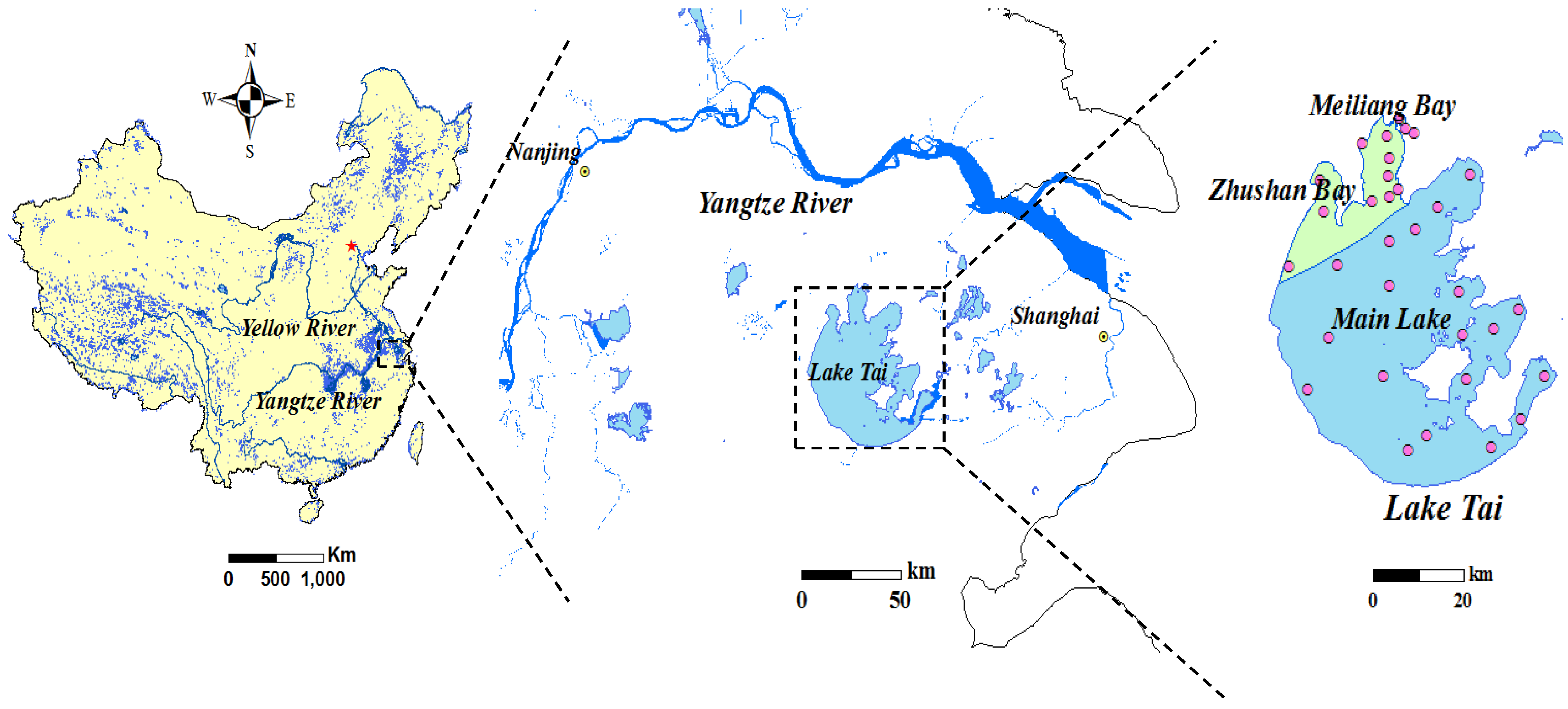
2.2. Data and Preprocessing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Model Description
2.3.2. Estimation of Model Parameters in Equation (4)
2.3.3. Approach Used for Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Observed Temporal Variations of Nutrients and Temperature
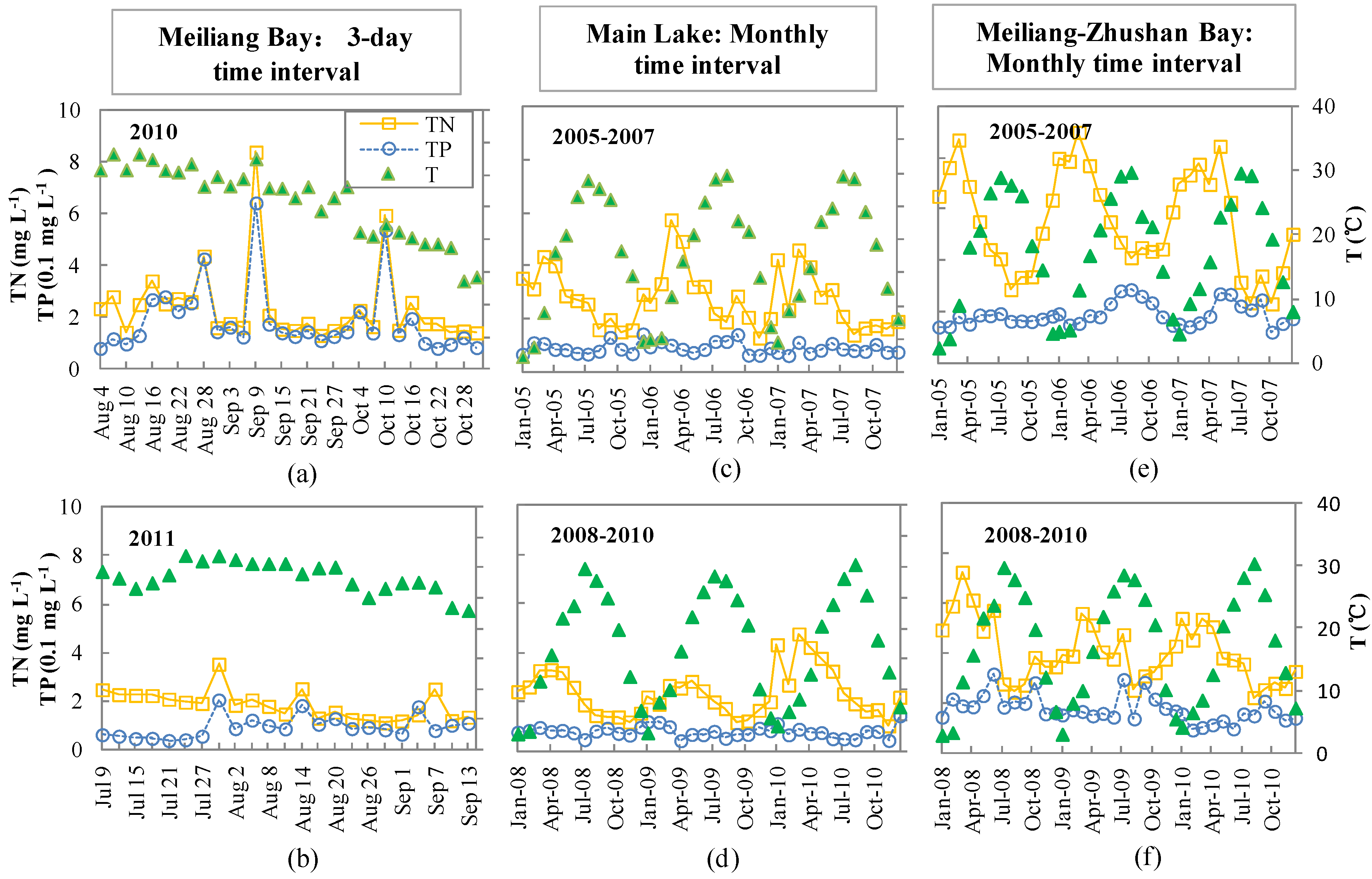
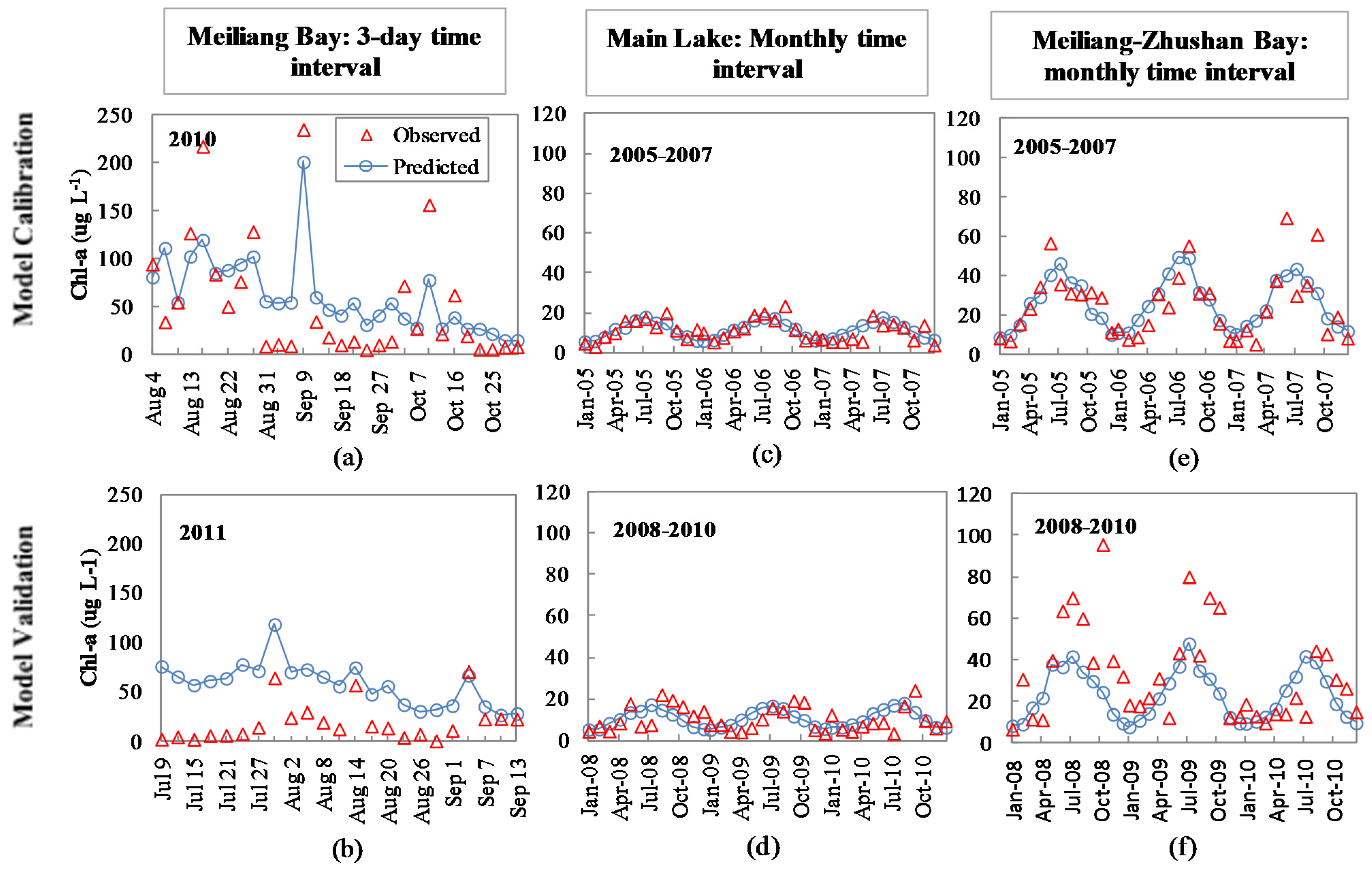
3.2. Model Parameters
| Observation Location | Measurement Years | Model | No Constraints | With Constraints | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Within Lake Tai 2 | (Time Interval) | Parameter 3 | TN | TP | TN | TP |
| Meiliang Bay | a | 2144.23 | 190.77 | 30.88 | 14.07 | |
| 2010 | b | 1.05 | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.11 | |
| (once every three-days ) | k | 330.91 | 4.04 | 7.00 | 0.50 | |
| RMSE | 33.59 | 35.64 | 38.00 | 39.08 | ||
| AIC | 13.43 | 13.54 | 13.67 | 13.73 | ||
| Main Lake | a | 6.15 | 6.14 | 6.15 | 5.24 | |
| 2005–2007 | b | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.05 | 1.04 | |
| (once every month) | k | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.08 | |
| RMSE | 3.40 | 3.40 | 3.40 | 3.49 | ||
| AIC | 8.95 | 8.95 | 8.95 | 9.00 | ||
| Meiliang-Zhushan Bay | a | 10.56 | 10.56 | 10.56 | 9.89 | |
| 2005–2007 | b | 1.07 | 1.07 | 1.07 | 1.06 | |
| (once every month) | k | 2.54 | 2.65 | 2.54 | 0.08 | |
| RMSE | 10.06 | 10.06 | 10.06 | 12.12 | ||
| AIC | 11.12 | 11.12 | 11.12 | 11.49 | ||
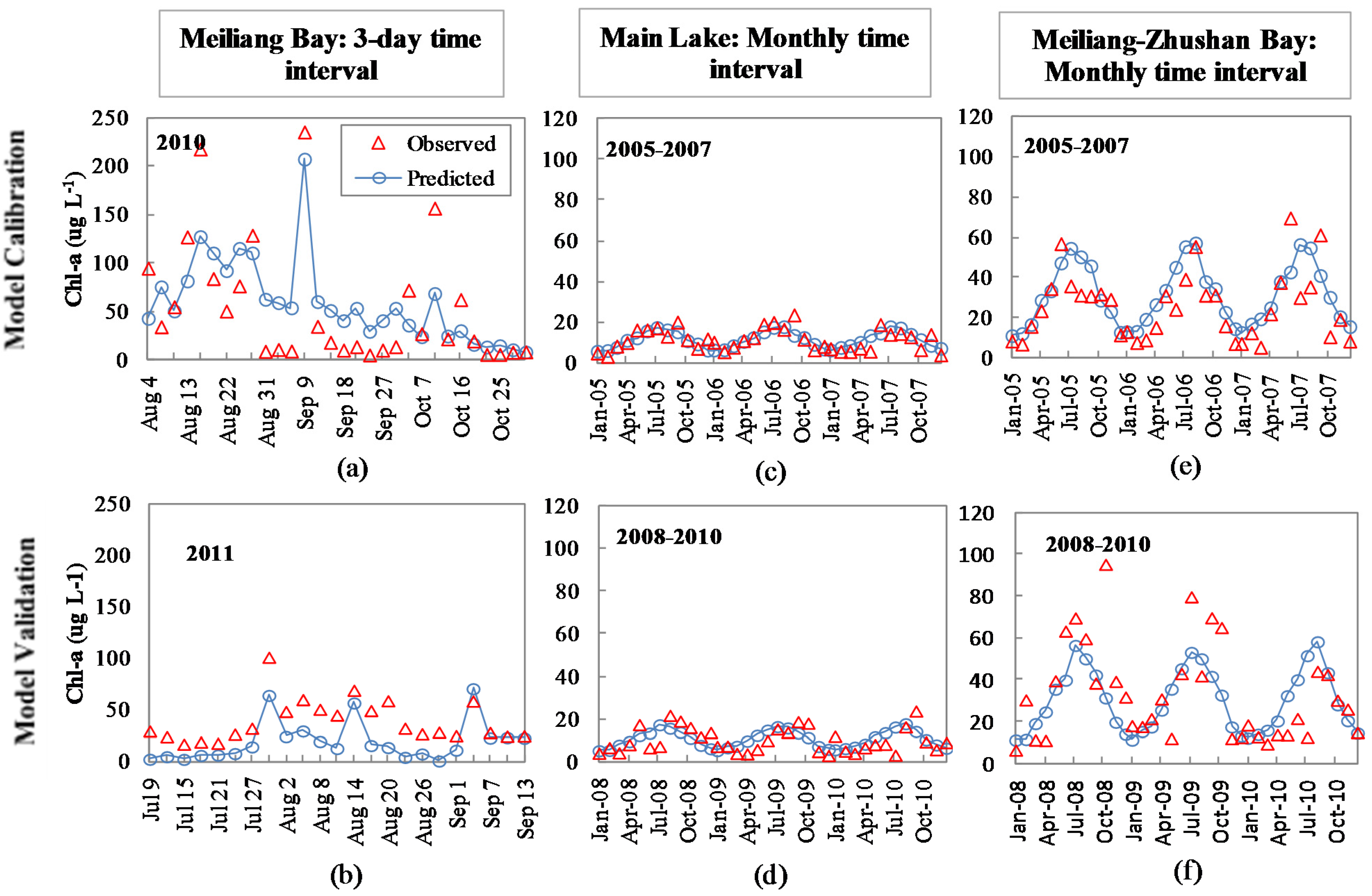
3.3. Model Performance with TN Versus TP as the Independent Variable
| Time Series | TN as an Independent Variable | TP as an Independent Variable | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | RMSE | AIC | Model | RMSE | AIC | |
| Meiliang Bay 2011 (three-day) | Cchl-a = 30.88 × 1.08WT × TN/(7.00 + TN) | 44.51 | 10.50 | Cchl-a = 14.07 × 1.11WT × TP/(0.5 + TP) | 24.15 | 9.56 |
| Main Lake 2008–2010 (monthly) | Cchl-a = 6.15 × 1.05AT × TN/(0.71 + TN) | 5.63 | 9.96 | Cchl-a=5.24 × 1.04AT × TP/(0.08 + TP) | 5.15 | 9.78 |
| Meiliang-Zhushan Bay 2008–2010 (monthly) | Cchl-a = 10.56 × 1.07AT × TN/(2.54 + TN) | 21.22 | 12.61 | Cchl-a = 9.89 × 1.06AT × TP/(0.08 + TP) | 18.59 | 12.34 |
3.4. Control Variables of Chl-a
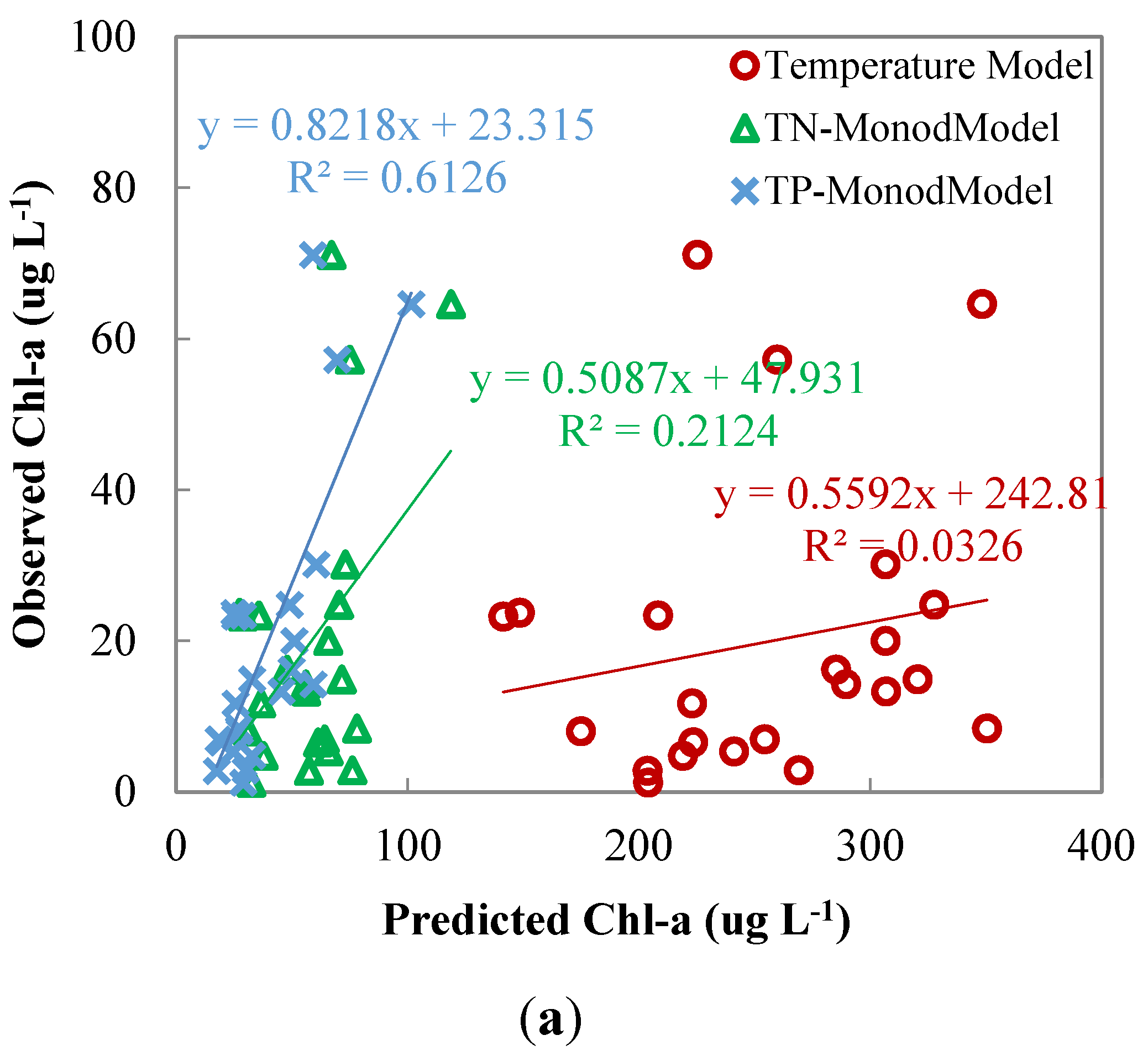
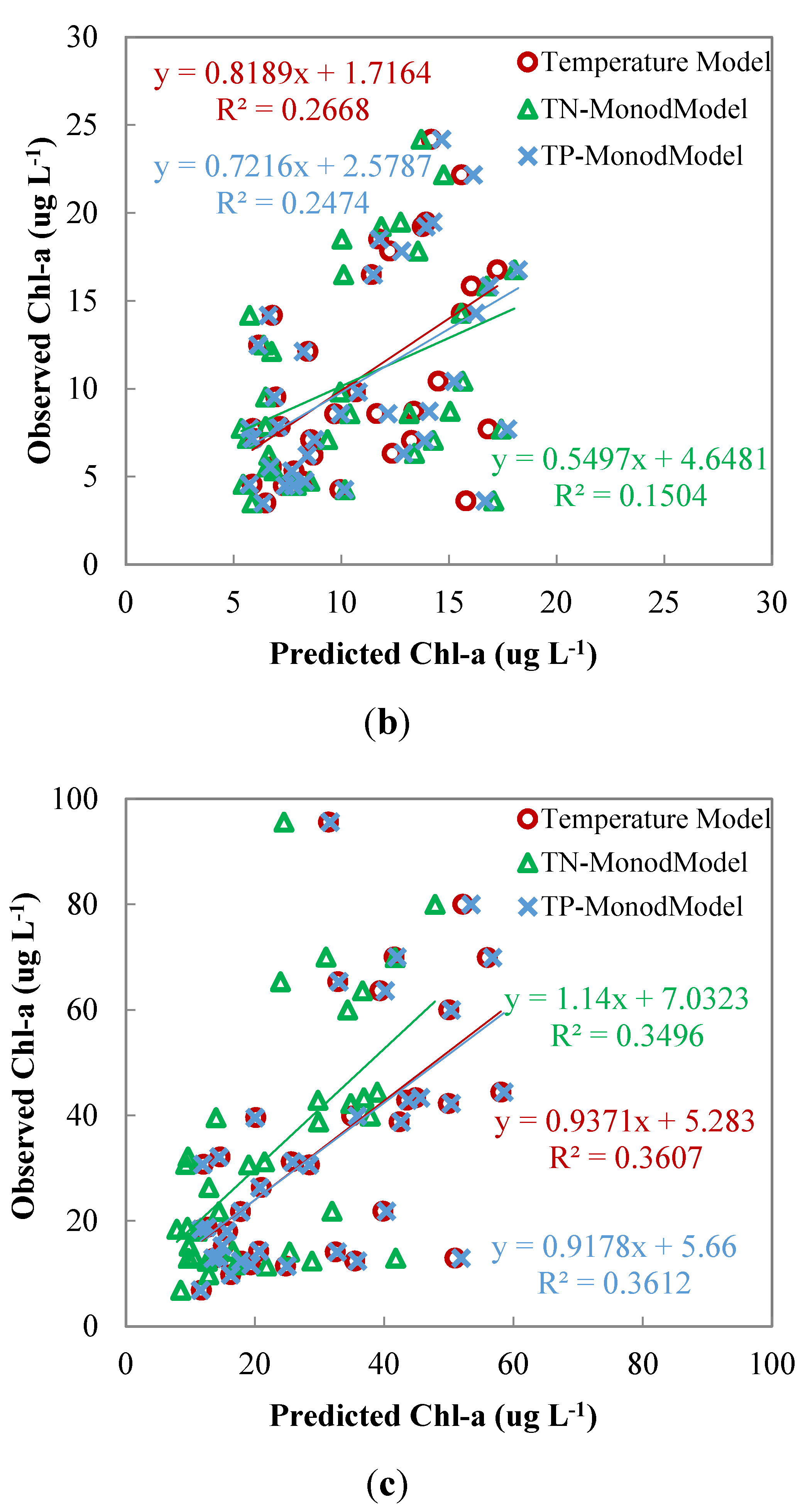
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hudnell, H.K. The state of U.S. freshwater harmful algal blooms assessments, policy and legislation. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, C.C.; Ibelings, B.W.; Hoffmann, E.P.; Hamilton, D.P.; Brookes, J.D. Eco-Physiological adaptations that favour freshwater cyanobacteria in a changing climate. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, T.W.; Berry, D.B.; Boyer, G.L.; Gobler, C.J. The effects of temperature and nutrients on the growth and dynamics of toxic and non-toxic strains of Microcystis during cyanobacteria blooms. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.L.; Shuter, B.J.; Zhao, Y.M.; Stockwell, J.D. Forecasting effects of climate change on Great Lakes fisheries: Models that link habitat supply to population dynamics can help. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A. The use of TN:TP and DIN:TP ratios as indicators for phytoplankton nutrient limitation in oligotrophic lakes affected by N deposition. Aquat. Sci. 2010, 72, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jeppesen, E.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Skov, C.; Van Nes, E.H.; Roijackers, R.; Lammens, E.; Portielje, R.O.B. Lake restoration: Successes, failures and long-term effects. J. Appl. Ecol. 2007, 44, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Gao, J.; Hörmann, G. Hydrodynamic-phytoplankton model for short-term forecasts of phytoplankton in Lake Taihu, China. Limnol. Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2012, 42, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.P.; Schladow, S.G. Prediction of water quality in lakes and reservoirs. Part I. Model description. Ecol. Model. 1997, 96, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arhonditsis, G.B.; Brett, M.T. Eutrophication model for Lake Washington (USA): Part I. Model description and sensitivity analysis. Ecol. Model. 2005, 187, 140–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, S.E. A review of recent developments in lake modeling. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayombo, S.; Mbwette, T.S.A.; Katima, J.H.Y.; Jorgensen, S.E. Effects of substrate concentrations on the growth of heterotrophic bacteria and algae in secondary facultative ponds. Water Res. 2003, 37, 2937–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, H.; Ma, J. Study on the algal dynamic model for West Lake, Hangzhou. Ecol. Model. 2002, 148, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, T.; Fan, M.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, J. Long-Term joint effect of nutrients and temperature increase on algal growth in Lake Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswanto, E.; Ishizaka, J.; Tripathy, S.C.; Miyamura, K. Detection of harmful algal blooms of Karenia mikimotoi using MODIS measurements: A case study of Seto-Inland Sea, Japan. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 129, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N &P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, S.W.; Farnsley, S.E.; LeCleir, G.R.; Layton, A.C.; Satchwell, M.F.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Boyer, G.L.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W. The relationships between nutrients, cyanobacterial toxins and the microbial community in Taihu (Lake Tai), China. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Paerl, H.W.; Carmichael, W.W. A drinking water crisis in Lake Taihu, China: Linkage to climatic variability and lake management. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, H.; Sun, D.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Xu, L. Detection of algal bloom and factors influencing its formation in Taihu Lake from 2000 to 2011 by MODIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3705–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xie, P.; Tang, H. Enhancement of dissolved phosphorus release from sediment to lake water by Microcystis blooms: An enclosure experiment in a hyper-eutrophic, subtropical Chinese lake. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 122, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SEPA (State Environmental Protection Administration). Water and Wastewater Monitoring and Analysis Methods, 4th ed.Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Li, F.; Gao, R.; Duan, L.; Luo, Y. Trend and extreme occurrence of precipitation in a mid-latitude Eurasian steppe watershed at various time scales. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 28, 5547–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.C.; Carpenter, E.J. A kinetic approach to the effect of temperature on algal growth. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1974, 19, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans. Autom. Contrl. 1974, 19, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, W.; Hood, J.; Benstead, J.P.; Huryn, A.D.; Nelson, D. Interactions between temperature and nutrients across levels of ecological organization. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capblancq, J. Nutrient dynamics and pelagic food web interactions in oligotrophic and eutrophic environments: An overview. Hydrobiologia 1990, 207, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokulil, M.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q. Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: The Tai Hu example. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 81–94. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, C.; Teubner, K.; Dokulil, M. Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: An 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506–509, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Xu, Q.; Xi, B.; Wang, X.; Jia, K.; Huo, S.; Su, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, C. Effects of lake-basin morphological and hydrological characteristics on the eutrophication of shallow lakes in east China. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Hall, N.S.; Wu, Y. Determining critical nutrient thresholds needed to control harmful cyanobacterial blooms in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orihel, D.M.; Schindler, D.W.; Ballard, N.C.; Graham, M.D.; O’Connell, D.W.; Wilson, L.R.; Vinebrooke, R.D. The “nutrient pump:” Iron-poor sediments fuel low nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios and cyanobacterial blooms in polymictic lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 856–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molot, L.A.; Watson, S.B.; Creed, I.F.; Trick, C.G.; McCabe, S.K.; Verschoor, M.J.; Sorichetti, R.J.; Powe, C.; Venkiteswaran, J.J.; Schiff, S.L. A novel model for cyanobacteria bloom formation: The critical role of anoxia and ferrous iron. Freshw. Biol. 2014, 59, 1323–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, M.; Pick, F.; Palmer, M.; Watson, S.; Winter, J.; Zurawell, R.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Comparing predictive cyanobacterial models from temperate regions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 71, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranu, Z.E.; Gregory-Eaves, I.; Leavitt, P.R.; Bunting, L.; Buchaca, T.; Catalan, J.; Domaizon, I.; Guilizzoni, P.; Lami, A.; McGowan, S.; et al. Acceleration of cyanobacterial dominance in north temperate-subarctic lakes during the Anthropocene. Ecol. Lett. 2015, 18, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, X.; Xi, B.; Jia, K.; Huo, S.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Xu, B. Evaluation of a Modified Monod Model for Predicting Algal Dynamics in Lake Tai. Water 2015, 7, 3626-3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7073626
Huang J, Xu Q, Wang X, Xi B, Jia K, Huo S, Liu H, Li C, Xu B. Evaluation of a Modified Monod Model for Predicting Algal Dynamics in Lake Tai. Water. 2015; 7(7):3626-3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7073626
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jian, Qiujin Xu, Xixi Wang, Beidou Xi, Keli Jia, Shouliang Huo, Hongliang Liu, Changyou Li, and Bingbing Xu. 2015. "Evaluation of a Modified Monod Model for Predicting Algal Dynamics in Lake Tai" Water 7, no. 7: 3626-3642. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7073626






