Sources and Formation Processes of Short-Chain Saturated Diacids (C2–C4) in Inhalable Particles (PM10) from Huangshi City, Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Samples and Analytical Procedure
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Chemical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Characteristics of Diacids
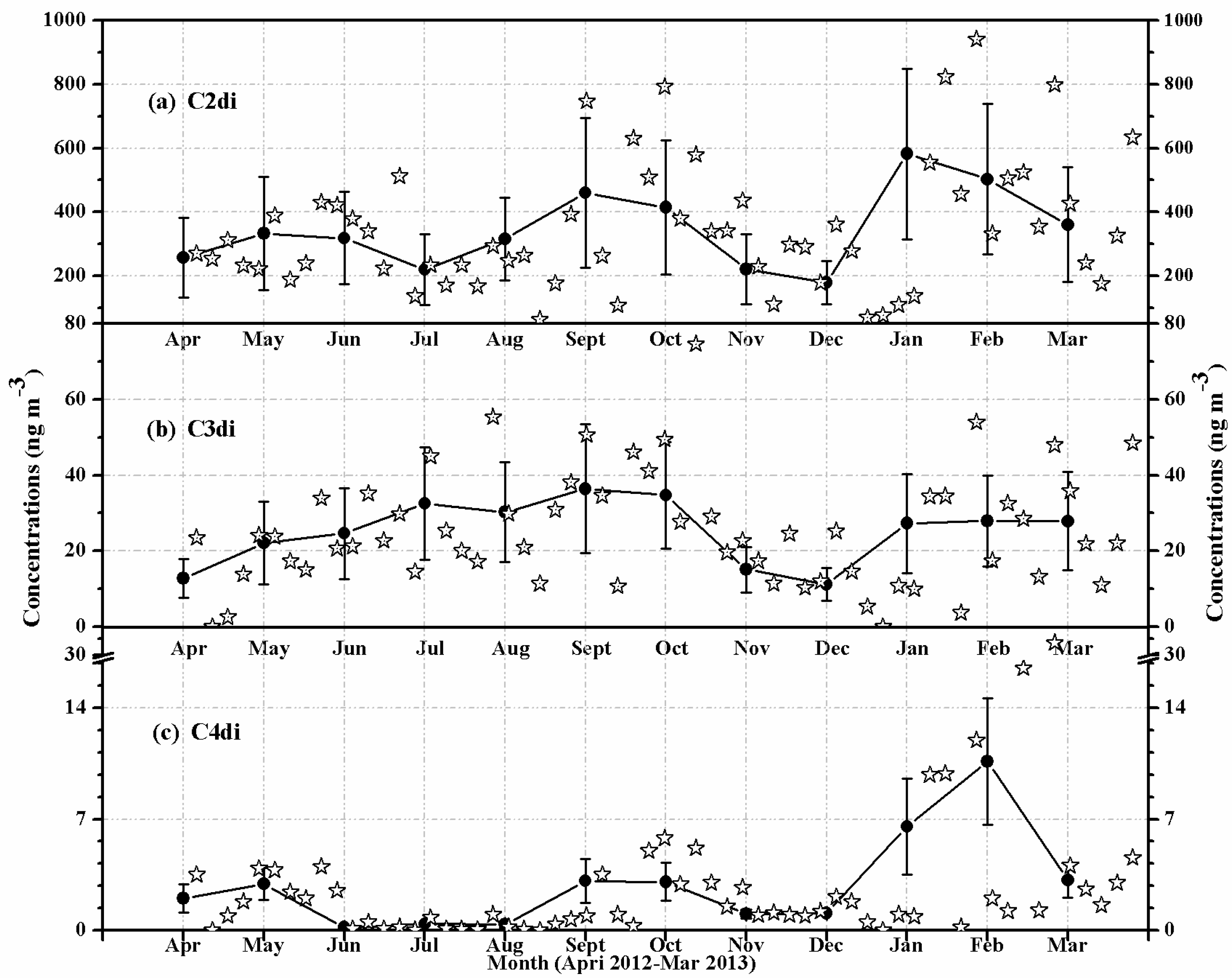
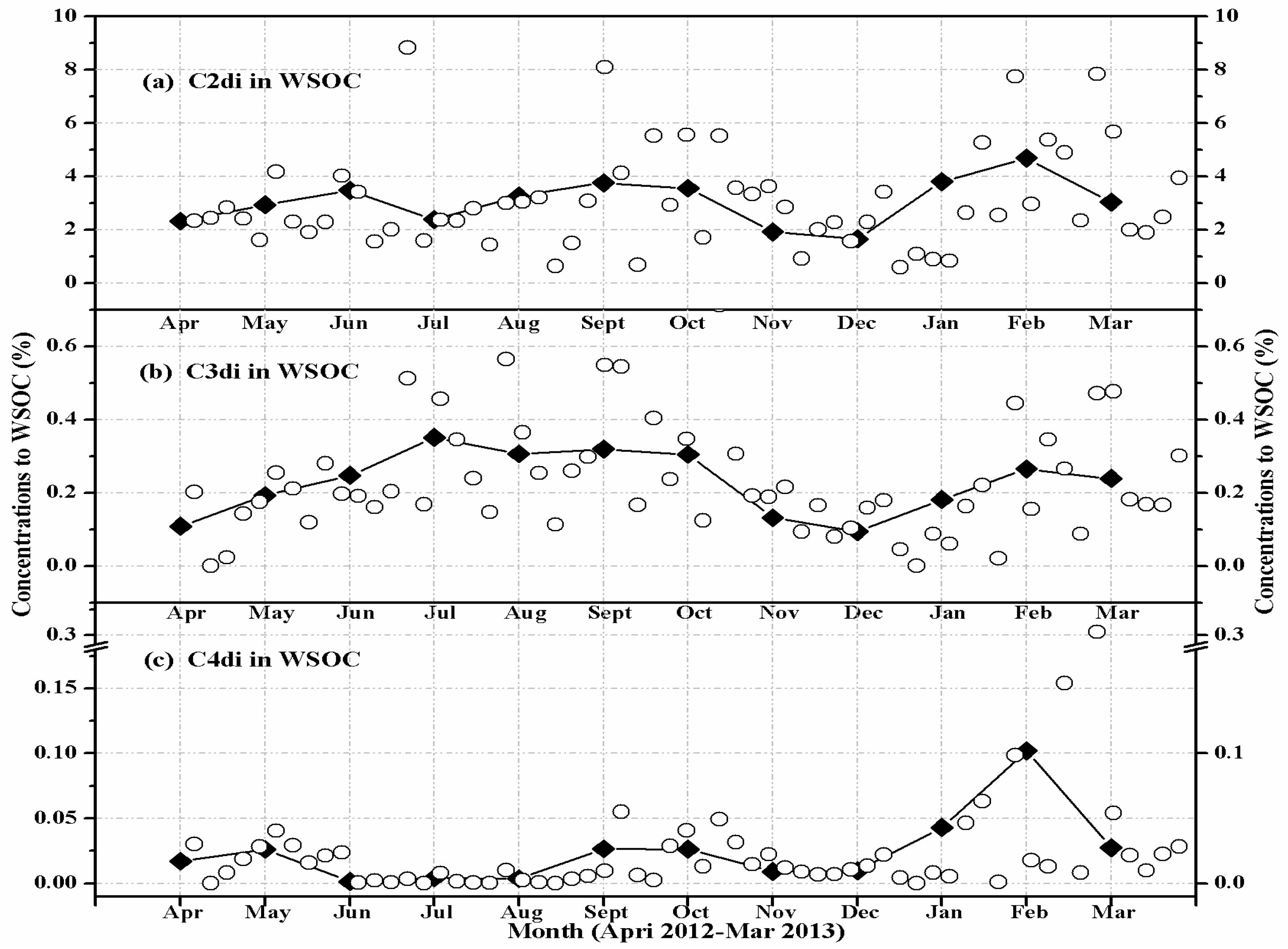
3.2. Seasonal Variations of Diacids
3.3. Possible Sources of Diacids
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis of Diacids
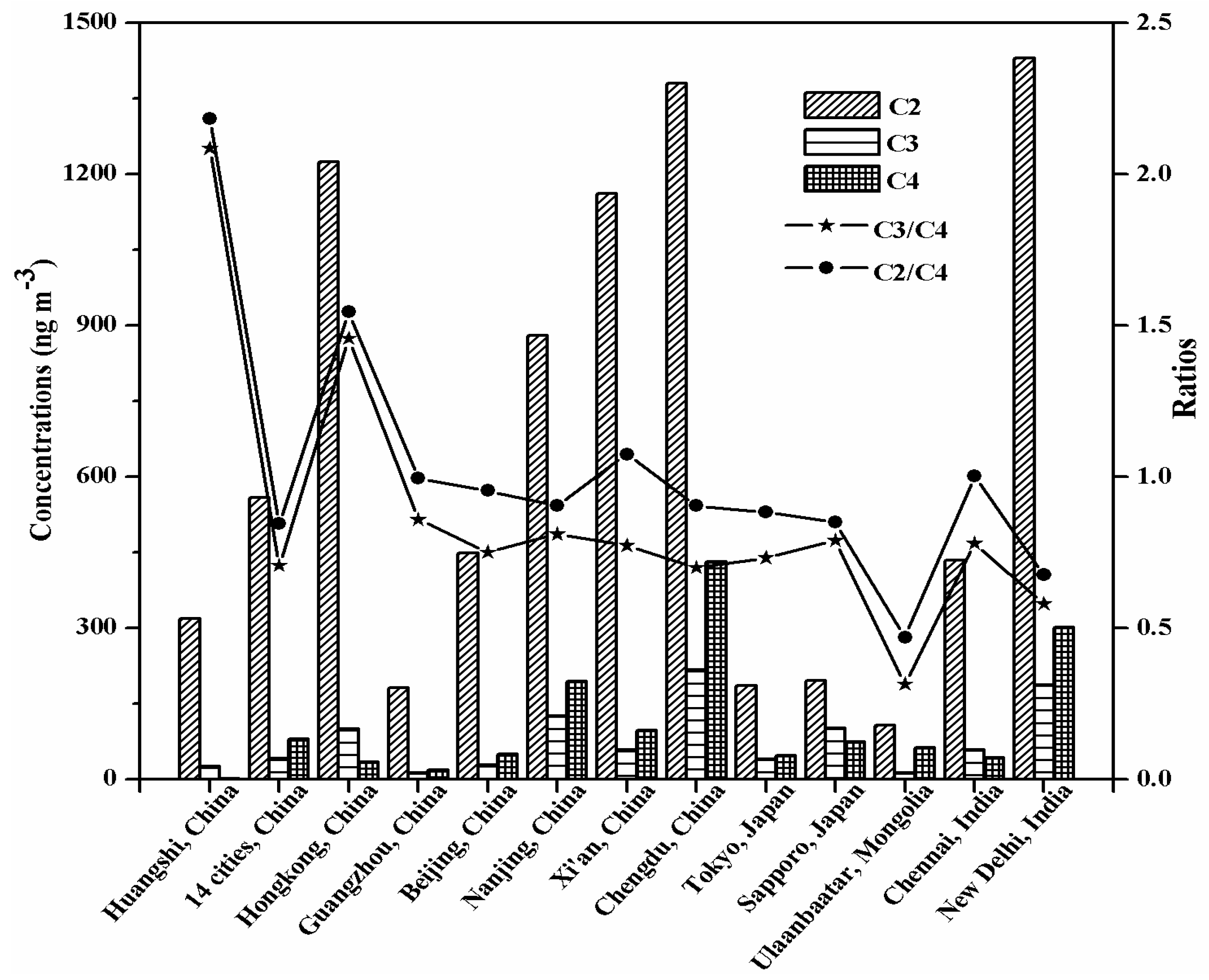
3.3.2. Concentration Ratios of Diacids
3.3.3. Principal Component Analysis of Diacids
3.4. Formation Processes of Diacids
4. Summary and Conclusions
Reference
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawamura, K.; Usukura, K. Distributions of low molecular weight dicarboxylic acids in the North Pacific aerosol samples. J. Oceanogr. 1993, 49, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, V.M.; Teinila, K.; Hillamo, R.; Makela, T. Size-segregated chemistry of particulate dicarboxylic acids in the Arctic atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierlus, K.M.; Laskina, O.; Abernathy, T.L.; Grassian, V.H. Laboratory study of the effect of oxalic acid on the cloud condensation nuclei activity of mineral dust aerosol. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 46, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highwood, E.J.; Kinnersley, R.P. When smoke gets in our eyes: The multiple impacts of atmospheric black carbon on climate, air quality and health. Environ. Int. 2006, 32, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Kaplan, I.R. Motor exhaust emissions as a primary source for dicarboxylic acids in Los Angeles ambient air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Kawamura, K.; Watanabe, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chow, J.C. Dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids and dicarbonyls in the urban roadside area of Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 3030–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Kawamura, K.; Andreae, T.W.; Hoffer, A.; Andreae, M.O. Molecular distributions of dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids and α-dicarbonyls in biomass burning aerosols: Implications for photochemical production and degradation in smoke layers. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2209–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, J.J.; Kleeman, M.J.; Cass, G.R.; Simoneit, B.R.T. Measurement of emission from air pollution sources. 4. C1–C27 organic compounds from cooking with seed oils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedetti, M.; Kawamura, K.; Charriere, B.; Chevalier, N.; Sempéré, R. Determination of low molecular weight dicarboxylic and ketocarboxylic acids in seawater samples. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 6012–6018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, K.; Ikushima, K. Seasonal changes in the distribution of dicarboxylic acids in the urban atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 2227–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Tachibana, E.; Okuzawa, K.; Aggarwal, S.G.; Kanaya, Y.; Wang, Z.F. High abundances of water-soluble dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids and α-dicarbonyls in the mountain top aerosols over the North China Plain during wheat burning season. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 8285–8302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Kasukabe, H.; Barrie, L.A. Source and reaction pathways of dicarboxylic acids, ketoacids and dicarbonyls in arctic aerosols: One year of observations. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 1709–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ervens, B.; Feingold, G.; Frost, G.J.; Kreidenweis, S.M. A modeling study of aqueous production of dicarboxylic acids: 1. Chemical pathways and speciated organic mass production. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 1265–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, S.; Ohno, M.; Weng, J.H.; Takagi, H.; Akimoto, H. Mechanism for the formation of gaseous and particulate products from ozone-cycloalkene reactions in air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1987, 21, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myriokefalitakis, S.; Tsigaridis, K.; Mihalopoulos, N.; Sciare, J.; Nenes, A.; Kawamura, K.; Segers, A.; Kanakidou, M. In-cloud oxalate formation in the global troposphere: A 3-D modeling study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 5761–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bikkina, S.; Kawamura, K.; Miyazaki, Y.; Fu, P.Q. High abundances of oxalic, azelaic, and glyoxylic acids and methylglyoxal in the open ocean with high biological activity: Implication for secondary OA formation from isoprene. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 3649–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Kawamura, K. Molecular characteristics of urban organic aerosols from Nanjing: A case study of a mega-city in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 7430–7438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; Kawamura, K.; Xie, M.J.; Hu, S.Y.; Cao, J.J.; An, Z.S.; Waston, J.G.; Chow, J.C. Organic molecular compositions and size distributions of Chinese summer and autumn aerosols from Nanjing: Characteristic haze event caused by wheat straw burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 6493–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.J.; Zhu, C.S.; Tie, X.X.; Geng, F.H.; Xu, H.M.; Ho, S.; Wang, G.H.; Han, Y.M.; Ho, K.F. Characteristics and sources of carbonaceous aerosols from Shanghai, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 803–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhuang, G.S.; Chen, S.; An, Z.S.; Zheng, A.H. Characteristics and sources of formic, acetic and oxalic acids in PM2.5 and PM10 aerosols in Beijing, China. Atmos. Res. 2007, 84, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Lee, S.C.; Ho, S.S.H.; Kawamura, K.; Tachibana, E.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, T. Dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids, α-dicarbonyls, fatty acids, and benzoic acid in urban aerosols collected during the 2006 Campaign of Air Quality Research in Beijing (CAREBeijing-2006). J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D19312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Huang, L.; Duan, F.; Zhang, W.; He, K.; Ma, Y.; Brook, J.R.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Q.; Cheng, Y. Carbonaceous species in PM2.5 at a pair of rural/urban sites in Beijing, 2005–2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 7893–7903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Wang, G.H.; Zhou, B.H.; Meng, J.J.; Li, J.J.; Cao, J.J.; Xiao, S. Comparison of dicarboxylic acids and related compounds in aerosol samples collected in Xi’an, China during haze and clean periods. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.C.; Yu, J.Z. Composition profile of oxygenated organic compounds and inorganic ions in PM2.5 in Hong Kong. Environ. Chem. 2010, 7, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.X.; Peng, P.A.; Song, J.Z.; Zhao, J.P.; He, L.L.; Sheng, G.Y.; Fu, J.M. Stable carbon isotopic compositions of organic acids in total suspended particles and dusts from Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Res. 2010, 98, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Ho, S.S.H.; Lee, S.C.; Kawamura, K.; Zou, S.C.; Cao, J.J.; Xu, H.M. Summer and winter variations of dicarboxylic acids, fatty acids and benzoic acid in PM2.5 in Pearl Delta River Region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, C.L.; Zhang, J.Q.; Cao, J.J.; Han, Y.M.; Wang, P.; Zheng, J.R.; Yao, R.Z.; Liu, H.X.; Xiao, W.S. Characteristics and sources of black carbon in atmospheric dustfall particles from HS, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Qu, C.K.; Qi, S.H.; Cao, J.J.; Zhan, C.L.; Xing, X.L.; Xiao, Y.L.; Zheng, J.R.; Xiao, W.S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in atmospheric dustfall from the industrial corridor in Hubei Province, Central China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Zheng, J.R.; Qu, C.K.; Zhang, J.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; Zhan, C.L.; Yao, R.Z.; Cao, J.J. Characteristics and source analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM10 in a typical mining city, Central China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K. Identification of C2-C10 ω-oxocarboxylic acids, pyruvic acid, and C2-C3 α-dicarbonyls in wet precipitation and aerosol samples by capillary GC and GC/MS. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 3505–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, B.; Kawamura, K. Seasonal distributions and sources of low molecular weight dicarboxylic acids, ω-oxocarboxylic acids, pyruvic acid, α-dicarbonyls and fatty acids in ambient aerosols from subtropical Okinawa in the western Pacific Rim. Environ. Chem. 2014, 11, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.M.M.; Kawamura, K. Longitudinal distributions of dicarboxylic acids, ω-oxoacids, pyruvic acid, α-dicarbonyls, and fatty acids in the marine aerosols from the central Pacific including equatorial upwelling. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavuluri, C.M.; Kawamura, K.; Kikuta, M.; Tachibana, E.; Aggarwal, S.G. Time-resolved variations in the distributions of inorganic ions, carbonaceous components, dicarboxylic acids and related compounds in atmospheric aerosols from Sapporo, northern Japan during summertime. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavuluri, C.M.; Kawamura, K.; Swaminathan, T. Water-soluble organic carbon, dicarboxylic acids, ketoacids, and α-dicarbonyls in the tropical Indian aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Yasui, O. Diurnal changes in the distribution of dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids and dicarbonyls in the urban Tokyo atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 1945–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Tsatsral, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Kawamura, K. Organic and inorganic aerosol compositions in Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia, during the cold winter of 2007 to 2008: Dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids, and α-dicarbonyls. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.L.; Wang, G.H.; Meng, J.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Li, J.J.; Wang, J.Y. Size-resolved airborne particulate oxalic and related secondary organic aerosol species in the urban atmosphere of Chengdu, China. Atmos. Res. 2015, 161–162, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, D.K.; Kawamura, K.; Lazaar, M.; Kunwar, B.; Boreddy, S.K.R. Dicarboxylic acids, oxoacids, benzoic acid, α-dicarbonyls, WSOC, OC, and ions in spring aerosols from Okinawa Island in the western North Pacific Rim: Size distributions and formation processes. Atmos. Chem. Phys. Discuss. 2016, 16, 5263–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Chen, J.; Zhao, W.T.; Cheng, J.X.; Cheng, S.G. Seasonal variations and correlation analysis of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5 in Wuhan, 2013. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Z.Y.; Kawamura, K.; Kang, S.C.; Fu, P.Q. Penetration of biomass-burning emissions from South Asia through the Himalayas: New insights from atmospheric organic acids. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunwar, B.; Torii, K.; Zhu, C.M.; Fu, P.Q.; Kawamura, K. Springtime variations of organic and inorganic constituents in submicron aerosols (PM1.0) from Cape Hedo, Okinawa. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 130, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasoe, M.A.; Artaxo, P.; Miguel, A.H.; Allen, A.G. Chemical composition of aerosol particles from direct emissions of vegetation fires in the Amazon Basin: Water soluble species and trace elements. Atmos. Environ. 2000, 34, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Hegg, D.A.; Hobbs, P.V.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Magi, B.I.; Sadilek, M. Water-soluble organic components in aerosols with savanna fires in southern Africa: Identification, evolution, and distribution. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.F.; Cao, J.J.; Lee, S.C.; Kawamura, K.; Zhang, R.J.; Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G. Dicarboxylic acids, ketocarboxylic acids, and dicarbonyls in the urban atmosphere of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, S27-1–S27-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Sakaguchi, F. Molecular distributions of water soluble dicarboxylic acids in marine aerosols over the Pacific Ocean including tropics. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1999, 104, 3501–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, A.G.; Turpin, B.J.; Lim, H.J.; Altieri, K.E.; Seitzinger, S. Link between isoprene and secondary organic aerosol (SOA): Pyruvic acid oxidation yields low volatility organic acids in clouds. Geophy. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 272–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.C.; Prather, K.A. Investigations of the diurnal cycle and mixing state of oxalic acid in individual particles in Asian aerosol outflow. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 8062–8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compounds | Spring (n = 15) | Summer (n = 16) | Autumn (n = 15) | Winter (n = 15) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median and Range | Mean ± SD | Median and Range | Mean ± SD | Median and Range | Mean ± SD | Median and Range | Mean ± SD | |
| Dicarboxylic Acids (ng·m−3) | ||||||||
| Oxalic, C2 | 270 (137−513) | 303 ± 100 | 255 (63.5−793) | 331 ± 111 | 291 (69.7−579) | 272 ± 92 | 457 (137−941) | 482 ± 187 |
| Malonic, C3 | 21.9 (2.57−35.1) | 21.3 ± 10.1 | 32.7 (10.7−55.3) | 32.9 ± 9.08 | 18.5 (5.31−74.6) | 21.8 ± 5.08 | 28.5 (3.67−53.9) | 27.7 ± 10.1 |
| Succinic, C4 | 2.45 (0.00−4.00) | 2.53 ± 1.01 | 2.00 (0.03−5.80) | 2.34 ± 0.97 | 1.35 (0.50−5.17) | 1.84 ± 0.78 | 6.54 (0.86−32.2) | 7.25 ± 2.73 |
| Carbonaceous Components (μg·m−3) | ||||||||
| EC | 2.95 (1.41−3.58) | 3.06 ± 0.77 | 5.17 (2.64−12.4) | 5.84 ± 1.91 | 7.89 (4.15−12.0) | 7.77 ± 1.01 | 7.52 (4.84−14.3) | 8.67 ± 2.07 |
| OC | 22.6 (11.4−46.6) | 24.0 ± 6.37 | 14.6 (7.75−32.8) | 17.1 ± 4.88 | 21.6 (13.1−43.8) | 23.3 ± 3.55 | 21.8 (12.9−35.5) | 23.5 ± 10.8 |
| WSOC | 11.0 (5.81−21.8) | 11.6 ± 2.98 | 9.93 (6.36−17.4) | 10.8 ± 3.12 | 11.8 (7.04−22.2) | 11.8 ± 3.09 | 13.2 (7.51−21.1) | 13.7 ± 3.99 |
| Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions (μg·m−3) | ||||||||
| F− | 0.44 (0.25−1.01) | 0.53 ± 0.19 | 0.31 (0.23−0.64) | 0.35 ± 0.26 | 0.62 (0.35−1.16) | 0.68 ± 0.45 | 0.60 (0.32−0.99) | 0.61 ± 0.19 |
| Cl− | 3.09 (1.70−5.57) | 3.26 ± 1.11 | 2.11 (1.04−4.83) | 2.31 ± 1.06 | 4.97 (2.23−11.0) | 5.31 ± 2.01 | 8.27 (3.60−37.6) | 8.14 ± 3.66 |
| NO3− | 12.5 (4.82−33.8) | 15.4 ± 5.05 | 4.99 (1.31−15.7) | 6.73 ± 2.10 | 22.4 (7.52−38.3) | 21.1 ± 7.96 | 43.6 (16.8−77.7) | 39.8 ± 11.9 |
| SO42− | 29.4 (13.1−43.4) | 29.2 ± 9.15 | 18.2 (2.65−60.4) | 23.1 ± 5.23 | 25.3 (14.6−42.8) | 25.4 ± 10.8 | 44.6 (16.7−99.8) | 42.5 ± 11.4 |
| Na+ | 5.28 (4.43−6.38) | 5.34 ± 2.22 | 5.02 (0.78−6.05) | 4.94 ± 1.99 | 5.11 (4.71−7.40) | 5.31 ± 2.10 | 5.19 (4.19−6.67) | 5.15 ± 1.02 |
| NH4+ | 6.39 (1.37−12.2) | 6.08 ± 2.36 | 2.13 (0.24−13.3) | 3.52 ± 0.67 | 7.34 (1.78−15.7) | 6.30 ± 2.76 | 15.6 (5.30−32.0) | 14.7 ± 3.01 |
| K+ | 1.45 (0.46−6.37) | 1.86 ± 0.90 | 0.71 (0.16−2.33) | 0.92 ± 0.29 | 1.57 (1.09−3.38) | 1.68 ± 0.77 | 2.83 (0.87−27.4) | 2.62 ± 1.04 |
| Mg2+ | 0.54 (0.23−0.91) | 0.56 ± 0.35 | 0.38 (0.11−0.71) | 0.41 ± 0.11 | 0.59 (0.40−0.93) | 0.61 ± 0.21 | 0.63 (0.22−2.00) | 0.61 ± 0.17 |
| Ca2+ | 5.01 (2.39−8.28) | 5.37 ± 2.41 | 4.58 (1.46−6.78) | 4.44 ± 1.95 | 6.89 (3.80−10.7) | 6.63 ± 2.05 | 4.31 (1.97−8.50) | 4.83 ± 1.31 |
| Spring | C2 | C3 | C4 | EC | F− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
| C2 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.12 | −0.23 | −0.26 | −0.15 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.37 | −0.13 | 0.01 |
| C3 | 1.00 | 0.33 | −0.06 | −0.55 | −0.53 | −0.53 | −0.17 | −0.20 | −0.42 | 0.11 | −0.27 | −0.09 | |
| C4 | 1.00 | −0.20 | 0.04 | 0.18 | 0.20 | −0.19 | 0.27 | −0.14 | 0.17 | 0.43 | 0.12 | ||
| Summer | C2 | C3 | C4 | EC | F− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
| C2 | 1.00 | 0.74 ** | 0.54 * | 0.57 * | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.81 ** | 0.69 ** | 0.34 | 0.74 ** | 0.64 ** | 0.71 ** | 0.74 ** |
| C3 | 1.00 | 0.43 | 0.51 * | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.51 * | 0.48 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.31 | 0.62 * | 0.77 ** | |
| C4 | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.35 | 0.48 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.37 | ||
| Autumn | C2 | C3 | C4 | EC | F− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
| C2 | 1.00 | 0.85 ** | 0.89 ** | 0.60 * | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 0.48 | −0.04 | 0.26 | 0.58 * | 0.40 | 0.29 |
| C3 | 1.00 | 0.90 ** | 0.66 ** | 0.23 | −0.04 | −0.03 | 0.12 | −0.07 | −0.12 | 0.65 ** | 0.57 * | 0.51 | |
| C4 | 1.00 | 0.49 | 0.08 | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.29 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.57 * | 0.47 | 0.37 | ||
| Winter | C2 | C3 | C4 | EC | F− | Cl− | NO3− | SO42− | Na+ | NH4+ | K+ | Mg2+ | Ca2+ |
| C2 | 1.00 | 0.82 ** | 0.65 ** | 0.68 ** | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.74 ** | 0.74 ** | 0.22 | 0.70 ** | 0.14 | 0.29 | 0.49 |
| C3 | 1.00 | 0.62 * | 0.51 | 0.28 | 0.11 | 0.52 * | 0.40 | −0.07 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.56 * | |
| C4 | 1.00 | 0.37 | 0.03 | −0.01 | 0.61 * | 0.66 * | −0.03 | 0.64 * | −0.05 | 0.03 | 0.23 |
| Compounds | Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F3 | |
| C2 | 0.00 | 0.79 | −0.31 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 0.91 | 0.17 | 0.93 | 0.14 | 0.16 |
| C3 | −0.44 | 0.74 | 0.13 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 0.92 | −0.22 | 0.75 | 0.24 | 0.49 |
| C4 | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.77 | 0.46 | 0.72 | 0.90 | −0.06 | 0.79 | −0.09 | −0.05 |
| NO3− | 0.92 | −0.06 | 0.11 | 0.95 | −0.10 | 0.22 | 0.81 | 0.89 | −0.28 | −0.17 |
| SO42− | 0.85 | 0.16 | −0.40 | 0.87 | −0.37 | 0.40 | 0.85 | 0.87 | 0.05 | −0.38 |
| NH4+ | 0.90 | −0.02 | −0.34 | 0.89 | −0.33 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.87 | −0.25 | −0.40 |
| K+ | 0.15 | 0.61 | −0.36 | 0.79 | −0.23 | 0.78 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.97 | −0.21 |
| Mg2+ | 0.83 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.93 | −0.13 | 0.59 | −0.55 | 0.18 | 0.97 | 0.00 |
| Ca2+ | 0.76 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.87 | 0.13 | 0.55 | −0.62 | 0.46 | −0.09 | 0.78 |
| Characteristic Value | 3.84 | 1.85 | 1.44 | 6.20 | 1.17 | 3.97 | 3.13 | 4.59 | 2.12 | 1.24 |
| Contribution Rate (%) | 43 | 21 | 16 | 69 | 13 | 45 | 35 | 51 | 24 | 14 |
| Cumulative Contribution Rate (%) | 43 | 64 | 80 | 69 | 82 | 45 | 80 | 51 | 75 | 89 |
| Season | Linear Relation between C2 and C3 Diacids | Mean Concentration of C2 Diacid (ng·m−3) * | C2 Concentration Formed by Pathway 2 (ng·m−3) ** | Contribution from Pathway 2 *** | Contribution from Pathway 1 **** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | C(C2) = 5.14 C(C3) + 201 (R2 = 0.24) | 303 | 201 | 66% | 34% |
| Summer | C(C2) = 11.56 C(C3) + 49.0 (R2 = 0.55) | 331 | 49.0 | 15% | 85% |
| Autumn | C(C2) = 7.15 C(C3) + 126 (R2 = 0.72) | 272 | 126 | 46% | 54% |
| Winter | C(C2) = 12.77 C(C3) + 129 (R2 = 0.67) | 482 | 129 | 27% | 73% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Kawamura, K.; Kunwar, B.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, C.; Zheng, J.; Yao, R.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; et al. Sources and Formation Processes of Short-Chain Saturated Diacids (C2–C4) in Inhalable Particles (PM10) from Huangshi City, Central China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110213
Liu H, Kawamura K, Kunwar B, Cao J, Zhang J, Zhan C, Zheng J, Yao R, Liu T, Liu X, et al. Sources and Formation Processes of Short-Chain Saturated Diacids (C2–C4) in Inhalable Particles (PM10) from Huangshi City, Central China. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(11):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110213
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hongxia, Kimitaka Kawamura, Bhagawati Kunwar, Junji Cao, Jiaquan Zhang, Changlin Zhan, Jingru Zheng, Ruizhen Yao, Ting Liu, Xianli Liu, and et al. 2017. "Sources and Formation Processes of Short-Chain Saturated Diacids (C2–C4) in Inhalable Particles (PM10) from Huangshi City, Central China" Atmosphere 8, no. 11: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8110213





