Cancers 2022, 14(20), 5089; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14205089 - 18 Oct 2022
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 2558
Abstract
New techniques are being developed to improve the results of laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer. This paper analyzes the learning curves for transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) and robot-assisted surgery in our colorectal surgery department. We analyzed retrospectively data from patients undergoing curative
[...] Read more.
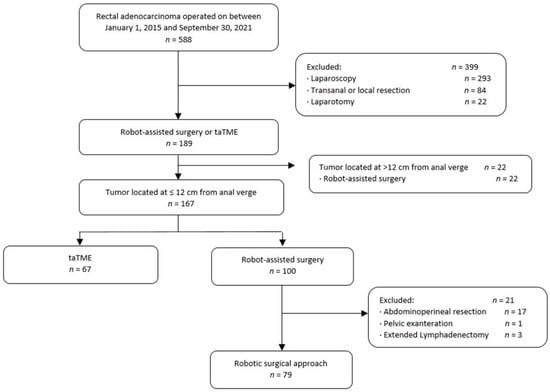
New techniques are being developed to improve the results of laparoscopic surgery for rectal cancer. This paper analyzes the learning curves for transanal total mesorectal excision (taTME) and robot-assisted surgery in our colorectal surgery department. We analyzed retrospectively data from patients undergoing curative and elective surgery for rectal cancer ≤12 cm from the anal verge. We excluded extended surgeries. We used cumulative sum (CUSUM) curve analysis to identify inflection points. Between 2015 and 2021, 588 patients underwent surgery for rectal cancer at our center: 67 taTME and 79 robot-assisted surgeries. To overcome the operative time learning curve, 14 cases were needed for taTME and 53 for robot-assisted surgery. The morbidity rate started to decrease after the 17th case in taTME and after the 49th case in robot-assisted surgery, but it is much less abrupt in robot-assisted group. During the initial learning phase, the rate of anastomotic leakage was higher in taTME (35.7% vs. 5.7%). Two Urological lesions occurred in taTME but not in robot-assisted surgery. The conversion rate was higher in robot-assisted surgery (1.5% vs. 10.1%). Incorporating new techniques is complex and entails a transition period. In our experience, taTME involved a higher rate of serious complications than robot-assisted surgery during initial learning period but required a shorter learning curve.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Robotic Cancer Surgery)
►
Show Figures