Comparative QSTR Study Using Semi-Empirical and First Principle Methods Based Descriptors for Acute Toxicity of Diverse Organic Compounds to the Fathead Minnow
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Procedures and Calculations Methods
2.1. Computational details
2.2. Theory
3. Results and Discussion
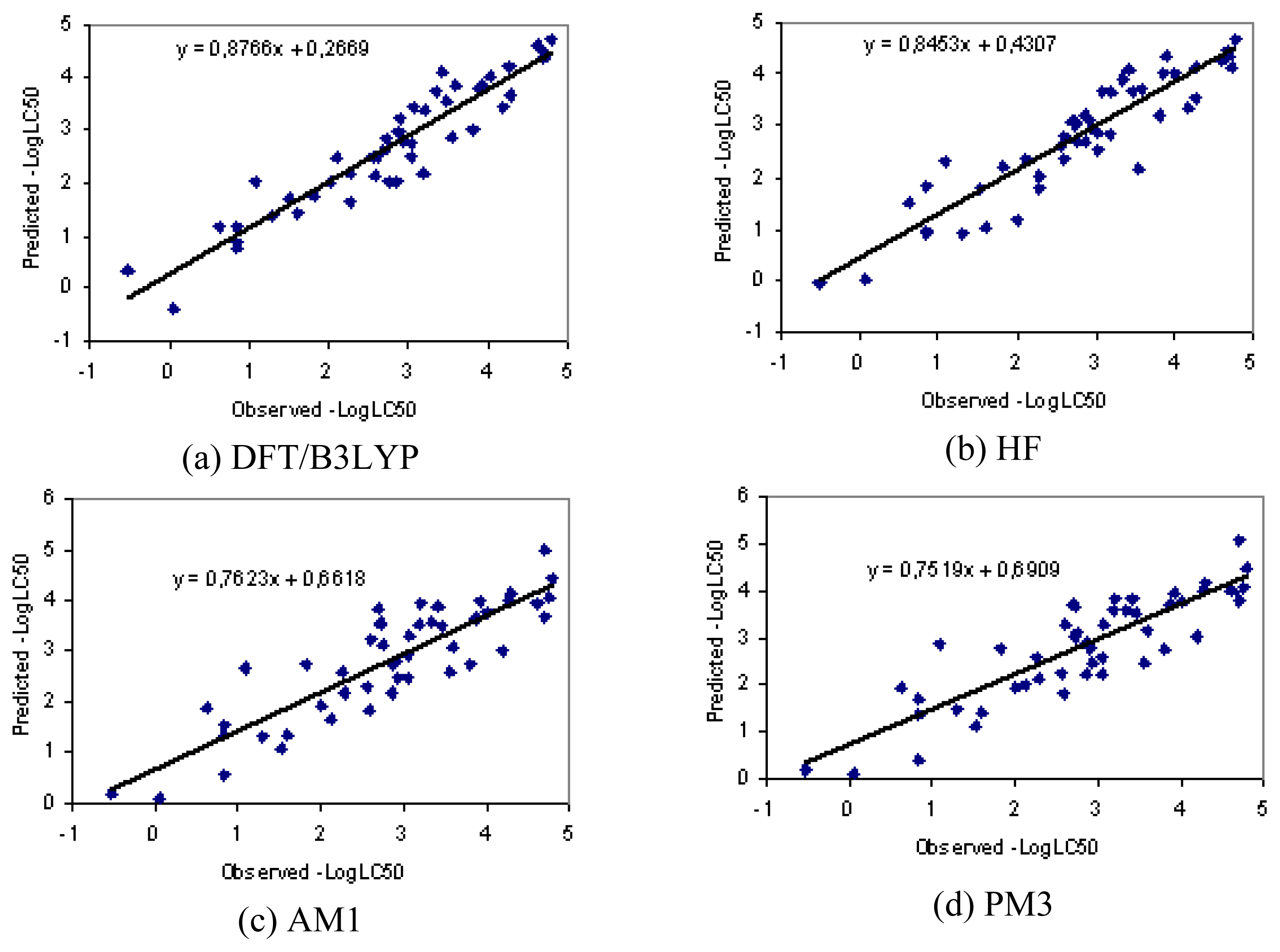
3.1. Results
3.2. Discussion
3.3. Conclusion
| Comp. No | CAS No | Chemical Name | aLogP | aLogLC50 (mol/l) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 57-55-6 | 1,2-Propanediol | −0.78 | −0.838 |
| 2 | 68-12-2 | Formamide, N,N-dimethyl- | −0.93 | −0.839 |
| 3 | 71-36-3 | 1-Butanol | 0.84 | −1.601 |
| 4 | 78-87-5 | Propane, 1,2-dichloro- | 2.25 | −2.907 |
| 5 | 78-92-2 | 2-Butanol | 0.77 | −1.305 |
| 6 | 79-00-5 | Ethane, 1,1,2-trichloro- | 2.01 | −3.214 |
| 7 | 79-34-5 | Ethane, 1,1,2,2-tetrachloro- | 2.19 | −3.917 |
| 8 | 80-05-7 | Phenol, 4,4′-(1-methylethylidene)bis- | 3.64 | −4.696 |
| 9 | 80-62-6 | 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, methyl ester | 1.28 | −2.552 |
| 10 | 95-50-1 | Benzene, 1,2-dichloro- | 3.28 | −3.411 |
| 11 | 96-18-4 | Propane, 1,2,3-trichloro- | 2.5 | −3.346 |
| 12 | 96-29-7 | 2-Butanone, oxime | 1.69 | −2.014 |
| 13 | 100-37-8 | Ethanol, 2-(diethylamino)- | 0.05 | −1.818 |
| 14 | 106-46-7 | Benzene, 1,4-dichloro- | 3.28 | −4.015 |
| 15 | 107-06-2 | Ethane, 1,2-dichloro- | 1.83 | −2.931 |
| 16 | 107-41-5 | 2,4-Pentanediol, 2-methyl- | 0.58 | −1.089 |
| 17 | 107-98-2 | 2-Propanol, 1-methoxy- | −0.49 | −0.637 |
| 18 | 108-88-3 | Benzene, methyl- | 2.54 | −3.549 |
| 19 | 120-83-2 | Phenol, 2,4-dichloro- | 2.8 | −4.277 |
| 20 | 122-99-6 | Ethanol, 2-phenoxy- | 1.1 | −2.604 |
| 21 | 123-54-6 | 2,4-Pentanedione | 0.05 | −2.860 |
| 22 | 123-86-4 | Acetic acid, butyl ester | 1.85 | −3.810 |
| 23 | 124-04-9 | Hexanedioic-acid- | 0.23 | −3.178 |
| 24 | 141-78-6 | Acetic-acid-ethyl-ester- | 0.86 | −2.583 |
| 25 | 760-23-6 | 1-Butene, 3,4-dichloro- | 2.6 | −4.184 |
| 26 | 770-35-4 | 2-Propanol, 1-phenoxy- | 1.52 | −2.735 |
| 27 | 868-77-9 | 2-Propenoic acid, 2-methyl-, 2-hydroxyethyl ester | 0.3 | −2.758 |
| 28 | 1634-04-4 | Propane, 2-methoxy-2-methyl- | 1.43 | −2.118 |
| 29 | 4169-04-4 | 1-Propanol, 2-phenoxy- | 1.52 | −2.735 |
| 30 | 101-84-8 | Diphenyl ether | 4.21 | −4.62 |
| 31 | 693-65-2 | Dipentyl ether | 4.04 | −4.69 |
| 32 | 108-20-3 | Diisopropyl ether | 1.52 | −3.04 |
| 33 | 109-99-9 | Tetrahydrofuran | 0.46 | −1.52 |
| 34 | 142-96-1 | Dibutyl ether | 3.21 | −3.60 |
| 35 | 110-00-9 | Furan | 1.34 | −3.04 |
| 36 | 64-17-5 | Ethanol | −0.31 | 0.51 |
| 37 | 5673-07-4 | 2,6-dimethoxytoluene | 2.64 | −3.87 |
| 38 | 115-20-8 | 2,2,2-trichloroethanol | 1.42 | −2.69 |
| 39 | 120-82-1 | 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene | 4.05 | −4.79 |
| 40 | 541-73-1 | 1,3-dichlorobenzene | 3.52 | −4.27 |
| 41 | 150-78-7 | 1,4-dimethoxybenzene | 2.15 | −3.07 |
| 42 | 4412-91-3 | 3-furanmethanol | 0.30 | −2.28 |
| 43 | 95-75-0 | 3,4-dichlorotoluene | 4.06 | −4.74 |
| 44 | 67-64-1 | Acetone | −0.24 | −0.85 |
| 45 | 98-86-2 | Acetophenone | 1.58 | −2.87 |
| 46 | 67-56-1 | Methanol | −0.77 | −0.06 |
| 47 | 108-94-1 | Cyclohexanone | 0.81 | −2.27 |
| 48 | 79-01-6 | Trichloroethene | 2.42 | −3.47 |
| Comp. No | Str | IA | ωH | ωL | O-LogLC50 | P-LogLC50 | bResidual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.902 | 0.263 | 3774.1 | 114.565 | −0.838 | −0.788 | 0.049 |
| 2 | 38.782 | 0.296 | 3171.2 | 106.871 | −0.839 | −1.184 | −0.345 |
| 3 | 38.823 | 0.623 | 3755.3 | 110.929 | −1.601 | −1.423 | 0.177 |
| 4 | 40.055 | 0.224 | 3186.1 | 111.732 | −2.907 | −3.215 | −0.308 |
| 5 | 38.823 | 0.256 | 3742.2 | 102.240 | −1.305 | −1.394 | −0.089 |
| 6 | 40.544 | 0.114 | 3189.9 | 107.486 | −3.214 | −3.386 | −0.172 |
| 7 | 41.227 | 0.057 | 3167.6 | 73.008 | −3.917 | −3.826 | 0.090 |
| 8 | 42.176 | 0.029 | 3753.8 | 36.841 | −4.696 | −4.399 | 0.296 |
| 9 | 39.720 | 0.116 | 3242.6 | 51.096 | −2.552 | −2.496 | 0.055 |
| 10 | 40.845 | 0.062 | 3224.5 | 135.387 | −3.411 | −4.086 | −0.675 |
| 11 | 40.845 | 0.071 | 3188.4 | 80.855 | −3.346 | −3.727 | −0.381 |
| 12 | 39.305 | 0.125 | 3762.3 | 65.570 | −2.014 | −1.984 | 0.029 |
| 13 | 40.189 | 0.067 | 3759.7 | 25.457 | −1.818 | −1.764 | 0.053 |
| 14 | 40.845 | 0.188 | 3229.6 | 101.569 | −4.015 | −4.039 | −0.024 |
| 15 | 39.657 | 0.968 | 3196.7 | 118.164 | −2.931 | −2.813 | 0.117 |
| 16 | 40.214 | 0.103 | 3739.4 | 46.314 | −1.089 | −2.042 | −0.953 |
| 17 | 39.406 | 0.244 | 3754.1 | 84.761 | −0.637 | −1.175 | −0.538 |
| 18 | 39.472 | 0.184 | 3204.8 | 11.093 | −3.549 | −2.855 | 0.693 |
| 19 | 41.155 | 0.070 | 3674.9 | 144.475 | −4.277 | −3.677 | 0.599 |
| 20 | 40.680 | 0.150 | 3772.8 | 49.425 | −2.604 | −2.497 | 0.107 |
| 21 | 39.720 | 0.137 | 3163.5 | 44.404 | −2.860 | −2.051 | 0.809 |
| 22 | 40.163 | 0.179 | 3175.7 | 35.795 | −3.810 | −3.023 | 0.786 |
| 23a | 40.847 | 0.159 | 3680.2 | −46.051a | −3.178 | −2.194 | 0.983 |
| 24 | 39.339 | 0.279 | 3175.9 | 38.760 | −2.583 | −2.148 | 0.434 |
| 25 | 40.359 | 0.084 | 3242.2 | 80.663 | −4.184 | −3.443 | 0.740 |
| 26 | 40.968 | 0.107 | 3755.0 | 47.032 | −2.735 | −2.847 | −0.112 |
| 27 | 40.502 | 0.071 | 3782.8 | 44.232 | −2.758 | −2.050 | 0.707 |
| 28 | 39.340 | 0.145 | 3111.9 | 61.752 | −2.118 | −2.470 | −0.352 |
| 29 | 40.968 | 0.101 | 3772.7 | 38.393 | −2.735 | −2.820 | −0.085 |
| 30a | 41.301 | 0.080 | 3217.2 | 18.694 | −4.620 | −4.587 | 0.032 |
| 31 | 41.085 | 0.269 | 3099.9 | 28.820 | −4.690 | −4.511 | 0.178 |
| 32 | 38.570 | 0.314 | 3306.7 | 608.797 | −3.040 | −2.520 | 0.519 |
| 33 | 38.741 | 0.236 | 3126.8 | 47.891 | −1.520 | −1.697 | −0.177 |
| 34 | 40.503 | 0.304 | 3102.1 | 40.606 | −3.600 | −3.850 | −0.250 |
| 35 | 39.780 | 0.115 | 3136.5 | 85.249 | −3.040 | −2.767 | 0.272 |
| 36 | 37.406 | 1.144 | 3744.7 | 264.649 | 0.510 | −0.345 | −0.855 |
| 37 | 40.968 | 0.073 | 3232.8 | 63.657 | −3.870 | −3.794 | 0.075 |
| 38 | 40.885 | 0.062 | 3767.0 | −61.022a | −2.690 | −2.609 | 0.080 |
| 39 | 41.469 | 0.060 | 3238.4 | 95.552 | −4.790 | −4.697 | 0.092 |
| 40 | 40.845 | 0.093 | 3238.5 | 167.828 | −4.270 | −4.214 | 0.055 |
| 41 | 40.680 | 0.150 | 3222.7 | 60.164 | −3.070 | −3.432 | −0.362 |
| 42 | 39.659 | 0.236 | 3739.2 | 76.473 | −2.280 | −1.648 | 0.631 |
| 43 | 41.119 | 0.060 | 3217.4 | 5.630 | −4.740 | −4.405 | 0.334 |
| 44 | 38.096 | 0.336 | 3161.1 | −57.828a | −0.850 | −0.875 | −0.025 |
| 45 | 40.263 | 0.122 | 3222.8 | 61.969 | −2.870 | −2.961 | −0.091 |
| 46 | 36.324 | 4.240 | 3763.7 | 323.726 | −0.060 | 0.403 | 0.463 |
| 47 | 39.721 | 0.142 | 3738.8 | 160.354 | −2.270 | −2.174 | 0.095 |
| 48 | 40.498 | 0.127 | 3251.8 | 172.065 | −3.470 | −3.556 | −0.086 |
| Comp. No | Str | IA | ωH | ωL | O-LogLC50 | P-LogLC50 | bResidual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.862 | 0.229 | 4036.5 | 119.378 | −0.838 | −0.930 | −0.092 |
| 2 | 38.782 | 0.298 | 3335.0 | 116.641 | −0.839 | −1.828 | −0.989 |
| 3 | 38.823 | 0.625 | 4030.4 | 110.442 | −1.601 | −1.021 | 0.579 |
| 4 | 40.055 | 0.223 | 3408.6 | 108.918 | −2.907 | −3.128 | −0.221 |
| 5 | 38.823 | 0.258 | 4019.2 | 109.284 | −1.305 | −0.898 | 0.406 |
| 6 | 40.544 | 0.110 | 3412.8 | 102.260 | −3.214 | −3.622 | −0.408 |
| 7 | 41.227 | 0.055 | 3392.0 | 76.661 | −3.917 | −4.350 | −0.433 |
| 8 | 42.176 | 0.029 | 4039.8 | 39.720 | −4.696 | −4.441 | 0.254 |
| 9 | 39.720 | 0.171 | 3442.8 | 73.673 | −2.552 | −2.602 | −0.050 |
| 10 | 40.845 | 0.062 | 3409.3 | 152.827 | −3.411 | −4.063 | −0.652 |
| 11 | 40.845 | 0.068 | 3407.3 | 78.833 | −3.346 | −3.904 | −0.558 |
| 12 | 39.305 | 0.128 | 4134.1 | 79.521 | −2.014 | −1.172 | 0.841 |
| 13 | 40.189 | 0.067 | 4031.9 | 30.933 | −1.818 | −2.188 | −0.370 |
| 14 | 40.845 | 0.191 | 3415.0 | 112.760 | −4.015 | −4.014 | 0.000 |
| 15 | 39.657 | 0.965 | 3417.5 | 114.598 | −2.931 | −2.951 | −0.020 |
| 16 | 40.214 | 0.104 | 4013.3 | 49.077 | −1.089 | −2.296 | −1.207 |
| 17 | 39.406 | 0.247 | 4029.9 | 86.093 | −0.637 | −1.490 | −0.853 |
| 18a | 39.472 | 0.186 | 3385.2 | −39.526a | −3.549 | −2.154 | 1.394 |
| 19 | 41.155 | 0.071 | 4039.2 | 137.736 | −4.277 | −3.515 | 0.762 |
| 20 | 40.680 | 0.154 | 4044.1 | 46.404 | −2.604 | −2.796 | −0.192 |
| 21 | 39.720 | 0.140 | 3317.3 | 40.210 | −2.860 | −2.690 | 0.169 |
| 22 | 40.163 | 0.181 | 3331.4 | 49.892 | −3.810 | −3.211 | 0.598 |
| 23a | 40.847 | 0.160 | 3980.7 | −60.874a | −3.178 | −2.837 | 0.340 |
| 24 | 39.339 | 0.280 | 3331.4 | 64.207 | −2.583 | −2.343 | 0.239 |
| 25 | 40.359 | 0.084 | 3418.0 | 85.160 | −4.184 | −3.357 | 0.826 |
| 26 | 40.968 | 0.110 | 4110.3 | 41.233 | −2.735 | −3.004 | −0.269 |
| 27 | 40.502 | 0.114 | 3975.3 | 53.356 | −2.758 | −2.689 | 0.068 |
| 28 | 39.340 | 0.146 | 3262.9 | 52.717 | −2.118 | −2.364 | −0.246 |
| 29 | 40.968 | 0.103 | 4045.4 | 32.456 | −2.735 | −3.071 | −0.336 |
| 30a | 41.301 | 0.081 | 3400.4 | −3.077a | −4.620 | −4.254 | 0.365 |
| 31 | 41.085 | 0.259 | 3248.3 | 24.087 | −4.690 | −4.345 | 0.344 |
| 32 | 38.570 | 0.315 | 3514.0 | 651.847 | −3.040 | −2.536 | 0.504 |
| 33 | 38.741 | 0.234 | 3293.5 | 103.901 | −1.520 | −1.787 | −0.267 |
| 34 | 40.503 | 0.284 | 3251.9 | 38.393 | −3.600 | −3.720 | −0.120 |
| 35 | 39.780 | 0.117 | 3290.4 | 77.601 | −3.040 | −2.870 | 0.169 |
| 36 | 37.406 | 1.147 | 4021.2 | 266.514 | 0.510 | 0.036 | −0.473 |
| 37 | 40.968 | 0.073 | 3407.1 | 59.104 | −3.870 | −4.002 | 0.132 |
| 38 | 40.885 | 0.061 | 4038.1 | 78.853 | −2.690 | −3.075 | −0.385 |
| 39 | 41.469 | 0.061 | 3416.5 | 106.258 | −4.790 | −4.659 | 0.131 |
| 40 | 40.845 | 0.093 | 3422.3 | 187.518 | −4.270 | −4.134 | 0.135 |
| 41 | 40.680 | 0.141 | 3402.2 | 39.039 | −3.070 | −3.662 | −0.592 |
| 42 | 39.659 | 0.236 | 4013.5 | 80.456 | −2.280 | −1.783 | 0.496 |
| 43 | 41.119 | 0.059 | 3401.6 | 36.388 | −4.740 | −4.125 | 0.614 |
| 44 | 38.096 | 0.342 | 3313.3 | 58.043 | −0.850 | −0.964 | −0.114 |
| 45 | 40.263 | 0.124 | 3406.3 | 53.685 | −2.870 | −3.208 | −0.338 |
| 46 | 36.324 | 4.417 | 4035.2 | 311.330 | −0.060 | −0.023 | 0.036 |
| 47 | 39.721 | 0.143 | 4015.3 | 168.667 | −2.270 | −2.013 | 0.256 |
| 48 | 40.498 | 0.123 | 3465.5 | 181.294 | −3.470 | −3.677 | −0.207 |
| Comp. No | Str | IA | ωH | ωL | O-LogLC50 | P-LogLC50 | bResidual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.916 | 0.263 | 3502.6 | 46.572 | −0,838 | −1,353 | −0.515 |
| 2 | 38.796 | 0.294 | 3103.6 | 133.306 | −0,839 | −1,541 | −0.702 |
| 3 | 38.838 | 0.612 | 3157.6 | 64.729 | −1,601 | −1,366 | 0.234 |
| 4 | 40.094 | 0.227 | 3154.8 | 73.827 | −2,907 | −2,773 | 0.133 |
| 5 | 38.838 | 0.265 | 3163.5 | 66.472 | −1,305 | −1,309 | −0.004 |
| 6 | 40.589 | 0.103 | 3079.7 | 224.825 | −3,214 | −3,945 | −0.731 |
| 7 | 41.273 | 0.060 | 3005.6 | 51.915 | −3,917 | −3,985 | −0.068 |
| 8 | 42.190 | 0.028 | 3461.1 | 26.172 | −4,696 | −4,974 | −0.278 |
| 9 | 39.734 | 0.129 | 3232.5 | 61.837 | −2,552 | −2,299 | 0.252 |
| 10 | 40.878 | 0.064 | 3197.0 | 121.451 | −3,411 | −3,847 | −0.436 |
| 11 | 40.887 | 0.074 | 3090.3 | 56.361 | −3,346 | −3,573 | −0.227 |
| 12 | 39.319 | 0.144 | 3156.8 | 83.654 | −2,014 | −1,910 | 0.103 |
| 13 | 40.203 | 0.074 | 3158.6 | 46.823 | −1,818 | −2,755 | −0.937 |
| 14 | 40.878 | 0.187 | 3192.5 | 95.185 | −4,015 | −3,759 | 0.255 |
| 15 | 39.699 | 0.983 | 3101.5 | 75.687 | −2,931 | −2,464 | 0.466 |
| 16 | 40.228 | 0.104 | 3161.8 | 17.174 | −1,089 | −2,665 | −1.576 |
| 17 | 39.420 | 0.245 | 3159.1 | 39.893 | −0,637 | −1,861 | −1.224 |
| 18 | 39.486 | 0.182 | 3202.7 | 196.531 | −3,549 | −2,590 | 0.958 |
| 19 | 41.186 | 0.070 | 3192.5 | 107.448 | −4,277 | −4,142 | 0.134 |
| 20 | 40.693 | 0.148 | 3206.1 | 19.546 | −2,604 | −3,223 | −0.619 |
| 21 | 39.734 | 0.172 | 3163.8 | 27.915 | −2,860 | −2,157 | 0.703 |
| 22 | 40.177 | 0.177 | 3157.5 | 47.599 | −3,810 | −2,748 | 1.061 |
| 23 | 40.861 | 0.162 | 3425.5 | 35.172 | −3,178 | −3,508 | −0.330 |
| 24 | 39.353 | 0.276 | 3162.1 | 47.922 | −2,583 | −1,824 | 0.759 |
| 25 | 40.395 | 0.090 | 3211.5 | 50.659 | −4,184 | −3,001 | 1.182 |
| 26 | 40.982 | 0.107 | 3206.1 | 19.068 | −2,735 | −3,544 | −0.809 |
| 27 | 40.515 | 0.081 | 3199.7 | 41.240 | −2,758 | −3,096 | −0.338 |
| 28 | 39.354 | 0.147 | 3163.9 | 13.189 | −2,118 | −1,655 | 0.463 |
| 29 | 40.982 | 0.091 | 3206.0 | 11.418 | −2,735 | −3,508 | −0.773 |
| 30 | 41.315 | 0.079 | 3204.6 | 25.514 | −4,620 | −3,948 | 0.671 |
| 31 | 41.098 | 0.258 | 3157.4 | 16.950 | −4,690 | −3,692 | 0.997 |
| 32 | 38.584 | 0.306 | 3304.1 | 513.629 | −3,040 | −2,927 | 0.113 |
| 33 | 38.756 | 0.235 | 3122.5 | 42.932 | −1,520 | −1,105 | 0.414 |
| 34 | 40.517 | 0.293 | 3157.5 | 26.151 | −3,600 | −3,070 | 0.529 |
| 35 | 39.794 | 0.116 | 3159.9 | 89.923 | −3,040 | −2,477 | 0.563 |
| 36 | 37.421 | 1.124 | 3161.4 | 146.790 | 0,510 | −0,183 | −0.693 |
| 37 | 40.982 | 0.073 | 3205.6 | 43.190 | −3,870 | −3,639 | 0.230 |
| 38 | 40.926 | 0.063 | 3073.9 | 105.914 | −2,690 | −3,823 | −1.133 |
| 39 | 41.505 | 0.061 | 3187.5 | 87.350 | −4,790 | −4,422 | 0.367 |
| 40 | 40.878 | 0.094 | 3195.2 | 162.544 | −4,270 | −4,026 | 0.243 |
| 41 | 40.693 | 0.146 | 3203.1 | 37.611 | −3,070 | −3,298 | −0.228 |
| 42 | 39.673 | 0.238 | 3299.0 | 43.605 | −2,280 | −2,181 | 0.098 |
| 43 | 41.150 | 0.061 | 3190.5 | 97.797 | −4,740 | −4,058 | 0.681 |
| 44 | 38.111 | 0.330 | 3157.3 | 83.337 | −0,850 | −0,558 | 0.291 |
| 45 | 40.277 | 0.122 | 3199.0 | 17.486 | −2,870 | −2,731 | 0.138 |
| 46 | 36.339 | 4.051 | 3149.1 | 295.043 | −0,060 | −0,118 | −0.058 |
| 47 | 39.735 | 0.143 | 3107.1 | 134.076 | −2,270 | −2,593 | −0.323 |
| 48 | 40.544 | 0.131 | 3152.6 | 166.703 | −3,470 | −3,505 | −0.035 |
| Comp. No | Str | IA | ωH | ωL | O-LogLC50 | P-LogLC50 | bResidual |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 38.916 | 0.261 | 3182.6 | 67.778 | −0.838 | −1.372 | −0.534 |
| 2 | 38.796 | 0.281 | 3131.1 | 198.042 | −0.839 | −1.702 | −0.863 |
| 3 | 38.838 | 0.620 | 3182.7 | 82.322 | −1.601 | −1.423 | 0.177 |
| 4 | 40.094 | 0.233 | 3176.2 | 69.425 | −2.907 | −2.763 | 0.143 |
| 5 | 38.838 | 0.269 | 3183.6 | 121.401 | −1.305 | −1.474 | −0.169 |
| 6 | 40.589 | 0.106 | 3051.0 | 209.619 | −3.214 | −3.815 | −0.601 |
| 7 | 41.273 | 0.057 | 2945.1 | 29.974 | −3.917 | −3.963 | −0.046 |
| 8 | 42.190 | 0.026 | 3162.5 | 41.232 | −4.696 | −5.086 | −0.390 |
| 9 | 39.734 | 0.111 | 3165.8 | 50.229 | −2.552 | −2.236 | 0.315 |
| 10 | 40.878 | 0.066 | 3078.0 | 122.576 | −3.411 | −3.835 | −0.424 |
| 11 | 40.887 | 0.077 | 3059.8 | 44.269 | −3.346 | −3.566 | −0.220 |
| 12 | 39.319 | 0.136 | 3183.9 | 100.781 | −2.014 | −1.935 | 0.078 |
| 13 | 40.203 | 0.062 | 3179.1 | 49.434 | −1.818 | −2.776 | −0.958 |
| 14 | 40.878 | 0.188 | 3073.9 | 93.850 | −4.015 | −3.763 | 0.252 |
| 15 | 39.699 | 0.963 | 3065.2 | 63.709 | −2.931 | −2.457 | 0.473 |
| 16 | 40.228 | 0.103 | 3182.6 | 56.271 | −1.089 | −2.841 | −1.752 |
| 17 | 39.420 | 0.244 | 3183.2 | 54.483 | −0.637 | −1.916 | −1.279 |
| 18 | 39.486 | 0.184 | 3171.8 | 191.436 | −3.549 | −2.470 | 1.078 |
| 19 | 41.186 | 0.072 | 3067.9 | 107.791 | −4.277 | −4.147 | 0.129 |
| 20 | 40.693 | 0.150 | 3081.5 | 22.099 | −2.604 | −3.277 | −0.673 |
| 21 | 39.734 | 0.175 | 3183.0 | 39.014 | −2.860 | −2.213 | 0.646 |
| 22 | 40.177 | 0.182 | 3182.4 | 40.669 | −3.810 | −2.744 | 1.065 |
| 23 | 40.861 | 0.164 | 3851.1 | 41.276 | −3.178 | −3.573 | −0.395 |
| 24 | 39.353 | 0.277 | 3185.8 | 39.706 | −2.583 | −1.792 | 0.791 |
| 25 | 40.359 | 0.093 | 3144.0 | 50.603 | −4.184 | −2.993 | 1.190 |
| 26 | 40.968 | 0.107 | 3902.2 | 19.928 | −2.735 | −3.569 | −0.834 |
| 27 | 40.515 | 0.073 | 3164.7 | 31.179 | −2.758 | −3.082 | −0.324 |
| 28 | 39.354 | 0.145 | 3182.3 | 115.054 | −2.118 | −2.030 | 0.087 |
| 29 | 40.982 | 0.091 | 3172.0 | 35.494 | −2.735 | −3.654 | −0.919 |
| 30 | 41.315 | 0.079 | 3081.0 | 15.268 | −4.620 | −3.969 | 0.650 |
| 31 | 41.098 | 0.260 | 3182.5 | 19.088 | −4.690 | −3.776 | 0.913 |
| 32 | 38.584 | 0.311 | 3176.5 | 507.271 | −3.040 | −2.571 | 0.469 |
| 33 | 38.756 | 0.238 | 3075.1 | 54.747 | −1.520 | −1.126 | 0.393 |
| 34 | 40.517 | 0.294 | 3182.3 | 29.091 | −3.600 | −3.134 | 0.465 |
| 35 | 39.794 | 0.111 | 3175.0 | 27.889 | −3.040 | −2.228 | 0.811 |
| 36 | 37.421 | 1.162 | 3187.0 | 169.851 | 0.510 | −0.200 | −0.710 |
| 37 | 40.982 | 0.062 | 3166.9 | 52.972 | −3.870 | −3.709 | 0.160 |
| 38 | 40.926 | 0.065 | 2969.0 | 70.581 | −2.690 | −3.701 | −1.011 |
| 39 | 41.505 | 0.063 | 3070.5 | 87.839 | −4.790 | −4.451 | 0.338 |
| 40 | 40.878 | 0.095 | 3076.5 | 157.507 | −4.270 | −3.968 | 0.301 |
| 41 | 40.693 | 0.142 | 3145.7 | 20.095 | −3.070 | −3.270 | −0.200 |
| 42 | 39.673 | 0.240 | 3164.6 | 30.095 | −2.280 | −2.125 | 0.154 |
| 43 | 41.150 | 0.063 | 3171.4 | 97.945 | −4.740 | −4.070 | 0.669 |
| 44 | 38.111 | 0.335 | 3181.9 | 60.492 | −0.850 | −0.413 | 0.436 |
| 45 | 40.277 | 0.122 | 3168.8 | 53.232 | −2.870 | −2.893 | −0.023 |
| 46 | 36.339 | 4.245 | 3141.5 | 283.579 | −0.060 | −0.110 | −0.050 |
| 47 | 39.735 | 0.142 | 3046.7 | 143.340 | −2.270 | −2.577 | −0.307 |
| 48 | 40.544 | 0.139 | 3065.4 | 147.246 | −3.470 | −3.503 | −0.033 |
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Yan, X.F.; Xiao, H.M.; Gong, X.D.; Ju, X.H. A comparison of semiempirical and first principle methods for establishing toxicological QSARs of nitroaromatics. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem) 2006, 764, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Newsome, L.D.; Johnson, D.E.; Lipnick, R.L.; Broderius, S.J.; Russom, C.L. A QSAR study of the toxicity of amines to the fathead minnow. Sci. Tot. Env. 1991, 109–110, 537–551. [Google Scholar]
- Protic, M.; Sabljic, A. Quantitative structure-activity relationships of acute toxicity of commercial chemicals on fathead minnows: effect of molecular size. Aquatic Toxicology 1989, 14, 47–64. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, C.J.; Adema, D.M.M.; Hermens, J. Quantitative structure-activity relationships for fish early life stage toxicity. Aquatic Toxicology 1990, 16, 321–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Cheng, Y.Y. Local and Global Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Modeling and Prediction for the Baseline Toxicity. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2007, 47, 159–169. [Google Scholar]
- Devillers, J. A new strategy for using supervised artificial neural networks in QSAR. Sar And Qsar In Environmental Research 2005, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Jurs, P.C. Assessing the reliability of a QSAR model’s predictions. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2005, 23, 503–523. [Google Scholar]
- Papa, E.; Villa, F.; Gramatica, P. Statistically Validated QSARs, Based on Theoretical Descriptors, for Modeling Aquatic Toxicity of Organic Chemicals in Pimephales promelas (Fathead Minnow). J. Chem. Inf. Model 2005, 45, 1256–1266. [Google Scholar]
- McKinney, J.D.; Richard, A.; Waller, C.; Newman, M.C.; Gerberick, F. The Practice of Structure Activity Relationships (SAR) in Toxicology. Toxicol. Sci 2000, 56, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Cronin, M.T.D.; Dearden, J.C. QSAR in Toxicology. 1. Prediction of Aquatic Toxicity. Quant. Struct.–Act. Relat 1995, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hermens, J. Prediction of environmental toxicity based on structure-activity relationships using mechanistic information. Sci. Total Environ 1995, 171, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Pavan, M.; Worth, A.; Netzeva, T. Preliminary analysis of an aquatic toxicity dataset and assessment of QSAR models for narcosis. JRC report EUR 21479 EN; European Commission, Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2005. http://ecb.jrc.it/Documents/QSAR/Report_QSAR_model_for_narcosis.pdf.
- Veith, G.D.; Mekenyan, O.G. A QSAR Approach for Estimating the Aquatic Toxicity of Soft Electrophiles QSAR for Soft Electrophiles. Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat 1993, 12, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Karabunarliev, S.; Mekenyan, O.G.; Karcher, W.; Russom, C.L.; Bradbury, S.P. Quantumchemical Descriptors for Estimating the Acute Toxicity of Substituted Benzenes to the Guppy (Poecilia reticulata) and Fathead Minnow (Pimephales promelas). Quant. Struct.-Act. Relat 1996, 15, 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Dewar, M.; Zoebisch, E.G.; Healy, E.F.; Stewart, J.J.B. Development use of quantum mechanical molecular models. 76. AM1: a new general purpose quantum mechanical molecular model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 5348–5356. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J.J.B. Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods I. Method. J. Comp. Chem 1989, 10, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, J.J.B. Optimization of parameters for semiempirical methods II. Applications. J. Comp. Chem 1989, 10, 221–264. [Google Scholar]
- Reis, M.; Lobato, B.; Lameira, J.; Santos, A.S.; Alves, C.N. A theoretical study of phenolic compounds with antioxidant properties. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2006, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Pasha, F.A.; Srivastava, H.K.; Singh, P.P. Comparative QSAR study of phenol derivatives with the help of density functional theory. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2005, 13, 6823–6829. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wan, J.; Yang, G. A DFT-based QSARs study of protoporphyrinogen oxidase inhibitors: phenyl triazolinones. Bioorg. & Med. Chem 2004, 12, 6183–6191. [Google Scholar]
- Trohalaki, S.; Giffort, E.; Pachter, R. Improved QSARs for predictive toxicology of halogenated hydrocarbons. Computers and Chemistry 2000, 24, 421–427. [Google Scholar]
- Eroglu, E.; Turkmen, H. A DFT-based quantum theoretic QSAR study of aromatic and heterocyclic sulfonamides as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors against isozyme, CA-II. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roothan, C.C.J. New Developments in Molecular Orbital Theory. Rev. Mod. Phys 1951, 23, 69–89. [Google Scholar]
- Pople, J.A.; Nesbet, R.K. Self-Consistent Orbitals for Radicals. J. Chem. Phys 1954, 22, 571–572. [Google Scholar]
- McWeeny, R.; Dierksen, G. Self-Consistent Perturbation Theory. II. Extension to Open Shells. J. Chem. Phys 1968, 49, 4852–4856. [Google Scholar]
- Parr, R.; Yang, W. Density Functional Theory of Atoms and Molecules; Oxford University Pres: New York, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional thermochemistry. III. The role of exact exchange. J. Chem. Phys 1993, 98, 5648–5652. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Montgomery,, J.A., Jr.; Vreven, T.; Kudin, K.N.; Burant, J.C.; Millam, J.M.; Iyengar, S.S.; Tomasi, J.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Cossi, M.; Scalmani, G.; Rega, N.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; Hada, M.; Ehara, M.; Toyota, K.; Fukuda, R.; Hasegawa, J.; Ishida, M.; Nakajima, T.; Honda, Y.; Kitao, O.; Nakai, H.; Klene, M.; Li, X.; Knox, J.E.; Hratchian, H.P.; Cross, J.B.; Bakken, V.; Adamo, C.; Jaramillo, J.; Gomperts, R.; Stratmann, R.E.; Yazyev, O.; Austin, A.J.; Cammi, R.; Pomelli, C.; Ochterski, J.W.; Ayala, P.Y.; Morokuma, K.; Voth, G.A.; Salvador, P.; Dannenberg, J.J.; Zakrzewski, V.G.; Dapprich, S.; Daniels, A.D.; Strain, M.C.; Farkas, O.; Malick, D.K.; Rabuck, A.D.; Raghavachari, K.; Foresman, J.B.; Ortiz, J.V.; Cui, Q.; Baboul, AG; Clifford, S.; Cioslowski, J.; Stefanov, B.B.; Liu, G.; Liashenko, A.; Piskorz, P.; Komaromi, I.; Martin, R.L.; Fox, D.J.; Keith, T.; Al-Laham, M.A.; Peng, C.Y.; Nanayakkara, A.; Challacombe, M.; Gill, P.M.W.; Johnson, B.; Chen, W.; Wong, M.W.; Gonzalez, C.; Pople, J.A. Gaussian 03, Revision C.02; Gaussian, Inc: Wallingford CT, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- CODESSA (Comprehensive Descriptors for Structural and Statistical Analysis), Semichem; 7204, Mullen, Shawnee, KS 66216 USA: Copyright© Semichem and the University of Florida, 1995–2004.
- Mayers, R.H. Classical and Modern Regression With Applications; PWS-KENT Publ. Co.: Boston, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- CODESSA™, References Manual, 2 13 (PC); Semichem, 7204, Mullen, Shawnee, KS 66216 USA; Copyright© Semichem and the University of Florida, 2002.
- Hollas, J.M. Modern Spectroscopy, 2nd Ed. ed; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- David, R.L. Handbook of the Chemistry and Physics, 85nd ed; CRC Press: Cleveland OH, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, A.M.; Heritage, T.W.; Jonatson, P.; Pack, S.E.; Phillips, L.; Rogan, J.; Snaith, P.J. EVA: A new theoretically based molecular descriptor for use in QSAR/QSPR analysis. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des 1997, 11, 143–152. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.B.; Willett, P.; Ferguson, A.M.; Heritage, T. Evaluation of a novel infrared range vibration-based descriptor (EVA) for QSAR studies. 1. General application. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des 1997, 11, 409–422. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.B.; Willett, P.; Ferguson, A.M.; Heritage, T. Evaluation of a novel molecular vibration-based descriptor (EVA) for QSAR studies: 2. Model validation using a benchmark steroid dataset. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des 1999, 13, 271–296. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, D.B.; Willett, P. Evaluation of the EVA descriptor for QSAR studies: 3. The use of a genetic algorithm to search for models with enhanced predictive properties (EVA_GA). J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des 2000, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ginn, C.M.R.; Turner, D.B.; Willett, P.; Ferguson, A.M.; Heritage, T.W. Similarity Searching in Files of Three-Dimensional Chemical Structures: Evaluation of the EVA Descriptor and Combination of Rankings Using Data Fusion. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 1997, 37, 23–37. [Google Scholar]
- Schultz, T.W.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Walker, J.D.; Aptula, A.O. Quantitative structure–activity relationships (QSARs) in toxicology: a historical perspective. Journal of Molecular Structure (Theochem) 2003, 622, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
© 2007 by MDPI Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Eroglu, E.; Palaz, S.; Oltulu, O.; Turkmen, H.; Ozaydın, C. Comparative QSTR Study Using Semi-Empirical and First Principle Methods Based Descriptors for Acute Toxicity of Diverse Organic Compounds to the Fathead Minnow. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2007, 8, 1265-1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms8121265
Eroglu E, Palaz S, Oltulu O, Turkmen H, Ozaydın C. Comparative QSTR Study Using Semi-Empirical and First Principle Methods Based Descriptors for Acute Toxicity of Diverse Organic Compounds to the Fathead Minnow. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2007; 8(12):1265-1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms8121265
Chicago/Turabian StyleEroglu, Erol, Selami Palaz, Oral Oltulu, Hasan Turkmen, and Cihat Ozaydın. 2007. "Comparative QSTR Study Using Semi-Empirical and First Principle Methods Based Descriptors for Acute Toxicity of Diverse Organic Compounds to the Fathead Minnow" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 8, no. 12: 1265-1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms8121265




