A Computational Study of Calcium(II) and Copper(II) Ion Binding to the Hyaluronate Molecule
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Methods
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Laurent, T.C. Glycosaminoglycans and Proteoglycans. In The Chemistry and Molecular Biology of the Intercellular Matrix; Balazs, E.A., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970; Volume 2, pp. 703–733. [Google Scholar]
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 1463–1473. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, T.C.; Fraser, J.R.E. Hyaluronan. FASEB J 1992, 6, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar]
- Goa, K.L.; Benfield, P. Hyaluronic-Acid-A review of its pharmacology and use as a surgical aid in ophthalmology, and its therapeutic potential in joint disease and wound-healing. Drugs 1994, 47, 536–566. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman, E.; Geiger, B.; Addadi, L. Initial stages of cell-matrix adhesion can be mediated and modulated by cell-surface hyaluronan. Biophys. J 2002, 82, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Moulabbi, M.; Broch, H.; Robert, L.; Vasilescu, D. Quantum molecular modeling of hyaluronan. Theochem. J. Mol. Struct 1997, 395, 477–508. [Google Scholar]
- Sipos, P.; Veber, M.; Burger, K.; Illes, J.; Machula, G. Hyaluronate-Metal ion interactions: Correlations between viscosimetric, potentiometric, polarographic and electrophoretic data. Acta Chim. Hungarica Models Chem 1992, 129, 671–683. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, E.R.; Rees, D.A.; Welsh, E.J. Conformation and dynamic interactions in hyaluronate solutions. J. Mol. Biol 1980, 138, 383–400. [Google Scholar]
- Figueroa, N.; Nagy, B.; Chakrabarti, B. Cu2+-hyaluronic acid complex-spectrophotometric detection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 1977, 74, 460–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sterk, H.; Braun, M.; Schmut, O.; Feichtinger, H. Investigation of the hyaluronic acid-copper complex by N.M.R. spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res 1985, 145, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lapcik, L.; Dammer, C.; Valko, M. Hyaluronic acid-copper(ii) complexes-spectroscopic characterization. Colloid Polym. Sci 1992, 201, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, J.K.; Atkins, E.D. X-Ray Fiber Diffraction study of conformational-changes in hyaluronate induced in the presence of sodium, potassium and calcium cations. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 1983, 5, 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, E.D.; Sheehan, J.K.; Phelps, C.F. Conformation of mucopolysaccharides-hyaluronates. Biochem. J 1972, 128, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, A.K; Raghunathan, S.; Sheehan, J.K.; Arnott, S. Hyaluronic-acid-molecular-conformations and interactions in the orthorhombic and tetragonal forms containing sinuous chains. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 169, 829–859. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, W.T.; Arnott, S. Hyaluronic acid: The role of divalent cations in conformation and packing. J. Mol. Biol 1977, 117, 761–784. [Google Scholar]
- Tratar Pirc, E.; Arcon, I.; Bukovec, P.; Kodre, A. Preparation and characterisation of copper(II) hyaluronate. Carbohydr. Res 2000, 324, 275–282. [Google Scholar]
- Tratar Pirc, E.; Arcon, I.; Kodre, A.; Bukovec, P. Metal-ion environment in solid Mn(II), Co(II) and Ni(II) hyaluronates. Carbohydr. Res 2004, 339, 2549–2554. [Google Scholar]
- Eklund, R.; Widmalm, G. Molecular dynamics simulations of an oligosaccharide using a force field modified for carbohydrates. Carbohydr. Res 2003, 338, 393–398. [Google Scholar]
- Warshel, A.; Levitt, M. Theoretical studies of enzymic reactions: Dielectric, electrostatic and steric stabilization of the carbonium ion in the reaction of lysozyme. J. Mol. Biol 1976, 103, 227–249. [Google Scholar]
- Masgrau, L.; Roujeinikova, A.; Johannissen, L.O.; Hothi, P.; Basran, J.; Ranaghan, K.E.; Mulholland, A.J.; Sutcliffe, M.J.; Scrutton, N.S.; Leys, D. Atomic description of an enzyme reaction dominated by proton tunneling. Science 2006, 312, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zidar, J.; Tratar, P.E.; Hodoscek, M.; Bukovec, P. Copper(II) ion binding to cellular prion protein. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2008, 48, 283–287. [Google Scholar]
- Tratar, P.E.; Zidar, J.; Bukovec, P.; Hodoscek, M. Molecular modeling of cobalt(II) hyaluronate. Carbohydr. Res 2005, 340, 2064–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter, T.E.; Howder, C.; Berden, G.; Oomens, J.; Armentrout, P.B. Structural elucidation of biological and toxicological complexes: Investigation of monomeric and dimeric complexes of histidine with multiply charged transition metal (Zn and Cd) cations using IR action spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 12648–12661. [Google Scholar]
- Remko, M.; Fitz, D.; Broer, R.; Rode, B.M. Effect of metal Ions (Ni2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+) and water coordination on the structure of l-phenylalanine, l-tyrosine, l-tryptophan and their zwitterionic forms. J. Mol. Model 2011, 17, 3117–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Khodabandeh, M.H.; Hamid, R; Zare, K.; Zahedi, M. A theoretical elucidation of coordination properties of histidine and lysine to Mn2+. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 313, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Siegbahn, P.E. The performance of hybrid DFT for mechanisms involving transition metal complexes in enzymes. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem 2006, 11, 695–701. [Google Scholar]
- Minenkov, Y.; Singstad, Å.; Occhipinti, G.; Jensen, V.R. The accuracy of DFT-optimized geometries of functional transition metal compounds: A validation study of catalysts for olefin metathesis and other reactions in the homogeneous phase. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 5526–5541. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic-behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.T.; Yang, W.T.; Parr, G. Development of the colle-salvetti correlation-energy formula into a functional of the electron-density. Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functional. Theor. Chem. Acc 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar]
- MacKerell, A.D.; Bashford, D.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Evanseck, J.D.; Field, M.J.; Fischer, S.; Gao, J.; Guo, H.; Ha, S.; Joseph-McCarthy, D.; et al. All-atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 3586–3616. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.; Karplus, M. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L., III; Mackerell, A.D., Jr.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The biomolecular simulation program. J. Comput. Chem 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.W.; Baldridge, K.K.; Boatz, J.A.; Elbert, S.T.; Gordon, M.S.; Jensen, J.H.; Koseki, S.; Matsunaga, N.; Nguyen, K.A.; Su, S.J.; et al. General atomic and molecular electronic-structure system. J. Comput. Chem 1993, 14, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar]
- Borštnik, U.; Hodošcek, M.; Janežic, D. Improving the performance of molecular dynamics simulations on parallel clusters. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2004, 44, 359–364. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graphics 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
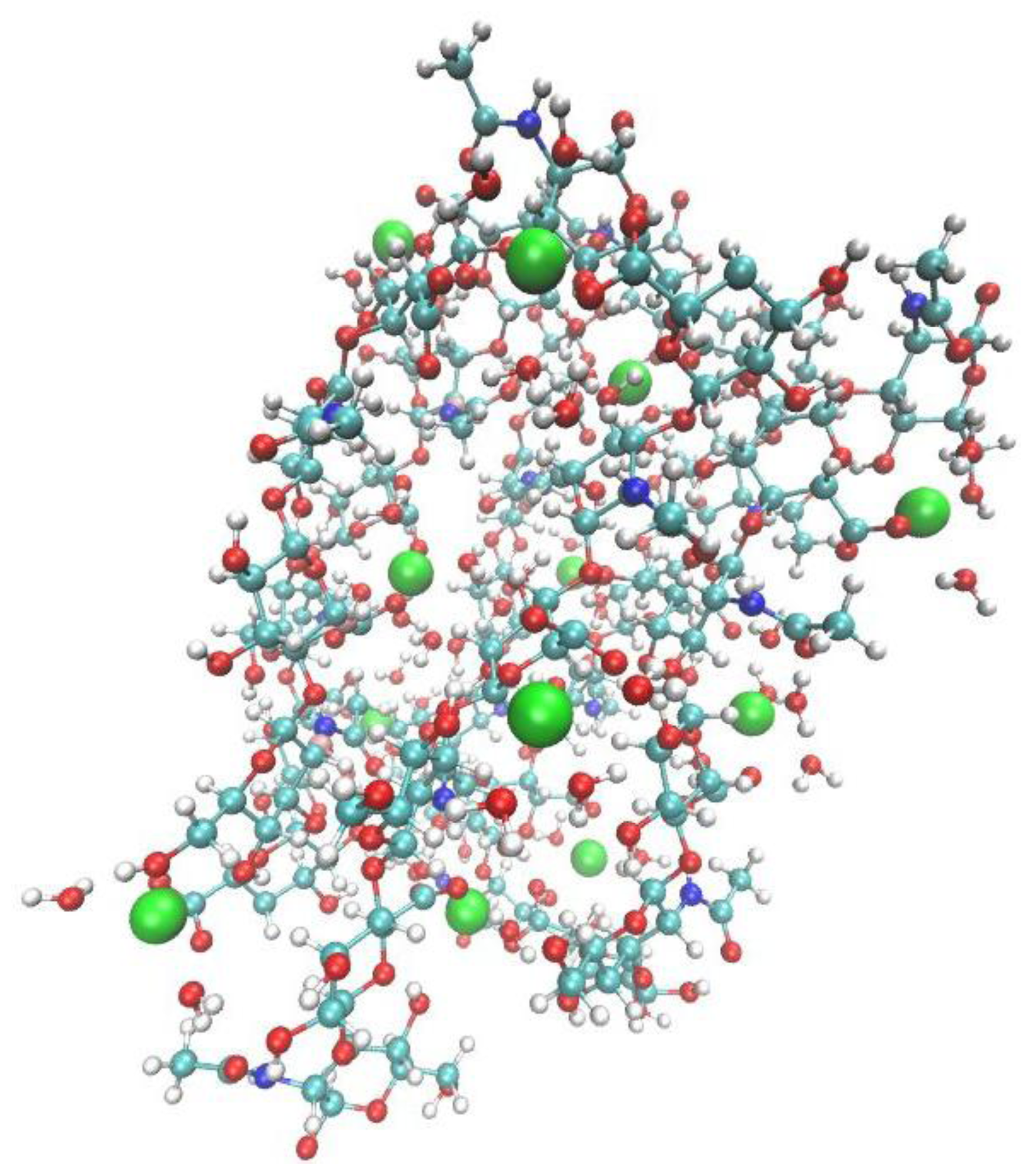
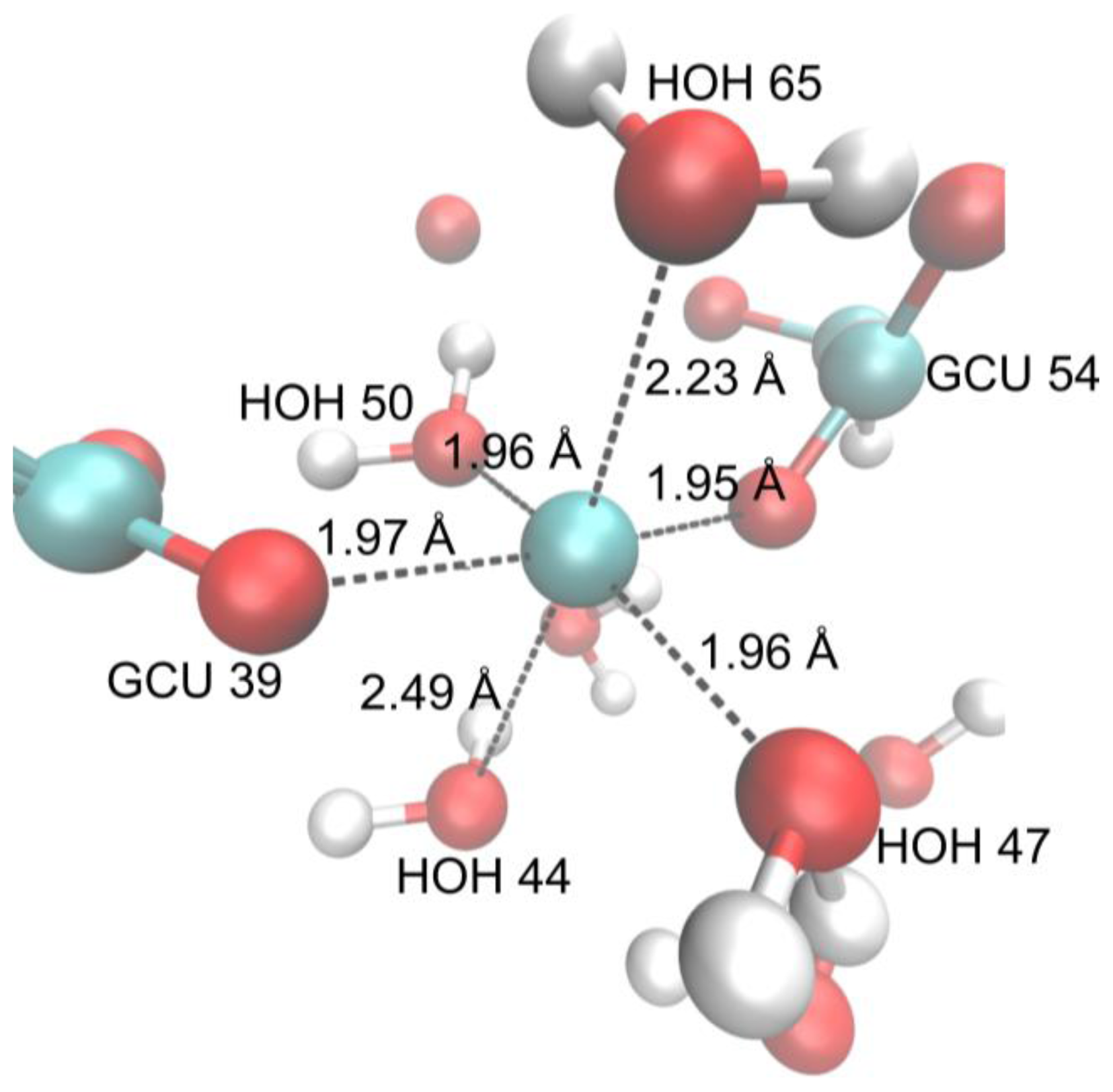
| Ligand | EXP [Å] | HF [Å] | B3LYP [Å] | M06 [Å] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G* | 6-31G(d,p) | ||
| GCU 39 O6A | 2.510 | 2.408 | 2.416 | 2.408 | 2.469 | 2.554 | 2.384 |
| HOH 44 O | 2.474 | 2.495 | 2.522 | 2.468 | 2.479 | 2.587 | 2.498 |
| HOH 47 O | 2.556 | 2.456 | 2.505 | 2.421 | 2.482 | 2.598 | 2.558 |
| HOH 50 O | 2.569 | 2.418 | 2.415 | 2.401 | 2.376 | 2.278 | 2.395 |
| GCU 54 O6A | 2.511 | 2.412 | 2.434 | 2.407 | 2.470 | 2.578 | 2.418 |
| HOH 59 O | 2.475 | 2.518 | 2.553 | 2.440 | 2.532 | 2.604 | 2.507 |
| HOH 62 O | 2.555 | 2.494 | 2.525 | 2.463 | 2.509 | 2.250 | 2.581 |
| HOH 65 O | 2.570 | 3.444 | 3.632 | 3.327 | 3.639 | 2.599 | 2.637 |
| EXP | HF | B3LYP | M06 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deviation | 6-31G* | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G* | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G* | 6-31G(d,p) | |
| 1.000 | 0.132 | 0.154 | 0.112 | 0.156 | 0.068 | 0.035 | |
| Ligand | EXP [Å] | HF [Å] | B3LYP [Å] | M06 [Å] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | ||
| GCU 39 O6A | 1.952 | 1.976 | 1.983 | 1.917 | 1.969 | 1.966 | 1.989 |
| HOH 44 O | 2.465 | 2.341 | 2.371 | 3.458 | 2.901 | 2.487 | 2.385 |
| HOH 47 O | 1.952 | 2.070 | 2.072 | 1.967 | 1.990 | 1.960 | 2.002 |
| HOH 50 O | 1.952 | 2.070 | 2.069 | 2.032 | 1.998 | 1.960 | 1.997 |
| GCU 54 O6A | 1.952 | 1.992 | 2.002 | 1.946 | 2.003 | 1.954 | 1.982 |
| HOH 59 O | 3.767 | 3.829 | 3.892 | 3.904 | 3.705 | 3.576 | 3.696 |
| HOH 62 O | 3.507 | 3.639 | 3.609 | 3.281 | 3.526 | 3.503 | 3.487 |
| HOH 65 O | 2.465 | 2.278 | 2.319 | 2.184 | 2.309 | 2.235 | 2.291 |
| EXP | HF | B3LYP | M06 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deviation | 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | 6-31G * | 6-31G(d,p) | |
| 1.000 | 0.049 | 0.043 | 0.157 | 0.069 | 0.037 | 0.034 | |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirc, E.T.; Zidar, J.; Bukovec, P. A Computational Study of Calcium(II) and Copper(II) Ion Binding to the Hyaluronate Molecule. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12036-12045. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130912036
Pirc ET, Zidar J, Bukovec P. A Computational Study of Calcium(II) and Copper(II) Ion Binding to the Hyaluronate Molecule. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(9):12036-12045. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130912036
Chicago/Turabian StylePirc, Elizabeta Tratar, Jernej Zidar, and Peter Bukovec. 2012. "A Computational Study of Calcium(II) and Copper(II) Ion Binding to the Hyaluronate Molecule" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 9: 12036-12045. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms130912036




