3D-QSPR Method of Computational Technique Applied on Red Reactive Dyes by Using CoMFA Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
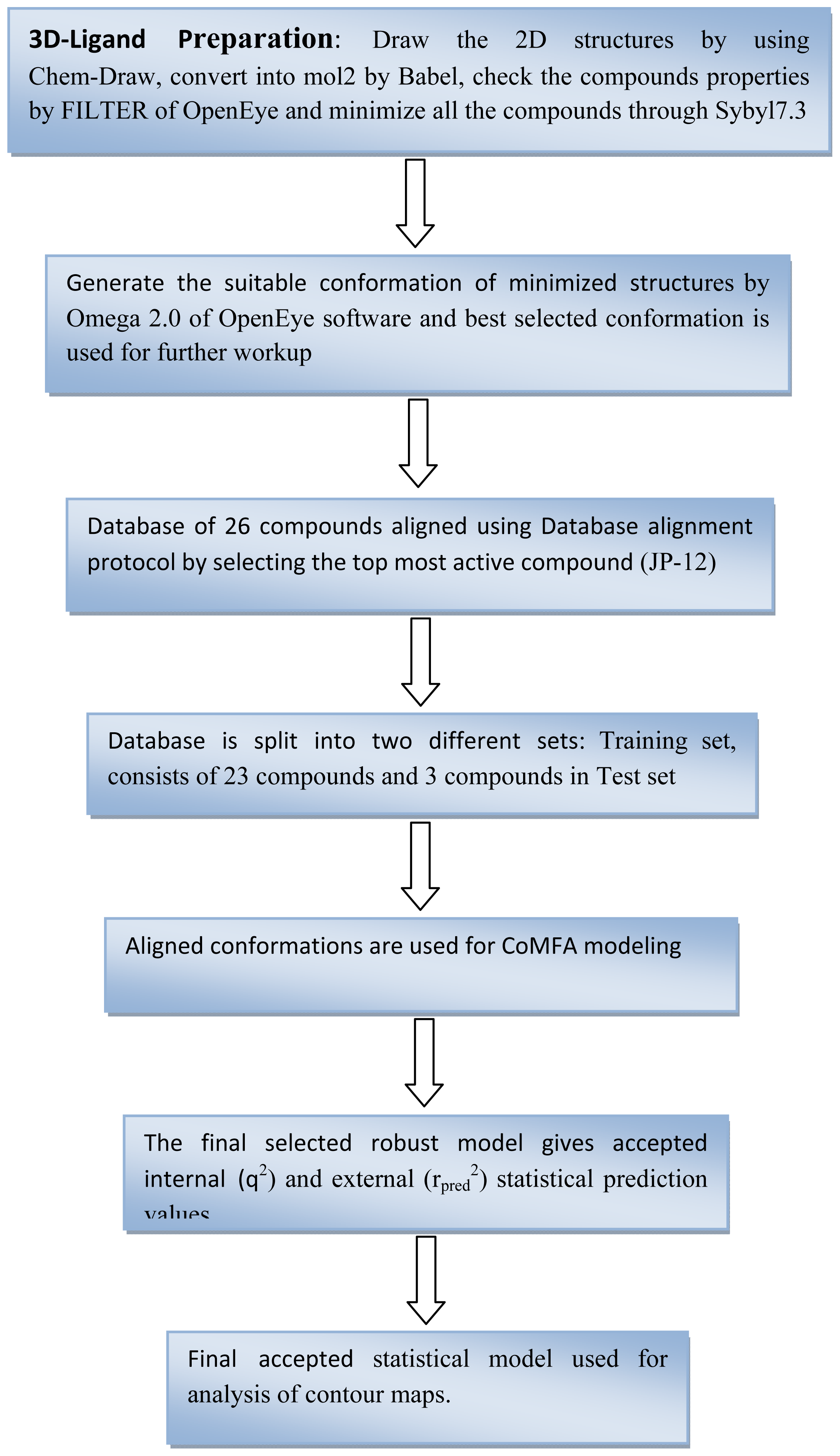
2. Computational Methodology
2.1. Molecular Modeling
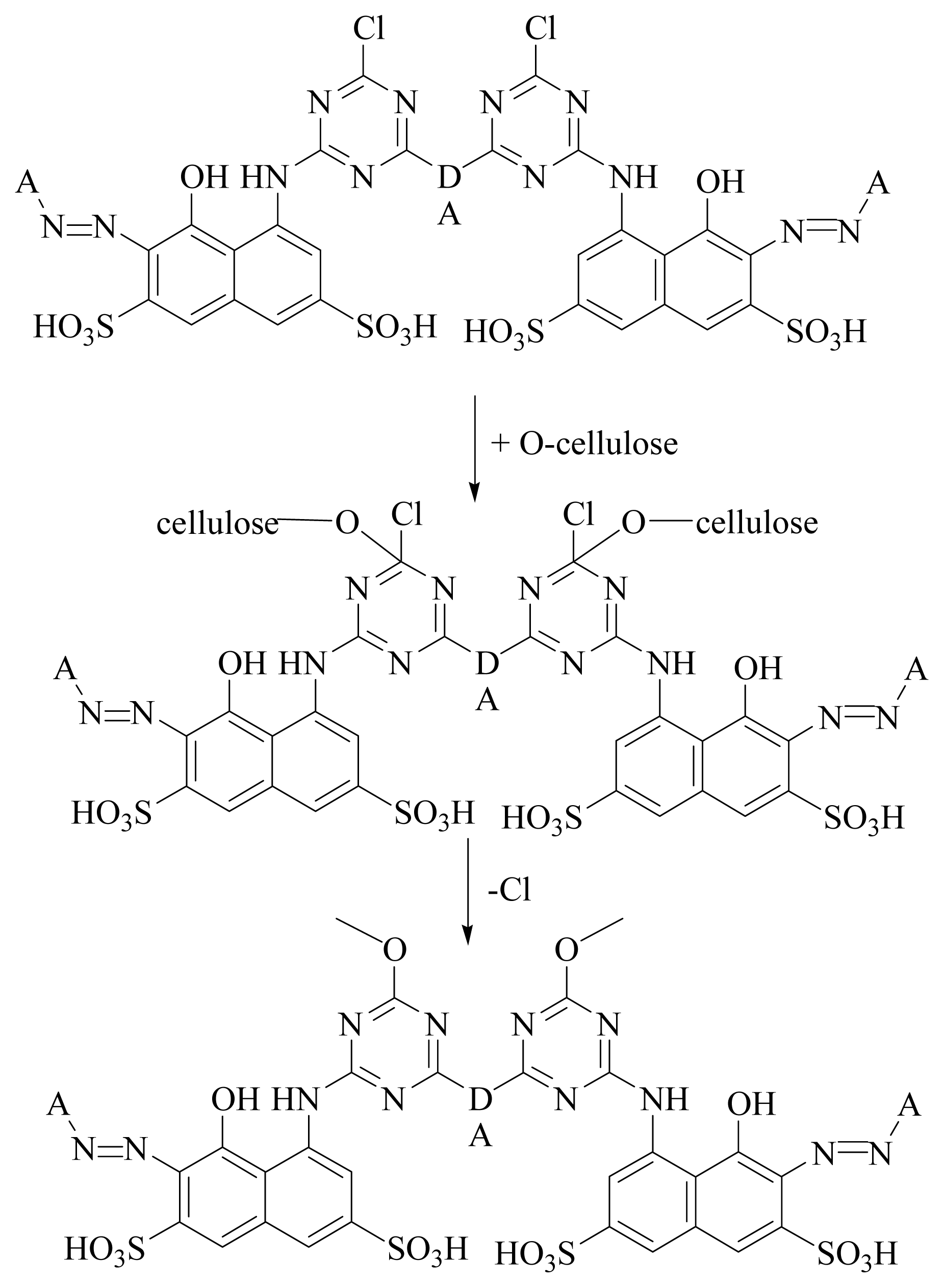
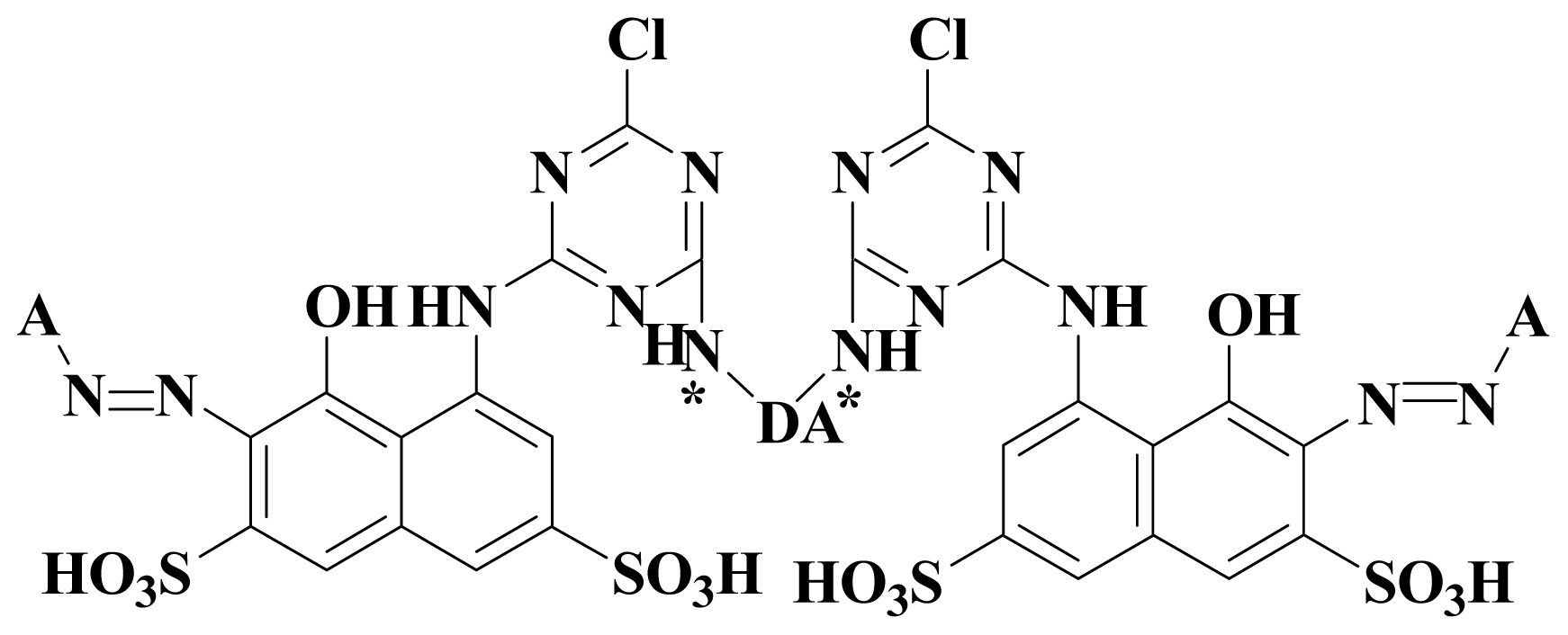
2.2. Selection of Molecules
2.2.1. Current Study Deals With The Two Different Data Sets
- Dataset I: A set of thirteen compounds were retrieved from the literature reported by the J Paluszkiewicz et al. (dye-codes JP-1 to JP-13). They synthesized red reactive dyes which are derivatives of 1-amine-8-hydroxynaphthalene-3, 6-disulfonic acid [36].
- Dataset II: Another dataset containing thirteen compounds was provided by Sitara et al. [37] with dye-codes (IS-14 to IS-26).
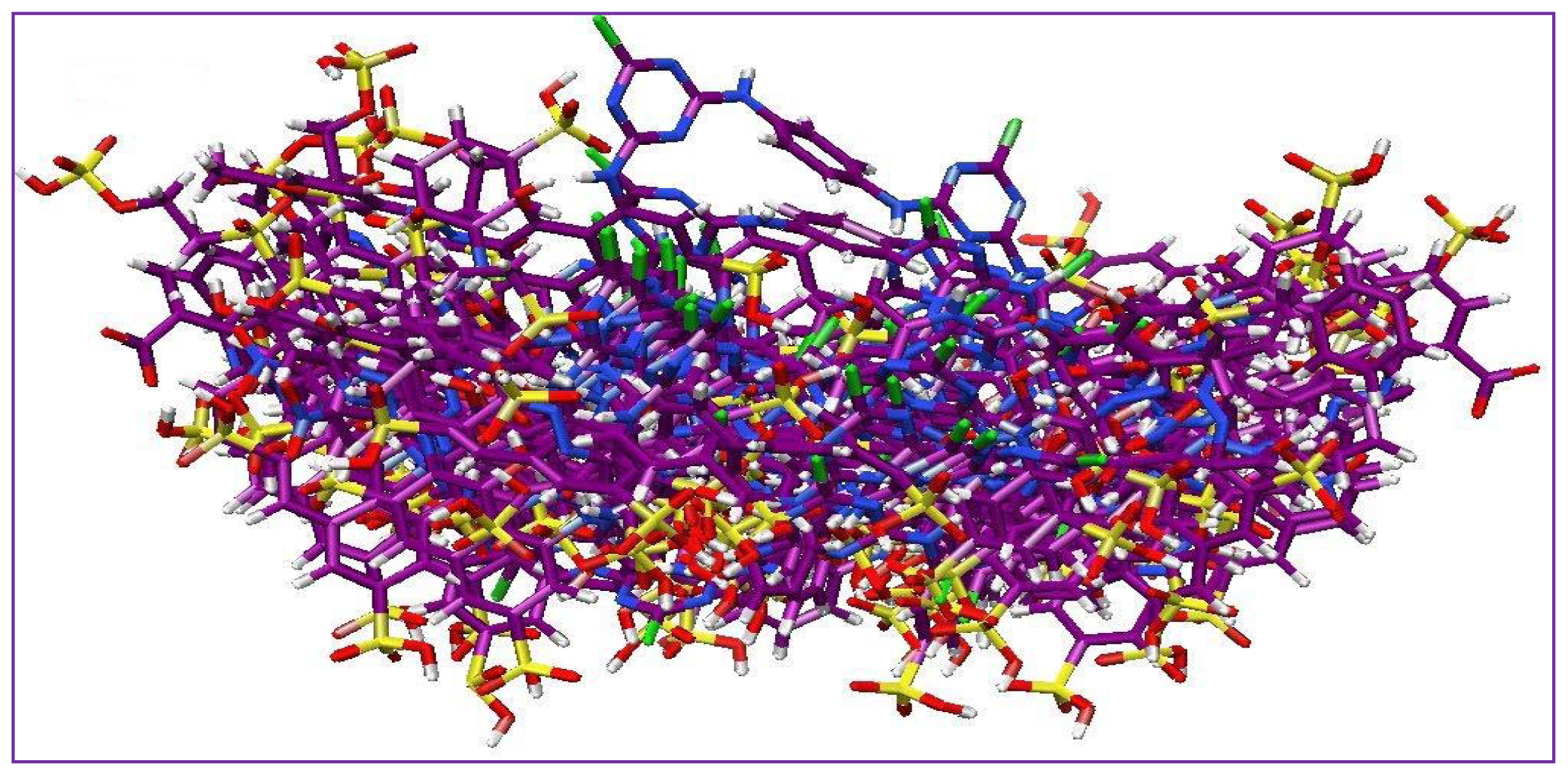
2.3. Dataset Preparation for the Alignment
2.4. Structural Alignment
2.5. Comparative Molecular Field Analyses (CoMFA) Study
2.6. Partial Least Square Analysis (PLS)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selectivity Profile
3.2. Alignment Protocol with Different Charges
3.3. Statistics of CoMFA Model
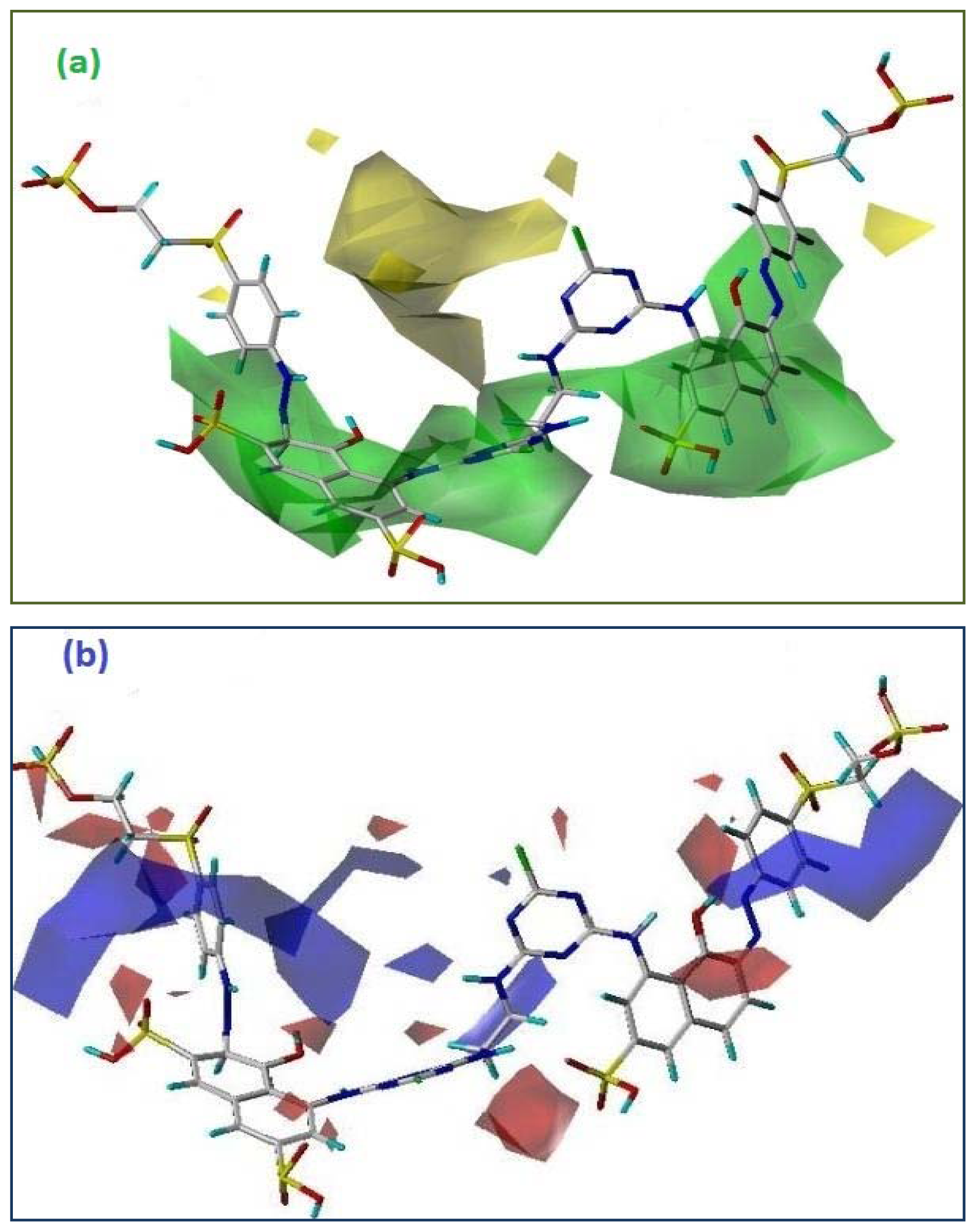
3.4. 3D Analysis of the CoMFA
3.5. Steric Fields
3.6. Electrostatic Fields
3.7. Validation of the 3D-QSPR Model
4. Conclusion
Acknowledgement
References
- He, Y.; Li, G.; Zhao, J.; Su, H. Membrane technology: Reactive dyes and cleaner production. Filtr. Separat 2007, 44, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Renfrew, A.H.M.; Taylor, J.A. Cellulose reactive dyes: Recent developments and trends. Rev. Prog. Color. Relat. Top 1990, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rattee, I.D.; Breuer, M.M. The Physical Chemistry of Dye Adsorption; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Lewis, D.M. Chemical modification of cotton to improve fibre dyeability. Color. Technol 2002, 118, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Hou, A.; Sun, Y. Chemical graft of cellulose with the ion-pair emulsion containing the reactive groups and its dyeing properties. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol 2008, 29, 1385–1390. [Google Scholar]
- Vickerstaff, T. The Physical Chemistry of Dyeing; Oliver and Boyd: Edinburgh, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Timofei, S.; Kurunczi, L.; Schmidt, W.; Simon, Z. Lipophilicity in dye-cellulose fibre binding. Dyes Pigment 1996, 32, 25–42. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Degs, Y.; Khraisheh, M.A.M.; Allen, S.J.; Ahmad, M.N. Effect of carbon surface chemistry on the removal of reactive dyes from textile effluent. Water Res 2000, 34, 927–935. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, S.H.; Motomura, H.; Morita, Z. Adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on cellulose. Dyes Pigment 1997, 34, 37–55. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, D.A.; East, G.C.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K. Synthesis and characterization of some disulfonyl azides as potential crosslinking agents for textile fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 2001, 79, 1092–1100. [Google Scholar]
- Pisuntornsug, C.; Yanumet, N.; O’Rear, E.A. Surface modification to improve dyeing of cotton fabric with a cationic dye. Color. Technol 2002, 118, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, I.; Gupta, V.K. Advances in water treatment by adsorption technology. Nat. Protoc 2007, 1, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Suhas. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal-A review. J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, M.M.L.R.; Suhas. Low-cost adsorbents: Growing approach to waste water treatment—A Review. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 783–842. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I. Removal of endosulfan and methoxychlor from water on carbon slurry. Environ. Sci. Technol 2008, 42, 766–770. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Mittal, A.; Jain, R.; Mathur, M.; Sikarwar, S. Adsorption of Safranin-T from wastewater using waste materials—Activated carbon and activated rice husks. J. Colloid Interface Sci 2006, 303, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Mittal, A.; Gajbe, V.; Mittal, J. Removal and recovery of the hazardous azo dye Acid Orange 7 through adsorption over waste materials: Bottom ash and de-oiled soya. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res 2006, 45, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Ali, I.; Saini, V.K. Adsorption studies on the removal of Vertigo Blue 49 and Orange DNA13 from aqueous solutions using carbon slurry developed from a waste material. J. Colloid Interface Sci 2007, 315, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Youssef, Y.A.; Ahmed, N.S.E.; Mousa, A.A. The use of sodium edate in dyeing: II. Union dyeing of cotton/wool blend with hetero bi-functional reactive dyes. Dyes Pigment 2007, 72, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Matyjas, E.; Rybicki, E. Novel reactive red dyes. AUTEX Res. J 2003, 3, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Hou, A.; Zhang, Y. New polymer materials based on silicone acrylic copolymer to improve fastness properties of reactive dyes on cotton fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci 2006, 100, 720–725. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, S.; Chickos, J.S.; Welsh, W.J. Three-dimensional quantitative structure-Property relationship (3D-QSPR) models for prediction of thermodynamic properties of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Enthalpy of sublimation. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 2002, 42, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yun, Y.; Li, H. Toward better QSAR/QSPR modeling: simultaneous outlier detection and variable selection using distribution of model features. J. Comput.-Aided Mol. Des 2011, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Fara, D.C.; Petrukhin. The present utility and future potential for medicinal chemistry of QSAR/QSPR with whole molecule descriptors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 1333–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Katritzky, A.R.; Maran, U.; Lobanov, V.S.; Karelson, M. Structurally diverse quantitative structure-property relationship correlations of technologically relevant physical properties. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 2000, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Karelson, M. Molecular Descriptors in QSAR/QSPR; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.J.; Panaye, A.; Doucet, J.P.; Zhang, R.S.; Chen, H.F.; Liu, M.C.; Hu, Z.D.; Fan, B.T. Comparative study of QSAR/QSPR correlations using support vector machines, radial basis function neural networks, and multiple linear regression. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 2004, 44, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Karelson, M.; Lobanov, V.S.; Katritzky, A.R. Quantum-chemical descriptors in QSAR/QSPR studies. Chem. Rev 1996, 96, 1027–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Devillers, J.; Balaban, A.T. Topological Indices and Related Descriptors in QSAR and QSPR; Gordon and Breach Science: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 21–57. [Google Scholar]
- Funar-Timofei, S.; Schüürmann, G. Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) of anionic azo dye-fiber affinities I: Gas-phase molecular orbital descriptors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci 2002, 42, 788–795. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Q. A QSPR treatment for the thermal stabilities of second-order NLO chromophore molecules. J. Mol. Model 2005, 12, 65–75. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, W.M.F.; Timofei, S. Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) of dye-fibre affinities. Part 2. Symmetrical bisazo dyes. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 1996, 362, 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- SYBYL-X; Tripos Associates Inc.: St. Louis, MO, USA. Available online: http:/www.tripos.com/sybyl accessed on 16 November 2011.
- Ultra CD: 6.0 and Chem3D Ultra; PerkinElmer Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA. Available online: http://www.cambridgesoft.com/software/chemdraw/ accessed on 16 November 2011.
- Noel, M.O.; Banck, M.; James, C.A.; Morley, C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Hutchison, G.R. Open babel: An open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminf 2011, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluszkiewicz, J.; Matyjas, E.; Blus, K. Di-and tetrafunctional reactive red dyes. Fibres Text. East. Eur 2002, 10, 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, S.; Ali, S.I.; Khan, K.M.; Aleem, A.; Parveen, R. Synthesis of Bis-monochloro triazine reactive dyes and their application on cellulose fabric. Open J. Tex. Chem 2011. in submit. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.; Cramer, R.D., Iii; van Opdenbosch, N. Validation of the general purpose Tripos 5.2 force field. J. Comput. Chem 1989, 10, 982–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, K.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsiao, N.W.; Wang, C.L.; Lin, C.L.; Lee, Y.C.; Li, M.; Wang, B. A comparison of different electrostatic potentials on prediction accuracy in CoMFA and CoMSIA studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem 2010, 45, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Jakalian, A.; Jack, D.B.; Bayly, C.I. Fast, efficient generation of high quality atomic charges. AM1 BCC model: II. Parameterization and validation. J. Comput. Chem 2002, 23, 1623–1641. [Google Scholar]
- Halgren, T.A. Merck molecular force field. V. Extension of MMFF94 using experimental data, additional computational data, and empirical rules. J. Comput. Chem 1996, 17, 616–641. [Google Scholar]
- QUACPAC; Openeye scientific software, Inc: Santa Fe, NM, USA. Available online: http://www.eyesopen.com/news/quacpac-v150-released accessed on 16 November 2011.
- Ul Haq, Z.; Mahmood, U.; Jehangir, B. Ligand based 3D QSAR studies of physostigmine analogues as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des 2009, 74, 571–581. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Y.; Yin, C.; Liu, H.; Yi, Z.; Wang, Y. 3D-QSAR study on atmospheric half-lives of POPs using CoMFA and CoMSIA. J. Environ. Sci 2008, 20, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, I.; Fall, Y.; Gomez, G. QSAR, Docking, and CoMFA studies of GSK3 inhibitors. Curr. Pharma. Des 2010, 16, 2666–2675. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Greco, G.; Novellino, E. A critical review of recent CoMFA applications. Perspect. Drug Discov. Des 1998, 12, 257–315. [Google Scholar]
- Geladi, P.; Xie, Y.L.; Polissar, A.; Hopke, P. Regression on parameters from three way decomposition. J. Chemom 1998, 12, 337–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ul Haq, Z.; Uddin, R.; Wai, L.K.; Wadood, A.; Lajis, N.H. Docking and 3D-QSAR modeling of cyclin-dependent kinase 5/p25 inhibitors. J. Mol. Model 2010, 17, 1149–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Wold, S.; Geladi, P.; Esbensen, K.; Öhman, J. Multi way principal components and PLS analysis. J. Chemom 1987, 1, 41–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, R.D., III; Patterson, D.E.; Bunce, J.D. Comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA). 1. Effect of shape on binding of steroids to carrier proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1988, 110, 5959–5967. [Google Scholar]
 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. No. | Dye Code | Group “A “ | Bridging Moiety “DA” | Absorbtivity dm3/mol/cm × 104 |
| 1 | JP-1 | Anthranilic acid | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 3.47 |
| 2 | JP-2 | Anthranilic acid | 1,2-Phenylenediamine | 5.37 |
| 3 | JP-3 | Anthranilic acid | 1,3 - Phenylen diamine | 5.30 |
| 4 | JP-4 | Anthranilic acid | Diaminestilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | 4.29 |
| 5 | JP-5 | Anthranilic acid | 4,4′-Diaminebenzoanilide | 3.74 |
| 6 | JP-6 | Anthranilic acid | Ethylene-1,2-diamine | 4.94 |
| 7 | JP-7 | 4-β-Sulphatoetyl-sulfonyl aniline | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 5.43 |
| 8 | JP-8 | 4-β-Sulphatoetyl-sulfonyl aniline | 1,2-Phenylenediamine | 6.21 |
| 9 | JP-9 | 4- β-Sulphatoetyl-sulfonyl aniline | 1,3-Phenylenediamine | 5.81 |
| 10 | JP-10 | 4- β-Sulphatoetyl-sulfonyl aniline | Diaminestilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | 5.49 |
| 11 | JP-11 | 4-β-Sulphatoetyl-sulfonyl aniline | 4,4′-diaminebenzoanilide | 4.95 |
| 12 | JP-12 | 4-β-Sulphatoetyl-sulfonyl aniline | Ethylene-1,2-diamine | 6.32 |
| 13 | JP-13 | Anrthanilic acid | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 4.67 |
| 14 | IS-14 | Aniline | Diaminestilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | 2.95 |
| 15 | IS-15 | Benzene-m-aminosulfonic acid | Diaminestilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | 1.85 |
| 16 | IS-16 | Benzene-m-aminosulfonic acid | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 0.71 |
| 17 | IS-17 | Benzene-p-aminosulfonic acid | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 1.95 |
| 18 | IS-18 | Aniline | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 0.37 |
| 19 | IS-19 | p-Toluidine | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 0.25 |
| 20 | IS-20 | p-Toluidine | Diaminestilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | 1.92 |
| 21 | IS-21 | p-Toluidine | 1,3-Phenylenediamine | 0.47 |
| 22 | IS-22 | p-Nitroaniline | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 2.44 |
| 23 | IS-23 | p-Nitroaniline | 1,3 - Phenylenediamine | 1.74 |
| 24 | IS-24 | m-Toluidine | 1,4 - Phenylenediamine | 0.47 |
| 25 | IS-25 | m-Toluidine | 1,3-Phenylenediamine | 1.40 |
| 26 | IS-26 | m-Toluidine | Diaminestilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid | 2.32 |
| Compounds | Experimental absorbtivity | Predicted absorbtivity by CoMFA |
|---|---|---|
| Training set | ||
| JP-02 | 5.37 | 5.38 |
| JP-03 | 5.30 | 5.46 |
| JP-04 | 4.29 | 4.18 |
| JP-05 | 3.74 | 3.67 |
| JP-06 | 4.94 | 4.91 |
| JP-07 | 5.43 | 5.66 |
| JP-08 | 6.21 | 6.24 |
| JP-09 | 5.81 | 5.85 |
| JP-10 | 5.49 | 5.37 |
| JP-12 | 6.32 | 6.51 |
| JP-13 | 4.67 | 4.35 |
| IS-14 | 2.95 | 2.52 |
| IS-15 | 1.85 | 1.95 |
| IS-16 | 0.71 | 0.67 |
| IS-17 | 1.95 | 2.02 |
| IS-18 | 0.37 | 0.43 |
| IS-19 | 0.25 | 0.31 |
| IS-20 | 1.92 | 1.35 |
| IS-22 | 0.47 | 0.75 |
| IS-23 | 2.44 | 2.41 |
| IS-24 | 0.47 | 1.08 |
| IS-25 | 1.4 | 1.39 |
| Test set | ||
| JP-01 | 3.47 | 5.40 |
| JP-11 | 4.95 | 4.37 |
| IS-21 | 0.47 | 2.18 |
| Parameters | CoMFA |
|---|---|
| aq2 | 0.509 |
| bONC | 03 |
| cSEP | 1.567 |
| dSEE | 0.257 |
| F-test ratio | 591.27 |
| er2 | 0.989 |
| fr2pred | 0.797 |
| Field contribution | Percentage (%) |
| Steric | 49.7 |
| Electrostatic | 50.3 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahmood, U.; Rashid, S.; Ali, S.I.; Parveen, R.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Ambreen, N.; Khan, K.M.; Perveen, S.; Voelter, W. 3D-QSPR Method of Computational Technique Applied on Red Reactive Dyes by Using CoMFA Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 8862-8877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128862
Mahmood U, Rashid S, Ali SI, Parveen R, Ul-Haq Z, Ambreen N, Khan KM, Perveen S, Voelter W. 3D-QSPR Method of Computational Technique Applied on Red Reactive Dyes by Using CoMFA Strategy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(12):8862-8877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128862
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahmood, Uzma, Sitara Rashid, S. Ishrat Ali, Rasheeda Parveen, Zaheer Ul-Haq, Nida Ambreen, Khalid Mohammed Khan, Shahnaz Perveen, and Wolfgang Voelter. 2011. "3D-QSPR Method of Computational Technique Applied on Red Reactive Dyes by Using CoMFA Strategy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 12: 8862-8877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128862





